Chapter 12. Observational Study Designs
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
research class textbook reading-> chapter 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
observational studies in clinical research can be classified as either
analytic or descriptive
analytic observational studies are
similar to randomized, controlled clinical trials
the goal is to estimate the causal effect of an exposure on an outcome
analytical observational studies always include
some type of comparison group
descriptive studies
aim to describe the characteristics or experiences of a particular pt group
well-designed analytic studies can
generate strong evidence for or against a stated hypothesis
analytic v descriptive studies
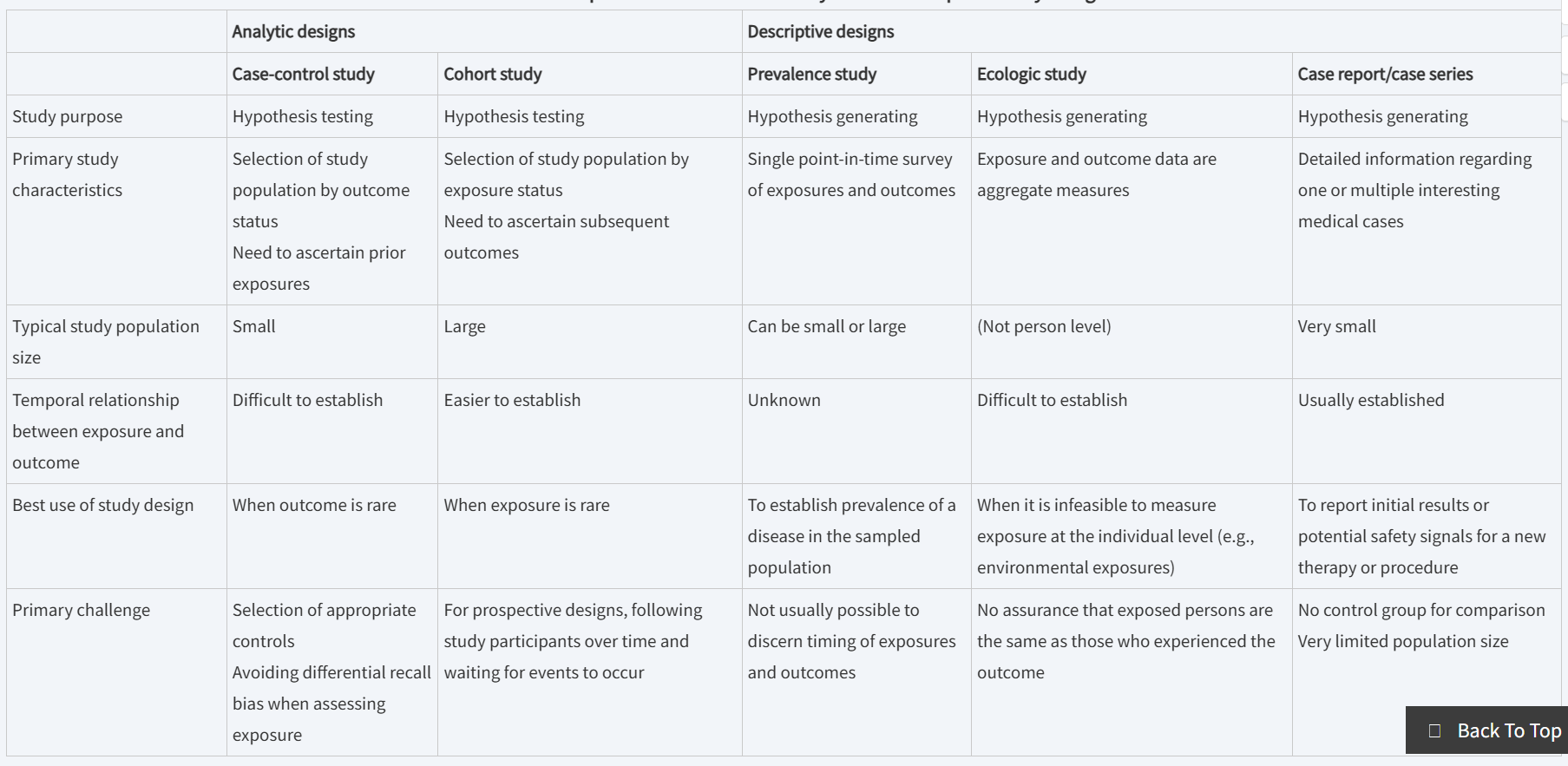
case-control study
the study population is selected based on a person’s outcome status
cases are
those that have or have had an outcome
controls are those
that lack the outcome
the principle that guides the selection of controls is that they
must be representative of the underlying population that generated the cases
the case-control study study design is well suited to the study of
rare outcomes
challenges of the case-control design
identifying a representative sample of controls can be difficult and expensive
asking study participants to recall details about past exposure can be problematic
cohort study begins by
classifying exposure status among a group at risk for having the outcome
in a prospective cohort study. . .
both the exposed group and the unexposed group are followed overtime as events occur
in a retrospective cohort study. . .
longitudinal data will have already been collected for the study group→ meaning the events will have already occurred and must be tallied
important characteristics of a well-designed cohort study
relative timing of the exposure and the outcome is more certain in a cohort-study than in a case-control study
ascertainment of the exposure should be unbiased bc the outcome has not yet occurred when the exposure is measured
ascertainment of the outcome should also be unbiased if procedures are in place to collect events systematically for all study subjects→ regardless of exposure status
analytic study designs
case-control studies
cohort studies
descriptive study designs
ecologic studies
cross-sectional (prevalence) studies
case reports and case series
ecologic studies
measurement is performed at the population level rather than at the individual level
the study hypothesis involves individual-level exposures and outcomes
an ecologic study can compare
outcome rates btwn populations in different geographic regions that have different exposures level
OR
it can examine outcome rates within a single population over time to see how they correlate with changes in exposure levels over time
main reason why researchers use ecologic studies
that aggregated rates of disease and other population characteristics are often readily available and can be analyzed quickly and inexpensively
ecologic studies are primarily used for
evidence generation
cross-sectional studies collect data about
health and exposure status of a population at a single point in time
members of a cross-sectional study ________ followed longitudinally
are NOT
in cross-sectional studies
it is possible to compare exposure rates among surveyed individuals with and without a disease, it is not possible to draw conclusions about causation because the timing of the collected information is difficult or impossible to determine
the best cross-sectional studies use
statistical sampling to select study individuals who accurately represent the population of interest
cross-sectional studies are useful for . . .
estimating the disease burden in a population
case report
a written presentation of a particular medical case encountered by a physician
case series
an aggregation of case reports
results of published case reports and case series are
suggestive