Hematology FINAL BOC
1/319
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
320 Terms
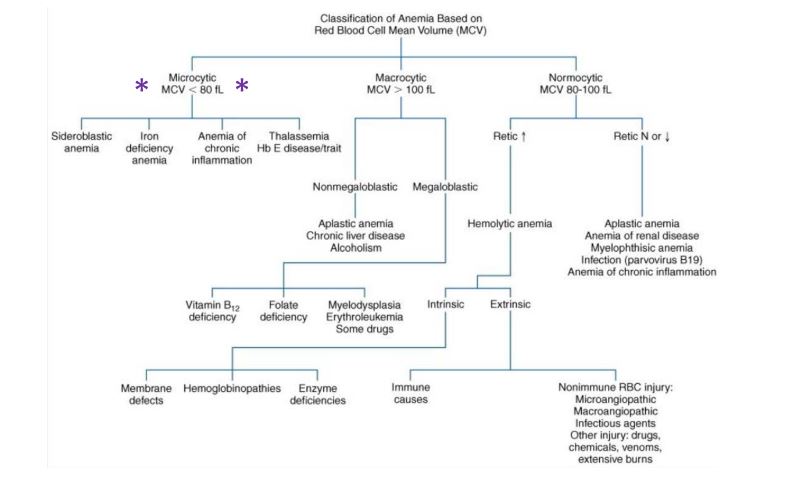
The majority of the iron in an adult is found as a constituent of?
a hemoglobin
b hemosiderin
c myoglobin
d transferrin
a hemoglobin
2/3 of iron in the body is bound to hemoglobin. Myoglobin also has iron, but in lesser amounts
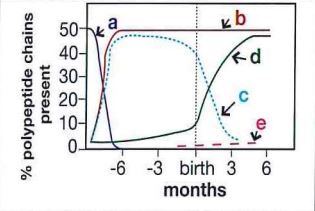
Which curve in this figure represents the production of alpha polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
a
b
c
d
b
alpha chains, a constiuent of embryonic gower 2 hemoglobin, fetal hemoglobin, and adult hemoglobins A and A2, are synthesized early in gestation and maintained throught embryonic, fetal, and infant development
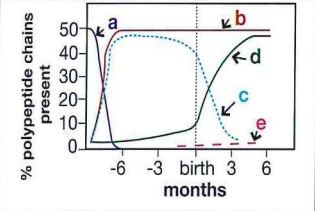
Which curve in this figure represents the production of beta polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
a
b
c
d
d
beta chains, a constiuent of adult hemoglobin A, are synthesized at a low level until about the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Beta chain production increases from approximately gestational week 30.
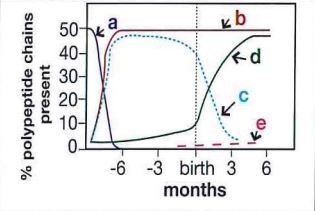
Which curve in this figure represents the production of gamma polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
a
b
c
d
c
Gamma chains, a consituent of fetal hemoglobin, are synthesized during liver and bone marrow erythropoiesis in the fetus, with production decreasing after birth.
In order for hemoglobin to combine reversibly with oxygen, the iron must be?
a complexed with haptoglobin
b freely circulating in the cytoplasm
c attached to transferring
d in the ferrous state
d in the ferrous state
The functional form of iron is the reduced state
Which description best fits the Donath-Landsteiner antibody?
a IgM cold agglutinin
b biphasic IgM hemolysin
c IgG biphasic hemolysin
d IgG warm agglutinin
c IgG biphasic hemolysin
The Donath-Landsteiner antibody is a biphasic, complement-fixing IgG antibody
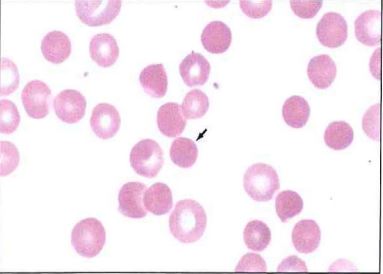
The abnormal erythrocyte in the center of this image (arrow) may result from which of the following processes?
a deficiences of cellular membrane proteins
b absence of plasma lipoproteins
c defects in the cellular lipid bilayer
d deficiencies of cellular enyzmes
a deficiences of cellular membrane proteins
This cell is a spherocyte and is most often associated with a deficiency or defect of membrane spectrin, though other proteins (band 3, ankyrin) may also be deficient or defective
What is the composition of the inclusion seen in this RBC?
a DNA
b RNA
c Iron
d denatured hemoglobin
a DNA
Howell-Jolly bodies represent nuclear fragments remaining within the RBC cytoplasm after the nucleus has been extruded
Which of the following ions is bound to hemoglobin in methemoglobin?
a Ca 2+
b Fe 3+
c Fe 2+
d Mg 2+
b Fe 3+
Methemoglobin results when iron is in the ferric (Fe +3) state
An increased amount of cytoplasmic basophilia in a blood cell indicates?
a increased cytoplasmic maturation
b decreased cytoplasmic maturation
c reduction in size of the cell
d decreased nuclear maturation
b decreased cytoplasmic maturation
An increased amount of cytoplasmic basophilia in a blood cell indicates decreased cytoplasmic maturation
Specific (secondary) granules of the neutrophilic granulocyte
a appear first at the myelocyte stage
b contain esterases
c are formed on the mitochondria
d are derived from azurophil (primary) granules
a appear first at the myelocyte stage
secondary granules first appear at the myelocyte stage, though primary granules are still retained
In normal adult bone marrow, the most common granulocyte is the?
a basophil
b myeloblast
c eosinophil
d metamyelocyte
d metamyelocyte
Normal bone marrow has more metamyelocytes than myeloblasts, with even fewer numbers of basophils and eosinophils
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells are capable of producing
a daughter cells of only one cell line
b only T and B lymphocytes
c eryhropoietin, thrombopoietin, and leukopoietin
d lymphoid and myeloid stem cells
d lymphoid and myeloid stem cells
Pluripotential hematopoietic stem cells are capable of producing cells of more than one lineage, specifically both lymphoid and myeloid
Which of the following cytokines is most responsible for eosinophil differentation and release from the bone marrow?
a IL-1
b IL-2
c IL-4
d IL-5
d IL-5
IL-5 released by T helper cells, mast cells, eosinophils and other lymphocytes has lineage specificity from eosinophils and is the major cytokine required for production and differentation of eosinophils
Auer rods are characterized as?
a fused primary granules
b DNA precipitates
c denatured hemoglobin
d large cytoplasmic granules
a fused primary granules
Auer rods are pinkish or reddish inclusions, often rod shaped, in the cytoplasm of malignant myeloblasts. They originate from fused primary granules.
Which of the following is characteristic of cellular changes as megakaryoblasts mature into megakaryocytes within the bone marrow?
a progressive decrease in overall cell size
b increasing basophilia of cytoplasm
c nuclear division without cytoplasmic maturation
d fusion of the nuclear lobes
c nuclear division without cytoplasmic maturation
Nuclear maturation and division occurs first and is generally complete before cytoplasmic maturation begins
Which of the following cells is the largest cell in the bone marrow?
a megakaryocyte
b histiocyte
c osteoblast
d mast cell
a megakaryocyte
megakaryocytes are typically the largest hematopoietic cell in the bone marrow
Which one of the following is a true statement about megakaryocytes in a bone marrow aspirate?
a an average of 5-10 should be found in each low power field (10x)
b the majority of forms are the MK1 stage
c morphology must be determined from the biopsy section
d quantitative estimation is done using the 40x lens
a an average of 5-10 should be found in each low power field (10x)
After the removal of red blood cells from the circulation hemoglobin is broken down into
a iron, porphyrin and amino acids
b iron, heme, and globin
c heme, protoporphyrin, and amino acids
d heme, hemosiderin, and globin
b iron, heme, and globin
normal degradation products of red blood cells include iron, heme, and globin
The main funtion of the hexose monophosphate shunt in the erythrocyte is to
a regulate the level of 2,3-DPG
b provide reduced glutathione to prevent hemoglobin oxidation
c prevent the reduction of heme iron
d provide energy for membrane maintenance
b provide reduced gluathione to prevent hemoglobin oxidation
The hexose monophosphate shunt prevents hemoglobin degradation by producing reduced glutathione
In the normal adult, the spleen acts as a site for?
a storage of red blood cells
b production of red blood cells
c synthesis of erythropoietin
d removal of imperfect and aging cells
d removal of imperfect and aging cells
The major function of the spleen is to remove defective and aging cells, especially RBCs, in the process called culling
Cells for the transport of O2 and CO2 are
a erythrocytes
b granulocytes
c lymphocytes
d thrombocytes
a erythrocytes
The major function of RBCs is the passive transport of gases
Erythropoietin acts to
a shorten the replication time of the granulocytes
b stimulate RNA synthesis of erythroid cells
c increase colony stimulating factors produced by the B lymphocytes
d decrease the release of marrow reticulocytes
b stimulate RNA synthesis of erythroid cells
Erythropoietin is a hormone that specifically targets the synthesis of RBCs
Cells that produced antibodies and are capable of direct cytolysis?
a erythrocytes
b granulocytes
c lymphocytes
d thrombocytes
c lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are a diverse type of cell with several functions. B cells produce antibodies, while NK cells can directly lyse other cell types
Phagocytosis is a function of
a erythrocytes
b granulocytes
c lymphocytes
d thrombocytes
b granulocytes
Phagocytosis is performed by neutrophils, a type of granulocyte
Which cells are involved in immediate hypersensitivity reactions?
a eosinophils
b basophils
c plasma cells
d reactive lymphocytes
b basophils
Basophils function as mediators of immediate type 1 hypersensitivity reactions
HEMOSTASIS N/A
One of the major glands in an infant primarily responsible for producing lymphocytes is the
a thymus
b adrenal
c thyroid
d pituitary
a thymus
In infants, the thymus is located above the heart and gives rise to lymphocytes. This gland is not active in adults.
When iron in hemoglobin is in the +3 state it is termed?
a sulfhemoglobin
b methemoglobin
c carboxyhemoglobin
d ferrihemoglobin
b methemoglobin
Abnormal hemoglobins include carboxyhemoglobin, methemoglobin, and sulfhemoglobin. Methemoglobin has iron in the +3 state and cannot bind oxygen.
Phagocytosis in neutrophils can be described as a process to
a defend against parasites
b mediate sensitivity reactions
c neutralize products from mast cells
d kill and degranulate bacteria
d kill and degranulate bacteria
Phagocytosis is an essential function of defense for neutrophils. Bacteria can be recognized, ingested, degranulated and killed by this process.
The characteristic erythrocyte found in pernicious anemia is?
a microcytic
b spherocytic
c hypochromic
d macrocytic
d macrocytic
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency resulting in impaired DNA synthesis and macrocytosis
Hemolysis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is:
a temperature dependent
b complement independent
c antibody mediated
d caused by a red cell membrane defect
d caused by a red cell membrane defect
RBC membrane defect increases susceptibility to complement mediated lysis
Which of the following is most closely associated with idiopathic hemochromatosis?
a iron overload in tissue
b target cells
c Cabot rings
d ringed sideroblasts
a iron overload in tissue
Hemochromatosis results in iron deposited in tissues
A patient with polycythemia vera who is treated by phlebotomy is most likely to develop a deficiency of?
a iron
b vitamin B12
c folic acid
d erythropoietin
a iron
Iron is lost during therapeutic phlebotomy and, although this slows RBC production, iron deficiency could also develop
The direct antiglobulin test can help distinguish
a inherited from acquired spherocytosis
b intravascular from extravascular hemolysis
c heterozygous from homozygous thalassemia
d sickle cell trait from sickle cell disease
a inherited from acquired spherocytosis
The direct antiglobulin test (DAT) is useful to distinguish inherited spherocytosis (a negative result) from acquired causes of spherocytosis resulting from immune mechanisms (positive DAT)
The anemia of chronic inflammation is characterized by
a decreased iron stores in the reticuloendothelial system
b decreased serum iron levels
c macrocytic erythrocytes
d increased serum iron binding capacity
b hepcidin causes iron to be trapped in macrophages and unavailable to developing RBCs, subsequently decreased iron levels
Factors commonly involved in causing anemia in patients with chronic renal disease include
a marrow hypoplasia
b inadequate erythropoiesis
c vitamin B12 deficiency
d increased erythropoietin production
b inadequate erythropoiesis
Erythropoietin production is decreased and results in decreased production of RBCs
A 20-year-old woman with sickle cell anemia, whose usual hemoglobin concentration is 8/gdL (80 g/L), develops fever, increased weakness and malaise. The hemoglobin concentration is 4 g/dL (40 g/L) and the reticulocyte count is 0.1%. The MOST likely explanation for her clinical picture is?
a increased hemolysis due to hypersplenism
b aplastic crisis
c thrombotic crisis
d occult blood loss
b aplastic crisis
Aplastic crisis is a severe complication of sickle cell disease, causing a temporary pause in RBC production, which dramatically worsens the anemia.
The hypoproliferative red cell population in the bone marrow of uremic patients is caused by
a infiltration of bone marrow by toxic waste products
b decreased levels of circulating erythropoietin
c defective globin synthesis
d overcrowding of bone marrow space by increased myeloid precursors
b decreased levels of circulating erythropoietin
Anemia results during uremia because of decreased erythropoietin and subsequent decreased production of RBCs
defined term: Uremic - when a patient has a build up of toxic products in their blood because of untreated kidney failure
Which of the following characteristics are common to hereditary spherocytosis, hereditary elliptocytosis, hereditary stomatocytosis, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria?
a autosomal dominant inheritance
b red cell membrane defects
c positive direct antiglobulin test
d measured platelet count
b red cell membrane defects
RBC membrane defects are common to these disorders
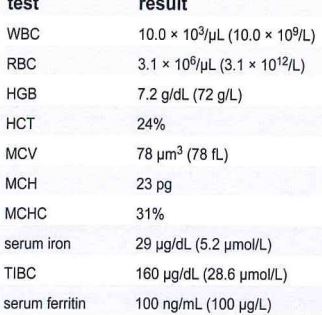
An 89 year old caucasian female is transferred to the hospital from a nursing facility for treatment of chronic urinary tract infection with proteinuria. The patient presents with the laboratory results shown in this table?
These data are most consistent with which of these clinical conditions?
a Iron deficiency anemia
b anemia of chronic inflammation
c hemochromatosis
d acute blood loss
b anemia of chronic inflammation
In anemia of chronic inflammation, iron is present, but is trapped in macrophages and unavailable to developing RBCs. Therefore, iron levels can be decreased, but the ability to bind iron (TIBC) will also be decreased.
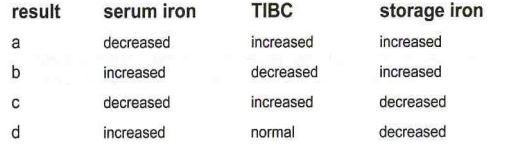
A patient is admitted with a history of chronic bleeding secondary to a peptic ulcer. Hematology resutls reveal a severe microcytic, hypochromic anemia. Iron studies are requested. Which result set would be expected in this case?
a result a
b result b
c result c
d result d
c result c
Iron deficiency anemia is associated with decreased serum iron and storage iron with a greater capacity to bind iron, as indicated by an elevated TIBC.
Which of the following is MOST closely associated with iron deficiency anemia?
a iron overload in tissue
b macrocytes
c basophilic stipling
d chronic blood loss
d chronic blood loss
chronic blood loss frequently results in iron deficiency anemia
Evidence indicates that the genetic defect in thalassemia usually results in?
a the production of abnormal globin chains
b a quantitative deficiency in RNA resulting in decreased globin chain production
c a structural change in the heme portion of the hemoglobin
d an abnormality in the alpha or beta chain binding or affinity
b a quantitiative deficiency in RNA resulting in decreased globin chain production
The mechanism of the genetic abnormality in thalassemia reduces globin chain production and does not affect the structure of the globin molecule or synthesis of heme.
A 20 year old African American man has peripheral blood changes suggesting thalassemia minor. The quantitative HbA2 level is normal, but the HbF level is 5% (normal <2%). This is most conistent with
a alpha thalassemia minor
b beta thalassemia minor
c delta-beta thalassemia minor
d hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin
c delta beta thalassemia minor
Heterozygous delta beta thalassemia is usually associated with normal HbA2 levels and slightly elevated HbF levels
Anemia secondary to uremia and chronic renal disease characteristically is
a microcytic, hypochromic
b hemolytic
c normocytic, normochromic
d macrocytic
c normocytic, normochromic
Anemia related to uremia and chronic renal disease has normal sized, normochromic cells; it is the number of RBCs that is decreased because of reduced erythropoietin levels
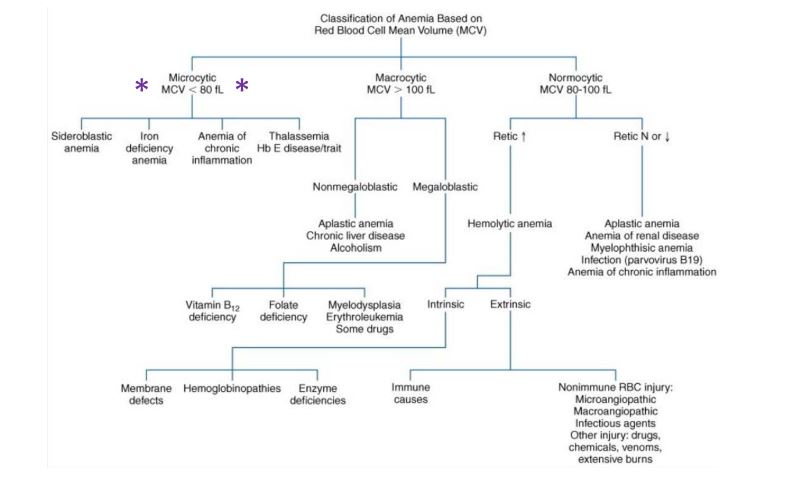
Which of the following sets of laboratory findings is consistent with hemolytic anemia?
a decreased bilirubin; normal reticulocyte count
b increased serum lactate dehydrogenase; increased catabolism of heme
c decreased serum lactate dehydrogenase; normal catabolism of heme
d increased concentration of haptoglobin; marked hemoglobinuria
b increased serum lactate dehydrogenase; increased catabolism of heme
Hemolytic anemia is associated with the breakdown of heme and lysis of RBCs, which have high levels of lactate dehydrogenase
Deficiency of this enzyme is associated with a moderate to severe hemolytic anemia after the patient is exposed to certain drugs and characterized by red cell inclusions formed by denatured hemoglobin
a lactate dehydrogenase
b G6PD
c pyruvate kinase
d hexokinase
b G6PD
G6PD deficiency is associated with the precipitation of oxidized and denatured hemoglobin as heinz bodies
Patients with G6PD deficiency are least likely to have hemolytic episodes in which of the following situations?
a following the administration of oxidizing drugs
b following the ingestion of fava beans
c during infections
d spontaneously
d spontaneously
G6PD-deficient RBCs are sensitive to oxidant stress induced by medications and several other drugs, fava beans, and infection
A patient has a congenital nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. After exposure to anti-malarial drugs, the patient experiences a severe hemolytic episode. This episode is characterized by red cell inclusions caused by hemoglobin denaturation. Which of the following conditions is most consistent with these findings?
a G6PD deficiency
b thalassemia major
c pyruvate kinase deficiency
d paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
a G6PD deficiency
G6PD-deficient RBCs are sensitive to the anti-malarial drug primaquine and oxidized and denatured hemoglobin can precipitate as heinz bodies
Which of the following is the most characteristic finding in autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
a increased reticulocyte count
b leukopenia and thrombocytopenia
c peripheral spherocytosis
d positive direct antiglobulin test
d positive direct antiglobulin test
Autoimmune hemolytic anemias result from the abnormal production of autoantibodies, which will be detected as a characteristic positive DAT
Peripheral blood smears from patients with untreated pernicious anemia are characterized by
a pancytopenia and macrocytosis
b leukocytosis and elliptocytosis
c leukocytosis and ovalocytosis
d pancytopenia and microcytosis
a pancytopenia and macrocytosis
The impaired DNA synthesis associated with pernicious anemia causes decreased production of all blood cells as well as abnormally large, macrocytic RBCs
Laboratory tests performed on a patient indicate macrocytosis and pancytopenia. Which of the following disorders is most likely?
a anemia of chronic inflammation
b vitamin B12 deficiency
c iron deficiency
d acute hemorrhage
b vitamin B12 deficiency
The impaired DNA synthesis associated with a vitamin B12 deficiency causes decreased production of all blood cells as well as abnormally large, macrocytic RBCs
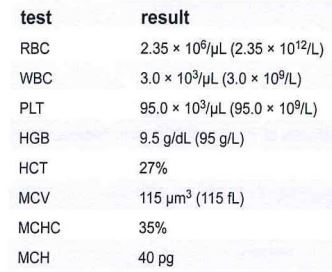
A patient has the laboratory results as shown in this table
Which of the following tests would contribute toward the diagnosis?
a reticulocyte count
b platelet factor 3
c serum B12 and folate
d leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
c serum B12 and folate
Deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folate result in pancytopenia and macrocytosis
The characteristic morphologic feature in folic acid deficiency is?
a macrocytosis
b target cells
c basophilic stippling
d rouleaux formation
a macrocytosis
In folate deficiency (megaloblastic anemia), the peripheral blood smear will characteristically show abnormally large RBCs
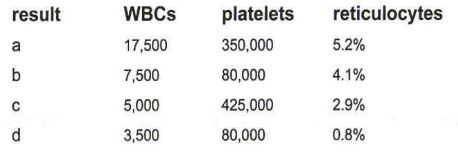
A 50 year old patient is found to have the laboratory results show below
HGB 7.0
HCT 20%
RBC 2.0
It is determined that the patient is suffering from pernicious anemia. Which of these sets of results is most likely to have been obtained from the same patient?
a result a
b result b
c result c
d result d
d result d
Pernicious anemia results in pancytopenia
Megaloblastic asynchronous development in the bone marrow indicates which one of the following?
a proliferation of erythrocyte precursors
b impaired synthesis of DNA
c inadequate production of erythropoietin
d deficiency of G6PD
b impaired synthesis of DNA
Megaloblastic anemia is caused by impaired DNA synthesis and results in asynchronous development of blood cells in the bone marrow
Which of the following are found in association with megaloblastic anemia?
a neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
b decreased LD activity
c increased erythrocyte folate levels
d decreased plasma bilirubin levels
a neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
Megaloblastic anemias result in pancytopenia, which include neutropenia and thrombocytopenia

Which of the results represents characteristic features of iron metabolism in patients with anemia of chronic inflammation?
a result a
b result b
c result c
d result d
d result d
In anemia of chronic inflammation, iron is present, but it is trapped in macrophages and unavailable to developing RBCs. Therefore, iron levels can be decreased, but the ability to bind iron (TIBC) will also be decreased. Transferrin saturation may also be low or normal.
A characteristic morphologic feature in hemoglobin C disease is
a macrocytosis
b spherocytosis
c rouleaux formation
d target cells
d target cells
a peripheral blood cell morphology in HbC disease characteristically includes target cells and hexagonal or rod shaped crystals (hemoglobin C crystals)
Thalassemias are characterized by
a structural abnormalities in the hemoglobin molecule
b absence of iron in hemoglobin
c decreased rate of heme synthesis
d decreased rate of globin synthesis
d decreased rate of globin synthesis
Thalassemias are quantitative decreases in the production of globin chains needed for hemoglobin synthesis
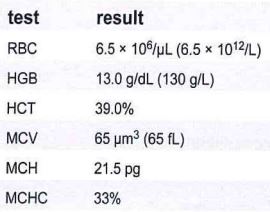
A patient has the laboratory results shown in this table
These results are compatible with
a iron deficiency
b pregnancy
c thalassemia minor
d beta thalassemia major
c thalassemia minor
Thalassemias are characterized by increased RBC counts, and microcytic, hypochromic red blood cells
Lab findings in hereditary spherocytosis include
a decreased WBCs
b decreased RBC band 3 protein
c reticulocytopenia
d positive direct antiglobulin test
b decreased RBC band 3 protein
The band 3 reduction test (also called the eosin-5-maleimide binding test or EMA) is a more sensitive procedure for confirming hereditary spherocytosis
Which of the following types of polycythemia is a severly burned patient most likely to have?
a polycythemia vera
b polycythemia, secondary to hypoxia
c relative polycythemia associated with dehydration
d polycythemia associated with renal disease
c relative polycythemia associated with dehydration
Burn patients can develop relative polycythemia that results from loss of body fluid and subsequent dehydration
The characteristic morphologic feature in lead poisoning is
a macrocytosis
b target cells (codocytes)
c basophilic stippling
d rouleaux formation
c basophilic stippling
Basophilic stippling is a classic laboratory finding in lead poisining
The white cell feature most characteristic of pernicious anemia is
a eosinophilia
b toxic granulation
c hypersegmentation
d reactive lymphocytes
c hypersegmentation
Hypersegmented neutrophils are the most prominent WBC feature associated with pernicious anemia and megaloblastic anemias in general
Which parameter is most consistently abnormal in cases of hereditary spherocytosis?
a RBC count
b MCV
c Hemoglobin
d MCHC
d MCHC
RBC indices are helpful in diagnosing hereditary spherocytosis, as the MCV and MCH are usually normal and the MCHC is increased. Spherocytes are the only erythrocytes with an elevated MCHC.
What protein is commonly defective in hereditary elliptocytosis
a ankyrin
b spectrin
c band 4.1
d elliptocin
b spectrin
Hereditary elliptocytosis may be linked to defects in several different RBC membrane proteins including spectrin
What is the most common mechanism resulting in hereditary stomatocytosis?
a abnormal Na/K permeability
b deficient cytoskeleton structural proteins
c inability to repair oxidative stress damage
d ATP depletion due to glycolytic enzyme deficiency
a abnormal Na/K permeability
Hereditary stomatocytosis includes a group of disorders in which the RBC membrane displays abnormalities in cation permeability
The basic mechanism associated with the development of sideroblastic anemia is
a enzymatic defect in heme synthesis causes iron accumulation
b quantitative decrease in the production of globin chains
c defective iron utilization
d ineffective erythropoietin production decreases RBC response
a enzymatic defect in heme synthesis causes iron accumulation
Sideroblastic anemias may be inherited or acquired and caused by either mutations in heme synthetic enzymes or impaired activity of heme. The enzymatic defects or impaired activity result in excess iron accumulation in mitochondira and developing RBCs.
Individuals with Fanconi anemia characterstically show
a increased HbF
b intravascular hemolysis
c ringed sideroblasts
d thrombocytosis
a increased HbF
Fanconi anemia is an autosomal recessive disorder showing normocytic anemia. Physically, patients show short stature, microcephaly and hyperpigmentation. HbF is elevated and patient survival is limited.
Which of the following tumors are associated with erythrocytosis due to excessive eryhropoietin production?
a renal cell carcinoma
b sarcoma
c basal cell carcinoma
d squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
a renal cell carcinoma
An inappropriate increase in eryhropoietin has been associated with certain tumors that secrete erythropoietin or an eryhropoietin like substance. Tumors are often associated with renal disease.
Which of the following features of G6PD deficiency are typically present on a Wright-Giemsa stained peripheral blood smear?
a cabot rings
b microcytosis
c bite cells
d heinz bodies
c bite cells
During or immediately following a hemolytic episode related to a G6PD deficiency, abnormalities in erythrocytes may inclue poikilocytosis, polychromasia, some spherocytes, and bite cells. Heinz bodies are only visible with a supravital stain.
Which abnormal RBC morphology is associated with pyruvate kinase deficiency?
a acanthocytes
b dacryocytes
c echinocytes
d drepanocytes
c echinocytes
The peripheral blood smear in pyruvate kinase deficiency may show echinocytes and sometimes irregularly contracted cells.
Which of the following hemoglobinopathies is associated with rod shaped crystals?
a HbS
b HbC
c HbSC
d HbD
b HbC
In hemoglobin C disease, hexagonal or rod-shaped crystals (hemoglobin C crystals) may be seen in RBCs, especially in patients who have received a splenectomy.
Which of the following statements about hemoglobins D and G is true?
a they are clinically abnormal
b they both migrate with HbS on alkaline gel
c they are both caused by mutations in the beta-globin gene
d they cannot be separated by solubility testing
b they both migrate with HbS on alkaline gel
HbD and HbG are abnormal variants that migrate at the same position as HbS on alkaline electrophoresis
This hemoglobinopathy results from a fusion product of the delta and beta gene
a HbD
b HbG
c HbLepore
d HbConstant spring
c HbLepore
HbLepore is a variant formed from the fusion of delta and beta genes that occurs from abnormal crossing over during meiosis. The resulting fusion of gene produced hybride delta/beta globin chains that combine with 2 alpha chains to synthesize HbLepore.
Which of the following is consistent with the diagnosis of heterozygous beta-thalassemia?
a increased red blood cell count
b high MCV
c decreased HbA2
d decreased iron stores
a increased red blood cell count
The RBC count is increased in heterozygous beta thalassemia more than expected for the hemoglobin concentration
Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH) is due to a loss of expression of this globin chain
a alpha
b beta
c gamma
d delta
c gamma
HPFH is caused by either the absence of beta and delta chain synthesis or a loss of suppression of the gamma globin gene through mutations of proteins inhibiting gene expression or in the gamma gene promoter region.
What is the specificity of cold autoagglutinin disease?
a anti-i
b anti-H
c anti-Pr
d anti-I
d anti-I
The antibody produced in cold agglutinin disease is usually an autoantibody with anti-I specificity
What is the most common presentation of paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria?
a older people with Raynaud syndrome
b children following a viral illness
c neonates with congenital syphillis
d alcoholics with advanced cirrhosis
b children following a viral illness
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria is most often seen in children with viral infections
Which of the following is the most common cause of anemia in hospitalized patients?
a inadequate iron intake
b inadequate folate intake
c hemolytic anemia
d anemia of chronic inflammation
d anemia of chronic inflammation
Anemia of chronic inflammation (disease) is a common cause of anemia in hospitilzed patients. It is associated with infections and inflammatory or malignant conditions
In a patient with an increased red cell mass into the 99th percentile and serum erythropoietin level below reference range for normal, which of the following criteria confirms diagnosis of polycythemia vera?
a bone marrow panmyelosis
b inv(16) mutation
c JAK2 V617F mutation
d BCR/ABL1 translocation
c JAK2 V617F mutation
in 95-100% of polycythemia vera patients the JAK2 V617 mutation is present
A medical technologist is examining a peripheral smear and notices 7 large segmented neutrophils with between 5 and 7 lobes. Everything else about the CBC is otherwise normal. This observed morphologic change might develop months ahead of which of the following changes
a an increase in MCV, MCH, and RDW
b a decrease in MCV, MCH, and RDW
c an increase in metamyelocytes and bands
d a bone marrow showing aplasia
a an increase in MCV, MCH, and RDW
The MCV and MCH are increased in megaloblastic anemia. Hypersegmented neutrophils are one of the distinguishing features of megaloblastic anemia. Anisocytosis (elevated RDW) is also present. Hypersegmented neutrophils may be seen before the megaloblastic anemia is fully developed.
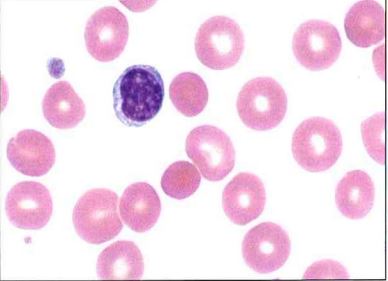
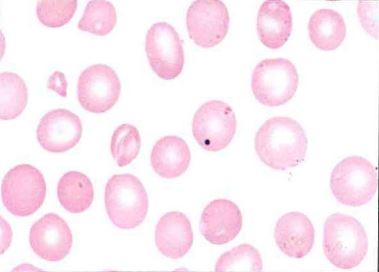
The red blood cells in this image are representative of an anemia that is
a microcytic, hypochromic
b nonmegaloblastic macrocytic
c normocytic normochromic
d myelodysplastic
b nonmegaloblastic macrocytic
Nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemias are characterized by erythrocytes that are round and macrocytic. This is in contrast to megaloblastic anemias in which macro-ovalocytes are present.
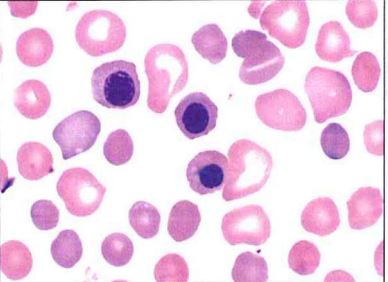
This image of the blood smear from a newborn most likely represents
a severe G6PD deficiency
b hereditary spherocytosis
c untreated megaloblastic anemia
d HDN due to ABO incompatibility
d HDN due to ABO incompatibility
Spherocytes and polychromasia are diagnostically important in findings in RBCs in hemolytic disease of the newborn due to ABO incompatibility. Nucleated RBCs may also be seen in the peripheral blood of newborns.
Hemoglobin H disease results from
a absence of 3 of 4 alpha genes
b absence of 2 of 4 alpha genes
c absence of 1 of 1 alpha genes
d absence of all 4 alpha genes
a absence of 3 of 4 alpha genes
HbH disease occurs when 3 of 4 alpha genes are deleted
The M:E ratio in polycythemia vera is usually
a 4:1
b 10:1
c 50:1
d 75:15
a 4:1
Granulopoiesis and erythropoiesis are both often increased in polycythemia vera, resulting in a normal M:E ratio.
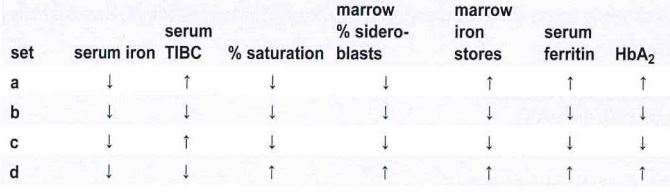
In an uncomplicated case of severe iron deficiency anemia, which of these sets of laboratory data represents the typically pattern of results?
a set a
b set b
c set c
d set d
c set c
Iron deficiency anemia laboratory features include: decreased serum iron, serum ferritin, percent saturation, bone marrow iron stores and increased TIBC.
A patient has a tumor that concentrates erythropoitetin. He is most likely to have which of the following types of polycythemia?
a polycythemia vera
b polycythemia, secondary to hypoxia
c benign familial polycythemia
d polycythemia associated with renal disease
d polycythemia associated with renal disease
Secondary polycythemia can occur inappropriately when renal tumors secrete erythropoietin
Which of the following types of polycythemia is most often associated with lung disease?
a polycythemia vera
b polycythemia, secondary to hypoxia
c relative polycythemia associated with dehydration
d polycythemia associated with renal disease
b polycythemia, secondary to hypoxia
Lung disease causes tissue hypoxia and results in secondary polycythemia
A patient has been treated for a malignant tumor for several years. His blood smear now shows
oval macrocytes
Howell-Jolly bodies
Hyper segmented neutrophils
Large, agranular platelets
The most probable cause of this blood picture is
a iron deficiency
b alcoholism
c dietary B12 deficiency
d chemotherapy
d chemotherapy
Some drugs interfere with DNA synthesis and result in megaloblastic anemia. Peripheral blood findings reflect the megaloblastic process and include characterstic cellular changes to include oval macrocytes, RBC inclusions, hypersegmented neutrophils, and platelet abnormalities
How does the bone marrow respond to anemic stress?
a expand production, release RBCs prematurely
b expand production, rush platelets into circulation
c diminish production, increase M:E
d diminish production, M:E remains normal
a expand production, release RBCs prematurely
When the bone marrow senses anemia, it increases production of red cells in a premature fashion, releasing nucleated red blood cells. Polychromasia will also be seen on the peripheral blood smear.
Which of the following conditions may contribute to lethargy, abdominal pain, and hemoglobinuria in some patients with a G6PD deficiency?
a dehydration
b excess iron
c ingesting fava beans
d increased glucose
c ingesting fava beans
Favism (consumption of fava beans) is the second most severe clinical condition of G6PD deficiency. After ingestion of fava beans an individual may experience hemogloinuria, lethargy, and abdominal pain.
The most likely cause of macrocytosis that often accompanies primary myelofibrosis is
a folic acid deficiency
b increased reticulocyte count
c inadequate B12 absorption
d pyridoxine deficiency
a folic acid deficiency
Myelofibrosis is often accompanied by a folate deficiency, which develops because of increased consumption by the malignant clone and results in macrocytic anemia.
Giant, vacuolated, multinucleated erythroid precursors are present in which of the following?
a chronic myelocytic leukemia
b primary myelofibrosis
c erythroleukemia
d acute myelocyte leukemia
c erythroleukemia
RBC precursors in eryhroleukemia display several dysplastic characteristics
Which of the following is a significant feature of dyserythropoiesis?
a persistently increased M:E ratio
b megaloblastoid erythropoiesis
c marked thrombocytosis
d decreased ferritin levels
b megaloblastoid erythropoiesis
Megaloblastoid erythropoiesis is a morphologic feature characteristic of dyserythropoiesis
The M:E ratio in erythroleukemia is usually
a normal
b high
c low
d variable
c low
In erythroleukemia, 50% or more of nucleated bone marrow cells are normoblasts, which indicates a decrease in the myeloid component and results in a low M:E
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is often a complication of
a PV
b CML
c CLL
d HCL
c CLL
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia may be associated with an underlying lymphoproliferative disease such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Elevation of the total granulocyte count about 7.5 is termed
a relative lymphocytosis
b leukocytosis
c relative neutrophilic leukocytosis
d absolute neutrophilic leukocysosis
d absolute neutrophilic leukocysosis
An absolute neutrophilic leukocytosis occurs when the total granuolcyte count (circulating neutrophils) is greater than 7.5