Activation energy
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Activation energy
minimum energy that a collision must possess for a reaction to occur (E) When the energy of a collision is equal to or greater than the activation energy, a reaction can occur.
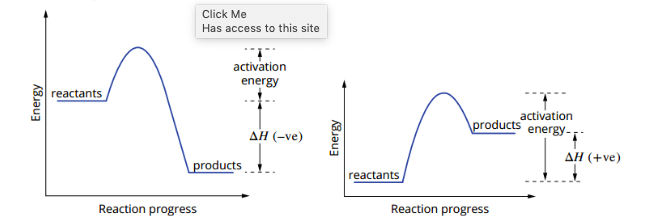
energy profile diagram
Ea is represented on an energy profile diagram
represents the enthalpy (chemical potential energy) of the reactants and the products over the course of the reaction.
endothermic vs exothermic (activation energy barrier)
have a peak that represents the activation energy.
represents minimum energy that must be absorbed to break the bonds of reactants so that a chemical reaction can progress. The activation energy is measured from the enthalpy of the reactants to the top of the peak.
explain endo/exo using this graph
exothermic reaction releases more heat energy during the reaction than it absorbs.
An endothermic reaction absorbs more heat energy during the reaction than it releases.
This is represented on the diagram as AH and is the difference in enthalpy between the reactants and the products.
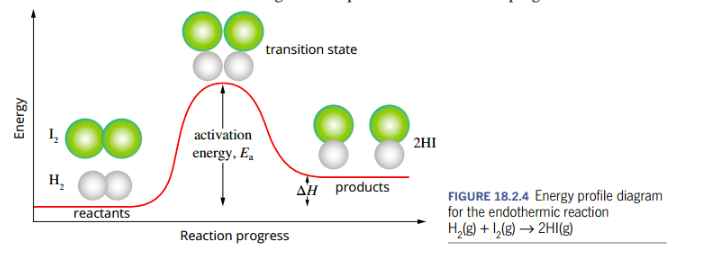
transition state (+ draw/label and example graph)
When the activation energy is absorbed, a new arrangement of the atoms occurs.
occurs at the stage of maximum potential energy in the reaction: the activation energy
Bond breaking/ bond forming both occurring at this stage = arrangement of atoms is unstable.
The atoms rearrange into the products as the reaction progresses.
activation energy and reaction rate
magnitude of activation energy = ability for reaction to occur = what proportion of collisions results in a successful reaction.
the reaction rate is dependent upon the activation energy.
does collison always mean a chemical change?
existence of an activation energy for a reaction means that collisions between reactants do not always result in a chemical change.
e.g., N and O molecules collide frequently in the air around us at room temperature.
only when energy is provided by a spark, such as in car engines or during a lightning strike = energy of collisions is increased enough to overcome the activation energy barrier.
allows nitrogen monoxide to be produced. The nitrogen monoxide formed in this process can then react to form brown nitrogen dioxide (NO)
importance of collision orientation?
Reacting molecules must also collide with each other in the correct orientation in such a way that particular bonds in the reactants are broken and new bonds are formed in the products.
In the decomposition of HI gas into H gas and I gas, two HI molecules must collide with H and I atoms orientated towards each other for a reaction to possibly occur.
orientation is incorrect= particles simply bounce off each other, and no reaction occurs.