enzymes
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is the definition of an enzyme
biological catalysts that speed up the rate of a reaction without being used up itself, therefore they can be used up over and over again even in small quantities, they are also proteins and synthesised by ribosomes
what is the structure of an enzyme
3D structure, containing an active site
what are substrates
molecules that bind to the active site, the structure is called an enzyme substrate complex
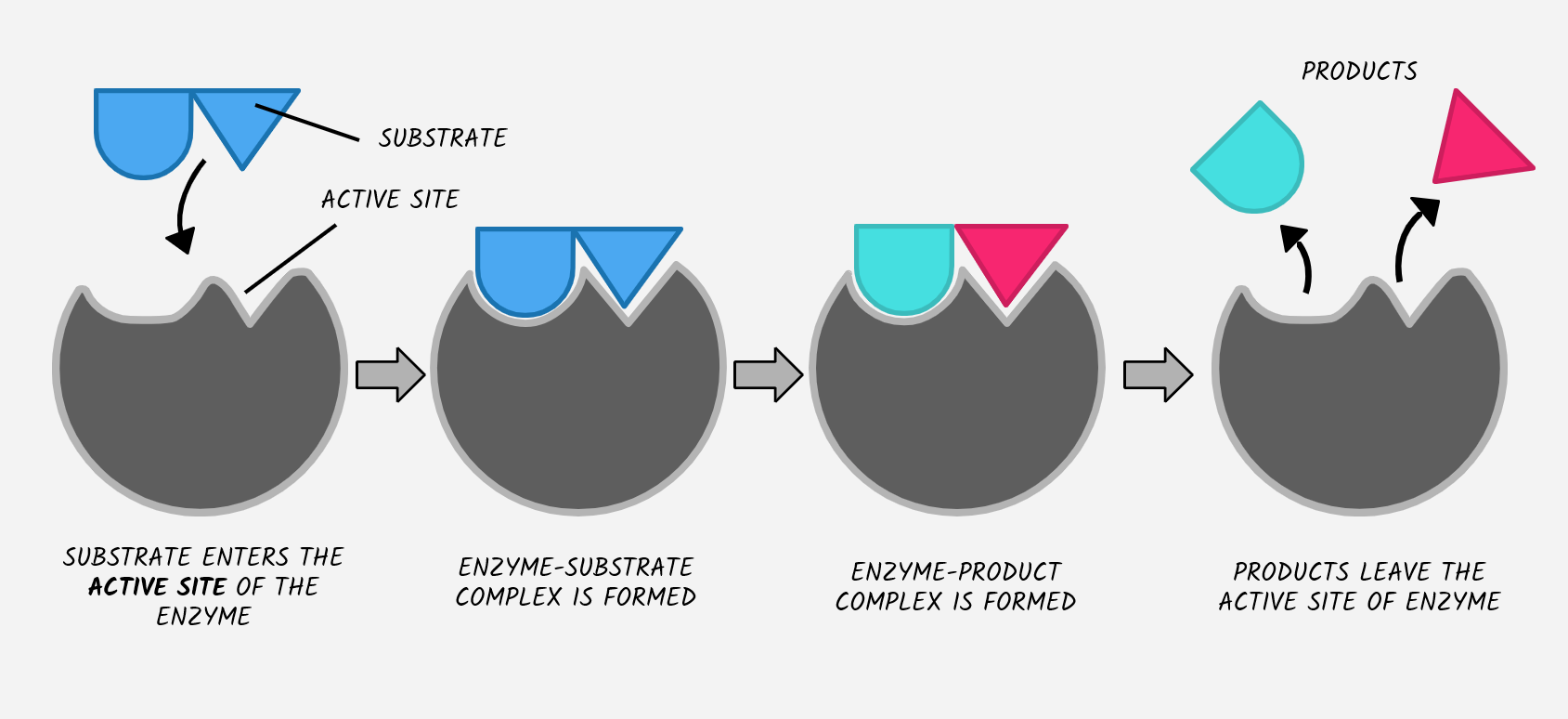
LEARN THIS
describe it
what is the relationship between enzymes and temperature
for an enzyme to work correctly, it must collide with the substrate. as temperature increases, so does kinetic energy causing the likelihood of a successful collision between enzyme and a substrate, enzymes work fastest at their optimum temperature (in the human body around 37 degrees celcius)
what is denaturation
at higher temperatures, enzymes can denature and bonds inside the site rupture. when enzymes denature, the rate of reaction decreases significantly because the active site and substrate are no longer complementary with each other
describe a practical involving temperature and enzymes
heat a solution containing starch to a spotting tile
add iodine to the wells (positive colour change orange → blue/black)
add amylase to the wells
the amylase will break down the starch slowly at low temperature
the amylase will break down the starch quickly at optimum temperature
at high temperatures the enzyme will denature and stop working
describe the relationship between enzymes and pH
pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is
each enzyme has a different optimum pH
most work well with a neutral pH (pH7)
if the pH is too far from the optimum the enzyme may denature, as it ruptures the bonds in the active site