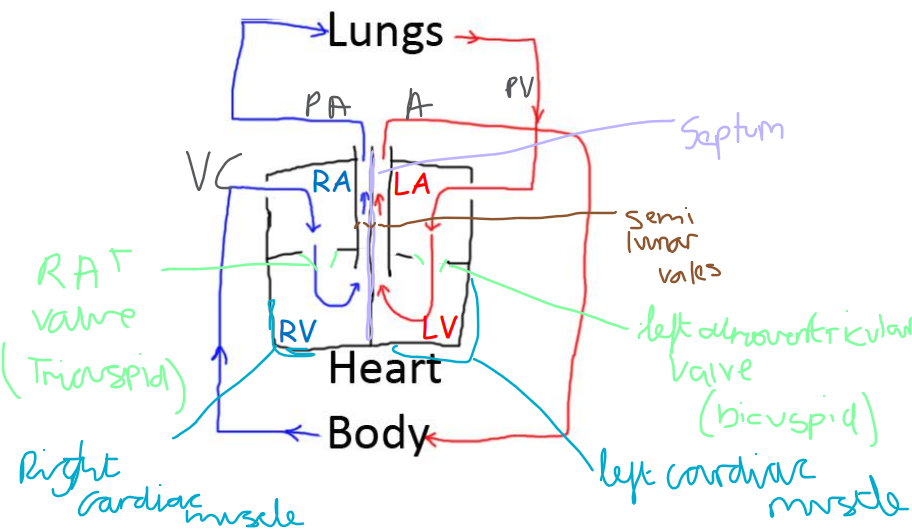
heart
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
Name the type of muscle the heart is made out of and describe its features.
Cardiac muscle:
Contracts & relaxes in regular rhythm, involuntarily
Does not get fatigued and need to rest like skeletal muscle
Contracts & relaxes in regular rhythm, involuntarily
Does not get fatigued and need to rest like skeletal muscle
2
New cards
Why are the cells branched (making cross bridges):
Faster spread of impulse across heart
synchronised pumping action
\
synchronised pumping action
\
3
New cards
What is the role of the "intercalated discs":
\
\
Good electrical continuity
•Good physical connection
\
•Good physical connection
\
4
New cards
What is a contractile unit in muscle called:
\
\
Sarcomere
\
\
5
New cards
What are the contractile fibres running the length of the cell called:
\
\
Myofibrils: containing the contractile proteins actin and myosin
\
\
6
New cards
What creates the cross striations:
\
\
Overlapping regions of actin and myosin
\
\
7
New cards
Why are there many mitochondria between the muscle fibrils:
\
\
Aerobic respiration, production of ATP. The energy in ATP is released for muscle contraction.
8
New cards
What structures inside the heart keep the blood flowing in the right direction?
Valves. The atrioventricular (AV) valves and the semilunar valves.
9
New cards
What is the function of the tendinous cords or heart strings?
Prevent the valves turning inside out.
10
New cards
Explain why the walls of the ventricles are much thicker than the walls of the atria?
Ventricles have more muscle and generate greater pressure because they have to pump blood out of the heart.
11
New cards
Which chamber of the heart has the thickest wall and why?
Left ventricle: has thickest muscle to create the highest pressure to pump blood to the whole body.
12
New cards
Why is the blood which passes through the right side of the heart deoxygenated?
It has returned from the body, where the oxygen was used, in the vena cava and is going to be pumped to the lungs.
13
New cards
Which chamber pumps blood to the lungs?
Right ventricle
14
New cards
Which chamber is the first to receive oxygenated blood from the lungs?
Left atrium
15
New cards
Explain why the wall of the aorta is thicker than the wall of the pulmonary artery
It has more elastic fibre and more smooth muscle. More elastic fibre withstands the pressure created by the left ventricle and more smooth muscle to generate more force to move blood through the arteries.
16
New cards
State location and function of the septum in the heart.
Septum:
Inner dividing wall of the heart
Prevents mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood
Inner dividing wall of the heart
Prevents mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood
17
New cards
What is the name of the blood vessels which supply the heart’s cardiac muscle with oxygen?
Coronary arteries
18
New cards
label blood flow and structures
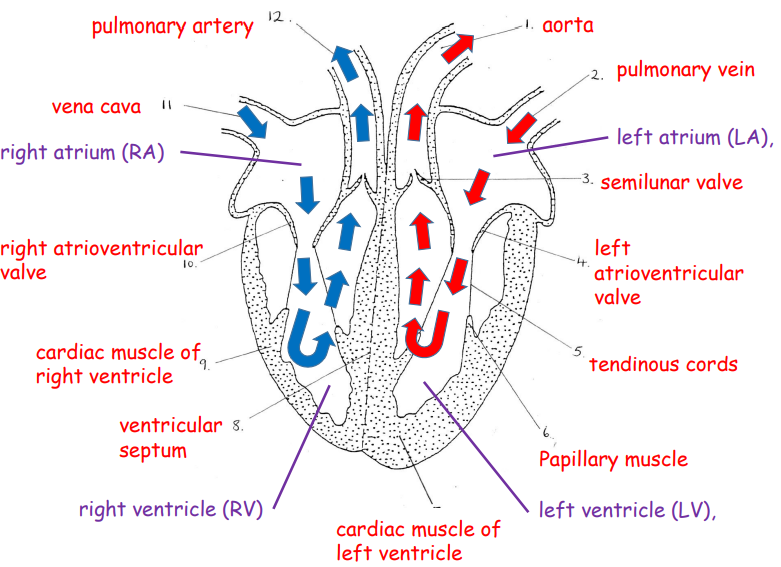
19
New cards
draw box diagram of heart