Speciation
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
species
a group of individuals capable of interbreeding, and reproductively isolated from other groups
may consist of several populations, all capable of interbreeding, but rarely having the opportunity
“biological species concept” - uses a biological trait (e.g, ability to interbreed) to define “species”
Problem 1: can you tell members of the same species from appearance alone?
it can be hard. some species are sexually dimorphic (males and females look different)
morphology can also be polymorphic (many forms or patterns) all of these are individuals of the same ladybug battle species
Problem 2: Who actually interbreeds?
we rarely watch. we use clues from morphology but clues can be deceive
what do paleontologist do? compare differences in fossil records, use aging of fossil,
people can force some species to interbreed that don’t in nature
some organisms never reproduce sexually to begin with (e.g, some bacteria, protists, fungi, and insects) these wasp all have a bacterium that causes every member of the species to be female no breeding.
the more we know (e.g, species range, morphology, genetic information, behavior, etc.) the more confident we can be
for living organisms, DNA sequences are becoming the tool of choice
How do new species form?
isolation/seperation
genetic divergence
reproductive isolation
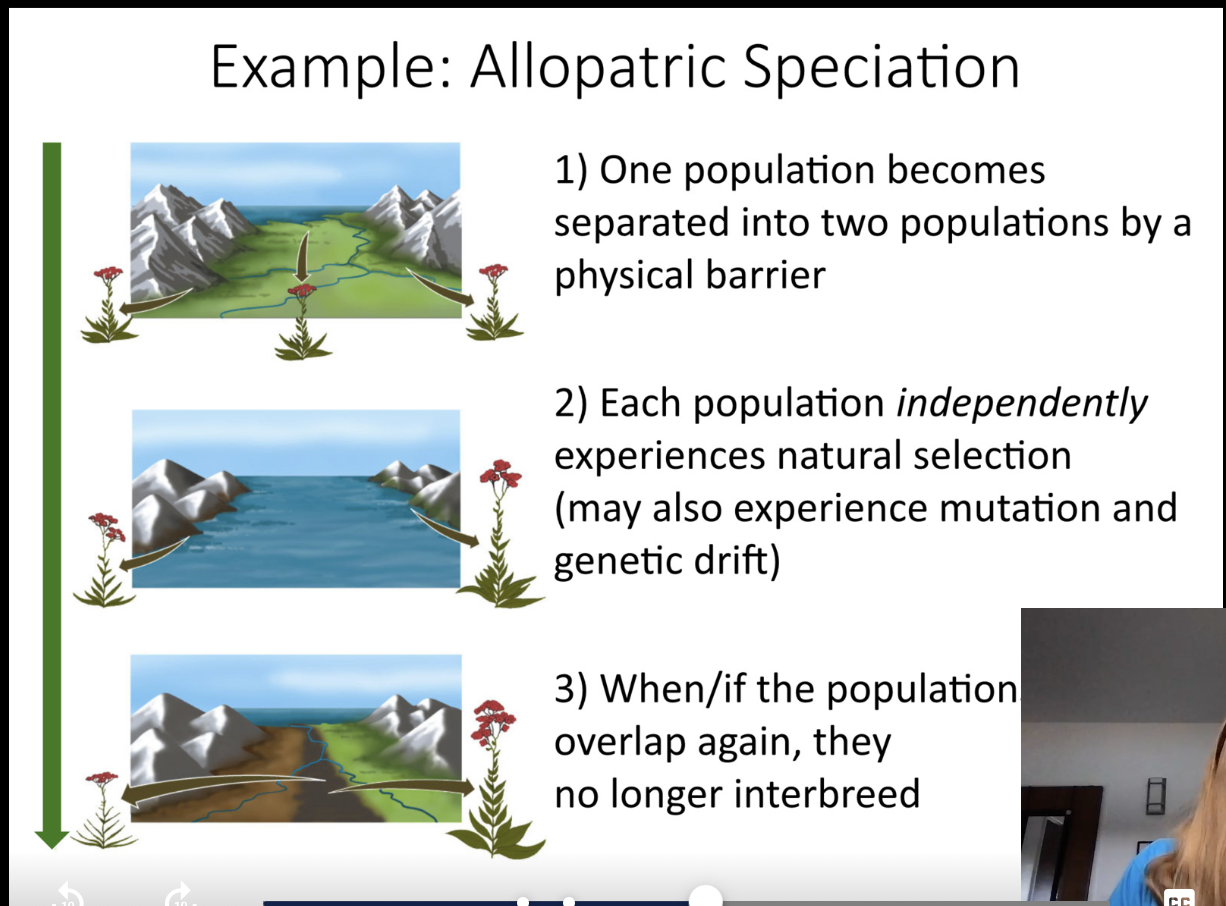
Isolation followed by genetic divergence:
one population becomes separated into two populations (often by a physical barrier but not always)
Each population independently experiences natural selection (may also experience mutation and genetic drift)
when/ if the population overlap again, they no longer interbreed
gene flow: usually reduces differences between populations
think about our two populations separated by a river
if several individuals were able to fly from one to the other each generation and interbreed, would speciation occur? no
How does the isolation of the population occur?
allopatric speciation: a physical barrier arises that prevent interbreeding. allopatric means “different countries”, considered the usual start to speciation
Sympatric speciation: no physical barrier arises; interbreeding between groups stops for another reason, sympatric means “same countries”, somewhat controversial but largely accepted
allopatric speciation
allopatric speciation example
Harris antelope squirrel (south rim) and white tailed antelope squirrel (north rim) due to the Colorado river
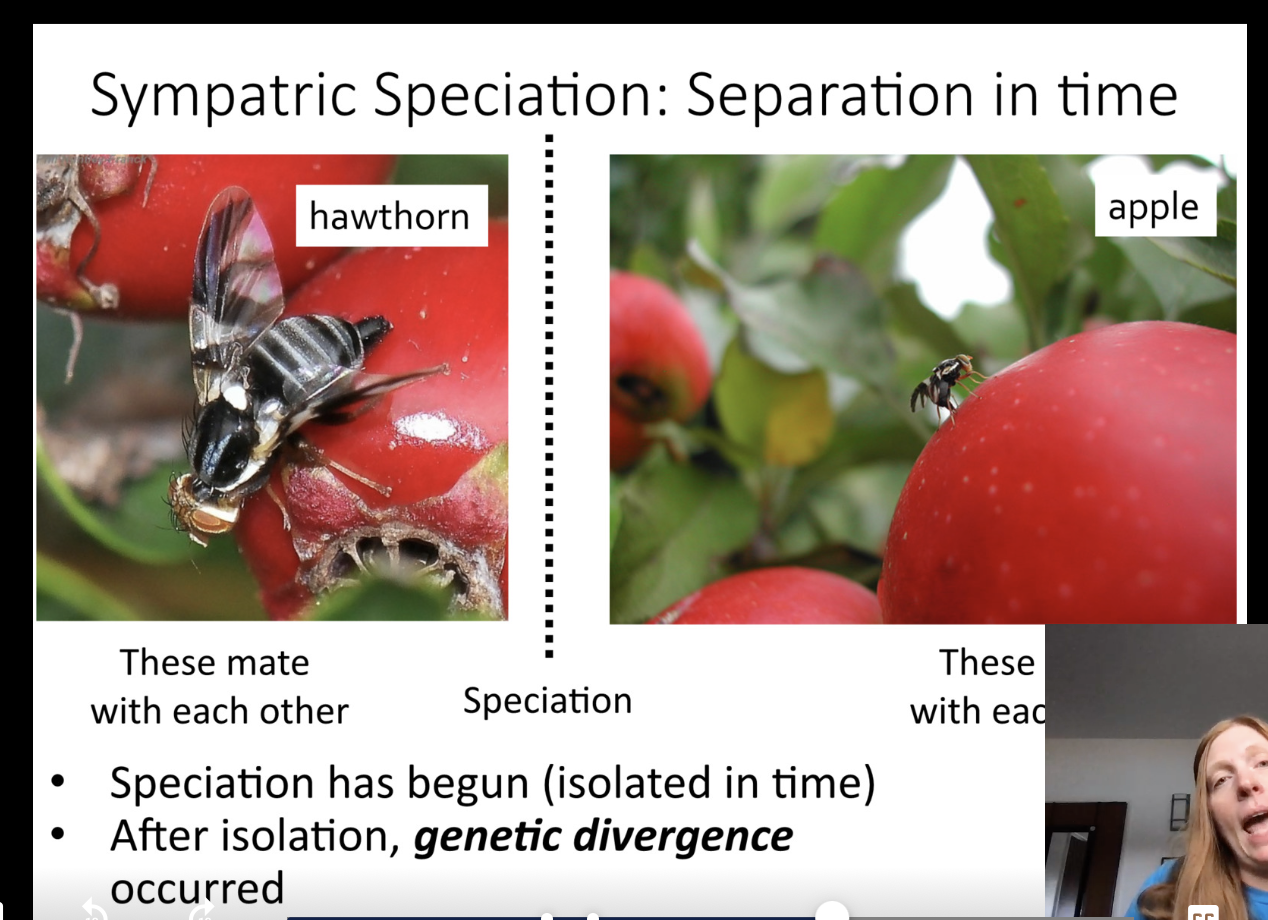
Sympatric Speciation Temporal isolation: separation in time
example: hawthorn fruit fly
native to US
attracted to fruit smell
lay eggs in (small) hawthorn fruit
than apples introduced to USA in 1623
mutated led some lies to be attracted to apples and lay eggs on apples instead
temporal isolation: separation in time (apples in early summer where hawthorn fruit later in summer)
genetic divergence: thought experiment
background: the bee battle is a mimic of bumblebees that feeds on pollen as an adult
their larvae live underground and feed on the plant roots
imagine that there is a wide, deep valley in the home range where this battle resides
in the valley between the two populations, a river forms, dividing the beetles into two populations
one population is now in a deeply shaded and very moist forest, while the other is in a dry, exposed, rocky area

Barriers to speciation
pre zygotic barriers
pre- before, zygotic: relating to the zygote
barriers that stop the zygote from forming
zygote: an egg cell after fusion of the egg and sperm nucleus (i.e., the first cell of a new organism)
post zygotic barriers
post: after, zygotic: relating to the zygote
occurs after zygote formation
examples for pre : barriers in space or time: individuals never meet, behavioral isolation: females reject their potential mates from the other population/species
examples of post: hybrid inviablilty: mating occurs, but hybrid (2 kinds of parents) and zygotes either don’t develop or die before birth. hybrid sterility: hybrids survive, they are sterile e.g, mule =sterile offspring of horse + donkey
Summary of Speciation
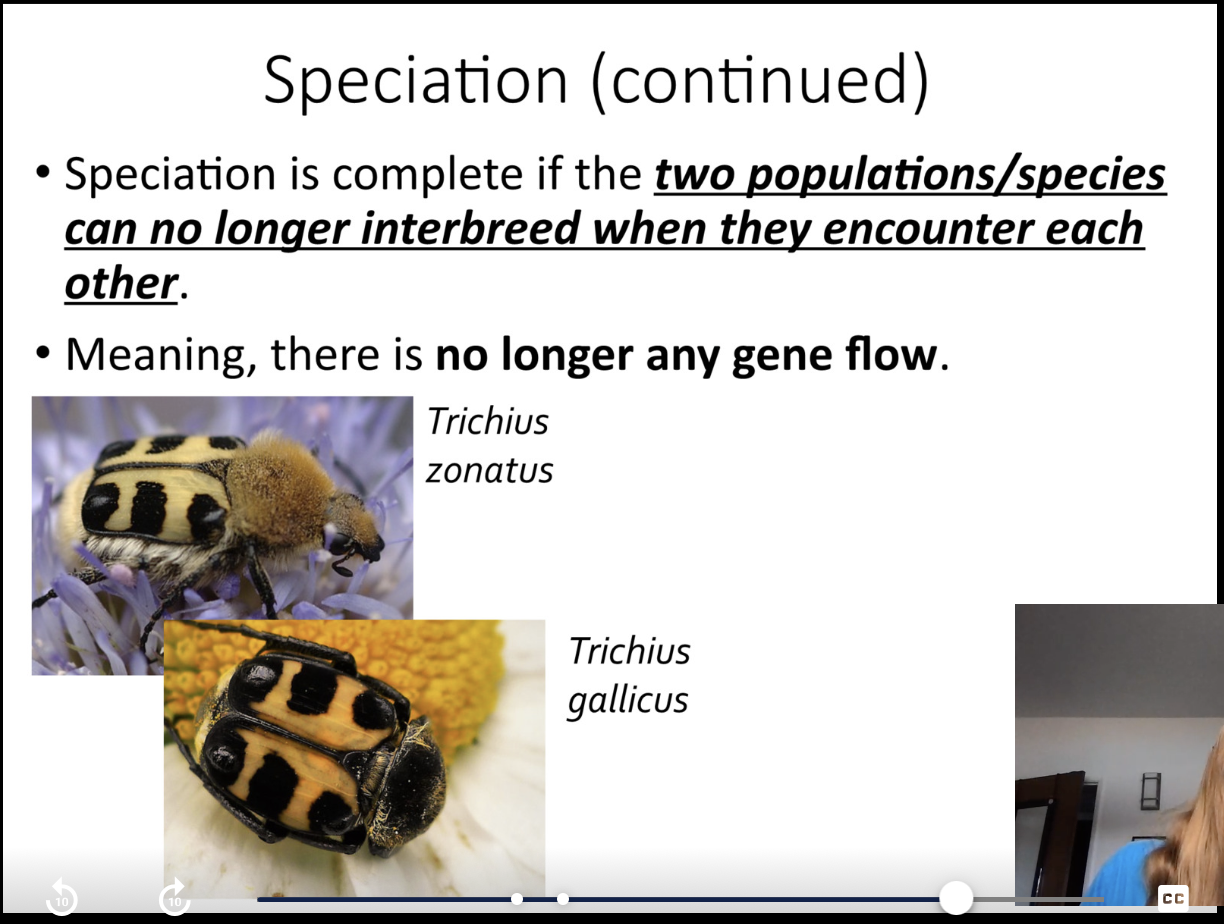
one population becomes divided into two and there’s no longer any gene flow
the populations become more and more genetically different over time
if they come back in contact with each other, they can no longer successfully mate and produce healthy offspring. barriers are a) pre b)post