NCM100j
1/159
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
Theory
organized system of accepted knowledge that is composed of concepts, propositions, definitions and assumptions intended to explain a set of facts, events or phenomena.
Theory according to Chin & Kramer
a creative and rigorous structuring of ideas that projects a tentative, purposeful and systemic view of phenomena.
Theory according to Smith & Parker (2015)
a notion, idea that explains experiences, interprets observation, describes relationships and project outcomes.
Theory according to Kozier (2008)
A system of ideas that is proposed to explain a given phenomenon.
Definition
various descriptions which convey a general meaning.
Assumptions
is a statement that specifies the relationship of factual concepts
Phenomena
an observable circumstance or event – disease concepts, racism
Proposition
is a logically and theoretically valid statement that explains relations between
variables/parameters/concepts under
consideration.
Conceptual Framework
defines the relevant variables for your study and maps out how they might relate to each other
Nursing, according to American Nursing Association (ANA)
diagnosis and treatment of human response to actual or potential health problems.
Nursing, according to International Council of Nurses (ICN)
encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups and communities, sick or well in all settings
Nursing Importance
enhance students understanding of the principles, values, and meanings of nursing profession.
Significance
useful in guiding nursing practice and scholarship
provide structure from which testable theories may be derived
Internal Consistency
requires all constructs of the theory to be congruent, including the philosophical claims, conceptual model, concepts, and proposition
Parsimony
This principle of Occam's razor dictates that a theory should provide the simplest possible (viable) explanation for a phenomenon
Testability
Can be questioned; subjected to examination + makes the most reliable guide to scholarly work
Empirical Adequacy
used to ascertain the congruence between theoretical assertions and empirical evidence.
Pragmatic Adequacy
refers to a criterion common to practice disciplines in which theories and research findings must be useful to enhance practice or solve issues arising from practice (Fawcett & Downs, 1992).
Theorist for Theory of Human Needs + its concepts
1.) Abraham Maslow
2.) Concepts:
Self Actualization (desire to accomplish everything that one can, and “to become everything one is capable of becoming”)
Self-esteem (the need for respect from others and the need for respect from oneself.)
Love and Belongingness (give and receive love)
Security and Safety (need for law, order, and protection)
Physiological Needs (basic needs - oxygen is the most basic)
Theory of Human Needs / Hierarchy of Needs
The theory states that humans are motivated to fulfill their needs in a hierarchical order. The ultimate goal, according to the theory, is to reach the fifth level of the hierarchy.
Abraham Maslow
Man is a wanting being was said by which theorist
Theory of Human Needs
This theory remind nurses that an individual's basic needs must be fulfilled before attempting to meet higher-level requirements.
Sullivan’s Interpersonal Theory
Role of interpersonal relationships and social experiences in shaping personality.
Stages of Development according to Sullivan
Infancy (0-18) - gratification of needs
Childhood (18 months - 6 yrs) - delayed gratification
Juvenile (6-9 yrs) - formation of peer group
Pre-adolescence (9-12 yrs) - developing relation with the same gender
Early Adolescence (12-14 yrs) - identity
Late Adolescence (14-21 yrs) - Forming lasting relationship
Three types of Self according to Sullivan
Good me (social appraisal), Bad me (based on fear and anxiety of negative feedback), Not me (repressed component of self)
Lewin’s Change Theory
The theory posits that there are three main stages in the change process: Unfreezing, Change, Refreezing
Unfreeze
Initial phase/stage of change according to Lewin’s theory
Change
When a change is implemented according to Lewin’s theory
Freeze
Final stage; stabilizing the change according to Lewin’s theory
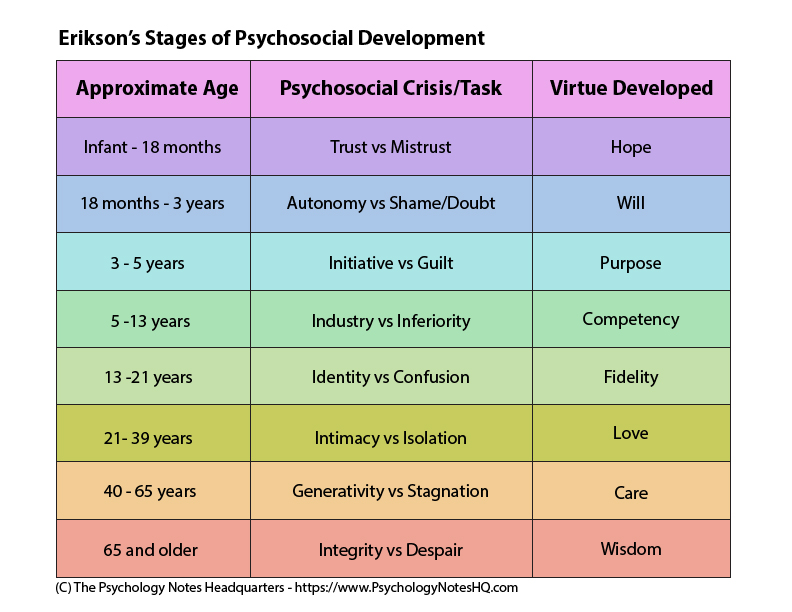
Erickson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development Theory
This theory focuses on the personality gained at each stage through social interaction and relationships. It highlights the conflicts humans face at each stage of development.
8 stages of Erickson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development Theory
Lawrence Kohlberg’s Moral Development Theory
Theorized that humans develop their moral judgements in 6 stages
Moral/Morality
defined as beliefs about what is wrong and right, good and bad
Pre-conventional Stage - Self-centered
Stage 1: Obedient and Punishment (fear/rewards)
Stage 2: Self-Interest (own needs / interest)
Type of stage of Stage 1 of MDT
Two stages of Stage 1
Conventional
Stage 3: Interpersonal Relationships (desire to be seen as a good person)
Stage 4: Maintaining Social order (values, laws, authorities)
Type of stage of Stage 2 of MDT
Two stages of Stage 2 in MDT
Post-Conventional
Stage 5: Social Contract (laws and rules are seen as flexible)
Universal Principle (justice, equality, and human rights)
Type of stage of Stage 3 of MDT
Two stages of Stage 3 in MDT
Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
a theory of development gathered through observing his own children's behavior on certain tasks during infancy and childhood.
Schema
an assumption that an individual has of the self, others, or the world; building blocks of knowledge in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Assimilation
process by which we incorporate new information into existing schemas in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Accommodation
new information or experiences cause you to modify your existing schemas in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Equilibration
process of balancing assimilation and accommodation to create schemes that fit the environment in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Sensorimotor (0-2 years old)
Babies develop their first schemas by using their senses in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive.
Object Permanence
ability to know that an object exists even when it is not being sensed in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive.
Pre-operational Stage (2-5 years old)
The thinking is influenced by the way things appear rather than logical reasoning in Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive.
Concrete Operational Stage (6-11 years old)
More frequent and accurate use of logical transformations and operation
Children at this age can think more logically about physical reality
Formal Operational Stage
Scientific & abstract reasoning
Metacognition - ability to reflect upon one’s thinking
Eric Berne’s Transactional Analysis Theory and Therapy
This theory looks at how we speak and respond to others and at the roles we play. It proposed that every individual has three ego states, which are distinct patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving.
Eric Berne’s Transactional Analysis Theory and Therapy
His theory was based on the ideas of Freud and Carl Jung but it was distinctly different.
Three Ego States
Parent
Adult
Child
Complementary Transactions
Transactions that occur when two people communicate with each other in the same role.
Crossed Transactions
Transactions that take place when two people communicate with each other in different roles.
Life Scripts
In TAT&T, the unconscious life plans or patterns of behavior that people develop in early childhood.
Florence Nightingale
known as the “Founder of Modern Nursing”
Environmental Theory
The act of utilizing the environment of the patient to assist him in his recovery
Four (4) Concepts of Environmental Theory
• Natural laws
• Mankind can achieve perfection
• Nursing is a calling
• Nursing is an art and science
Environment
can be external and internal, and is stressed in Nightingale’s writing, where she focused more on ventilation, warmth, noise, light, and cleanliness.
Florence Nightingale
states that “health is not only to be well, but to be able to use every power we have.”
Pure Air
Pure Water
Efficient Drainage
Light
Cleanliness
5 Essential Components of a healthy environment in Health of Houses
Virginia Henderson
The Modern-Day Nightingale
Virginia Henderson’s Nursing Need Theory
Focuses on the importance of increasing the patient’s independence so that progress after hospitalization would not be delayed
Abraham Maslow’s Theory
14 Human Basic Needs of Virginia Henderson was based on this theory
Faye Glen Abdellah’s 21 Nursing Problems
The practice of competent nursing care in the future is for the nursing student to realize that
identifying and answering overt and covert nursing problem is the core of Nursing
Identify the problem
Select the data
Devise hypothesis
Test hypothesis
Revise Hypothesis
Problem-Solving Process in Faye Glen Abdellah’s 21 Nursing Problems
Faye Glen Abdellah’s 21 Nursing Problems
conceptual model mainly
concerned with patient’s needs and
nurses’ role in problem identification using
a problem analysis approach
Ernestine Wiedenbach (Author of the Helping Art of Clinical Nursing)
known for her work in theory
development and maternal infant nursing
while teaching maternity nursing
Need for Help (Ernestine Wiedenbach)
A measure desired by the patient that has
the potential to restore or extend the ability
to cope with the demand implicit in his
actions. This is based on the individual’s
perception of his own situation.
Phenomenal Field (Theory of Human Caring)
The totality of human experience of one’s in
the world.
Subjectively; objectively
The present is more ______ real, and
the past is more ______ real in Jean Watson’s theory.
Jean Watson
stated the term “soul-satisfying”
when giving out care for the clients.
Patricia Benner
A nursing theorist famous for introducing
the Skill Acquisition in nursing
Patricia Benner
She is the first to develop the five different
stages of clinical competence
Patricia Benner’s from Novice to Expert
Presents a systematic way of how a nurse
develops their skills and understanding of
patient care over time.
Patricia Benner’s from Novice to Expert
Utilizes the Dreyfus Model of Skill
Acquisition by the Dreyfus brothers, Stuart
and Hubert, as basis or underlying principle
in creating the concept
Novice
Stage in Benner’s theory: Beginner with no experience
Advanced Beginner
Stage in Benner’s theory: Has gained prior experience in actual
situations to recognize recurring
meaningful components
Advanced Beginner
Stage in Benner’s theory: Principles, based on experiences, begin to
be formulated to guide actions
Competent
Stage in Benner’s theory: Typically, a nurse with 2-3 years of experience on the job in the same area or
in similar day-to-day situations
Competent
Stage in Benner’s theory: Gains perspective from planning own
actions based on conscious, abstract, and
analytical thinking and helps to achieve
greater efficiency and organization
Proficient
Stage in Benner’s theory: More holistic understanding improves
decision-making
Expert
Stage in Benner’s theory: No longer relies on principles, rules, or
guidelines to connect situations and
determine actions
Expert
Stage in Benner’s theory: Has intuitive grasp of clinical situations
Expert
Stage in Benner’s theory: Performance is now fluid, flexible, and
highly-proficient
Hildegard Peplau
“Mother of Psychiatric Nursing”
Hildegard Peplau
Published her 1st book “Interpersonal
relations in Nursing”
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory
Emphasizes the “nurse-client” relationship
as the main foundation of nursing practice.
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory
A “maturing force and an educative
instrument” involving an interaction
between two or more individuals with a
common goal.
Orientation
Phase in HP’s IRT: Initial interaction between
the nurse and client as strangers.
Orientation
Phase in HP’s IRT: Client
seeks assistance, asks questions, and
conveys needs to express desire for
professional help.
Identification
Phase in HP’s IRT: Client begins to open
up more to the nurse. Feelings of
relatedness and hope resonate.
Exploitation
Phase in HP’s IRT: Client makes full use of
the services offered.
Termination
Phase in HP’s IRT: Client earns
independence and no longer needs
professional service. Relationship ends.
Exploitation
Phase in HP’s IRT: Patient moves on from
a dependent role to an independent one.
Orientation
Phase in HP’s IRT: Nurse responds by
identifying problems, uses available
resources and services to help address the
needs of the client.
Stranger
Surrogate
Resource Person
Teacher
Leader
Counselor
6 Nursing roles according to H. Peplau
In Ida-Jean Orlano-Pelletier’s theory, ______ (metaparadigm) is replaced
by a sense of helplessness as the
initiator of a necessity for nursing.
Function of Professional Nursing
Presenting Behavior
Immediate Reaction
Nursing Process Discipline
Improvement
Ida Jean Orlando described her model as
revolving around the following five major
interrelated concepts:
Nurse Reaction
The patient’s
behavior stimulated a _______,
which marks the nursing process
discipline’s beginning.
Automatic / Deliberative
The
nurse’s action may be ________ or _________
Automatic
are nursing actions
decided upon for reasons other
than the patient’s immediate need
Deliberative
are nursing actions
decided upon after ascertaining a
need and then meeting this need.