Lo1-4 Opportunity costs and the Time Value of Money
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Personal opportunity costs
Every Financial decision involves giving up something to obtain something you consider more desirable
Personal resources like financial resources require careful management
Ex: Health, abilities, knowledge, time used for working or studying
Financial opportunity costs
Time Value of Money: Increases in an amount of money as a result of interest earned
Saving today means more money tomorrow
Saving and spending decisions involve considering the trade offs
Opportunity costs are present in retirement contributions, large purchases, and low risk savings
Interest calculations
Three amounts are required to calculate the time value of money
Principal (amount of savings)
Interest rate (annual)
Time period (length of time money is on deposit)
Computing simple interest
Amount in savings X annual interest X time period = interest amount
$500×6%x(6 months/12 months) = 500$ x .06 × ½ year = $15 gained
In six months, a $500 deposit (principal) will earn $15 interest. Therefore, you will have a total of $515 at the end of six months
methods for calculating the time value of money
Formula calculation
Time value of money tables
Financial calculator
Spreadsheet software
Websites and apps
Future value
The amount to which current savings will increase based on a certain interest rate and a certain time period
Also called compounding — earning interest in previously earned interest
Compounding allows for the future value of a deposit to grow faster than it would if interest were paid only on the original deposit
For example: $100 deposited in a 4 percent account for one year will grow to $104. This amount is computed as follows:
Future value = (100 × 0.04 × 1 year) = $104
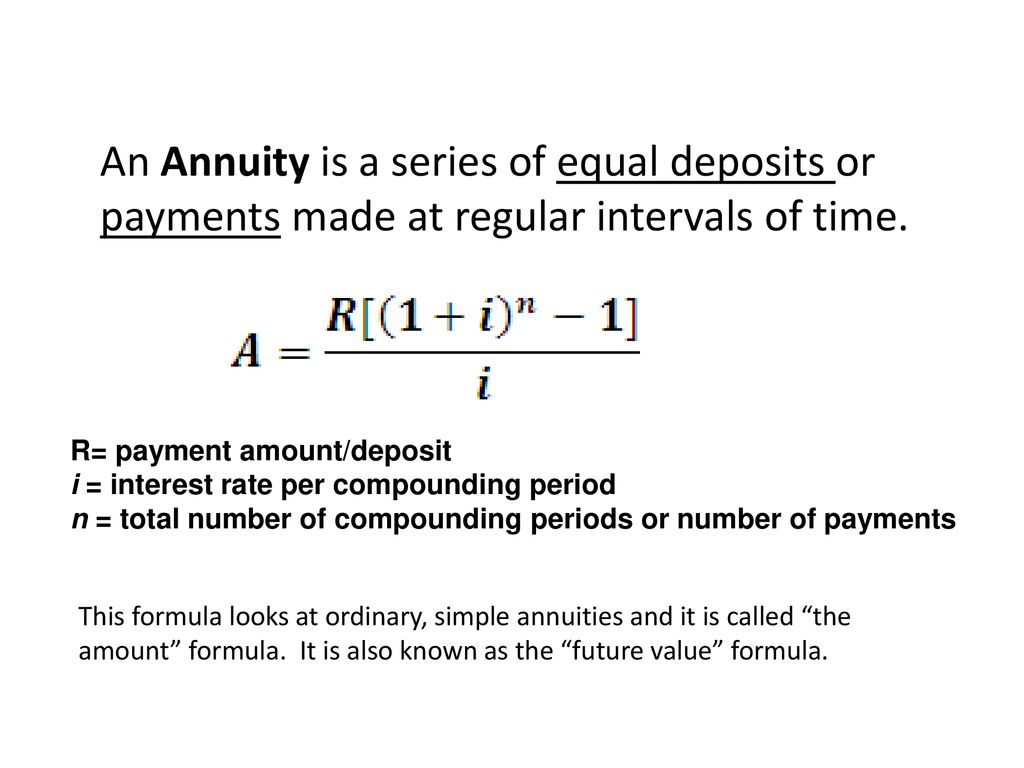
Future value of a series of deposits
Future value can be deposited for a single amount or for a series of deposits (or payments) called in annunity
$50 deposited a year at 7% for six years
Formula shown below
Present Value
the current value of a future amount based on a certain interest rate and a certain time period
present value calculations are also called discounting
The present value of the amount you want in the future will always be less than the future value
Present value can be computed for a single amount or for a series of deposits