Bio 5B Animal Reproductive systems
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
sexual reproduction in mammals
Copulatory organ in males (penis).
Testis usually in scrotum (suspended sack of skin and smooth muscle).
-Internal fertilization.
-Most viviparous.
-Amnion, chorion and allantoids
Hormonal levels determine expression of distinctive sexual characteristics
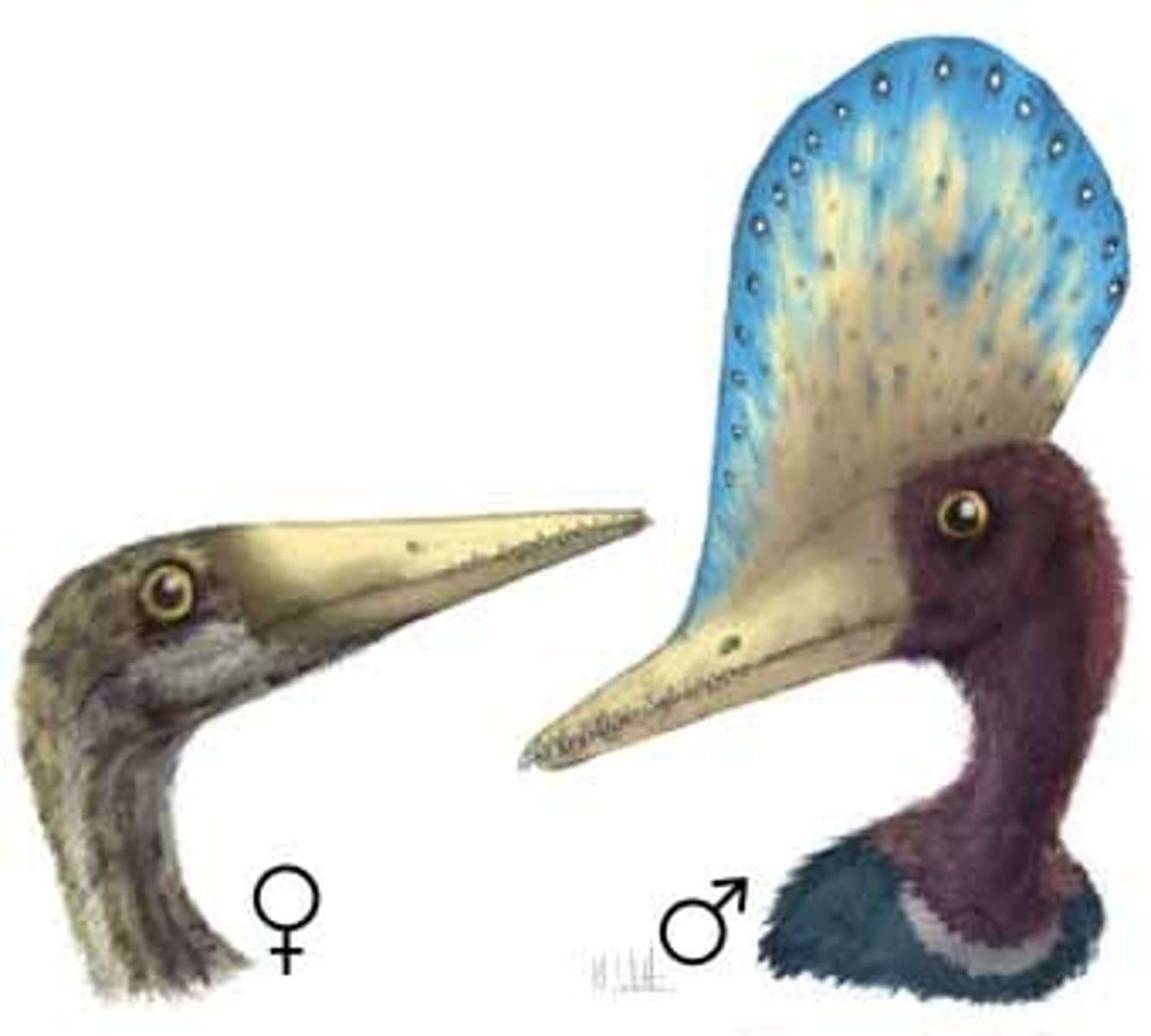
sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species.
size, coloration, morphology
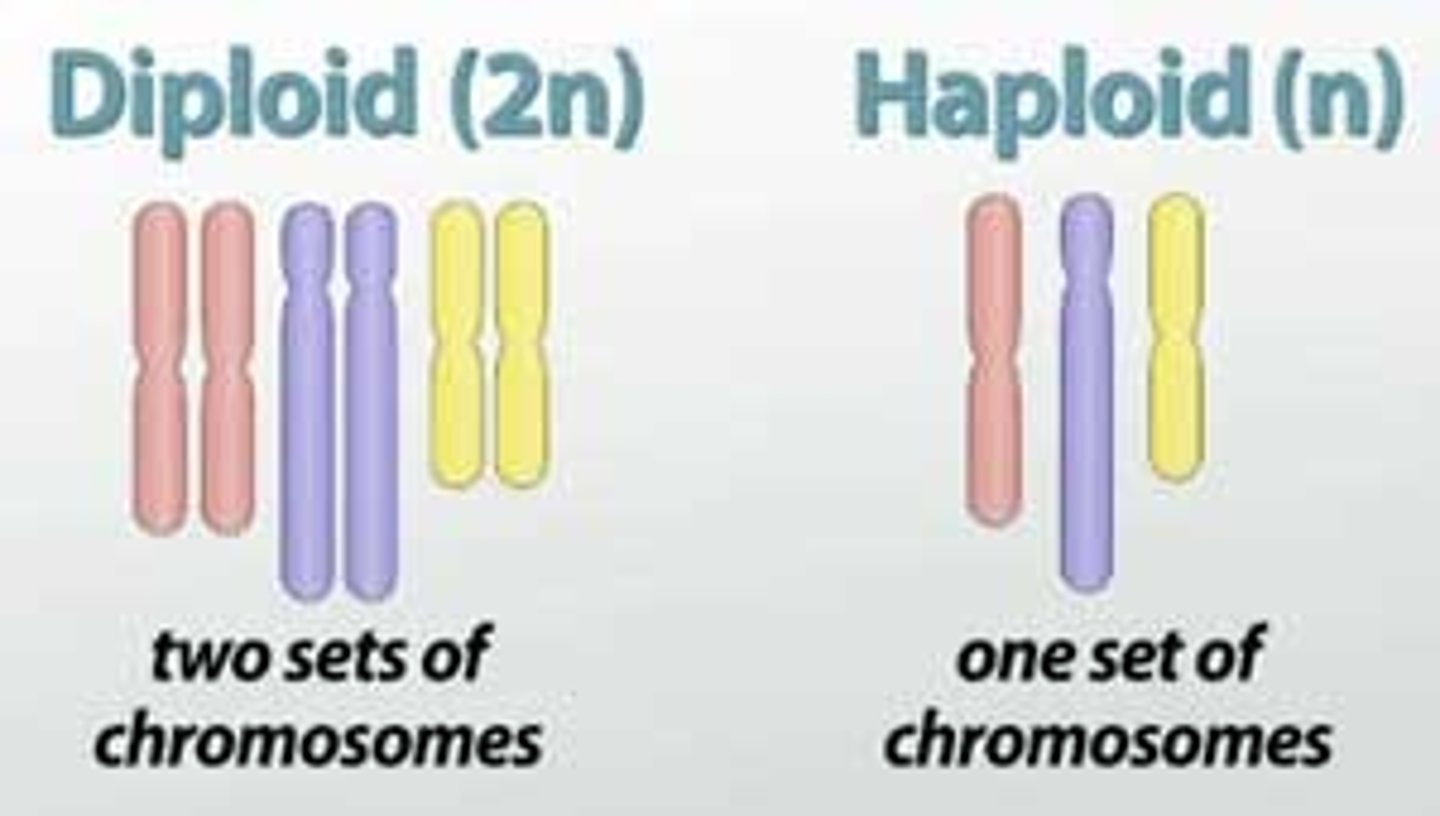
Diploid
Contains two full sets of chromosomes, one set is inherited from each parent. Humans: 46 chromosomes
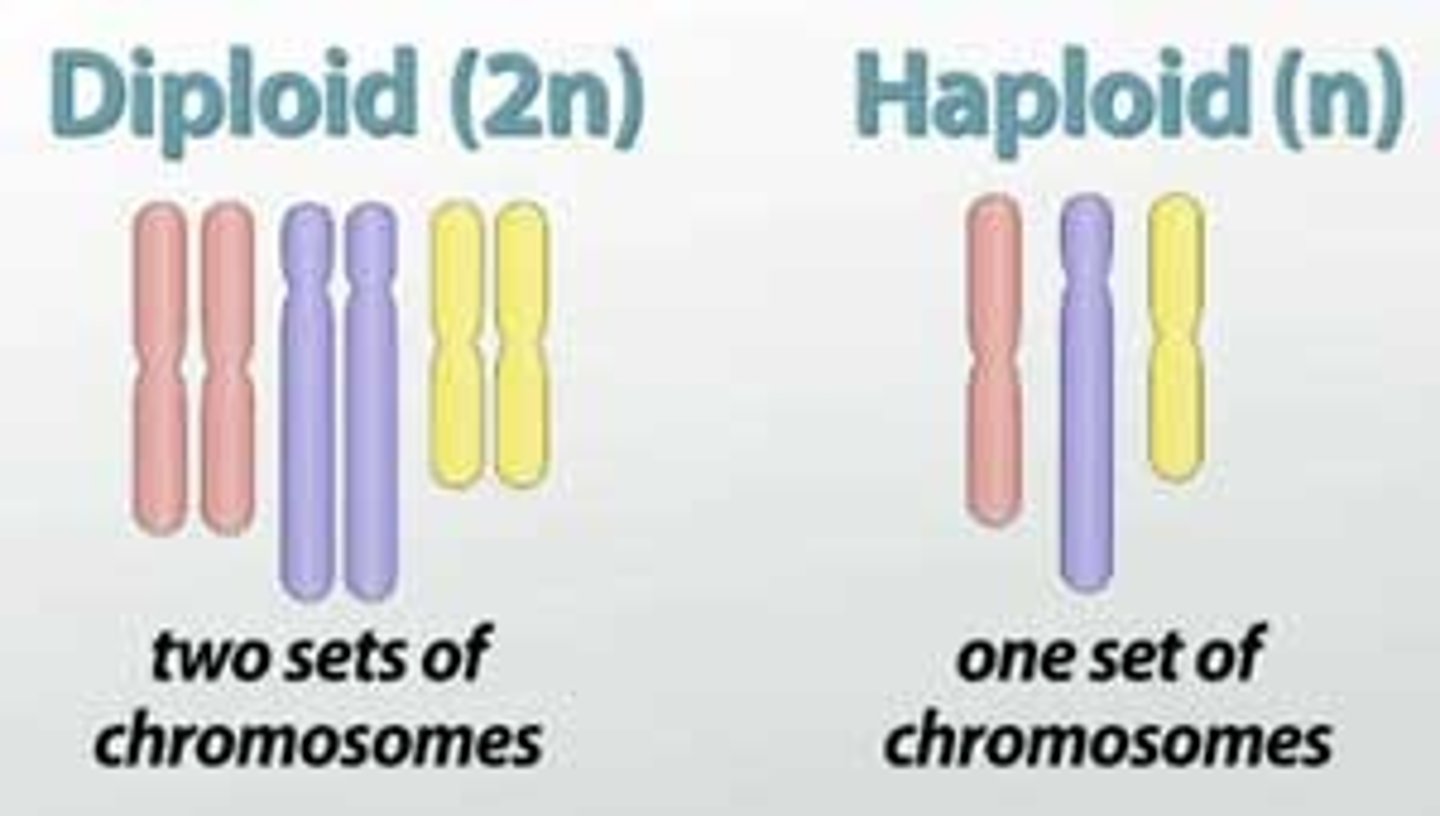
haploid
Contain just one set of chromosomes.
Gametes: Sperm cells and egg cells required for sexual reproduction
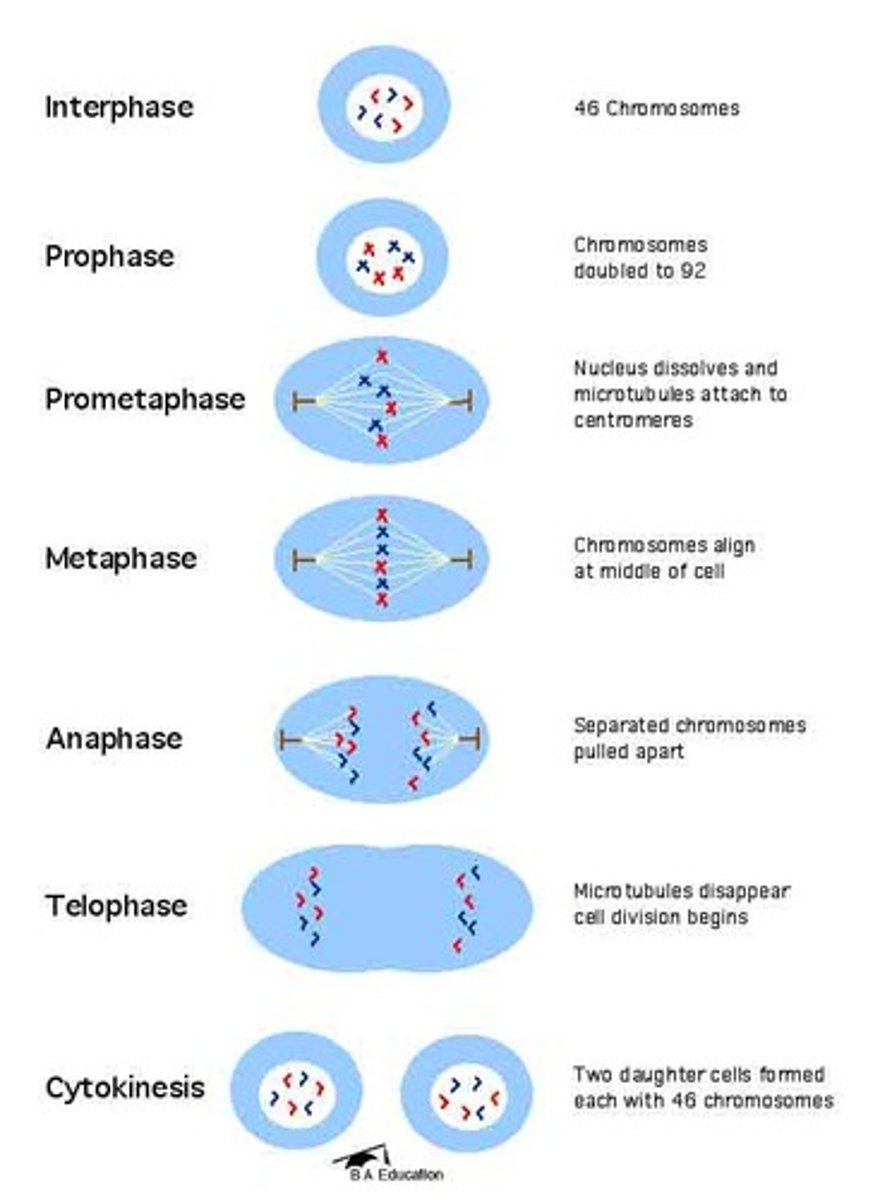
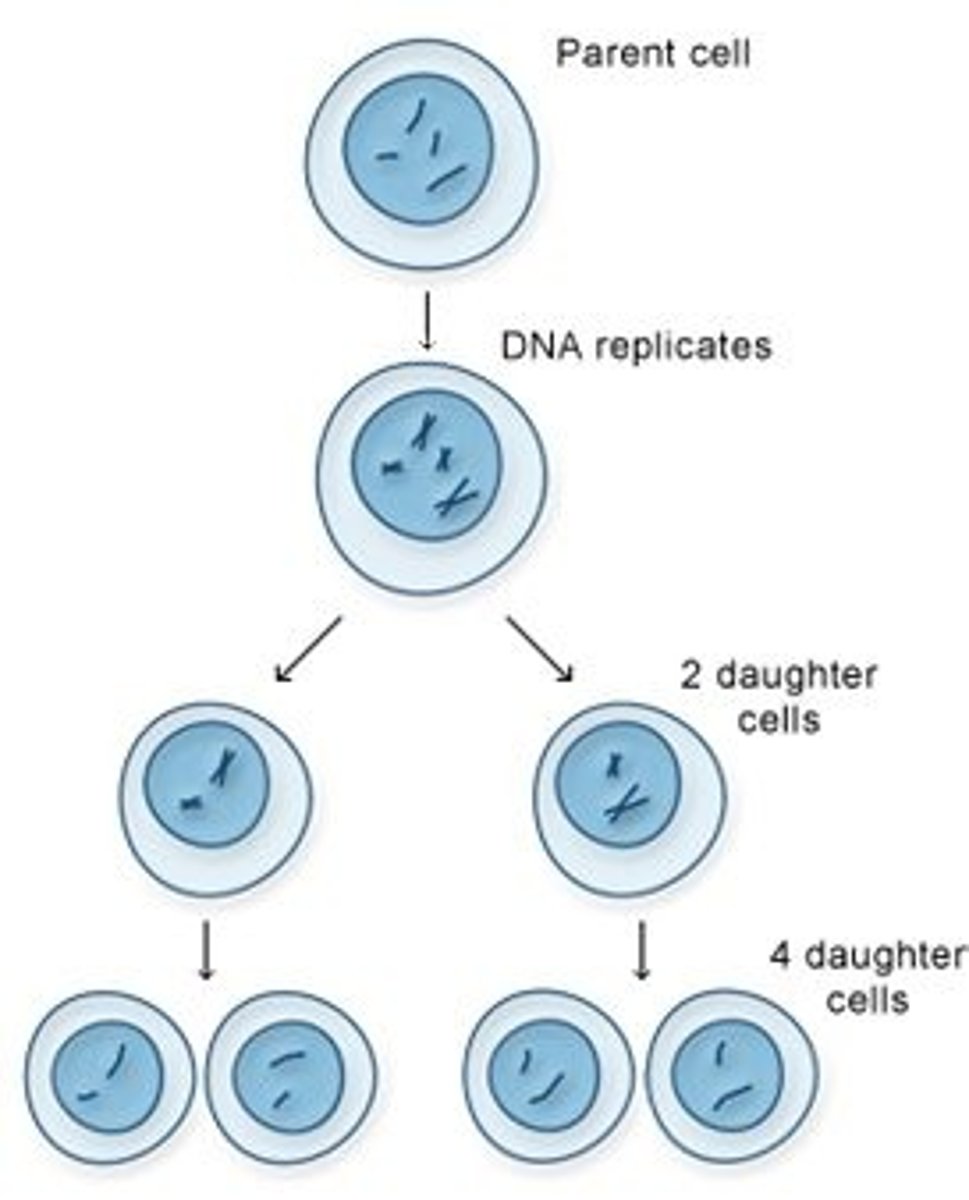
mitosis
Final product: 2 diploid daughter cells (2n) identical to the mother cell
sexual anisogamous reproduction
Recombination of genetic material from two individuals to create a third individual. Needs fertilization of an egg.
In humans:
- Eggs fertilized by X-bearing sperm become females (XX).
- Eggs fertilized by Y-bearing sperm become males (XY)
sex assignments in humans
A newborn baby is assigned a "biological sex" that reflects the genitals present at birth and the child's chromosomes
hormonal cycles in females
Hormonal fluctuations and specific periods of fertility.
menstrual cycle...
Luteinizing hormone, FSH, estrogen, progesterone
ovarian cycle in female humans
hormonal fluctuations and specific periods of fertility
hypothalamus= GnRH
Pituitary
- LH: Luteinizing hormone
-FSH: follicle stimulating hormone
ovaries= growing follicle, estrogen and progesterone
uterine menstrual cycle
LOOK AT PHOTO
sexual reproduction
-Isogamous: the fusion of morphologically similar gametes, having similar shapes and sizes
-Anisogamous: Dioecious (male and fem)
hermaphroditic (monoecious)
asexual reproduction
- Fission (bacteria)
- budding (marine invertebrate)
******************
- parthenogenesis (large animals and all-female, they have one stimulus that makes the development of an egg
sexual reproduction in spiders
Dioecious (male and female)
The male uses special cavities in his pedipalps and
*PEDIPALPS TRANSFER SPERM (look at photo)
sexual reproduction in insects
• Dioecious.
• release of Pheromones, courtship behavior, etc
sexual reproduction in vertebrates
external fertilization (fish release sperm into water)
internal fertilization (elephants have sex) birds, lizards

meiosis
Final product: 4 haploid daughter (n) cells not identical to the mother cell
A cell division in which the genetic information in the new cells is not identical to that of the original cell, "scrambles genetic information".
It results in cells with half the chromosomes of the parent cell, produces 4 daughter haploid cells, genetically variable and used in reproduction
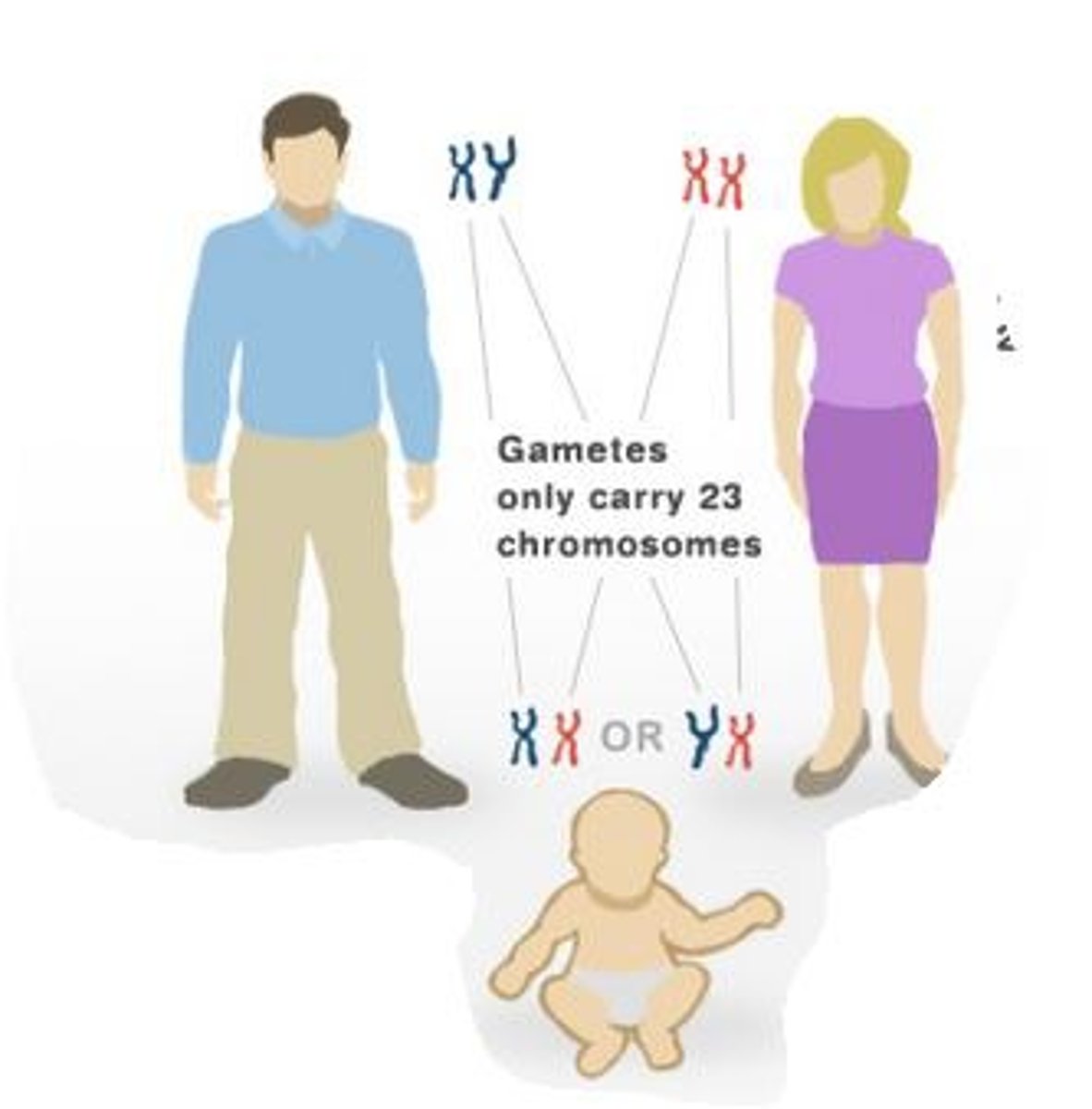
human genotype
Total of 46 chromosomes per somatic cell: Diploid number: Two sets of chromosomes per cell. Only gametes are Haploid: 23 chromosomes per gamete
you can tell if male or female with 23rd chromosome
female: XX
male XY
(look at photo)
pregnancy in eutherian mammals
Well-developed chorioallantonic placenta.
• Long gestation period in the uterus
Uterus: Muscular organ of the female reproductive system
Placenta: The vascular structure, both embryonic and maternal through which the fetus is nourished
Parental care in mammals
young may be altricial (completely dependent on mother ex: birds) or precocial (can walk immediately ex: zebra

components in milk produced by female mammals or women
the initial milk produced (colostrum) contains
- antibodies (immunoglobin, IgA)
- lactoferrin (protein: bactericide, fungicide)
- white blood cells