DDT - Diabetes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is diabetes?
A disorder that causes abnormally high glucose levels in the body due to insulin either being resistance or not produced at all
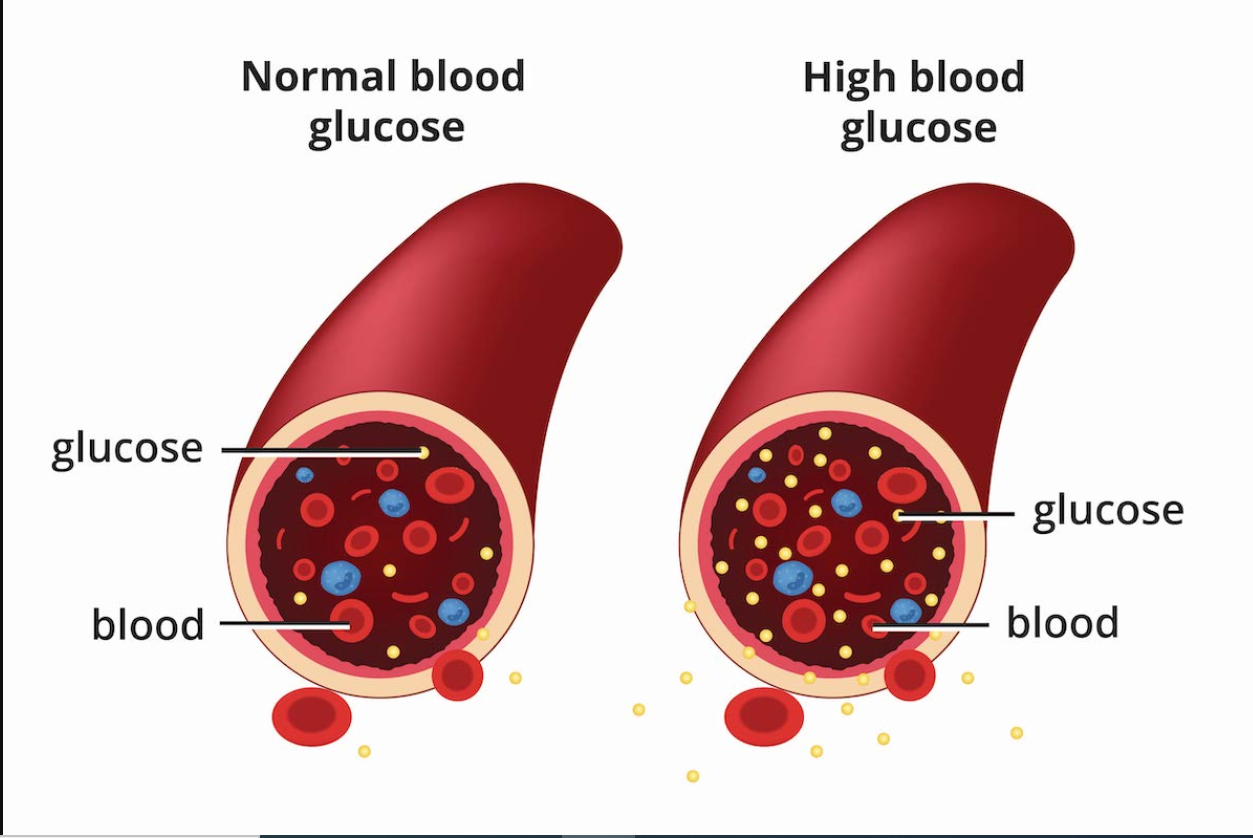
What are a few methods to possibly diagnose diabetes in a patient without requiring to take any samples?
BMI, Waist to hip ratio, libido (sexual activity) and blood pressure
What is the difference between glucagon and insulin?
Glucagon is released during low blood sugar levels to act on liver cells, turning glycogen to glucose. Insulin is produced when blood sugar levels are too high, and causes glucose to enter cells, increase amino acid uptake and protein synthesis, whilst stopping glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
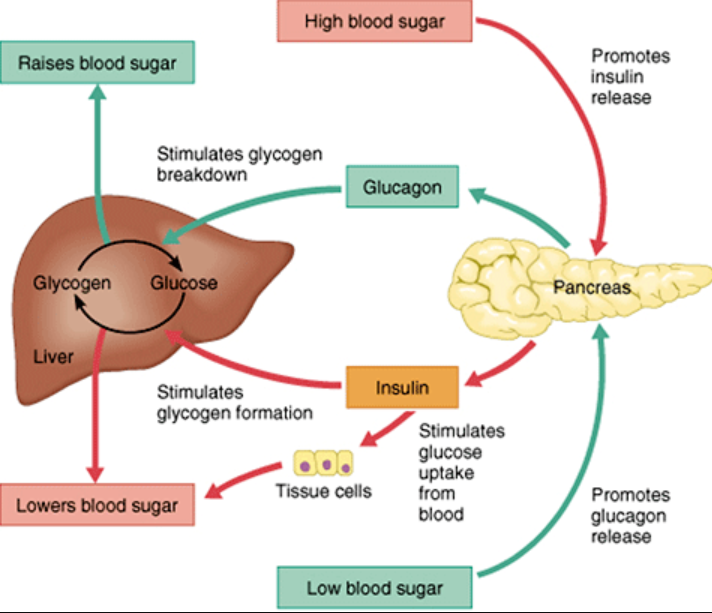
Types of pancreatic cells for, like alpha and beta
Alpha: Raise blood sugar levels
Beta: Lower blood sugar levels
Delta: Secrete somatostatin which inhibit insulin and glucagon
F cells: Pancreatic polypeptides that inhibit somatostatin, gallbladder contractions as well as secrete pancreatic digestive enzymes
What does insulin resistance ultimately result in?
Beta cell death, where are found in the pancreas. This would ultimately result in no insulin production, causing type 1 diabetes
What is type 2 diabetes?
Where the body is unable to use insulin effectively. This typically develops into type 1 diabetes, due to the body producing large amounts of insulin, however this would be over a long time frame, where absolutely no insulin is made at all
What is FPG diagnostic method?
FPG (Fasting plasma glucose) is a reading of glucose in the blood after roughly an 8 to 12 hour fast, of not digesting anything. Useful for measuring how body reacts to low blood sugar levels and is quite accurate, fasting is required and the values can change based on food and activity levels
What is HOMA 1-IR diagnostic method
HOMA 1-IR measures both fasting blood glucose and fasting insulin, measuring insulin resistance. Cheap and reliable as well as measuring beta-cell and insulin resistance but requires fasting
What is RPG diagnostic method?
RPG (Random plasma glucose) is a recording of glucose in the blood, at a random time. Useful for patients who would struggle with fasting, but can give spikes in glucose levels if just eaten
What is urinary glucose diagnostic method?
Urinary glucose is testing glucose levels in urine. Healthy urine should have no glucose, but those suffering from hyperglycaemia, would have glucose in their urine, which is called glucosuria. While quick, easy and not invasive, not as accurate as other testing methods and can be affecyed by certain renal factors

What is the HbA1c diagnostic method?
HbA1c measure % of glycated haemoglobin, useful for measuring blood glucose levels over a few month scale. Though it can be effected by certain conditions and can miss some diabetes cases
What is OGTT diagnostic method?
OGTT involves fasting, then ingesting highly concentrated glucose food or drink. Gives in depth results, but requires patient to vomit and can take a large amount of time to record and single measurement can’t give a diagnosis
What is euglycemic clamp diagnostic method?
Euglycemic clamp involves getting real-time reactions to increasing doses in glucose to detect insulin reactions. Considered the best in terms of accuracy (gold standard) and gives a large amount of information, it is inconvenient for the patient and is invasive, whilst being expensive
How does insulin resistance result in lipolysis? How would this cause an increase in VLDL? And what effects would VLDL have on the liver? What would the effect on the liver cause for the rest of the body?
Insulin resistance causes unhealthy levels of lipids (fat) in the body (dyslipidaemia), and due to the resistance, insulin cannot stop lipolysis (breaking down triglycerides), which will cause a build up of VLDL (Very low density lipoproteins). These will travel to the liver, decreasing lipoprotein lipids, which would otherwise put lipids back into cells. HDL levels will decrease, as it is cleared from circulation, but dense LDL will build up due to hydrolysis
What is MASLD and how is it linked to diabetes?
MASLD (Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease) is where fat builds up in the liver. Lipolysis, which would usually be stopped by insulin, is not, so fat build up in the liver, slowly losing functionality of the liver
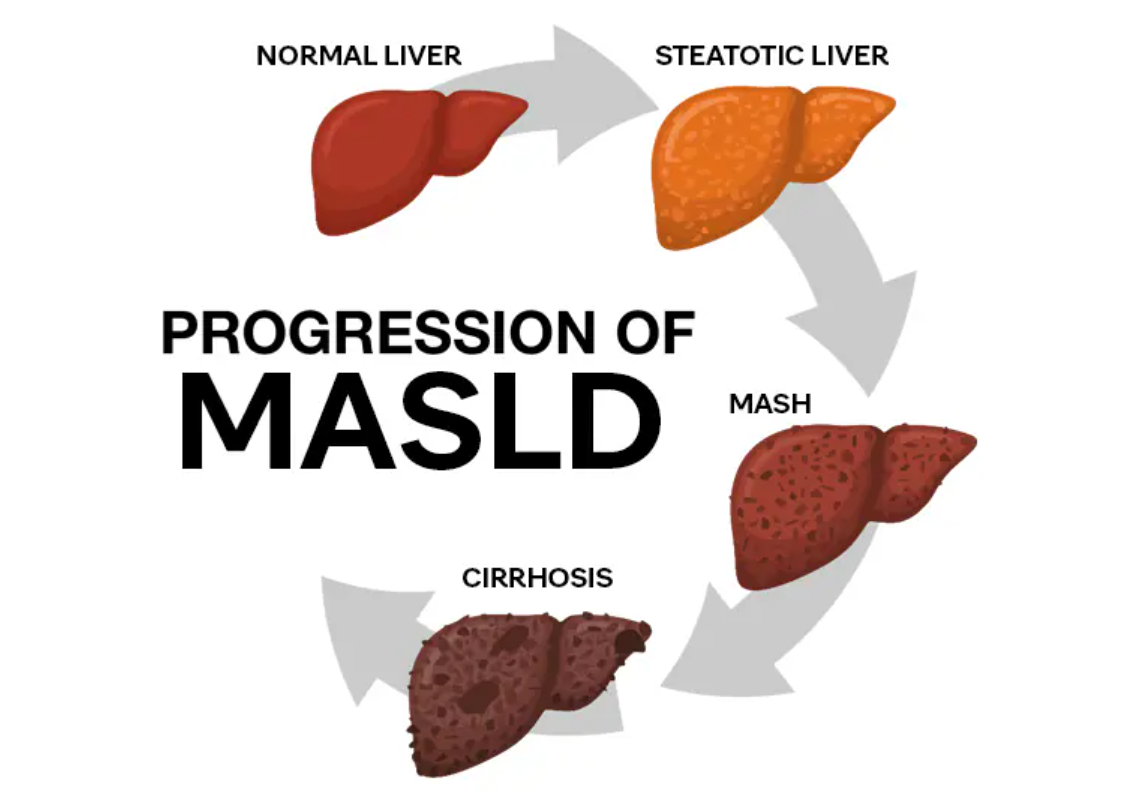
Complications of MASLD
De novo lipogenesis: Liver keeps synthesising fat as it is insulin sensitive
Impaired fat oxidation and export: Mitochondria impairment leaves liver unable to oxidise free fatty acids (FFA). Triglycerides not exported correctly, leading to fat build up
Oxidative stress: ROS and oxidative stress lead to liver inflammation and fibrosis, causing fat build up, causing hepatocyte injury
Inflammation: Adipose tissue inflammation release inflammatory cytokines, which promote inflammation in the liver, leading to MASH
What are a few ways to manage diabetes in terms of lifestyle choices? And how do each of these help when it comes to diabetes?
Consistent exercise release AMPK as well as PGC1a, which both have a lot of effects on different parts in the body. Weight management helps to reduce inflammation and free fatty acids, reducing insulin resistance and a healthy diet helps to deal with hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinemia. Appropriate sleep helps to manage appetite as well as heal muscles. It reduces cortisol, a stress hormone that naturally raises insulin and glucose levels
Oral treatment for diabetes
Metformin, increases AMPK levels, which has a lot of benefits for diabetes treatment. Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose levels, and secrete insulin for those suffering from type 1 diabetes (No insulin produced at all). SGLT2 inhibitors increase excretion of glucose in the urine to remove amount of glucose from the blood, due to lack of insulin. DPP-4 inhibitors lead to better insulin secretion
Injectable treatments for diabetes
GLP1 agonists: increase insulin secretion and decrease glucagon release and beta cells survive better. GLP1 agonists can be used alongside GIP agonists to have a synergistic effect, since it has very similar effects. Insulin can be given to treat t2d in cases where no other option is viable. Testosterone (used in low libido men) help with insulin signalling as well as mood and can give lifestyle benefits.
Experimental treatments for diabetes
Beta cell regeneration would help beta cells differentiate, proliferate and survive. Islet transplantation would be injected into the hepatic portal vein and begin to produce insulin. Using GLP-1/GIP/Glucagon tritagonists would activate receptors for all these things, with the benefits of the other two being similar, glucagon would help reduce liver fat and balance glucose regulation