Cumulative Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:53 PM on 5/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
Psychologist
* Ph.D.
* Therapy to treat mental illness
* Trains as a psychologist but specializes in clinical or counseling
* Views mental illness as a combination of disease and enviromental and personality factors
* Therapy to treat mental illness
* Trains as a psychologist but specializes in clinical or counseling
* Views mental illness as a combination of disease and enviromental and personality factors
2
New cards
Psychiatrist
* M.D.
* Primarily medication to treat mental illness
* Trains as doctor and completes additional training in the field of psychiatry
* Views mental illness as a disease
* Primarily medication to treat mental illness
* Trains as doctor and completes additional training in the field of psychiatry
* Views mental illness as a disease
3
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
* “The first psychologist”
* 1879 first documented psychological/experiment
* 1879 first documented psychological/experiment
4
New cards
William James
* The “father” of psychology
* Functionalism
* Behavior is on purpose
* Functionalism
* Behavior is on purpose
5
New cards
B.F. Skinner
* Rule of Consequence and what types of consequences are most effective
* Skinner Boxes
* Skinner Boxes
6
New cards
True Experiments must:
* MUST
* Have randomly assigned
* Have manipulation of an IV and measurement of a DV
* Have randomly assigned
* Have manipulation of an IV and measurement of a DV
7
New cards
Correlation Methods
* Access two variables that may be uncontrollable to the researcher
* Most common in psychological studies
\
* Advantages
* Allows prediciton of behavior
* Disadvantages
* Correlation =/= Causation
* Directional Problem
* Third Variable Problem
* Most common in psychological studies
\
* Advantages
* Allows prediciton of behavior
* Disadvantages
* Correlation =/= Causation
* Directional Problem
* Third Variable Problem
8
New cards
Experimental Methods
* Manipulation of an IV in a controlled enviroment in order to observe change in DV
* Allows us to make judgements about causation
* Most controll over variables
* Allows us to make judgements about causation
* Most controll over variables
9
New cards
Cones
* Needs a Lot of Light Information
* Located in Center of the Retina
* Used in Fine Details of an Image
* Percieves Color of the Light
* Located in Center of the Retina
* Used in Fine Details of an Image
* Percieves Color of the Light
10
New cards
Rods
* Sensitive to Light
* Needs very Little Light to Send Signals
* Located on the Edge of the Retina
* Only percieves in Black and White
* Needs very Little Light to Send Signals
* Located on the Edge of the Retina
* Only percieves in Black and White
11
New cards
Gate Control Theory
\
Limited Amount of Processing of a Certain Amount of Information from One Part of the Body
Limited Amount of Processing of a Certain Amount of Information from One Part of the Body
12
New cards
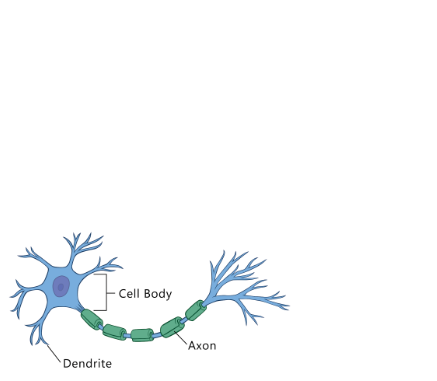
Neuron Structure
* Cell Body
* Dendrites
* Myelin Sheath
* Axon
* Dendrites
* Myelin Sheath
* Axon
13
New cards
Types of Neurotransmitters
* Serotonin
* Norepinephrine
* Dopamine
* Glutamate and GABA
* Acetylcholine
* Norepinephrine
* Dopamine
* Glutamate and GABA
* Acetylcholine
14
New cards
The Four Lobes
1. Frontal Lobe
2. Parietal Lobe
3. Temporal Lobe
4. Occipital Lobe
15
New cards
Frontal Lobe
Primary Motor Cortex
* Voluntary movements
\
Pre-Frontal Cortex
* Judgement
* Planning
* Attention
* Voluntary movements
\
Pre-Frontal Cortex
* Judgement
* Planning
* Attention
16
New cards
Parietal Lobe
\
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
* Touch
* Pain
* Temperature
* Body position
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
* Touch
* Pain
* Temperature
* Body position
17
New cards
Temporal Lobe
Primary Auditory Complex
* Process incoming sounds from ears
\
Recoginition of Visual Stimuli
* Objects
* Familiar People
\
Language Center
* Understanding speech
* Coherent Speech
* Process incoming sounds from ears
\
Recoginition of Visual Stimuli
* Objects
* Familiar People
\
Language Center
* Understanding speech
* Coherent Speech
18
New cards
Occipital Lobe
Primary Visual Cortex
* Interprets sensory information from the brain
* Connects to Temporal Lobe
* Identify what we see
* Connects to Parietal Lobe
* Process movement in what we see
* Interprets sensory information from the brain
* Connects to Temporal Lobe
* Identify what we see
* Connects to Parietal Lobe
* Process movement in what we see
19
New cards
Dendrites (Neuron Structure)
* Recieves Information
20
New cards
Axon (Neuron Structure)
* Sends Information
21
New cards
Myelin Sheat
* Glia cell that support communication
22
New cards
Cell Body (Neuron Structure)
* Brains of the Neuron
23
New cards
Neurotransmitters
* Chemical messages that changes charges of the fluid that neurons sit in
24
New cards
Depolarization
* Neuron becomes more-like its fluids charge
* More positive
* Positive Charge continues communication (Action Potential)
* More positive
* Positive Charge continues communication (Action Potential)
25
New cards
Hyperpolarization
* Neuron becomes even more negatively charged
* Negative Charge stops communication
* Negative Charge stops communication
26
New cards
Excitatory (Neurotransmitters)
* Depolarize the neuron
* Good communication
* Good communication
27
New cards
Inhibitory (Neurotransmitters)
* Hyperpolarizes the neuron
* No communication
* No communication
28
New cards
Subcortical Structures
* Sensory Processing
* Emotional Reaction
* Emotional Reaction
29
New cards
Thalamus (Subcortical)
* Sensory information processing
30
New cards
Basal Ganglia (Subcortical)
* Voluntary movement
31
New cards
Amygdala (Subcortical)
* Deals with fear and aggression response
32
New cards
Hippocampus (Subcortical)
* Create long term memories
33
New cards
Hypothalamus (Subcortical)
* Regulates human functions
* Themperature
* Hunger
* Sexual Arosual
* Themperature
* Hunger
* Sexual Arosual
34
New cards
Brain Stem
* Basic Functions
* Keep the human alive
* Keep the human alive
35
New cards
Medulla (Brain Stem)
* Controls
* Blood Pressure
* Heart Rate
* Blood Pressure
* Heart Rate
36
New cards
Pons (Brain Stem)
* Controls
* Sleep Alertness
* Awake Alertness
* Sleep Alertness
* Awake Alertness
37
New cards
Cerebellum (Brain Stem)
* Controls
* Motor Coordination
* Motor Balance
* Motor Coordination
* Motor Balance
38
New cards
Recticular Formation (Brain Stem)
* Controls with hormones (Sertonin/Norepinephrine)
* Mood
* Some Sleep
* Norepinephrin
* Important in the “fight/flight” response
* Mood
* Some Sleep
* Norepinephrin
* Important in the “fight/flight” response
39
New cards
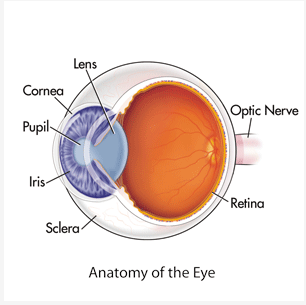
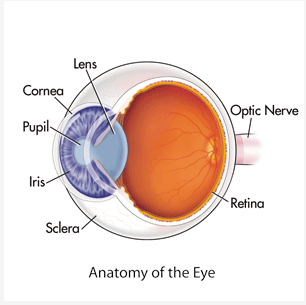
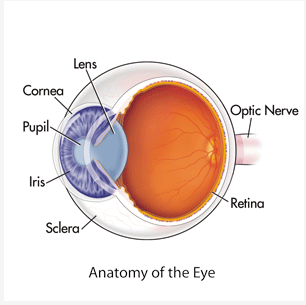
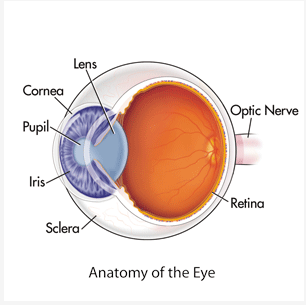
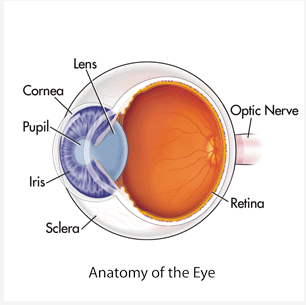
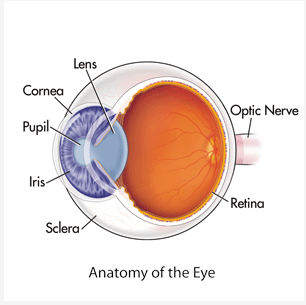
Cornea
\
* Outer-Most Layer
* First Part of Eye that Bends the Light
* Protects the Eye from Debri
* Outer-Most Layer
* First Part of Eye that Bends the Light
* Protects the Eye from Debri
40
New cards
\
Pupil
Pupil
* Center of the eye (literal black hole)
* Allows Light to Enter the Depths of the Eye
* Allows Light to Enter the Depths of the Eye
41
New cards
Retina
* All Light Information is Directed into the Retina
* Neurons that Translate Light to Neuron Signals
* Neurons that Translate Light to Neuron Signals
42
New cards
Forea
* Middle of the Retina
* Perception of Fine Details
* Perception of Fine Details
43
New cards
Iris
* A Muscle that can Relax, Constrict, and Constract
* Controls Size of Pupil // Light Allowed into the Eye
* Substances can also Control Constriction and Constraction
* Controls Size of Pupil // Light Allowed into the Eye
* Substances can also Control Constriction and Constraction
44
New cards
Lens
\
* Adjusts the Bending of the Light
* Makes the Image Sharper or Less Sharp
* Adjusts the Bending of the Light
* Makes the Image Sharper or Less Sharp
45
New cards
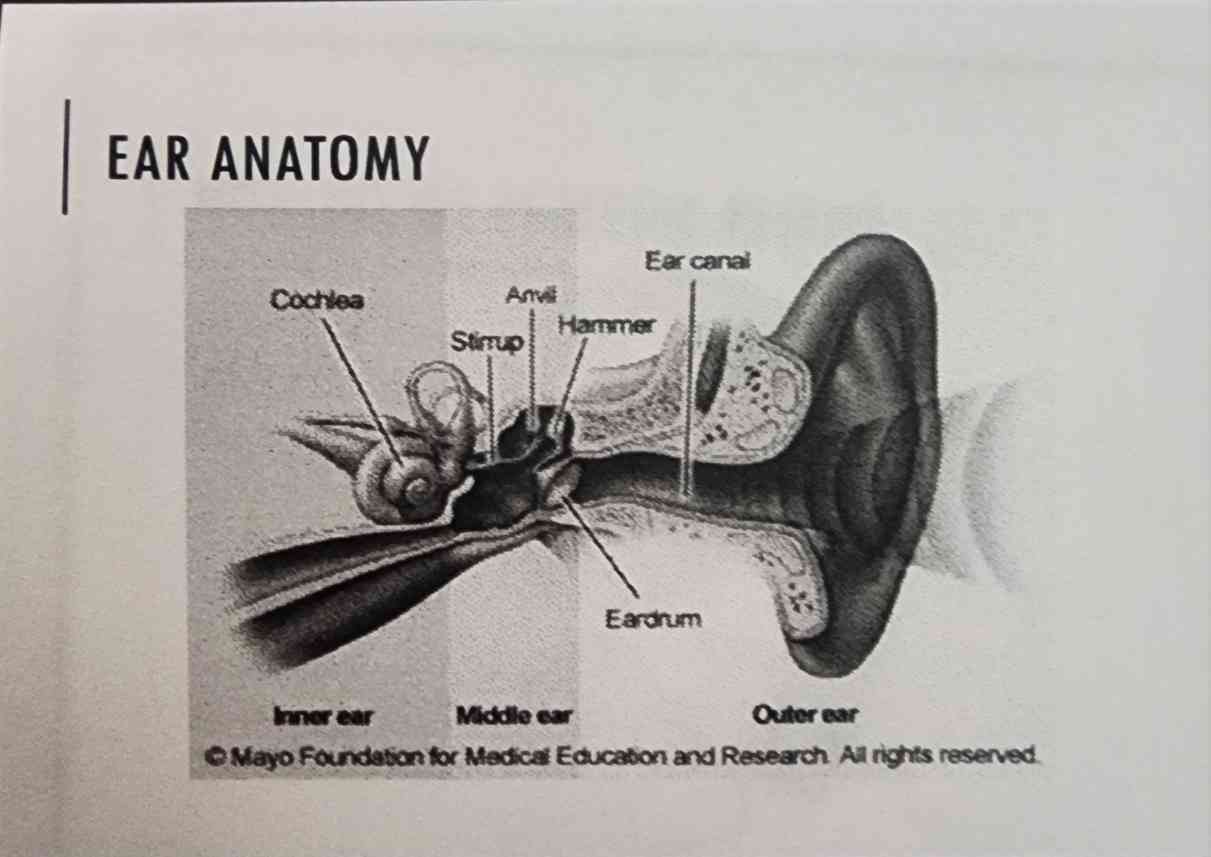
Pinna (Outer Ear)
\
Outer-most part of the ear that Funnels Sound Waves into Ear
Outer-most part of the ear that Funnels Sound Waves into Ear
46
New cards
Cochlea (Inner Ear)
Filled with Fluid that Vibrates with Input
\
* Cochlea Duct has Basiler Membrane
\
* Cochlea Duct has Basiler Membrane
47
New cards
Basiler Membrane (Inner Ear)
Turns Vibrations into Neuron Signals
\
* Movement of Organ of Corti causes Transduction
\
* Movement of Organ of Corti causes Transduction
48
New cards
Ear Canal (Outer Ear)
A Hole in the ear that Carries Sound Deeper into the Ear
49
New cards
Ear Drum (Outer Ear)
Seperates Outer Ear from Middle Ear, Waves of Sound Turn into Vibrations
\
* also known as Tympanic Membrane
\
* also known as Tympanic Membrane
50
New cards
\
Oscicles (Middle Ear)
Oscicles (Middle Ear)
Carries Vibrations Deeper into the ear
\
Made of:
* Hammer
* Anvil
* Stimup
\
Made of:
* Hammer
* Anvil
* Stimup
51
New cards
Oval Window (Inner Ear)
Seperates Middle Ear and Inner Ear
52
New cards
Ear Anatomy
53
New cards
Maslow’s Needs
* Self-Actualization
* Esteem
* Belongingness
* Saftey Needs
* Physiological Needs
* Esteem
* Belongingness
* Saftey Needs
* Physiological Needs
54
New cards
Physiological Needs (Maslow’s Needs)
* Most important and Least Gratisfying
\
Food, Water, and Shelter
\
Food, Water, and Shelter
55
New cards
Belongingness (Maslow’s Needs)
Relationships
56
New cards
Saftey (Maslow’s Needs)
Weather, Predators, Coldness/Hotness
57
New cards
Esteem (Maslow’s Needs)
Respect Ourselves and Feel Respected by Others
58
New cards
Self Actualization (Maslow’s Needs)
The Last Layer of the Pyrimad
\
* Met Your Full Potential
\
* Met Your Full Potential
59
New cards
Yerkes-Dodson Law
Perfect or Right Amount of Emotion/Arousal to Perform a Certain Level of Task
60
New cards
James-Lange Theory
Physical Sensation Results in Specific Conscious Feeling
\
* “I’m crying so I must be sad”
* Problem: Too Simple
\
* “I’m crying so I must be sad”
* Problem: Too Simple
61
New cards
Schacter-Singer Theory
Physical Sensation Evaluation First, then take into Account Subjective Feelings
62
New cards
SAME Theory
Physical Responses Vary in Intensity and Specificity
\
Specificity Levels Determines Level of Processing
* Dissappiontment (less Specific. more Processing)
* Disgust (more Specific, less Processing)
\
Specificity Levels Determines Level of Processing
* Dissappiontment (less Specific. more Processing)
* Disgust (more Specific, less Processing)
63
New cards
Classical Conditioning
Neutral Simulus paired with One Which Generates a Response
\
* Pavlov
* Bell (Neutral)
* Food (Salvation)
\
* Pavlov
* Bell (Neutral)
* Food (Salvation)
64
New cards
Operant Conditioning
Behavior and Conseqeunces of a Behavior
65
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
Continuation of a Behavior with the Addition of Something (Reward)
66
New cards
Negative Reinforcement
Continuation of a Behavior with the Taking Away of Something (Chores)
67
New cards
Positive Punishment
Stopping of a Behavior with the Addition of Something (Chores)
68
New cards
Negative Punishment
Stopping of a Behavior with the Taking Away of Something (Free Time/Phone)
69
New cards
Albert Bandura
was interested in explaining how people learn from others
\
* The Bobo Doll Experiment
\
* The Bobo Doll Experiment
70
New cards
Observational Learning Requires
* Attention
* Retention
* Production
* Motivation/Reinforcement
* Retention
* Production
* Motivation/Reinforcement
71
New cards
Observational Learning
Learning from observation through seeing punishment or reinforcement
72
New cards
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model of Memory
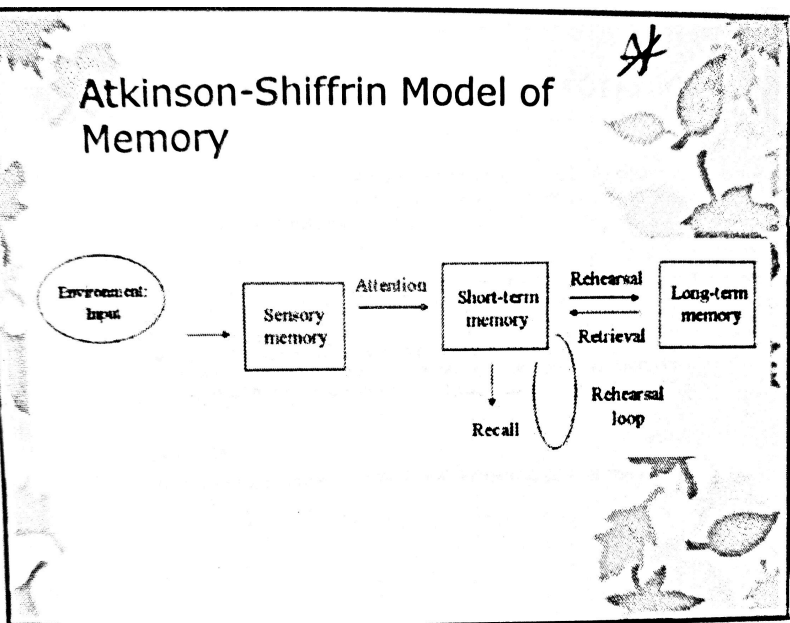
73
New cards
Declarative Memory (Long-Term)
Know it’s happening
74
New cards
Non-Declarative (Long-Term)
Things you use on daily basis but you don’t know it’s a memory
75
New cards
Semantic Declarative
Knowledge or Facts memory
76
New cards
Episodic Declarative
Personal experience memory
77
New cards
Classical Conditioning Non-Declarative
Learned associations between things through experience
78
New cards
Procedural Memories Non-Declarative
* Motor Skills/Procedures
* Hard to Verbalize without gesturing
* Hard to Verbalize without gesturing
79
New cards
Priming Non-Declarative
Change in our reaction due to a previous experience
80
New cards
Retrograde Amnesia
\
Inability to remember all or some of past memories
* Loss of memory just before head injury
Inability to remember all or some of past memories
* Loss of memory just before head injury
81
New cards
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new memories but can access old ones
* Damage to Hippocampus
* Damage to Hippocampus
82
New cards
Improve Memory
* Distribute Practice Over Time
* Take Practice Test
* Sleep
* Recite
* Mnemonic Devices
* Take Practice Test
* Sleep
* Recite
* Mnemonic Devices
83
New cards
Accomodation
Adaptation of schema based on new information
84
New cards
Assimilation
Compare new experience to current schemas
85
New cards
Piaget Stage Theory
* Sensorimotor (birth to 2)
* Preoperational (2 to 7)
* Concrete Operational (7-11)
* Formal Operational (12-Adulthood)
* Preoperational (2 to 7)
* Concrete Operational (7-11)
* Formal Operational (12-Adulthood)
86
New cards
Sensorimotor (birth to 2)
\
* Begins as reflex response interaction with the world aroun them
* Circular Reaction: Developement of schema through accidental reflex at first
* 8 - 12 months → Intentional behavior
* Object Permanence
* Begins as reflex response interaction with the world aroun them
* Circular Reaction: Developement of schema through accidental reflex at first
* 8 - 12 months → Intentional behavior
* Object Permanence
87
New cards
Preoperational Stage (2 to 7)
* Make-believe play
* Strengthen/Practice representational schema
* Ex. Drink from cup → drink from hat
* Major cognitive advancement:
* Symbols, Planning/Spatial Understanding
* Strengthen/Practice representational schema
* Ex. Drink from cup → drink from hat
* Major cognitive advancement:
* Symbols, Planning/Spatial Understanding
88
New cards
Concrete Operational Stage (7-11)
Developement to perform tasks that previously could not be done
* Egocentrism is lost
* Spatial Reasoning is gained
* Directions
* Use of Map
* Egocentrism is lost
* Spatial Reasoning is gained
* Directions
* Use of Map
89
New cards
Formal Operational (11+)
* Understand Abtract Thinking
* Have Horizontal Decalage
* Hyphothetico-Deductive reasoning
* Baby form of Scientific Reasoning
* Have Horizontal Decalage
* Hyphothetico-Deductive reasoning
* Baby form of Scientific Reasoning
90
New cards
Authoritative Parenting
* Best style of parenting
* Middle Childhood:
* Upbeat mood, self-control, persistance, and cooperative
* Adolescence:
* Academic acheivement, high self-esteem, social and moral maturity
* Middle Childhood:
* Upbeat mood, self-control, persistance, and cooperative
* Adolescence:
* Academic acheivement, high self-esteem, social and moral maturity
91
New cards
Authoritarian Parenting
Ideal child building
* Acceptance: Low
* Involvement: Low
* Control: High
* Autonomy: Low
* Acceptance: Low
* Involvement: Low
* Control: High
* Autonomy: Low
92
New cards
Permissive Parenting
Child has almost full control
* Acceptance: High
* Involvment: Too Low or Too High
* Control: Low
* Autonomy: High
* Acceptance: High
* Involvment: Too Low or Too High
* Control: Low
* Autonomy: High
93
New cards
Uninvolved Parenting
Self explanatory
* Acceptance: Low
* Involvment: Low
* Control: Low
* Autonomy: Indifference
* Acceptance: Low
* Involvment: Low
* Control: Low
* Autonomy: Indifference
94
New cards
Trust v.s Mistrust (Erikson)
* Infant
* Basic needs met
* Basis of future relationships
* Basic needs met
* Basis of future relationships
95
New cards
Autonomy v.s Shame/Doubt (Erikson)
* Terrible 2’s
* Experiment with independence
* Self efficancy or self doubt develops
* Experiment with independence
* Self efficancy or self doubt develops
96
New cards
Identity v.s Role Confusion
* Adolecence
* Who Am I?
* Who Am I?
97
New cards
Initiative v.s Guilt (Erikson)
* 3 to 6 years old
* Imitation of adults
* Ambition or Guilt develops
* Imitation of adults
* Ambition or Guilt develops
98
New cards
Aviodant Attachment
* Explores independently not concerned with parent
* When parent leaves there is no reaction to that or stranger
* When parent returns child continues to aviod and ignore
* When parent leaves there is no reaction to that or stranger
* When parent returns child continues to aviod and ignore
99
New cards
Disorganized/Disoriented Attachment
* Counterdictatory behavior, mix of different patterns previously listed
100
New cards
Resistant Attachment
* Clinges to parent in new enviroment
* When parent leaves child throws full tantrum
* When parent returns child refuses to be comforted however does go to parent for it
* When parent leaves child throws full tantrum
* When parent returns child refuses to be comforted however does go to parent for it