peripheral nervous system (4)
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
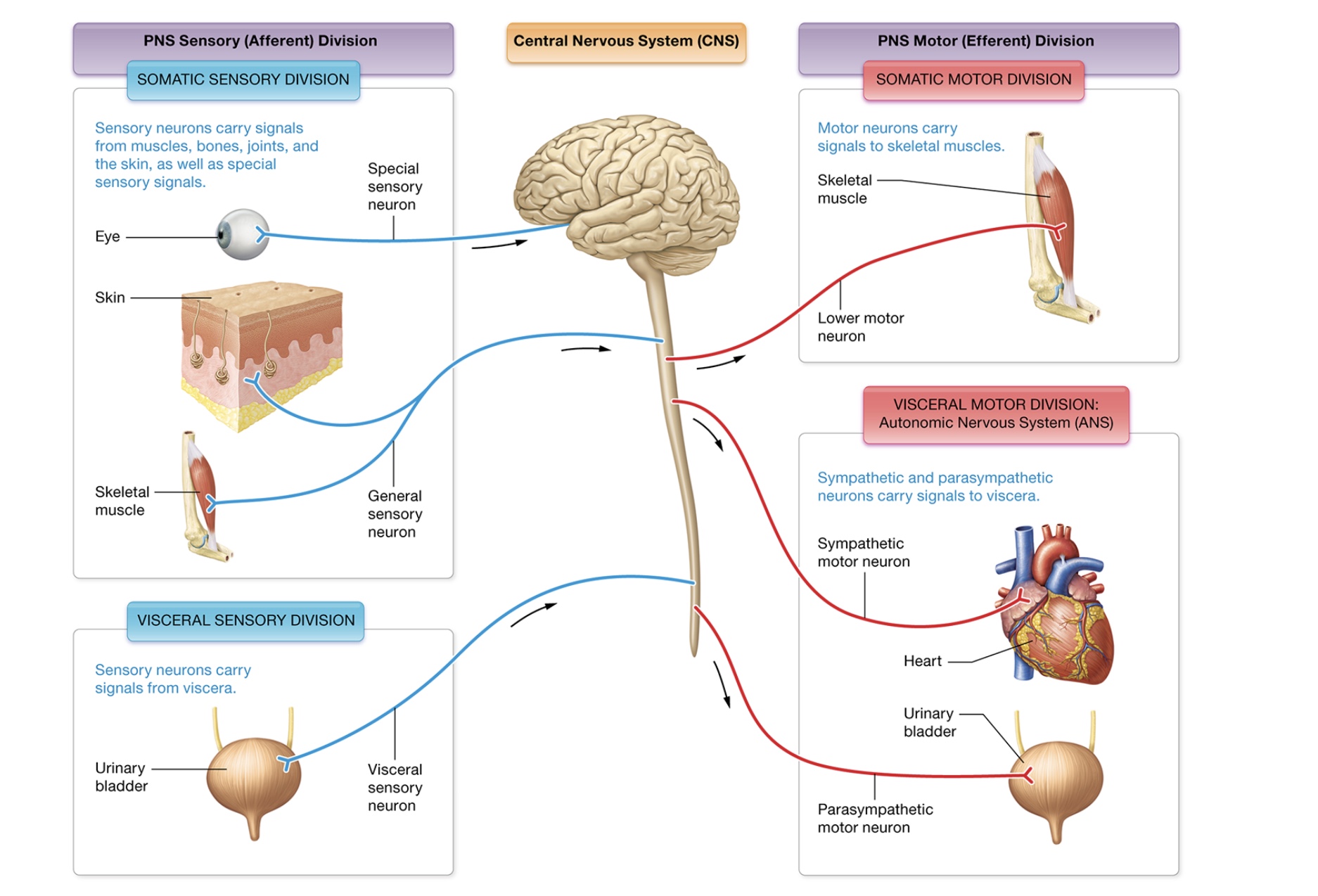
Peripheral nervous system
sensory (afferent) division
motor (efferent) division
somatic (body)
visceral (internal organs)
sensory division
detect stimuli + bring it to CNS
somatic, visceral
somatic sensory
skin + musculoskeletal system
general senses - touch, temp, pain, muscle stretch, chemical concentration
special senses - vision, equilibrium, taste, smell
somatic visceral
abdominopelvic + thoracic cavity organs, blood pressure + organ stretch
motor division somatic
voluntary movements → lower motor neurons triggering contraction when stimulated by upper motor neurons
motor division visceral
autonomic nervous system
homeostasis through involuntary motor functions
sympathetic NS - fight or flight, maintains homeostasis when body engaged in physical work, mediates visceral response to emotions
parasympathetic NS - maintain homeostasis at rest, digest
peripheral nerves
axons of many neurons bound together by CT sheath
innervate structures of the body
mixed nerves - motor + sensory, most common, can be seperated
spinal + cranial
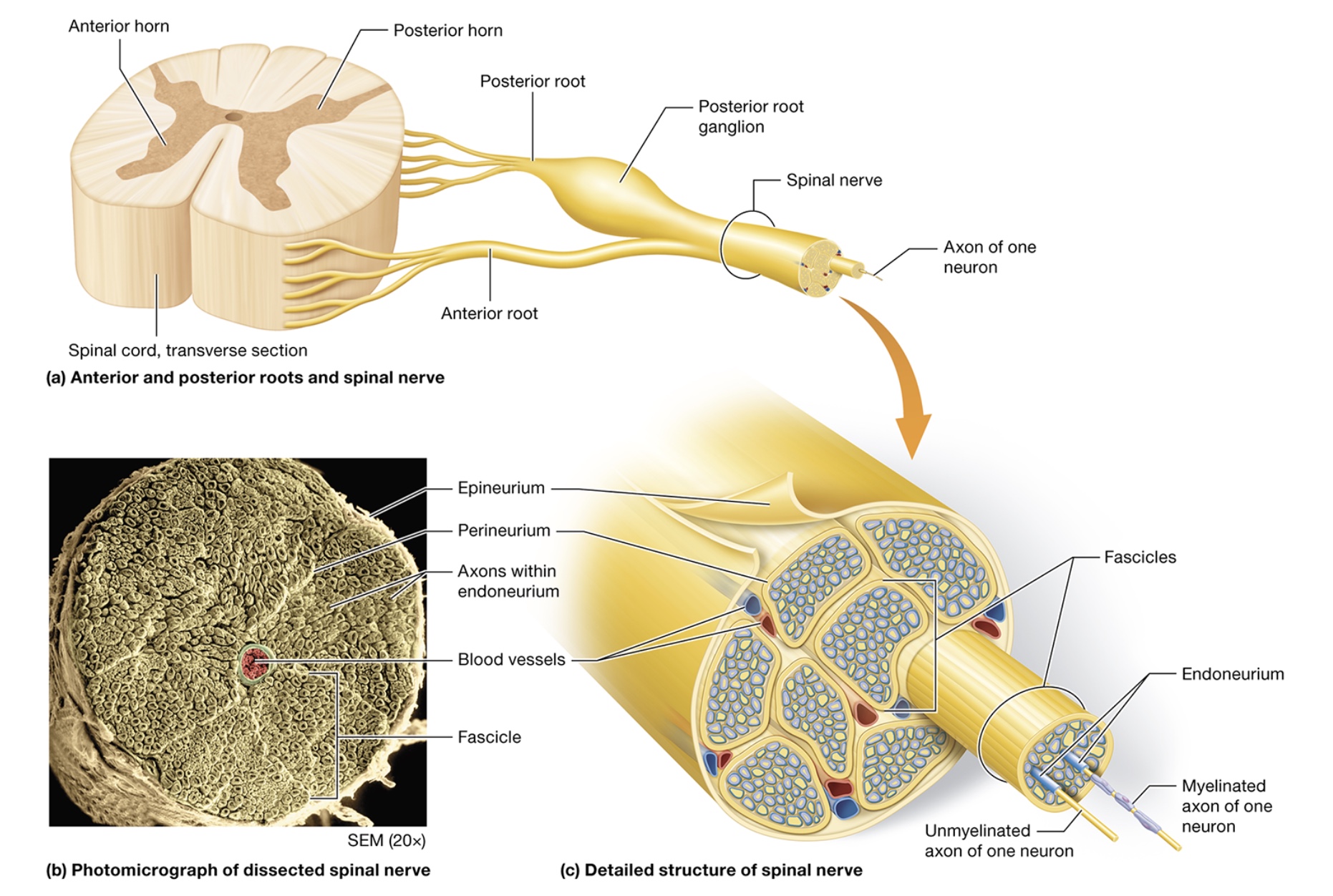
spinal nerves
from spinal cord, innervate head + neck
anterior root - motor neurons entering from anterior horn
posterior root - motor neurons entering from posterior horn, posterior (dorsal root) ganglion
axons connect PNS w/ spinal cord gray matter
fuse to form spinal nerves, 31 pairs
cranial nerves
from brain, innervate head + neck, 12 pairs of cranial nerves
structure
epineruium - CT sheath wrapping around entire nerve
fascicles - bundled axon groups, have blood vessels
perineurium - CT sheath wrapping up fascicles
endoneurium - CT sheath wrapping each axon in a fascicle
functional overview
sensory receptors detect stimuli at sensory receptors
transmitted along sensory neurons via spinal / cranial nerves to sensory neurons of CNS
signals transmitted to cerebral cortex for interpretation + integration
motor response initiated by commands from motor areas of the brain to upper motor neurons
impulses travel to spinal cord + synapse on interneurons then lower motor neurons
lower motor neurons carry impulse to appropriate muscle fibers via spinal / cranial nerves
contraction is triggered
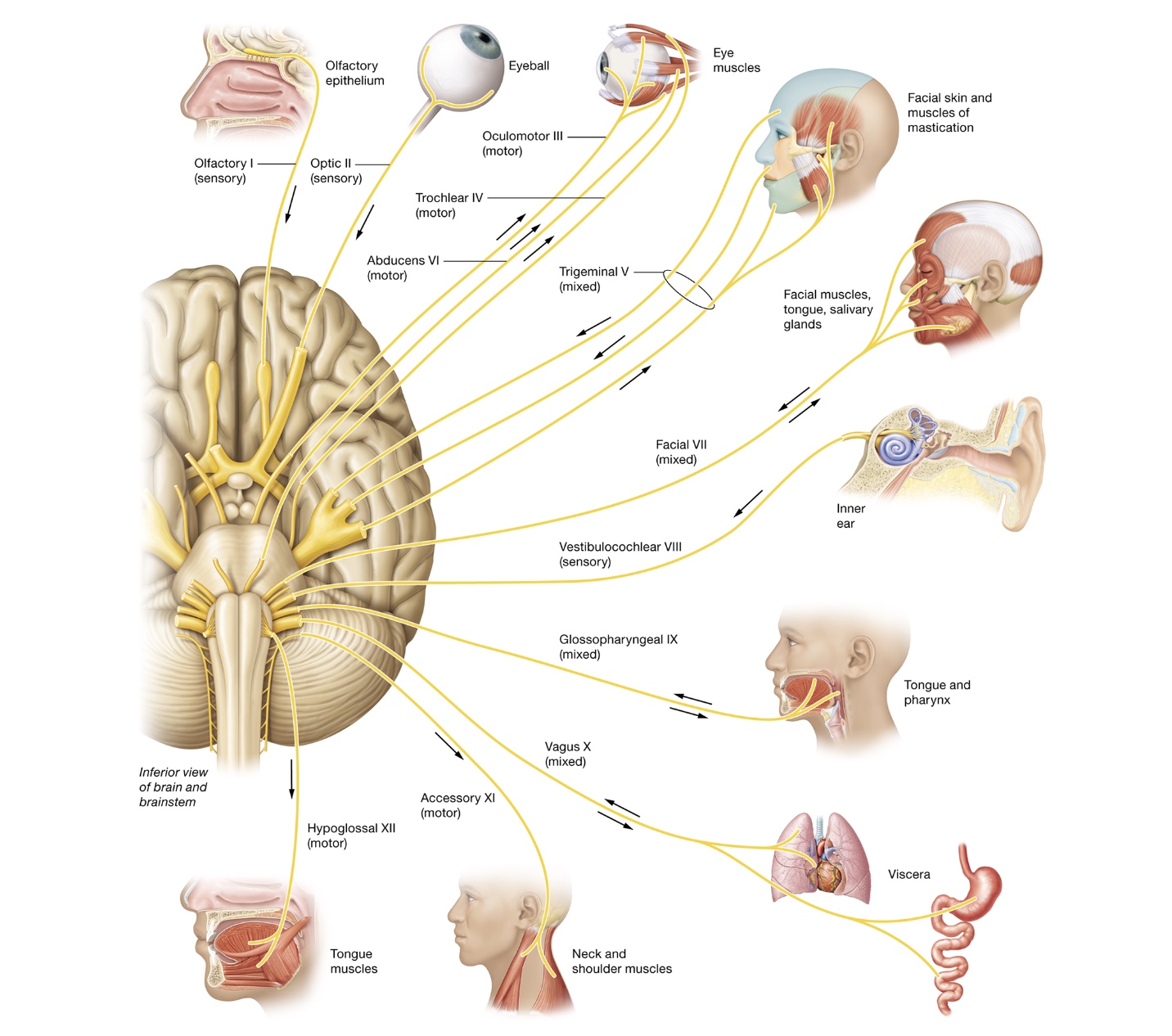
Cranial nerves
roman numeral - attachment site in the brain, name - function
sensory - olfactory (I), optic (II), vestibulocochlear (VIII)
motor - oculomotor (III), trochlear (IV), abductens (VI), accessory (XI), hypoglossal (XII)
mixed - trigeminal (V), facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X)
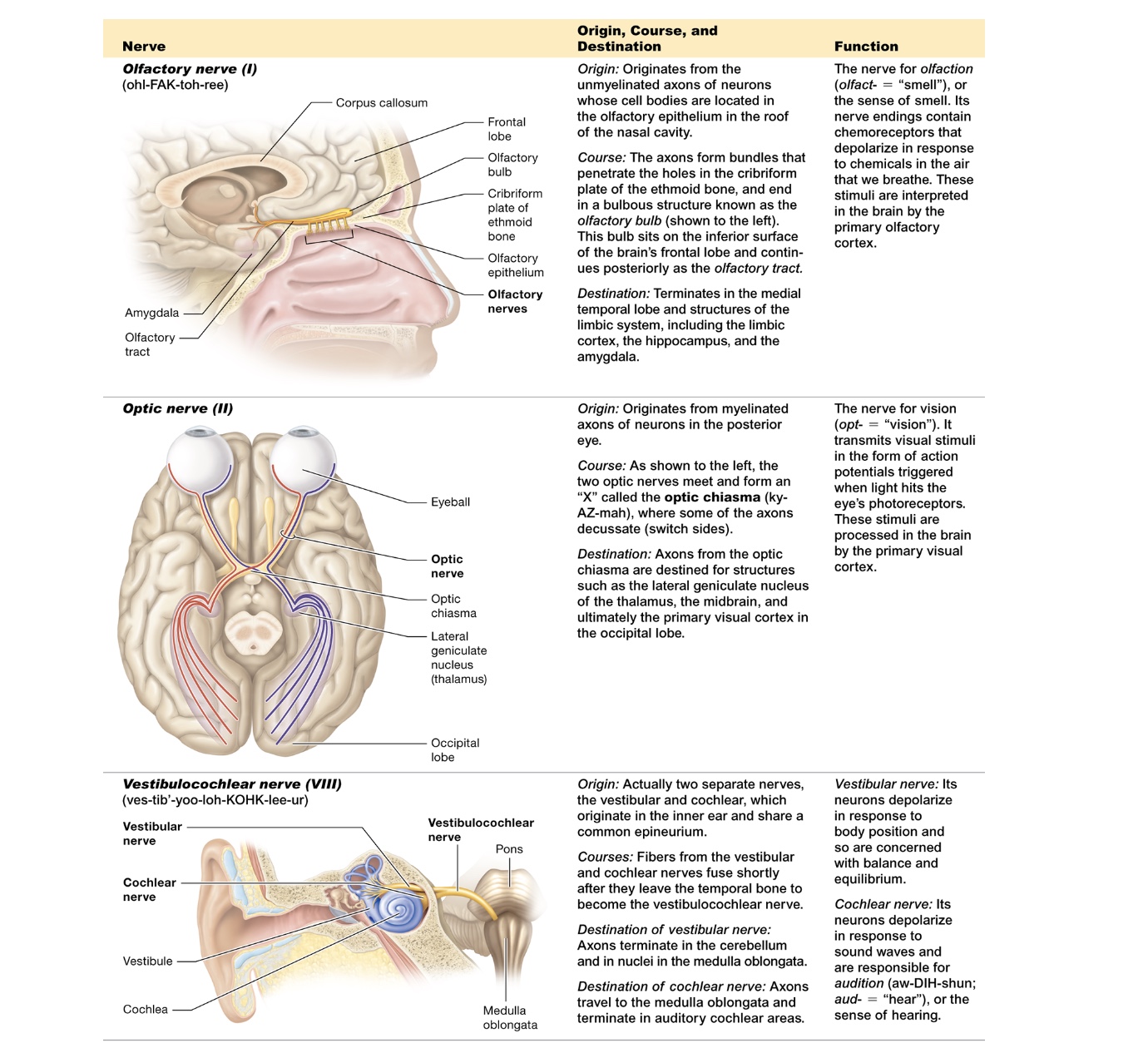
olfactory (I)
originates from unmyelinated axons in cell bodies of olfactory epithelium
penetrate through cribriform plate + ethmoid bone, olfactory bulb
terminates medial temporal bone
smell
optic (II)
originates myelinated axons in posterior eye
both nerves meet forming X - optic chiasmia
terminate primary visual cortex on occipital lobe
vision
vestibulocochlear (VIII)
originates vestibular + cochlear → share epineruium
fuse together when they leave temporal bone
vestibular terminates cerebellum + medulla oblongata, balance + equilibrum
cochlear terminates auditory cochlear areas in medulla oblongata, hearing
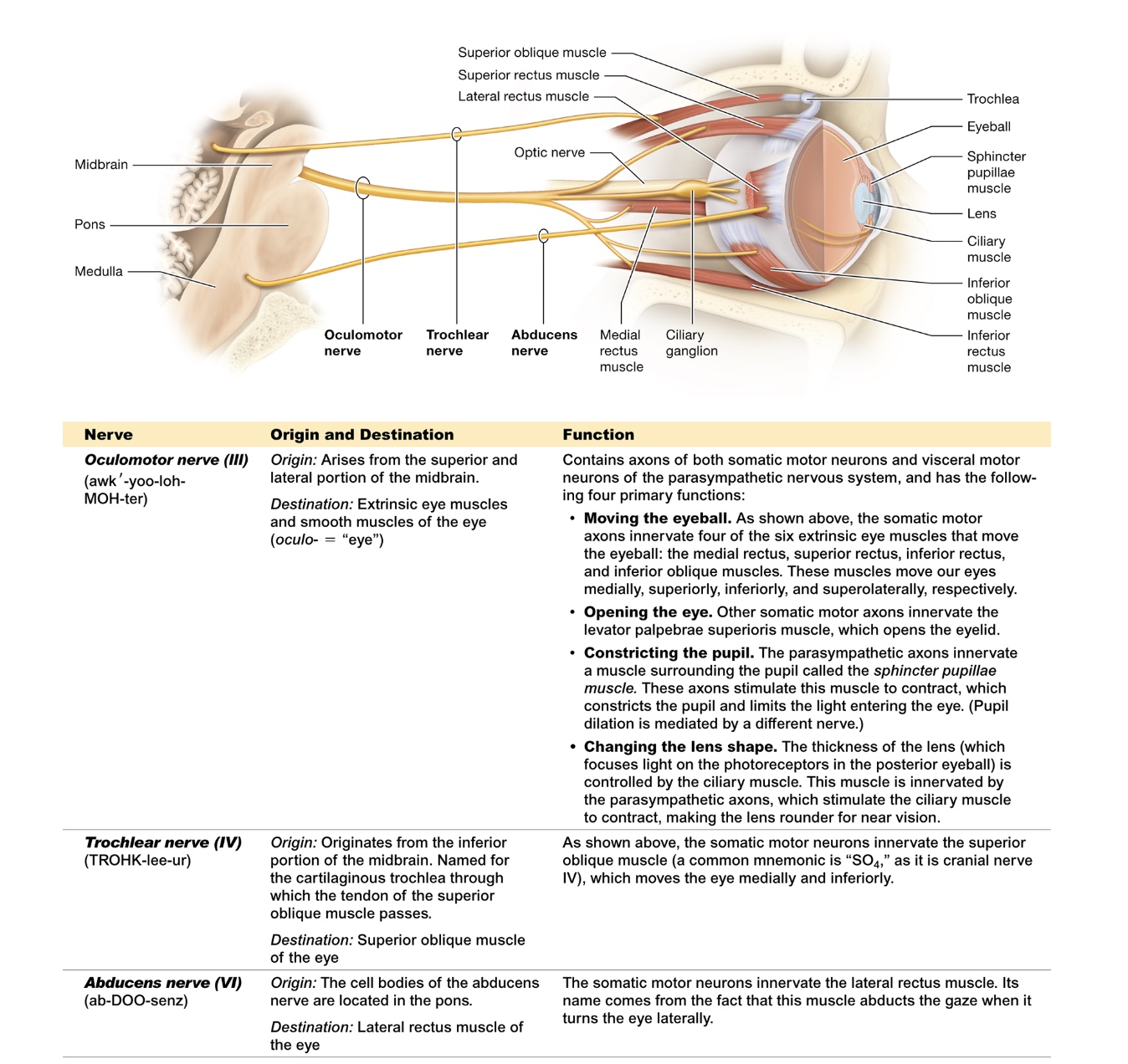
oculomotor (III)
originates midbrain + innervates extrinsic eye muscles + smooth eye muscles
moves the eyeball, opening the eye, constricting the pupil, changing lens shape
trochlear (IV)
originates inferior midbrain
innervates superior oblique eye muscle
abductens (VI)
originates in pons
innervates lateral rectus (eyes)
turns eye laterally
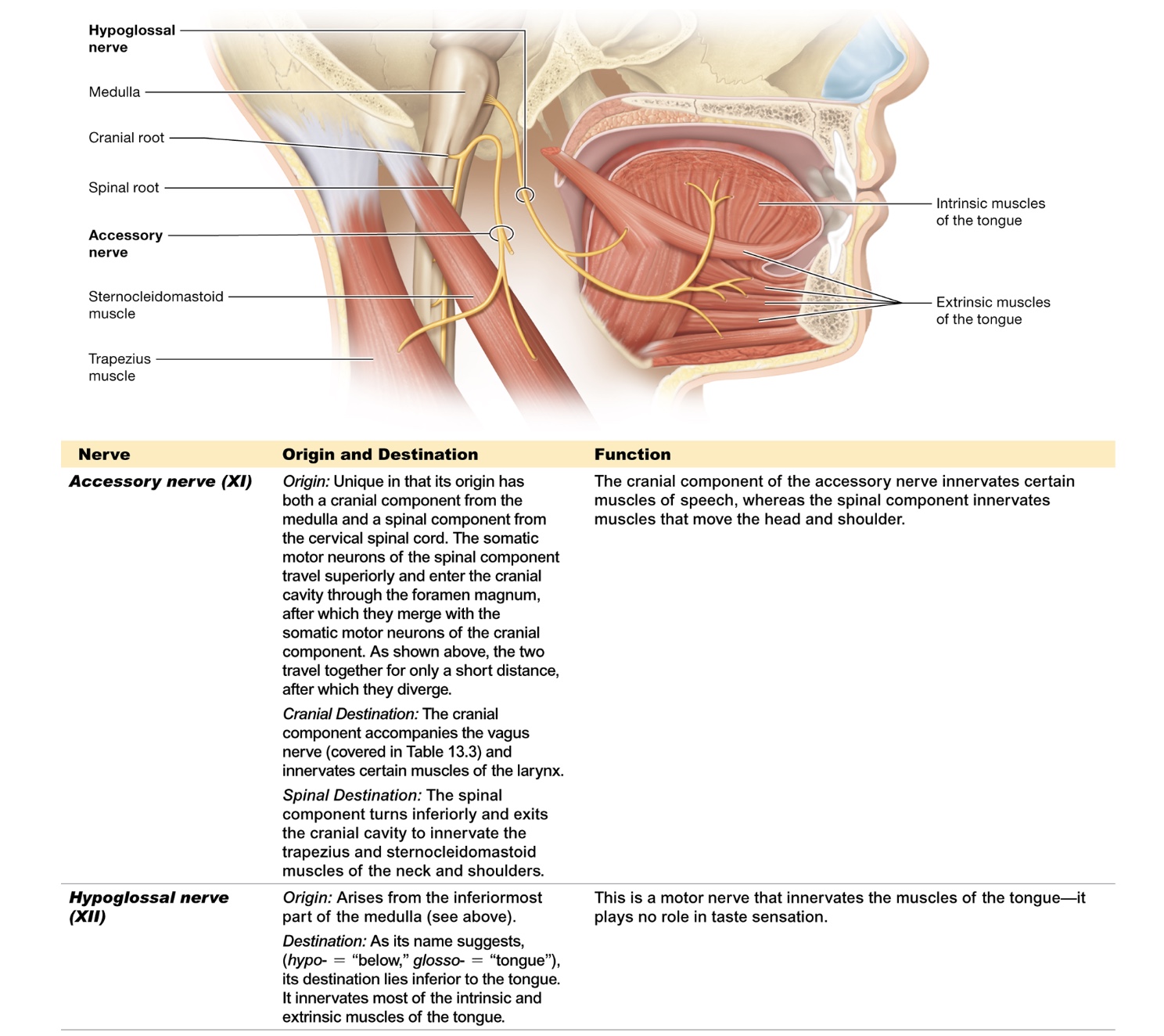
accessory (XI)
originates medulla + cervical + spinal cord
cranial destination - innervates larynx, speech
spinal destination - innervates trapezius + sternocleidomastoid, move head + shoulders
hypoglossal (XII)
originates inferior medulla
innervates intrinsic + extrinsic tongue muscles
moves tongue
trigeminal (V)
originates midbrain, pons, sensory receptors around face
trigeminal ganglia → split into ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular nerves
all terminate in primary somatosensory cortex, mandibular terminates in mastication muscles
ophthalmic - scalp, forehead, eyes, nose
maxillary - skin of middle of face
mandibular - chin + lateral face, motor - masseter + temporalis muscles
facial (VII)
originates medulla, pons, sensory portion of tongue, inner ear, palate, nasal cavity
geniculate ganglion, more
innervates somatosensory areas of cerebral cortex - sensory
innervates facial expression + neck muscles - motor
split into 5 branches temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cranial nerves
taste + somatic sensation, salivatory glands
glossopharyngeal (IX)
motor originate medulla
sensory originate tongue, pharynx, ear, blood vessels of neck
superior + inferior ganglion
innervate tongue + throat,
swallowing + salivation
vagus (X)
motor originate medulla
sensory originate tongue, pharynx, ear skin, blood vessels of neck
superior + inferior ganglion
innervates throat, neck, thoracic + abdominal viscera
taste, mucus membranes of throat, blood O2 concentration
speaking, swallowing
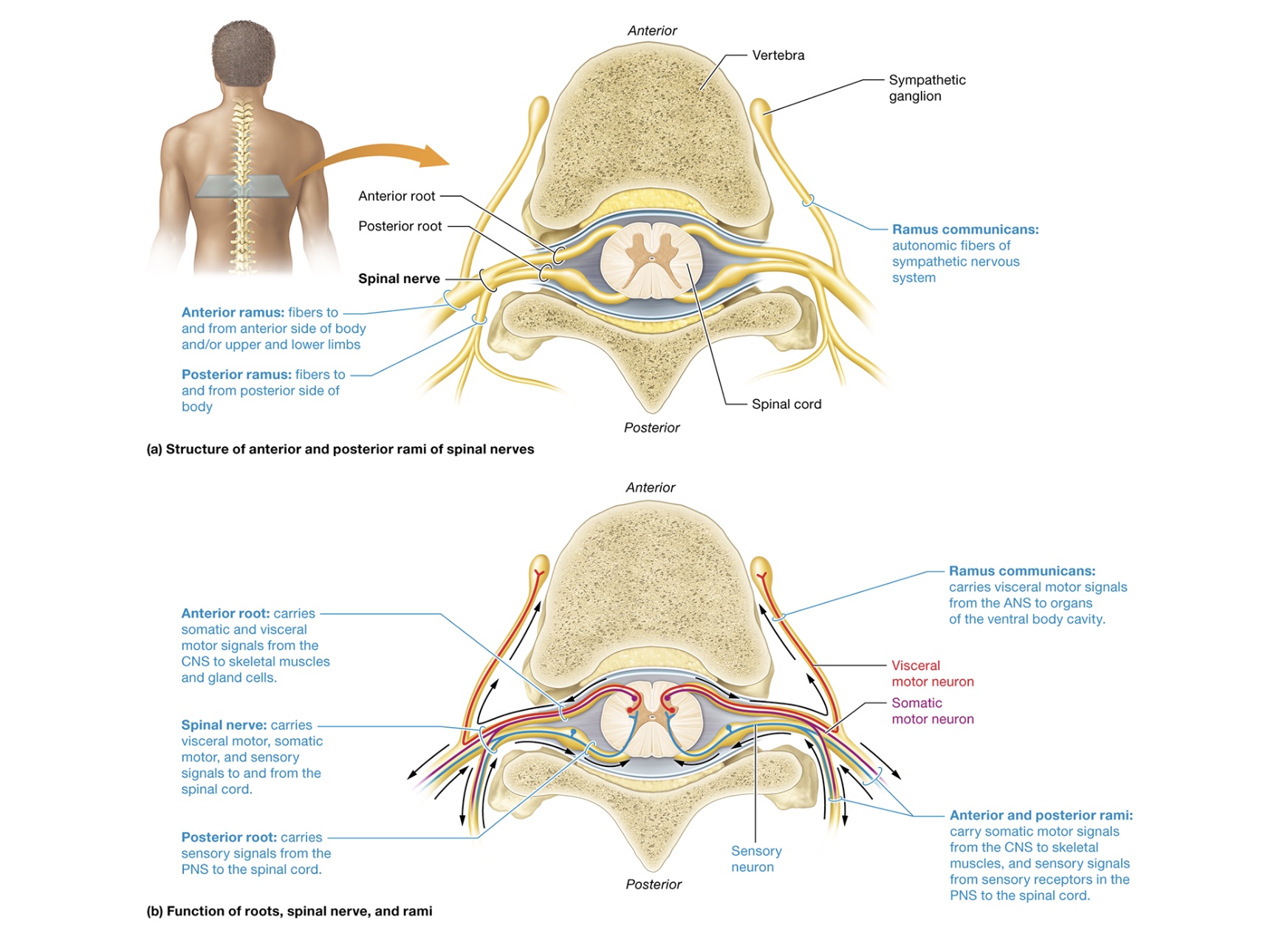
spinal nerves structure
spinal nerve splits - posterior + anterior ramus (mixed nerves)
rami communicates - small branches stemming from anterior ramus, visceral motor of sympathetic nervous system
nerve plexuses - anterior rami of cervical, lumbar, sacral spinal nerves merge forming complex nerve networks
axons of spinal nerves enter different nerve plexuses preventing complete nerve cutoff
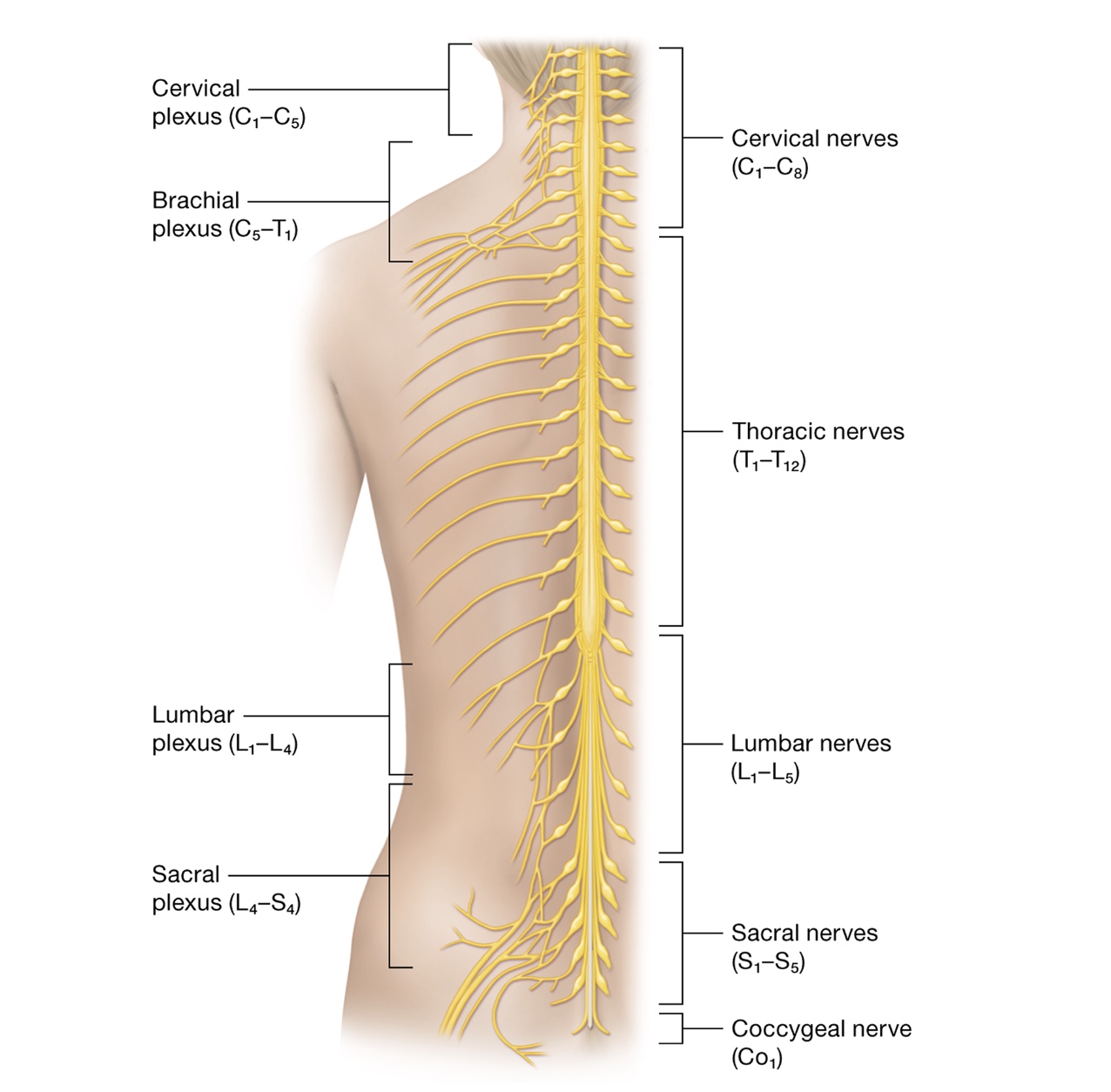
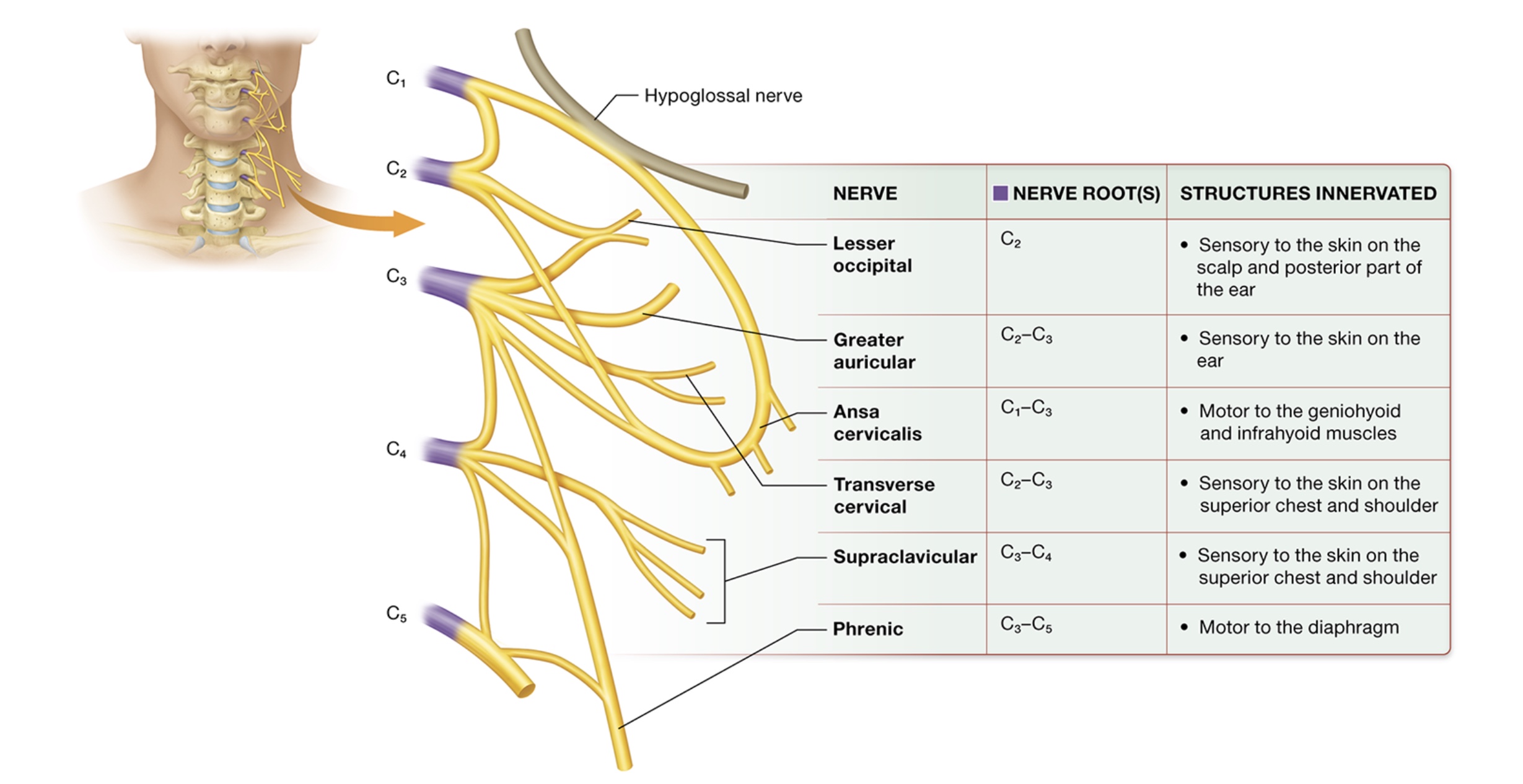
Cervical plexuses
deep lateral neck, anterior rami of C1-4
phrenic nerve - motor branch C3-5, drives ventilation (diaphragm)
supraclavicular - sensory to skin on superior chest + shoulder C3+4
transverse cervical - sensory to skin superior chest + shoulder, C2+3
ansa cervicalis - motor to geniohyoid + infrahyoid muscles C1-3
greater auricular - sensory to ear skin, C2+3
lesser occipital - sensory to scalp skin + posterior ear C2
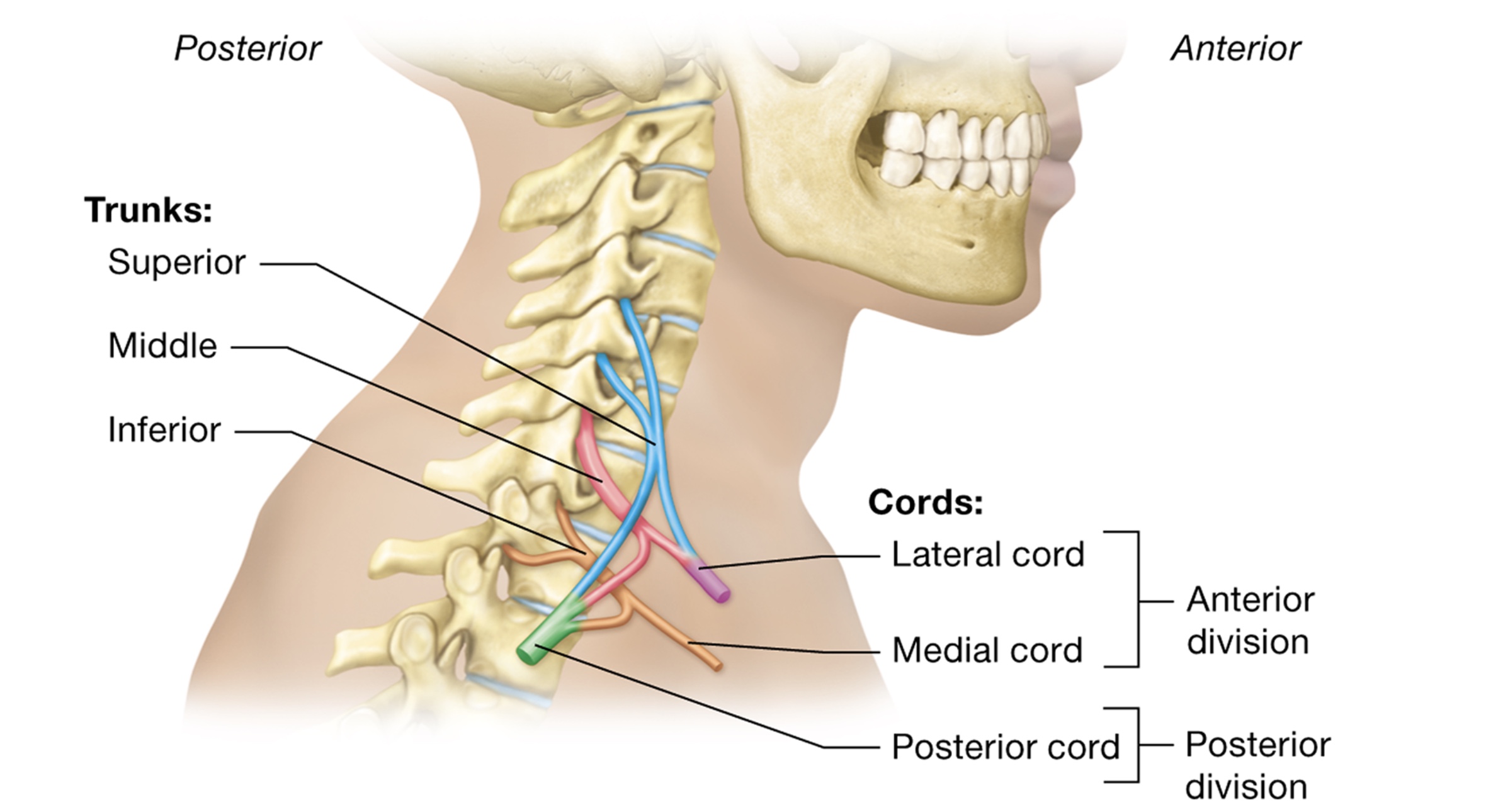
Brachial plexuses
motor + sensory to upper limbs
anterior rami of C5-T1
trunks - 1st structure formed
superior C5+6, middle C7, inferior C8-T1
cords - anterior + posterior division of trunks
medial cord - anterior division of inferior trunk
lateral cord - anterior division of superior + middle trunk
posterior cord - posterior divisions
*all descend into arm
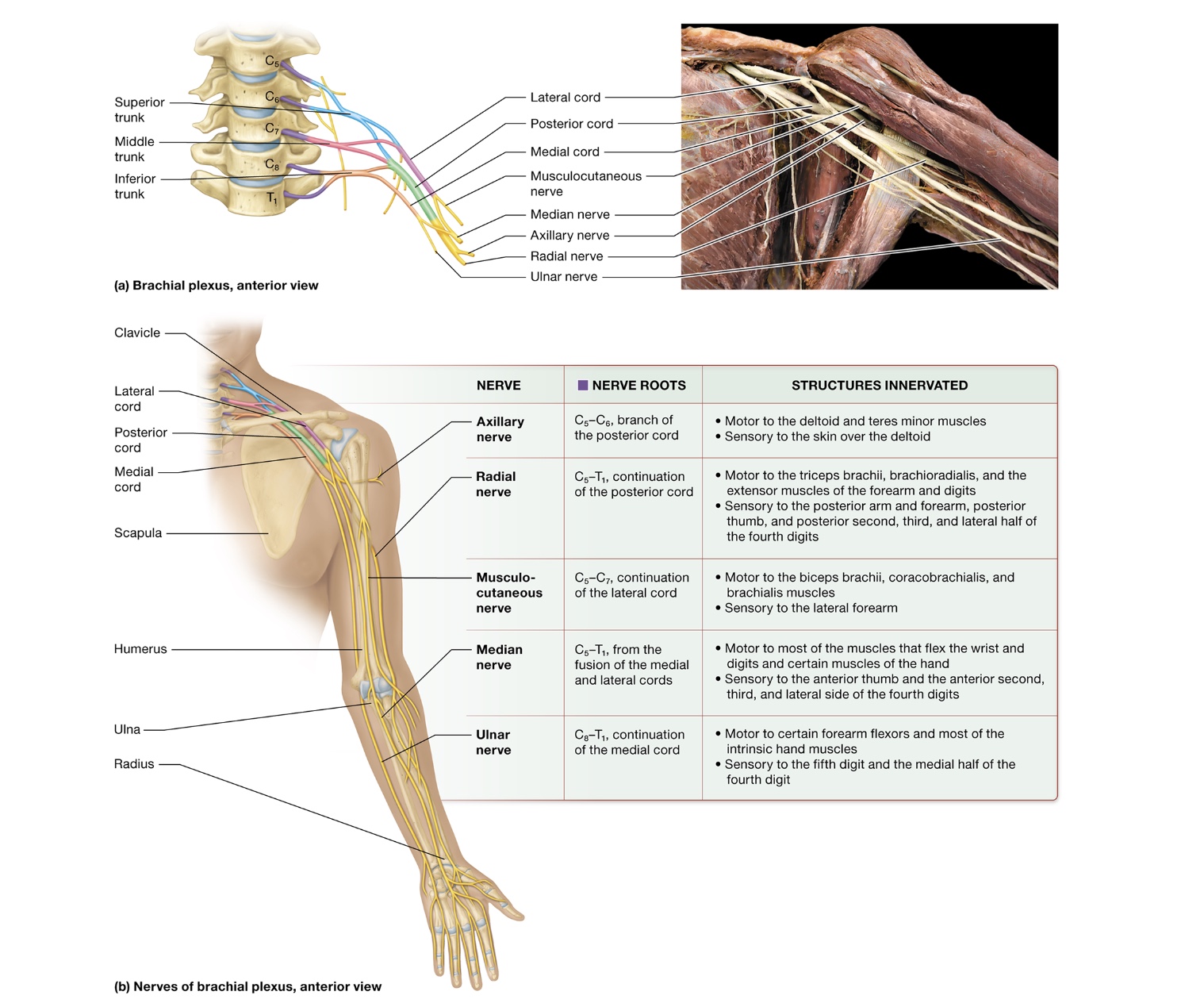
brachial plexuses nerves
axillary nerve - branch of posterior cord, near axilla, deltiod, teres minor
radial nerve - posterior cord descends + becomes radial nerve, triceps brachii, forearm, thumb, fingers
musculocutaneous nerve - lateral nerve, forearm, biceps brachii
median nerve - merged medial + lateral cords, forearm, sensory innervation to hand
flexor retinaculum - CT band that median nerve can get trapped under → carpal tunnel
ulnar nerve - medial cord continuation, superficial forearm, funny bone
Thoracic spinal nerves
posterior rami serve deep back muscles
intercostal nerve - each anterior ramus traveling between 2 ribs
1) intercostal branch of anterior ramus of T1 travels in 1st intercostal space innervating intercostal muscles + axilla skin
2) T2-6 serve intercostal muscles + skin of chest wall
3) T7-12 serve intercostal muscles overlaying skin + abdominal walls
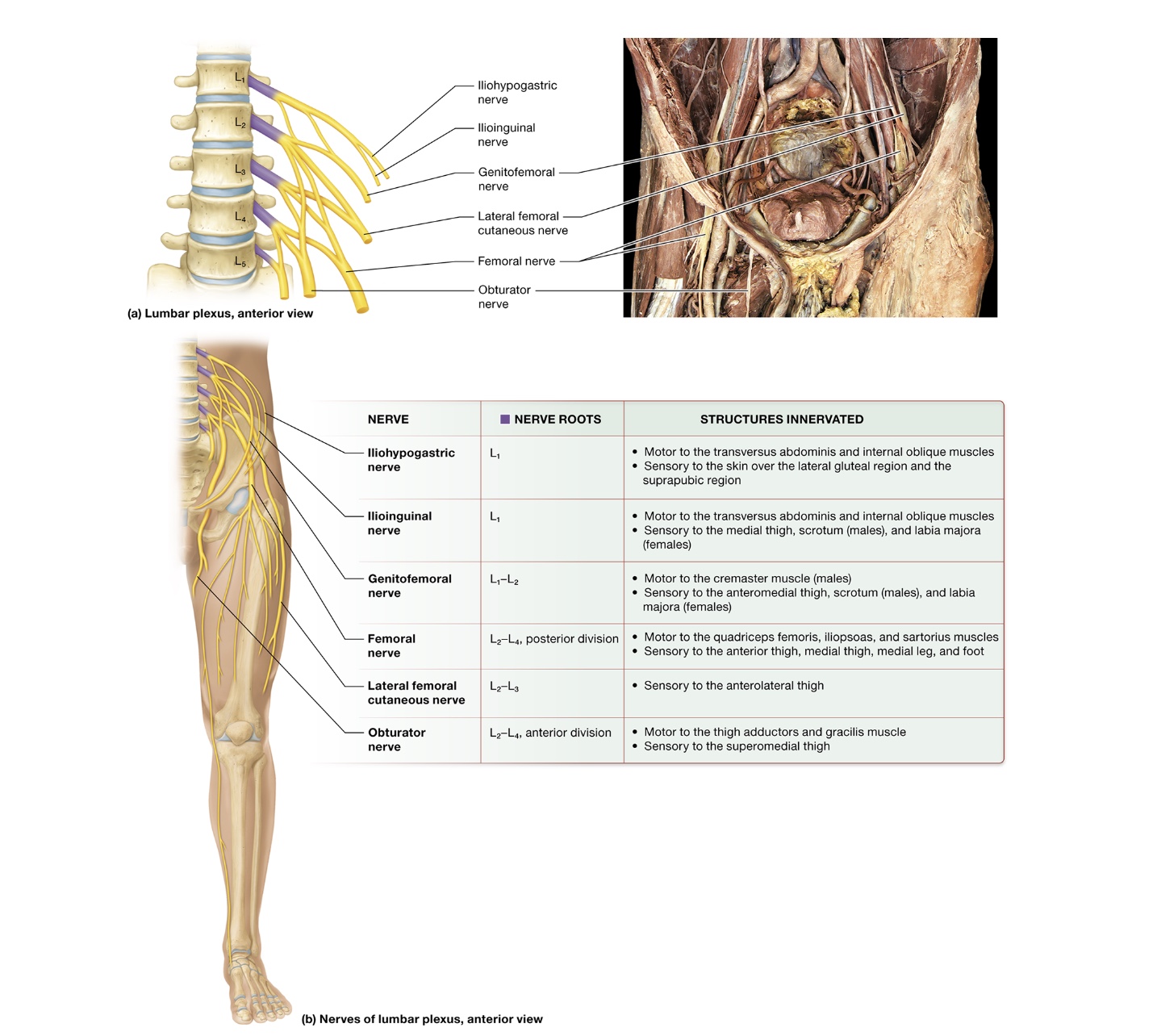
Lumbar plexuses
anterior rami L1-4
anterior to vertebrae + embedded in posterior psoas major muscle
iliohypogastric nerve - L1, motor to transversus abdominus + internal oblique, sensory to skin of lateral gluteal region + suprapubic region
Ilioinguinal nerve - L1, motor to transversus abdominus + internal oblique, sensory to medial thigh, scrotum, labia majoria
Genitofemoral nerve - L1-2, motor to cremaster, sensory to anteromedial thigh, scrotum, labia majoria
femoral nerve - L2-4 posterior division, motor to quadriceps femoris, iliopsoas, sartorus, sensory to anterior + medial thigh, medial leg, foot
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve - L2+3, sensory to anterolateral thigh
obturator nerve - L2-4, anterior division, motor to thigh adductors, gracilis, sensory to superiomedial thigh
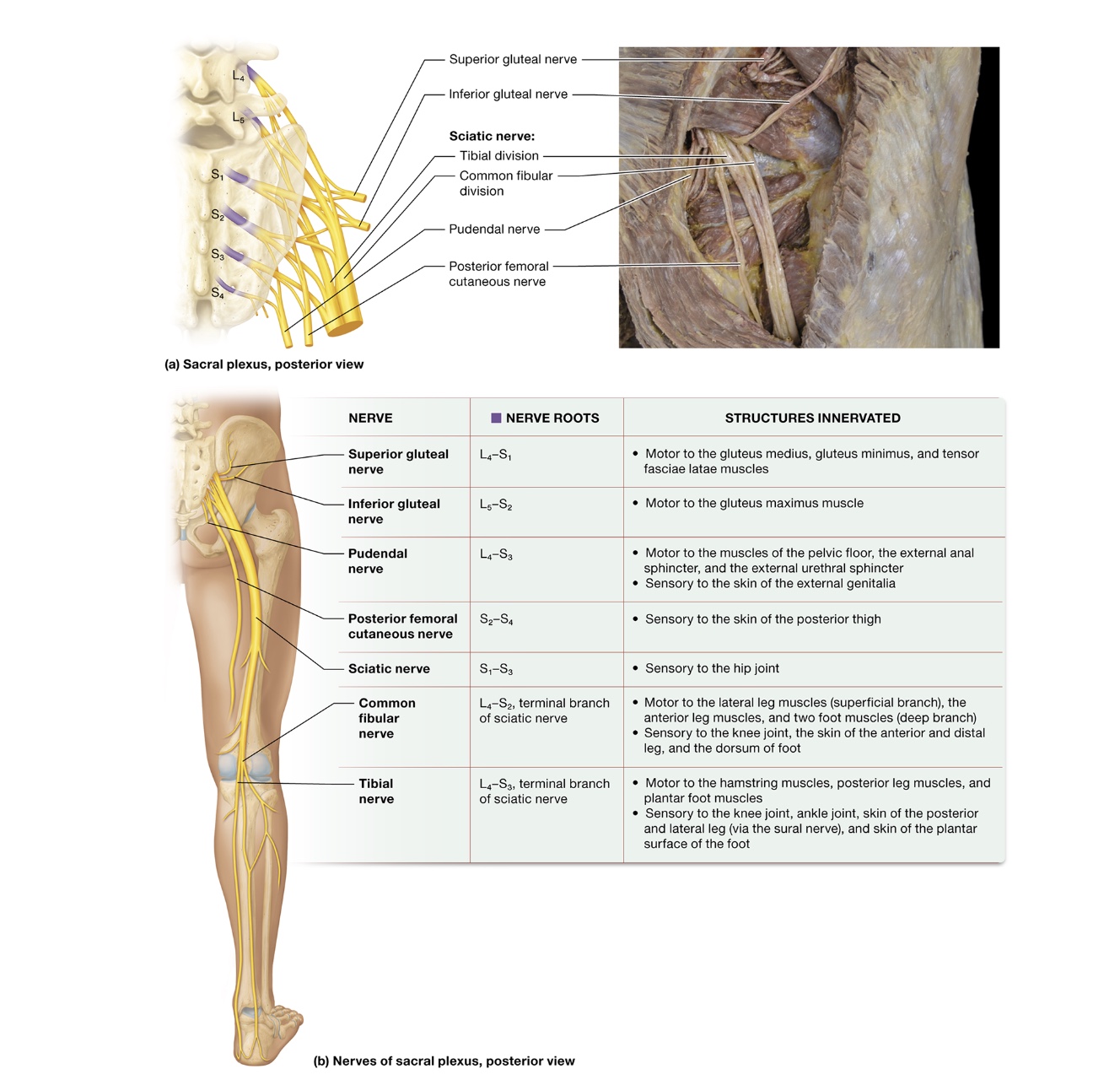
Sacral plexuses
anterior rami L4-S4, innervate gluteal region
superior gluteal nerve - L4-S1, motor to gluteus medius + minimus, tensor fasciae latae
inferior gluteal nerve - L5-S2, motor to gluteus maximus
pundendal nerve - L4-S3, motor to pelvic floor muscles, external anal sphincter + urethral sphincter, sensory to skin of genitalia
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve - S2-4, sensory to posterior thigh skin
sciatic nerve - S1-3, sensory to hip joint, axons from anterior + posterior divisions travel together + share epineruium
splits into common fibular + tibial nerve
common fibular nerve - L4-S2, motor to lateral + anterior leg muscle, foot muscles, sensory to knee joint, anterior + distal leg skin, dorsum of foot
branches into common peroneal nerve
tibial nerve - L4-S3, motor to hamstring + posterior leg muscles, plantar foot muscles, sensory to knee + ankle joint, posterior + lateral leg skin, plantar surface of foot skin
branches into sural nerve
sensory receptors
sensory transduction - conversion of sensory stimulus to electrical signal
sensory receptor - region of nerve ending
encapsulated nerve endings - surrounded by specialized + supportive cells
free nerve endings - lack of specialized cells
sensory receptors
1) before any stimulus, ion channels in the axolemma of somatic sensory neurons are closed
2) stimulus applied + mechanically gated Na+ channels open, Na+ enters axoplasm → receptor potential generated
3) enough Na+ enter + membrane potential reaches threshold, voltage gated Na+ channels open + action potential is generated down spinal cord
receptor potential
temporary depolarization from Na+ entering axoplasum
rapidly adapting receptors
respond rapidly w/ high intensity but stop sending stimuli after a certain period - adaptation
slowly adapting receptors
respond w/ constant action potentials that don’t diminish w/ time
classification of sensory receptors
location of stimuli - exoreceptors, interoceptors
type of stimuli they depolarize to - mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptor, chemoreceptor, photoreceptor, nociceptor
exoreceptors
close to surface of body, detect stimuli originating outside of body
interoceptors
within body interior, detect stimuli originating inside body
mechanoreceptors
encapsulated exo/ineroceptors in skin + musculoskeletal system
respond to mechanical touch, mechanically gated ion channels
thermoreceptor
exoreceptor responding to thermal stimuli
slowly adapting receptors
small knobs on ends of free nerve endings
cold - 10-40 C, superficial
hot - 32-48 C, deep
painful - 49+ C
chemoreceptor
exo/interoceptor responding to chemicals in air or bodily fluids
smell + taste
photoreceptor
special sensory exoreceptors responding to light, eye
nociceptor
slowly adapting receptors respond to pain or noxious stimuli
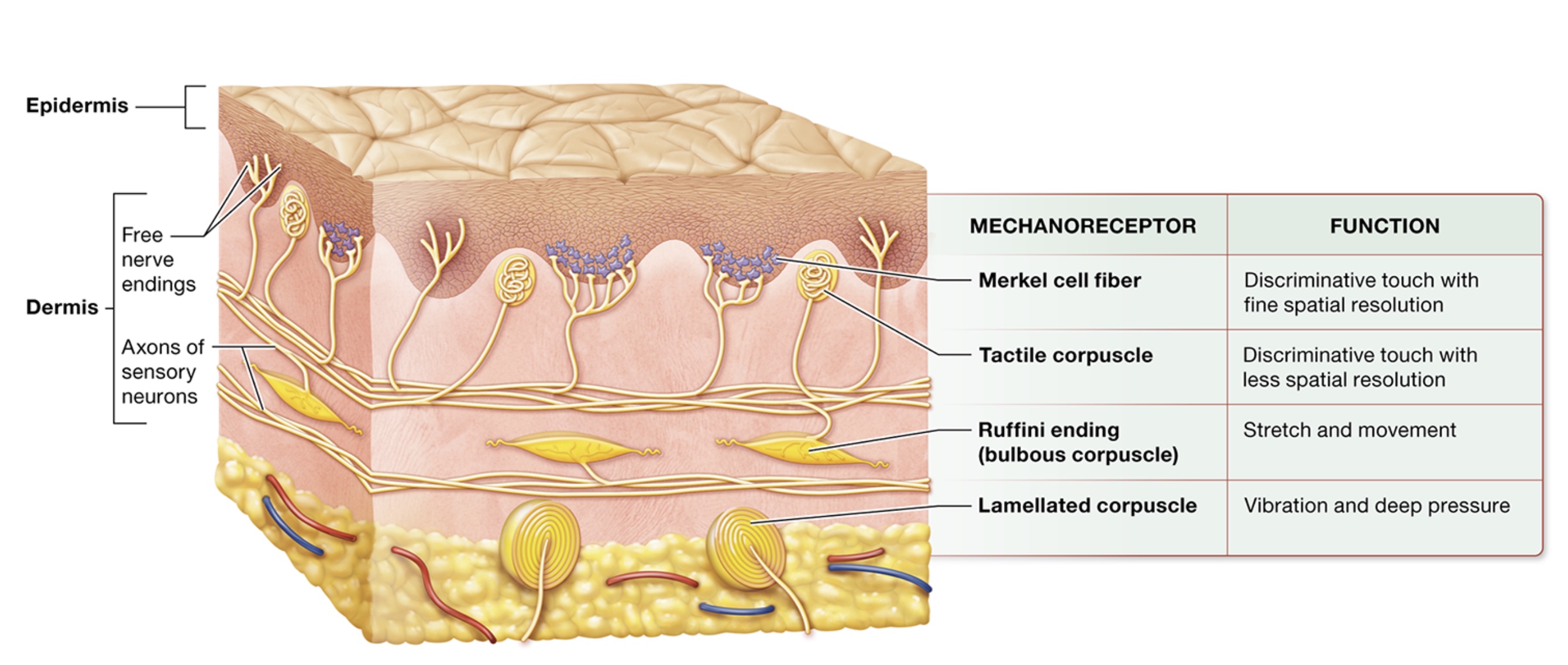
mechanoreceptors
superficial → deep
merkel cell fibers, tactile corpuscles, ruffini endings, lamellated corpuscles, hair follicle receptors, proprioceptors
merkel cell fibers
nerve endings surrounded by merkel capsule
slowly adapting receptors, mechanically gated ion channels
in floors of epidermal ridges
discriminative touch stimuli - fine touches
tactile corpuscles
in dermal papillae
projections of dermis into epidermis
discriminative touch stimuli - genral touches
ruffini endings
spindle shaped, dermis + hypodermis + ligaments
slowly adapting receptors
lamellated corpuscles
onion like layers, deep in dermis, vibrations
layers act as filters for what stimuli activates them
rapidly adapting receptors
hair follicle receptors
free nerve endings wrapped around base of hair follicle in dermis + hypodermis
proprioceptors
musculoskeletal system
detect movement + position of joint / body part
bodies sense of its position in space
sensory neuron structure
cell body of neuron in posterior root ganglion (dorsal), lateral to spinal cord
cell body of cranial nerves in cranial nerve ganglia
peripheral process + central process
peripheral process
long axon splits into nerve endings each associated w/ sensory receptor
terminates near neurons cell body
central process
exits cell body + travels through posterior root of spinal cord to enter posterior horn
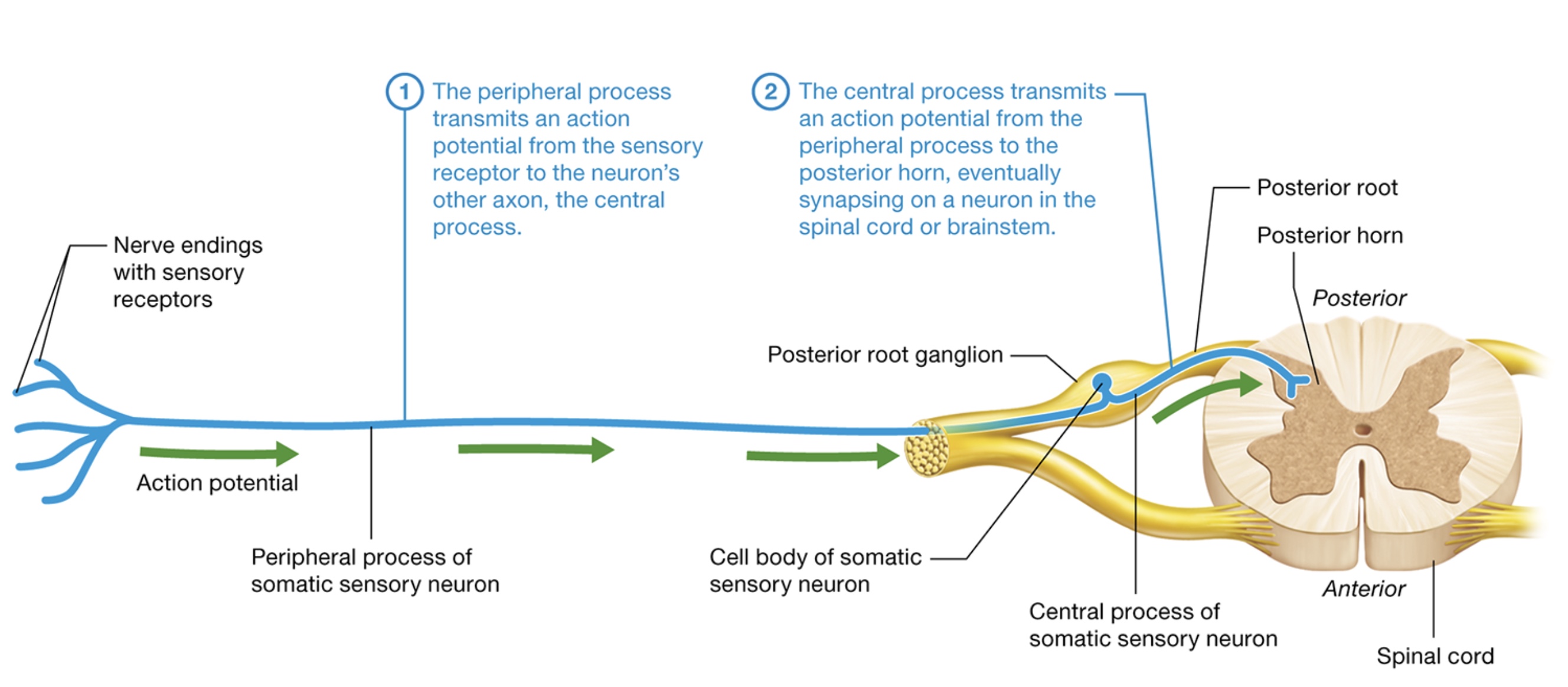
somatic sensory neuron structure
1) peripheral process transmits action potential from sensory receptor to neurons other axon, the central process
2) central process transmits action potential from peripheral process to posterior horn eventually synapsing on a neuron
Sensory neuron classification
speed which peripheral axons conduct action potentials
large diameter + myelin sheath → fastest
proprioceptive, discriminative, nondiscriminative stimuli
small diameter + no myelin sheath → slowest
pain + temp
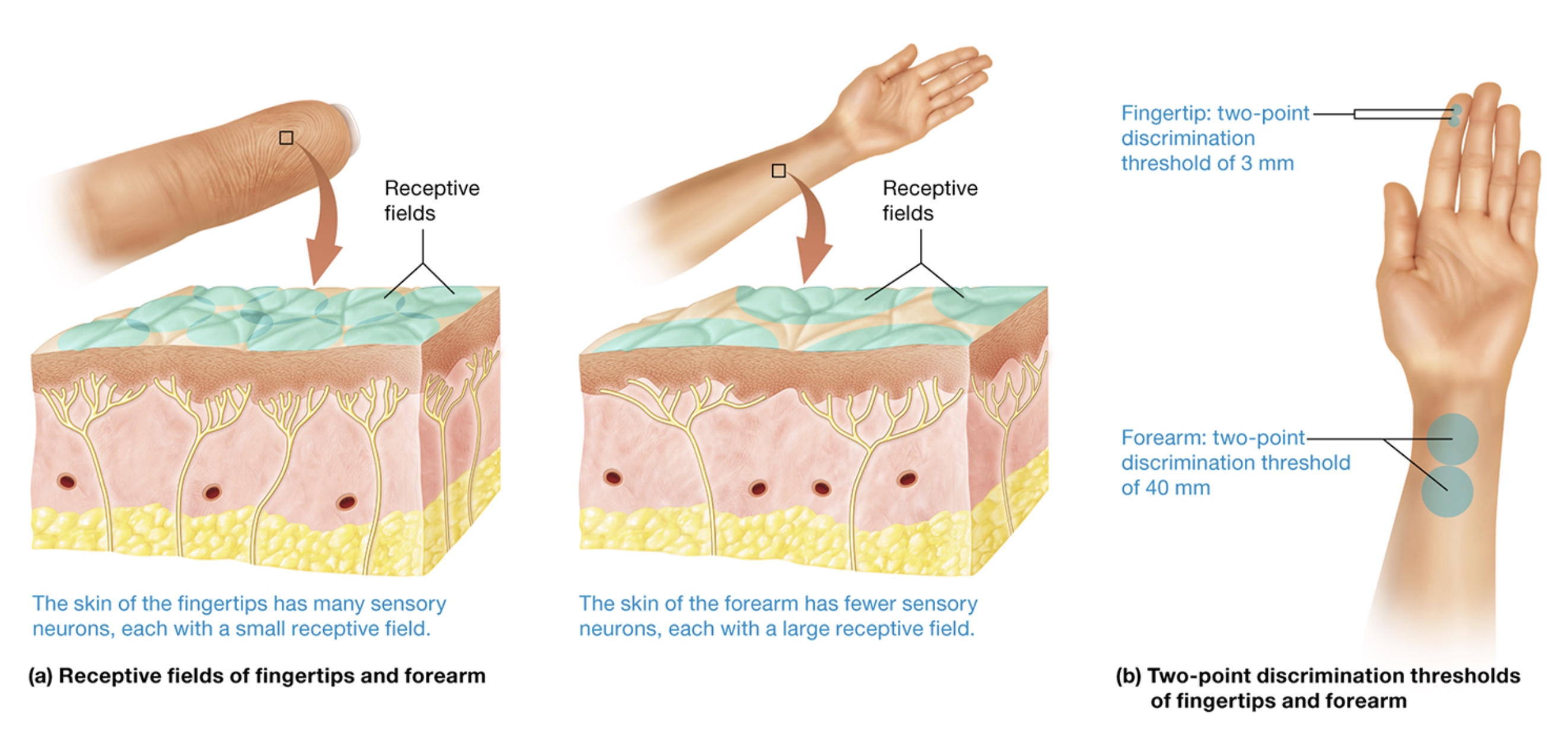
receptive fields
area served by a particular neuron
dependent on neuron branching + number
more neurons → smaller receptive field
two point discrimination threshold - 2 stimuli paced close together on skin + moved apart until subject can feel 2 distinct points
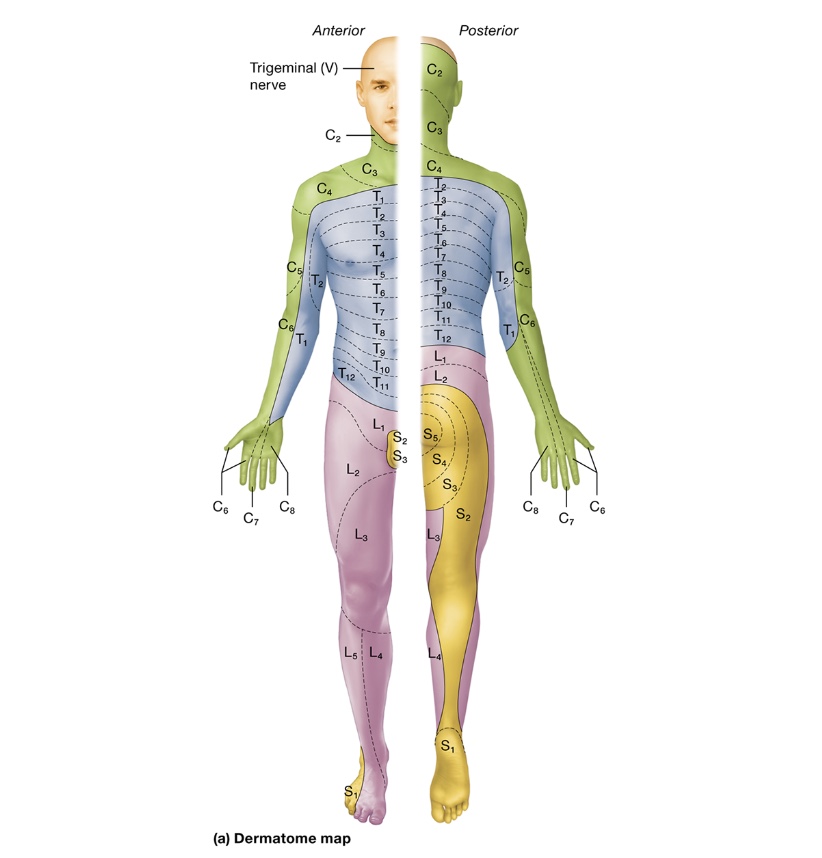
dermatomes
skin divided into segments based on spinal nerve that supplies the region w/ somatic sensation
dermatome map - clinically test integrity of sensory pathways to different parts of the body
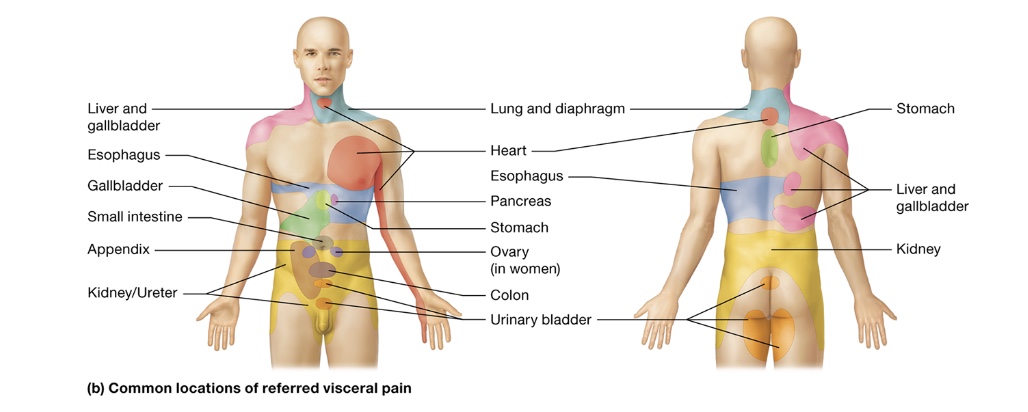
referred pain
pain that originates in organ being perceived as cutaneous pain
usually along dermatome nerve
many spinal nerves carry 1st order somatic + visceral sensory neurons causing referred pain
motor output
upper motor neurons repay messages to lower motor neurons which releases acetylcholine onto muscle fiber initiating muscle contraction
lower motor neurons
multipolar neurons
cell bodies - CNS large myelinated axons - PNS
α-motor neurons - stimulate muscle fibers to contract by excitation-contraction mechanism
γ-motor neurons - innervate muscle fibers called intrafusal fibers (stretch receptors)
reflex arcs
programmed automatic responses to stimuli
protective, prevent tissue damage
sensory stimulus + rapid motor response
golgi tendon organs
mechanoreceptors in tendons monitoring tension created by muscle contractions
golgi tendon organ consists of encapsulated bundle of collagen fibers attached to 20 extrafusal muscle fibers
contain 1 somatic sensory axon whose endings are wrapped around its enclosed collagen fibers
greater tension generated → greater rapid firing
muscle spindles
tapered structures embedded among extrafusal muscle fibers (regular contractile muscle fibers)
intrafusal muscle fibers - specialized + have contractile filaments made of actin + myosin
innervated by γ-motor neurons (muscles above)
Classes of sensory neurons innervating intrafusal fibers
primary afferent - responds to stretch when first initiated
secondary afferent - responds to sciatic length of muscle + position of limb
mechanically gated ion channels open when intrafusal fibers are stretched
more spindles → finer movement
reflex types
monosynaptic - involve 1 synapse in spinal cord
polysynaptic - multiple synapses
visceral reflexes - innervate internal organs, connected w/ autonomic nervous system
somatic reflexes - somatic sensory + motor neurons
simple stretch, flexion + crossed extension, golgi tendon, cranial nerve endings
cranial nerve endings
polysynaptic, 2 nerves (one afferent, one efferent)
gag reflex - somatic motor neurons of vagus nerve trigger pharynx muscle contractions
corneal blink reflex - blink when something touches cornea of eye, somatic sensory receptors
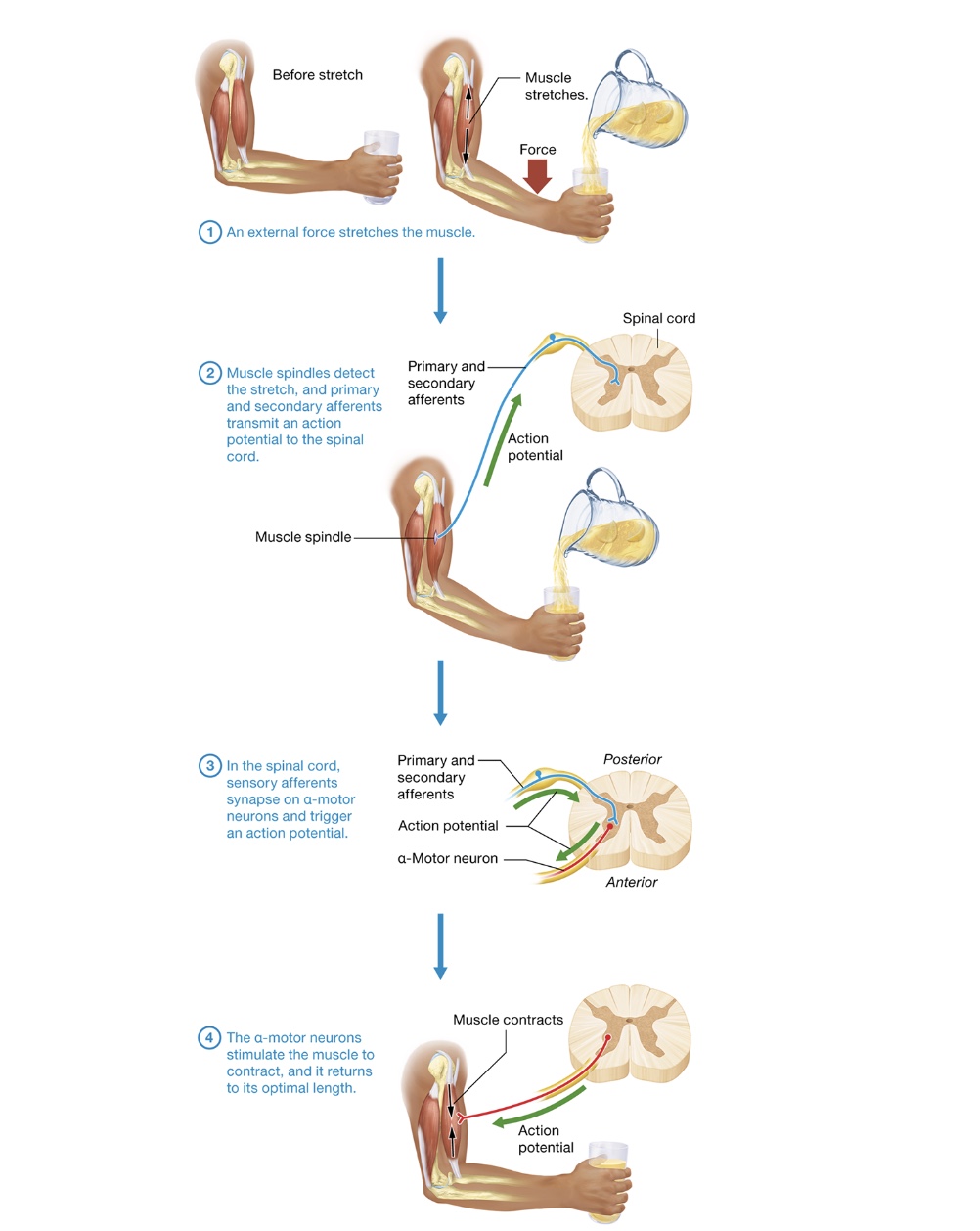
simple stretch
upper motor neurons have optimal length for skeletal muscles, when it deviates from that, simple stretch reflex kicks in
monosynaptic reflex, shortens muscle
sensory afferent synapse on interneurons inhibiting antagonist muscles
tapping on certain tendons - patellar reflex, jaw-jerk
1) external force stretches muscle
2) muscle spindles detect stretch, primary + secondary afferents transmit action potential to spinal cord
3) in spinal cord, sensory afferents synapse on α-motor neurons triggering action potential
4) α-motor neurons stimulate muscle to contract + returns to optimal length
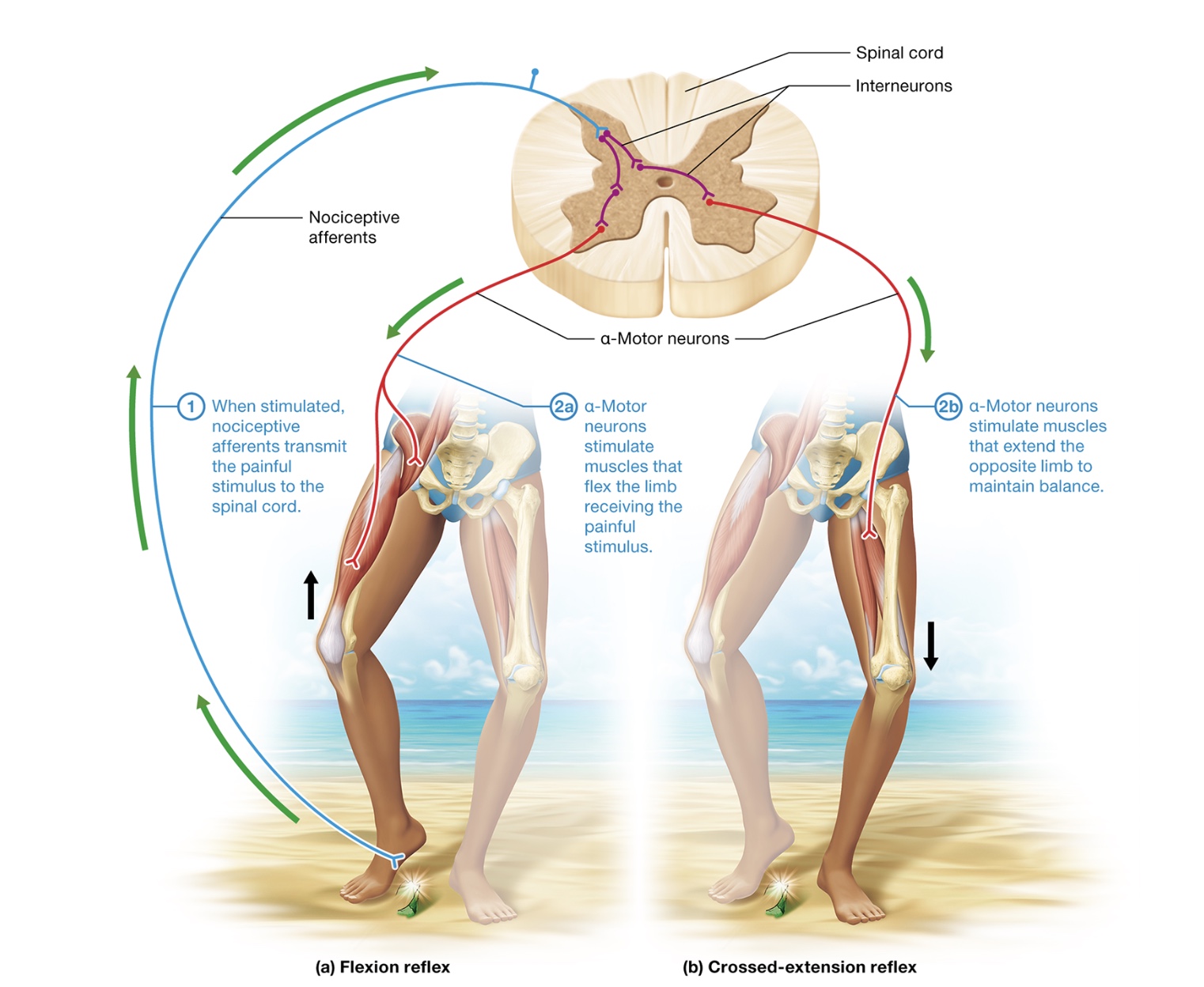
flexion withdrawal + crossed extension
involve rapidly conducting nociceptive afferents + multiple synapses in spinal cord - polysynaptic
pulling hand away from hot stove
crossed extension reflex - preserves balance by triggering opposite limb
1) when stimulated, nociceptive afferents transmit painful stimulus to spinal cord
2) α-motor neurons stimulate muscle to flex the limb receiving painful stimulus
3) α-motor neurons stimulate muscles that extend the opposite limb to maintain balance
golgi tendon
polysynaptic causing muscle relaxation to protect muscle
happens when tension increased dramatically
dropping heavy weight when working out
peripheral neuropathies
disorder effecting sensory + motor neurons
sensory neuron disorders
sensory peripheral neuropathy
dependent on which nerve was injured
decreases / eliminates sensation
“shooting” pain from inflammation + inappropriate firing of nociceptors
proprioceptive damage - damaged ligaments + tendons, difficult monitoring + contracting movement
lower neuron disorders
motor peripheral neuropathies
injury to spinal / cranial nerve or lower motor neurons
muscles can’t contract bc damaged α-motor neuron
paralysis + paresis (muscle weakness)
upper motor neuron disorder
can result from damage or disease anywhere along the pathways from motor cortices to spinal cord
spinal shock - initial response, paralysis, wears off in a few days + spasticity develops
Babinski sign - stroking bottom of foot, healthy adult will cause plantar reflex, patient with an upper motor neuron disorder will extend the hallux + splay out the other toes
spasticity
increase in stretch reflexes + muscle tone,
clonus - the alternating contraction + relaxation of a stretched muscle
caused by a loss of normal inhibition mediated by upper motor neurons
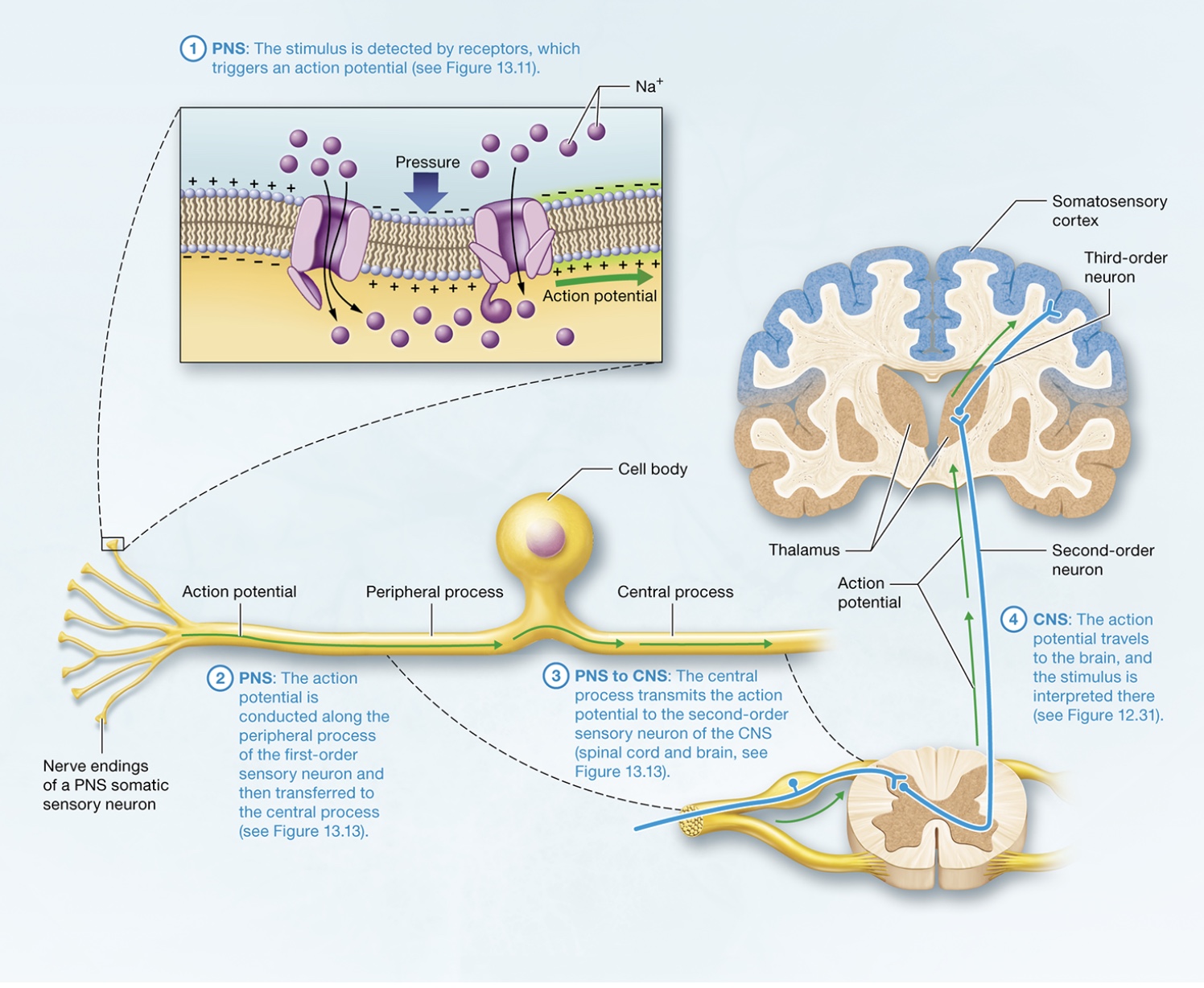
Detection and Interpretation of Somatic Sensation by the Nervous System
cf
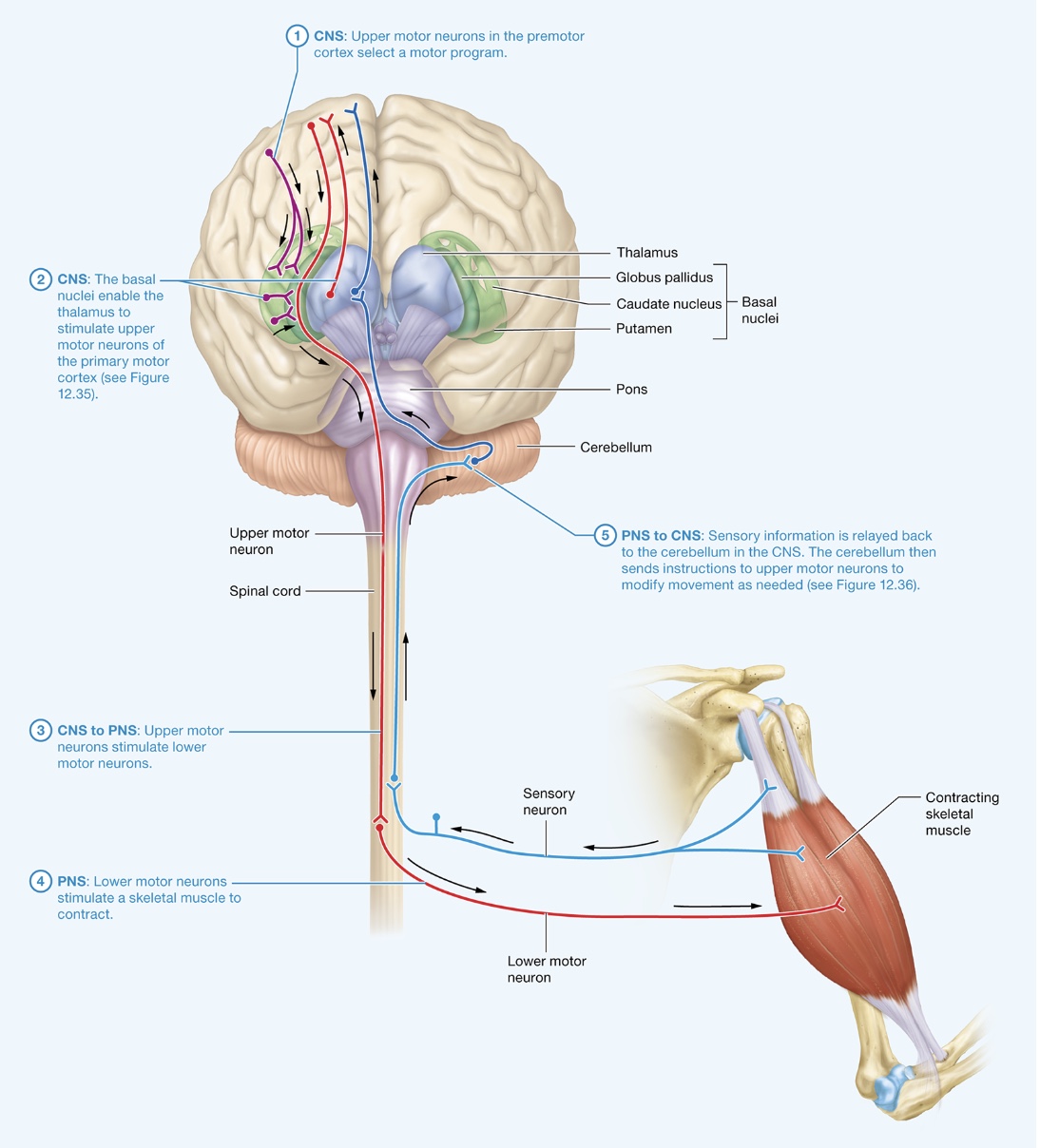
Control of Movement by the Nervous System
vb