GC650 Lecture 3 - Measuring Effectiveness
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Clinical Measures of Effectiveness Examples (7)
Hospitalizations avoided
ER visits avoided
Healthy days
LDL goal attainment
Blood pressure goal attainment
Progression Free Survival
Overall Survival
Patient Focused Measures of Effectiveness Examples (4)
Health-related quality of life
Patient satisfaction with treatment
Patient preference
Productivity (self-reported)
WHO Health Definition
A state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
WHO Quality of Life Definition
An individual’s perceptions of their position in life in the context of the culture and value system in which they live and in relation to their goals, standards, and concerns. This extends beyond health.
Use of Quality of Life Measures in PROs and RCTs
QoL endpoints can be a better indicator of health than clinical measures, pain is subjective, and EQ-5D is increasingly common
Why measure quality of life? (3 Perspectives)
Assess impact of illness
Assess impact of treatment
Inform what a clinically meaningful difference is on objective measures
Types of Quality of Life Instruments (2)
Health Profile Measures - SF36
Health Utility or Preference Measures - EQ-5D
SF-36 Domains (2 Overarching)
Physical Health
Mental Health
SF-36 PCS Subcategories (4)
Physical Functioning
Role-Physical
Bodily Pain
General Health
SF-36 MCS Subcategories (4)
Vitality
Social Functioning
Role-Emotional
Mental Health
Quality Adjusted Life Year (QALY)
Measures both the quantity (duration) of life and the quality of life, need to know how much people value a year of life in a particular health state
Typically uses the EQ-5D
QALY is a measure of…
Health Utility
Steps to Developing Health Utilities
Select method for describing health
Develop weights for valuing each health state
Combine the weights with life expectancy in the health state to calculate good years remaining or years lost
EQ-5D Dimensions (5)
Mobility
Self-Care
Usual Activities
Pain/discomfort
Anxiety-depression
Old version had 3 levels (243 states), new has 5 (3215 states). Higher numbers are worse health states.
Time Trade Off Calculation
You will live the next 10 years with a disease. How many years of life are you willing to give up to have perfect health?
Ex. Give up 2 years. 8 Years Remaining/10 Years Total. Each disease year is worth 0.8 healthy years.
Shaw Calculation
Based on the 4,000+ respondents from the Shaw study, uses their collective answers to weigh health states.
Adding up each deviation above 1 and doing a calculation using the regression from their study.
EQ-5D Visual Analog Scale (VAS) Calculation
Patient rates their health on a scale of 1 to 100, divide the answer by 100 to get the value of time in that health state.
QALY Calculation
(time in that quality of life state) x (individual’s utility for life during that time)
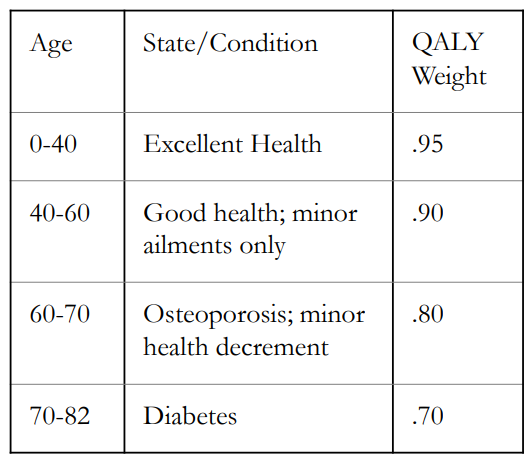
Example QALY: Good Health with Minor Comorbidity in older years
Multiply the value of each category by the number of years spent in that category to get QALY
Total in the picture is 72.4 QALY out of 82 Years
Societal Value of a Treatment Calculation
The sum of QALYs experienced by individuals with the disease and receiving the treatments/programs of interest
When to Measure Quality of Life?
Ideally you want to know what a person’s Quality of Life is before, during and after an intervention.
Some conditions/treatments have different stages or exacerbations, so you would want to know the quality of life for any changes in the health state
Ethical Considerations of Measuring Quality of Life (5)
Source of the value/weighting scheme
Age weighting
Failure to give priority to those in worst health
Discriminate against those with limited treatment potential – because the score cannot be improved with intervention
Fail to account for qualitative differences in outcome
Disability Adjusted Life Year (DALY)
It represents the total years of healthy life lost due to illness, disability, or premature death.
Includes Years of Life Lost (YLL) and Years Lived with Disability (YLD).