Unit 4, AOS 2 - Energy
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Energy types, energy sources, peak oil, impact of energy sources, electricity grids, and mine rehabilitation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Define Energy
The ability to do work.
Define Power
The rate at which energy is produced/consumed over time.
Define Joules
A measure of the amount of energy needed to do work.
(eg. 1 joule is the amount of energy needed to lift 100g of mass 1m, or raise the temperature of 1cm2 of water 0.25oC)
Define Watts
The unit that measures power.
Watt hours measure how much power is produce/consumed over time.
Define Amps (amperes)
Measure electric current - the strength of the electromagnetic force between two conductors carrying electrical current.
Define Volts
Measures the electrical potential difference (how much energy each unit carries when moving between too points)
Define Ohms
Measure electrical resistance, or how much power it takes to make electrons flow through an object.
Describe the Energy Conversion Equations Triangle

W on top, then A and V on the bottom
Define Potential Energy
Energy that is stored due to its position or configuration.
List 4 forms of Potential Energy with an example for each
Chemical energy locked in the bonds of molecules (eg. food or fuels)
Gravitational energy (eg. water in a dam)
Elastic energy in a stretched or compressed object (eg. coiled spring)
Nuclear energy in the nucleus holding protons and nuetrons together (eg. nuclear power plants, unstable or radioactive nuclei)
Define Kinetic Energy
The energy of a body in motion.
List 4 forms of Kinetic Energy with an example for each
Thermal or the heat energy within a substance (eg. body heat or steam)
Radiant energy transmitted as rays, waves or particles (eg. a torch or the sun)
Electrical energy from the movement of charged particles (eg. powerlines)
Sound energy transmitted in waves through a medium (eg. radio)
Define Mechanical Energy with an example
Energy associated with a mechanical device - the energy an object possesses due to its position or motion (it’s sum of kinetic and potential energy).
For example, a hammer, bow and arrow or wind/generator turbine.
Describe the First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is neither created nor destroyed, it can merely be changed from one form to another.
Describe the Second Law of Thermodynamics
The total amount of useful energy decreases with each transformation in the energy’s form.
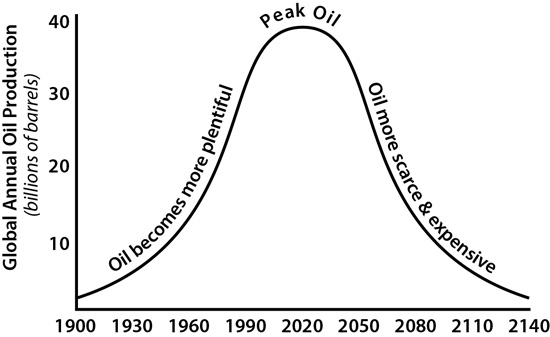
Define what is meant by Peak Oil
The concept that the rate of oil extraction will increase until it reaches it’s highest level (or peak) after which the oil’s quality, amount and ease of extraction will decline.
Describe the process of Fracking
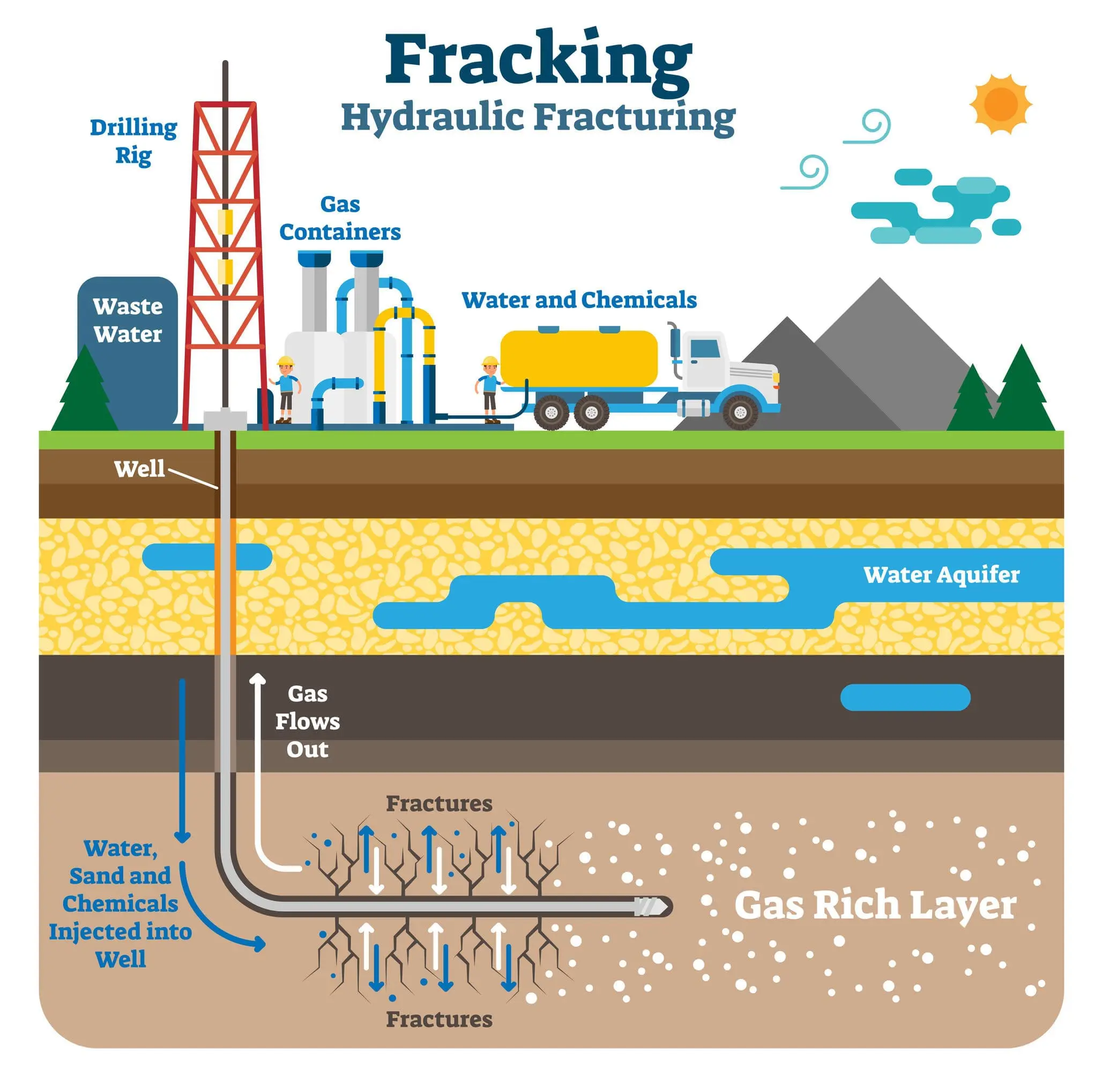
A extraction method for natural gas and oil from shale rock by drilling into the earth and injecting a high-pressure mix of water, sand and chemicals to fracture the rock and release the oil and gas.
Identify 3-4 environmental concerns around Fracking
Groundwater and soil contamination from fracking chemicals
Intensive water consumption
Methane emissions from fractured rock
Potential increases in seismic activity
Outline what is meant by the Electrical Grid
Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, transmission lines, local utilities and transformers. These components work to generate, transmit and distribute electricity.
Define the term Capacity
The maximum power output from an energy facility or electricity system (ie. if generators operated at 100%)
Define the term Capacity Factor
The ratio of actual energy produced and the capacity.
(The actual output of a generator over time compared to the generator working at 100%)
Define the term Efficiency
How effectively input energy is converted into the output.
(eg. chemical energy in coal converted to electricity in a power plant)
Define the term Base Load Demand
The minimum level of demand for electricty over a span of time (eg. 24 hours)
Define the term Peak Demand
The highest demand consumed at any given time.
Define the term Dispatchable Energy
When an energy source has an adjustable output to help balance supply and demand.
Compare the reliability of fossil fuels and renenewable energy from solar and wind power
Fossil fuels are far more reliable because they can produce energy on demand, either continuously or when needed. Solar and wind produce energy intermittently, lowering their capacity factors and ability to consistently meet the base load.
List 3 Pros of Fossil Fuels
Reliable and consistent
Easy to transport and store
Infrastructure already in place
Easiest to use with current machinery and in many industrial processes, particularly those involving combustion (eg. cement)
List 3 Cons of Fossil Fuels
Most significant source of GHG emissions
Pollution from waste, runoff, particulate matter, combustion
Relies on environmentally harmful extraction methods
Finite, non-renewable and resources
Increasingly damaging extractions as quality and quantity decline (peak oil)
List 3 Pros of Nuclear Power
Reliable and constant power
Very efficient energy production
Expensive infrastructure
Low carbon
Lesser areas of land required for infrastructure
List 3 Cons of Nuclear Power
Safe storage is extremely important
Associated with development of nuclear weaponry
Radioactive waste
Extreme pollution/radiation risks
Uranium, the fuel, is non-renewable
Intensive water use
List 3 Pros of Hydro Power
More reliable than renewables such as solar and wind
Low carbon, renewable
In the long term, it is cost-effective
Dams can have multiple purposes (eg. irrigation, flood control)
High efficiency
Doesn’t rely on constant resource extraction
List 3 Cons of Hydro Power
Impacts on waterways, peak flow and aquatic/interconnected ecosystems
Interrupts fish migration routes
Location can’t be chosen for convenience of transportation or storage
Reservoir creation can displace people
List 3 Pros of Solar and Wind Power
Low carbon, renewable
Doesn’t rely on constant resource extraction
Can be implemented in already cleared areas such as farmland
Can be implemented on small scales
List 3 Cons of Solar and Wind Power
Fluctuating ability to meet base load
Inconsistent power supply, dependent on factors outside of control
Batteries and the panels/turbines require mining for precious metals
Large areas of land required
Wind turbines can be loud, have disruptive shadows and pose a threat to high-flying birds
Identify 5-8 impacts of Fossil Fuel Mining
Damage or destruction of natural environments and landforms with environmental, cultural and spiritual significance
Permanent change to natural topography and landcover
Losses of biodiversity
Interruption, diversion, pollution and loss of waterways
Toxic waste disposal and runoff
Fire hazards of discarded low-quality coal
Define the term Ore
Natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals.
Define the term Mine Void
The remaining area of excavation after mining is complete.
Define the term Overburden
The rock or soil layer that needs to be removed to access the ore being mined.
Define the term Tailings
The waste material after the target mineral has been extracted from the ore.
Define the Mechanical Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation efforts that involve physically moving components to, from and within the site.
Provide 3 examples of Mechanical Rehabilitation of a mining site
Clearing out mining infrastructure
Clearing out contaminate soil
Reshaping the site to represent natural topography
Backfilling of tunnels and shafts
Define Chemical Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation efforts that involve returning the chemical properties of the soil and water to safe, normal levels.
Provide 3 examples of Chemical Rehabilitation of a mining site
Treating polluted water
Treating soil and tailings
Fertilising topsoil to encourage revegetation
Define Biological Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation efforts that involve reintroducing wildlife to the site.
Provide 3 examples of Biological Rehabilitation of a mining site
Revegetation programs
Reintroduction of fauna
Creating and supporting habitats for native animals
Outline what is meant by the Cumulative Impacts of Mining
The collective impacts of mines across a region/country rather than individual mines, taking into account direct and indirect impacts.
Identify 3 sources of Indirect Mining Impacts
Construction and maintenance
Operatation of infrastructure
Transportation
Surrounding infrastructure (eg. pipes, roads, etc.)
Define and describe the purpose of Bioindicators
Living organisms used to judge the health of an ecosystem, often by measuring population trends in species vulnerable to physical or chemical change in their environments.
Define and describe the purpose of Benchmark/Reference Sites
Undisturbed sites in the region used to provide a specific, realistic and holistic goal of rehabilitation and measurement of comparitive success.