Invertebrate Practical 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/238
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:22 AM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
1
New cards
Grade of Construction of Sponges
Asconoid, Syconoid, Leuconoid
2
New cards
Ascinoid
The body wall is not folded to form chambers
3
New cards
Syconoid
Single osculum with folding of the body wall to allow for a greater number of choanocytes
4
New cards
Leuconoid
There is extensive folding of the interior body wall’ multiple ostia and oscula may be present
5
New cards
Porifera taxonomy
Class Calcarea, Class Demospongiae, Class Hexactinellida, Class Homoscleromorpha
6
New cards
Class Calcarea
shallow water, marine sponges; all three body plans represented with calcium carbonate spicules, 3-4 rayed spicules
7
New cards
Class Demospongiae
freshwater and marine sponges comprise over 95% of all known sponge species; network of siliceous spicules held together by a network of a collagen-like protein called spongin; all demonstrate leuconoid grade of construction
8
New cards
Class Hexactinellida
These marine sponger occur in deep water and are normally quite large; their body plans are similar to the syconoid grade of construction, though much of the body consists of a syncytium; spicules are six sided and made of silicon
9
New cards
Class Homoscleromorpha
sister group to class calcarea; exclusively marine sponges, most of which inhabt shallow hard bottom; small and encrust on surfaces
10
New cards
Grantia
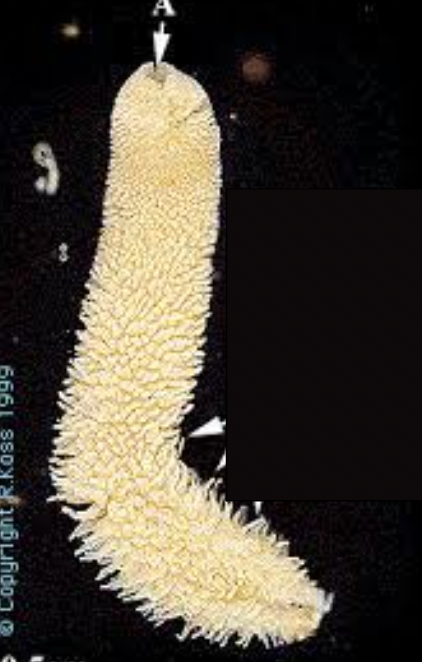
11
New cards
Grantia whole mount slide

12
New cards
1. osculum
2. choanocyte chamber (flagellum face in)
Grantia whole mount slide labeled
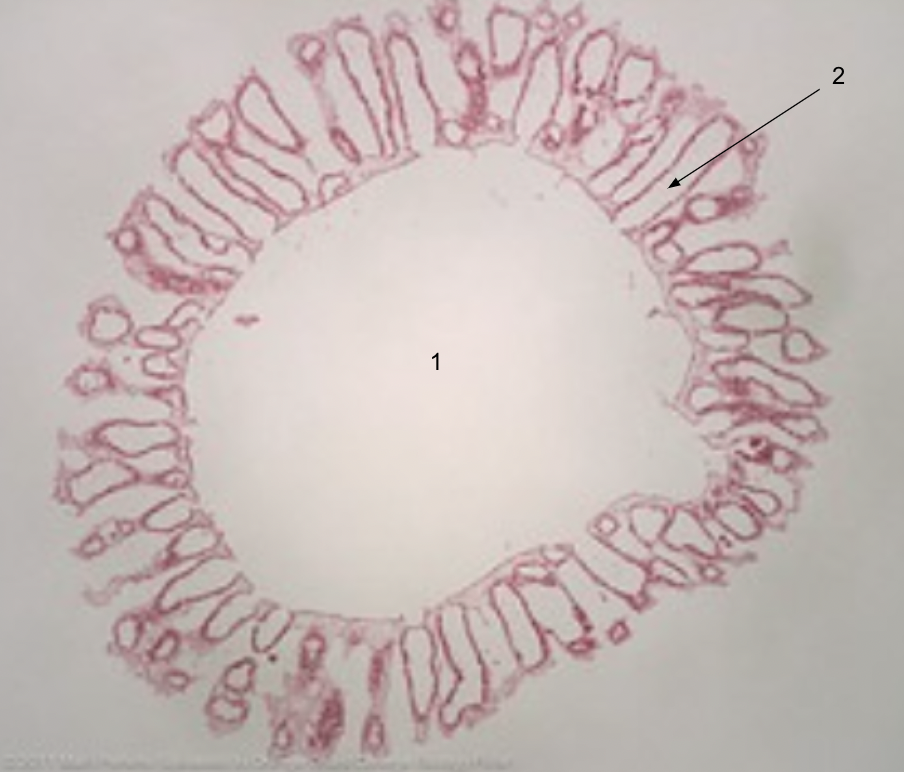
13
New cards
Grantia spicules
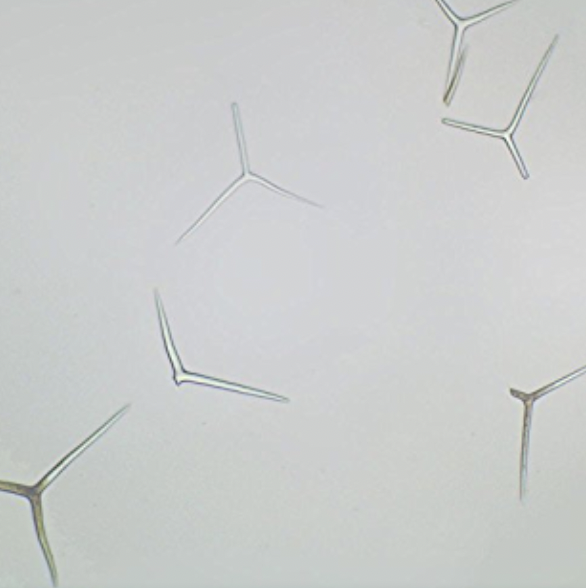

14
New cards
Grantia grade of construction
syconoid
15
New cards
Spongia graminea
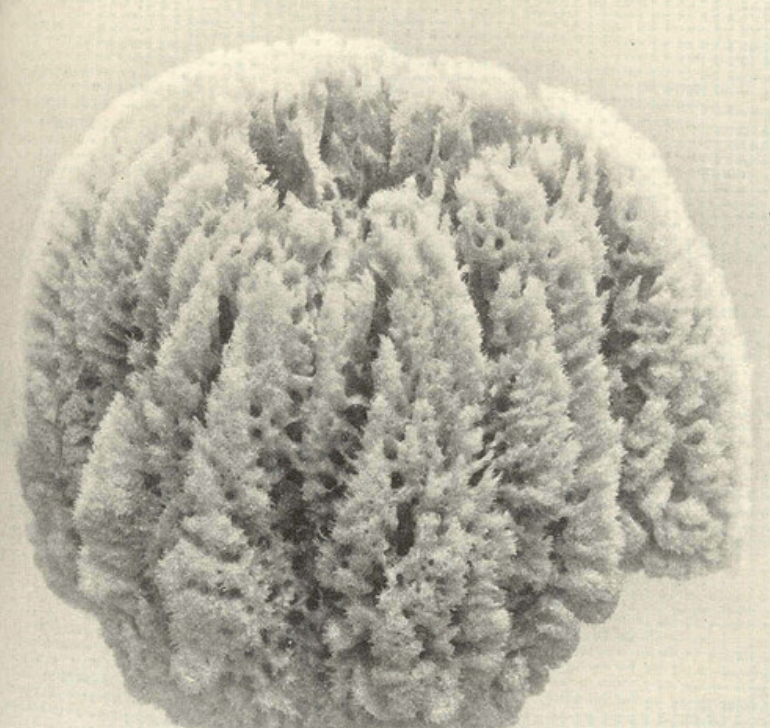

16
New cards
If spicules fizz when in contact with hydrochloric acid, they are composed of
calcium carbonate
17
New cards
Monaxon spicules

18
New cards
Triaxons

19
New cards
Triaxons
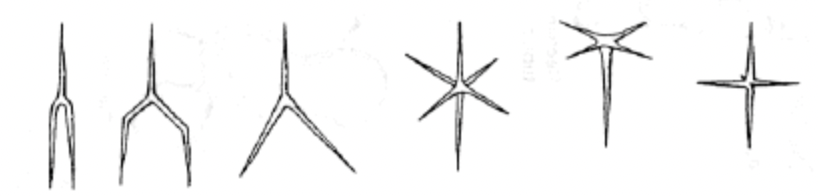
20
New cards
What is the best morphology a sponge could assume to maximize the photosynthetic potential of its symbionts?
Complex morphology because it create greater surface area as well desirable shelter for symbionts through increases crevices and branching.
21
New cards
Since sponges need to compete for hard substrate to attach to, what are other strategies to maximize photosynthetic potential?
Branching and growing upward and tall
22
New cards
Why would simple structures not work for large sponges?
They need more complexity to generate more time for filtration to obtain food as filter feeders
23
New cards
Best indicator of sponges environment
Shape due to adaptation to flow condition and predation
24
New cards
Relationship between number of spicules and environment of sponges
High energy sites require more spicules to increase the rigidity and toughness of the sponge in the high energy environment, whereas high spicule numbers are unnecessary in low energy environment
25
New cards
Relationship between shape of spicules and texture of sponge
More complex spicules resulted in harder sponges
26
New cards
Sponge Gemmule
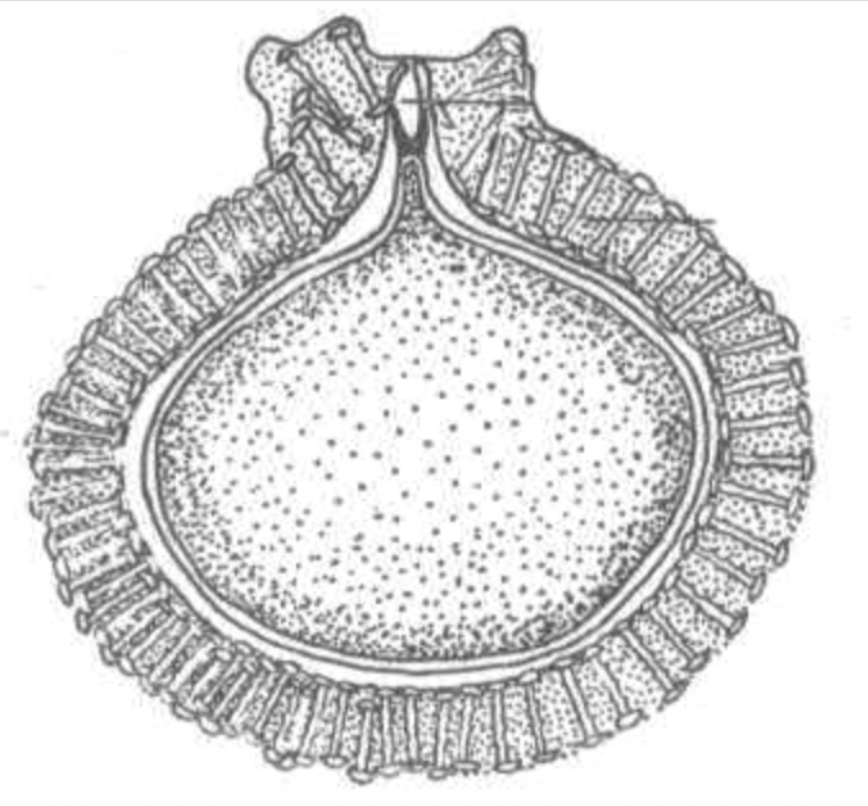
27
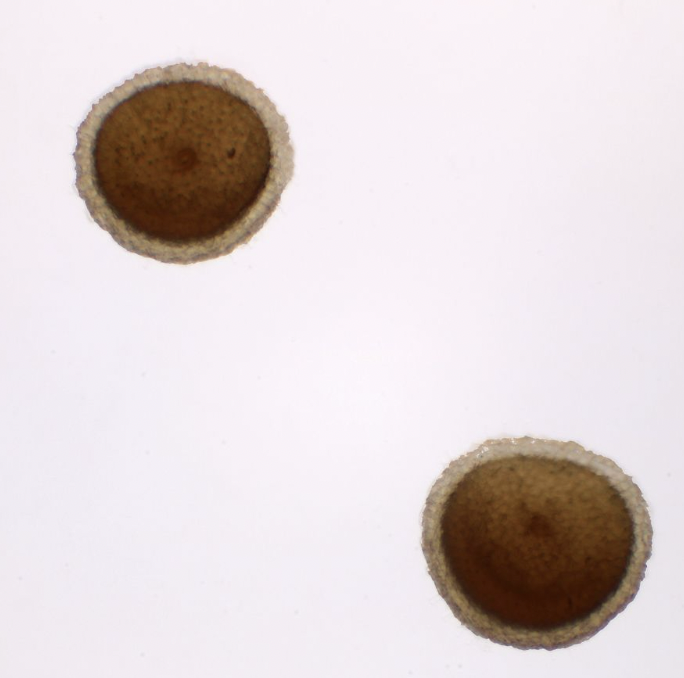
New cards
Sponge gemmules
28
New cards
Gemmules
seed like capsules formed by sponges containing cells from which a new sponge can grow
29
New cards
Are gemmules produced sexually or asexually
asexually
30
New cards
Reason for sponges to include durable phase (gemmule) in its lifecycle
Changes to environment can result in extreme conditions that incentivize sponges to have a durable phase to ensure reproduction
31
New cards
What are the layer of hexactinellida made of
syncytial
32
New cards
Syncytial
multiple nuclei are contained within a single plasma membrane
33
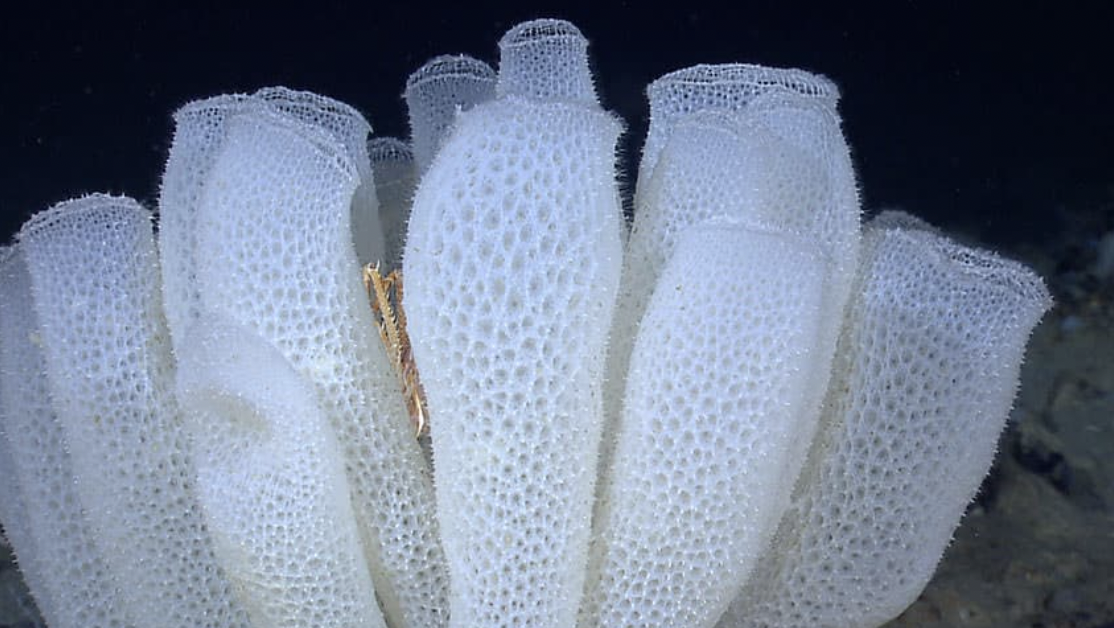
New cards
Hexactinellida

34
New cards
Commensal relationship for class hexactinellida
Male and female commensal shrimpy enter the glass sponge when small and live inside together for their life
35
New cards
Hexactinellida spicule
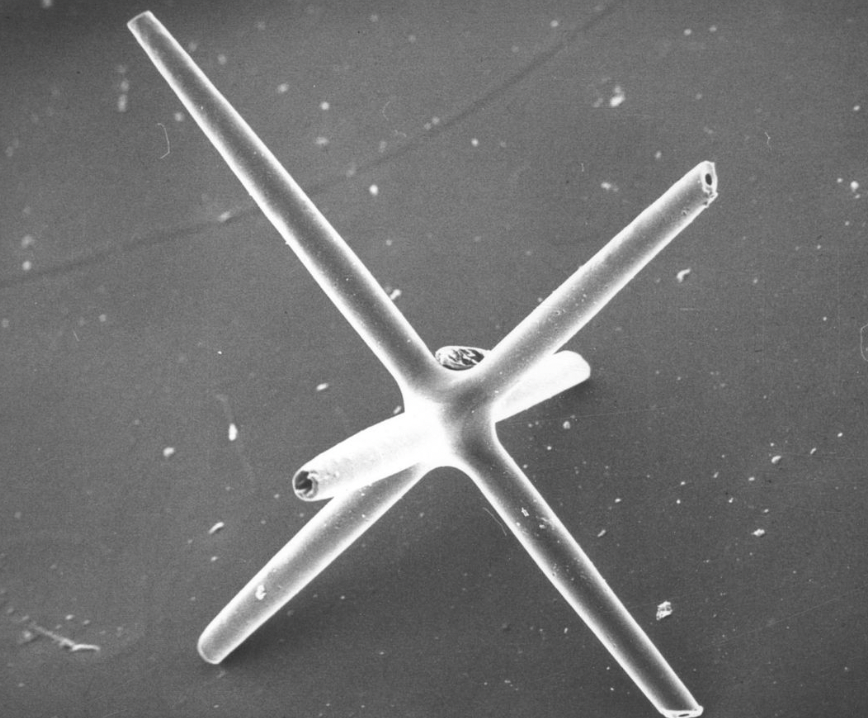
36
New cards
Cnidarian Taxonomy
Subphylum Medusozoa (Class Hydrozoa, Class Scyphozoa, Class Cubozoa, Class Staurozoa), Subphylum Anthozoa (Class Anthozoa)
37
New cards
Class Hydrozoa Taxonomy
Order Thecata, Order Athecata (Suborder Aplantulata, Suborder Capitata), Order Siphonophora
38
New cards
Class Cubozoa Taxonomy
Order Cubomedusae
39
New cards
Class Anthozoa Taxonomy
Subclass Octocorallia (Order Alcyonacea (form. Order Gorgonacea), Order Pennatulacea), Subclass Hexacorallia (Order Actiniaria, Order Scleractinia)
40
New cards
sea fan

41
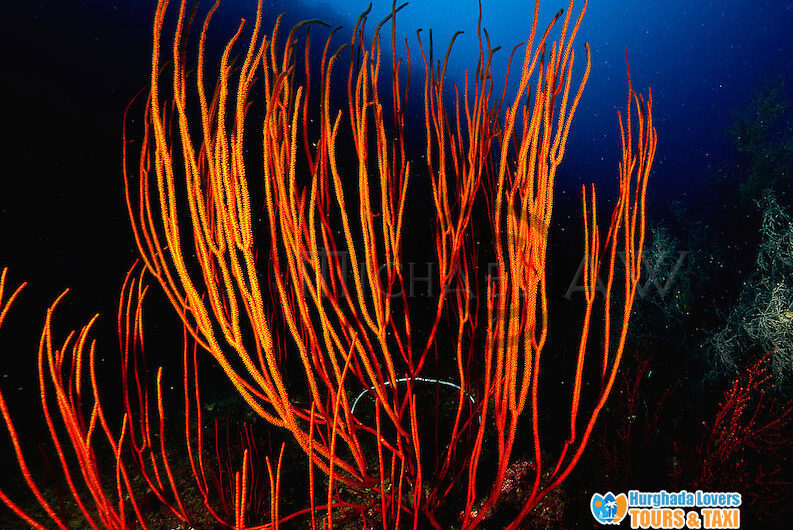
New cards
sea whip

42
New cards
Taxonomy of Sea Fans/Sea Whips
Subphylum Anthozoa, Class Anthozoa, Subclass Octocorallia, Order Gorgonacea
43
New cards
Sea fan orientation in the water
perpendicular to allows feeding of polyps on downstream end
44
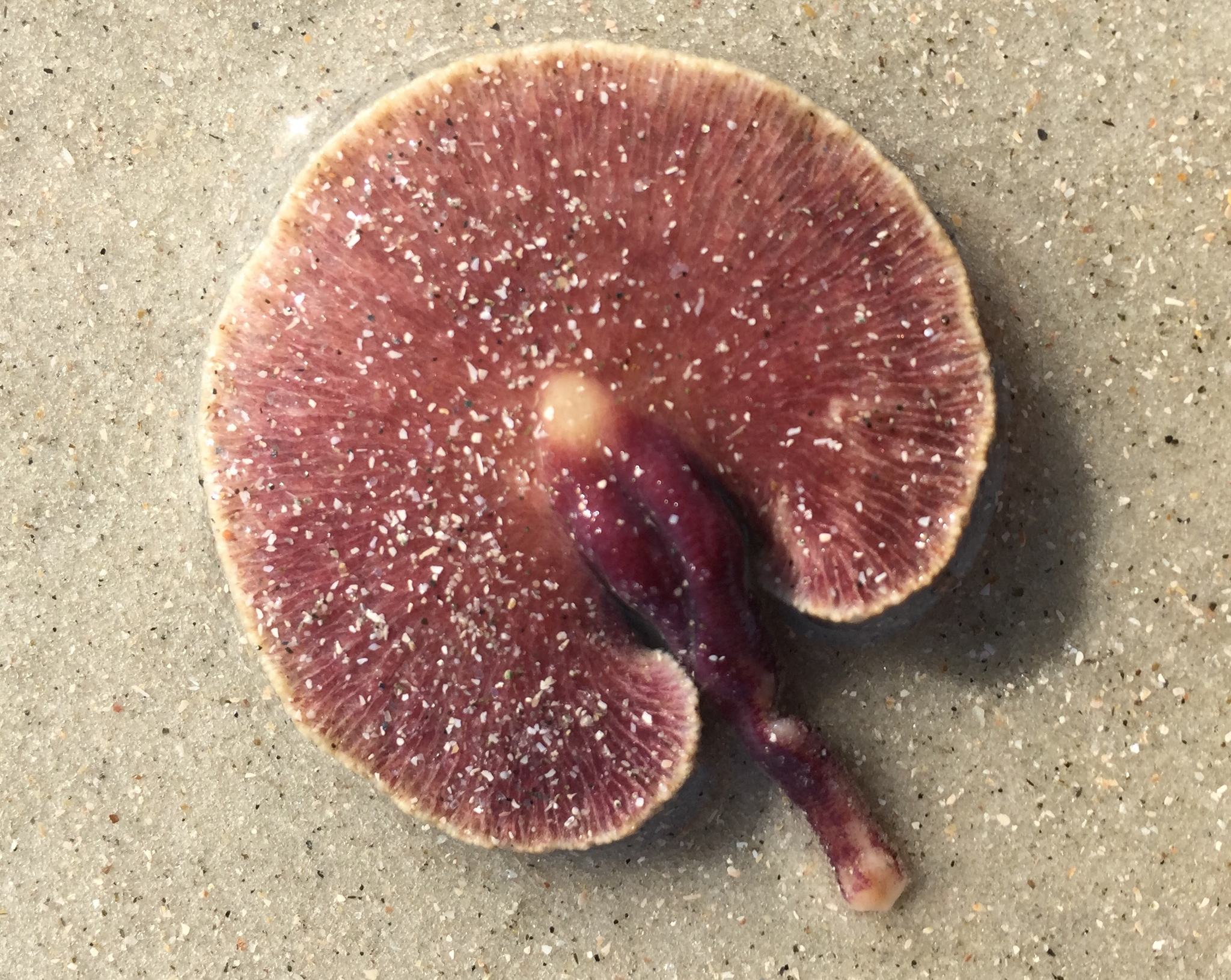
New cards
Sea Pansy (Renilla vermiformis)

45
New cards
Taxonomy of sea pansy
Subphylum Anthozoa, Class Anthozoa, Subclass Octocorallia, Order Pennatulacea
46
New cards
Gastrozooid (feeding) and Siphonozoid (Water intake)
Polyps on sea pansy
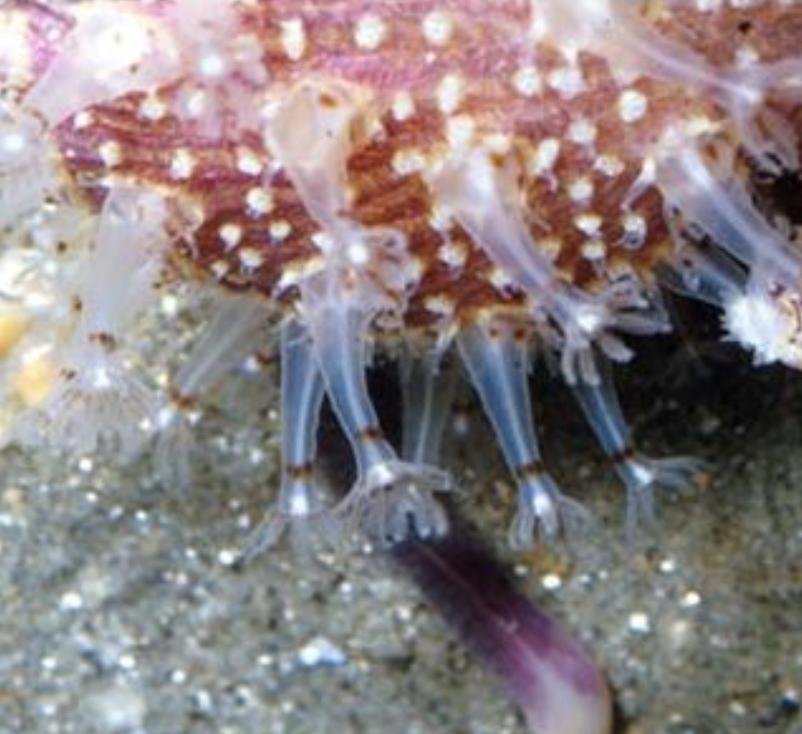

47
New cards
What does the addition of spicules in the hydrostatic skeleton of the sea pansy do to the mechanical function of tissue?
The addition of spicules makes it more rigid
48
New cards
General structure of stony corals
Polyps sit in the grooves/holes
49
New cards
Metridium senile
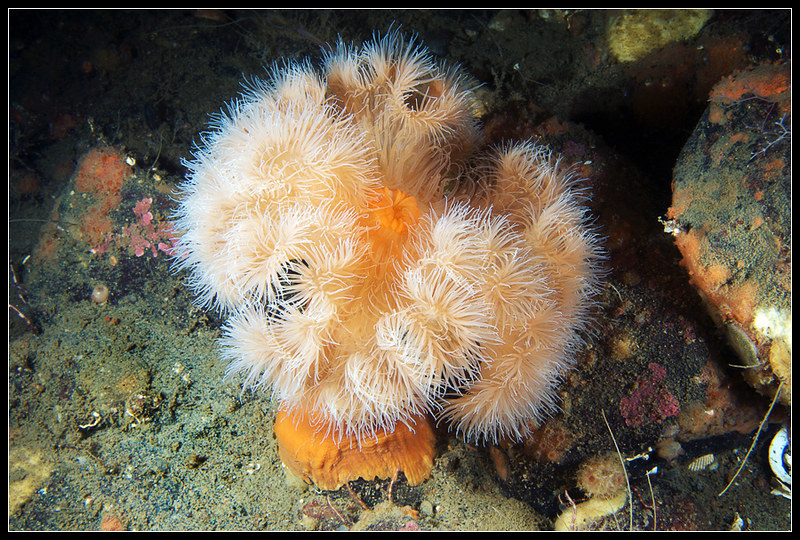

50
New cards
Metridium senile taxonomy
Subphylum Anthozoa, Class Anthozoa, Subclass Hexacorallia, Order Actiniaria
51
New cards
Representatives of Order Scleractinia
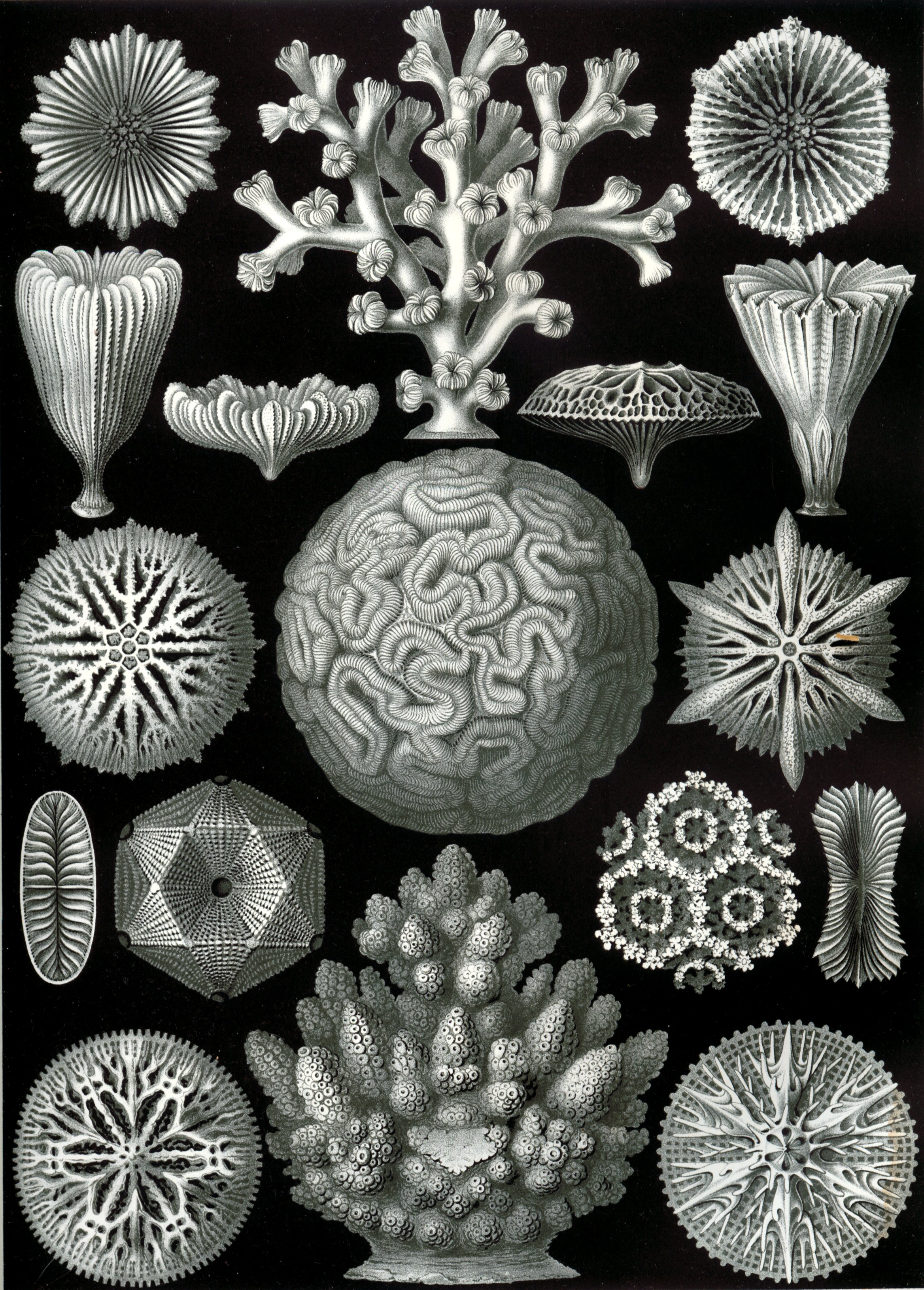

52
New cards
Fire Coral (Millepora)
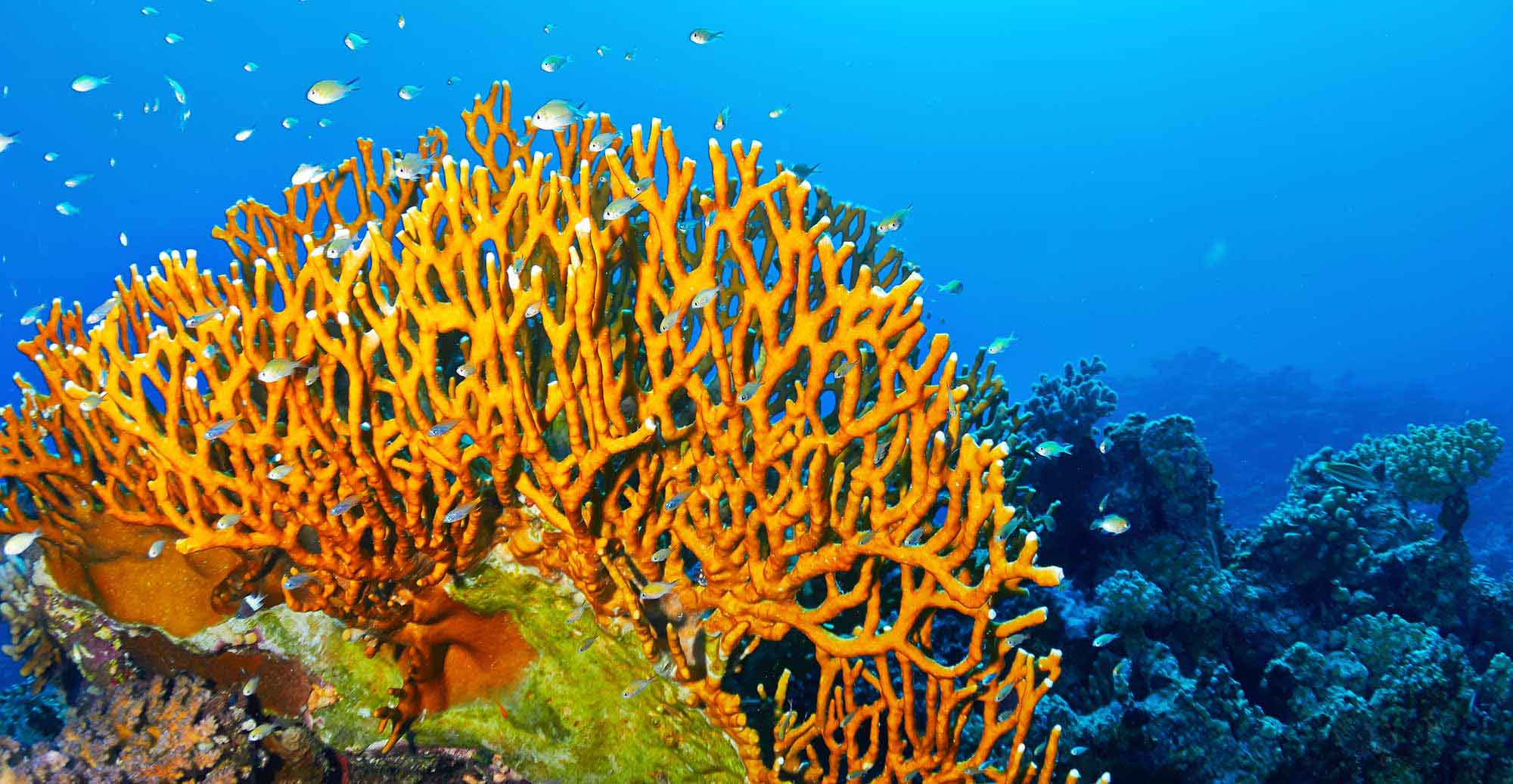

53
New cards
Fire Coral Taxonomy
Subphylum Medusozoa, Class Hydrozoa, Order Athecata, Suborder Capitata
54
New cards
Northern Star Coral (Astrangia poculata)
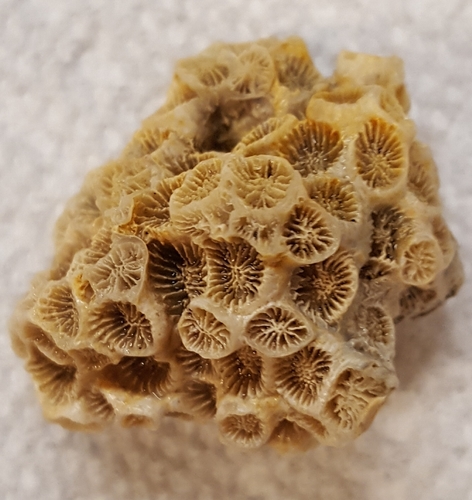

55
New cards
Northern Star Coral (Astrangia poculata)

56
New cards
Which organism exhibits facultative symbiosis?
Astrangia poculata
57
New cards
Facultative symbiosis
Can live with very few symbionts
58
New cards
Polyps of astrangia poculata
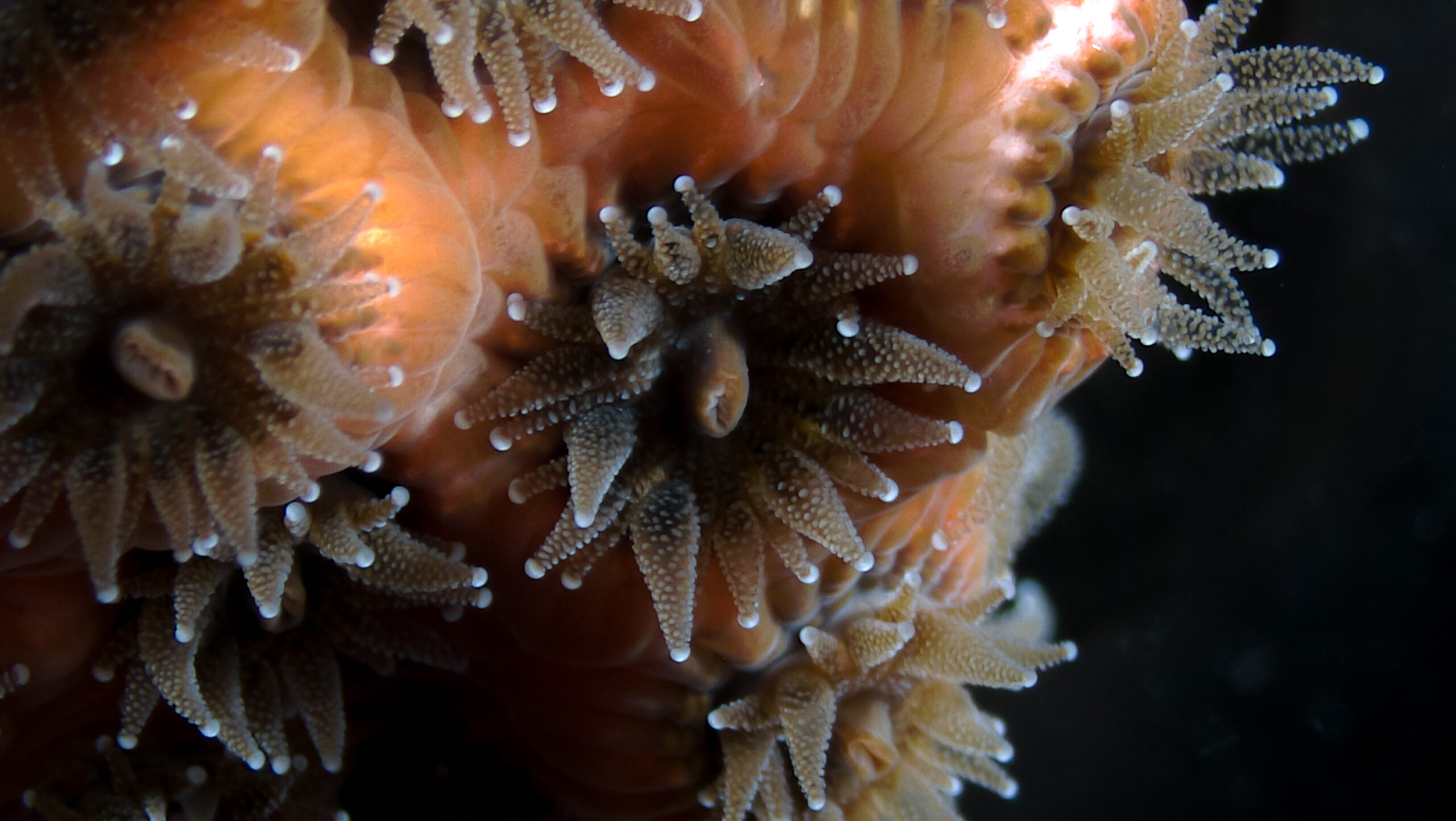

59
New cards
Astrangia poculata taxonomy
Subphylum Anthozoa, Class Anthozoa, Subclass Hexacorallia, Order Scleractinia
60
New cards
Why might an organism exhibit facultative symbiosis/have very different morphological states?
So that it is able to exist in harsh conditions in which there is unstable number of symbionts. It remains hardy.
61
New cards
Portuguese man of war (Physalia physalis)
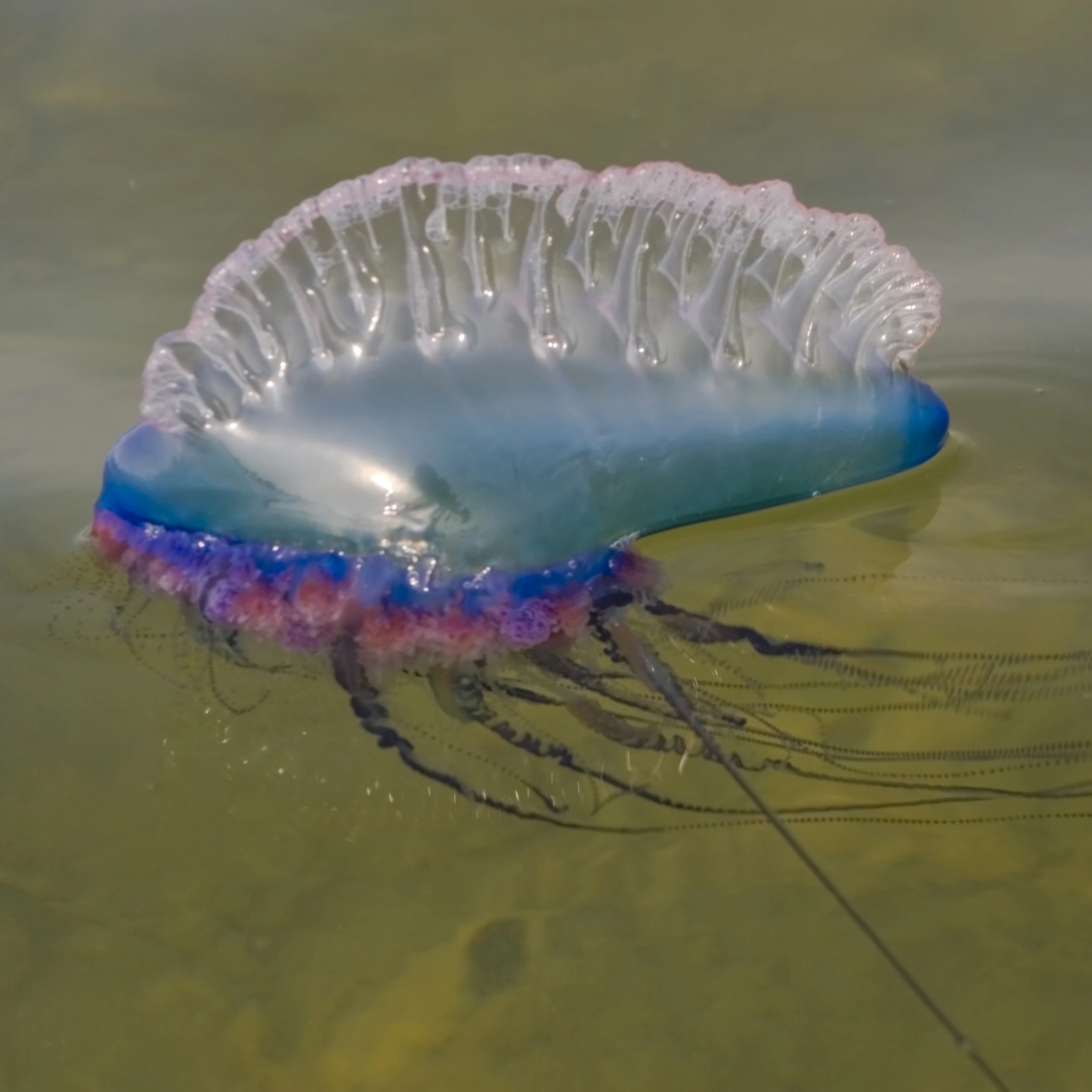

62
New cards
By-the-wind-sailor (Velella velella)

63
New cards
Little blue button (Porpita porpita)
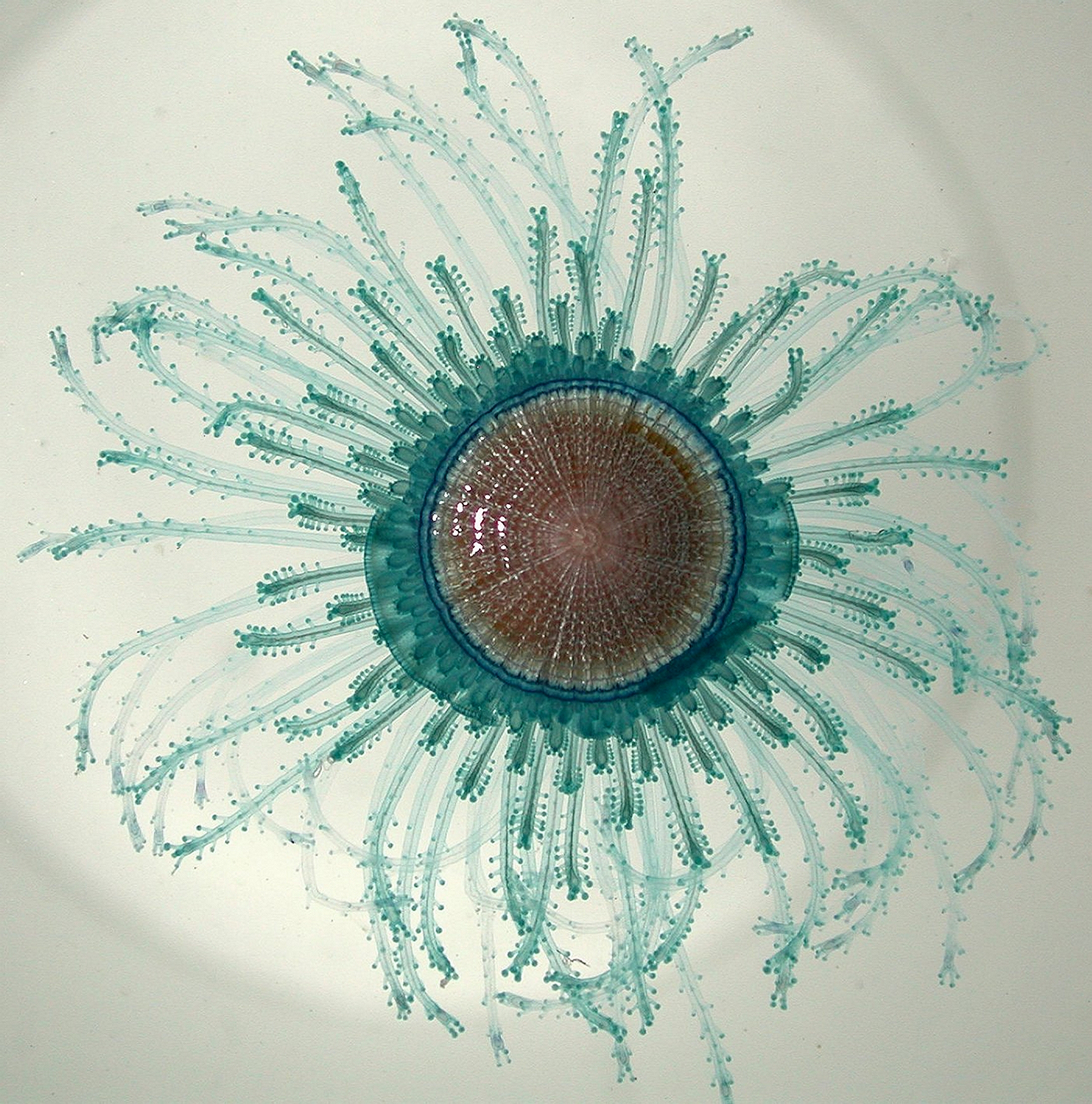

64
New cards
Ostrich Plume hydroid (Aglaophenia rigidida)
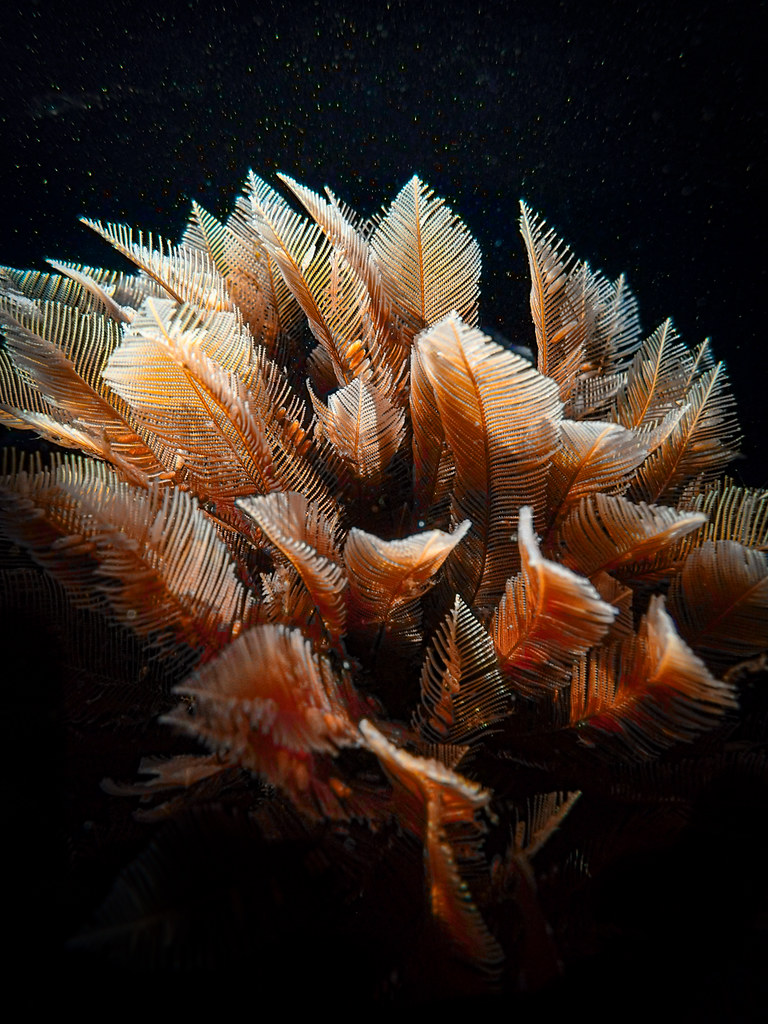

65
New cards
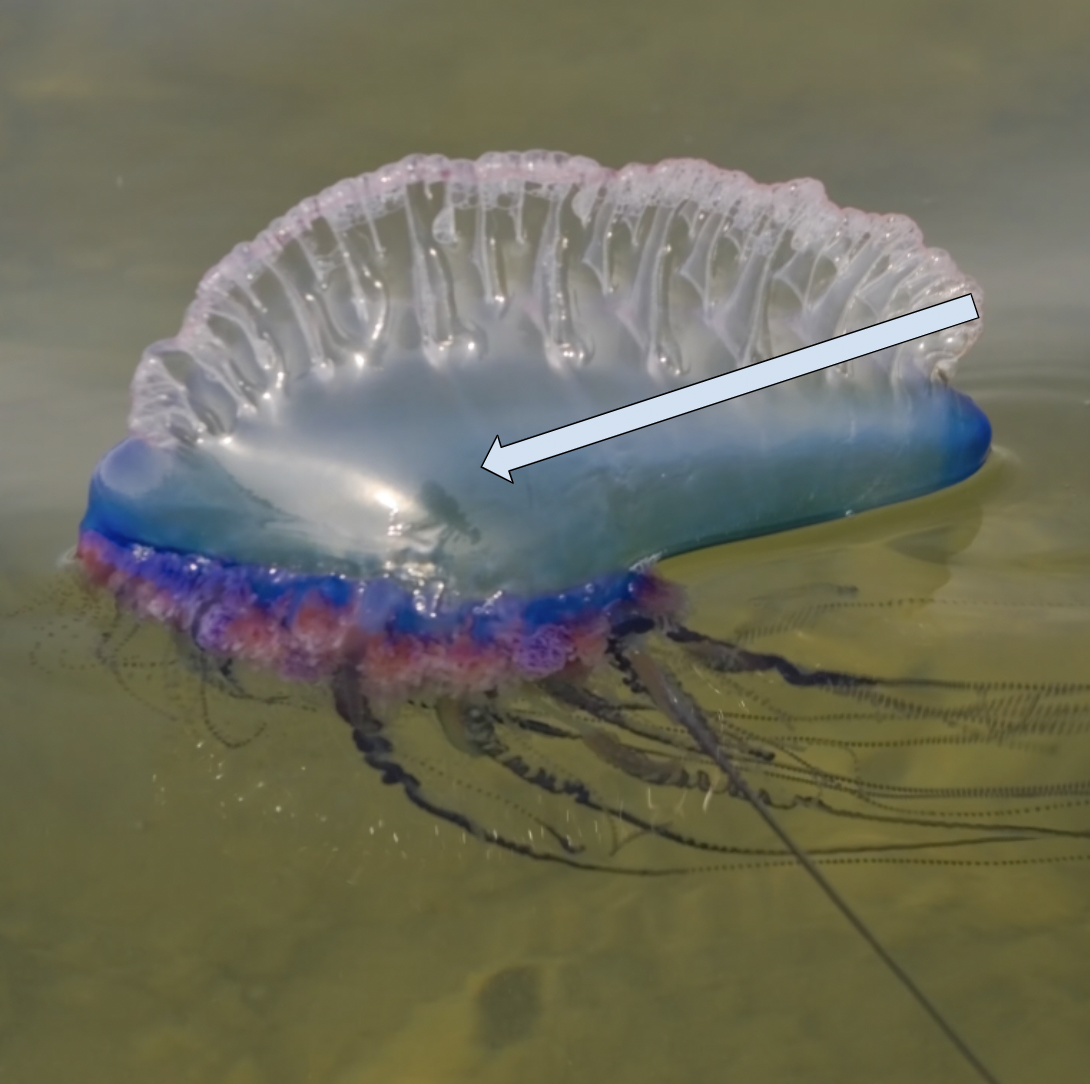
Siphonophore pneumatophore

66
New cards
1. pneumatophore
2. gonozooids
3. gastrozooids
4. dactylozooids
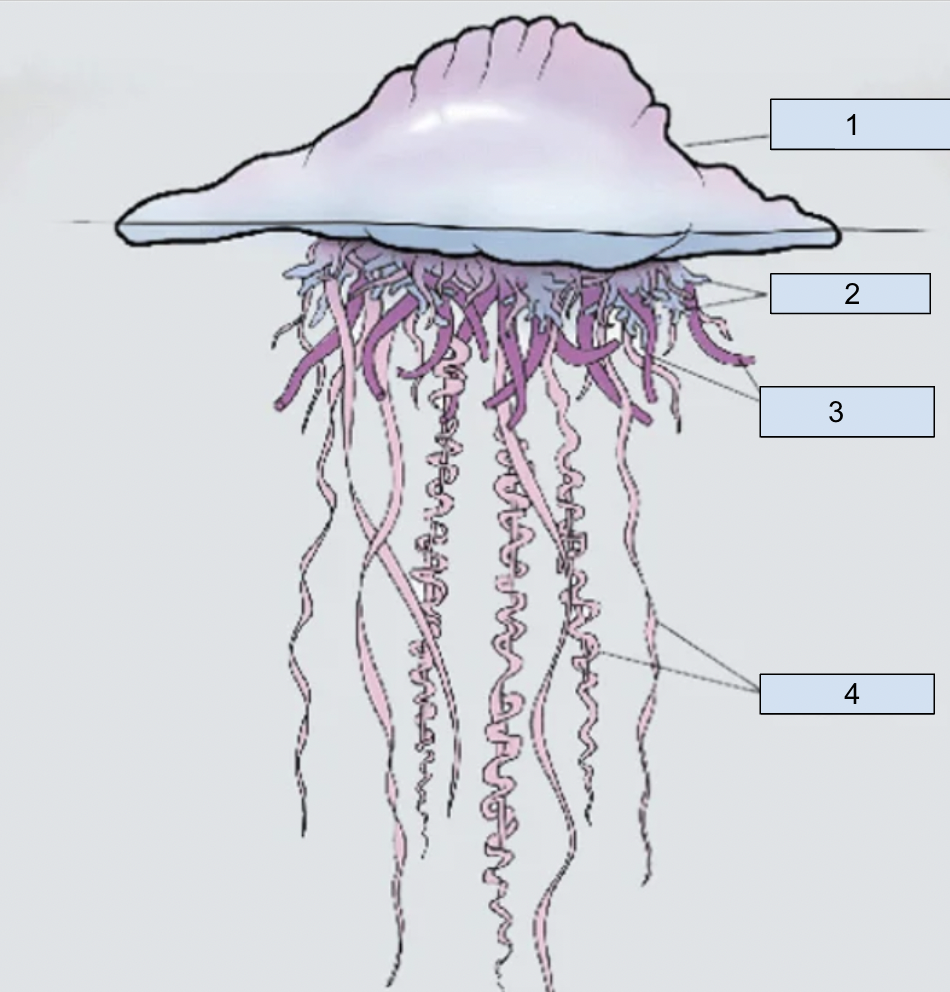
67
New cards
Taxonomy of siphonophores
Subphylum Medusozoa, Class Hydrozoa, Order Siphonophora
68
New cards
Taxonomy of Obelia
Subphylum Medusozoa, Class Hydrozoa, Order Thecata
69
New cards
Obelia hydroid colony
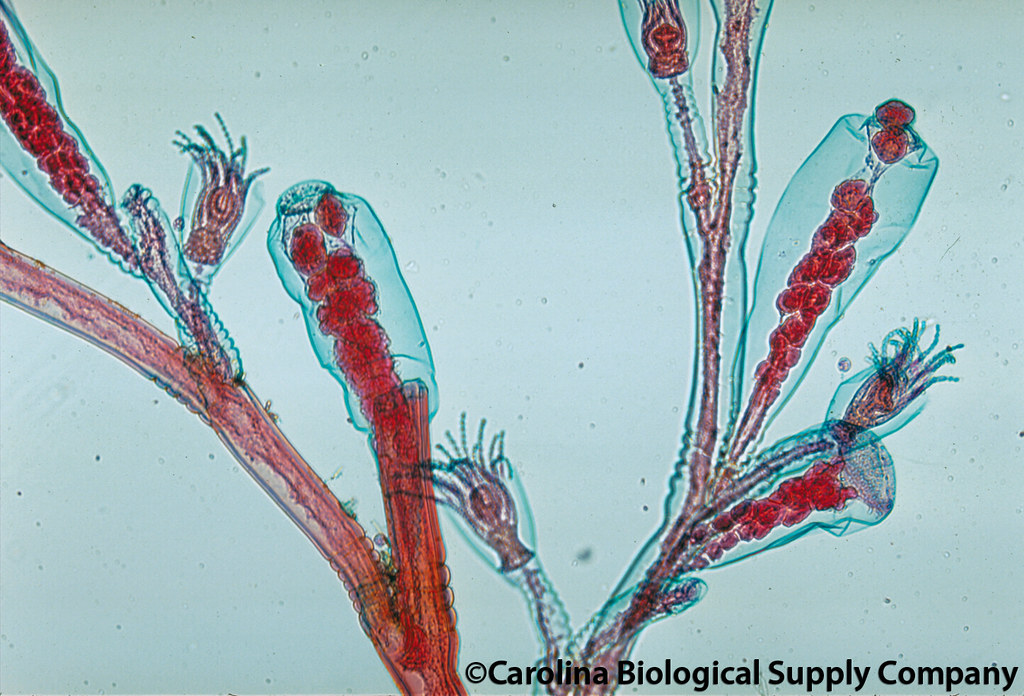
70
New cards
1. gastrozooids
2. gonozooids
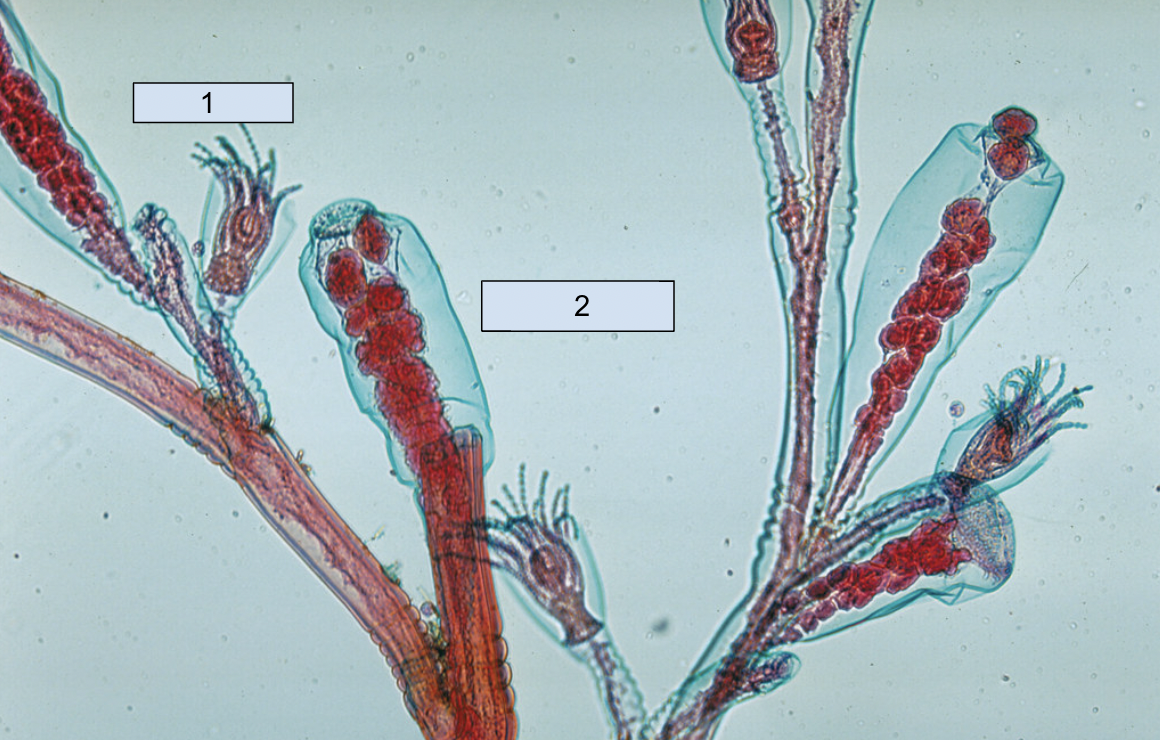
71
New cards
Taxonomy of Aurelia aurita
Subphylum Medusozoa, Class Scyphozoa
72
New cards
Aurelia aurita

73
New cards
How do scyphozoa use the mesoglea for locomotion?
Water contained between the bell and the mesoglea is expelled by muscle contraction and the jellyfish is propelled
74
New cards
Why is the mesoglea springy?
It is muscular and required for locomotion and needs to be able produce force
75
New cards
What opposes the action of the muscles that contract the bell during the powerstroke of swimming?
The pressure of water filling the shape of the bell forces it to return back to its shape
76
New cards
Does the mesoglea in the bell of a medusa constitute a hydrostatic skeleton?
The mesoglea functions as a hydrostatic skeleton
77
New cards
1. epidermis
2. mesoglea
3. gastrodermis
4. stomach
5. mouth
6. oral-aboral axis
7. manubrium
8. gonad
9. tentacle
10. subgenital pit
11. oral arm
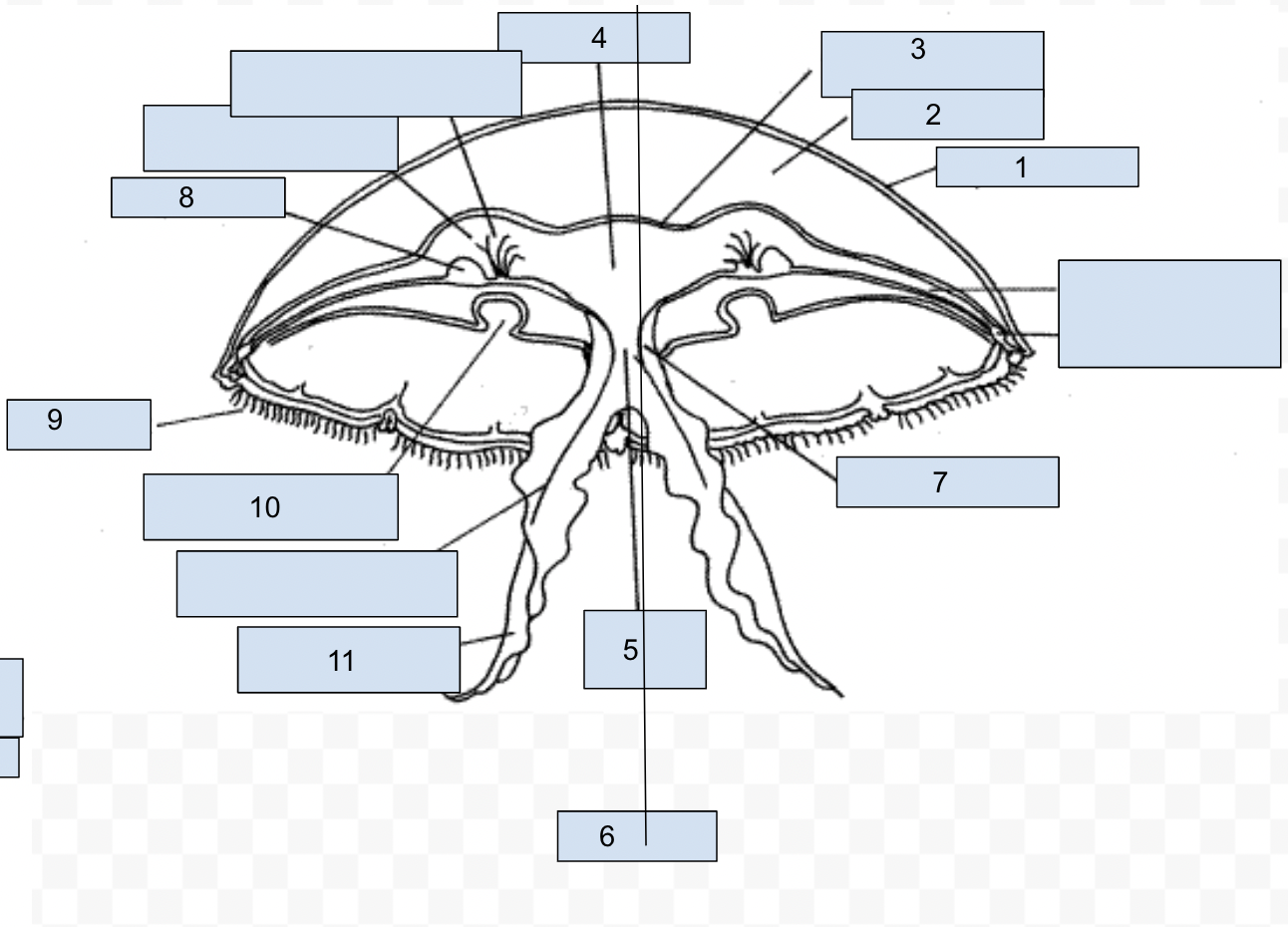
78
New cards
1. oral arms
2. perradial brachial grooves
3. mouth
4. marginal tentacles
5. rhopalium
6. gastric pouches
7. oral arms
8. ring canal
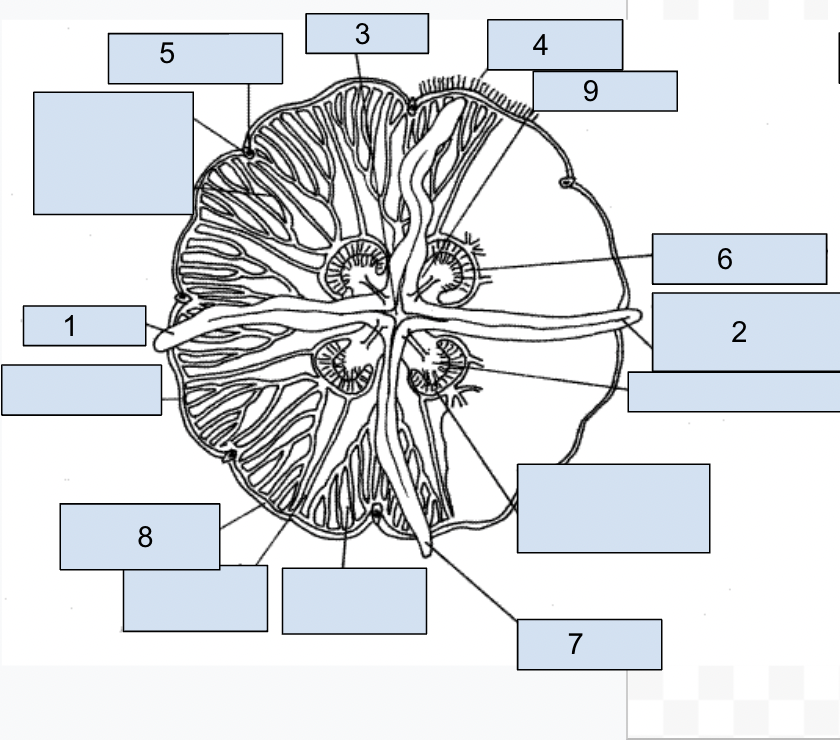
79
New cards
Where are the cnidocytes on Auralia
on the marginal tentacles
80
New cards
1. sensory lappet
2. ocellus
3. protective hood
4. statocyst
5. rhopalium lappet
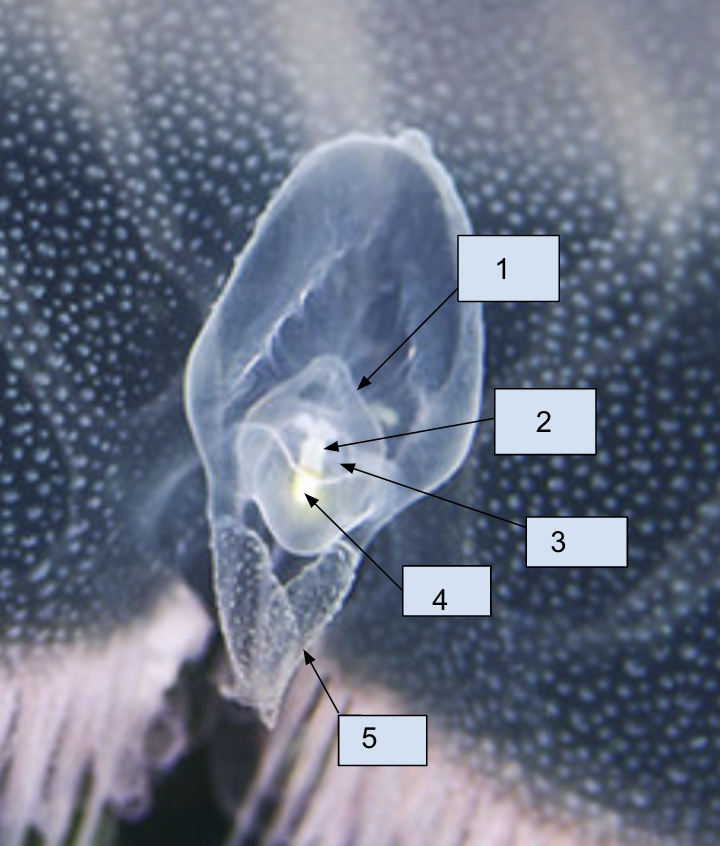
81
New cards
function of rhopalium
maintain equilibrium and permit photo reception
82
New cards
Why do scyphomedusae have a more complex system of gastric canals than hydromedusae?
They are larger and thus need a more complex system to distribute nutrients
83
New cards
nematocyst
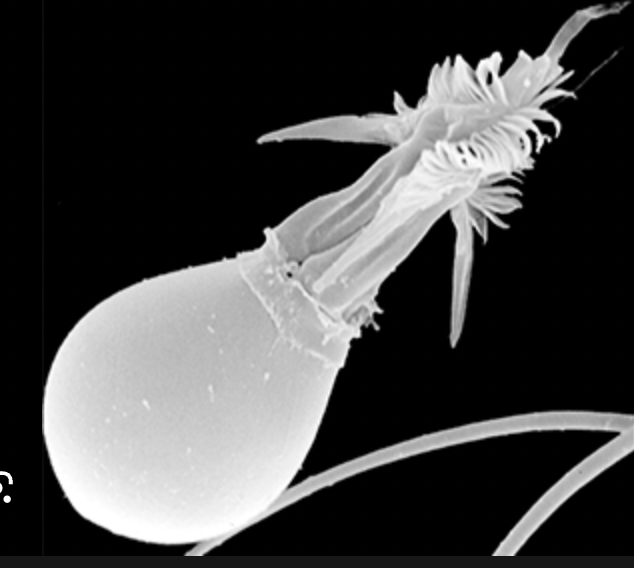
84
New cards
Aurelia ephyra
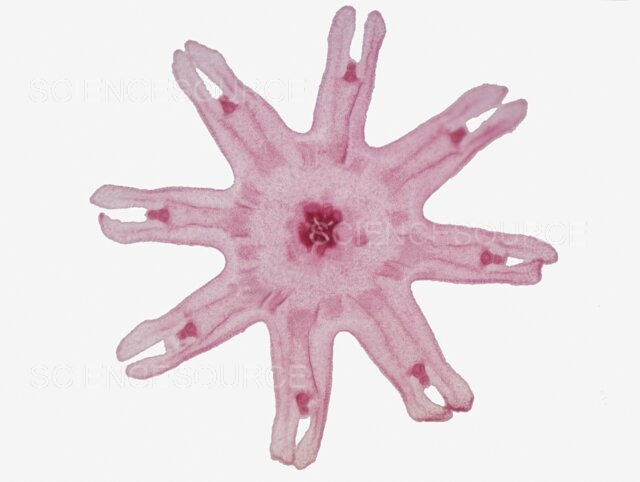
85
New cards
Aurelia scyphistoma
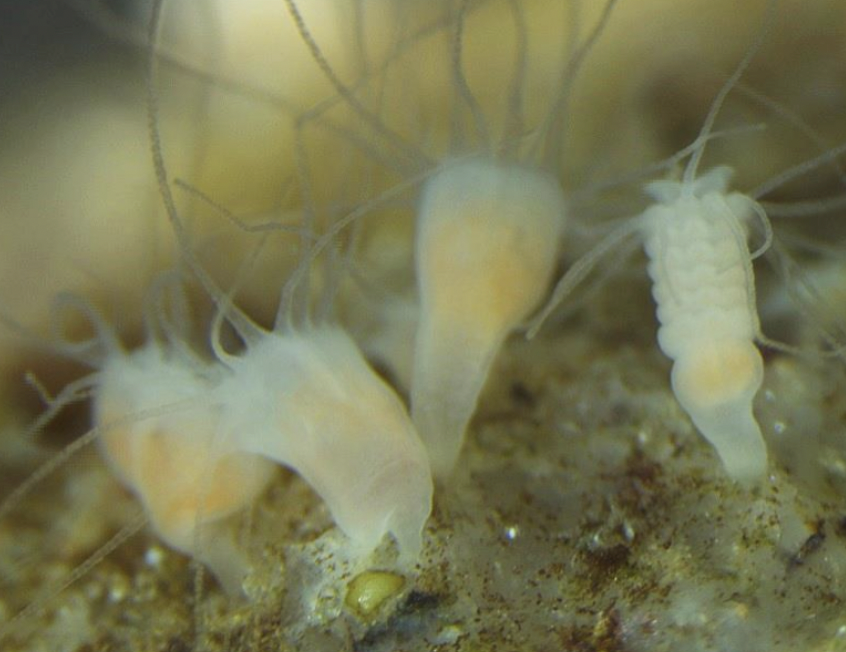

86
New cards
Aurelia scyphistoma

87
New cards
Aurelia planula larva
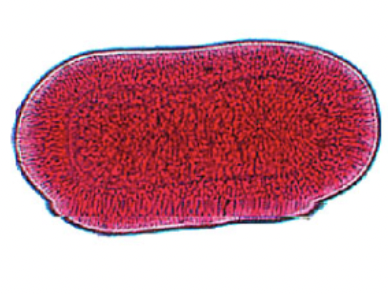
88
New cards
Gonionemus medusa
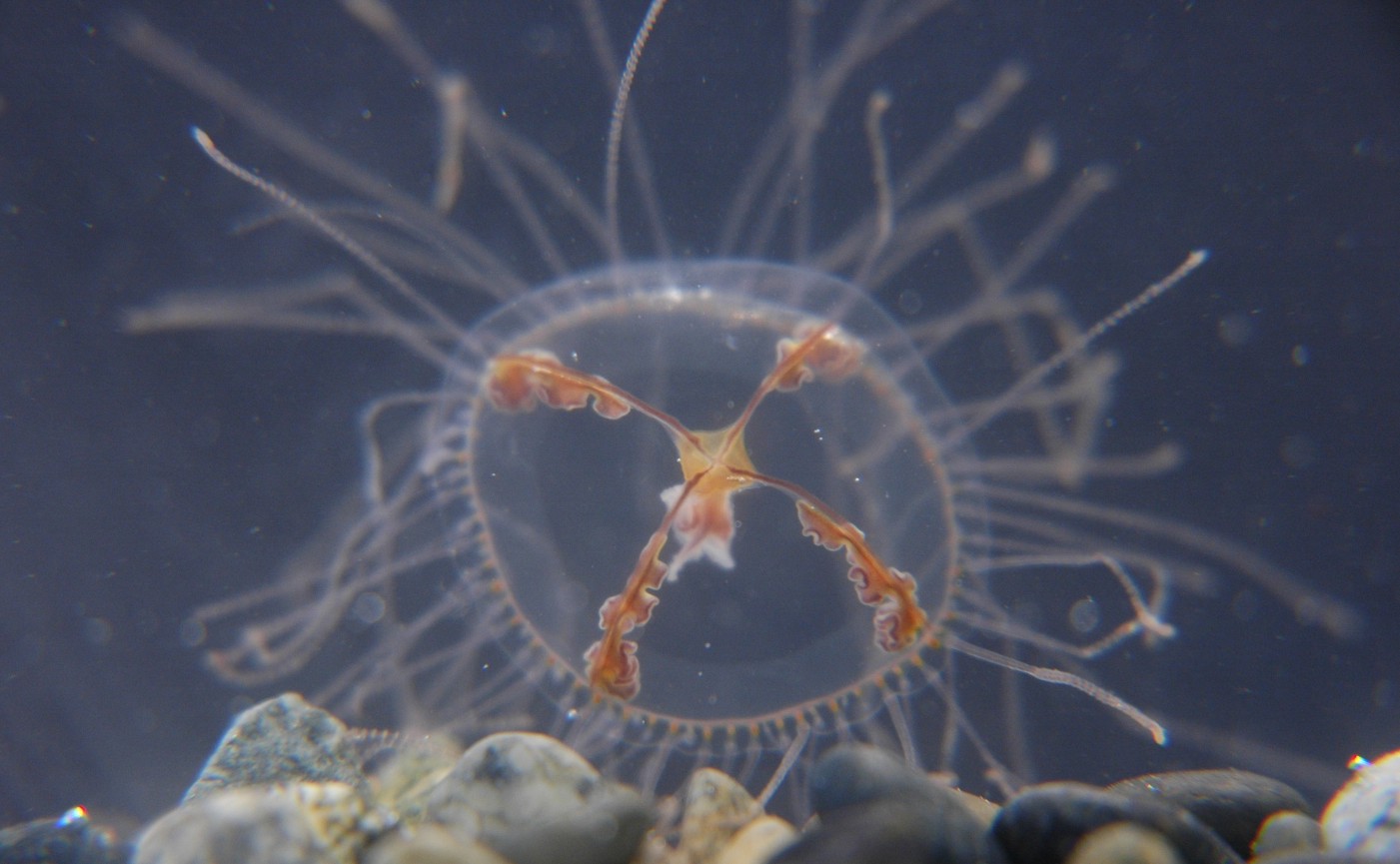

89
New cards
1. Manubrium
2. Radial canals
3. Gonads
4. Tentacles
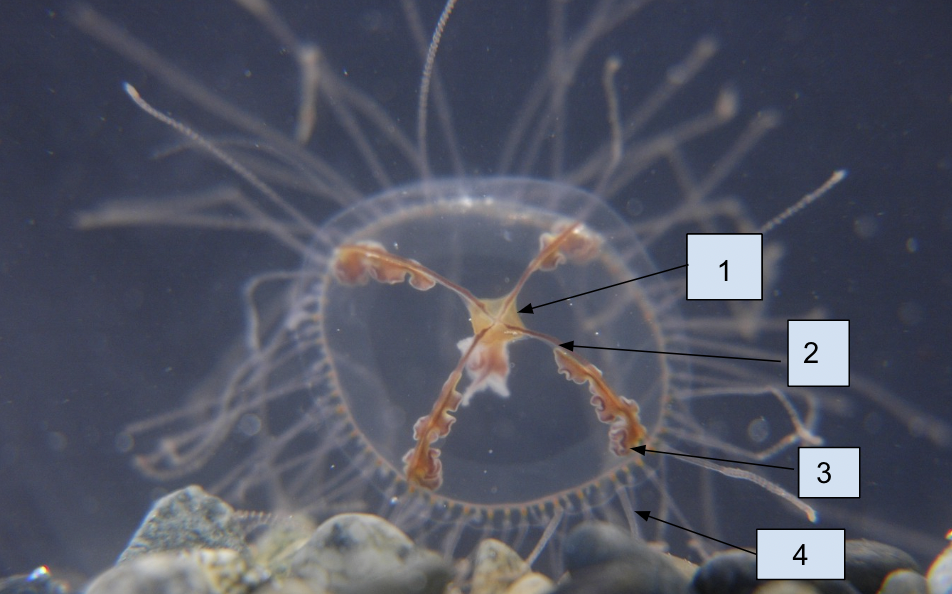
90
New cards
Taxonomy of Gonionemus medusa
Subphylum Medusa, Class Hydrozoa
91
New cards
Why are the medusae of hydrozoans so much smaller than the medusae of scyphozoans
They have simpler body structure and thus need to be smaller
92
New cards
Phylum Ctenophora taxonomy
Class Tentaculata and Class Nuda
93
New cards
Order of Mnemiopsis
Order Lobata
94
New cards
Mnemiopsis macrydi

95
New cards
1. Anal pores
2. Statocyst
3. Opening of tentacle sheath
4. Gastrovascular cavity
5. Mouth
6. Pharynx
7. Base of tentacle sheath
8. Comb
9. Tentacle
10. Tentacular plane
11. Pharyngeal plane
12. Ciliary comb
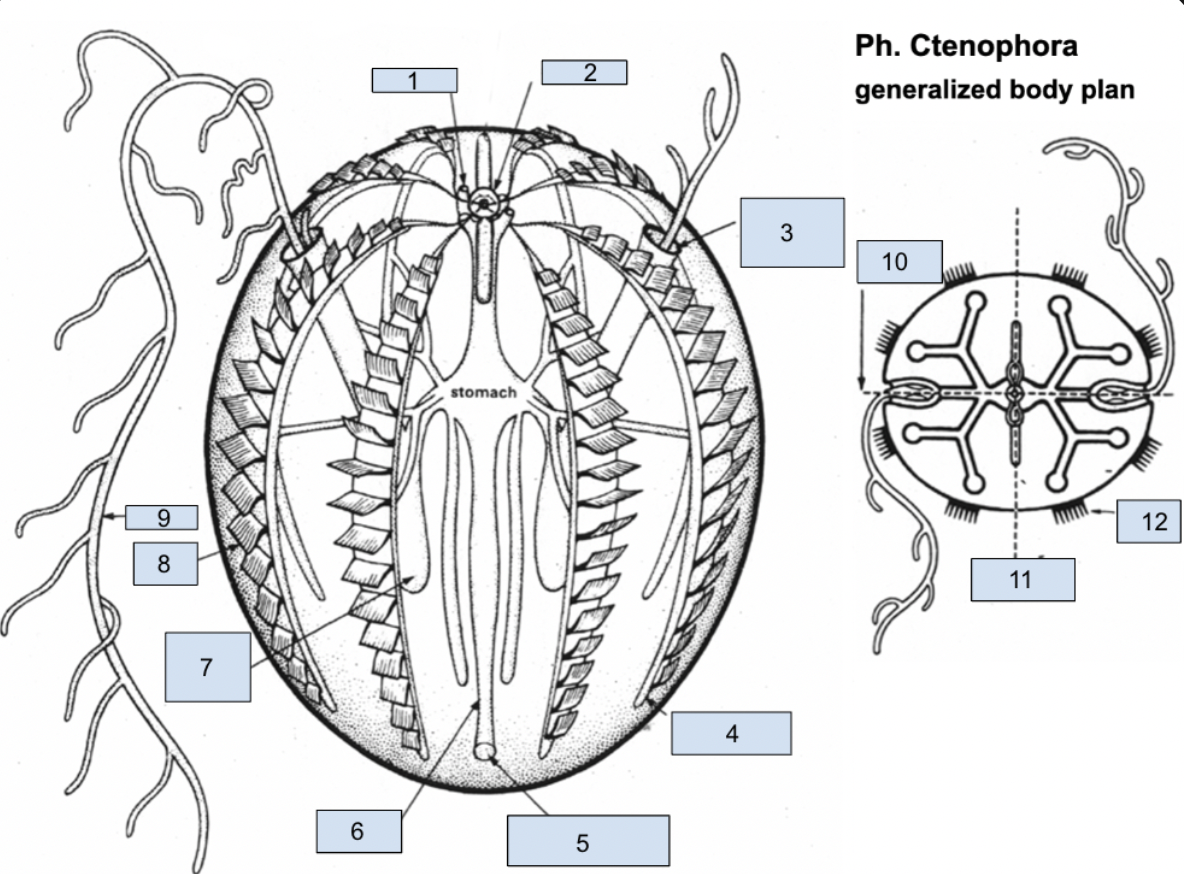
96
New cards
Locomotion of ctenophores
ciliary and muscular (for orientation and rapid escape)
97
New cards
Why do ctenophores use muscular movement to escape from predators?
it is more precise, allows them to flatten and contract
98
New cards
How could jellyfish use sensory information from ocelli to alter its visibility
Use ocelli to detect light sources and contract and flatten to create minimal visibility
99
New cards
Taxonomy of Phylum Platyhelminthes
Order Polycladida, Order Tricladida, Cohort Monogenea, Cohort Trematoda, Cohort Cestoda
100
New cards
Taxonomy of Phylum Xenacoelomorpha
Subphylum Acoelomorpha, Class Acoela