Patterns of Inheritance CH 12
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Mendelian Genetics
Study of inheritance patterns established by Gregor Mendel.
Mendel's Experimental Method
Produce true-breeding strains for each trait being studied
Cross-fertilize true breeding stains having alternate forms of trait (PP x pp)
Allowed hybrid (Pp) offspring to self-fertilize for several generations and counted number of offspring showing each trait form
Monohybrid Cross
Cross used to study only two variations of a single trait
One dominant, the other recessive
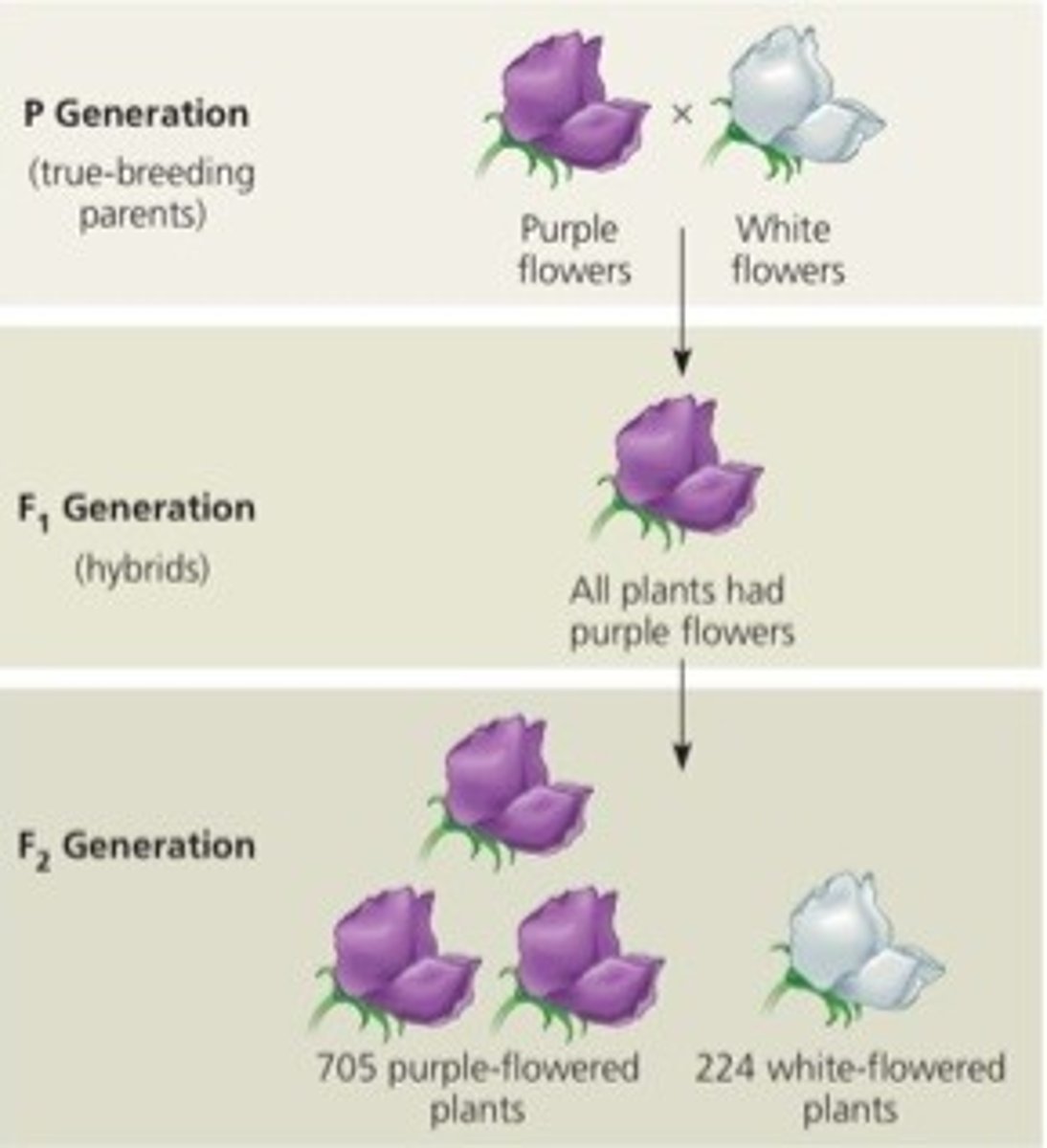
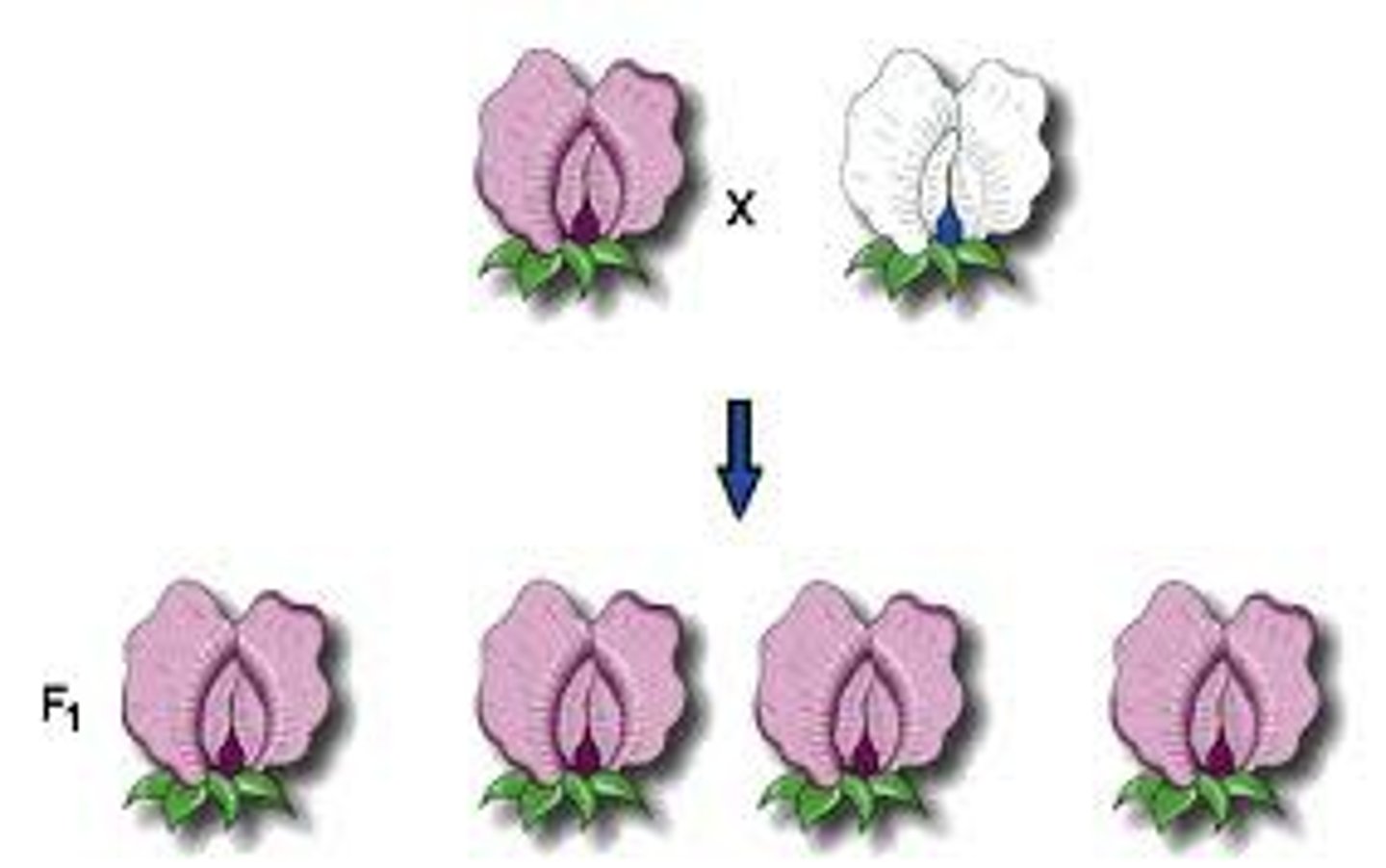
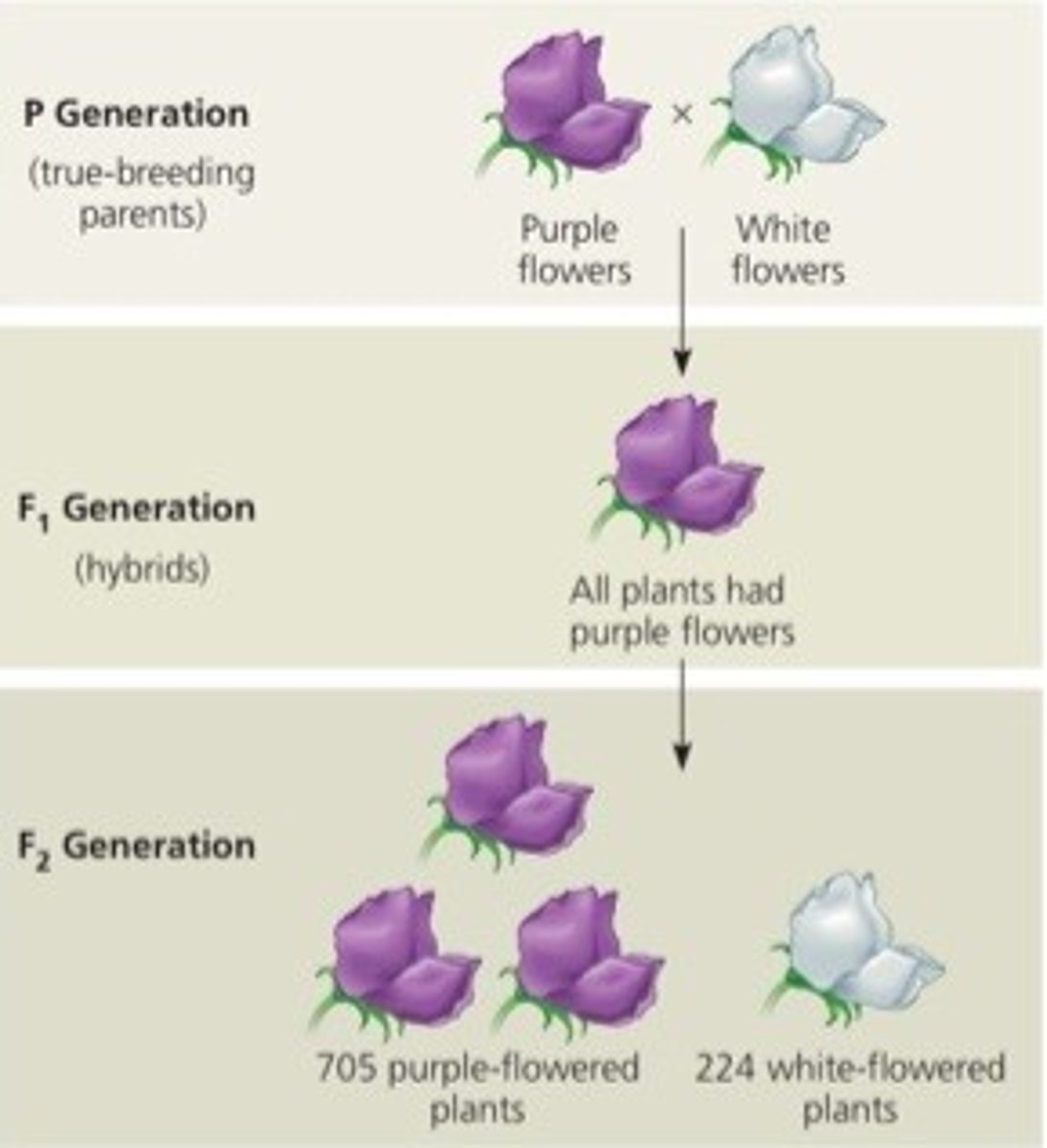
F1 generation
Offspring produced from cross b/w two true-breeding strains
all offspring resemble/expressed same parent (dominant trait)
No intermediate characteristics = no blending inheritance
F2 generation
Produced from self-fertilization of F1 plants
Dominant masked other expressions in F1, but in F2 recessive trait reappeared
Counted in 3:1 ration,
really 1 (PP): 2(Pp): 1(pp)
1:2:1 ratio of Monohybrids
F2 plants
¾ with dominant form (2 hetero, 1 homo)
¼ recessive form (homo)
Mendel’s Conclusion About Traits
Traits are intact and discrete (don’t mix)
Each pair of traits has a dominant and recessive form
Pairs of alternative traits examined were segregated among offspring of particular cross
F2 generation ratio of ¾ dominant, 1.4 recessive
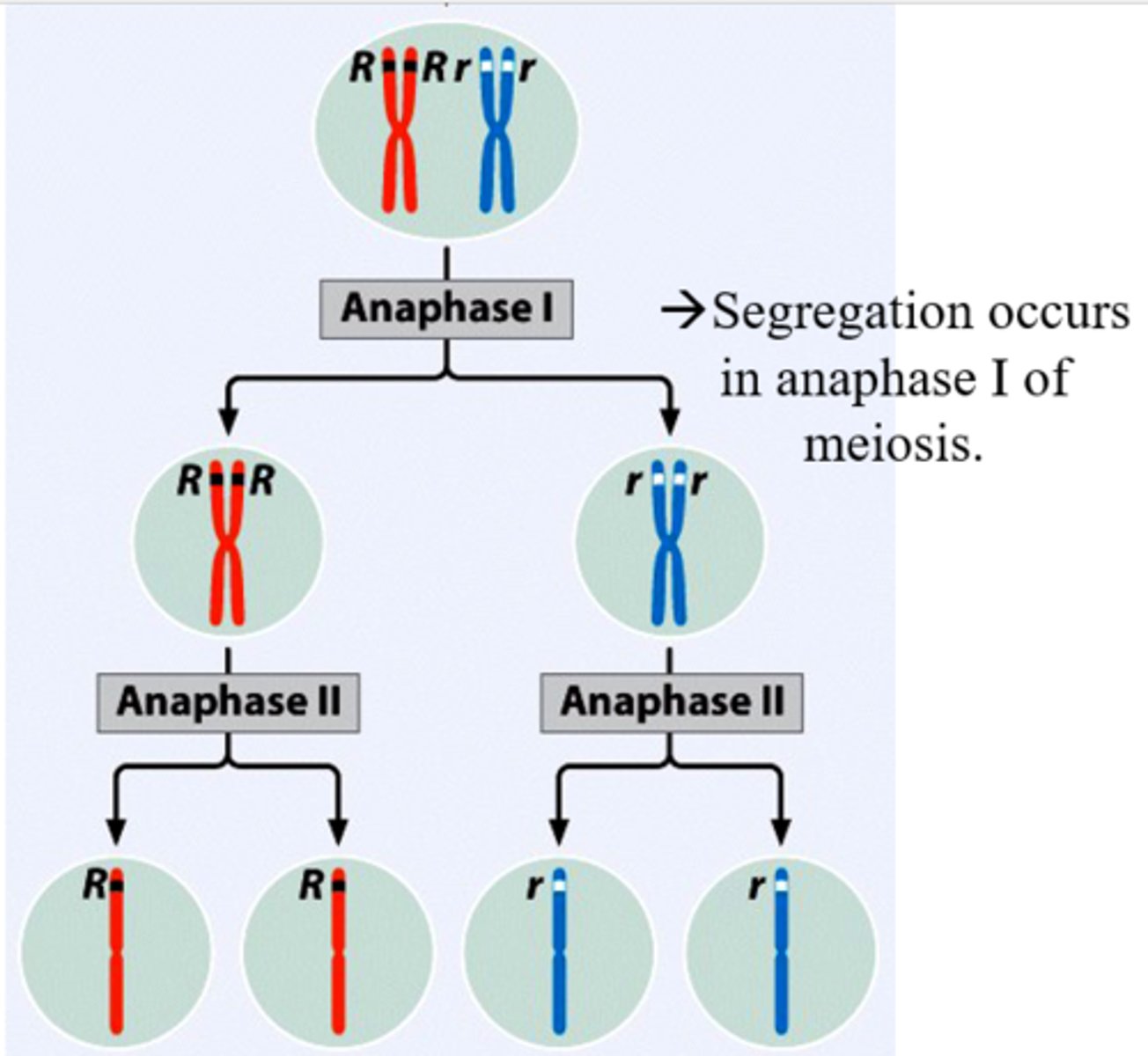
Principle of segregation
Two alleles from a gene segregate/separate during formation of gametes (parent has Aa→ A and a separate and go to separate gametes)
Then alleles will combine randomly with other alleles from other parent
Physical basis for allele segregation is movement of chromosomes during meiosis (crossover) (after Mendel’s time)
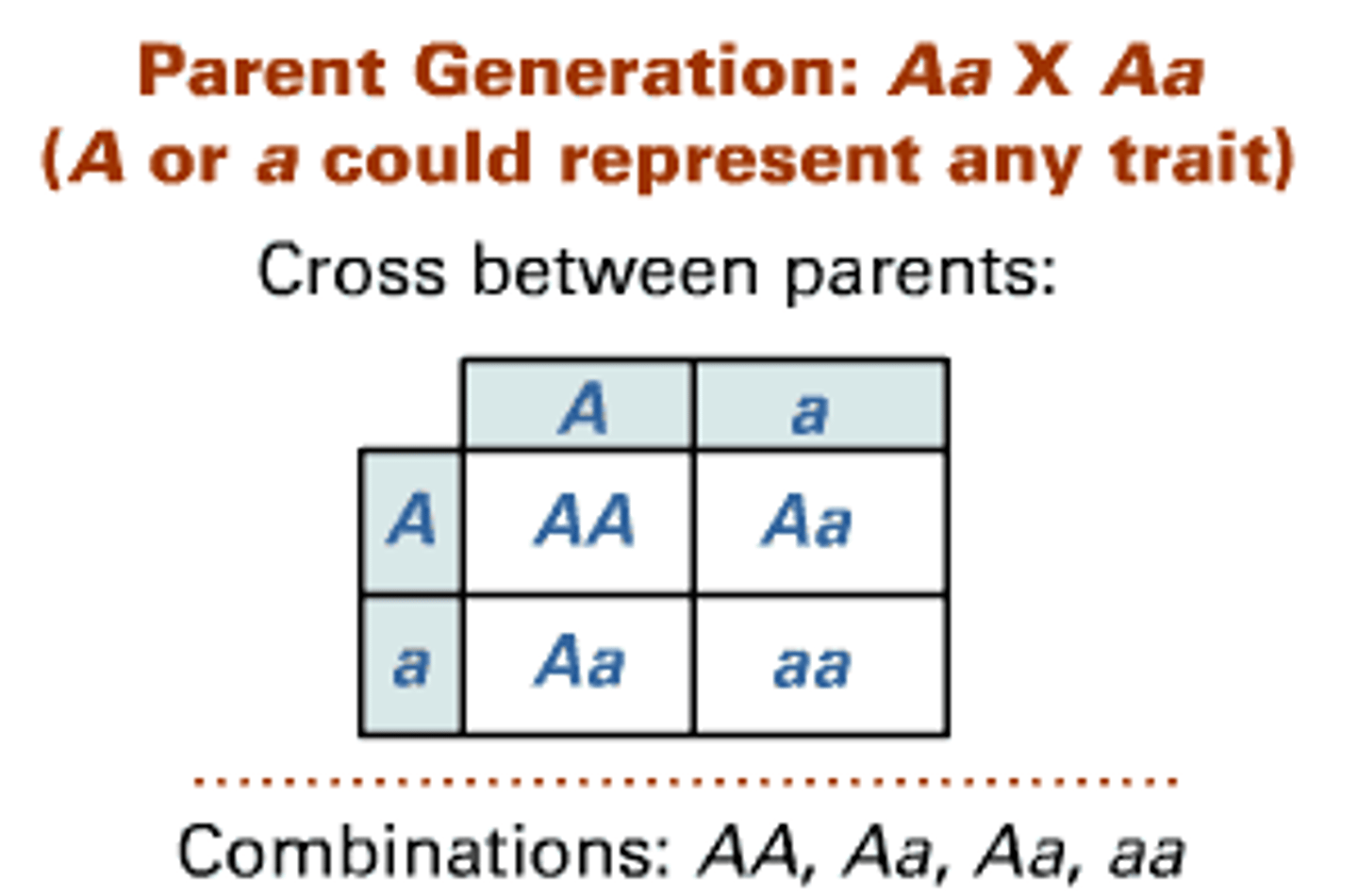
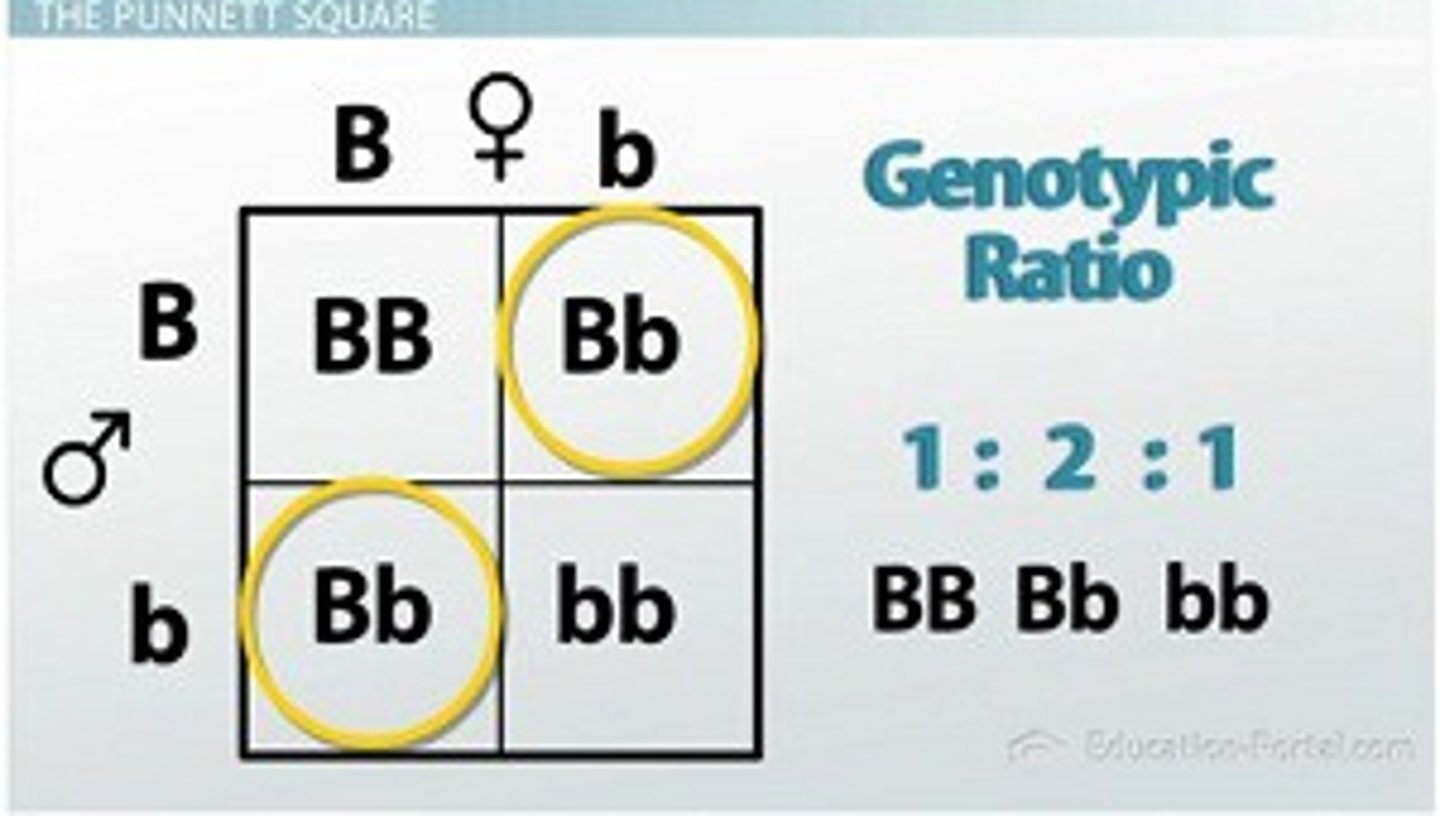
Punnett Square for Mendel’s Cross
F1 are all purple heterozygotes (Pp)
F2 offspring produce
PP homozygous dominant (purple)
Pp heterozygous (purple)
pp homozygous recessive (white)
Dihybrid Cross
Study of two variations of two traits in a single cross
Mendel produced true-breeding lines each with two traits (RRYY x rryy)
F1 (RrYy) all show dominant phenotype
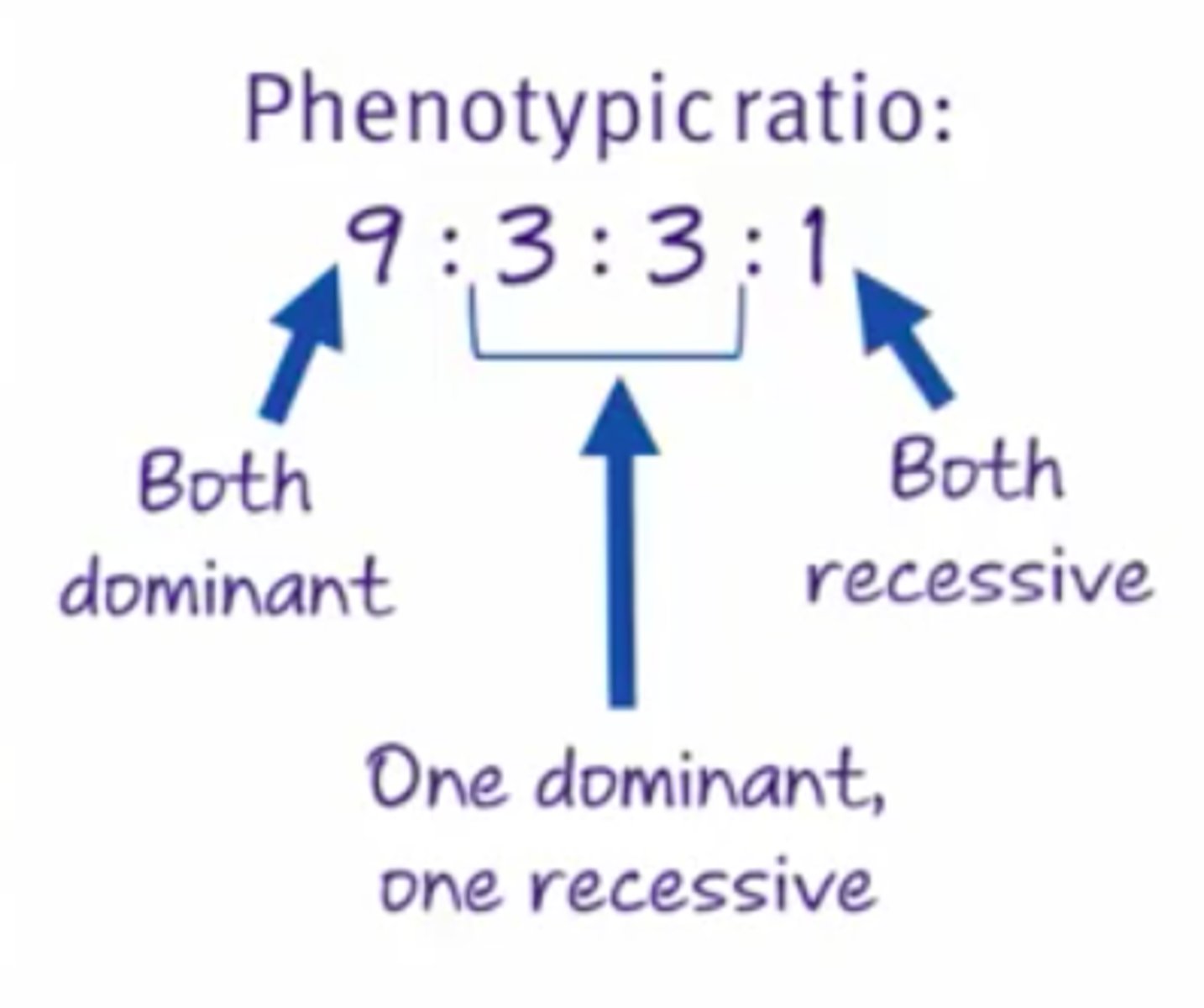
F2 9:3:3:1 ratio
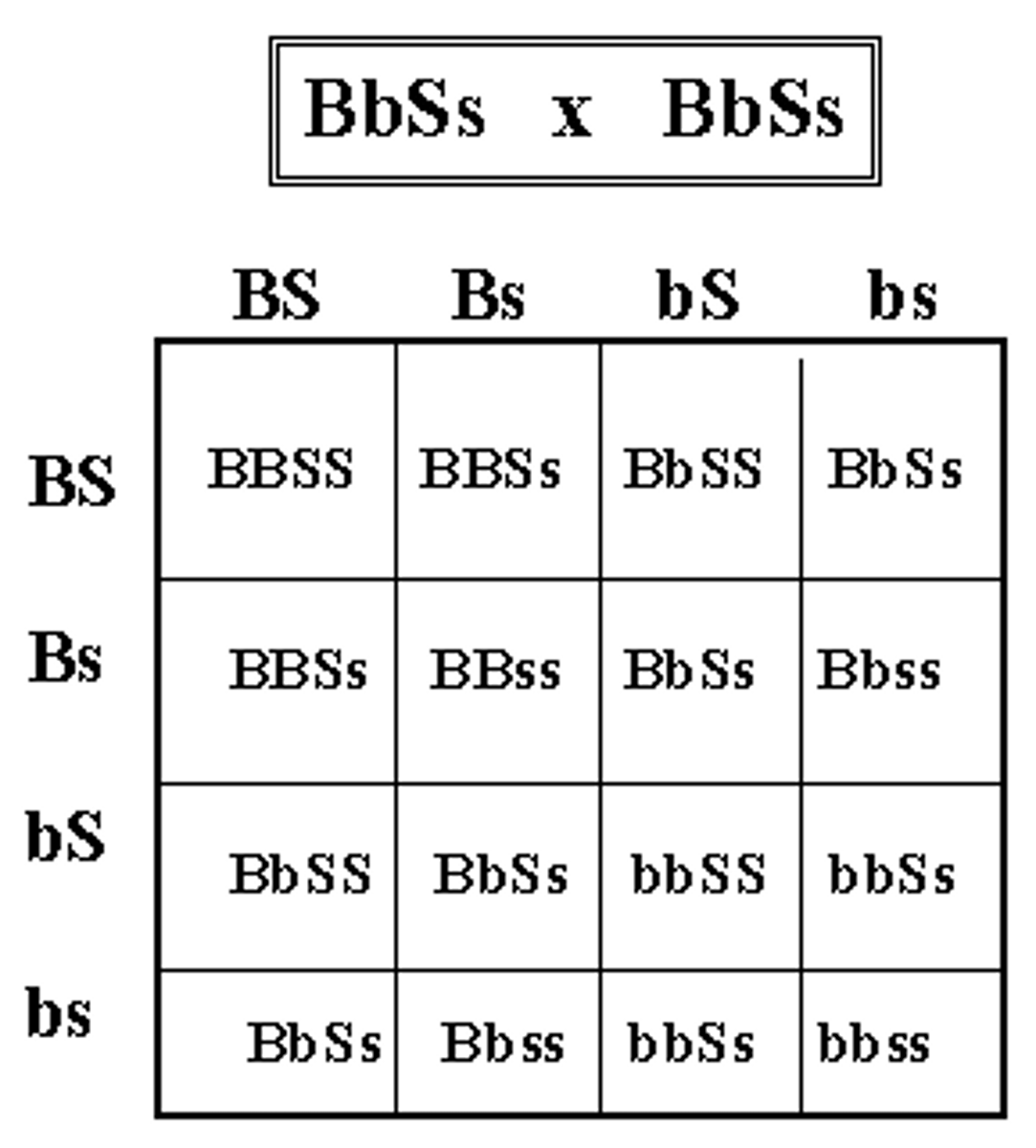
9:3:3:1 ratio of Dihybrids
9(R_Y_), 3(R_yy), 3(rrY_), 1(rryy)
R: Round, r: wrinkled, Y: yellow, y: green
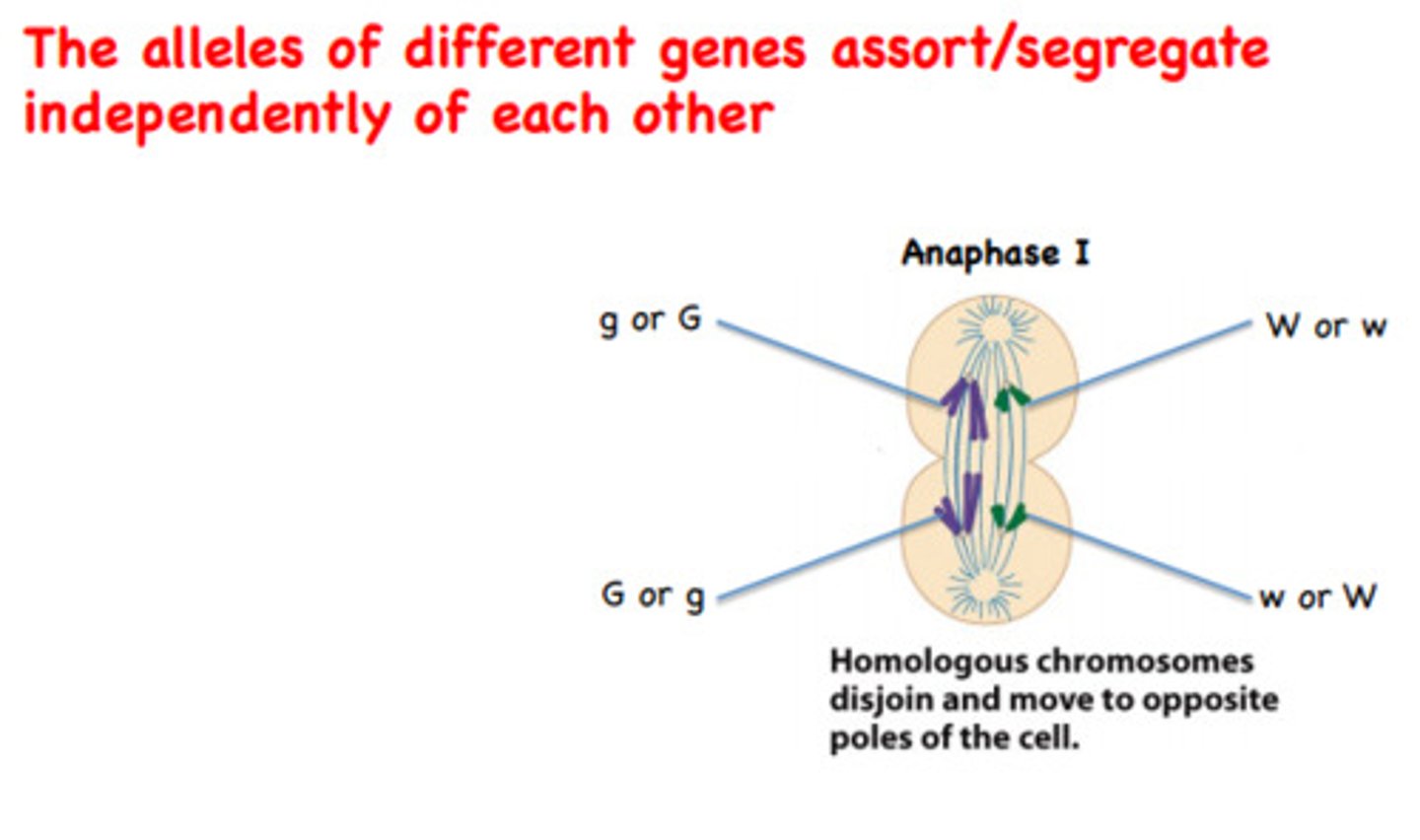
Principle of Independent assortment
Segregation of different allele pairs is independent (seed color is independent of seed shape)
Independent alignment of different homolog pairs during metaphase = independent segregation of allele pairs
(after crossing over, allele pair randomly in meta I)
Testcross
Used to determine genotypes of unknown phenotype
Cross unknown with homozygous recessive (pp)
Phenotypic ratio among offspring are different depending on genotype of unknown ar different (determine unknown)
Probablity of Monohybrid
Rule of Addition: probability of two mutually exclusive events is sum of their individual probabilities
Pp x Pp; probability of Pp production
Pp ¼ + pP ¼ = ½ Pp
Rule of Multiplication: Probability of two independent events is the product of individual probabilities
Pp x Pp; probability of pp
Prob from father (1/2) x probe from mother (1/2)
½ x ½ = ¼
Dihybrid probablities
Based on Monohybrid probabilities; dihybrid is equivalent to two independent monohybrid cross
Probability of 1 gene (rr : ¼ )
Probability of 2 gene (yy: ¼ )
Probability of both genes together ( ¼ x ¼ = 1/16)
Dominant Trait
Visible trait in F1, covers up recessive trait when present (AA)
Recessive Trait
Alternative trait in F1, only expressed in F2, must be homozygous to be expressed (aa)
Phenotypic Ratio
Both monohybrid and dihybrid; 3:1 (dominant to recessive)
Genotypic Ratio
Monohybrid; 1:3:1 (Aa, 2Aa, aa)
Dihybrid; 9:3:3:1 (9R_Y_, 3R_yy, 3rrY_, rryy)
Allele
alternative forms of the gene (recessive, dominant, or multiple like ABO)
Homozygous
two of the same allele
Heterozygous
different alleles
Genotype
individual’s complete set of alleles
Phenotype
individual’s physical appearance (based on genotype)
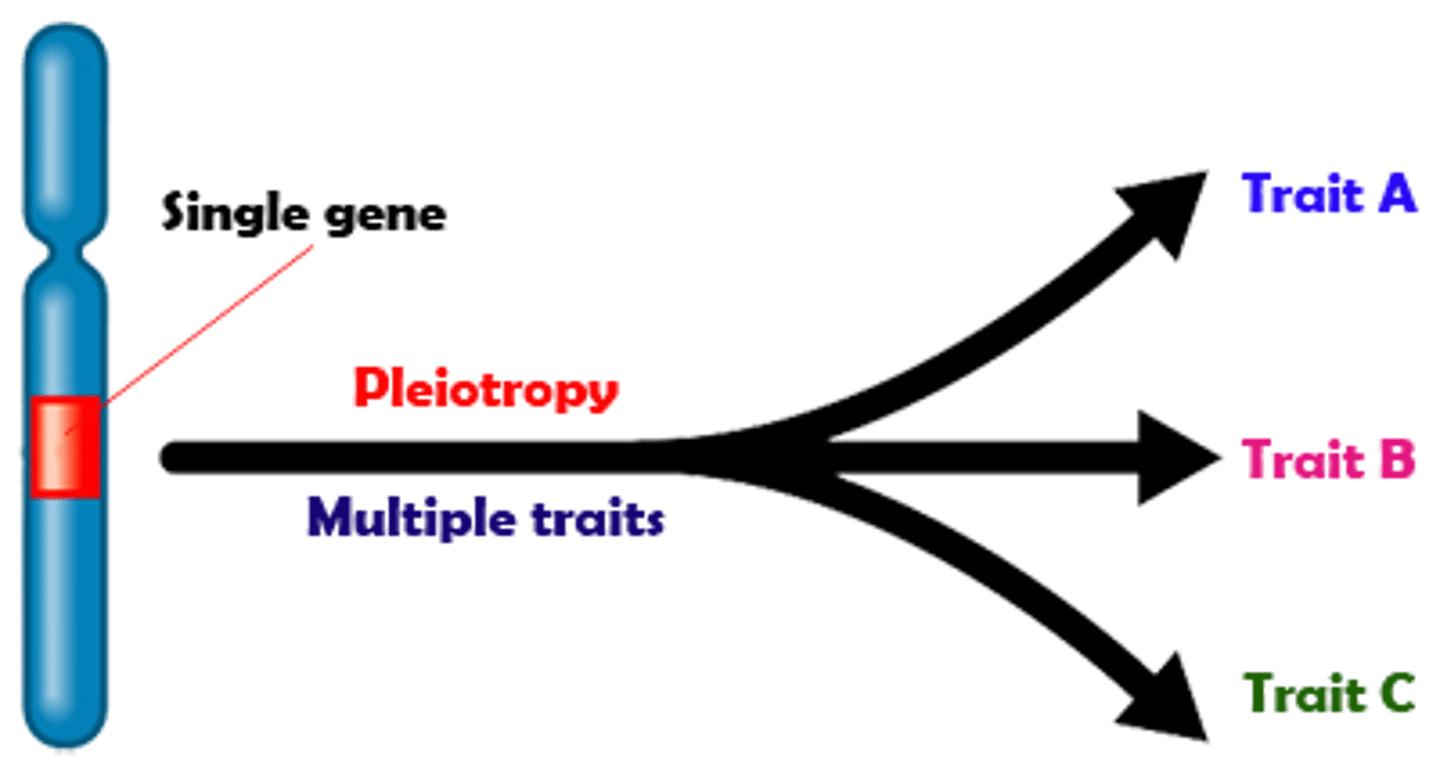
Pleiotropy (extension)
allele that has more than one effect on the phenotype
difficult to predict b/c a gene that affects one trait often performs other unknow functions
(ex. sickle cell anemia; multiple symptoms track back to one defective allele)
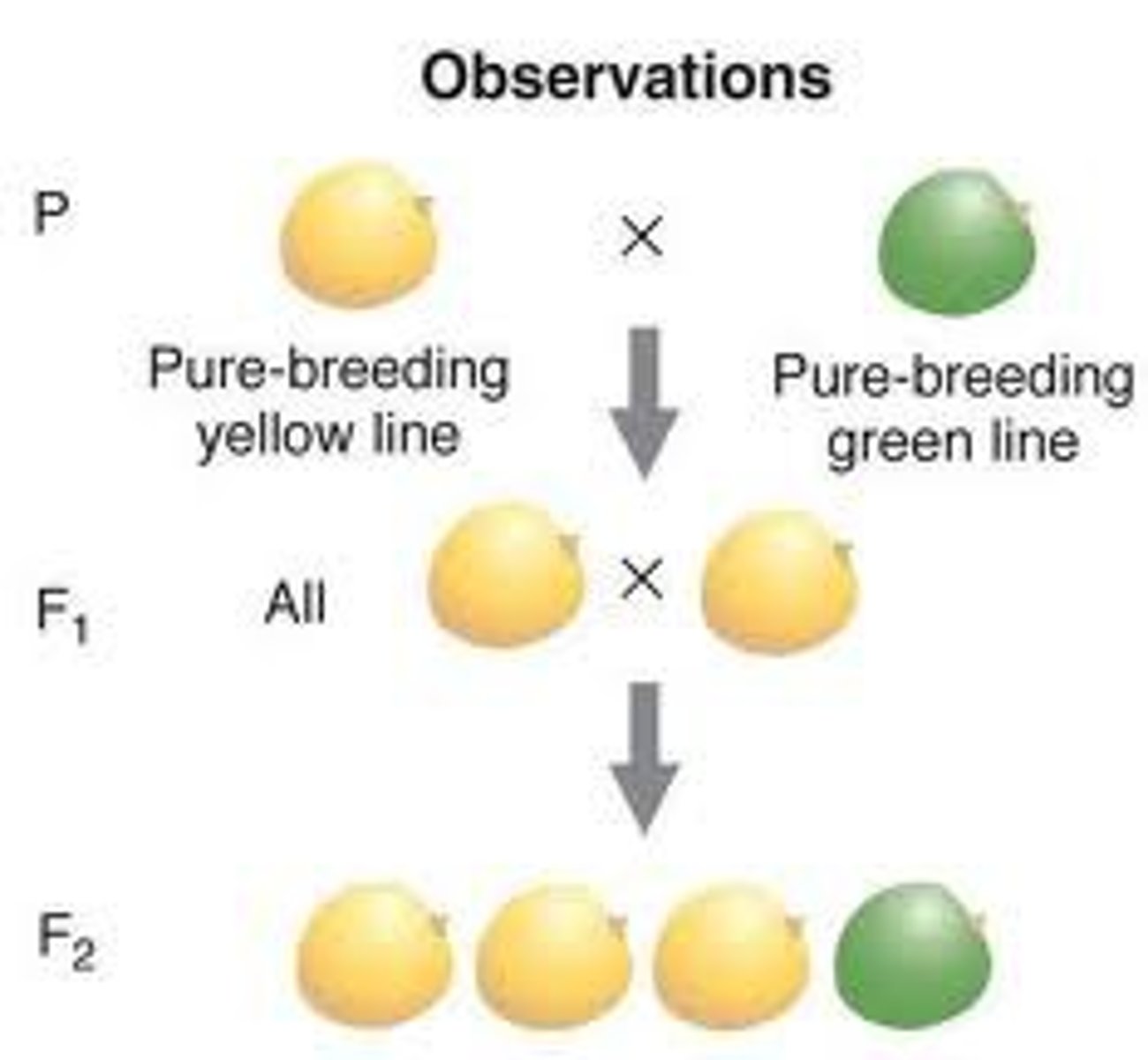
Why where pea plants used by Mendel?
Could produce hybrids/ many varieties available
small plants and easy to grow
Can self-fertilize or cross-fertilize
True-breeding Parent
Produces one type of gamete consistently; homozygous dominant or recessive
Homozygous Dominant
Genotype with two dominant alleles (PP).

Homozygous Recessive
Genotype with two recessive alleles (pp).

Multiple Alleles (extension)
more than two alleles for a gene in a population (usually the case for genes in outbreeding populations)
(ex. ABO blood types in humans)
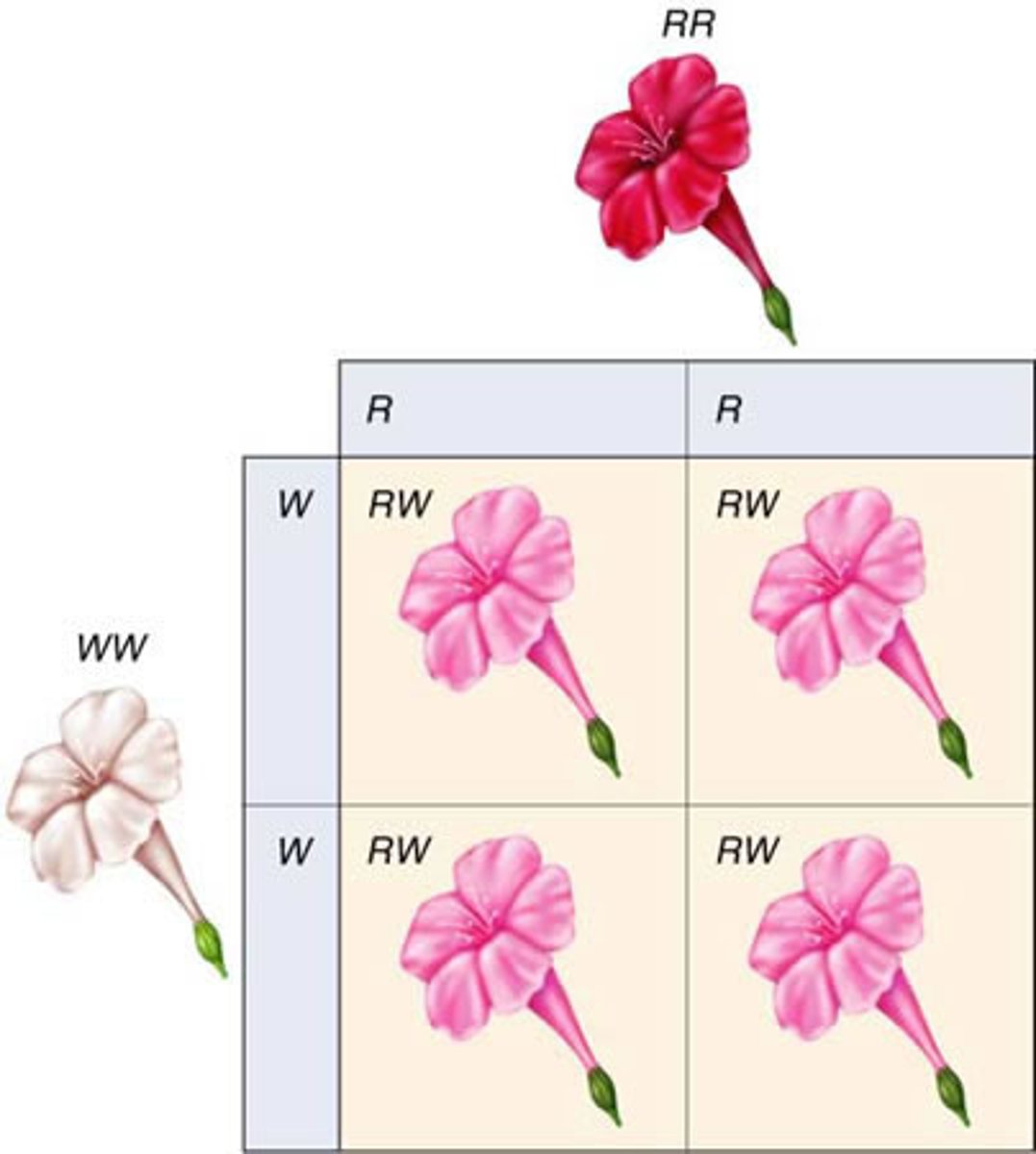
Incomplete Dominance (extension)
Heterozygote shows intermediate phenotype.
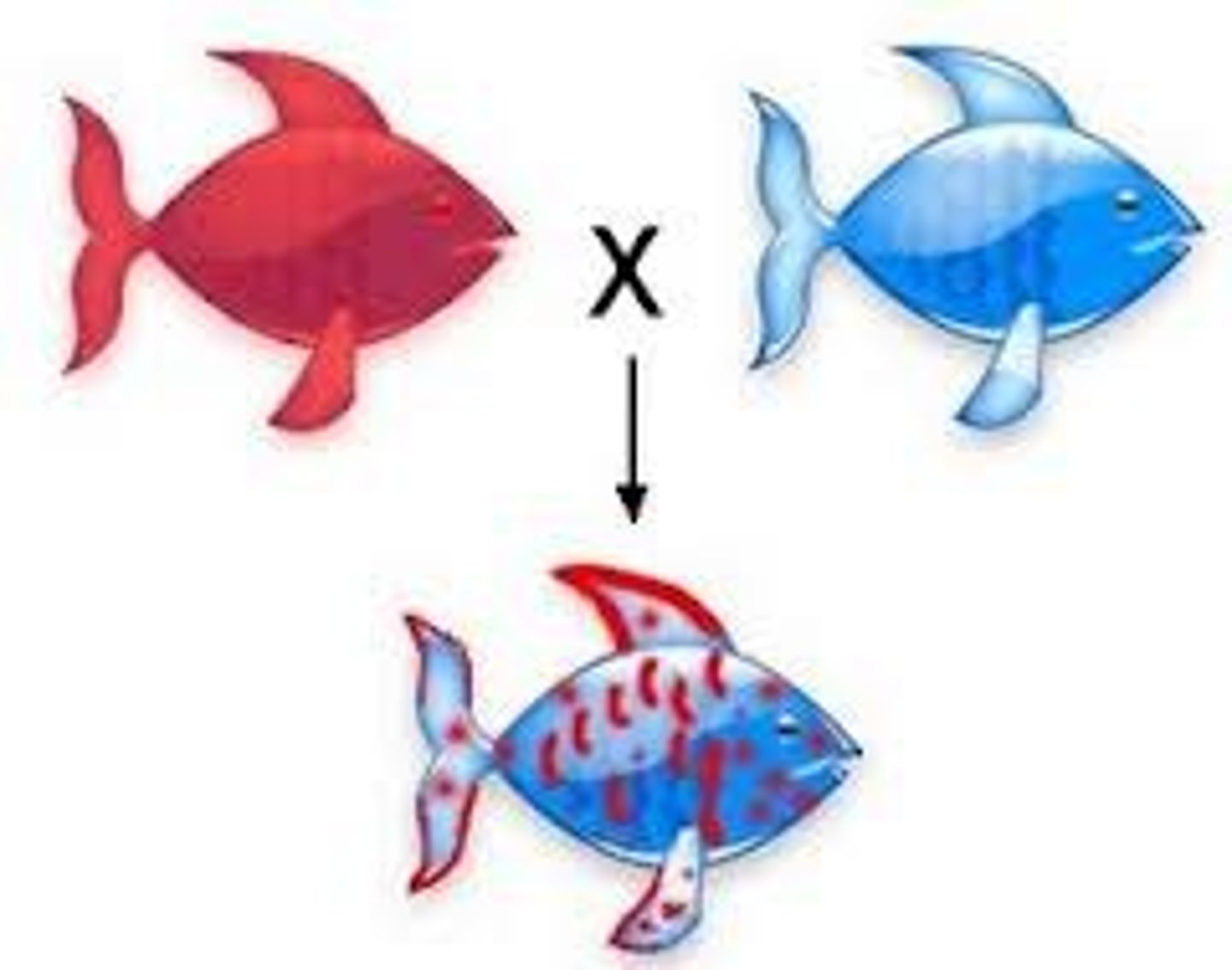
Codominance (extension)
Both alleles expressed equally in phenotype.
Epistasis (extension)
Action of one gene obscures/masks effects of another gene
(ex. color of Labrador retrievers; controlled by two genes [brown and extension], interaction b/w brown and extension result in three coats not four)
![<p>Action of one gene obscures/masks effects of another gene</p><p>(ex. color of Labrador retrievers; controlled by two genes [brown and extension], interaction b/w brown and extension result in three coats not four)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/320507d3-f081-403d-82db-b8cc66b975c0.jpg)
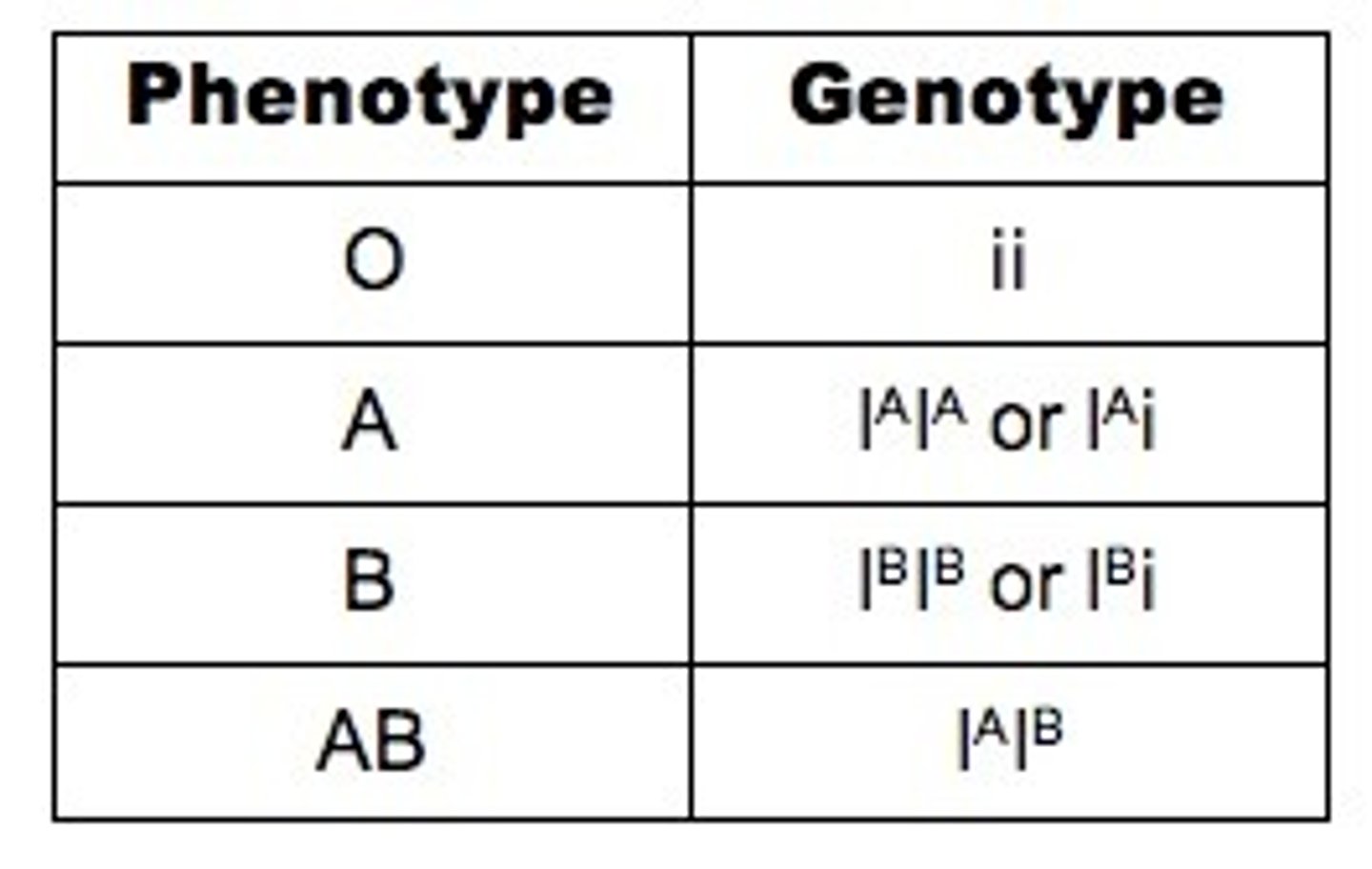
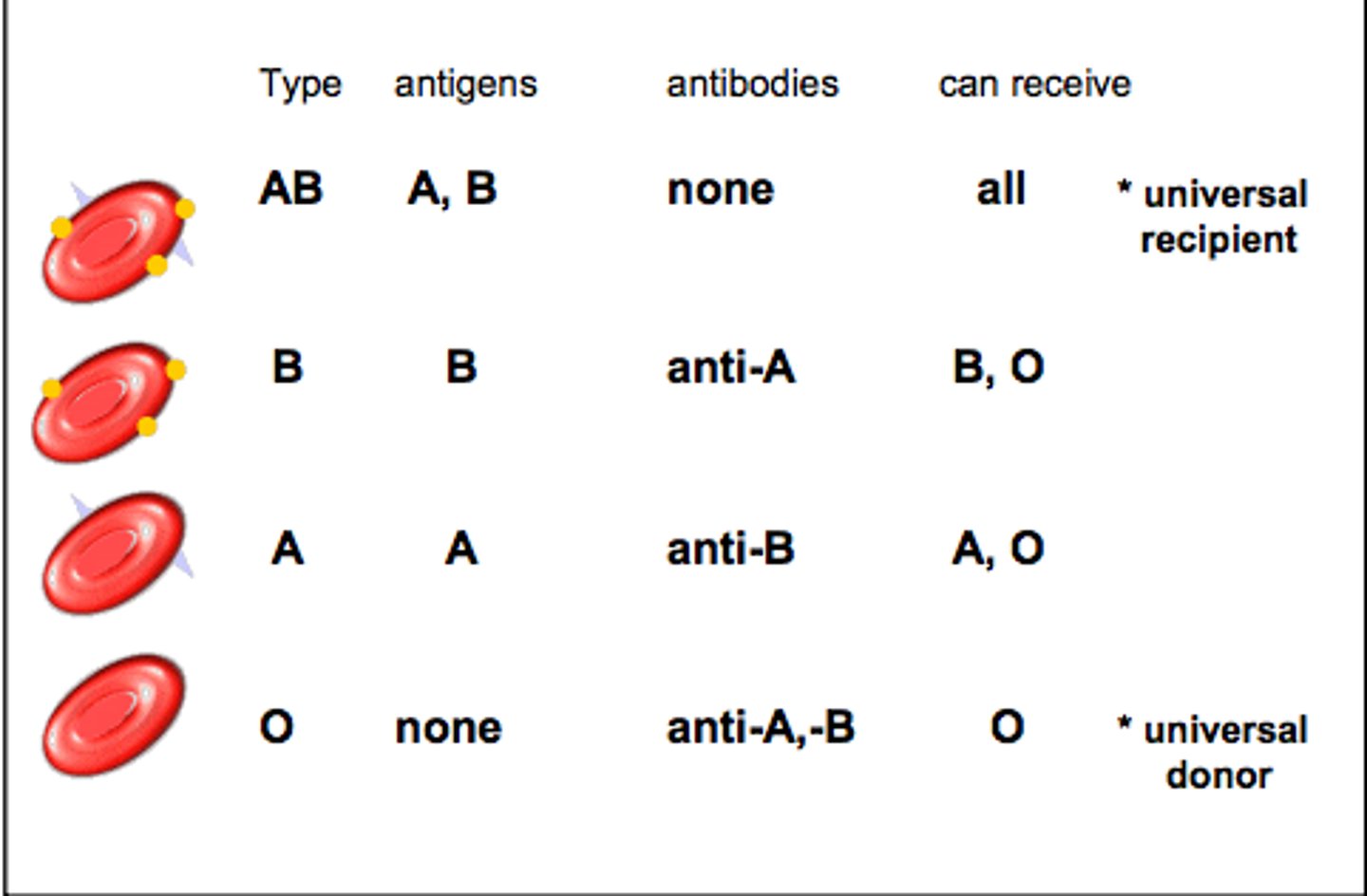
ABO Blood Group
Example of multiple alleles and codominance. (A & B are dominate, and can be codominant together, O is recessive)
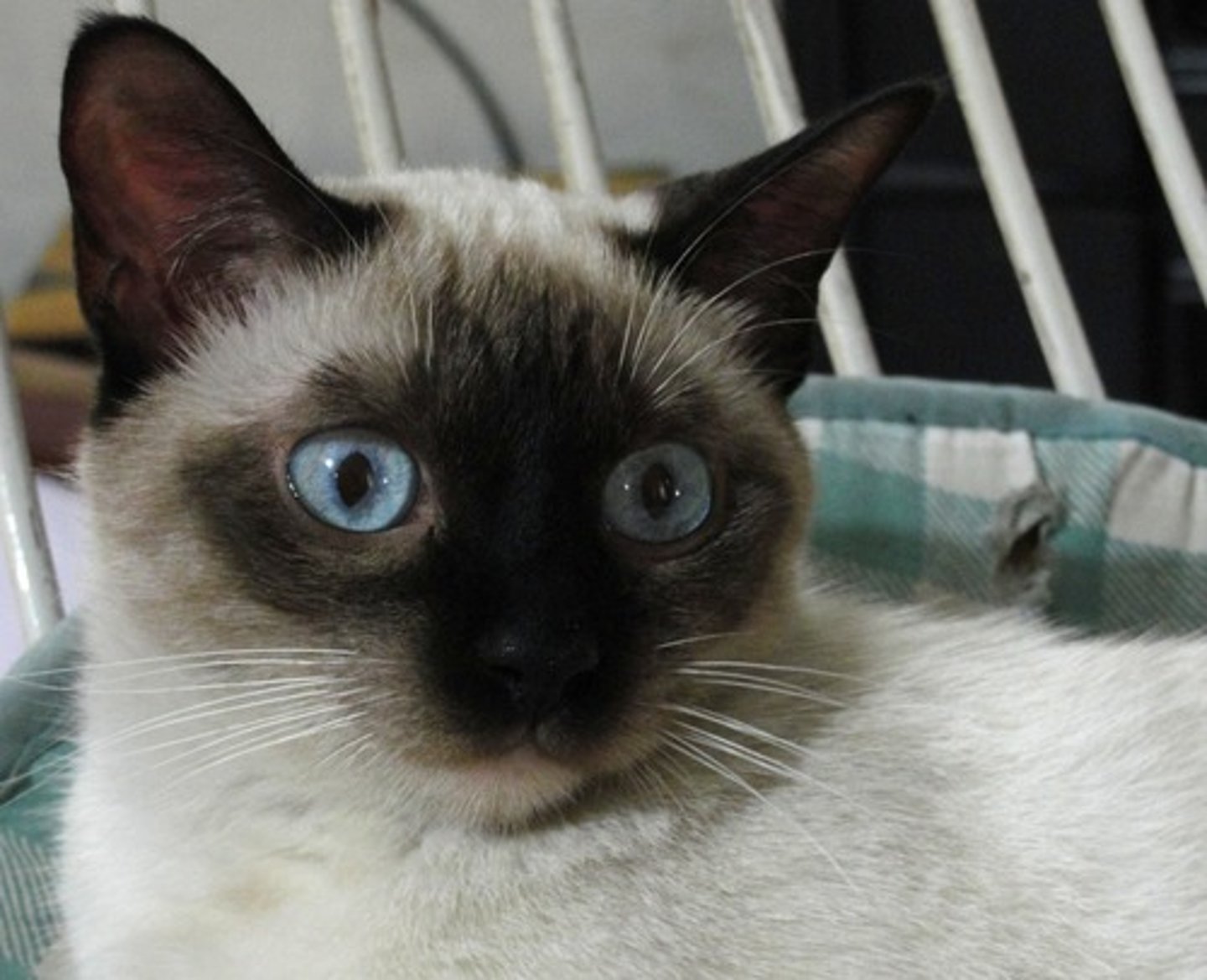
Environmental Influence (extension)
Environment alters phenotypes from the same genotype.
Phenotypes plasticity: different phenotypes form same genotypes due to environmental conditions
(ex. siamese cat coats over 30oC)

Mendel's Assumptions
Each trait as one dominant and one recessive version
Pairs of alternative traits are segregated among offspring (seed color, and texture traits stayed independent for each other)
Alternative traits in F2 generations expressed in ¾ dominant, ¼ recessive
Gamete Types
Formed during meiosis from parent genotypes; one variation of a gene given to offspring from each parent
Sickle Cell Anemia
Example of pleiotropy multiple symptoms from one defective gene