mgmt exam 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Planning
setting goals and deciding how to achieve them
coping with uncertainty by formulating future courses of action to achieve specified results
strategy
sets the long-term goals and direction for organization
strategic management
the formulation and implementation of strategies and strategic goals
important to provide direction and momentum
encourage new ideas
develop a sustainable competitive advantage
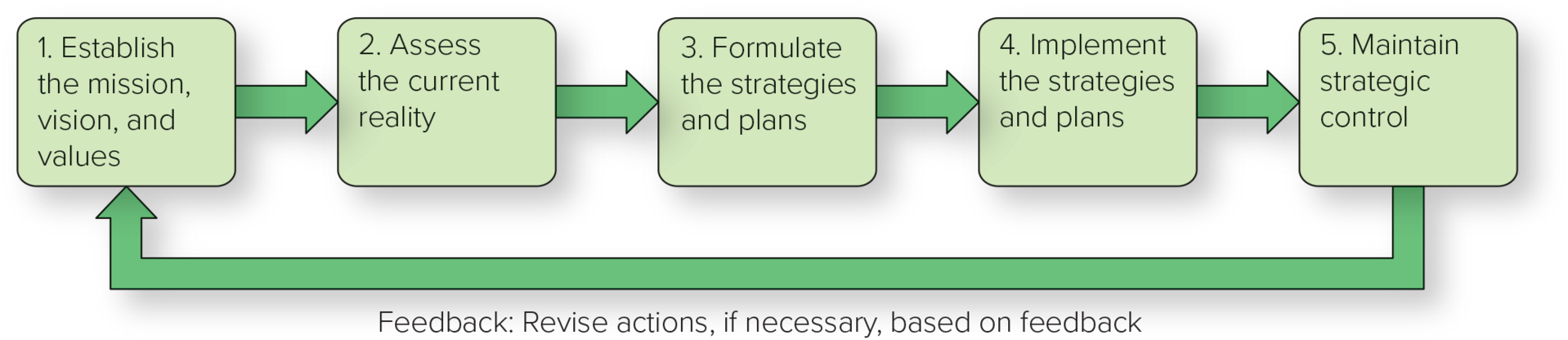
process of strategic management
Establish mission, vision, and values
asses current reality
formulate the strategies and plans
implement the strategies and plans
maintain strategic control
making plans - statements
mission, vision, values
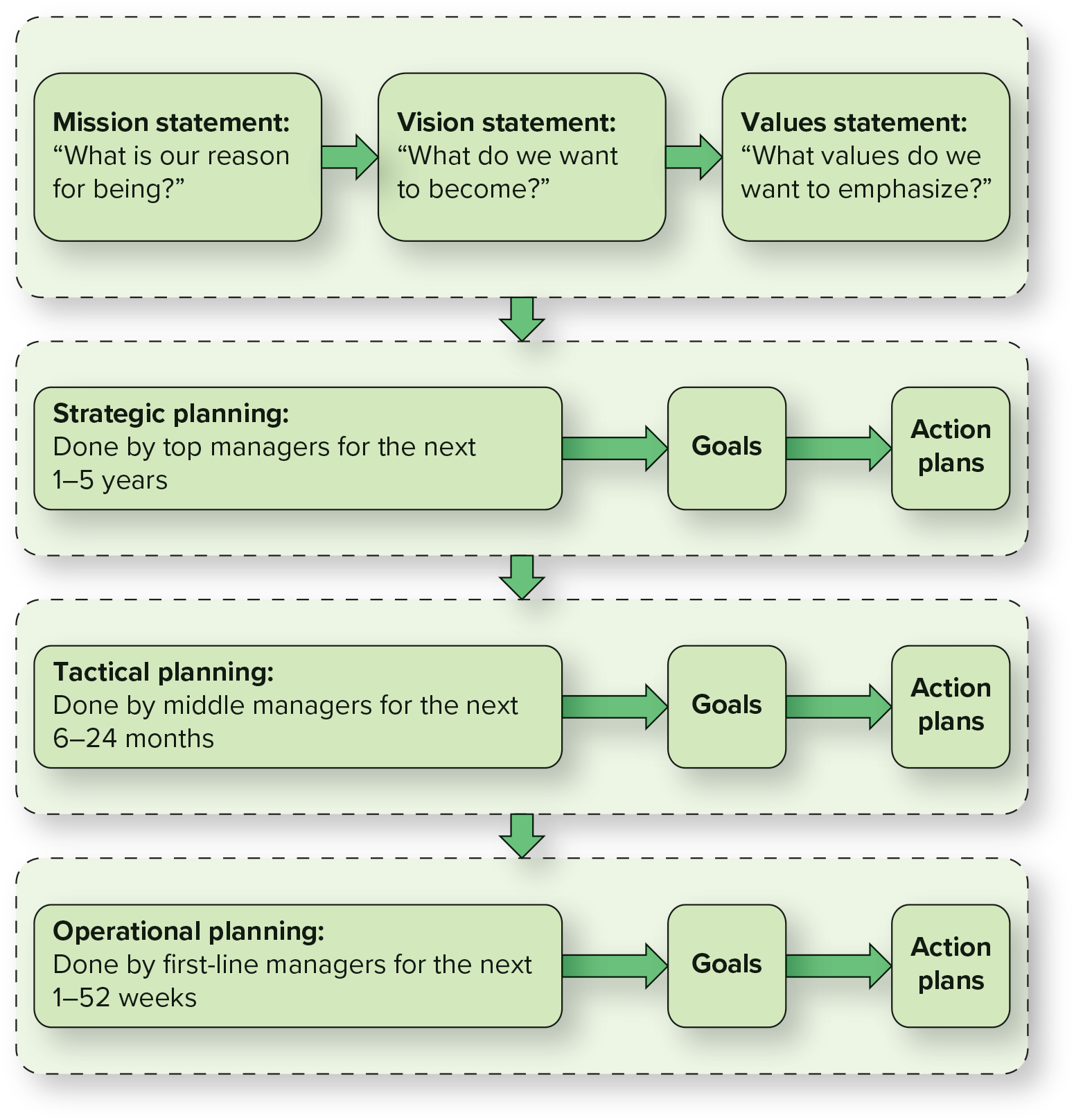
mission statement
“what is our reason for being?”
purpose of the organization and identifies the goods/services that the org provides/will provide
top management/board of directors determine the mission
vision statement
“What do we want to become?”
what organization should become/where it wants to go strategically
exhibit clarity = employees understand
future focus = describes future
abstractness and challenge = future described as hypothetical but achievable
idealism - future = highly desirable
values statement
“What values do we want to emphasize?”
expresses what the company stands for, its core priorities, the values its employees embody, and what products contribute to the world
strategic planning
top management
determines an organization’s long-term goals (1-5 years) with the expected available resources
Managers need to pay attention to the environment outside the organization, be future oriented, and deal with uncertain and highly competitive conditions
tactical planning
middle management
(6-24 months) determine what contributions their departments or similar work units can make with their given resources
operational planning
first-line management and team leaders
(1 to 52 weeks) direct, daily tasks; decisions often predictable, following a well-defined set of routine procedures.
top management
CEO, president, VP, general managers, division heads
middle management
functional managers, product-line managers, department managers
first-line management and team leaders
unit managers and first-line supervisor
SMART Goals
Specific, measurable, attainable, results-oriented, and has target dates
SMART - specific
goals should be stated in specific terms (instead of vague)
ex: focuses on achieving a 3.5 GPA through clear study habits and support
SMART - measureable
goals should be quantifiable/measurable
ex: GPA/study hours can be tracked
SMART - Attainable
goals should be realistic
ex: 2hrs a day and bi-monthly meetings
SMART - Results-oriented/Relevant
goals should support the organization’s vision
ex: directly support the student’s desire for good grades.
SMART - Target date/time-bound
goals should have deadline dates for attainment
ex: target is set for end of the semester
management by objectives
4-step process to motivate instead of control subordinates through clearly defined goals
jointly set objectives for the employee
develop action plans
periodically review the employee’s performance
make a performance appraisal and reward the employee according to results
cascading goals
process ensuring that the strategic goals set at the top level align w/ more specific short-term goals at lower levels, including employees’ objectives and activities.
strategic > divisional > departmental > individual
strategic positioning
process where a company or organization creates a unique and valuable position for itself in the market, differentiating its offerings from competitors to attract and retain customers
broad or narrow/niche market
corporate level strategy
focuses on organization as a whole
“C-suite”; “what business are we in?” & “What services/products should we offer?”
ex: acquisitions and joint-ventures
VRIO
a framework for analyzing a resource or capability to determine its competitive strategic potential by answering four questions about its value, rarity, imitability, and organization
VRIO - value
is the resource or capability valuable?
if no: competitive disadvantage
VRIO - Rarity
is the resource or capability currently controlled by only a few firms or no other firms?
if no: temporary competitive advantage
VRIO - imitability
is the resource or capability costly for other firms to imitate?
if no: unexploited competitive advantage
VRIO - organization
is the firm structured to utilize its resources or capabilities effectively?
if no: you have an unexploited competitive advantage
trend analysis
a hypothetical extension of a past series of events into the future. The basic assumption is that the picture of the present can be projected into the future.
scenario analysis
the creation of alternative, hypothetical, but equally likely future conditions
benchmarking
process when a company compares its performance with that of high-preforming organizations
objective is to find examples of superior performance and understand the processes and practices driving that performance
copy them and do it better!
porter’s 5 competitive forces
Michael Porter’s model for industry analysis: business level strategies originate by evaluating the 5 competitive forces in the firm’s environment
Threat of new entrants
Bargaining power of suppliers
Bargaining power of buyers
Threats of substitute products or services
Rivalry among competitors
growth strategy
used when an organization wants to expand the number of markets served or products offered through current or new business(es)
stability strategy
An organization continues to do what it’s currently doing
defensive/retrenchment strategy
a grand strategy that involves reducing the organization’s efforts. designed to address declining performance
understanding growth strategies
concentration - additional branches; do what works
diversification - related/unrelated: breaking into something new, doesn’t appeal to the same consumer)
horizontal integration - buy the competition
vertical integration - expand into our supply chain
BCG matric
? - growth or retrenchment strategy; poor position, growing industry
★ - growth strategy; dominant position, growing industry
🐶- retrenchment; poor position, low-growth industry
💰🐮- stability or modest growth strategy; dominant position, low-growth industry
decision-making
process od identifying opportunities
decision
a choice madse from available alternatives
optimizing decision
choose the absolute best among alternatives
classical:
structured problem
clearly defined
certain environment
complete information
all alternatives and consequences known
satisficing decision
Choose first “satisfactory” alternative
behavioral model:
unstructured problem
not clearly defined
uncertain environment
incomplete information
not all alternatives/consequences known
rational decision making
managers should make logical and optimal decisions
bounded rationality
numerous constraints limit decision maker’s ability to be rational
hubris
extreme, inflated sense of pride, certainty, and confidence
satisficing model
seeks alternatives to find one that is satisfactory
intuition
choosing w/o the use of conscious thought or logical inference
“it just feels right.”
pros: can speed up decision-making, helps when limited resources
cons: hard to convince that hunch makes sense, less effective when people face structured problems
SYSTEM 1 thinking
fast thinking; revert to what we know (or think we know); intuitive; reaction; innate skills
SYSTEM 2 thinking
slow thinking; rational, concentration use brain, eyes dialate
groupthink
when group members strive to agree for the sake of unaimity and thus aboid accurately assessing the decision situation