Lesson 15: The Nucleus
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
nuclear pores
_______ ______ allow proteins and mRNA to move between the nucleus and cytoplasm
2
the nucleus is surrounded by ___ membrane bilayer(s)
ER, lumen
the outer membrane of the nucleus is continuous with the _____, meaning they share the same ______
nuclear lamins
the ______ ______ form a basket-like network of filaments that protect nucleus from mechanical forces
intermediate, eukaryotic
nuclear lamins are _______ filaments in the nucleus of all ________ cells
mechanical, chromosomes, interphase
Lamins:
protect the nucleus from _________ forces
provide an attachment site for _________ during ________
likely contribute to gene expression in some way
lamins, nucleus
Mutations in ______ cause Hutchinson-Gilford syndrome (progeria):
-symptoms of premature aging
-altered by a single amino acid residue
-causes an abnormal shape of the _______
rRNA
10 chromosomes contribute a loop of ______ genes to the nucleolus
fluorescence in situ hybridization
_______ __ ____ ________ allows for the visualization of chromosomes by microscopy:
1. probe used to label, DNA denatured
fluorescent molecs attach to ssDNA, ssDNA attaches to target
interphase
________ chromosomes occupy distinct territories within the nucleus
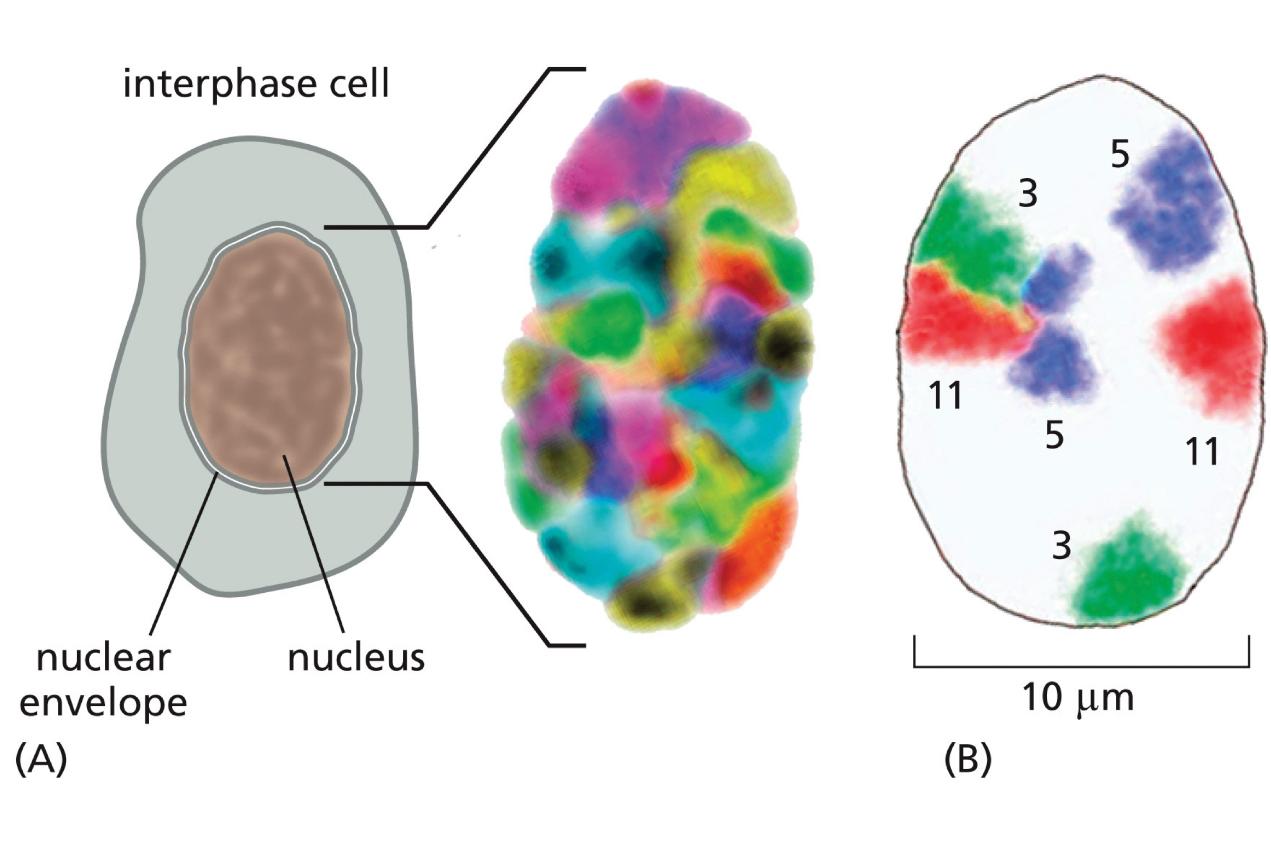
regulation, recombination, epigenetic
Advantages of Chromosome Territories:
independent gene _________: diff based on local nuclear environment, one copy may be near activative transcription factors whil ethe other copy may be near repressive heterochromatin
Prevents inappropriate __________: keeping homologs apart reduces risk of out of place recombination in somaticcells, should not be occurring in regular body cells, but proximity increases the chance of DNA breaks triggering recombination
Maintains distinct _______ states: maintains diff chromatin modifications without interference (like imprinted genes or X-inactivation
cytoskeleton
-lamins are proteins that are part of the __________
-maintains nuclear shape when cell deforms
-protects chromatin
False
True or false: the nucleolus has a membrane
-5 diff chromosome pairs come together
-synthesize ribosomal components
-churns out ribosomes
noncoding, doesn’t
“Junk” DNA is (coding/noncoding) DNA that (does/doesn’t) provide instructions for making proteins
-regulates some genes
-controls 3D chromos structure
-prod noncoding RNA molecules (tRNA/rRNA)
-some may still be non-functional
nucleosomes, 8, H1
________ are the basic units of eukaryotic chromosome structure
-contain DNA wrapped around a protein core of ____ histone molecules
-histone ___ provides additional packaging of nucleosomes in the chromatin fiber by acting as a linker between the DNA and nucleosome - makes more compact
cohesins, condensins, DNA
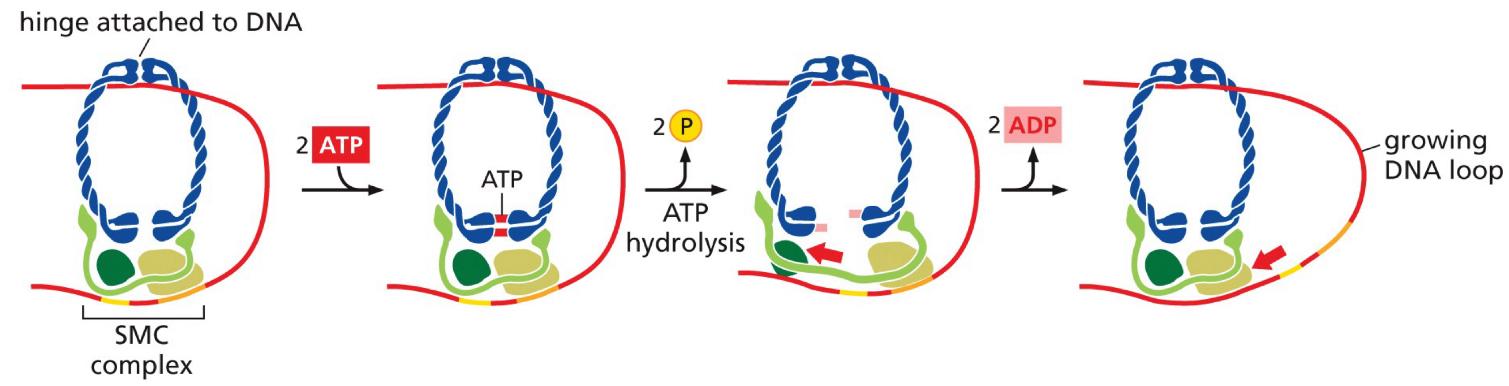
SMC Ring Complex: molecular motor that windds DNA into loops
-_______: organize interphase chromatin
-______: Chromos → mitotic chromosome (before cell division)
-ATP hydrolysis to “walk” along fiber of ____
2
Steps of SMC Complex ATP hydrolysis:
Hydrolyzes __ ATP
hinge attaches to DNA, threads through SMC complex
2 ATP attaches to the ATPase domain end
hydrolyzes, releases 2 Phoshate ions
stretches region further down DNA, 2 ADP leave so it returns to original state, effectively inchworming down the line of DNA to create a loop between the ATPase domain and the hinge
clamp
Size of chromatin loops is regulated by sequence-specific _____ proteins:
-cohesin binds and creates loop until two clamps hit each other
-cohesins are stuck in the loop, do not detach, but do not do anything
condensins
______ form loops within preexisting loops from cohesins, folding amitotic chromosome into a compact configuration
-when cells enter mitosis, most cohesins organized by an interphase chromosome are replaced by the condensins
-Condensin II forms initial large chromatin loops, condensin I forms second set of loops inside them
interphase
cohesins are used during ______
M phase
condensins are used during _____
many, 1, 2
Each chromosome has (one/many) origins of replication _ centromere, and _ telomeres
Packing
Levels of DNA ______:
DNA Double helix
“Beads on a string” chromatin (nucleosomes)
chromatin fiber of associated nucleosomes
folded into loops by cohesins
condensed further into chromosome by condensins
ATP
ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes (REGULATE CONDENSED CHROMATIN):
-How to access? locally reposition the DNA wrapped around the nucleosomes instead of unraveling!
-use ____ hydrolysis to shift position
Histone
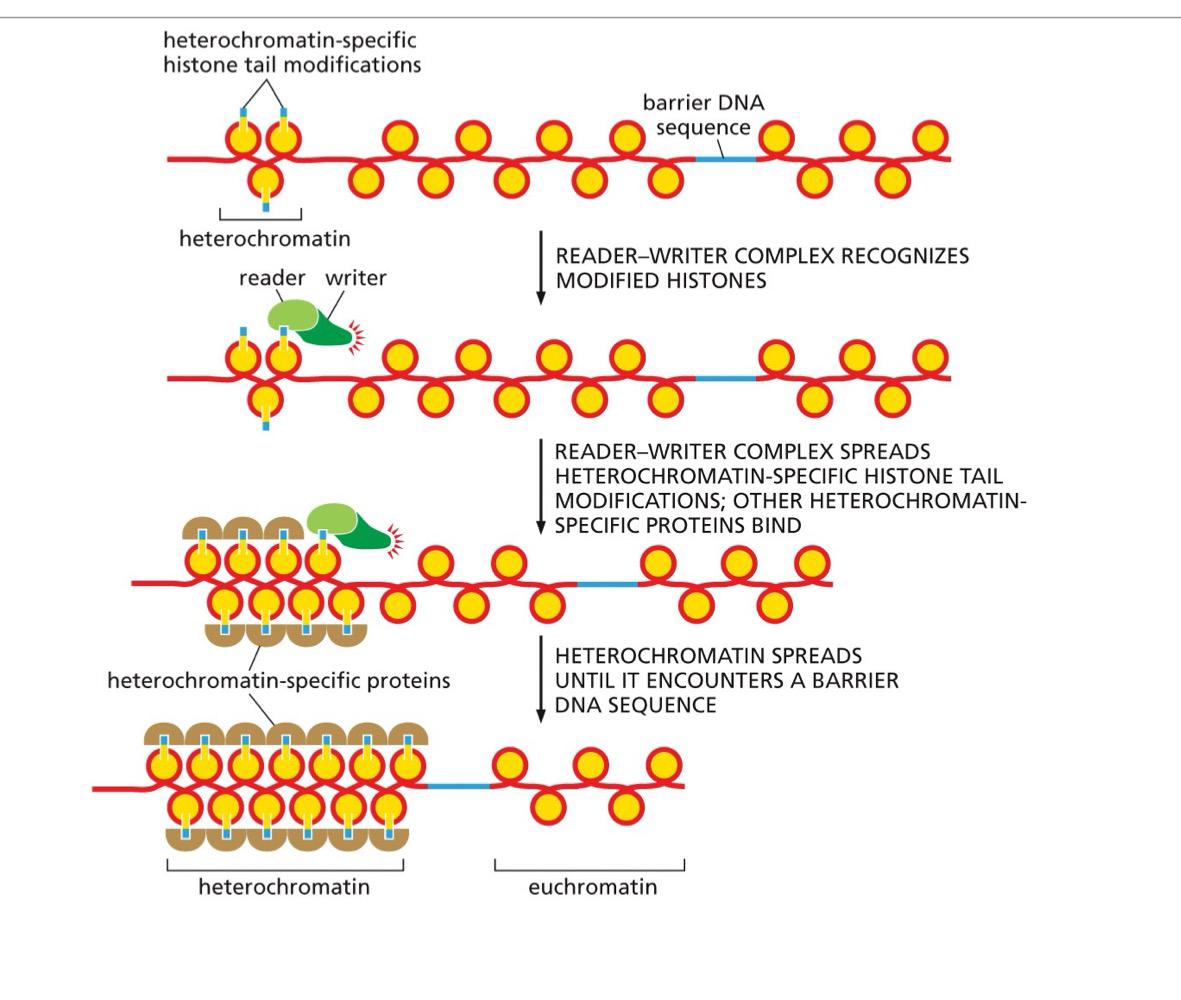
_______ tail post-translational modification:
-methylated, acetylated, phosphorylated (promote condensation or expansion of chromatin)
-modifications made by “writers”, removed by “erasers”, and acted on by “readers'“
heterochromatin
_____: highly condensed interphase chromatin containing “silent” genes that aren’t expressed
facultative, constitutive
_______: temporarily condensed chromatin
_______: permanently condensed (centromeres, telomeres)
euchromatin
_____: less condensed interphase chromatin, genes actively expressed
-QUIESCENT ________: decondensed but not actively transcribing anything (“QUIEt”)
Spread
Reader-Writer Complexes ______ Heterochromatin until it reaches a barrier sequence
X
Chromatin Regulation: One __ chromosome is inactivated, silencing the genes of the entire chromosome:
-women born with a maternal and paternal X chromos, one of them is randomly inactivated and the active one is passed on to offspring
yes
epigenetic inheritance: can heterochromatin be inherited after DNA replication?