Music Tech Flashcards
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Particularly aimed at Comp 4 revision
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Explain MIDI messages in 5 points:
Consists of a status byte and 1-2 data bytes
Each byte consists of 8 bits
The farthest left bit is called the MSB (most important bit)
The farthest right bit is called the LSB (least important bit)
The status byte always begins with 1 and data bytes always begin with 0
What is the difference between a status byte and a data byte?
The status byte tells us the type of MIDI message
The data byte(s) provides more information about the associated parameters
What are 2 specific types of MIDI message and what does each byte represent in each message?
Note messages and controller messages
Note messages:
Status byte = Note on/Channel
Data byte 1 = Note number
Data byte 2 = Velocity value
Controller messages:
Status byte = Control change/Channel
Data byte 1 = Controller number
Data byte 2 = Controller value
Explain how MIDI messages transmit velocity data:
Velocity data is always transmitted as part of the 2nd data byte
7 bits are used to represent velocity (because the 1st bit is used to distinguish status and data bytes)
Because binary is a base 2 system, the number of possible values is figured out using a 2x calculation
Therefore, velocity is found using a 27 calculation
This equals 128 which means that there are 128 possible values for a notes velocity - 0-127
Other then velocity, what are 3 other MIDI messages?
Aftertouch
Pitch bend
Program changes
Explain how to convert from decimal to binary:
Example: convert 98 to a binary number
Step 1: List the factors of 27 from 128 to 1 (128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1)
Step 2: Find the first number in the list which is smaller than 98 and label that number as 1 (in this case 68 is the first number which will go into 12
Step 3: Label any number before this as 0 (in this case 128 is labled as 0 because it goes 0 times into 98)
Step 3: Subtract 64 from 98 (which equals 34) and find the next number that is smaller than this number (in this case 32) and label this as 1 (label any numbers in between as 0)
Step 4: Repeat step 3 until the whole number is converted (34-32=2, neither 16, 8, or 4 are smaller than 2, so they are labled as 0, Lastly, 2=2, therefore 2 is labled 1 and 1 is labled 0)
What is AAC Codec?
Advanced Audio Coding
What type of data compression is used for AAC and mp3?
Lossy compression
What are 5 benefits of ACC?
Better sound quality even at lower bitrates
Uses less power to play audio files
Supports a wider range of bitrates
Can handle up to 48 channels whilst mp3 is limited to 2
Manages higher audio frequencies more effectively
What are 6 compressed digital audio formats and what do they stand for (in alphabetical order - AAFMOW)?
AAC (Advanced audio coding)
ALAC (Apple lossless audio codec)
FLAC (Free lossless audio codec)
MP3
OGG (Ogg vorgbis)
WMA (Windows media audio)
What are MIDI CC?
MIDI Control Changes Messages
Which MIDI CC messages have a value of 0-127?
MIDI CC messages 0-63 (plus many over 70)
Which MIDI CC messages can either be on or off?
64-69 (≤63 off, ≥64 on)
What MIDI CC messages are undefined?
MIDI CC 3, 14-15, and 20-31
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 0:
Purpose: Bank select
Description: Allows user to switch bank for patch selection. MIDI can access 16,384 patches per MIDI channel
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 1:
Purpose: Modulation
Description: Generally controls a vibrato effect (pitch, loudness, brightness). What is modulated is based on a patch.
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 2:
Purpose: Breath Controller
Description: Associated with aftertouch messages, originally intended for use with a breath MIDI controller in which blowing harder produced higher MIDI control values, can also be used for modulation
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 4:
Purpose: Foot controller
Description: Often used with aftertouch messages, can send a continuous stream of messages depending on how the pedal is used
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 5:
Purpose: Portamento time
Description: Controls portamento rate between 2 notes played subsequently
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 6:
Purpose: Data entry MSB
Description: Controls value for NRPN or RPN parameters
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 7:
Purpose: Volume
Description: Controls the volume of the channel
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 8:
Purpose: Balance
Description: Controls the left and right balance for stereo patches, 0 = hard left, 64 = centre, 127 = hard right
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 10:
Purpose: Pan
Description: Controls the the left and right balance for mono patches, 0 = hard left, 64 = centre, 127 = hard right
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 11:
Purpose: Expression
Description: A percentage of volume (see CC 7)
Give a purpose for MIDI CC 32-63:
Purpose: Controller 0-31 LSB
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 64:
Purpose: Damper Pedal/sustain pedal
Description: On/off switch that controls sustain (0-63 = On, 64-127 = Off)
Give a purpose and description for MIDI CC 65:
Purpose: Portamento On/Off Switch
Description: On/off (0-63 = On, 64-127 = Off)
What is a patch?
A collection of synthesiser settings that make a specific sound
What is the difference between a pulse wave and a square wave?
A square wave has an equal duty cycle (50% - the on/off times are equal) whereas the duty cycle of a square wave is not necessarily equal
What is pulse width?
The duration of “on time” is the pulse width
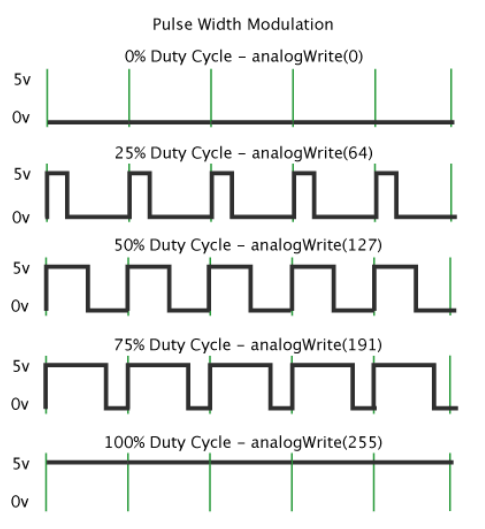
What is pulse width modulation?
A technique for getting analogue results through digital means. The pulse width is modulated (or changed) to achieve varying analog values