Neurological Aspects of Cognition and Communication Unit #5
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Lateralization
When the function of something turns from a two hemisphere function to a one-hemisphere function
Left Hemisphere
Primarily involved with receptive and expressive language (Phonology, morphology, syntax and semantics).
Right hemisphere
Primarily involved in pragmatics, attention, visuoperception, comprehension of linguistic and emotional prosody. Language activation weakens in the right hemisphere in adults. (Comprehension of pragmatics)
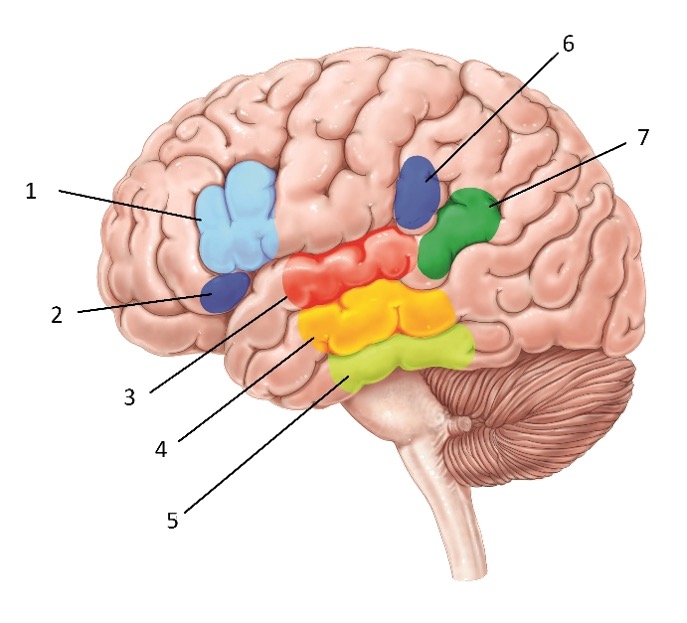
Structure #1
Broca’s area - Involved in speech and language production
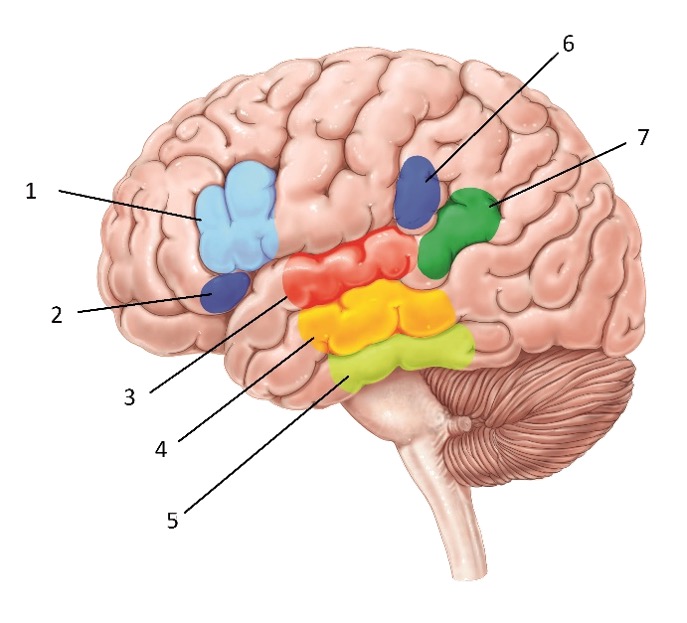
Structure #2
Inferior frontal gyrus - Involved in speech and language production
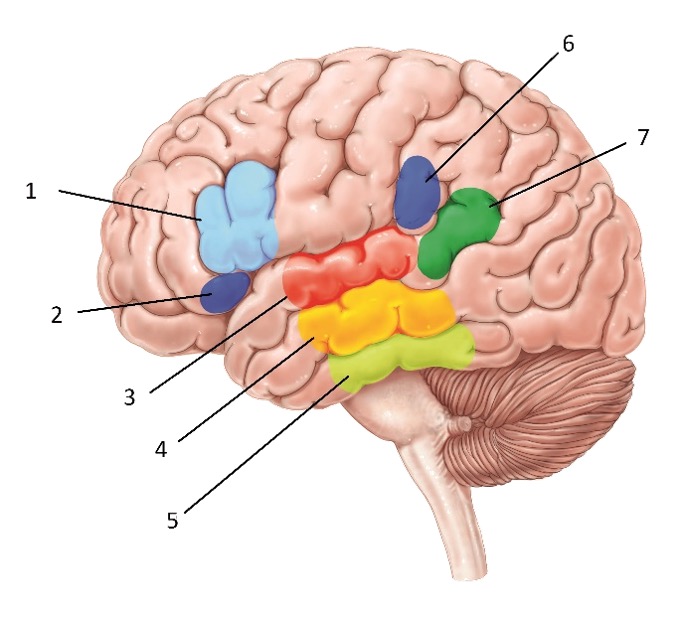
Structure #3
Superior temporal gyrus - Involved in speech comprehension

Structure #4
Middle temporal gyrus - Involved in language comprehension

Structure #5
Inferior temporal gyrus - Involved visual processing

Structure #6
Supramarginal gyrus - Involved in phonological processing
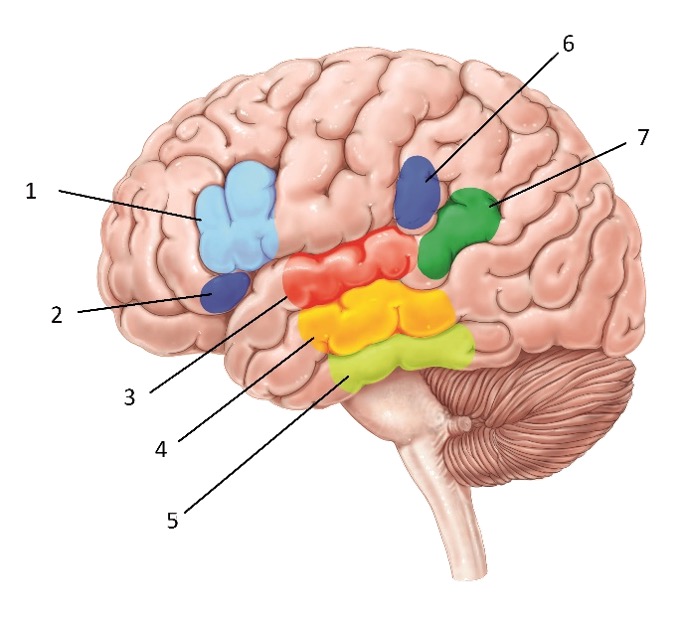
Structure #7
Angular gyrus - Involved in language comprehension
Global Aphasia
Issues with fluency, comprehension, and repetition
Broca’s Aphasia (non-fluent aphasia)
Good comprehension but poor fluency (slow and effortful speech)
Wenicke’s Aphasia (fluent aphasia)
Good fluency, but poor comprehension. Usually linked with paraphasias.
Conduction Aphasia
Troubles with repetition
Anomic Aphasia
Troubles with word finding
Paraphasias
Words that sound like real words, but aren’t
What is the condition caused by right hemisphere damage?
Apragmatism
What is the condition caused by left hemisphere damage?
Aphasia
Dorsal Language stream
involved in the motor processing of speech (the output)
Ventral language stream
Involved in the processing of language (the input)
Dorsal prosodic network
Involved in the expressing emotional prosody (the output)
Ventral prosodic network
Involved in the processing of emotional prosody (the input)
Dorsal visual pathway
The “where” pathway. involved in processing information about motion and spatial relationships between objects (pathfinding, sense of self in space)
Ventral visual pathway
The “what” pathway. involved in processing information about form, color, shape, faces, letters, and other visual stimuli.
Apragmatism
A right hemisphere disorder relating to deficits in communication (difficulty with figurative language, emotional prosody, egocentrism, etc) and cognition (attention, executive dysfunction, and memory deficits).
Dorsal Attention Network
Function: Running when we have sustained and focused attention to contralateral spaces.
Structures: Dorsal parietal fields, frontal eye fields, and the superior longitudinal fascicules.
Ventral Attention Network
Function: Running when alerting, attention to novel or sudden stimuli
Structures: Frontal lobe, insula, superior temporal gyrus, and temporoparietal junction.
Default mode network
Function: Running when at rest or mind drifting
Structures: Prefrontal cortex, cingulate, and intraparietal sulcus
Attention control network
Function: Running when we are using alternating and divided attention
Structures: Prefrontal cortices, cerebellum, basal ganglia, and thalamus.
Theory of mind
Understanding that others have different thoughts, feelings, ideas, and knowledge.
Declarative memory
Explicit and conscious memory
Semantic memory
Fact-based memory
Episodic memory
Experience-based memories
Non-declarative
Unconscious and implicit memory (actions/behaviors)
Procedural memory
Memories of how to do something
Working memory
Processes and temporally stores memories
Meta-memory
Knowledge about one’s own memory abilities
Prospective memory
Remembering to do something in the future
Focused attention
Being able to attend to 1 stimulus without distractions
Sustained attention
Holding focused attention over time
Selective attention
Attending to a stimulus while ignoring other internal or external distractions
Divided attention
Splitting attention between 2 stimuli or task
Alternating attention
Switching focus between 2 stimuli or tasks
Encoding
Function: Analyzing information (visualization, chunking, etc)
Structures: Frontal lobes + modality-specific regions (e.g., temporal lobes for auditory stimuli)
Consolidation
Function: Converting short-term to long-term memories
Structures: Hippocampus
Storage
Function: Memory stored for later retrieval
Structures: Temporal lobes, modality-specific areas
Retrieval
Function: Accessing information
Structures: Frontal lobes
Post-traumatic amnesia
Period of anterograde amnesia that shrinks over time
Retrograde amnesia
Loss of memories prior to a brain injury
Anterograde amnesia
Reduced ability to form new memories
Causes of amnesia
Strokes, tumors, TBI

Portion #1 of the prefrontal cortices
Dorsolateral / Dorsomedial prefrontal cortices (COLD)
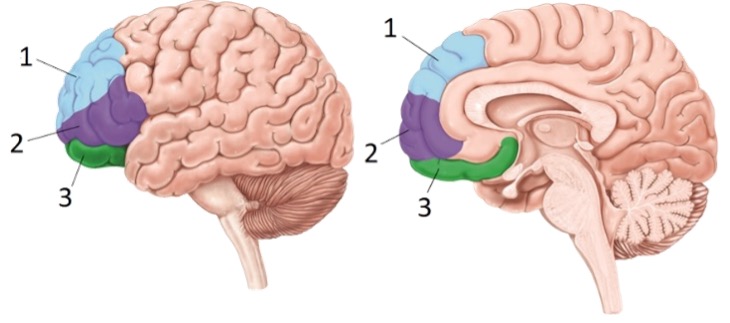
Portion #2 of the prefrontal cortices
Ventrolateral / Ventromedial Prefrontal cortices (HOT)
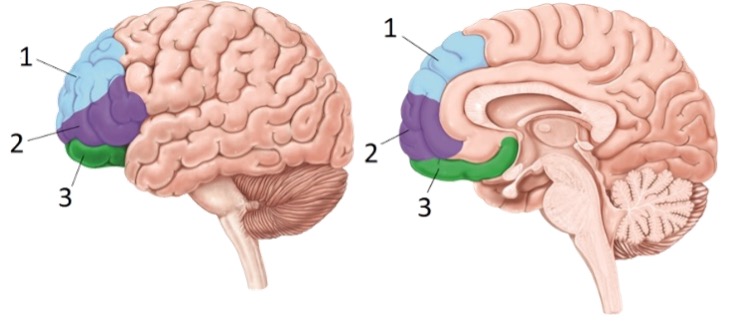
Portion #3 of the prefrontal cortices
Orbitofrontal prefrontal cortices (HOT)
The paradox of assessing executive functions in a clinical setting
Clinical environments do not have as much external stimuli that could impact executive functioning as real-world environments
Hot executive functions
The use of executive functions in emotionally charged situations. Processed in the orbitofrontal/ventromedial prefrontal cortices
Cold executive functions
When executive functions are used without an emotional connection. Processed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortices
Executive functions
High-level cognitive functions (organization, prioritizing, goal-setting, decision-making, planning, reasoning and problem-solving, self-regulation, initiation, cognitive flexibility, etc.)
Neuroplasticity
How the brain adapts and changes from the things you do, your environment and your environment
Maladaptive neuroplasticity
When a therapy activity is different from the context a person will use it in– making that activity difficult to do when out of therapy.
Functional reactivation
The regrowth of neurons within a former penumbra. This can cause new neuronal branching inside the ischemic core or the infarct region
Functional reorganization
When another area of the brain takes over the functions of the damaged areas.
Neuromodulation
The process of changing nerve activity in the nervous system. This can help relieve some neurological symptoms and pain.