PathoPharm 1 Cumulative Final Exam
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Schedule I
High potential for abuse & dependance w NO medical acceptance
EX: Peyote, Heroin, Cocaine, Marijuana
Schedule II
High potential for abuse and dependence, with accepted medical uses.
EX: Morphine, Oxycodone, Amphetamines, Fentanyl, Hydromorphone
Schedule III
Low-Moderate potential for abuse and dependence w accepted medical uses
EX: Aspirin (w codeine), Testosterone, Ketamine
Schedule IV
Low potential for abuse and dependence, accepted medical uses
EX: Ativan, Xanax, Diazepam, Lorazepam
Schedule V
Low potential for abuse, accepted medical uses.
EX: Codeine cough med (Robitussin)
Teratogenic Drugs
Drugs that potentially harm the fetus
Category A = Safest
Category B-D = Gets progressively more dangerous
Category X = Greatest threat
Side effect
Can be harmful OR therapeutic
Not as damaging as adverse & usually stops using the drug
Adverse effect
An undesirable and harmful effect that can occur due to the use of a medication —> discontinuation of the drug
More severe than side effects
Anaphylaxis
A severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention & can lead to respiratory failure, shock, or death
s/s of anaphylaxis shock
Hypotension
AMS
SOB
Angioedema r/t massive systemic release of histamine
Increased BP & HR
Phlebitis
Inflammation of the vein
Infiltration
Inadvertent administration of NON-VESSICANT(0.9% norm saline) solution into tissues surrounding the vein
s/s of infiltration
Edema
Erythema
Cool to the touch
(improves w ice packs or heat pads & elevate)
Extravasation
Infiltration of vesicant (highly irritating/destructive) medication into tissues surrounding vein
s/s of Extravasation
NECROSIS!!!
Burning
Redness
Swelling
(stop infusion & notify HCP!)
CVC
Central Venous Catheter
When do we give a patient a CVC?
A CVC is used as opposed to a peripheral IV because IVs can’t handle some medications so the central line is a better option due to the bigger vein
Multiple incompatible meds due at same time
TPN
Chemotherapy
Someone that needs labs drawn frequently
Can stay in for 4-6 weeks
Give highly vesicant solutions & watch out for bloodstream infections!!
Where are the veins that we can place CVC?
Femoral
Subclavian
Internal jugular
What CVC site do we try to avoid r/t infection risk?
Femoral vein
What is a risk for any CVC we place in the chest/neck?
PNEUMOTHORAX!! (collapsed lung)
s/s: absent lung sounds, dyspnea, decreased O2, pleuritic pain, & tracheal deviation)
SOB
Hypoxia
What situation would we insert an IO under?
Life-threatening situation
Intraosseous or IO is only for 1 day and only used when PIV cannot be inserted (cardiac arrest situation)
TPN
Total Parental Nutrition
Overview of TPN
Veins and arms cannot handle a TPN, need a central line (AKA Central Venous Access Device)
Something is wrong w GI tract
Change tubing q 24hrs
Infusion pump & micron filter to prevent air emboli, micro-precipitates, and microorganisms from getting into patient's bloodstream
Watch for HYPERGLYCEMIA
HARD ON LIVER (check liver enzymes)
DNC
Do Not Crush
What meds are DNC?
LA (long-acting)
XR (extended-released)
EC (enteric coated)
What is the sodium-potassium pump responsible for?
Maintains excess of Na+ ions outside of the cell & more K+ ions inside of the cell.
(Transports 3Na+ ions to the outside cell & 2k+ ions inside)
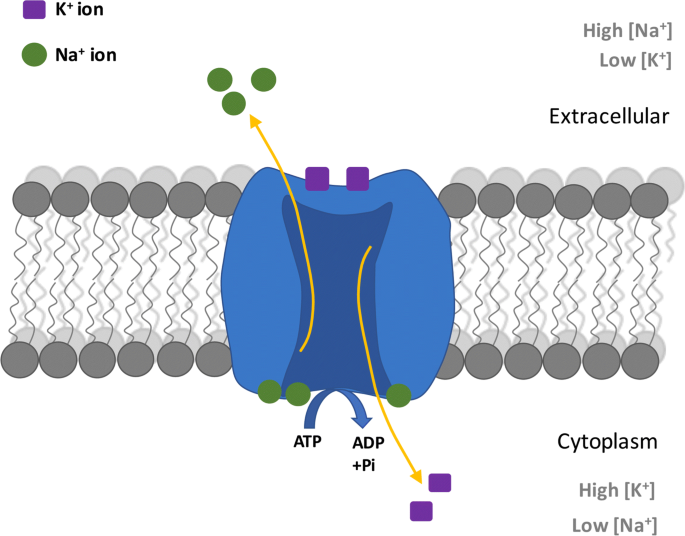
Sodium-potassium pump
What is resting membrane potential?
It keeps the inside of the cell more negative than the outside.
Nerve stimulates cell —> sodium channels open —> sodium rushes in = creates action potential
Why is energy needed for the sodium potassium pumps?
Low to high concentration (Na+ out, K+ in)
Process of Glycolysis (draw this out)
Glycolysis
O2 Present: Takes glucose & converts it to pyruvate first & then into Acetyl CoA
NO O2: Pyruvate —> lactic acid
Why is too much lactic acid bad for the body?
Disrupts the body’s normal pH balance that could lead to lactic acidosis
Process of Krebs cycle (draw this out)
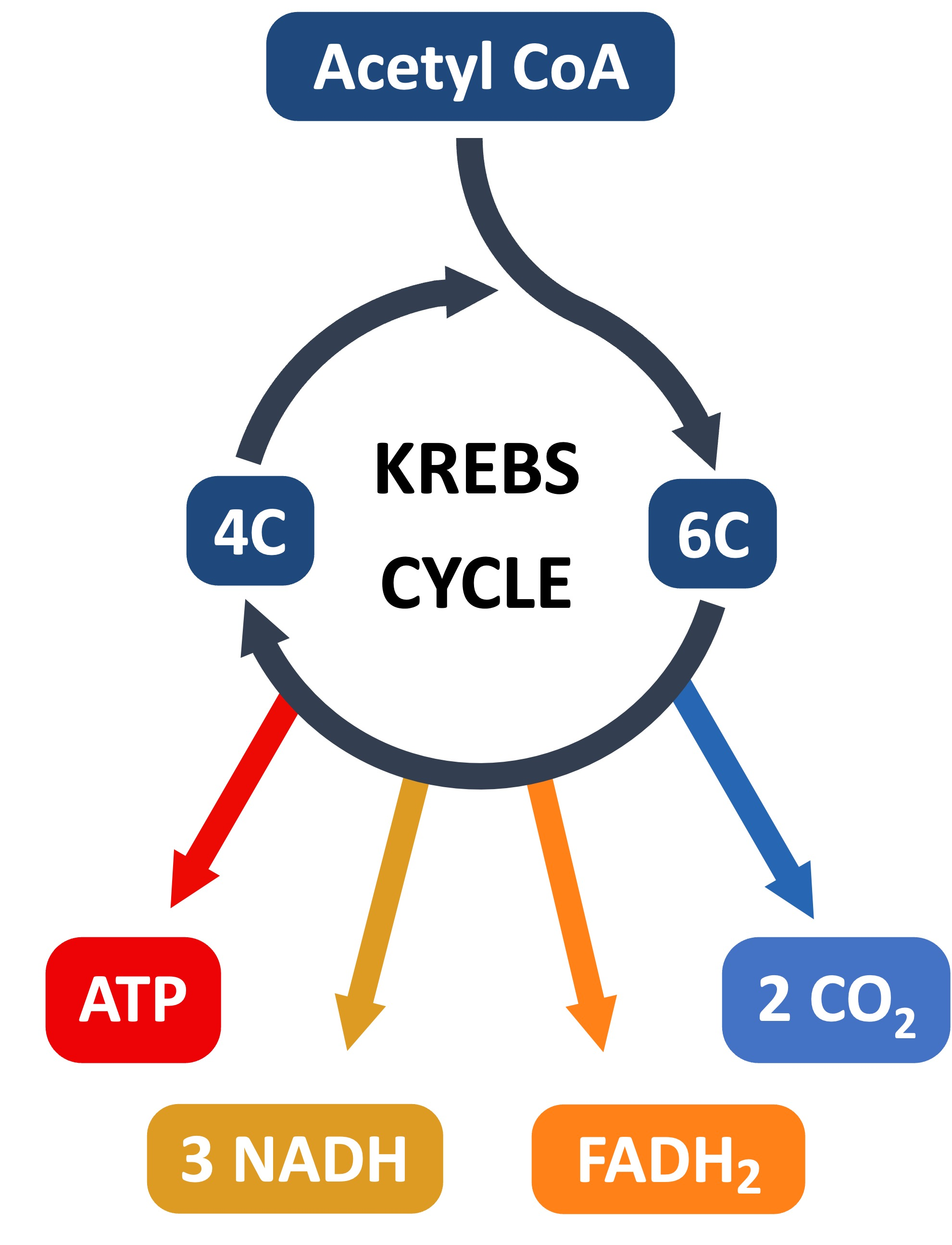
ETC (Electron Transport Chain)
Creates BULK of ATP (net 36 ATP)
What cycles create the most ATP & what do they require?
Krebs Cycle & ETC
OXYGEN!!
What is apoptosis?
Planned cell death & safely removing old, damaged, or unnecessary cells w/o causing harm
What is an RBCs most important function?
Carry hemoglobin
What does hemoglobin do in the spleen?
Breaks down as “heme” portion (iron) that moves into bile —> stool
“globulin” portion (protein) —> recycled by the body
What is necrosis?
Unplanned cell death caused by poisoning, decreased perfusion to the site, & decreased O2 to the site
Process of Necrosis
The body doesn’t respond to the ruptured necrotic cells & so the cells that rupture aren’t cleared away by the macrophages
Explain the life of a cell
RBCs live 120 days —> signal that tells it’s time to die —> goes to spleen to break down
Functions for kidney, liver, & spleen
Kidney = Excretes
Liver = Metabolizes
Spleen = Recycles & destroys
Intrinsic
Warfarin
PT/INR
Warfarin
Extrinsic
Heparin
aPTT
Heparin
What are the 4 clotting factors of the liver?
II
VII
IX
X
What do pts w hepatic impairment indicate?
Impaired coagulation = EXCESSIVE BLEEDING!
Anticoagulants
Warfarin & Heparin
Antiplatelets
Aspirin & Clopidogrel
Who’s at risk for bleeding?
Anybody on anticoagulants, antiplatelets meds or liver failure
What are arterial clots mostly made of?
Platelets
What are venous clots mostly made of?
Fibrin
Arterial clot conditions
Stroke
Peripheral arterial occlusion
MI
Venous clot conditions
Pulmonary edema
DVT
What meds can treat venous clots?
Anticoagulants (IV Heparin & PO Warfarin)
What’s heparin’s OD antidote?
Protamine sulfate
What’s warfarin’s & INR OD antidote?
Vitamin K
What foods should be avoided w Warfarin?
Grapefruit juice
What food should be consistent w Warfarin?
Vitamin K & green leafy veggies
DVT s/s
ELEVATE
Warm
Edema
Pain
Blue-purple discoloration
Peripheral Arterial Clot s/s
DEPRESS
Cold
Pale
Pulseless
Pain
Will go necrotic if we do not restore blood flow!
Anemia
MC from iron-deficiency
Treating mild anemia
Eating meat, fish, whole grains, dark leafy veggies, beans, & shellfish
Treating severe anemia
Give ferrous sulfate (and Vitamin C to help w iron absorption)
What are cautions when taking IV ferrous sulfate?
Extravasation
Black, tarry stool
AVOID ANTACIDS!!
What is sickle cell disease?
A type of anemia that is autosomal recessive (MC in African-Americans & Mediterranean)
Pathophysiology of sickle cell disease
Hgb becomes crescent shaped —> decrease O2 delivery to tissues & clogs blood vessels (especially kidneys & brain)
How long does sickle cell RBCs stay in the body?
20 days
What’s the treatment for sickle cell disease?
HOP
Hydrate (IVF 0.9 NaCl)
Oxygen
Pain meds
S/S of SCD
Vaso-occlusion (Stroke bc RBCs get stuck in vessels of brain, MI, Spleenomegaly, Pain, etc.)
What med do we avoid giving to SCD pts?
Meperidine bc it increases seizures & leads to renal failure
What organs associate w upper GI bleeds?
Esophagus, stomach, & duadenum
What organs associate w lower GI bleeds?
Anything below duodenum (colon, small/large intestines, etc.)
S/S of Hypoperfusion
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Decreased urine
Dizzy/Lightheaded/AMS/syncope
Dyspnea
Hypoxia
Pale
Clammy
Cold extremities
How to stabilize GI bleed
Lie pt supine, elevate legs (brings BP up.. helps return blood to the heart)
Oxygen therapy to maintain pulse ox
IV fluids (NOT PO!!) - start 2 large bore peripheral IV
Insert nasogastric tube to extract blood and gastric secretions that can make the bleeding worse/promote infection or inflammation.
Prevent hypothermia
Blood transfusion
When do we admin blood transfusions?
If their blood is 7- 8g/dL
What clotting factor is missing in hemophilia A?
Clotting factor 8
What clotting factor is missing in hemophilia B?
Clotting factor 9
Tx for Hemophilia A
Desmopressin bc it releases VIII in the body
What is innate immunity?
ALWAYS PRESENT, READY TO FIGHT, RESPONDS IMMEDIATELY!!
First line of defense that protects against infections & ANY foreign substance in the body (ex: paper cut)
What is adaptive immunity?
NOT ALWAYS PRESENT! TAKES 7-10 DAYS TO BE ACTIVATED! “SHARPSHOOTERS”
For stronger & more protection against specific invaders
What do adaptive immunity produce?
Humoral B-cells **antibodies to remember the pathogen for future**
Cell-mediated T-cells **activates b-cells**
Cytotoxic T-cells (CD8)
Helper T-cells (CD4)
Memory B-cells
Process of innate immunity (5 steps) (ex: paper cut)
Trauma & tissue damage trigger the inflammatory response & prostaglandin (AKA histamine & pain receptors) (erythema, edema, heat, and pain)
S1: Vasoconstricts to prevent blood loss
S2: —> Vasodilation to bring WBC to injury site
S3: —> Leukocytes go to capillary walls, then into tissue space
S4: —> Neutrophils & macrophages gobble up pathogens. Basophils, eosinophils, & mast cells contain histamine = more vasodilation & more WBCs to injury site
S5: —> (inactive protein, activated with damage) turns into fibrin “net” to make a stable blood clot
What are pyrogens?
Helps cause fever by released from macrophages when they are exposed to bacteria
What impact do pyrogens have on the body?
Travel to the hypothalamus (thermostat in the body) to turn the temp. up in the body to inhibit/limit bacterial growth
Are pyrogens good for the body?
Yes, bc it inhibits bacterial growth & promotes healing process
Are pyrogens bad for the body?
Yes, bc severe fevers can cause seizures (life-threatening)
Fever for immunocompromised
101.4°F
Function of spleen (5)
RBCs go there to die
Erythropoiesis (RBC production) happens in spleen
Stores some blood & platelets in case
Filters blood & traps antigens
Produce T & B lymphocytes
Why do we give immunosuppressants?
To try to STOP the immune system from “over-reacting” to an antigen/allergic reaction or bc an organ transplant from another person
Drugs r/t causing immunosuppression
Corticosteroids/Glucocorticoids (Prednisone0
Cyclosporine
Infliximab
NSAIDs (not as strong as cortico.)
Naturally Active Immunity
natural exposure (ex: kids getting sick in school from contact) & then makes their own antibodies to never have the disease again (ex: chicken pox)
Artificial Active Immunity
Induced by vaccines
ex: after exposure to tetanus, botulinum, HBV, or rabies
Naturally Passive Immunity
Maternally passed down —> transfer of IgA antibodies found in breast milk
ex: mom to baby by feeding breast milk
Artifically Passive Immunity
Healthcare CREATED immunizations to prevent illness
ex: recovering serum/plasma from COVID-19 pts
Convalescent
Recovering
Stage 1 HIV s/s
Presents like almost any viral infection
Fever, lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes), pharyngitis (sore throat), rash, arthralgia (joint pain), and myalgia (muscle pain). “Worst flu ever.”
High viral load but may or may not test positive for antibodies
CD4 T cells count < 500 (normal: 800-1000)
Transmissible
Stage 2 HIV-II s/s
Latency (may last years or decades with antiretroviral therapy (ART)
Lymphadenopathy, may be asymptomatic, & will test positive for antibodies.
CD4 T cell count < 200
Stage 3 HIV-III s/s
Profound reduction in immunity, high risk for infection, and increased risk for cancer
ALL body systems are impacted: GI, respiratory, neuro, cardio, & skin.
OI (opportunistic infections) occur
CD4 T cells count < 200
Wasting syndrome (10% or greater unintended weight loss)
AIDS related dementia
Weakness and malaise (tired)
Psychosocial: Anxiety, depression, body image.