genetics quiz
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Lag strand
synthesized as short Okazaki fragments in the direction away from the replication fork
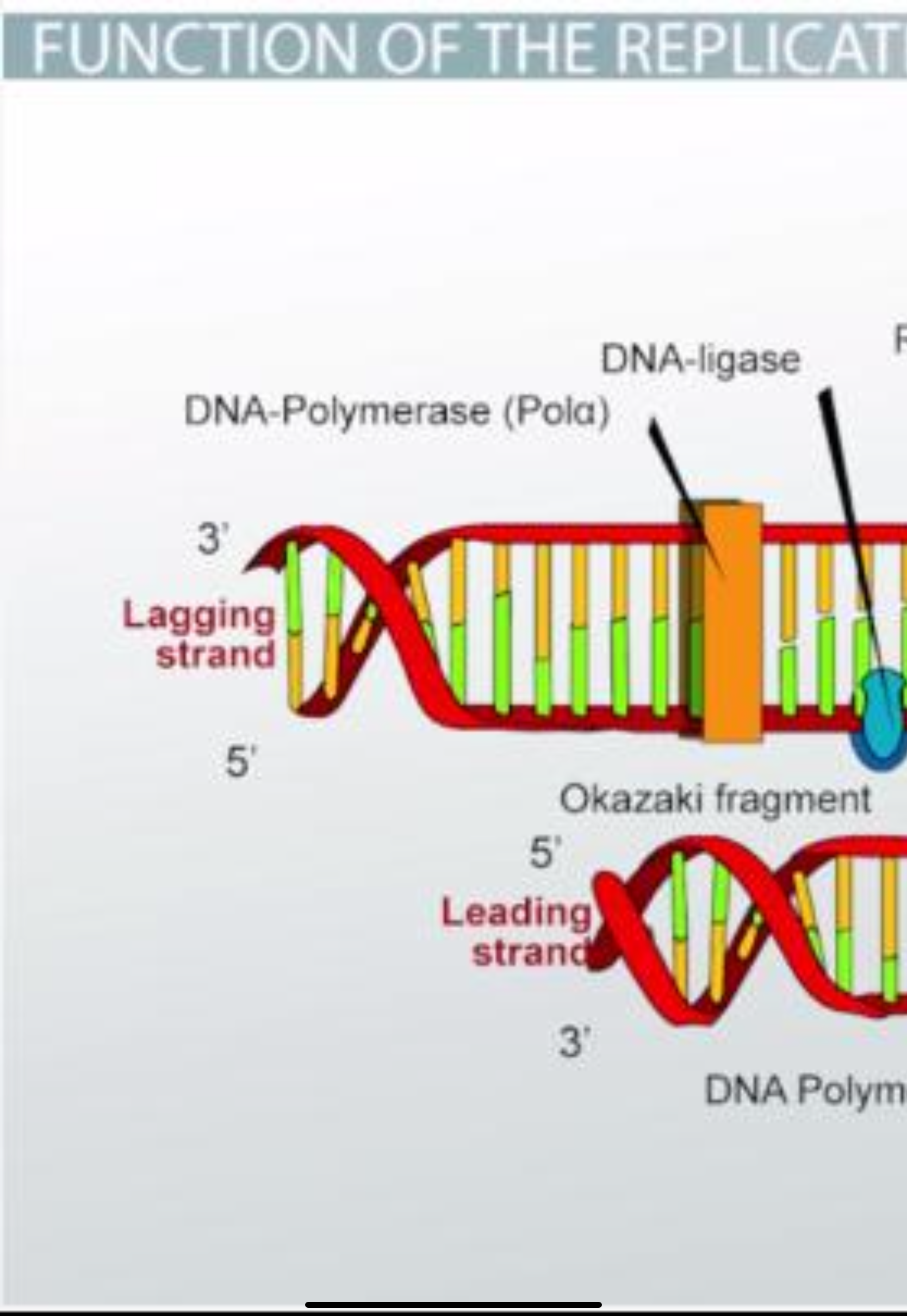
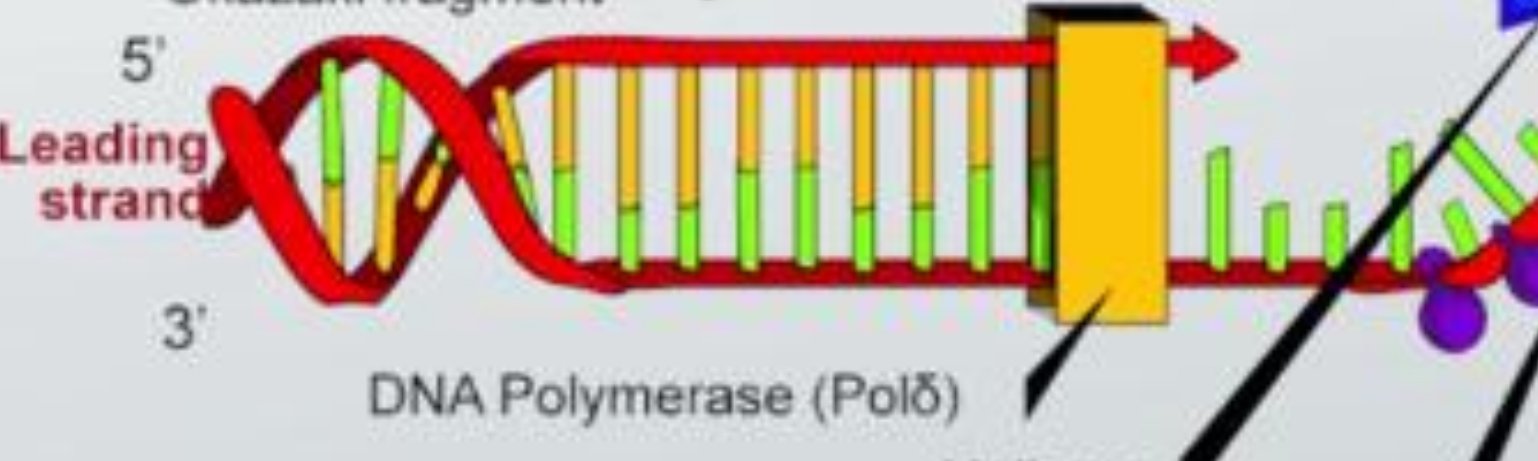
Lead strand
synthesized continuously toward the replication fork.

DNA Polymerase
an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between nucleotides to form a strand of DNA.
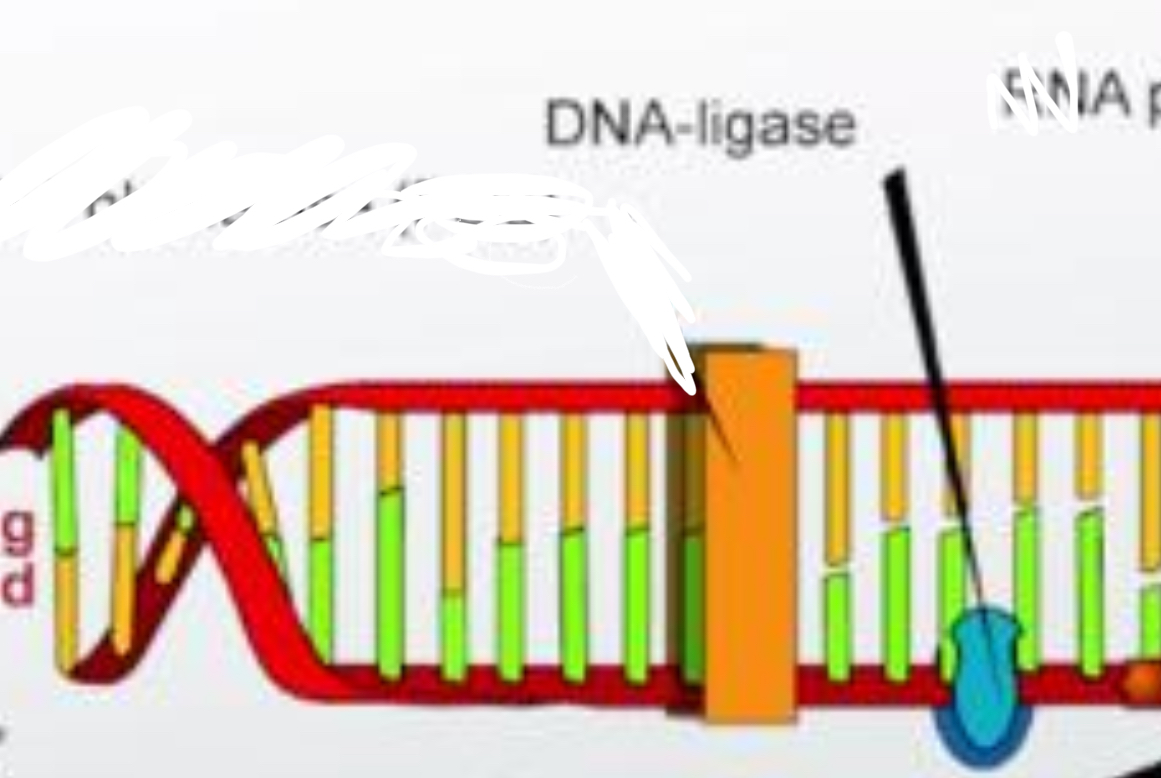
DNA Ligase
an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds within the sugar-phosphate backbones of two DNA strands.
DNA Primase
an enzyme that synthesizes a short RNA primer for DNA replication.
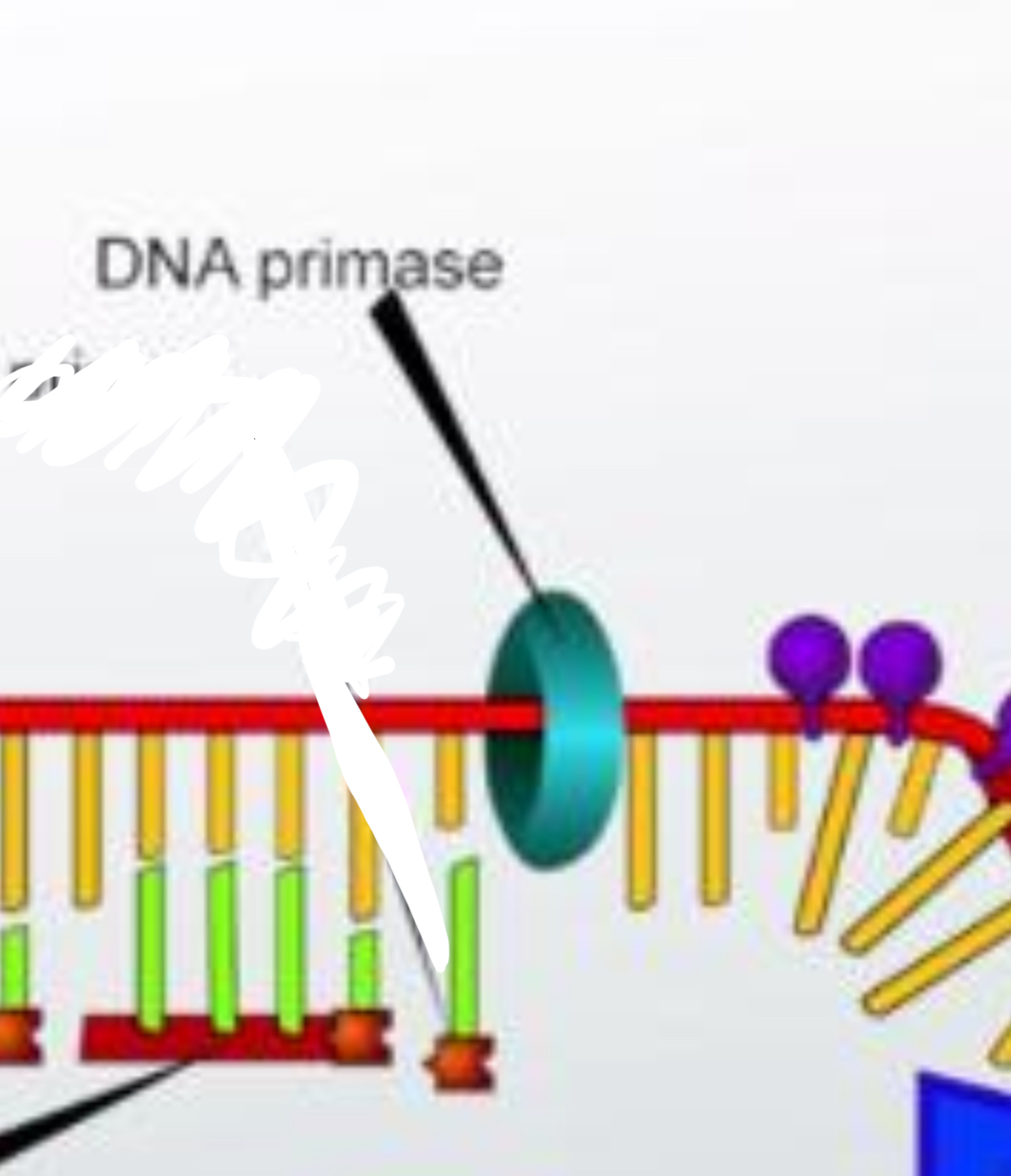
RNA Primer
a short strand of RNA, made by primase, that is used to elongate a strand of DNA during DNA replication.
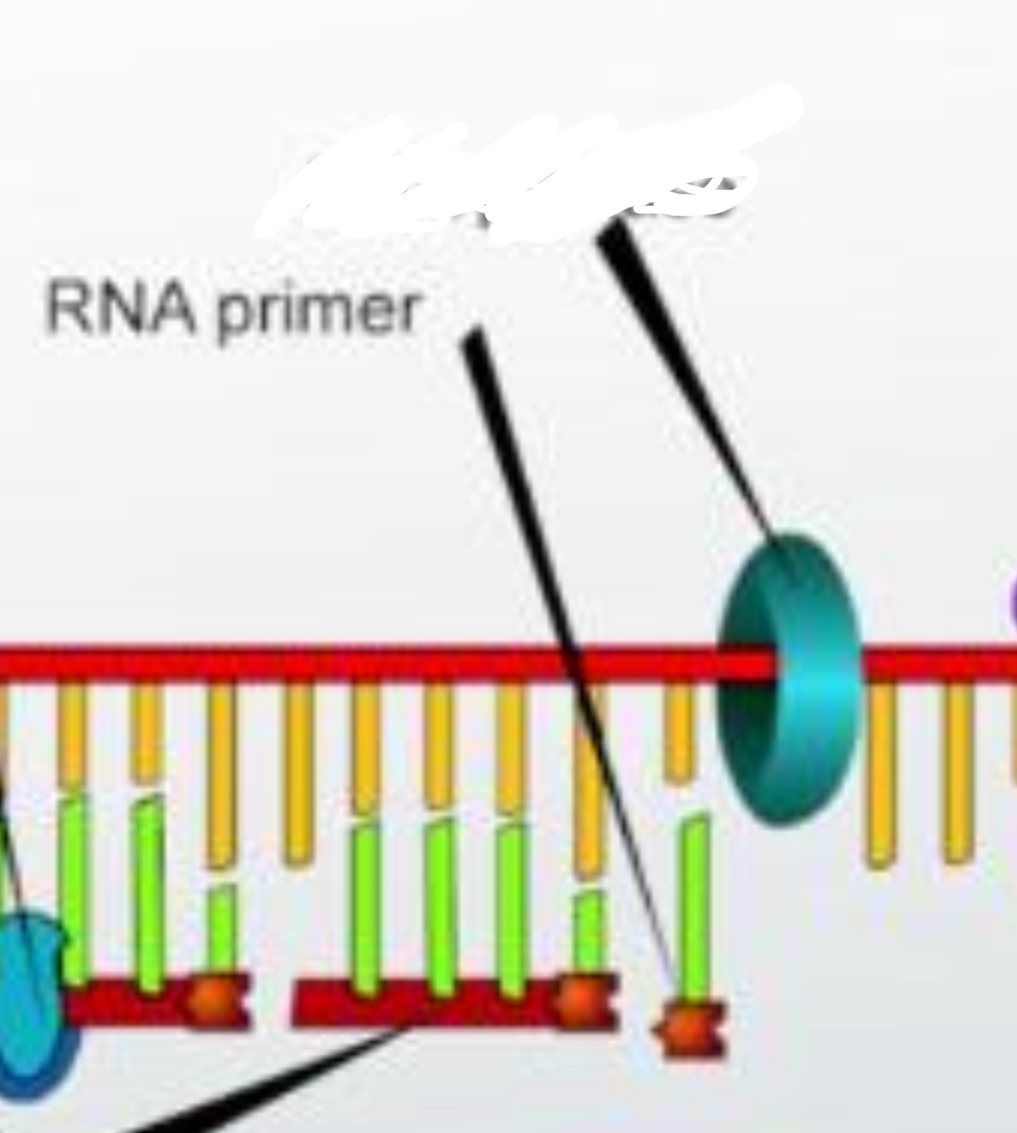
Helicase
an enzyme that separates the two strands of DNA.
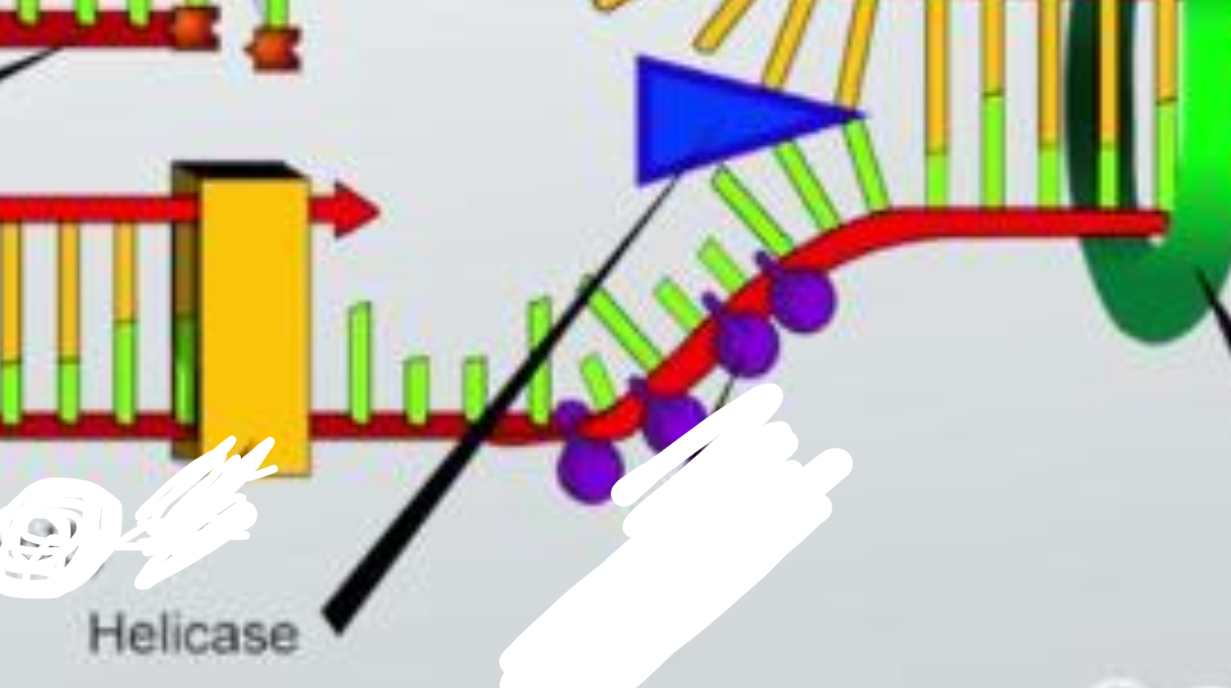
Single strand binding proteins
proteins that bind to both of the single strands of DNA during DNA replication and prevent them from re-forming a double helix.

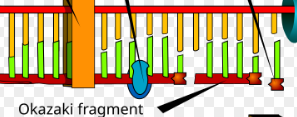
Okazaki Fragments
short segments of DNA that are synthesized to produce the lagging strand during DNA replication.
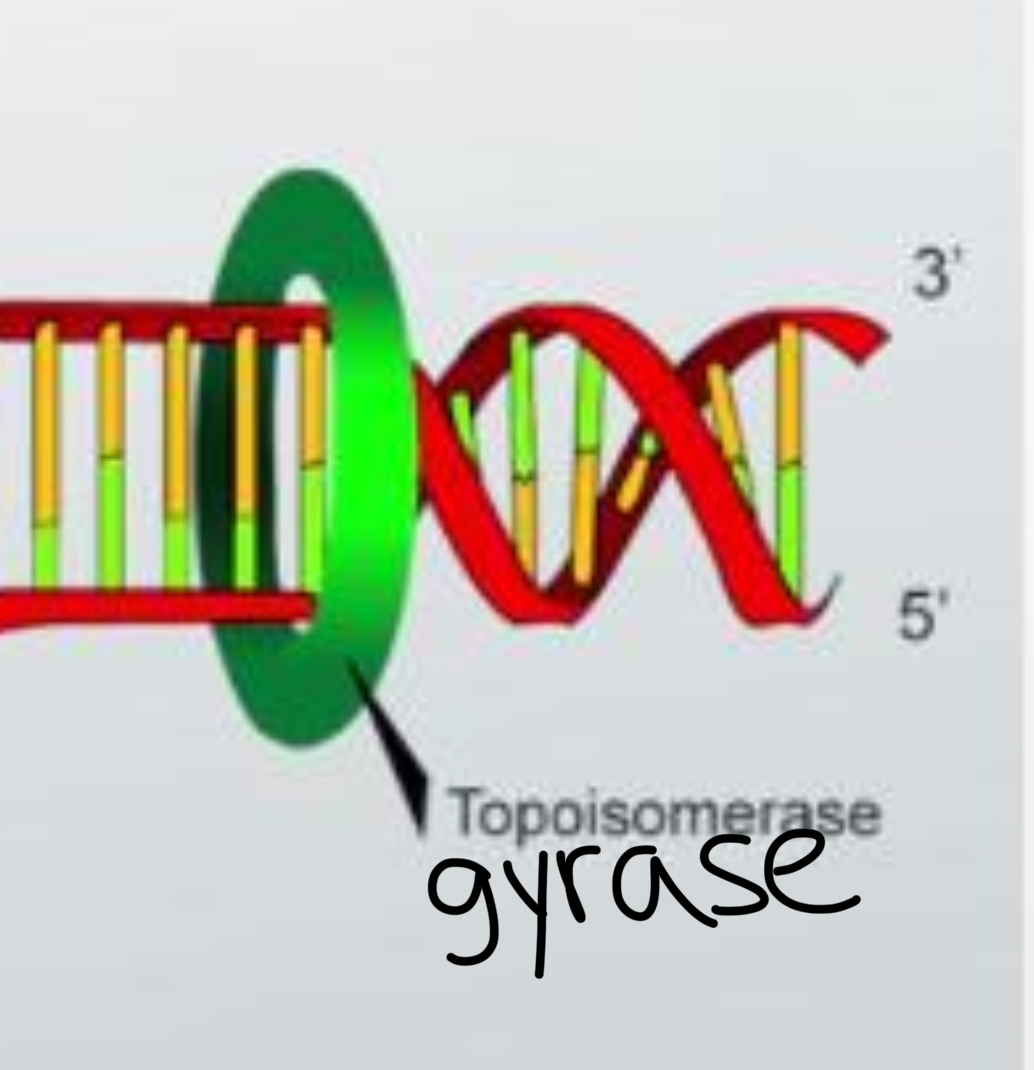
DNA Gyrase
an enzyme that introduces negative supercoils into DNA using energy from ATP and that can also relax positive supercoils when they occur.
Intron
noncoding intervening sequences.
Exon
a region of an RNA molecule that remains after splicing has removed the introns. is coding
what are the stages of central dogma
replication- DNA > transcription- RNA > translation- Protein
considering the structure of double-stranded DNA which kinds of bonds hold one complementary strand to the other
hydrogen bonds