Chemistry is Life - Biology
1/114
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Where is the proton located, w/ the charge?
Location: nucleus
Charge: Positive (+)
Where is the neutron located, w/ the charge?
Location: nucleus
Charge: Neutral (0)
Where the is electron located, w/ the charge?
Location: electron cloud/outside of nucleus
Charge: Negative (−)
Protons is the same number as the __
electrons
Atomic Number
# of protons in atom
Mass Number
# of prtons & neutrons in the atom
Elements
pure substances - one chemical
Isotope
unstable atom with more neutrons that usual
radioactive isotype
radiates due to a surplus of neutrons
Compound
2+ elements bonded
Molecule
group of atoms held by chemical bonds
First three levels of electrons?
2
8
8
Stable atom
When the outer electron level is full. Atoms want to achieve this.
Ionic bond
most likely bond by metal and a nonmetal. the metal gives their electrons to the nonmetals
Cation
Positive
Anion
negative
Covalent bond
chemical bonds. these bonds share pairs of electrons
What are the two types of covalent bonds?
nonpolar & polar
polar molecule
molecules w/ unequal distribution of electrical changes. partially negative, and partially positive, like water molecules.
In a hydrogen bond, which element is partially positive?
hydrogen
In a hydrogen bond, which element is partially negative?
oxygen
Cohesion
attraction by the same molecules
Surfance tension
water molecules resisting external forces
adhesion
attraction by different molecules
Capillarity
movement of liquid thought cohesion and adhesion
High Heat Capacity
absorbing large amount of energy by heat with small or no changes in temperature
Density
compactness of a substance
Why does ice float over water?
Density of ice is less dense that liquid water.
Solvent
large # of substances dissolved by a material
Mixture
two or more materials, elements, or compounds that are physically mixed, but not physically combined or chemically
Solution
ions becoming dispered in a material
Solute
The substance that is dissolved
Solvent
The substance that the solute is dissolved in
High heat of vaporization
How much heat is pulled from a surface when a substance evaporates
Suspension
mixture of water with a substance that cannot be dissolved in water
ph scale
scale w/ values that measures H+ ions
scale ranges from
0-14
Hydroxide Ion
-OH
Hydronium Ion
H3O
hydrogonium
when the # of hydrogen ions is greater than hydroxide ions, positive
Hydroxide
more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions
in the pH scale, where are the acids? what number is the strongest acid
left side, 0
in the pH scale, where are the bases? what number is the strongest bases
right side, 14
ph scale is measured in what quantity?
logarithmic scale
what # on the ph scale is neutral
7
Organic compound
any compund that has carbon
What type of covalent bonds can carbon form?
single, double, & triple
What does a hydroxyl/alcohol function group look like?
ends w/ -OH
Polar molecules are hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophilic, meaning soluble in water
Carbonyl group
carbon forming a double bond with an oxygen atom
what are the two types of carbonyl groups?
aldehyde & ketone
What does an aldehyde look like?
double bond oxygen at end of chain
C-C-C=O
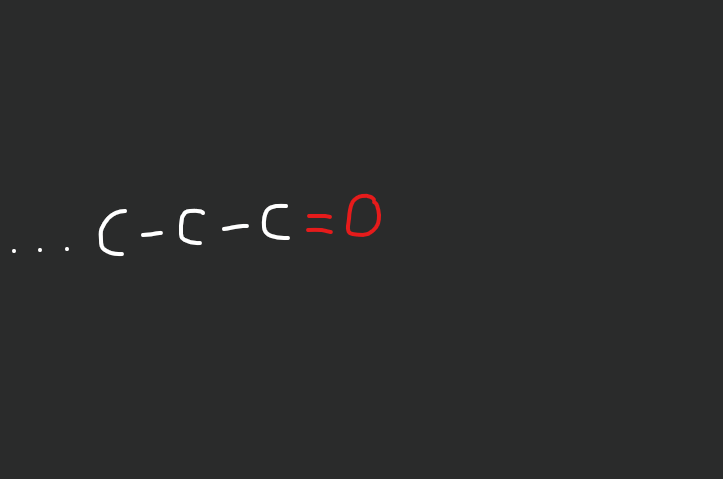
What does a ketone look like?
double bond oxygen in the middle of the chain (image on right)
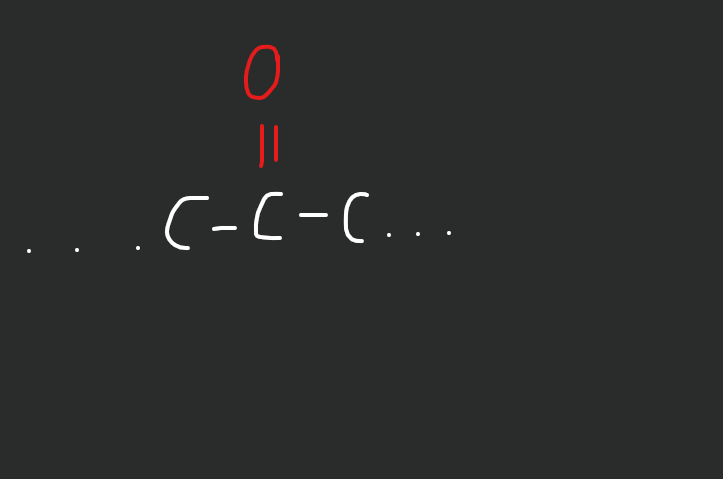
What does a sulfhydryl/thiol group look like?
sulfur and hydrogen
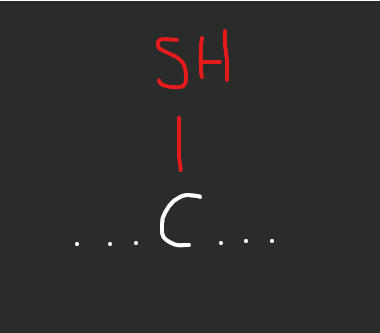
memorize this lil bro

Macromolecules
large molecules formed by combining smaller molecules
4 groups of macromolecules found in living things
Carbohydrates, lipids, protein, & nucleic acid
Monomers
molecules that can react with other molecules to form larger molecules
polymer
molecules made from repeating units of identical or nearly identical compounds
What is the compound for carbohydrates w/ their ratio
C:H:O
1:2:1
What is the compound for Lipids w/ their ratio
C:H:O
1:1:1
What is the compound for protein w/ their ratio
C:H:O:N sometimes S
1:1:1:1
What is the compound for nucleic acid w/ their ratio
C:H:O:N:P
1:1:1:1:1
what is dehydration synthesis?
monomers linked by a chemical reaction which removes water to form macromolecules. Goes from small to big.
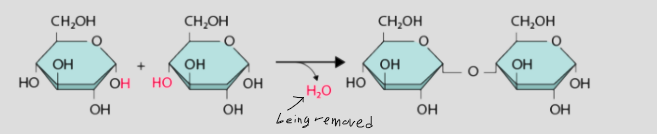
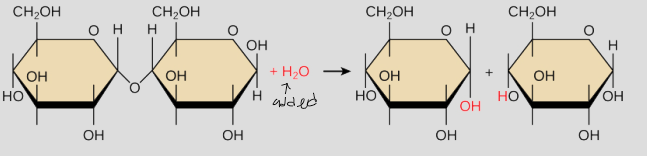
What is hydrolysis?
water molecule is added to break apart a polymer. Goes from big to small.
What do carbohydrates do?
provide energy
provide dietary fiber
important part of cell wall
Name at least one example of each:
1. monosaccharides
Disacchardies
Polysaccharied
Glucose, fructose, galactose
sucrose, lactose, maltose
glycogen, starch, cellulose, chitin
fun fact! chitlin is found in exoskeletons
What do lipids do?
Provide long term energy
important part of cell membrane
What are the monomers of lipids?
fatty acid chains & glycerol
identify the two main parts of this lipid
1.glycerol
fatty acid tail
Examples of lipids
Fats, oils, waxes
Saturated fatty acid are good or bad for you?
bad
unsaturated fatty acid are good or bad for you?
good
Proteins are formed by
amino acids
what bond are in amino acids?
peptide bond
How many different amino acids are there?
20
What differentiates the amino acid?
the “R”/side chain
Examples of protein in the body
Collagen
structural proteins
antibodies
hemoglobin
enzymes
Side chains can be: (type of bond)
polar
nonpolar
charged/ionic
Primary level of protein structure
Linear chain of amino acids
Secondary level of protein structure
starts to become 3d and folds due to hydrogen bonding by polypeptides
tertiary level of protein structure
3d between side chains and amino acids
hydrophobic interactions
covalent bonds are formed
quaternary level of protein structure
association of two or more polypeptides
found in a few proteins
what makes up nucleic acids
long chain of molecules called nucleotides
nucleotides
monomers of nuclear acid, has 3 basic parts
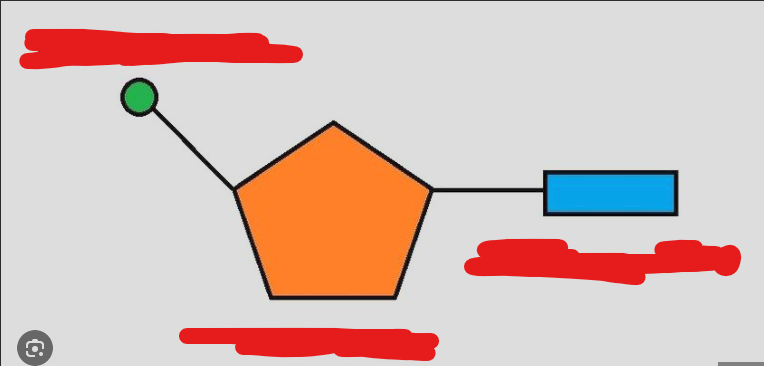
identify each nucleotide
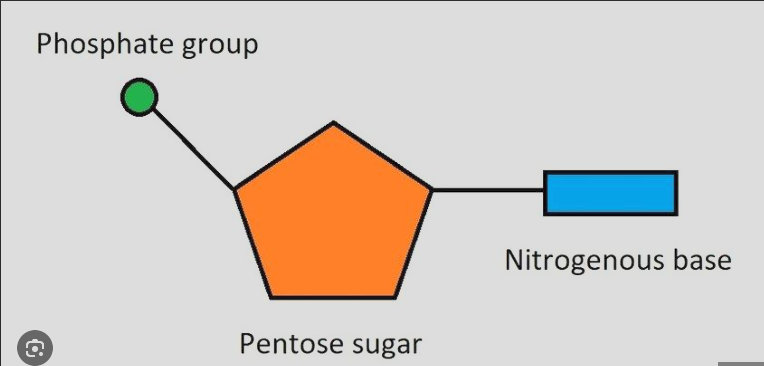
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
What is the job of a nucleic acid?
store and trasmit genetic information
direct synthesis of new proteins
Give examples of chemical reaction
burning, rotting, rusting, ect.
After reactants, the outcome is the?
products
In the flow of energy, when energy is absorbed into the reaction, that is called
endergonic
in the flow of energy, when energy is released from the reaction, that is called
exergonic
activation energy is
minimum amount of energy needed for reactions to form products in a chemical reaction
catalyst is
substance that speeds up rate of chemical reaction.
is not consumed by reaction
enzymes
catalyst that takes place in cell walls
most enzymes are proteins
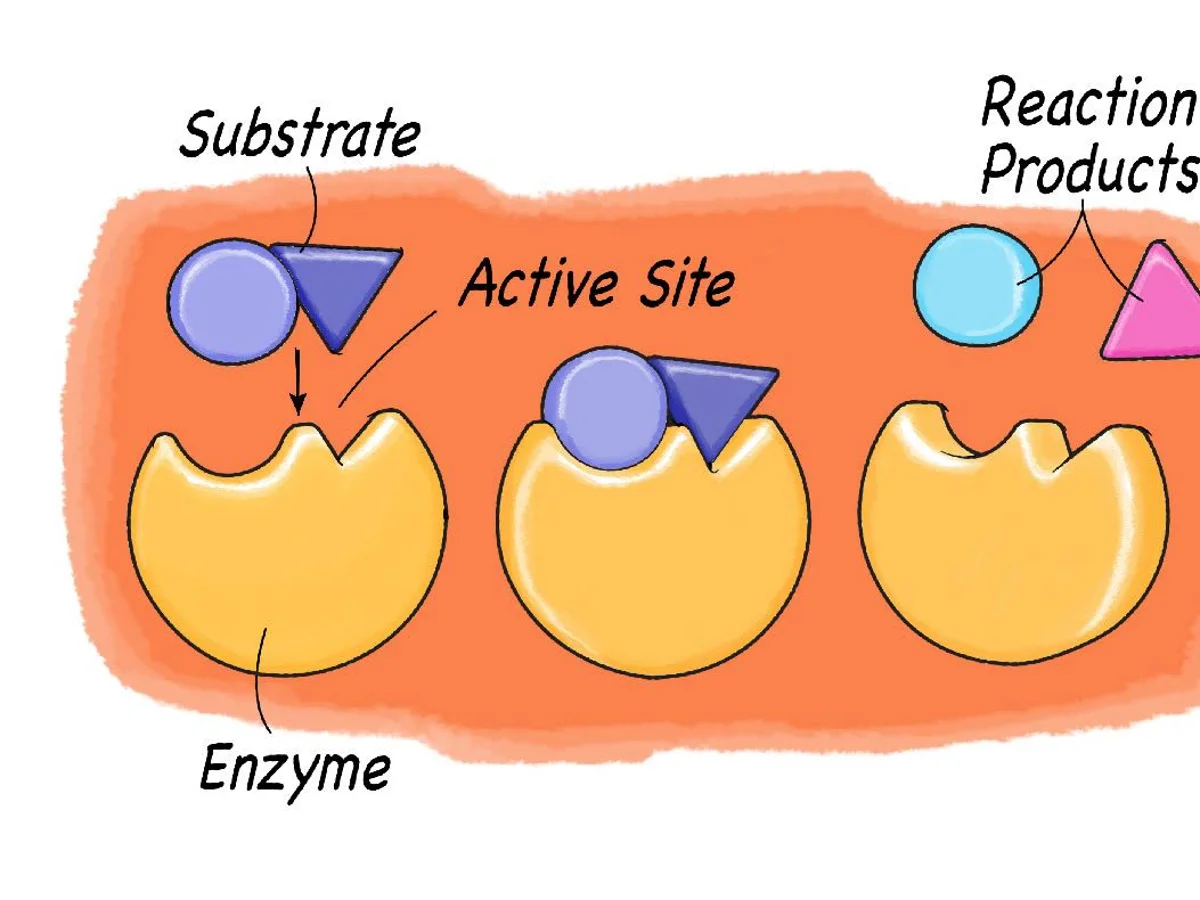
substrate
reactant of enzymes
active site
where the substrate and enzyme connect
enzyme specificity
the fact that substrates can fit into specific enzymes
what is denaturation?
when an enzyme will not work because of change of structure
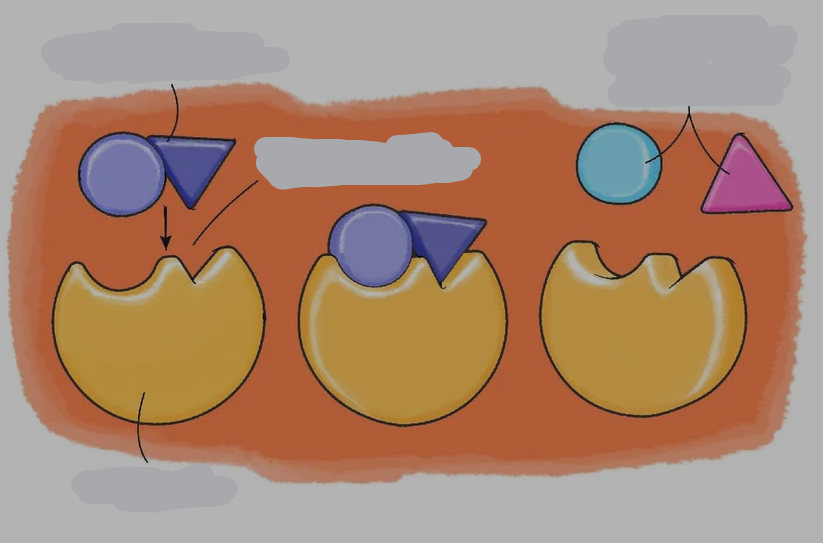
identify parts of this diagram