Measures and factors influencing Growth and Development in the global economy
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Human Development Index / HDI
An indicator of the level of development for each country, constructed by the United Nations, it is a composite index based on education (Years of attainment), literacy, health (Life expectancy) and income (Real GNI per head).
IHDI
Modification of the HDI to account for inequality within a country. As inequality rises, a bigger percentage deflator is attached to the initial HDI index number to account for the loss in human development. The difference between HDI and IHDI shows this loss.
Economic Development
When different parameters of economic life, such as QOL or SOL of an individual, community, region or nation are improved in accordance with targets and objectives. The quality of growth, not the quantity of growth.
Economic Growth
An increase in the amount of goods and services produced per head of the population over a period of time. The quantity of growth, not the quality of growth.
Standard of Living
The degree of wealth and material comfort available to a person or community.
LEDC
Less economically developed country: a country with a low HDI, low to moderate industrialisation and low to moderate average PPP per capita.
NIC
Newly Industrialised Country, recently attained a high level of development following industrialisation policies, examples include Taiwan, Argentina, Mexico.
MEDC
More economically developed country: a highly industrialised country, world-leading technological infrastructure with high average PPP per capita and HDI.
BRIC Economies
The BRIC grouping - Brazil, Russia, India and China, and later South Africa - short hand for the rise of emerging markets. The BRICs have a bigger share of world trade than the USA
MINT Economies
Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria and Turkey. Emerging economic giants which are classified in this group due to shared large populations, rapidly growing economies, and increasing global importance due to commodity production.
Tiger Economies
Fast-growing economies of Southeast Asia, including Hong Kong, South Korea, Singapore, and Taiwan.
Constraints to growth and development
Primary product dependency, volatility of commodity prices, savings gap, foreign currency gap, capital flight, demographic factors, debt, credit access, infrastructure, education, absence of property rights.
Hard Commodity
Non-renewable commodities which are mined or extracted such as coal and oil.
Soft Commodity
Renewable commodities that are more agriculturally based.
Primary Product Dependency
When a country is too heavily reliant on primary products as a driver of economic growth, which leaves them, and their economic development crucially, at the mercy of volatile commodity prices. This is often due to a lack of diversification. This is often measured as the % of commodity sold as per GDP, exports and employment.
Buffer Stock Schemes
One way to smooth out the volatile fluctuations of commodities, the government to operates price support schemes through the use of buffer stocks. These schemes seek to stabilise the market price of agricultural products by buying up supplies of the product when harvests are plentiful and selling stocks of the product onto the market when supplies are low, in order to stabilise the price of the product.
OPEC (Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries)
An organisation of countries formed in 1961 to agree on a common policy for the production and sale of petroleum. They are an exception to the PPD rule as they are actually heavily significant on the major oil market price. They have 80% of the world's crude oil reserves and 40% of the world's oil production.
Resource Curse
The difficulties faced by resource-rich developing countries, including dependence on exporting one or a few commodities whose prices fluctuate, as well as potentials for corruption and inequality.
Deindustrialisation
Loss of manufacturing base as a result of a sharp rise in the value of the domestic currency, making the economy less internationally competitive in the secondary industry.
Terms of Trade
the relationship between a country's export prices and its import prices. An increase in this is known as an improvement, a decline known as a worsening. (index of average price of export / index of average price of imports) x 100.
Prebisch-Singer Hypothesis
The argument that countries exporting primary commodities will face declining terms of trade in the long run, which will trap them in a low level of development, and a worsening financial account as more and more exports will need to be sold to 'pay for' the same volume of imports of secondary sector or capital goods. This is due to a higher rise in the prices of imports involving manufactured goods or services due to a higher YED.
Human Capital
the skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience
Brain Drain
The loss of highly educated and skilled workers to other countries, this is often from a low HDI country to a high HDI country.
Infrastructure
Physical capital used for transportation and communication purposes.
Dependency Ratio
The number of people who are too young or too old to work, compared to the number of people in their productive years
Credit
the ability of a customer to obtain goods or services before payment, based on the trust that payment will be made in the future, usually in return for interest.
Collateral
An asset or something pledged as security for repayment of a loan, to be forfeited in the event of a default.
Savings Gap
The difference between the level of savings needed to finance investment for growth by banks and the actual level of savings
Harrod-Domar model
A model of economic growth that emphasises the importance of savings and investment in a positive feedback loop. Savings is at the heart of growth and development. However, dependent on the effect of interest rates which incentivise the saving, on borrowing.
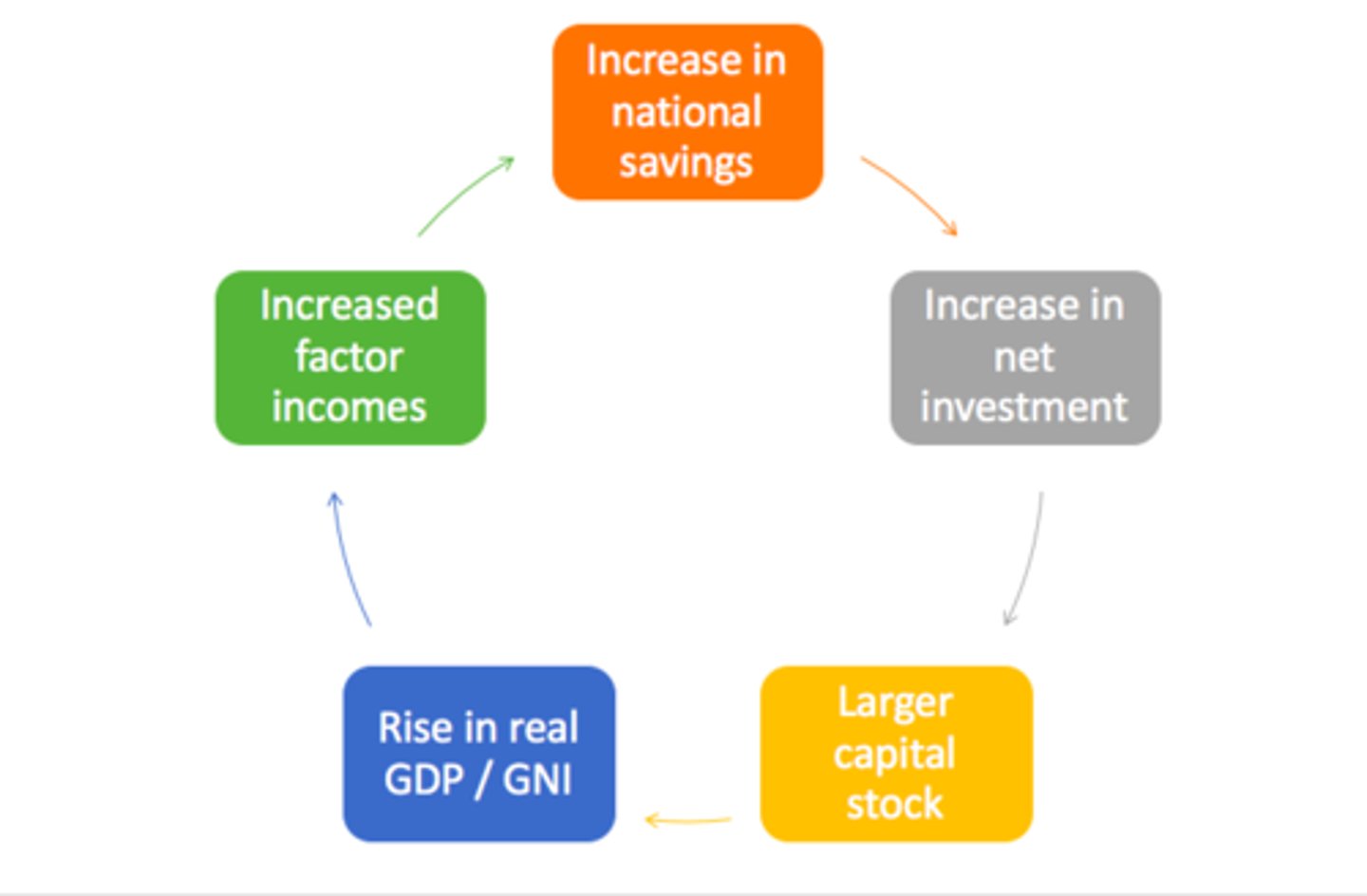
Capital Flight
In Africa, this is 10x the size of inward foreign aid and investment. When savings and assets are sent abroad, through the purchase of foreign assets and currencies, by citizens and firms of a country to another country which is seen as more secure or where the money can be hidden from governments.
Capital Control
any restriction that limits or alters the rate or direction of capital movement into or out of a country. Restrictions can be on capital inflows (foreigners acquiring domestic assets) and capital outflows (us acquiring foreign assets)
Currency Control
Restrictions on foreign currency transactions used by some developing countries; limits on foreign currency that can be bought and sold.
Expropriation
A government's seizure of a domestic or foreign company's assets and private property deemed to be in the national interest without the consent of the company. Leads to investment becoming disincentivised as owners may fear expropriation in the future.
Appropriation
Taking assets with consent of the company you're taking it from, often with compensation.
Patent
Exclusive rights over an idea or invention.
Foreign Currency Gap
Situation often happening to PPD countries when a country does not export enough to finance the purchase of goods from overseas which it needs to create higher economic growth and development. This is because they face a shortage of the amount of foreign currency needed to pay for these imports.
Debt Relief
The partial or total remission of debts, especially those owed by developing countries to external creditors.
Debt Rescheduling
an agreement between a lending nation and a debtor nation that lengthens the time of debt repayment and forgives part of the loan
Dutch Disease
The negative impact on an economy of anything that gives rise to a sharp inflow of foreign currency, such as the discovery of large oil reserves. The currency inflows lead to currency appreciation, making the country's other products less price competitive on the export market.
Capital Accumulation
the growth of capital resources, which includes human capital, funded by investment as per the Harrod-Domar model.
Poverty trap
self-reinforcing mechanisms that cause the poor to stay poor