Radioactivity (general)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is proton / atomic number and nucleon / mass number respectively?
Proton → no. of protons in an atom
Nucleon → total no. of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom
Define nuclides
Atoms of a specific no. of neutrons and protons
Define isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
Define nuclear / radioactive decay
A random process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses its energy by emission of electromagnetic radiation or particles
Radiation is spontaneous and random in direction
How does an atomic nucleus become unstable?
Nuclear forces within the nuclei are unable to bind the nucleons together
What factors remain the same before and after nuclear reaction?
Total no. of protons and neutrons
Total relative charge
What is alpha decay?
Nucleus emits an alpha particle identical to helium nucleus 4/2 He
The nucleon number decreases by 4 and the proton number decreases by 2
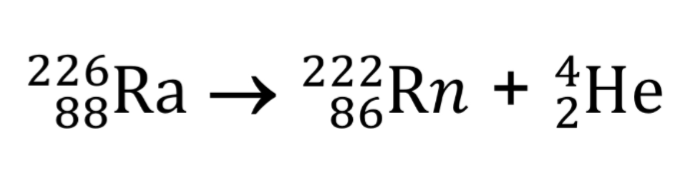
What is beta decay?
Nucleus emits a beta particle (electron)
Nucleon number remains the same and proton number increases by 1
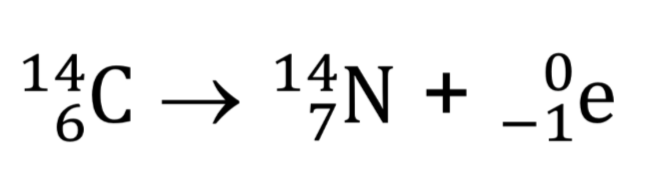
What is gamma radiation?
When a nuclei undergo alpha or beta decay, gamma radiation is also emitted
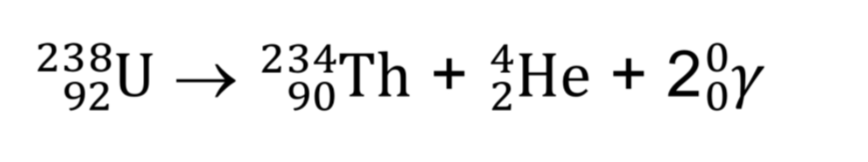
Define ionisation
The ability of an atom to eject electrons from atoms to form ions
What is the nature of alpha particles?
2 protons and 2 neutrons tightly bound together
Identical to a helium nucleus
What is the relative ionizing effect and relative penetrating ability of alpha particles?
Ionizing effect → highest
Penetrating ability → least
They are easily absorbed by a piece of paper
What is the nature of beta particles?
A fast-moving electron ejected from radioactive nucleus
What is the relative ionizing effect and relative penetrating ability of beta particles?
Ionizing effect → medium
Penetrating ability → medium
Absorbed by aluminium a few meters away
What are gamma rays?
Electromagnetic radiation emitted by a radioactive nucleus with excess energy
What is the relative ionizing effect and relative penetrating ability of gamma rays?
Ionizing effect → lowest
Penetrating ability → highest
Pass through most materials easily
Absorbed by lead that is a few cm thick or very thick concrete
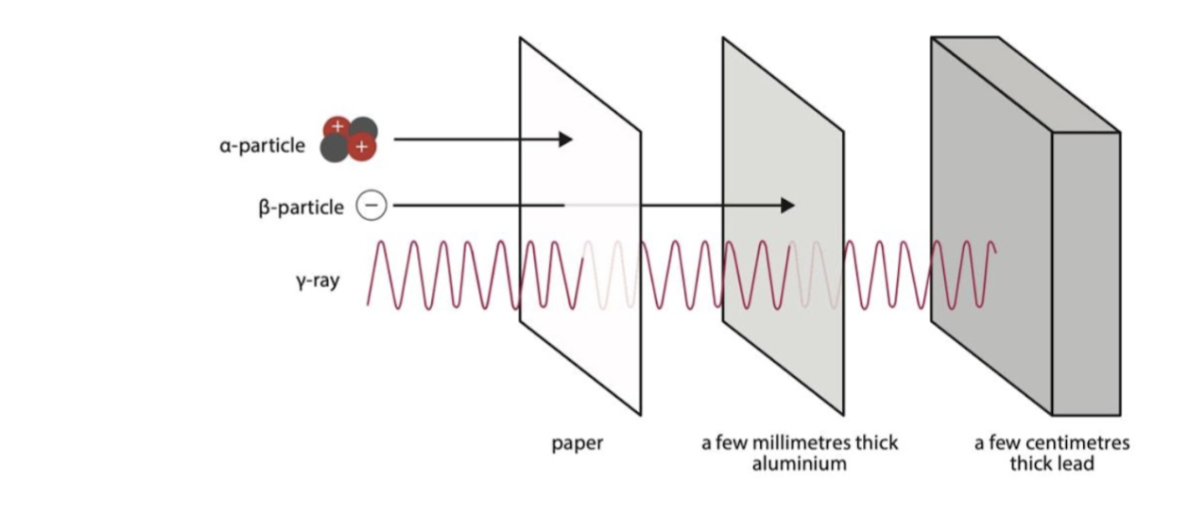
Define background radiation
Nuclear radiation in an environment where no radioactive source is deliberately introduced
What are natural and artificial sources of radiation?
Artificial
Medical rays
Building materials
Waste products from nuclear power stations
Natural
Rocks
Radon gas in the air
Food and drink with radioactive elements
Define ionizing radiation
Radiation with high energies that can knock off electrons from atoms to form ions e.g. UV rays, X rays, gamma rays
Where can non-ionizing radiation be found?
Visible light and infra-red radiation from the sun
Microwaves and radio waves in communication systems
How can background radiation be measured?
Using a GM (Geiger-Muller) counter
SI: Bq (Becquerel) / rate of counts per unit time / count rate
Remove all radioactive sources
Start the counter and stopwatch
Stop the counter after 10min and record counts per minute
*BG radiation should be first measured then subtracted from measurements
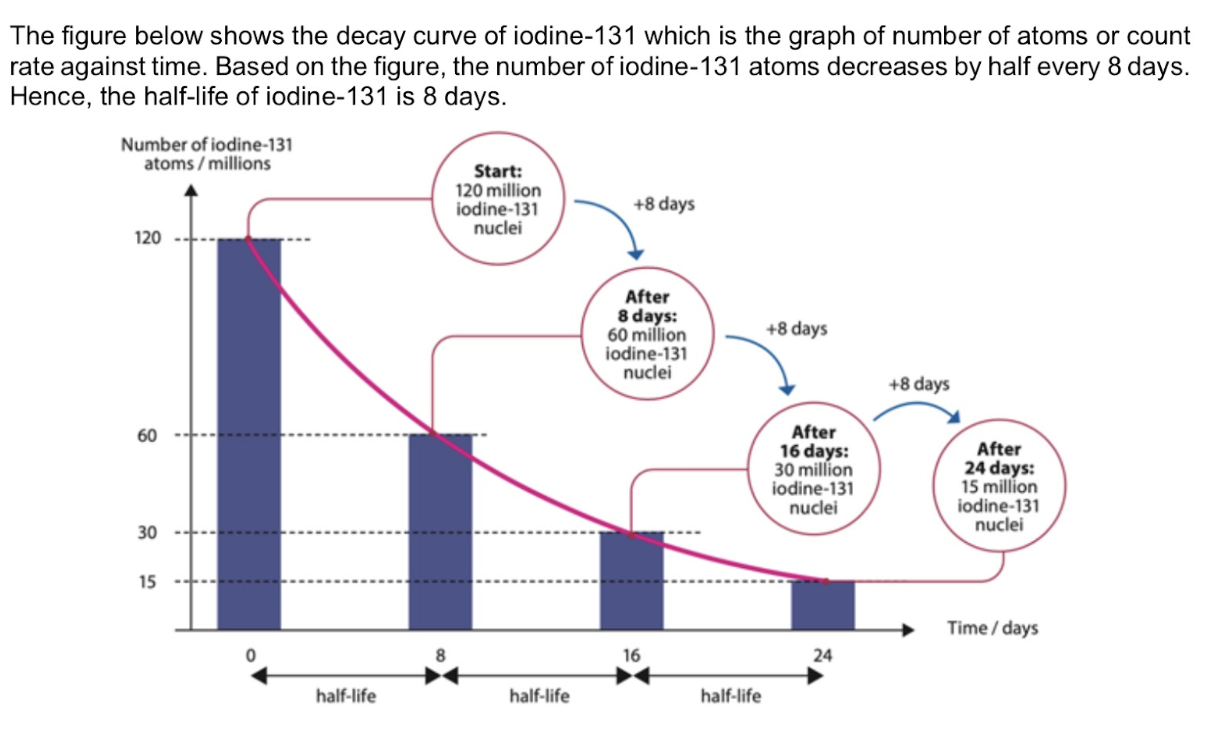
Define half-life of a radioactive nuclide
Time taken for half the nuclei of the sample to decay
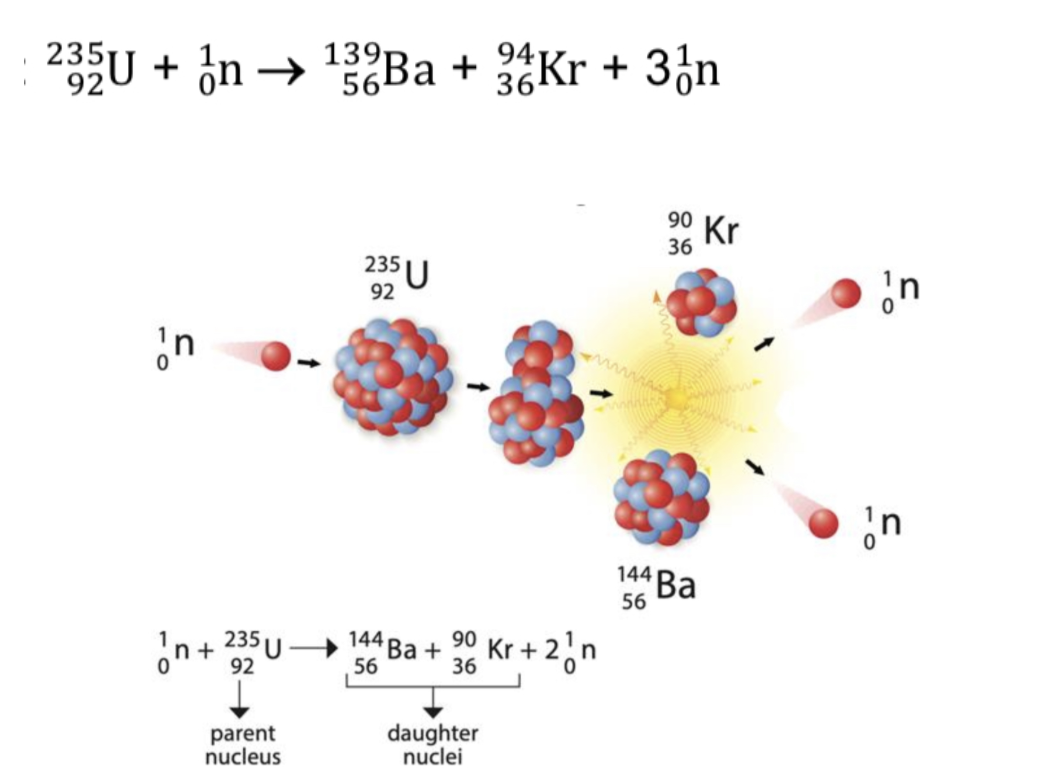
Define nuclear fission
A process in which the nucleus of an atom splits and releases a huge amount of energy
What is nuclear fuel?
A material used in nuclear power stations that undergoes nuclear reactions to release energy
What happens during nuclear fission?
Parent nucleus decays to form daughter nuclei which may decay or be stable
Neutrons produced will go on to split more nuclei in a self-sustaining chain reaction controlled in a nuclear reactor
Where is energy from the nuclear store of the unstable nucleus transferred to during nuclear fusion?
Kinetic, internal and nuclear stores of the daughter nuclei / bigger nucleus
Internal store of the surrounding media
Used to heat water so that in changes into steam
Can be used in the electrical power generation process
Define nuclear fusion
A process in which 2 light atomic nuclei combine to form one heavier atomic nucleus and release a huge amount of energy
Why is a lot of work done during nuclear fusion?
Nuclei of atoms are positively charged and it is difficult for 2 nuclei to combine as like charges repel
A lot of work is done to overcome the repulsive forces between nuclei
Requires very high temperature and pressures
*Once combined, the nuclear forces hold the nucleus together
Where is energy from the nuclear
2 nuclei ca