Chapter 19: Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Recombination
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:02 AM on 2/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
mutation
a permanent change in the genetic material that can be passed from cell to cell or, if it occurs in reproductive cells, from parent to offspring
2
New cards
allelic
mutations provide _____ variation
3
New cards
evolutionary, adapt
mutations are the foundation for _____ change
* provide the variation that enables species to _____ to their environment via natural selection
* provide the variation that enables species to _____ to their environment via natural selection
4
New cards
harmful, diseases
new mutations can be _____ to the individual and often are the cause of _____
5
New cards
chromosome mutation
big changes in chromosome structure
6
New cards
genome mutation
changes in chromosome number
7
New cards
gene mutation
relatively small changes in DNA structure that affects a single gene
8
New cards
point mutations
a change in a single base pair within DNA
9
New cards
base substitution
a point mutation in which one base is substituted for another
10
New cards
transition
a point mutation involving a change of a pyrimidine to another pyrimidine (ex. C to T) or a purine to another purine (ex. A to G)
11
New cards
transversion
a point mutation in which a purine is interchanged with a pyrimidine, or vice versa
12
New cards
silent mutation
a mutation that does not alter the amino acid sequence of the encoded polypeptide even though the base sequence has changed
13
New cards
degenerate, third
because the genetic code is _____, silent mutations can occur in certain bases within a codon, such as the _____ base, and the specific amino acid is not changed
14
New cards
missense mutation
a base substitution that leads to a change in the amino acid sequence of the encoded polypeptide
15
New cards
nonsense mutation
a mutation that involves a change from a normal codon to a stop codon. This change terminates the translation of the polypeptide earlier than normal, producing a truncated polypeptide.
16
New cards
frameshift mutation
a mutation that involves the addition or deletion of a number of nucleotides not divisible by 3. Because the codons are read in multiples of 3, this type of mutation shifts the reading frame. The translation of the mRNA then results in a completely different amino acid sequence downstream from the mutation.
17
New cards
reduced, enhanced
except for silent mutations, new mutations are more likely to produce polypeptides that have _____ rather than _____ function
18
New cards
neutral mutation
a missense mutation that has no detectable effect on protein function or no detectable effect on the survival of the organism
19
New cards
neutral
a missense mutation that substitutes an amino acid with a chemistry similar to that of the original amino acid is likely to be _____
20
New cards
enhanced, greater, natural selection
A mutation can occasionally produce a polypeptide with an _____ ability to function. Although such a favorable mutation is relatively rare, it may result in an organism with a _____ likelihood of surviving and reproducing. If this is the case, _____ _____ may cause the favorable mutation to increase in frequency within a population.
21
New cards
non-coding
a mutation can occur within a _____ sequence, thereby affecting gene expression (promoter and regulatory regions)
22
New cards
up promoter mutation
a mutation in a promoter that increases the rate of transcription
23
New cards
down promoter mutation
a mutation in a promoter that decreases the rate of transcription
24
New cards
wild type
a relatively prevalent genotype in a natural population
25
New cards
mutant allele
an allele that has been created by altering a wild-type allele by mutation
26
New cards
forward mutation
a mutation that changes the wild-type genotype into some new variation
27
New cards
reverse mutation
a mutation that changes a mutant allele back to a wild-type allele
28
New cards
deleterious mutation
* a mutation that is detrimental with regard to its effect on phenotype
* decreases the chances of survival and reproduction
* decreases the chances of survival and reproduction
29
New cards
lethal mutation
* a mutation that produces an allele that results in the death of a cell or an organism
* extreme example of a deleterious mutation
* extreme example of a deleterious mutation
30
New cards
beneficial mutation
a mutation that enhances the survival or reproductive success of an organism
31
New cards
conditional mutant
a mutant whose phenotype depends on the environmental conditions, such as temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant
32
New cards
suppressor mutation
a mutation at a second site that suppresses the phenotypic effects of another mutation
33
New cards
intragenic, intergenic
two types of suppressor mutations
34
New cards
intragenic suppressor
a suppressor mutation that is within the same gene as the first mutation that it suppresses
35
New cards
inhibits, same, restores
intragenic suppressor:
* mutation 1: _____ protein function
* mutation 2: occurs in _____ protein and _____ protein function
* mutation 1: _____ protein function
* mutation 2: occurs in _____ protein and _____ protein function
36
New cards
intergenic suppressor
a suppressor mutation that occurs in a different gene than the gene that contains the first mutation
37
New cards
inhibits, another
intergenic suppressor:
* mutation 1: _____ protein function
* mutation 2: alters _____ protein to perform that function
* mutation 1: _____ protein function
* mutation 2: alters _____ protein to perform that function
38
New cards
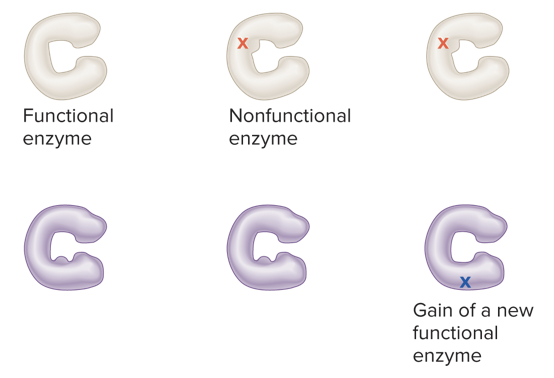
inhibits, different
redundant function (intergenic suppressor):
* a first mutation _____ the function of a protein, and a second mutation alters a _____ protein to carry out that function
* a first mutation _____ the function of a protein, and a second mutation alters a _____ protein to carry out that function
39
New cards
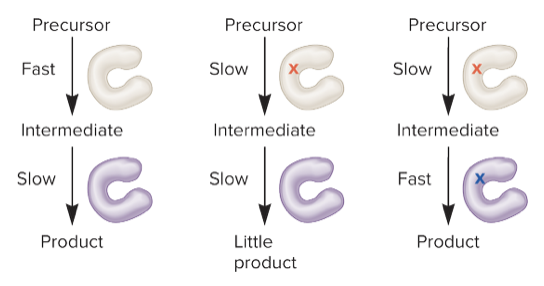
defect, increases
common pathway (intergenic suppressor):
* two or more different proteins may function as enzymes in a common pathway
* a mutation that causes a _____ in one enzyme may be compensated for by a mutation that _____ the function of a different enzyme in the same pathway
* two or more different proteins may function as enzymes in a common pathway
* a mutation that causes a _____ in one enzyme may be compensated for by a mutation that _____ the function of a different enzyme in the same pathway
40
New cards
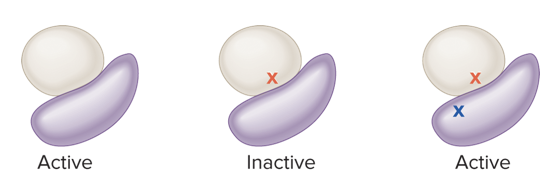
inhibits, suppressed
multimeric protein (intergenic suppressor):
* a mutation in a gene encoding one protein subunit that _____ function may be _____ by a mutation in a gene that encodes a different subunit
* a mutation in a gene encoding one protein subunit that _____ function may be _____ by a mutation in a gene that encodes a different subunit
41
New cards
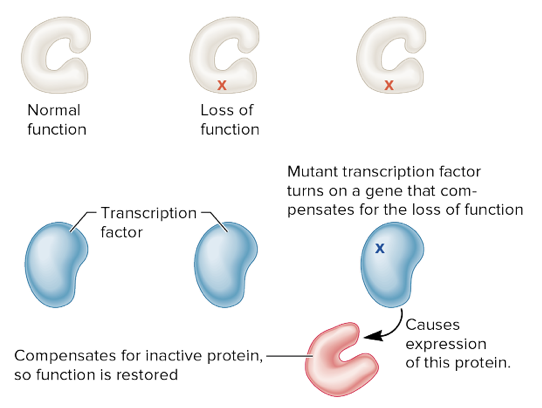
loss, activate
transcription factor (intergenic suppressor):
* a first mutation causes _____ of function of a particular protein
* a second mutation may alter a transcription factor and cause it to _____ the expression of another gene
* this other gene encodes a protein than can compensate for the loss of function causes by the first mutation
* a first mutation causes _____ of function of a particular protein
* a second mutation may alter a transcription factor and cause it to _____ the expression of another gene
* this other gene encodes a protein than can compensate for the loss of function causes by the first mutation
42
New cards
breakpoint
a region where two chromosome pieces break apart and rejoin with other chromosome pieces
43
New cards
position effect
a change in phenotype that occurs when the location of a gene changes from one chromosomal site to a different one
44
New cards
inversion
* type of position effect
* a gene may be moved next to regulatory sequences for a different gene, such as silencers or enhancers, and those then influence the expression of the relocated gene
* a gene may be moved next to regulatory sequences for a different gene, such as silencers or enhancers, and those then influence the expression of the relocated gene
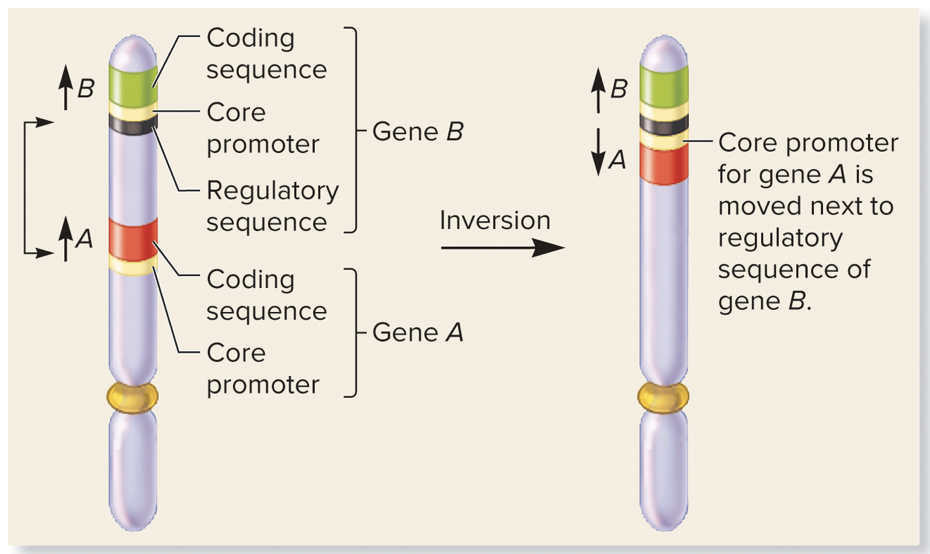
45
New cards
translocation
* type of position effect
* a chromosomal rearrangement may reposition a gene from a less condensed, or euchromatic region of the chromosome, where it is active, to a very highly condensed, or heterochromatic region of a chromosome, where its expression may be turned off
* a chromosomal rearrangement may reposition a gene from a less condensed, or euchromatic region of the chromosome, where it is active, to a very highly condensed, or heterochromatic region of a chromosome, where its expression may be turned off
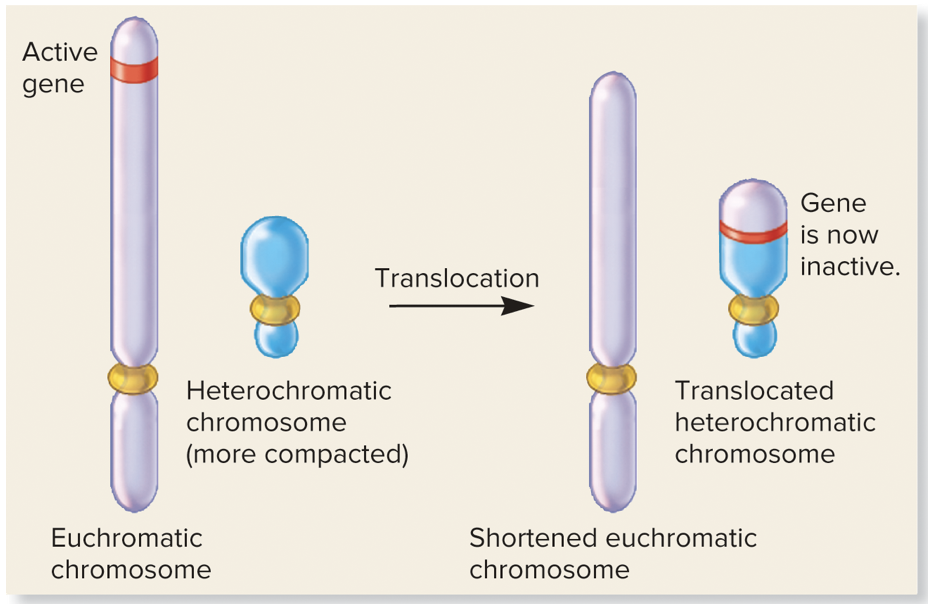
46
New cards
germ-line and somatic
two types of animal cells
47
New cards
germ-line
refers to cells that give rise to gametes
48
New cards
germ-line mutation
a mutation in a sperm or egg cell, or in a precursor cell that produces the gametes
49
New cards
entire, half, can
germ-line mutation → mutation is found throughout the _____ body → _____ of the gametes carry the mutation → _____ be passed down
50
New cards
somatic cell
any cell of the body except for gametes and germ-line cells that give rise to gametes
51
New cards
somatic mutation
a mutation in a somatic cell
52
New cards
portion, none, cannot
somatic mutation → _____ of the body contains the mutation → _____ of the gametes carry the mutation → _____ be passed down
53
New cards
spontaneous mutation
a change in DNA structure that results from natural biological or chemical processes
54
New cards
depurination
* type of spontaneous mutation
* the removal of a purine base (adenine or guanine) from DNA
* the removal of a purine base (adenine or guanine) from DNA
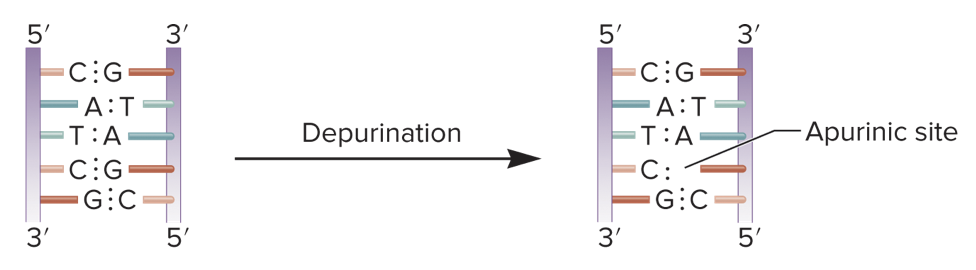
55
New cards
purine, covalent, unstable, apurinic, 75%
depurination:
* the removal of a _____ base from DNA
* the _____ bond between deoxyribose and a purine base is somewhat _____ and occasionally undergoes a spontaneous reaction with water that releases the base from the sugar, thereby creating an _____ site
* replication across from AP site has a _____ chance of being a mutation during DNA replication
* becomes a mutation if repair system fails to fix the apurinic site and during DNA replication
* the removal of a _____ base from DNA
* the _____ bond between deoxyribose and a purine base is somewhat _____ and occasionally undergoes a spontaneous reaction with water that releases the base from the sugar, thereby creating an _____ site
* replication across from AP site has a _____ chance of being a mutation during DNA replication
* becomes a mutation if repair system fails to fix the apurinic site and during DNA replication
56
New cards
apurinic site
a site in DNA that is missing a purine base
57
New cards
any
resulting mutation of depurination:
* because a complementary base is not present to specify the incoming base for the new strand at the apurinic site, _____ of the four bases are added to the new strand in the region that is opposite the apurinic site
* because a complementary base is not present to specify the incoming base for the new strand at the apurinic site, _____ of the four bases are added to the new strand in the region that is opposite the apurinic site
58
New cards
deamination
* type of spontaneous mutation
* the removal of an amino group from a cytosine base to produce uracil
* the removal of an amino group from a cytosine base to produce uracil
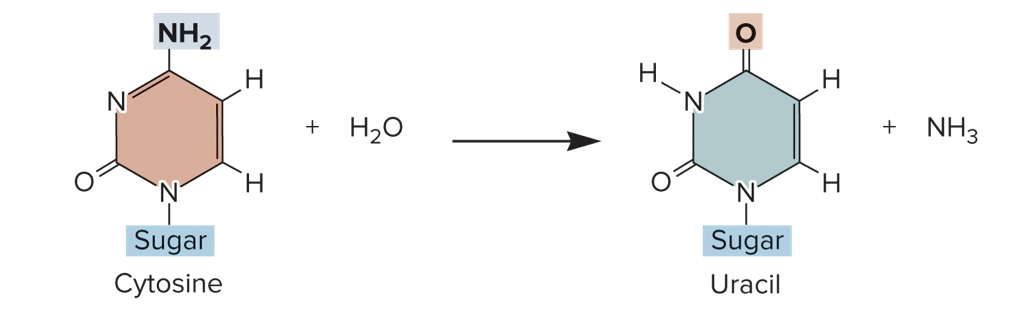
59
New cards
amino, cytosine, uracil, adenine, guanine
deamination:
* the removal of an _____ group from the _____ base to produce _____
* if repairing does not take place, a mutation may result because uracil hydrogen bonds with adenine during DNA replication
* if a DNA template strand has uracil instead of cytosine, a newly made strand will incorporate _____ instead of _____
* the removal of an _____ group from the _____ base to produce _____
* if repairing does not take place, a mutation may result because uracil hydrogen bonds with adenine during DNA replication
* if a DNA template strand has uracil instead of cytosine, a newly made strand will incorporate _____ instead of _____
60
New cards
adenine, guanine
resulting mutation of deamination:
* if a DNA template strand has uracil instead of cytosine, a newly made strand will incorporate _____ instead of _____
* if a DNA template strand has uracil instead of cytosine, a newly made strand will incorporate _____ instead of _____
61
New cards
tautomeric shift
* type of spontaneous mutation
* a temporary change in chemical structure, such as an alternation between the keto and enol forms of the bases that are found in DNA
* a temporary change in chemical structure, such as an alternation between the keto and enol forms of the bases that are found in DNA
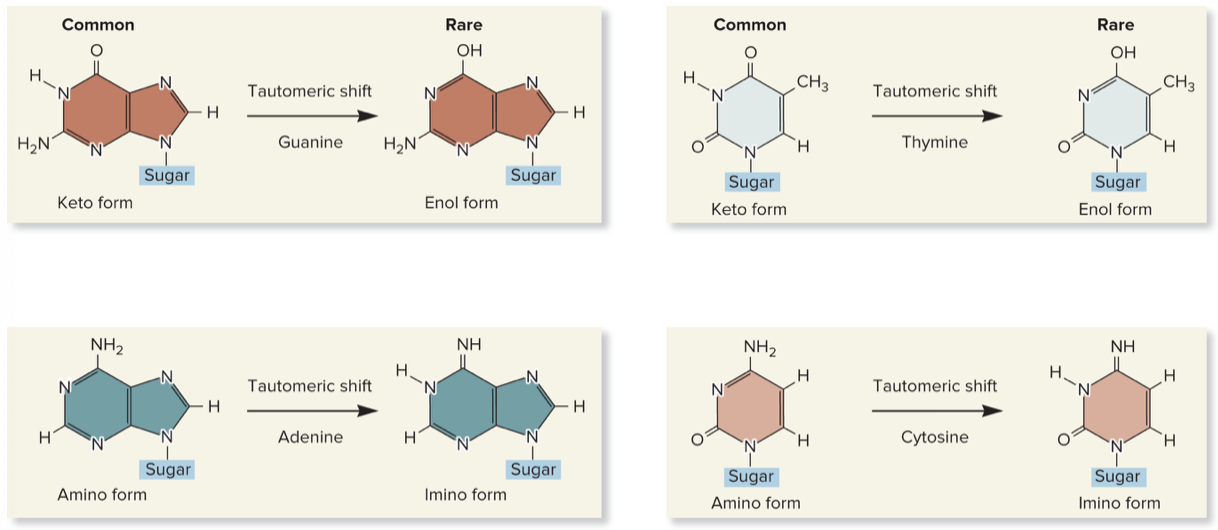
62
New cards
tautomers
chemically similar forms of certain small molecules, such as bases, which can spontaneously interconvert
63
New cards
temporary, keto, enol, amino, imino, keto, amino, TG, CA
tautomeric shift:
* _____ change in base structure
* G and T: _____ & _____
* A and C: _____ & _____
* common, stable form of G and T: _____
* common, stable form of A and C: _____
* the presence of enol and imino can cause a mutation because these rare forms do not conform to the AT/GC rule of base pairing
* instead, if one of the bases is in the enol or imino form, hydrogen bonding will promote _____ and _____ base pairs
* mutation if shift occurs during DNA replication
* _____ change in base structure
* G and T: _____ & _____
* A and C: _____ & _____
* common, stable form of G and T: _____
* common, stable form of A and C: _____
* the presence of enol and imino can cause a mutation because these rare forms do not conform to the AT/GC rule of base pairing
* instead, if one of the bases is in the enol or imino form, hydrogen bonding will promote _____ and _____ base pairs
* mutation if shift occurs during DNA replication
64
New cards
AC/GT
resulting mutation of tautomeric shift:
* _____ base pairing instead of AT/GC base pairing
* _____ base pairing instead of AT/GC base pairing
65
New cards
oxidative damage
* type of spontaneous mutation
* changes in DNA structure that are caused by reactive oxygen species ROS
* changes in DNA structure that are caused by reactive oxygen species ROS
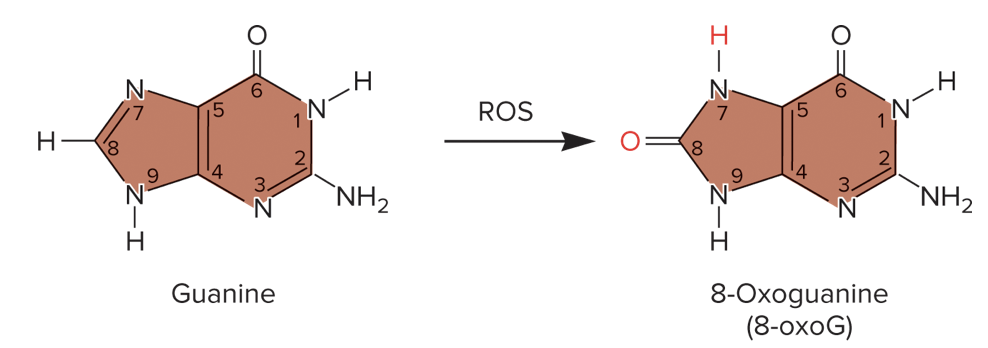
66
New cards
hydrogen peroxide, superoxide, and hydroxyl radical
examples of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
67
New cards
8-oxoguanine, 8-oxoguanine, transversion
oxidative damage:
* guanine → _____
* _____ base-pairs with adenine, not cytosine, during DNA replication (_____: purine to pyrimidine)
* guanine → _____
* _____ base-pairs with adenine, not cytosine, during DNA replication (_____: purine to pyrimidine)
68
New cards
adenine, cytosine
resulting mutation of oxidative damage:
* 8-oxoguanine base-pairs with _____, not _____, during DNA replication, causing mutations in which a GC base pair becomes a TA base pair
* 8-oxoguanine base-pairs with _____, not _____, during DNA replication, causing mutations in which a GC base pair becomes a TA base pair
69
New cards
trinucleotide repeat expansion (TNRE)
a type of mutation that involves an increase in the number of tenderly repeated trinucleotide sequences
70
New cards
increase, symptoms, CAG, glutamine, glutamine, longer, stronger
trinucleotide repeat expansion (TNRE):
* a type of mutation that involves an _____ in the number of tenderly repeated trinucleotide sequences
* the length of a trinucleotide repeat has increased above a critical size → causes disease _____
* commonly _____ repeats
* encodes _____
* long tracts of _____ → causes proteins to aggregate
* each generation can have _____ tracks and _____ symptoms
* a type of mutation that involves an _____ in the number of tenderly repeated trinucleotide sequences
* the length of a trinucleotide repeat has increased above a critical size → causes disease _____
* commonly _____ repeats
* encodes _____
* long tracts of _____ → causes proteins to aggregate
* each generation can have _____ tracks and _____ symptoms
71
New cards
hairpin, increase, gamete, longer
How does TRNE occur?
* _____ formation (formation of CG base pairs)
* causes _____ in length of repeat during replication
* when the trinucleotide repeat sequence is abnormally long, such expansions may frequently occur during _____ formation, and therefore offspring in successive generations may have trinucleotide repeat sequence that are even _____ than those in their parents
* _____ formation (formation of CG base pairs)
* causes _____ in length of repeat during replication
* when the trinucleotide repeat sequence is abnormally long, such expansions may frequently occur during _____ formation, and therefore offspring in successive generations may have trinucleotide repeat sequence that are even _____ than those in their parents
72
New cards
induced mutation
a change in DNA structure causes by an environmental agent
73
New cards
chemical, physical
environmental agents of induced mutations can be either _____ or _____
74
New cards
base modifier, intercalating agent, base analogue
chemical mutagens (induced mutation)
75
New cards
ionizing radiation, nonionizing radiation
physical mutagens (induced mutation)
76
New cards
mutagen
an agent that can alter the structure of DNA, causing a mutation
77
New cards
deamination, amino, keto, NH2, O, uracil, adenine, hypoxanthine, cytosine, nitrogen mustard, ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS)
base modification:
* covalently modifies the structure of bases
* _____
* nitrous acid replaces _____ groups with _____ groups
* _____ to _____
* deamination changes cytosine to _____ → binds to _____ instead of guanine
* deamination changes adenine to _____ → binds to _____ instead if thymine
* examples of alkylating agents: _____ (2 words) and _____ (2 words)
* covalently modifies the structure of bases
* _____
* nitrous acid replaces _____ groups with _____ groups
* _____ to _____
* deamination changes cytosine to _____ → binds to _____ instead of guanine
* deamination changes adenine to _____ → binds to _____ instead if thymine
* examples of alkylating agents: _____ (2 words) and _____ (2 words)
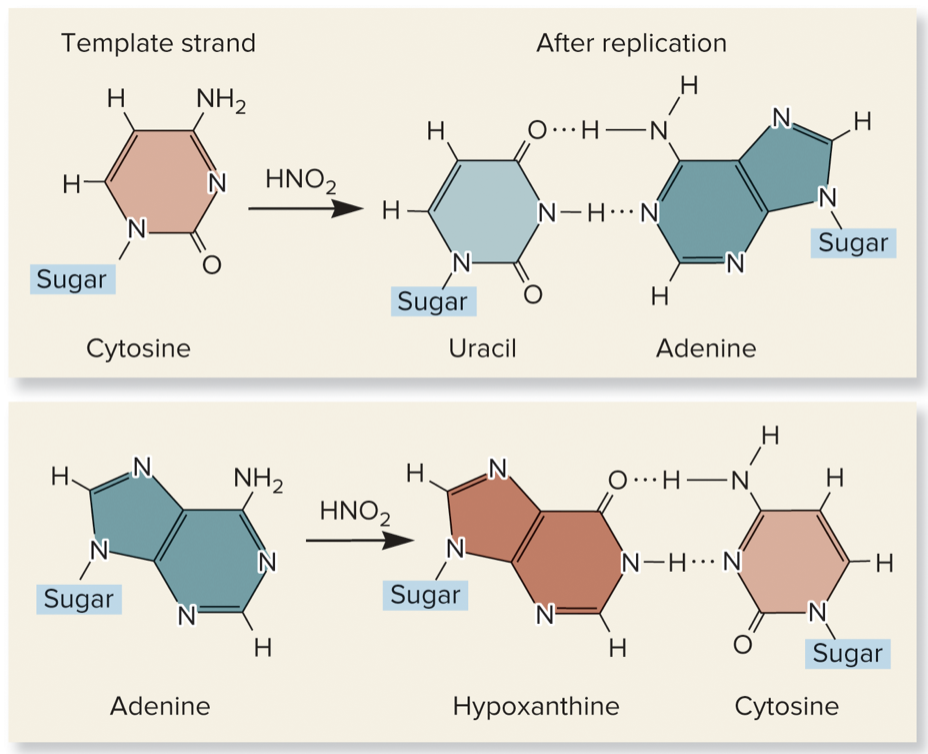
78
New cards
ethidium bromide, acridine dyes, frameshift
intercalating agents:
* directly interferes with the DNA replication process
* _____ _____ and _____ _____ contain flat structures that insert themselves between adjacent base pairs, thereby distorting the helical structure
* when DNA containing these mutagens is replicated, single-nucleotide additions and/or deletions can occur in the newly made daughter strands, creating _____ mutations
* directly interferes with the DNA replication process
* _____ _____ and _____ _____ contain flat structures that insert themselves between adjacent base pairs, thereby distorting the helical structure
* when DNA containing these mutagens is replicated, single-nucleotide additions and/or deletions can occur in the newly made daughter strands, creating _____ mutations
79
New cards
5-bromouracil, keto, enol
base analogues:
* _____: thymine analog that can be incorporated into DNA instead of thymine & base pairs with adenine
* tautomeric shift:
* _____ form: binds with adenine
* _____ form: binds with guanine
* promotes the change of an AT base pair into a GC base pair
* _____: thymine analog that can be incorporated into DNA instead of thymine & base pairs with adenine
* tautomeric shift:
* _____ form: binds with adenine
* _____ form: binds with guanine
* promotes the change of an AT base pair into a GC base pair
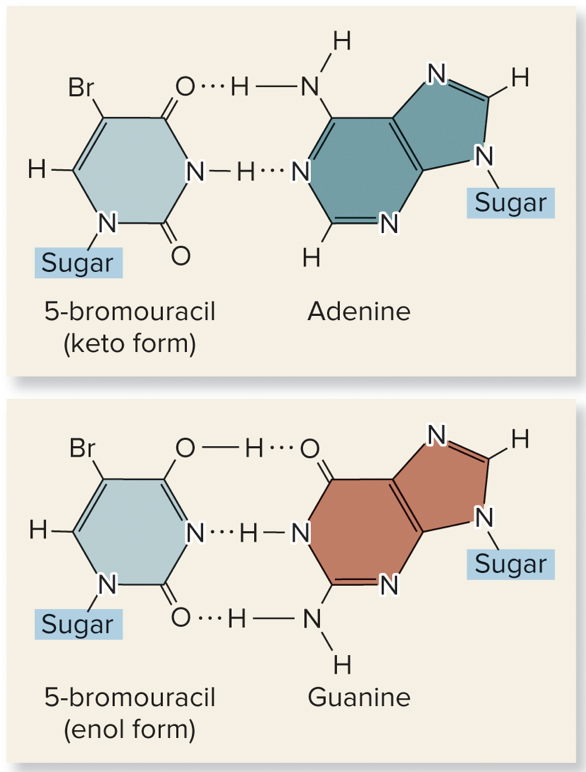
80
New cards
short, high, X, gamma, free radicals, deletions, breaks, oxidized
ionizing radiation:
* _____ wavelength and _____ high energy
* _____-rays and _____ rays
* produces chemically reactive molecules known as _____ _____
* can cause:
* base _____
* single-stranded and double-stranded _____ in the DNA backbone
* crosslinking
* _____ bases
* _____ wavelength and _____ high energy
* _____-rays and _____ rays
* produces chemically reactive molecules known as _____ _____
* can cause:
* base _____
* single-stranded and double-stranded _____ in the DNA backbone
* crosslinking
* _____ bases
81
New cards
long, low, UV, thymine dimers
nonionizing radiation:
* _____ wavelength and _____ high energy
* _____ light
* causes the formation of _____ _____ (do not base-pair properly during DNA replication → produce a mutation when the DNA strand is replicated)
* _____ wavelength and _____ high energy
* _____ light
* causes the formation of _____ _____ (do not base-pair properly during DNA replication → produce a mutation when the DNA strand is replicated)
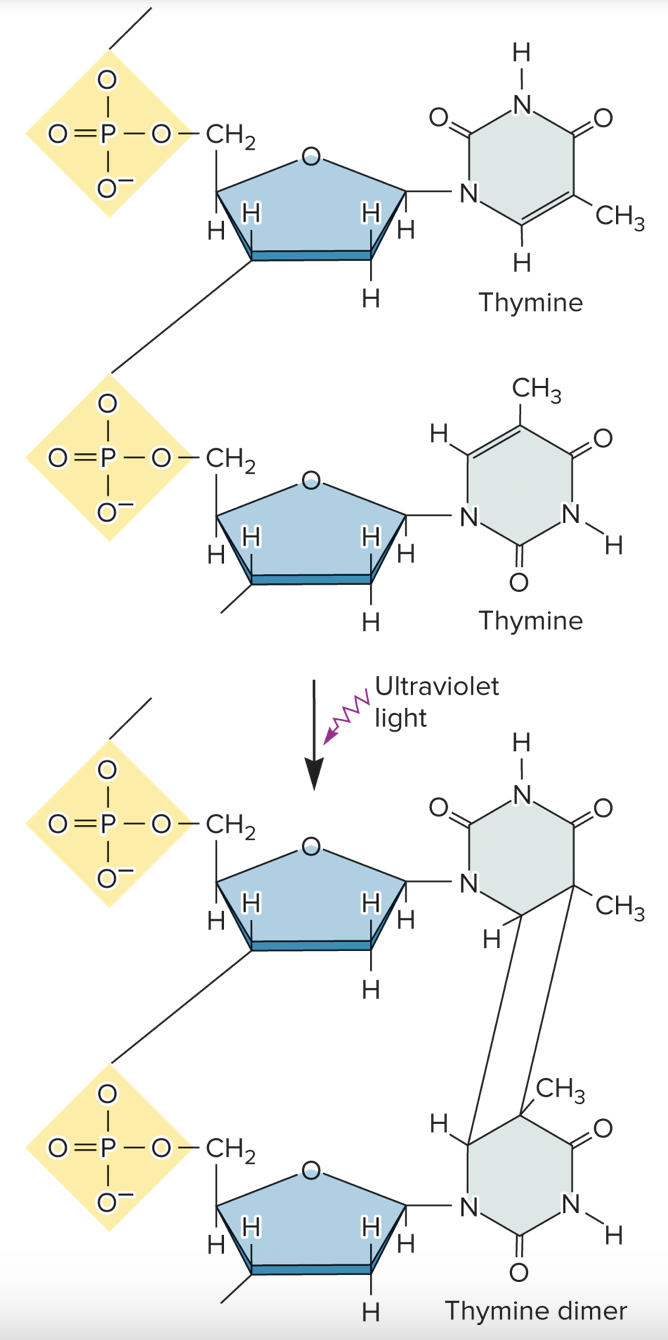
82
New cards
thymine dimer
two adjacent thymine bases in DNA strand that have become covalently linked because of nonionizing radiation
83
New cards
Ames test
a test using strains of a bacterium, Salmonella typhimurium, to determine if a substance is a mutagen
84
New cards
Salmonella typhimurium, histidine, histidine, histidine histidine, wild-type
Ames test
* uses strains of a bacterium, _____ _____, that cannot synthesize the amino acid _____
* these strains contain a point mutation within a gene that encodes an enzyme required for _____ biosynthesis (mutation renders the enzyme inactive)
* the bacteria cannot grow on petri plates unless _____ has been added to the growth medium
* second mutation (reversion)
* restores the ability to synthesize _____
* cause a reversion back to the _____ condition
* the Ames test monitors the rate at which the second mutation occurs, thereby indicating whether an agent increases the mutation rate above the spontaneous rate
* uses strains of a bacterium, _____ _____, that cannot synthesize the amino acid _____
* these strains contain a point mutation within a gene that encodes an enzyme required for _____ biosynthesis (mutation renders the enzyme inactive)
* the bacteria cannot grow on petri plates unless _____ has been added to the growth medium
* second mutation (reversion)
* restores the ability to synthesize _____
* cause a reversion back to the _____ condition
* the Ames test monitors the rate at which the second mutation occurs, thereby indicating whether an agent increases the mutation rate above the spontaneous rate
85
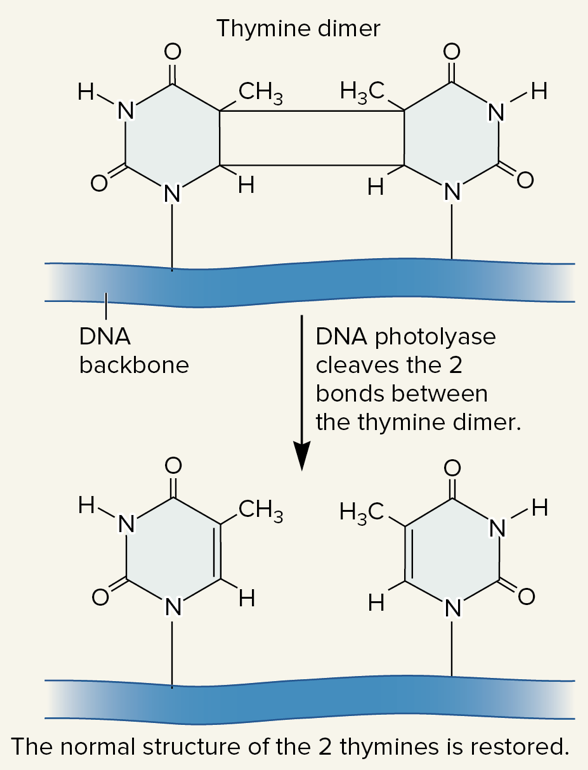
New cards
photolyase
an enzyme found in bacteria, fungi, most plants, and some animals that can recognize and split thymine dimers, which returns the DNA to its original condition
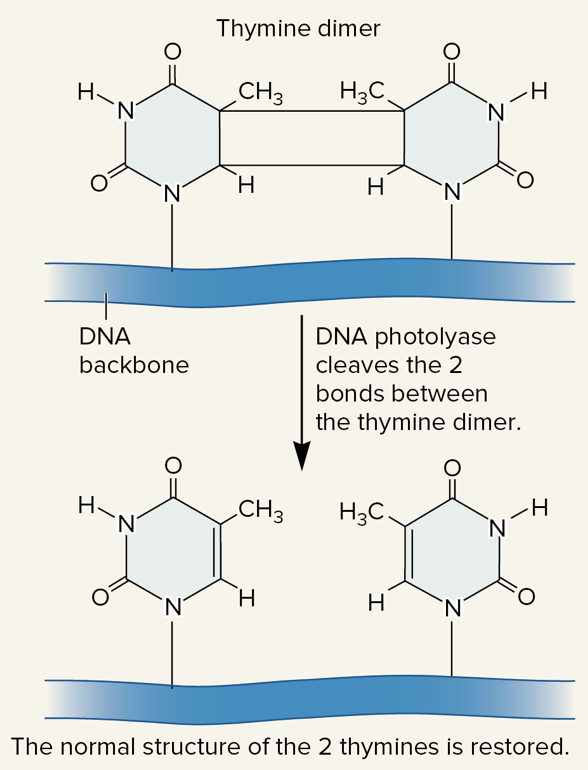
86
New cards
photoreactivation
a type of DNA repair mechanism of thymine dimers that involves photolyase and requires light
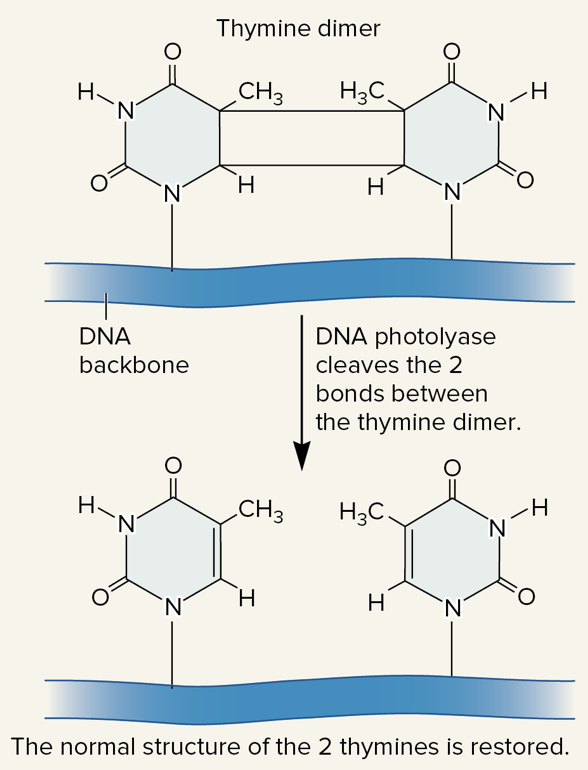
87
New cards
thymine dimers, light
photolyase/photoreactivation:
* enzyme called photolyase recognizes _____ _____ and splits them, returning the DNA to its original condition
* repair mechanism requires _____ (photolyase contains two light-sensitive cofactors)
* enzyme called photolyase recognizes _____ _____ and splits them, returning the DNA to its original condition
* repair mechanism requires _____ (photolyase contains two light-sensitive cofactors)
88
New cards
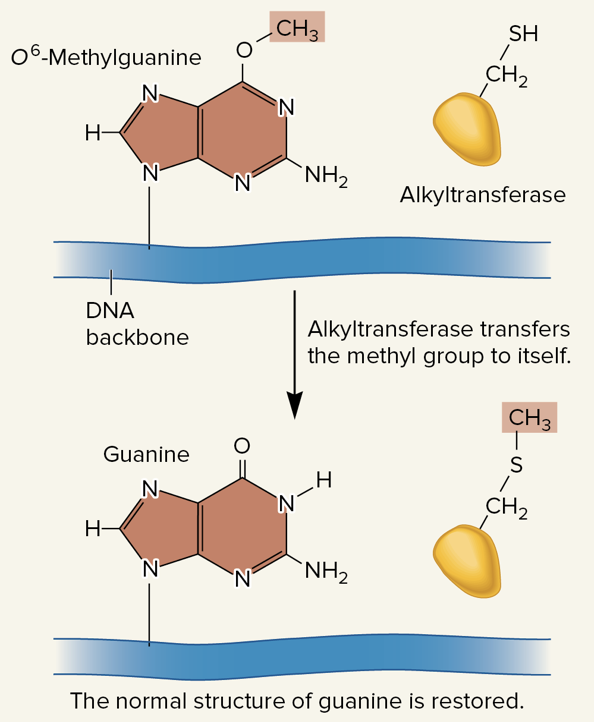
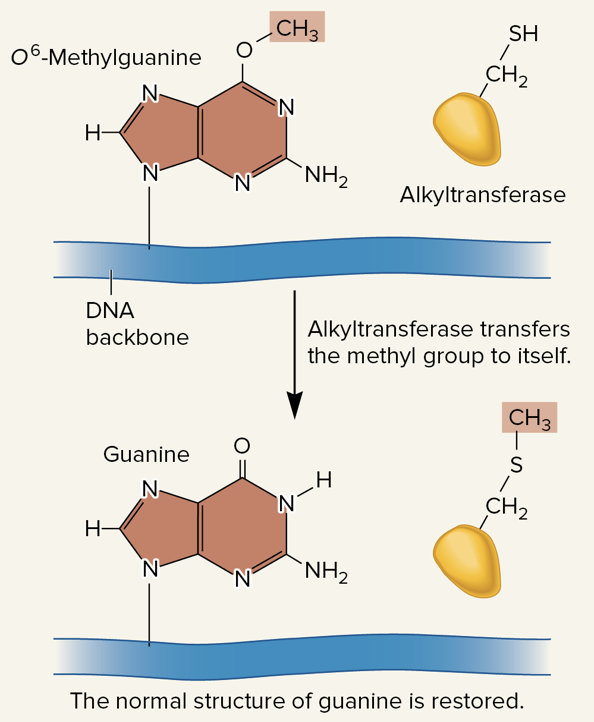
alkyltransferase
an enzyme that can remove methyl or ethyl groups from guanine bases
89
New cards
guanine, alkylating, suicide
alkyltransferase:
* enzyme that can remove methyl or ethyl groups from _____ bases that have been mutagenized by _____ agents such as nitrogen mustard and EMS
* “_____” enzyme: action permanently inactivates alkyltransferase, which means it can be used only once
* enzyme that can remove methyl or ethyl groups from _____ bases that have been mutagenized by _____ agents such as nitrogen mustard and EMS
* “_____” enzyme: action permanently inactivates alkyltransferase, which means it can be used only once
90
New cards
base excision repair
a type of DNA repair in which a modified base is removed from a DNA strand. Following base removal, a short region of the DNA strand is removed and then resynthesizes using the complementary strand as a template.
91
New cards
DNA N-glycosylase
an enzyme that can recognize an abnormal base and cleave the bond between it and the sugar in the DNA backbone
92
New cards
AP endonuclease
a DNA repair enzyme that recognizes a DNA region that is missing a base and makes a cut in the DNA backbone near that site
93
New cards
DNA N-glycosylase, AP endonuclease, uracil, AP, 3-methyladenine, methylguanine
base excision repair:
* _____ _____: recognizes an abnormal base and cleaves the bond between the base and the sugar
* _____ _____: recognizes a missing base and cleaves the DNA backbone, removing the sugar/phosphate
* eliminate abnormal bases:
* _____
* _____ sites
* _____
* _____
* _____ _____: recognizes an abnormal base and cleaves the bond between the base and the sugar
* _____ _____: recognizes a missing base and cleaves the DNA backbone, removing the sugar/phosphate
* eliminate abnormal bases:
* _____
* _____ sites
* _____
* _____
94
New cards
nucleotide excision repair
a DNA repair system in which several nucleotides in the damaged strand are removed from the DNA and the undamaged strand is used as a template to resynthesizes a normal strand
95
New cards
thymine dimers, UvrA, UvrB, UvrC, UvrD
nucleotide excision repair:
* can repair many different types of DNA damage, including _____ _____ (caused by UV light), chemically modified bases, missing bases, and certain types of crosslinks
* requires four key proteins: _____
* recognize and remove a short segment of a damaged DNA strand
* can repair many different types of DNA damage, including _____ _____ (caused by UV light), chemically modified bases, missing bases, and certain types of crosslinks
* requires four key proteins: _____
* recognize and remove a short segment of a damaged DNA strand
96
New cards
transcription-coupled repair
special type of nucleotide excision repair that recognizes thymine dimers and removes RNA polymerase from the damages region of the DNA during transcription
97
New cards
nucleotide excision repair, thymine dimer
transcription-coupled repair:
* special type of _____ (3 words)
* TRCF functions as a helicase and removes RNA polymerase from the damaged region (_____ _____)
* several biological advantages:
* active genes are more _____ packed
* _____ may make DNA more susceptible to damage
* regions more likely to be important for survival
* special type of _____ (3 words)
* TRCF functions as a helicase and removes RNA polymerase from the damaged region (_____ _____)
* several biological advantages:
* active genes are more _____ packed
* _____ may make DNA more susceptible to damage
* regions more likely to be important for survival
98
New cards
base pair mismatch
a DNA abnormality in which two bases opposite each other in a double helix do not conform to the AT/GC rule
99
New cards
mismatch repair system
a DNA repair system that recognizes base pair mismatches and repairs the newly made daughter strand that contains the incorrect base
100
New cards
mismatched, MutS, MutL, MutH
mismatched repair:
* correction of _____ bases after DNA synthesis
* E. coli proteins:
* _____
* _____
* _____
* correction of _____ bases after DNA synthesis
* E. coli proteins:
* _____
* _____
* _____