11) Nitrogen Metabolism 3
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Essential amino acids
Body cannot synthesize; must get from dietary intake
The essential amino acids are:
Leucine Isoleucine Valine (BRANCHED CHAIN AMINO ACIDS)
Phenyalanine Tryptophan (Aromatics; Tyrosine not included because it can be synthesized from Phenylalanine)
Methionine (source of sulfur)
Lysine Arginine Histidine (positive charges)
Threonine (has a side chain with a chiral carbon)
Arginine
Not required for adults but is required for growth in children
Nonessential amino acids
We still need them, but our body can synthesize them
Non essential amino acids
serine, cysteine, alanine, and their metabolically close relative glycine (three carbon amino acids)
aspartate and asparagine (the four carbon amino acids)
glutamate, glutamine, proline, and their close relative arginine (the five carbon amino acids)
tyrosine (made from phenylalanine)
Tyrosine is made from _______ which is an _________ __________ _________
phenylalanine; essential amino acid
Amino acid metabolism
depends on the activities of many enzymes, often working in conjunction with co-factors, to prevent accumulation of potentially toxic molecules.
Disruption of enzyme function can lead to
accumulation of toxic substrates, resulting in disease; this mechanism is common to many disorders of amino acid metabolism.
Treatments for amino acid metabolism disorders, when possible, are often aimed at
minimizing accumulation of toxic substrates by limiting availabilities of their precursors, or by promoting degradation of the toxic substrates.
Branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) metabolism in muscle:
BCAA’s are deaminated and metabolized in _______ and _______ to drive ____ __________.
Amine groups are transferred to _________ to generate _________
__________ can be released into the bloodstream; absorbed by liver
In the liver, alanine is broken down to _________(drives ______________); excess NH3 drives formation of _____
muscle and brain; ATP production.
pyruvate; alanine
Alanine
pyruvate; gluconeogenesis; urea
All essential amino acids make
glucogenic substrates
_________ ___________ and _____________ have side chains that are carbon groups that make a branch
Leucine, isoleucine, and valine
Leucine—>
ketogenic amino acids
isoleucine—>
ketogenic and glucogenic substrates
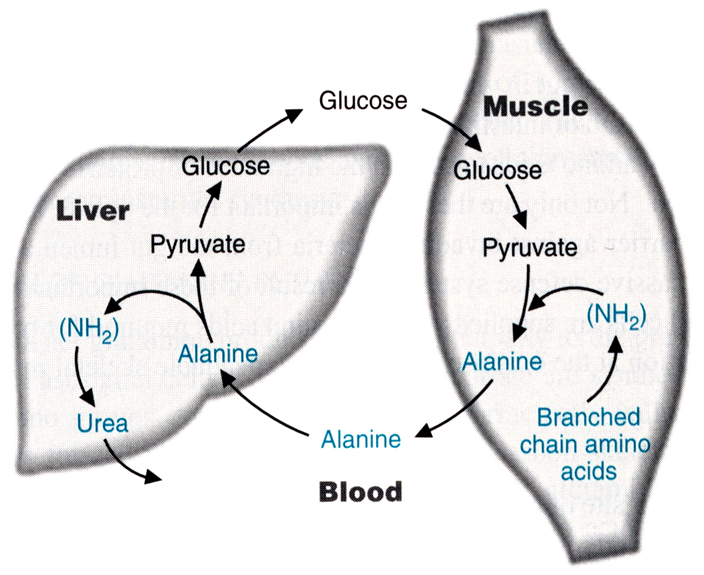
Cori cycle
Conversion of pyruvate to lactate in muscle, transport of lactate to the liver and conversion to glucose.
BCAA’s are converted to ___________ ___________ in muscle (and brain) and used for fuel
carbon skeletons
Cahill cycle
Ammonium is transferred to pyruvate to make alanine, transported to liver
De-aminated to make pyruvate. ammonia is packaged to urea,
Overall metabolism of BCAA’s:
Transamination: generates ____________
Alpha-ketoacids must next be metabolized by ____________ _______________
Carbon skeletons are metabolized to form propionyl coA -> ____________ or __________ __________ to drive TCA cycle
“alpha-ketoacids”.
alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
succinyl coA (Val, Ile) or ketone bodies (Ile, Leu)
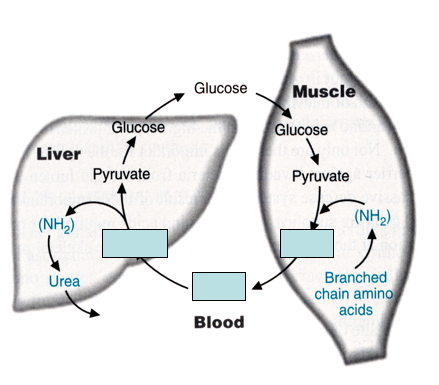
Fill in the blanks
Transamination
generates “alpha-ketoacids”
Alpha-ketoacids must next be metabolized by _______________
alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
Carbon skeletons are metabolized to form
propionyl coA -> succinyl coA (Val, Ile)
OR
ketone bodies (Ile, Leu) to drive TCA cycle
Key Steps of BCAA Metabolism:
Take off amine group (transamination) to make an a-keto
Remove carboxylate group (via decarboxylation). This is achieved by a-ketoacid dehydrogenase
Form ketone bodies to drive TCA
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Hereditary variant causing decrease in α-ketoacid dehydrogenase activity.
Symptoms include feeding difficulties, developmental delay, convulsions, failure to thrive.
Name of the disease comes from the characteristic sweet odor (like maple syrup or burnt sugar), due to accumulation of branched-chain alpha-ketoacids and by-products.
Treatment requires special low-protein diet, to limit levels of branched-chain amino acids.
Maple Syrup Urine Disease Treatment
Requires special low-protein diet, to limit levels of branched-chain amino acids.
Catecholamine biosynthesis
Conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine depends on phenylalanine hydroxylase
Classical phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylalanine hydroxylase is defective
Phenylalanine (Phe) cannot be converted to tyrosine. Phe is converted to other products such as phenylpyruvate and phenylacetate (ketones which can accumulate in urine), which can accumulate to toxic levels.
Newborns with complete lack of enzyme activity develop symptoms within a few months if untreated; intellectual disability, developmental delay, pigmentation deficit. Screening test of newborns for PKU is routinely performed. Partial deficiencies also exist, may show up in later childhood.
Classical phenylketonuria (PKU) Treatment
Diet must restrict levels of phenylalanine, with supplementation of tyrosine.
Aspartame (Nutrasweet) contains phenylalanine equivalents and must be avoided because they will be metabolized to phenylalanine when ingested
*Tyrosine now becomes essential
_________________ contains phenylalanine equivalents and must be avoided in people with PKU
Aspartame (Nutrasweet)
Alkaptonuria
Defect in homogentisate dioxygenase (in Tyr degradation pathway); leads to accumulation of homogentisate in tissues, bone, urine.
Homogentisate turns dark brown/black upon oxidation (to “alkapton”, oxidation product). Urine turns black after exposure to air.
Alkapton can also accumulate in cartilage, bone, sclera.
Can precipitate, leading to arthritis, also damage to heart valves and kidneys; sialolithiasis (stones in salivary gland) can also occur.
Homocysteine metabolism:
Homocysteine is an intermediate metabolite in the generation of______
It is metabolized to ___________ (by ___________ ____________) This metabolism depends on ________, which is derived from dietary vitamin B6.
Can also be metabolized from _____
SAM
cystathionine; cystathionine synthase; PLP (pyridoxal phosphate)
B12
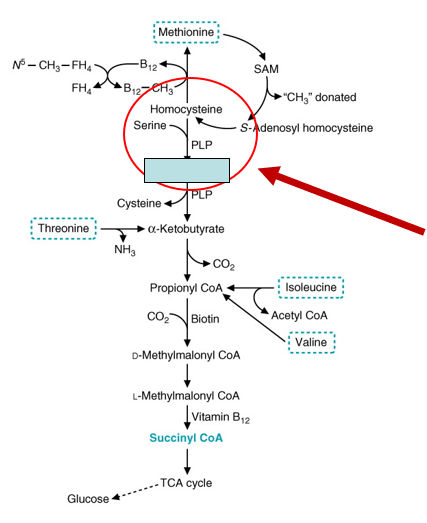
Fill in the blanks
(a)
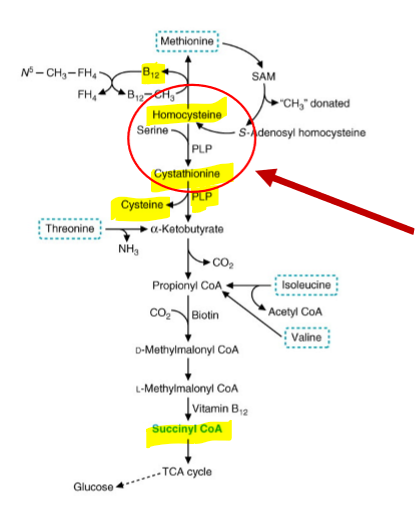
Homocystinuria (HCU)
Defect in cystathionine synthase, leads to accumulation of homocystine (oxidized homocysteine) in blood and urine.
HCU symptoms
Risk of cardiovascular disease and thromboembolisms (25% mortality by age 30).
Linked to pectus excavatum (see above); lens dislocation is frequent (90%). Mechanisms underlying these are unclear.
HCU Treatment
High dose of vitamin B6, aimed at maximizing activity of defective enzyme. Also treated by decreasing intake of methionine, increase intake of B12, folic acid, to metabolize HC through methionine synthase pathway.
Elevated purine degradation can lead to _______
gout
Purine nucleotides can either be ________ or __________
recycled or degraded
The major purine degradation product is _____ _______, formed by xanthine oxidase.
uric acid
Uric acid is a by-product of _________ ____________
Nucleotide metabolism
Insolubility of uric acid leads to its ___________ in joints, can lead to __________/___________
precipitation; inflammation/gout (sometimes a side effect of diuretics).
Allopurinol
drug that inhibits xanthine oxidase (treatment for gout).
Two Methods of Allopurinol Inhibition of xanthine oxidase
hypoxanthine —//—> xanthine
xanthine —//—> uric acid
Hypoxanthine and xanthine excreted in urine
These two methods result in less uric acid build-up
Uric acid is in fact acidic, and what we actually have is _______, generally __________. Both “sodium urate” and uric acid are used to describe the compound.
urate; NaUrate
Hypercatabolic state
Syndrome; HS
Characterized by increased fuel utilization and negative nitrogen balance (nitrogen excreted is greater than the amount consumed). HS occurs following trauma, surgery, or critical illness.
Enough protein =
enough nitrogen
Not enough protein =
excretion of more nitrogen than nitrogen being taken in
HS is associated with elevated levels of ____________; __________ release stimulates glucose / fatty acid metabolism
cortisol (glucocorticoid); cortisol
The resulting mobilization of protein, lipid and carbohydrate serves to
maintain normal tissue function in the presence of limited dietary intake, as well as to support the requirements of the immune response and wound healing
Cells of the immune system receive top priority in terms of utilization of________ ________
amino acids (released from muscle)
Glutamine is taken up by liver, immune cells:
serves as a nitrogen donor for purine nucelotide synthesis
Fatty acids are mobilized from adipose to provide alternative fuels and to spare ________.
glucose
Fatty acids become major source of fuel for muscle under these conditions
Starvation vs HS
Starvation- decreased metabolic rate
HS- increased metabolic rate (this may help drive repair and drive immune system)
HS is characterized by __________ nitrogen balance; protein breakdown and nitrogen excretion are ________ than dietary protein intake.
negative; greater
Amino acids are directed toward building ____________ ______________ ____________ to promote recovery
immune system proteins
Amino acids are important for
building proteins, cellular energy, and providing raw material for synthesis of neurotransmitters, hormones, and nucleotides.
Metabolism of amino acids can generate ___________, which is packaged into urea via the Urea cycle.
ammonium
Vitamin B12 and folate (vitamin B9) are both important cofactors in ____________ ____________, which is critical for production of blood cells and other dividing cells.
nucleotide biosynthesis
Several amino acids are __________ of important neurotransmitters
precursors
Purine and pyrimidine synthesis involves raw materials from several key ________ ________ __________
amino acid precursors
Disruption of amino acid metabolism can lead to
accumulation of toxic molecules, resulting in disease
Physical trauma or critical illness results in a _________ _________, in which amino acid metabolism is altered to drive immune cell production and fight infection
hypercatabolic state