Section A: Urban issues and challenges
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
Define Urban
Towns and cities
Define Rural
Countryside
What is urbanisation?
When an increasing percentage of a country’s population comes to live in towns/cities
What percentage was the urban population in 2023?
57%
Are more people living in urban areas or rural?
Urban
Do HICs, LICs or NEEs have the highest percentage of people living in urban areas?
HICs
2 reasons why urban populations in LICs/NEEs are growing rapidly
Rural-urban migration
Natural increase
What is rural-urban migration?
People moving into cities from the countryside
What is a natural increase?
When birth rates are higher than death rates
What is a megacity?
A large city with a population of over 10 million people.
Where is the highest concentration of megacities?
Asia
Which continent has no megacities?
Oceania
What are the 3 types of megacities?
Slow-growing
Growing
Rapid-growing
Slow-growing megacities- WHERE?
South East Asia
Europe
North America
Slow-growing megacities- What are its FEATURES?
Population at 70% urban
No squatter settlements
Slow-growing megacities- EXAMPLES?
Osaka in Japan
Growing megacities- WHERE?
South America
South East Asia
Growing megacities- FEATURES
Population at 40-50% urban
Under 20% in squatter settlements
Growing megacities- EXAMPLES?
Beijing in China
Rapid-growing megacities- WHERE?
South Asia
South east Asia
Africa
Rapid-growing megacities- What are their FEATURES? (two)
Population under 50% urban
Over 20% in squatter settlements
Rapid-growing megacities- EXAMPLES?
Jakarta in Indonesia
What are push factors?
Bad things about an area which force people to leave
What are pull factors?
Good things about an area which attract people to move there
Examples of push factors on rural areas 3
Farming - the main job - earns very little money, meaning low incomes
Lack of available healthcare leads to high "infant mortality"
Poor living conditions and widespread disease
3 examples of pull factors on urban areas
There is a greater choice of jobs available, including secondary and tertiary jobs
Better infrastructure is available
Better healthcare = life expectancy increases
Effects of push factors on rural areas (the source area) 3
Because it is mainly the young people who leave, those left behind are elderly and weak
The area left behind becomes abandoned and derelict
Poverty increases for the people left behind
Effects of pull factors on urban areas (the destination area) (4)
The new arrivals put a strain on public services e.g. health and education.
Massive overcrowding due to so many newcomers.
More people creates more pollution from traffic and rubbish.
More people competing for jobs means higher levels of unemployment.
Example of a urbanisation CASE STUDY (NEE)
Lagos, Nigeria
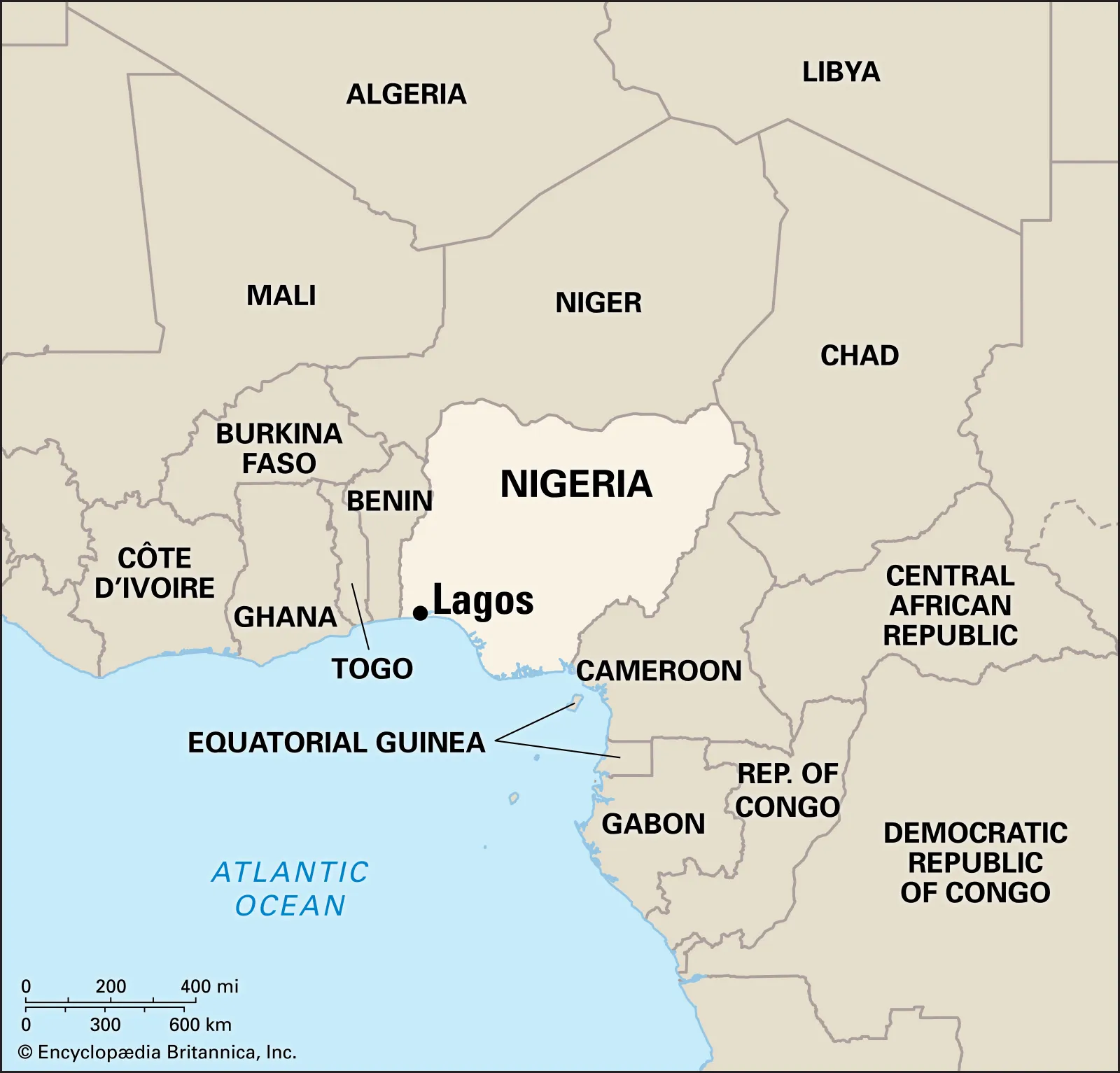
Location of Lagos
Surrounded by Benin, Niger and Cameroon
In South-West Africa
Right on the south-west border of Nigeria
In the Northern hemisphere
On the coast of the Gulf of Guinea
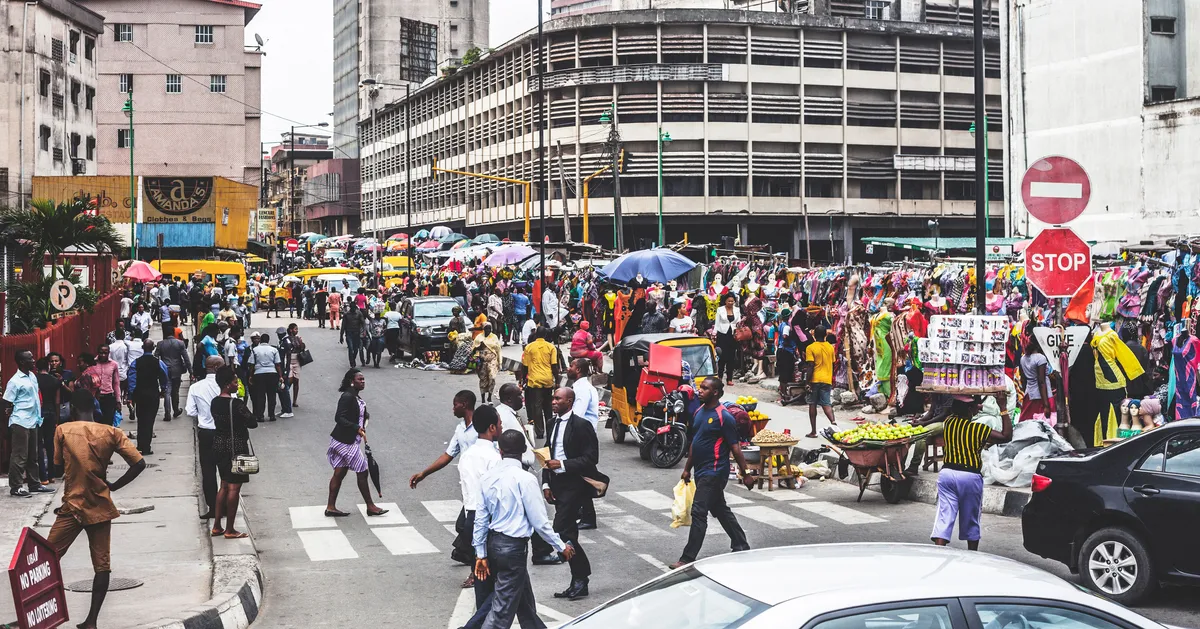

What is Lagos like? (4)
Very congested
Lagos is Africa's most populated city
High amount of pollution
Very hot, humid weather
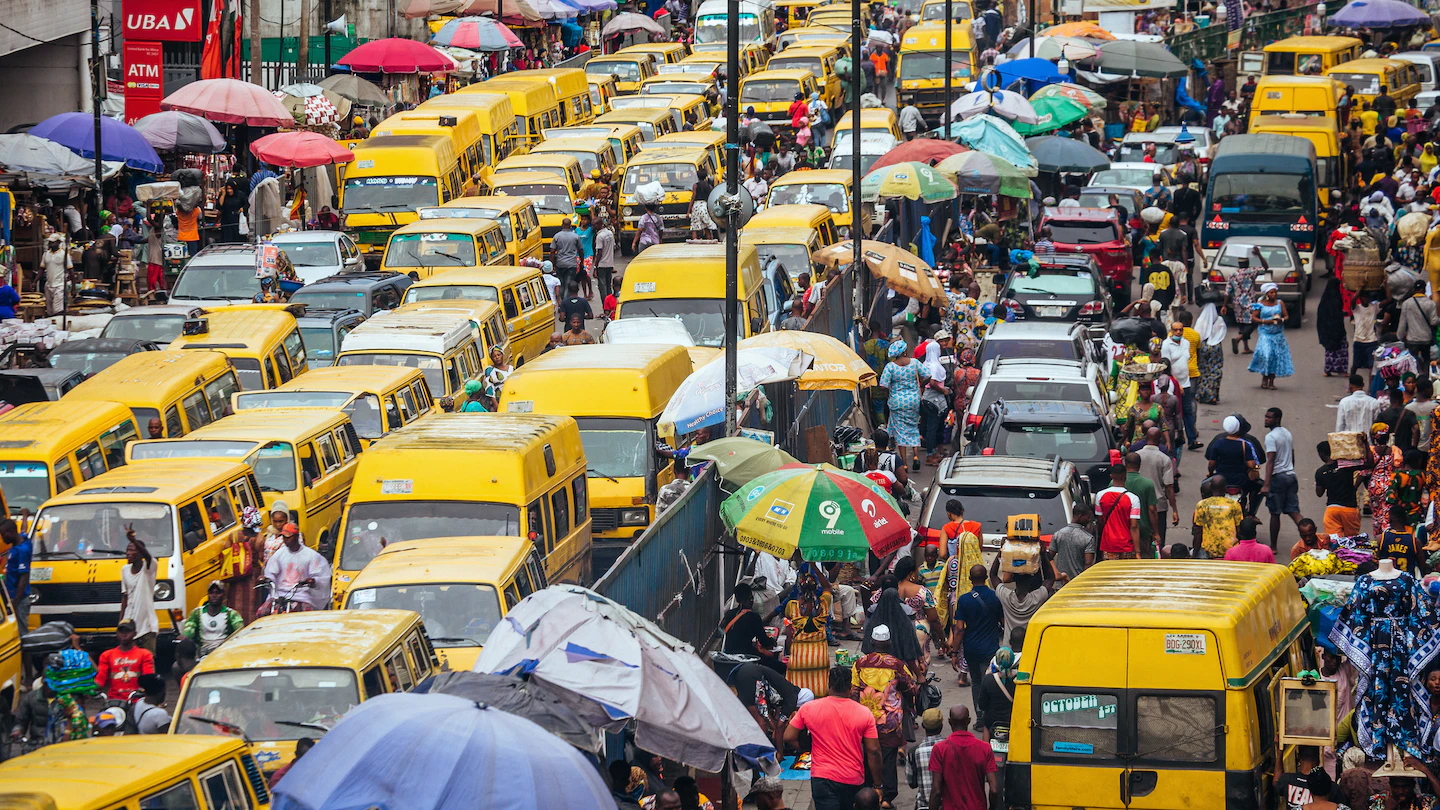

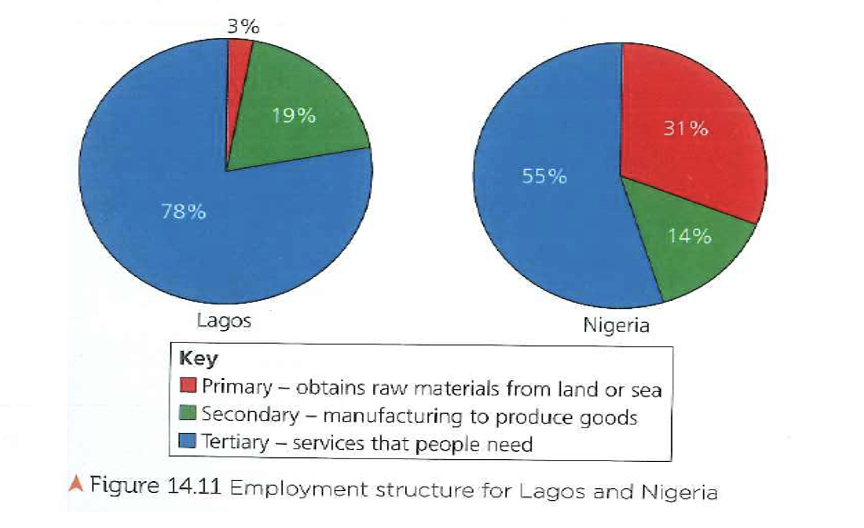
What is the local/regional importance of Lagos? (2)
The city is a transport hub, providing raw materials for local industries
iit generates the most money in all of Nigeria
What is the national importance of Lagos? (2)
The city generates about 30% of Nigerias GDP
80% of Nigeria's imports and 70% of its exports pass through its docks
What is the international importance of Lagos? (2)
The main financial centre for West Africa
Lagos has one of the highest standards of living in Africa
What is the history of Lagos? (15th century-1991)
15th century- Lagos was a small fishing village
Early 20th Century- Under British rule, Lagos was made the capital of Nigeria
1960- Lagos remained the capital after independence from the British in 1960
1991- Nigerian government moved to Abuja, which became the new capital, although Lagos still kept its importance.
How did Lagos grow?
Lagos's expansion took off during the oil boom in the 1970's
What 2 factors caused population growth in Nigeria, Lagos?
Natural increase
Rural-Urban migration
How did natural increase increase population in Lagos?
Due to the city’s youthful population since most migrants are young
How did rural-urban migration increase population in Lagos?
People moved from rural to urban areas like Lagos
What are the economic advantages of Lagos’s location? (3)
Good transport connections
Growing population provides a large market for goods and services
With many schools and universities, Lagos has a well-educated and skilled workforce, attracting more companies
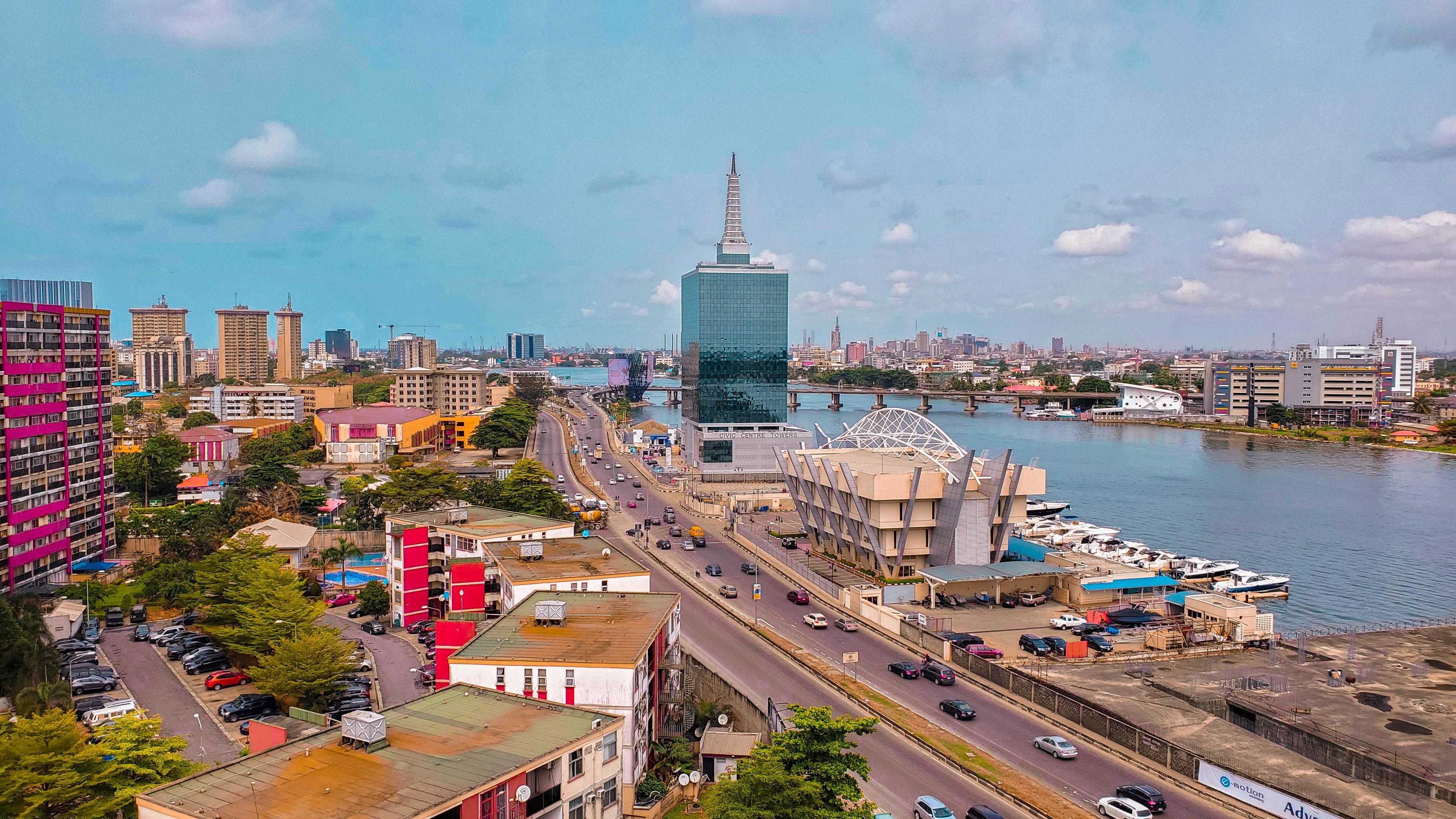

What contribution does Lagos make to the Nigerian economy? (2)
Lagos contributes about 30% of its GDP.
Almost 80% of Nigeria’s manufacturing is based there
What is Eko Atlantic?
A new city on the Lagos coast, designed to be the new financial hub of West Africa.
What are the economic advantages of Eko Atlantic? (2)
It will provide luxury homes to a quarter of a million people
and employ 150,000 more
What is formal work?
Contracted work, paid a regular salary, receive sick pay and generally a pension
What is informal work?
When work is unregulated, has no guaranteed wage, no work benefits
What is an informal economy?
A sector of an economy that is neither taxed or monitored by the government
What are some issues with employment in Lagos? (3)
Unemployment in Lagos is much lower than the rest of Nigeria
There is no unemployment benefit for those without work
40% of the workforce work in the informal sector
Benefits of working at Olusosun landfill in Lagos (2)
Without the dump, a lot of reusable items would go to waste. People in Lagos can save money by buying recycled goods.
Rubbish can be turned into energy by harnessing methane gas
Problems of working at Olusosun landfill in Lagos (2)
Workers live at the dump, building their homes out of discarded materials.
Only 13% of this waste is recycled.

Social opportunities In Lagos (5)
Education
Health care
Transport
Electricity
Crime reduction
How is education a social opportunity in Lagos?
There are more schools and universities in Lagos than you find outside the city.
How is health care a social opportunity in Lagos?
Although it is not always free, health care is available in Lagos. You will have to wait and queue if you cannot afford to pay.
How is transport a social opportunity in Lagos?
The first stage of the STMP has been started with the rapid transit system.
How is electricity a social opportunity in Lagos?
Two new power stations planned to reduce the city's shortage of electricity.
How is crime reduction a social opportunity in Lagos?
In order to tackle high levels of armed muggings, burglaries and carjackings, the city has bought helicopters for police to spot criminal activities.
The Makoko floating school in Lagos
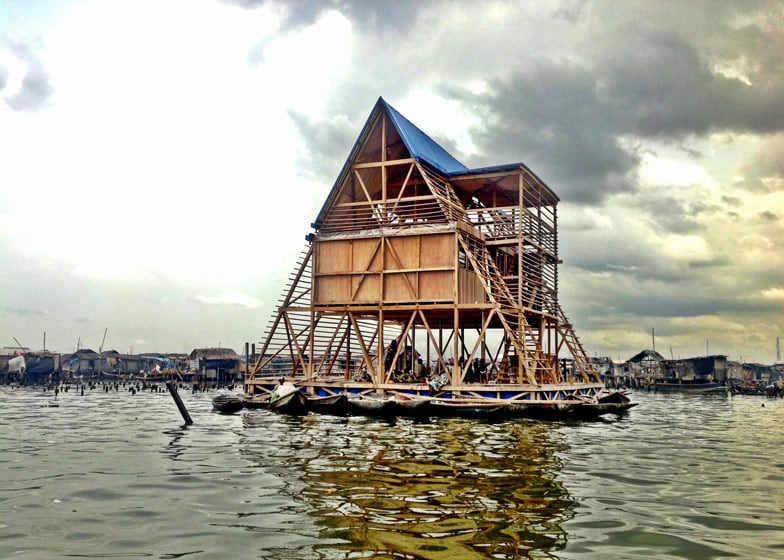


Why is the floating Makoko school important? (2)
Provides education for children
Provides a community centre for adults
SUMMARY: What are the social opportunities in Lagos? (4)
Good healthcare available in Lagos
Lagos has almost 20,000 schools
Lagos has water treatment plants which provide clean water
Lagos has better access to electricity compared to the rest of Nigeria
SUMMARY: What are the economic opportunities in Lagos? (2)
Many jobs are available in Lagos due to its rapid growth, in particular the construction industry
There is a growing fishing industry in Lagos
What are challenges in Lagos? (3)
Water supply
Squatter settlements
Traffic congestion
What percentage of Lagos’s population has clean water?
10%
Where do 90% of people in Lagos get its water?
The rest of the population rely on digging their own wells to reach groundwater.
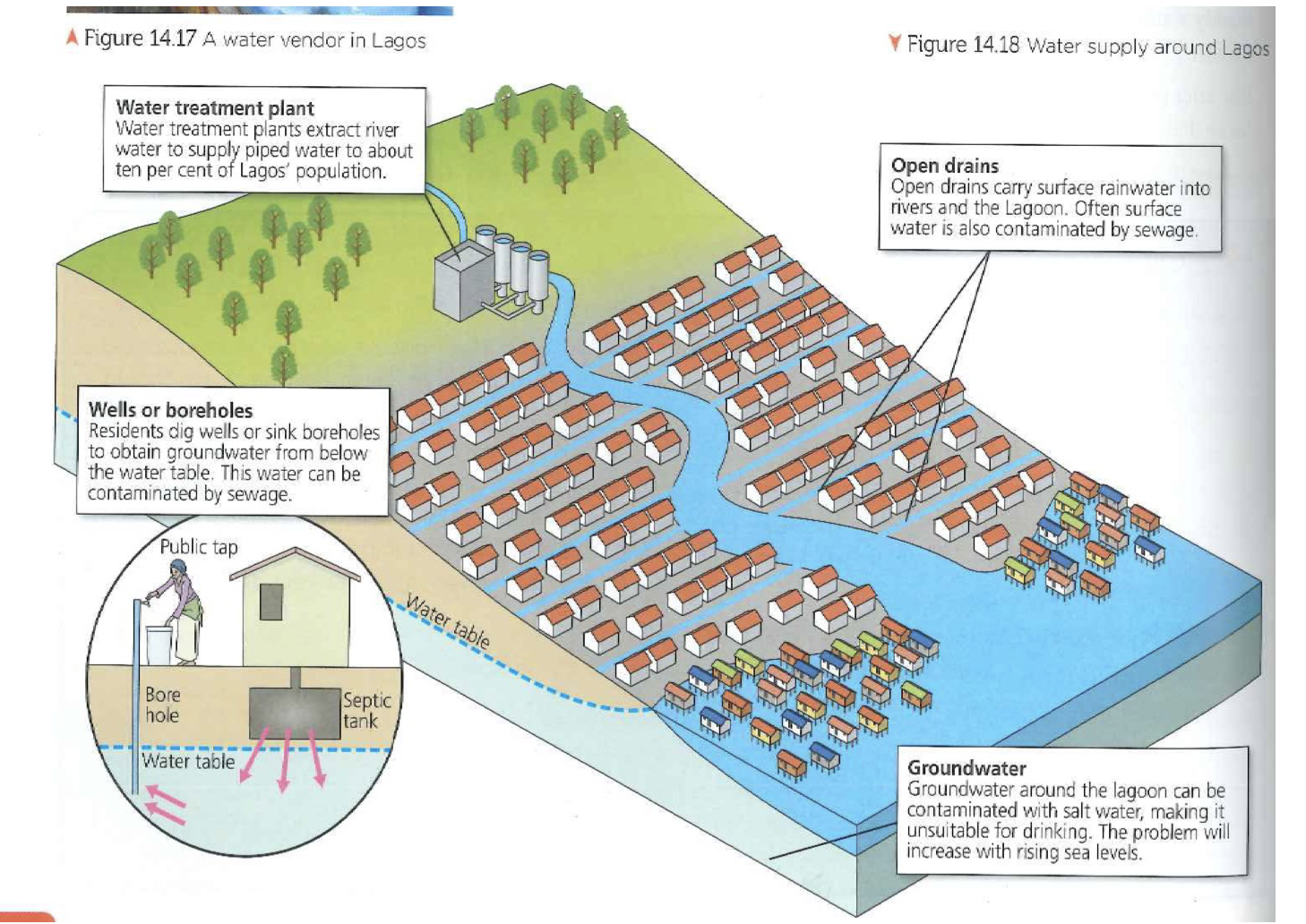
Why are some areas in Lagos not suitable for drinking?
The water is not suitable for drinking as it is salty and polluted
2 reasons how pollution affects Lagos’ water supply
Drinking water contains bacterial or chemical pollution that can lead to waterborne diseases
Lagos lacks a proper sewage system as rainwater causes sewage to flow into rivers.
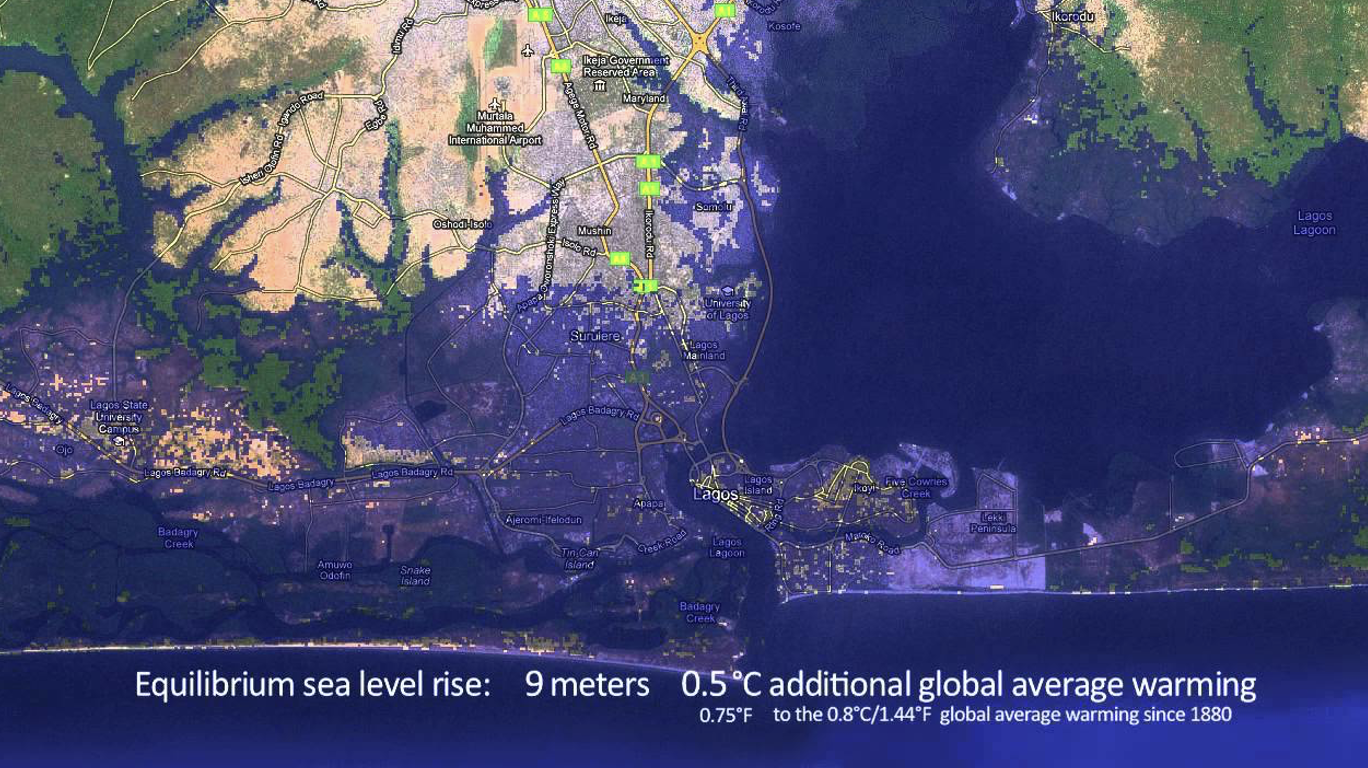
2 reasons why the impact of sea-level rise in Lagos could be more severe than in other cities
Most of Lagos is only 2m above sea level
Flooding will increase and groundwater will become contaminated.
2 facts about traffic congestion in Lagos
There is 3 hours in traffic every day on average
Air pollution rates are 5x higher than the internationally recommended limit
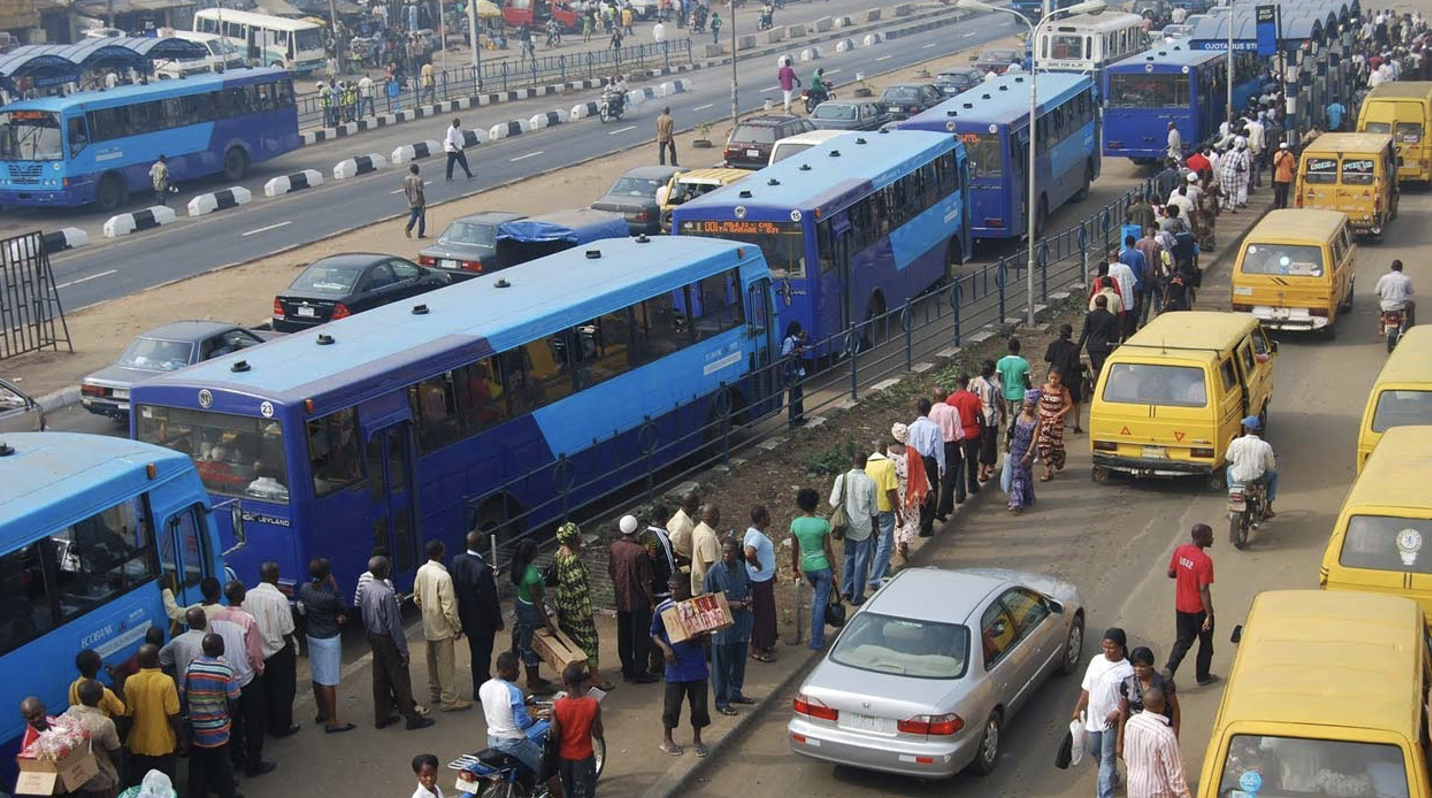

What efforts have been made to reduce traffic congestion and who by?
In 2003, the LAMATA was set up. It introduced a bus rapid transit to provide a separate lane for buses.
What are some of the key features of the Strategic Transport Master Plan for Lagos? 2
Another scheme in 2016 will create a new light railway, designed to carry 7x more passengers
There are plans for 7 new railways lines called LMT
What are squatter settlements?
A squatter settlement is an illegally built home
Where can squatter settlements be found?
In cities in LICs and NEEs
What are the problems of living in squatter settlements? (3)
Densely populated due to the shortage of land
Lack basic facilities and good sanitation.
Most people work in the informal economy
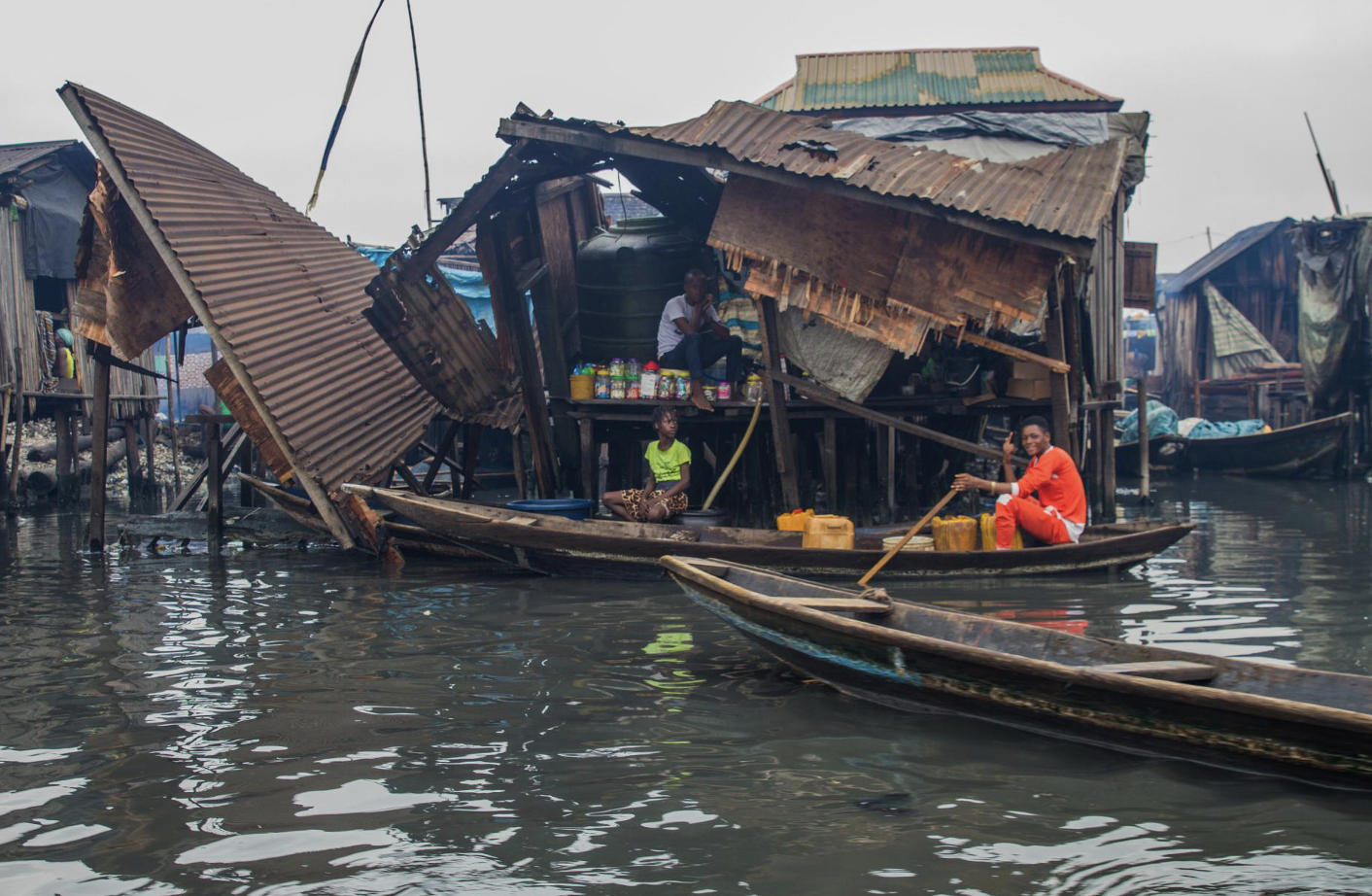

What are challenges of urban planning in Lagos? (4)
Population is predicted to reach 40 million by 2035
Lack of a clean water supply
Lack of a reliable/efficient power supply
Sea levels are expected to rise (Lagos is a low-lying coastal city)
What is Lagos’s solution for the challenges of urban planning?
They will take advantage of the vast area of water by creating new floating communities that are eco-friendly e.g. Makoko Floating School
How many children can Makoko floating school hold?
100
Who designed Makoko floating school?
A Nigerian architect with local people
Who half-funded Makoko floating school?
NGO’s and the UNDP
How does the Makoko floating school work?
It floats to adapt to rising sea levels
How is the Makoko floating school eco-friendly? (2)
Generates its electricity from solar panels
School was built using local materials
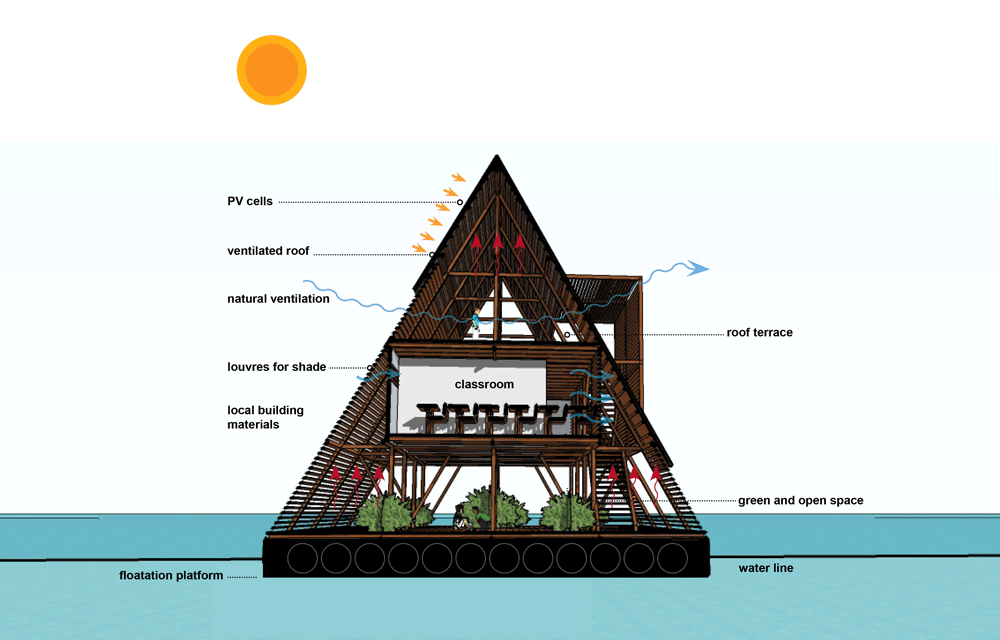
Social benefits of Makoko floating school (2)
Up to 100 students got education for free
It was build by unskilled local workers
Economic benefits of Makoko floating school (3)
Education improved local children's job prospects
School provided jobs for local teachers
School’s success encouraged the government to launch MRP -this aims to develop the slums further.
Environmental benefits of Makoko floating school (3)
School was built using locally sourced materials -construction didn't harm the local environment
Runs on solar power which is sustainable
School collects rainwater to meet its water needs
What is population distribution?
How spread out the population is
What is population density?
The number of people per square km
(how packed it is)
What is a HIC Case study for Urban Change?
London, UK
What can population distribution be? (2)
Even
Uneven
What can population density be? (2)
Dense
Sparse
How distributed is the UK population?
It’s unevenly distributed with 82% living in urban areas
What is the UK’s population density like in the South?
Densely populated
What is the UK’s population density like in the North?
Sparsely populated
Why is the North of UK sparsely populated? (2)
It’s very mountainous so it is difficult to build on steep land.
Hilly areas make it hard to build transport links so the location remains isolated
Why is the South of UK densely populated? (3)
Has flat land which is easy to build on.
Has transport links.
Lots of job opportunities
UK’s population distribution and density map
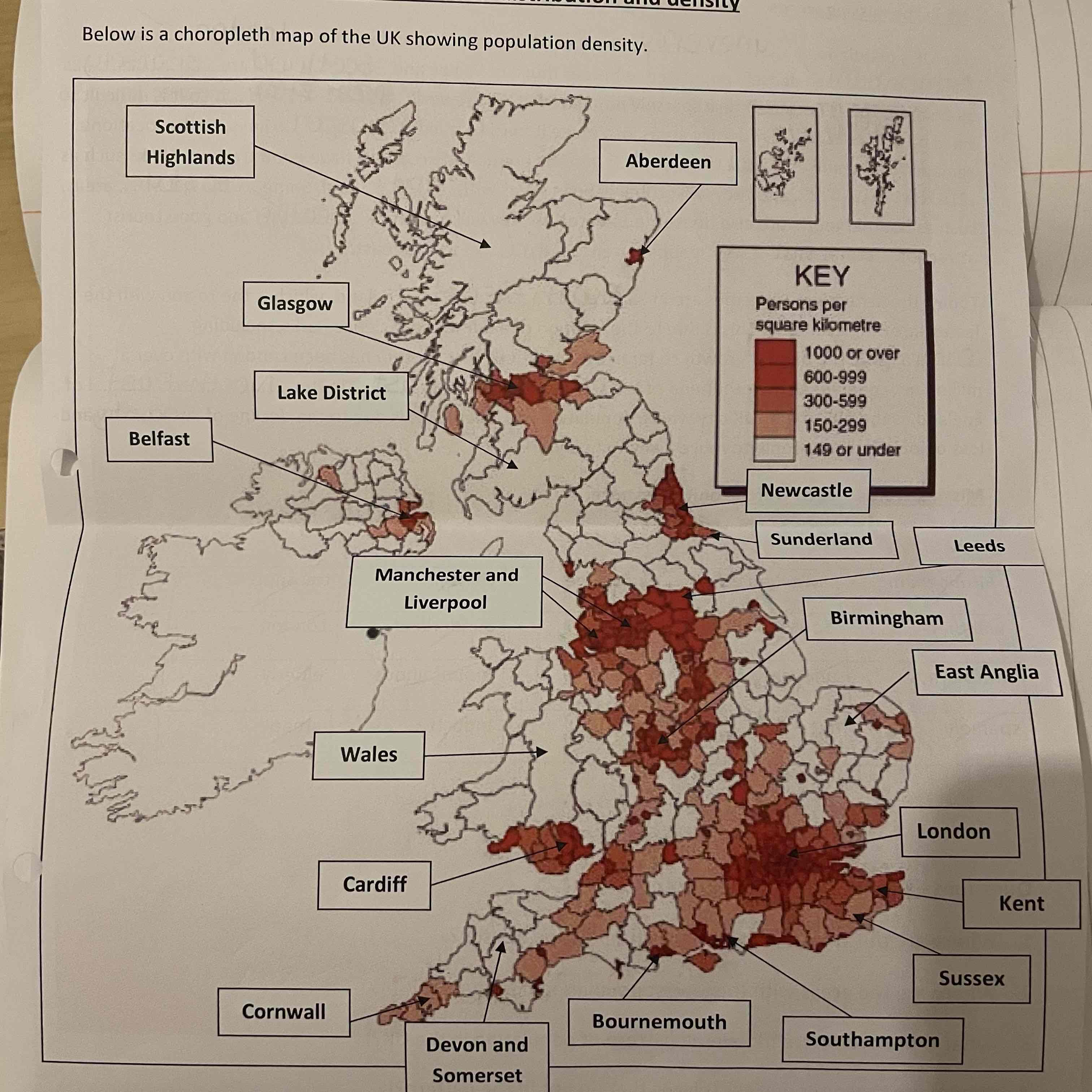
Where is London located? (2)
South-East of UK
It’s grown around the river thames which leads to the North Sea
Why is London important nationally and internationally? (3)
Transport networks
Medical facilities e.g. NHS
UK’s most wealthiest and largest city
How did London’s population change during the Industrial Revolution?
It attracted migrants during the Industrial Revolution in the C19th (domestic migration).
How did London’s population change at the start of WW2?
Reached its previous population peak at the start of WW2 in 1939 (Blitz evacuations).
How did London’s population change at the end of WW2?
Numbers declined after the war as housing was demolished and people moved out (counter-urbanisation)
How did London’s population change after 1991?
Numbers increased again after 1991 (re-urbanisation) due to many migrants from Europe and elsewhere
How big is UK’s population?
67.7 million
How big is London’s population?
9.6 million