biol121 - week 1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
chemical level
atoms are the smallest chemical units of matter (small particle)
molecules: a group of atoms working together
elements: substance that is made up of only one type of atom
all living orgamisms are made up of chemicals
proteins
diverse & have a variety of roles, insulin and growth hormones, enzymes that help all of the metabolic reactions occur in the body, structural proteins
largely responsible for structure of body tissues, enzymes
carbs
example: glucose - source of energy to create ATP, some can have structural or messaging roles
lipids/fats
energy storage and structural role: cell membrane is created with lipid - fatty acid, triglycerides, phospholipids
nucleic acids
building blocks of DNA, inherited genetic material - DNA & RNA
functions: structure, storage, messengers, control
cellular level
a group of atoms, molecules and organelles working together - cell membrane, nucleus, structure is related to their function
basic unit of life, living structural, functional unit of the living body, units that are doing the jobs to contribute to homeostasis
three main parts: plasma, cytoplasm & nucleus
tissue level
a group of similar cells working together
organ level
two or more tissues working together with a common purpose = organ
an organ: a group of different tissues working together
organ system level
group of organs working together
series of tubes to deliver blood to the organs, deliver nutrients, pick up wastes and remove them
we have 11 organ systems
control/direct, cool and warm, digest, move, protect, remove, reproduce, store, support and transport
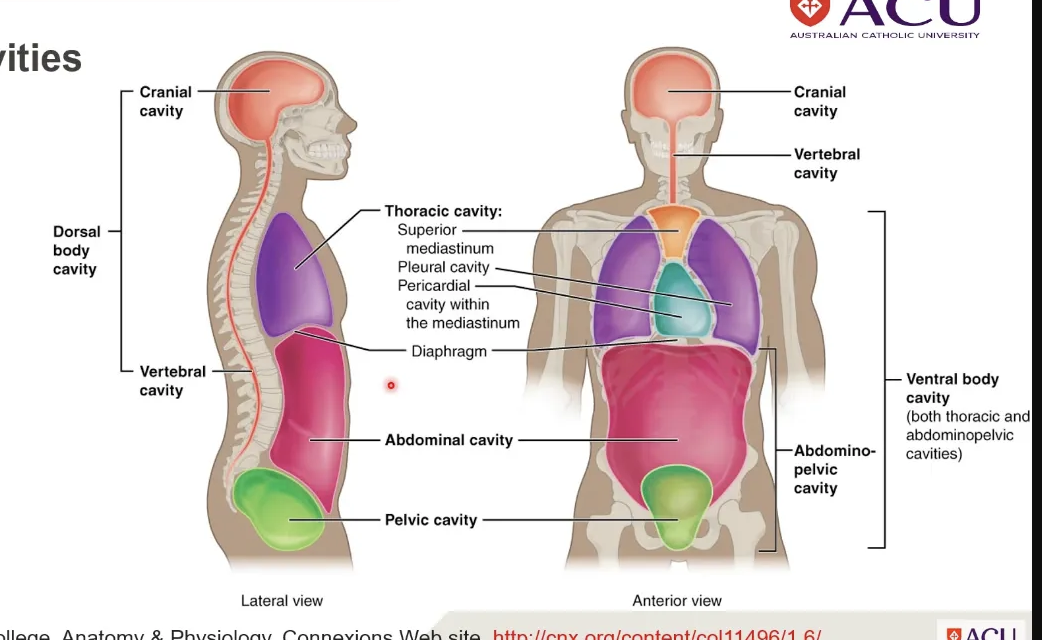
body cavities
spaces that inclose internal organs, fully inclosed sacs,
organs are suspended within these body cavities
separated by bones, muscles, ligaments and membranes
function: protect (fluid by membrane tissue that surronds them - protects from shocks and impacts), seperate and support internal organs
contract and relax - requires changes in shape and movement - body cavities allows them to do this,, without distorting or changing surrounding tissue and disrupting activity
thoracic & abdominopelvic: are separated by the diaphragm
anatomical position
standing erect, head level and eyes facing forward, hangs at side and palms forward, legs parallel and feet flat on the floor
anterior
towards the front
posterior
towards the back
cranial
towards the head
cadudal
towards the tail
above
superior
below
inferior
away from the midline
lateral
medial
towards the midline
proximal
closer to the point of attachment
distal
futher to the point of attachment
superficial
closer to the surface
deep
futher from the surface
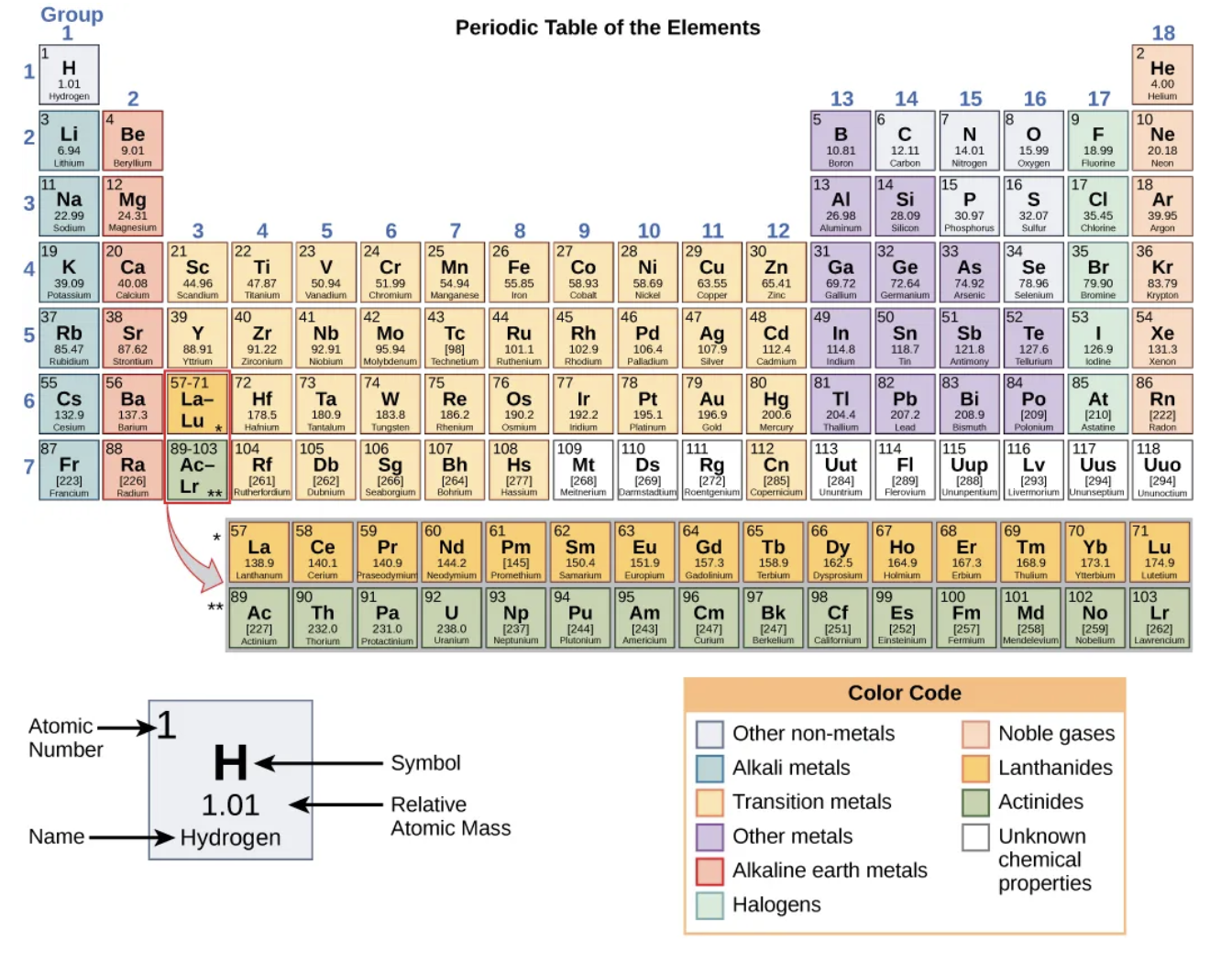
periodic table
each element has own name and chemical symbol
horizontal = period and vertical = groups
in groups - similar proprieties - group 0 are noble gases
atoms cont.
mall central nucleus made up of smaller sub-atomic particle - protons and neutrons. nucleus is surrounded by even smaller particles called electrons
protons (positive) and electrons (negative): electrical charge and neutrons are neutral
electrons
in an atom are arranged in energy levels - orbits or shells, each electron are found in a particular shell
innermost shell - lowest energy level fills with electrons first
each shell can only hold a certain amount until it becomes full
first = 2, other shells = 8
outmost = valance - these electrons can participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms, so chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of electrons in the outermost shell
molecules and compounds
molecule: two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds
can be an element or compound - when atoms from two or more different elements react/bond together (h20)
some atoms are unlikely to react with other atoms - single atoms & have a stable electron substance because outer shell is full
other atoms react and bond together to become stable
elements form compounds in chemical reactions
atoms have fixed ratios & held together by chemical bonds
ion
an atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons
atoms can loose or gain electrons from their outer shell - when they do they form charged particles called ions
ions cont
when atoms lose electrons they form positively charged ions known as cations. When atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged ions known as anions. - these are attracted to each other due to being opposite
during ionic bonds - electrons are transferred between atoms, leaving some with fewer electrons and others with more electrons
organic compounds
all contain the elements carbon and hydrogen
carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids = small biological molecules & large biological molecules and polymers
usually lack carbon - cant be used by cells to peform complicated biological functions
inorganic compunds
not made up of living things, they usually dont contain the element carbon (besides carbon dioxide and monoxide)
water and salts (contains ions)
when inorganic acids, bases or salts in water - they seperate into ions and are surrounded by water molecules
acidic
the more H+ dissolved in a solution, the more acidic solution and the LOWER the pH
basic
the more more OH dissolved in a solution, the more basic solution and the HIGHER the pH
neutral
hydrogen ions = hydroxide ions
distilled water
when the H+ ions from an acid react with the OH– ions from an alkali, a neutralisation reaction occurs to form water. ****
plasma membrane function
physical barrier, separated ICF and ECF
very different in ICF AND ECF and this maintains homeostasis
gatekeeper - controls the entry and nutrients, elimination of wastes and release of secretions = determines movements in and out of cells
communication with cells and organs by receptors
maintaining homeostasis is vital for cell and organisms
links adjacent cells - specialises connections between cells and membranes - gives tissues stability
plasma membrane function
phospholipid: basic structure
hydrophilic phosphate heads - at membrane surface, in contact with aqueous environment
hydrophobic tails - on the inside, wont associate with water molecules
proteins (peripheral - bound to outer surface of the membrane or integral - span the membrane, if removed = membrane would be destroyed)
channels, gates or pumps = transport - by passing the hydrophobic tails
carrier proteins
receptors
anchoring
selective permeability
due to the structure of the membrane and lipid bilayer, it lets some substances in.out and stops others due to solubility, size, and charge
water souble molecule: transport chanell because it doesn’t want to interact with hydrophobic fatty acid tails
small fat-souble: directly passes through
small charged ion: ion channel, as it’s charged
epithelial
covers exposes surfaces, lines internal passage ways and chambers and forms glands, all substances must pass through if leaving body
protection, absorption, filtration, exertion, secretion
exposed to external surfaces
classified by shape (second name) and number of layers (first name)
simple layers: transport
multiple: protection
outer layer of the skin, lining of intenstine
connective
supports
supports and binds other tissues
structural framework
storing energy
protecting delicate organs and defending them from invading organisms
provides insulation and protection
extra-cellular matrix - heaps
amount of cells present - less
classified according to physical properties
connective tissue proper: fat, tendons, ligaments,
fluid connective tissue: blood and lymph
supporting connective tissue: blood and bone
= dermis of skin
= bone, blood & fat cells
= ligaments and tendons
muscle
moves
specialised for contraction to facilitate movement
capable of contribution
joint stability, provides structural control and produces heat
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
very well organised - heaps of cells
nervous
controls
main component of nervous system, which regulates and controls body functions
primary function is communication
two basic cells: neurons - electrical impulses (nerve cells), neurogila (support cells - repairs and supplies nutrients to neurons)
contenous membrane
skin, covers the entire body surface, organ system attached to epithelium, exposed to air and is a dry membrane - protection
mucous membrane
line all body cavities that upon to the outside of the body - digestive, respiratory, urainary and reproductive tracts - coated with the secretions of mucous glands, prevents organs from drying out and protects from microbes - adaptive for absorption and secretion
serous membrane
line body cavities closed to the exterior of the body (organ within cavities, and aren't directly open to exterior), secrete lubricating fluid
synonvial membrane
synovial: line joint cavities and produce fluid within the joint, lacks an epitelium and only connective tissue
diffusion
the net movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to low
osmosis
he movement of water molecules across a semi-pearbale membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration
active transport
the movement of an ion or molecule from an area of lower concentration to an area of high concentration, via a channel or carrier protein, against a concentration gradient
hyPERtonic
have a higher concentration of soultes compared to what is inside the cell - the cell looses water via osmosis and shrives - cell dehydration (crenation)
hyPOtonic
have a lowe solute concentration, gain water via osmosis and swell - most extremed example = distilled water , bursts (lysis)
isotonic
have same solute water concentration as inside of the cell - same amount of water leaving and entering - cells retain normal shape
homeostasis
maintenance of normal physiological parameters within the body
the body’s ability to maintain a stable and balanced internal environment
detects when something is out of balance, processes this information and bring about changes that will restore this balance
this equilibrium is required to keep us alive
feedback systems
controlled condition (variables that is monitored - temp) & stimulus (any disruption to the controlled condition)
receptor (eg: nerve ending):: detects the change and notifies the control centre
control centre (eg: brain) sets the range upper and lower limits of the controlled condition, receives info from the receptor, evaluates and processes, thus determines which action to take, send outputs commands
effector: receives commands from the control centre and produces the response
RESPONSE: effect that changes the controlled condition
when restored - receptor stop picking up messages/change, control centre can switch off commands, effector stop doing the response
negative feedback
negative feedback: the response OPPOSES the initial stimulus to reverse the change
responses work in the opposite direction to the stimuli
negative feedback does not refer to the absolute direction of the response
most homeostasis mechanisms are negative feedback system
something that is going up, to go back down & etc
conditions that need frequent adjustments
body temp, blood sugar levels, blood pressure, blood calcium levels, blood pH
positive feedback
strengths or enhances the stimulus to produce an even great/amplified change
LARGE & RAPID change
release of oxytocin during childbirth and breast feeding, formation of the platelet, activation of immune cells
integumentary
skin, hair, nails, sweat glands -dermatology
protection, sensation and thermoregulation
nervous
brain, spinal cord, nerves , PNS - neuro & cerebro'
control communication, regulation of other body systems
endocrine
glands - hormone
secretion of hormones to regulate other body systems
skeletal
bone, cartlige - osteo, chondro
provides structure and protection, controls and supports movement, production of blood cells in bone marrow
muscular
muscles - smooth, cardaic, skletal
movements of the skeleton
cardiovascular
cardio, vaso, erythocyce (RBC), lympatic
transport 02, deliver blood, distribution of nutrients and wastes
respiratory
lungs - bronch, pulmno
gas exchange
immune
lymphatic, organs, vessels, bone marrow - lymphocyte
defence against pathogens
urinary
kidneys, bladder, urainary track - renal
excrete wastes, regulation of blood volume
reproductive
ovaraities, testies, gentalalia - oocyte, spermatocyte
reproduction
digestive
stomach, small intestine, mouth, gall bladder, liver
digesting, absorption's of nutrients