Anatomy and Physiology - Integumentary System
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Skin functions
protects your body against infection and extreme temperatures, maintains your balance of fluids and synthesizes vitamin d
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail
Epidermis
Outer layer of skin
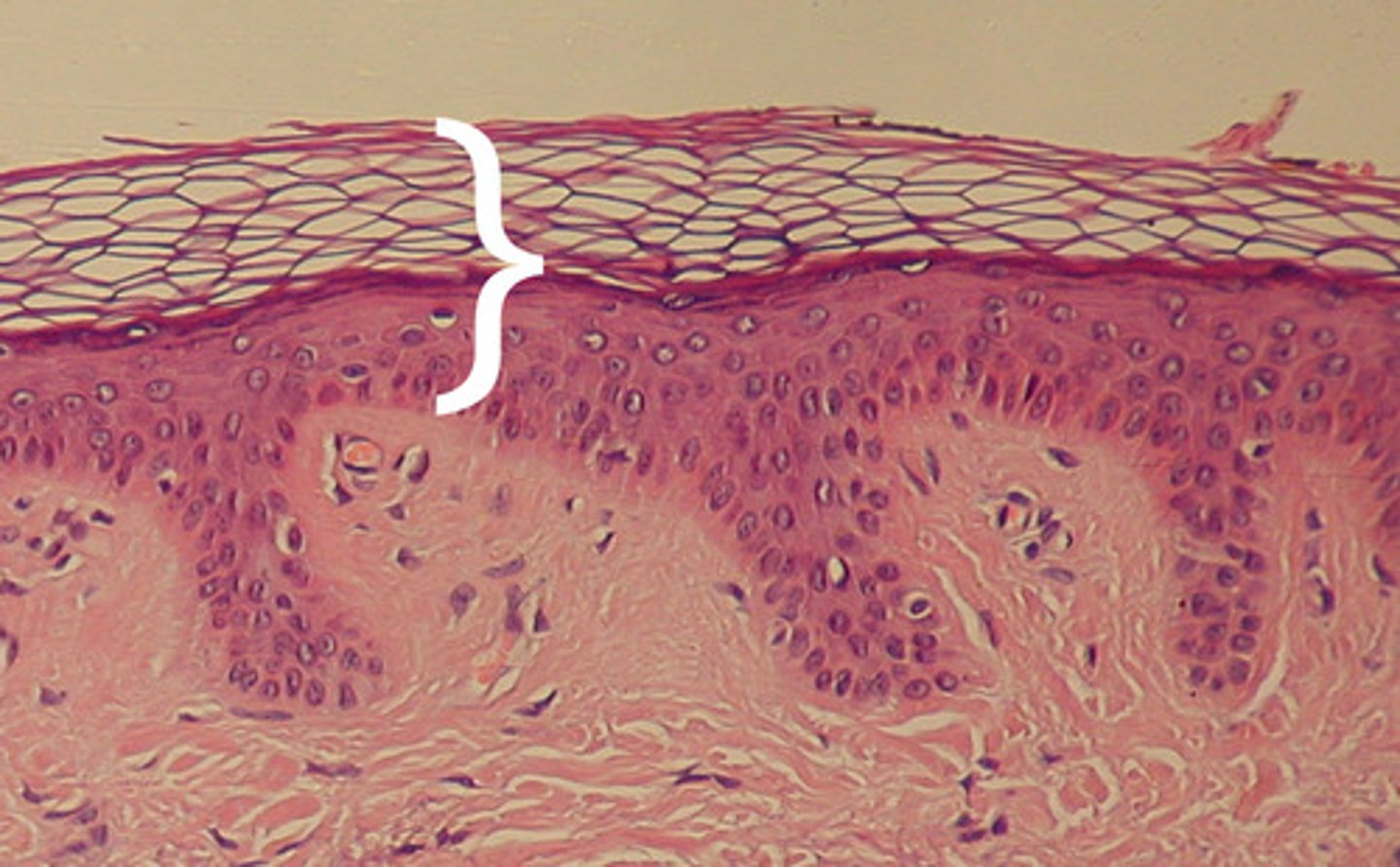
dermis
middle layer of skin
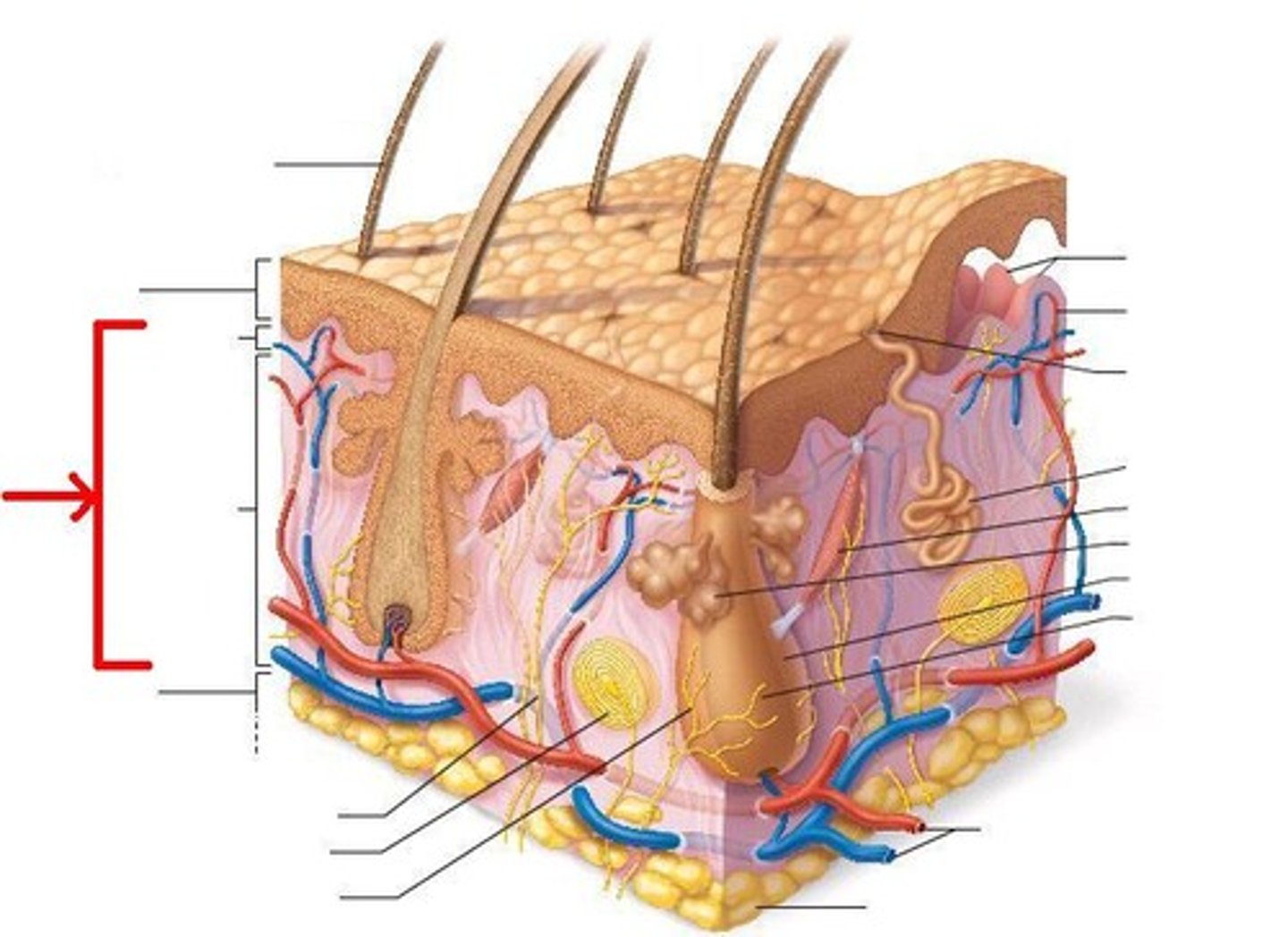
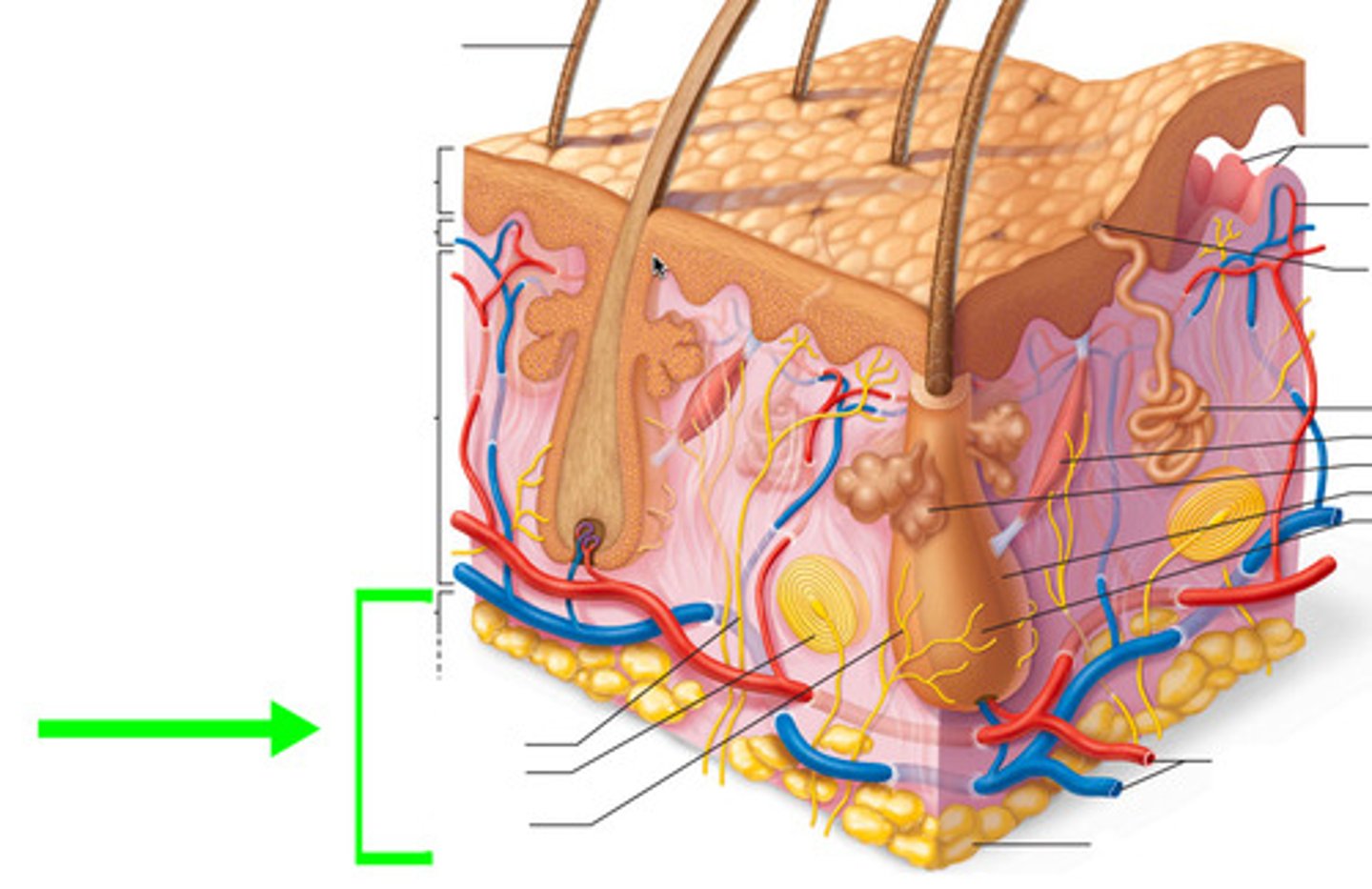
hypodermis
loose connective tissue layer of skin below the dermis
Epidermis is made up of
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinocytes
the building blocks of the tough fibrous protein keratin
Melanocytes
cells that produce melanin
langerhans cells
epidermal macrophages that help activate the immune system, located on epidermis
Merkel cells
combine with nerve endings to create a sensory receptor for touch
thick skin
Covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
Has five layers of keratinocytes
think skin
covers rest of the body
possesses hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands
stratum corneum
outermost layer of epidermis
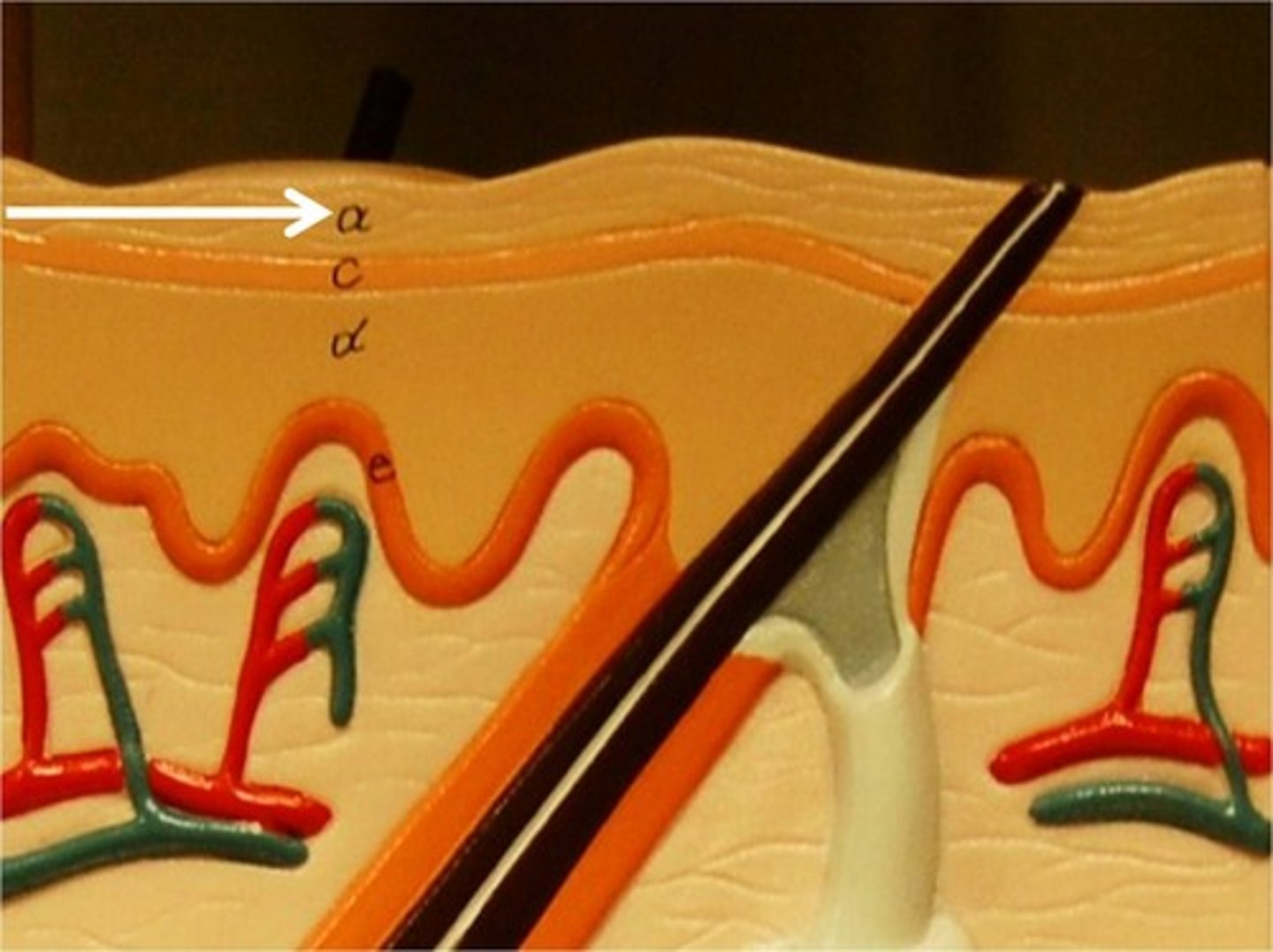

stratum lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin of the fingers, palms, and soles
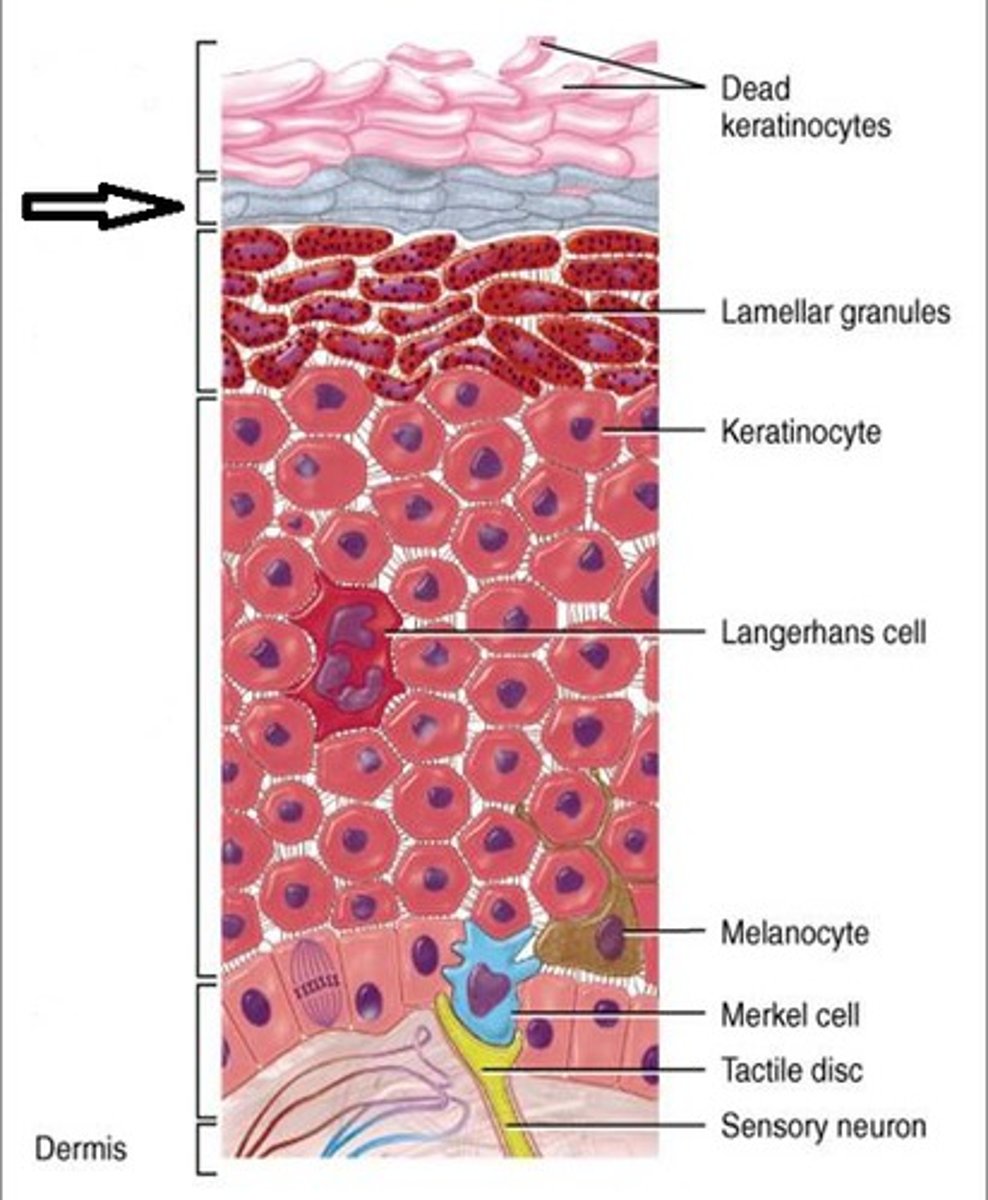
stratum granulosum
a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata and the dead cells of the more superficial strata
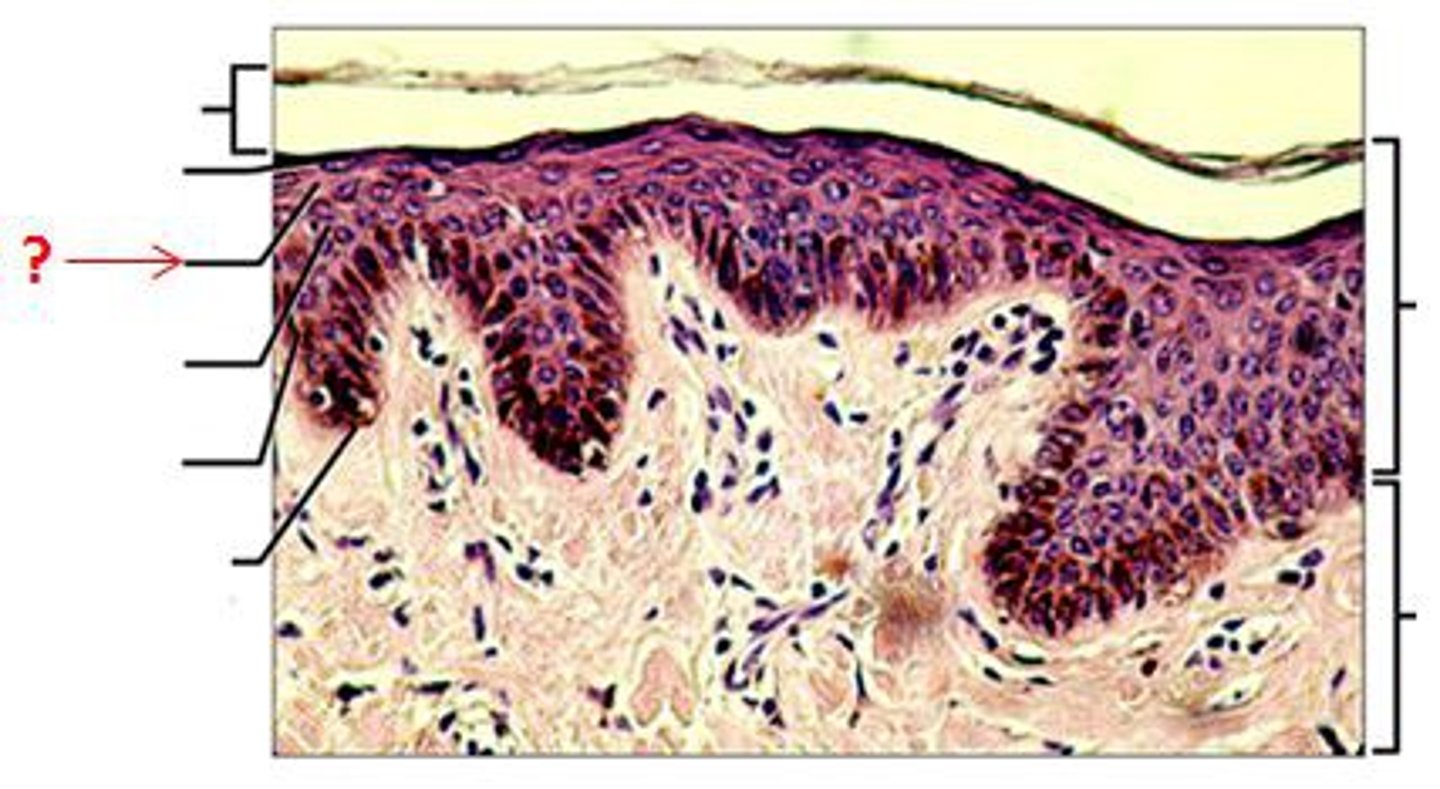
stratum spinosum
a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
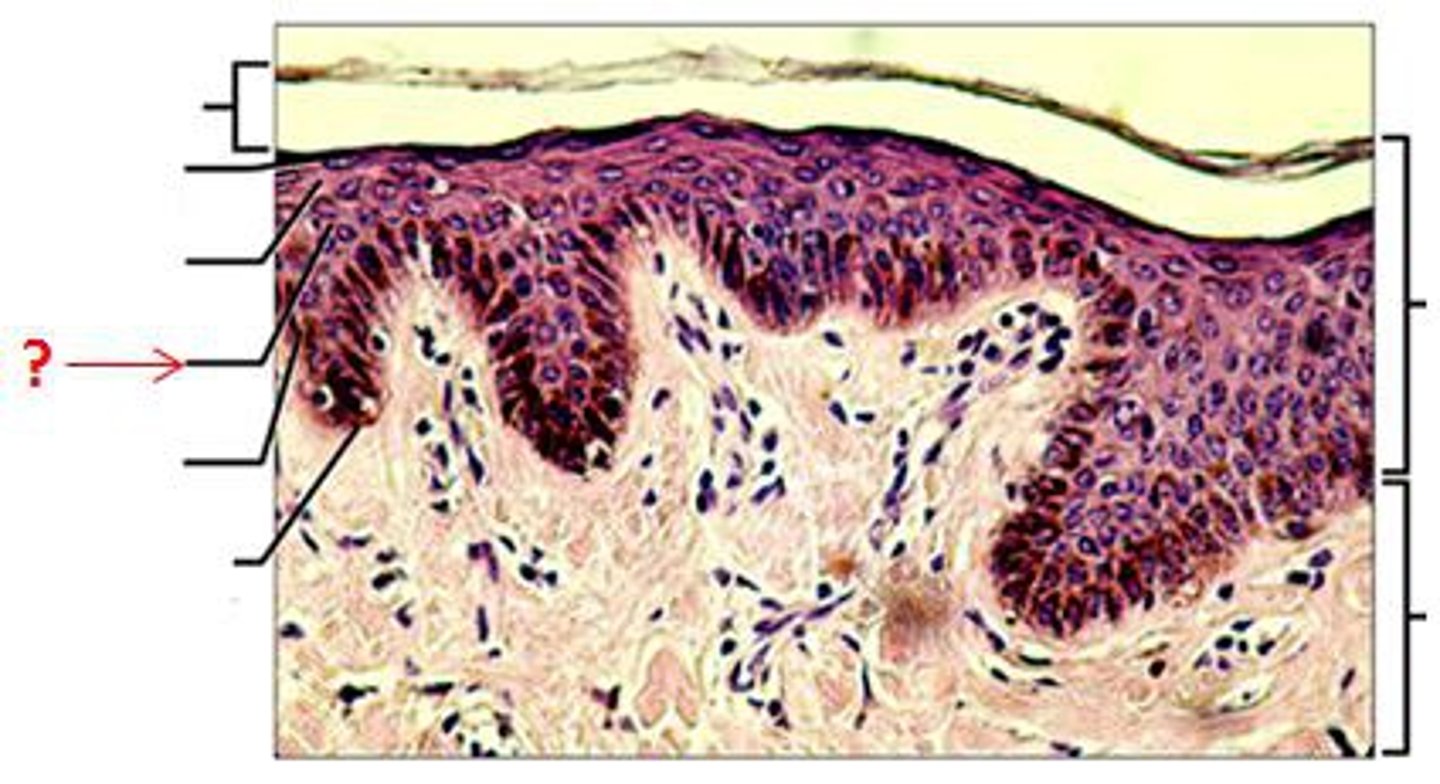
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis
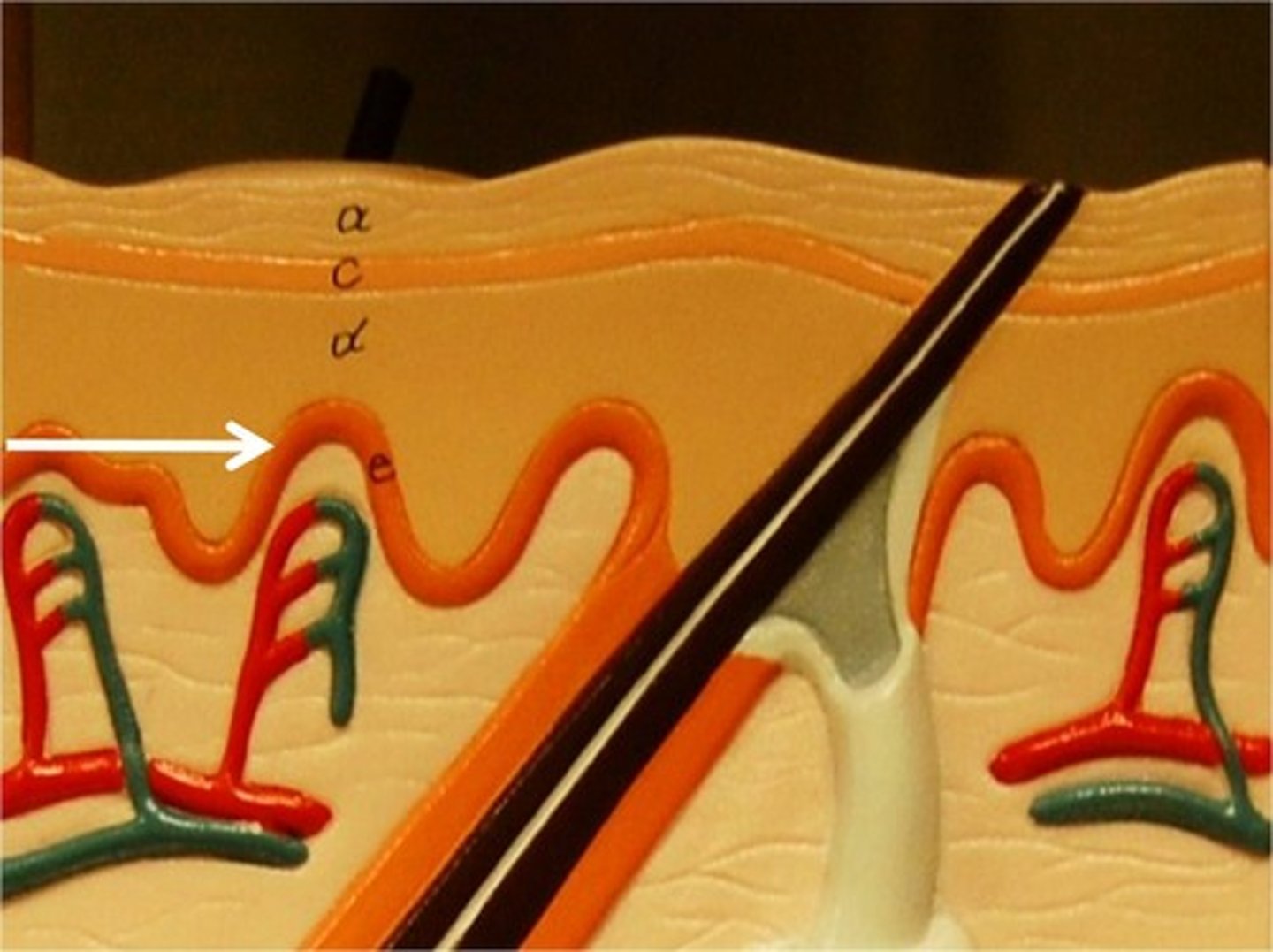
papillary layer
outer layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis
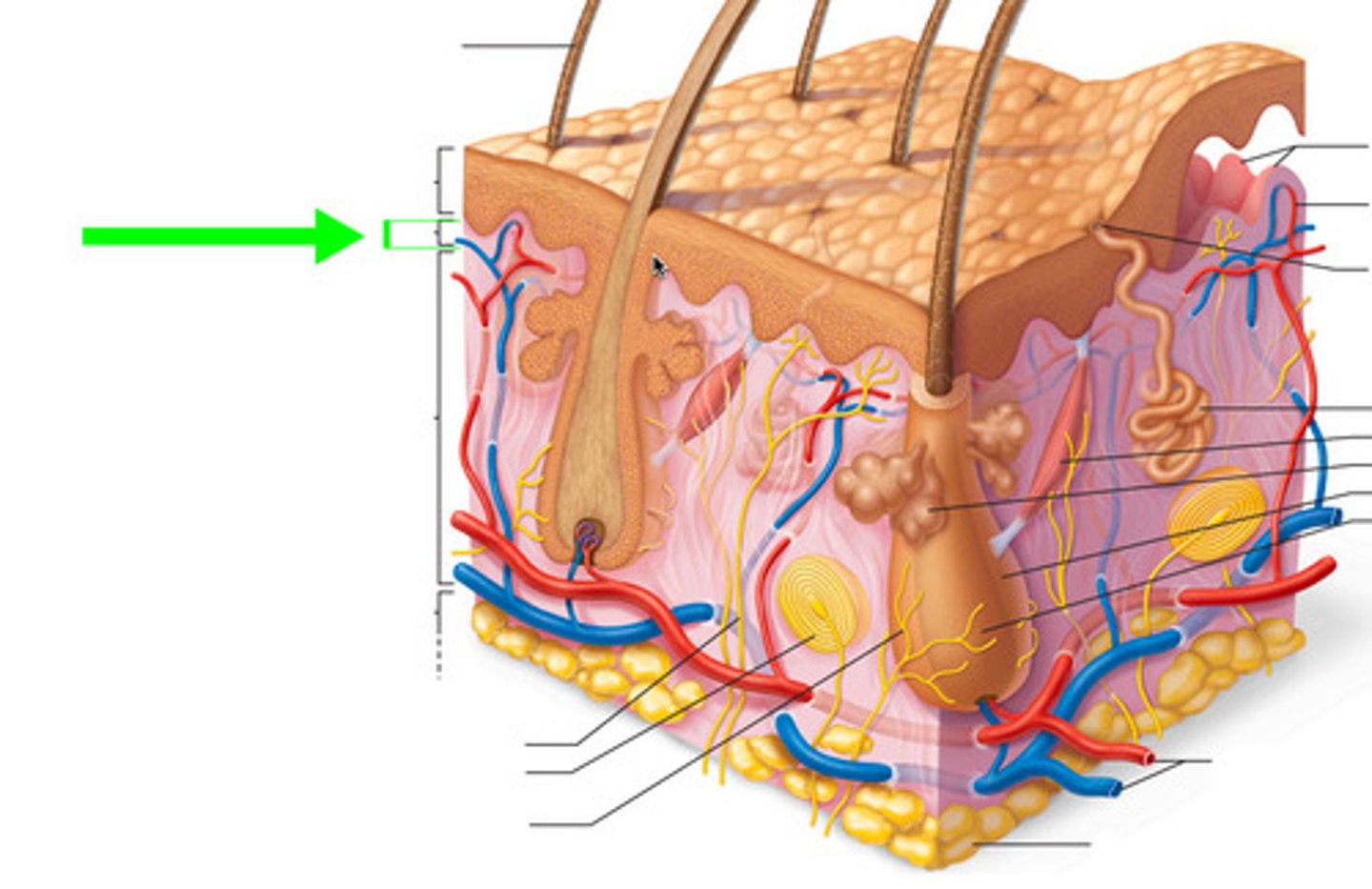
dermal papillae
a fingerlike projection of the dermis that may contain blood capillaries or Meissner corpuscles (of touch)
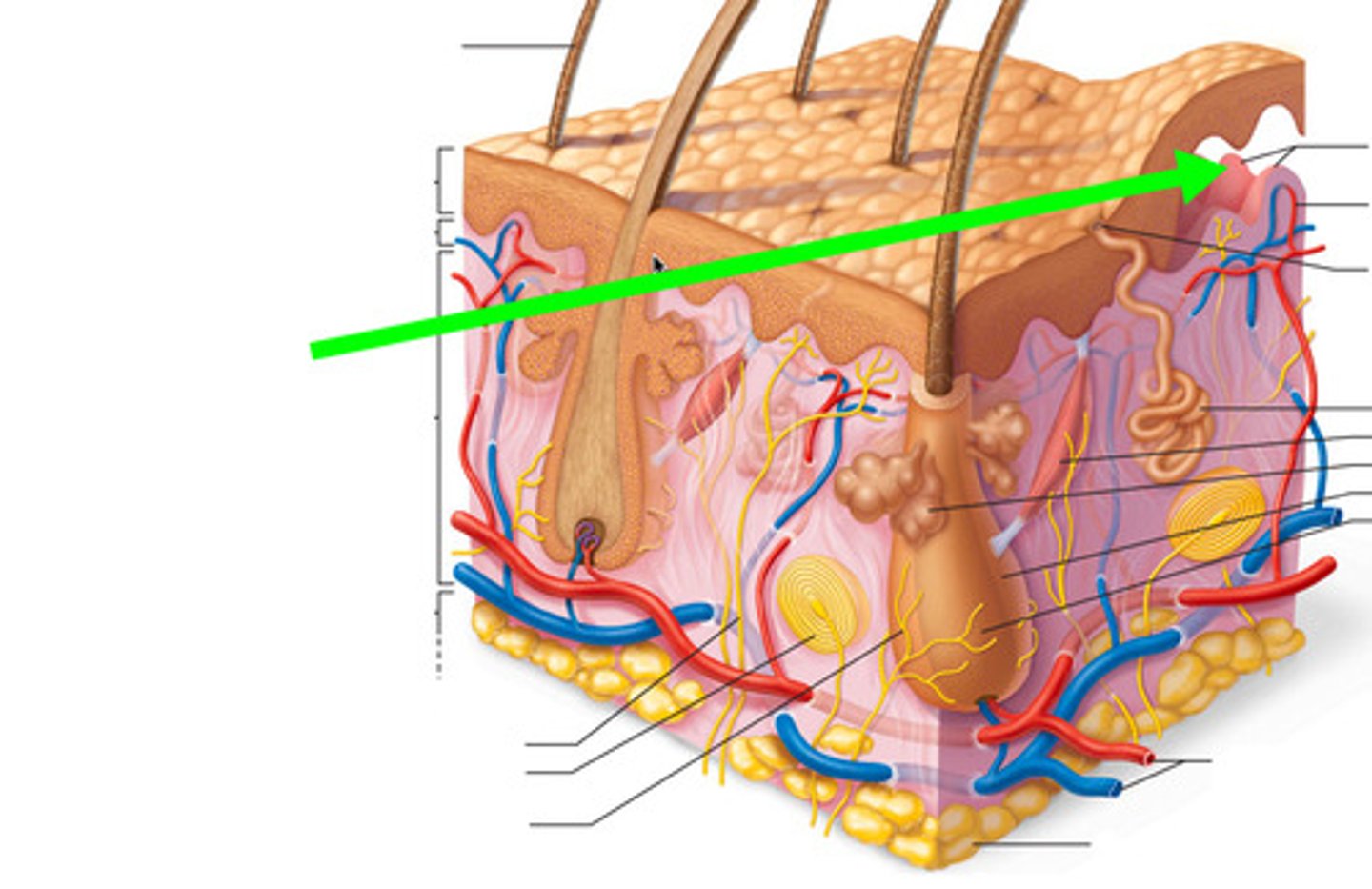
Friction ridges
the markings on the fingertips that leave oily fingerprints on surfaces we touch
reticular layer
Deeper layer of the dermis that supplies the skin with oxygen and nutrients
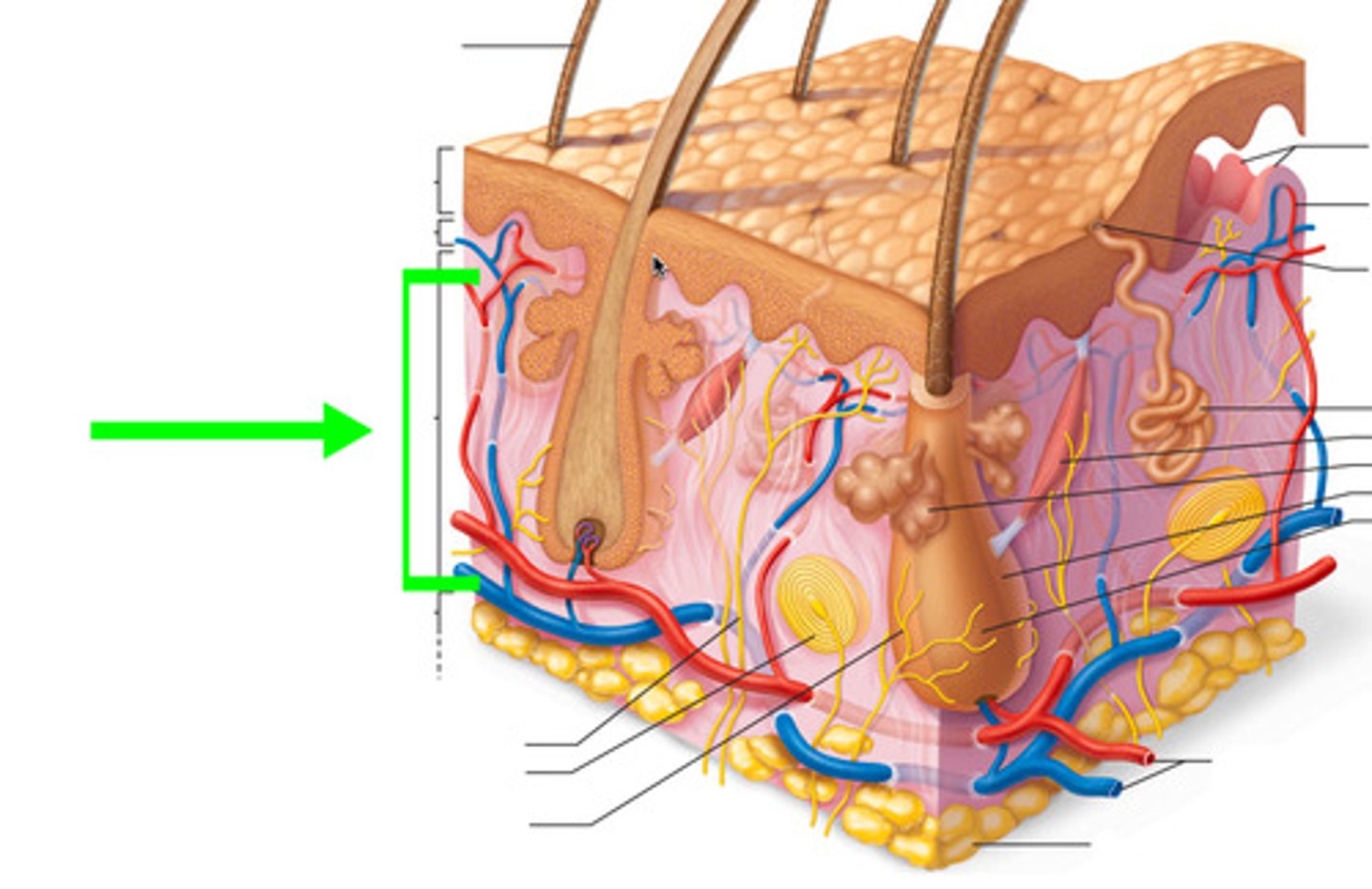
Hypodermis contains
adipose tissue
dermis contains
Blood vessels, sensory neurons, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, smooth muscle
Cutaneous sensory receptors
Receptors located throughout the skin that respond to stimuli arising outside the body; part of the nervous system.
corpuscles
living cells capable of moving about in a liquid
tactile corpuscles
small epidermal structures with nerve endings that are sensitive to touch and pressure
Lamellar corpuscles
deep pressure receptors
insensible perspiration
interstitial fluid lost by evaporation through the stratum corneum
sensible perspiration
produced by active sweat glands
hair cuticle
Outermost layer of hair; consisting of a single, overlapping layer of transparent, scale-like cells that look like shingles on a roof.
Hair shaft
The portion of hair that projects above the epidermis, keratinization is complete
Hair root
The part of the hair located below the surface of the epidermis, where keratinization is still happening
Eccrine sweat glands
Secreting glands, are far more numerous and are abundant on palms, soles of feet and forehead.
apocrine sweat glands
Found in armpits, around nipples, and groin; Secrete products into hair follicles; Produce sticky, cloudy secretions; Break down and cause odors;
Mammary glands
specialized sweat glands that secrete milk
Ceruminous glands
produce ear wax
sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
sebum
oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands