amt 124
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
The Wright Flyer, for instance, took off from a ____ and landed on ____.
rail
skids
soon after the basic problems of flight were solved, attention was turned to providing better _____ and ____of the aircraft while it was operated on the ground.
control
stability
______ and _____ wheels were first used, which in turn, gave way to specially designed landing gear and wheels that absorbed the extreme loads imparted during takeoffs and landings.
Bicycle
motorcycle
were installed to provide safer and more efficient control for slowing an airplane after landing.
braking systems
were provided to allow the landing gear to be stowed during flight to reduce aerodynamic loads, or drag.
retraction systems
The first airplanes with wheels used a ______
tricycle landing gear
In a tricycle gear configuration, the main wheels are located _____ the center of gravity and an auxiliary wheel (nose wheel) is located at the _____ of the aircraft.
behind
front
was used in order to keep the propeller further above the ground.
tail-wheel landing gear
This configuration became so popular that it is called "conventional" landing gear, even though it has the disadvantage of being difficult for ground.
tail-wheel landing gear
The most prevalent arrangement on modern aircraft is the _____
tricycle gear configuration
are configured with the two main wheels located ahead of the aircraft's center of gravity and a much smaller wheel at the tail.
Tailwheel aircraft
are highly susceptible to ground loop
Tailwheel aircraft
Prior to World War II, almost all airplanes used the _______.
tailwheel-type landing gear
During WWII such airplanes such as the_______, the _____, and the _____, as well as the commercial ______, proved that the tricycle gear configuration was superior in ground handling ease.
Lockheed Lightning
Consolidated Liberator
Boeing Superfortress
Douglas DC-4
is seldom used on civilian aircraft other than gliders.
tandem wheel arrangement
The main wheels are located in line under the fuselage and outrigger wheels support the wings.
tandem landing gear
produced by the friction of the airflow over the structure
parasitic drag
is caused by the production of the lift.
induced drag
Parasitic drag ______ as the speed increases
increases
induced drag _______ as the speed increases because of the lower angle of attack required to produce the needed lift
decreases
Non-absorbing gear include _____, ____, ____, and _____ construction.
spring steel
composite
rigid
bungee cord
do not absorb shocks but rather accept the energy in some form of elastic medium and return it at a rate and time that the aircraft can accept.
spring steel and composites
transmit all the loads of landing touchdown directly to the airframe's structure.
rigid landing gear
Some aircraft use rubber to cushion the shock of landing.
bungee cord
The most widely used shock absorber for aircraft
oleo strut
The cylinder of this strut is attached to the aircraft structure, and a close fitting piston is free to move up and down inside the cylinder.
oleo strut
Aircraft wheels must be _____ and _____ .
lightweight
strong
Most wheels are made of either _______ or ______
aluminum
magnesium alloys
the most critical part of a wheel.
bead seat area
is the half of a two-piece wheel that houses the brake.
inboard wheel half
bolts to the inboard half and holds a shrunk-in bearing cup in which a bearing is installed.
outboard wheel half
cushions aircrafts weight force on the ground
shock absorbers
types of shock absorbers (3):
rigid struts
steel struts
oleo pneumatic shock absorber
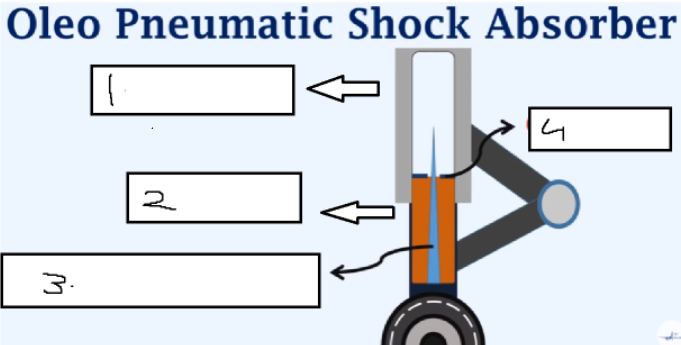
air
hydraulic fluid
flow metering pin
orifice
shock absorber compressed = ______
on ground
shock absorber extended = _______
in flight
types of extension & retraction (4);
mechanical link
electrically operated
electric-hydraulic
hydraulic
main landing gear retracts ______
inboard
nose landing gear retracts ______
forward
extension sequence for landing gear
doors open - landing gear extends - doors close
retraction sequence for landing gear
doors open- landing gear retracts - doors close
engages when the landing gear is fully retracted into the fuselage
uplock
engages when the landing gear are fully extended
downlock
prevents accidental extension of landing gear
safety valve
uses gravity for the landing gear during loss of hydraulics, loss of landing gear control unit, or electrical control.
gravity extension
safety features (4);
downlock
uplock
safety valve
gravity extension
landing gear types (5);
fixed landing gear type
retractable landing gear type
ski type
skid type
float type