int to biochem prelab week 14
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
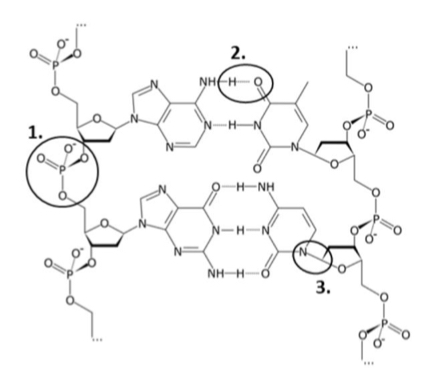
Name the following three, circled bonds in the structure of the DNA
Phosphodiester bond
Hydrogen bond
N-glycosidic
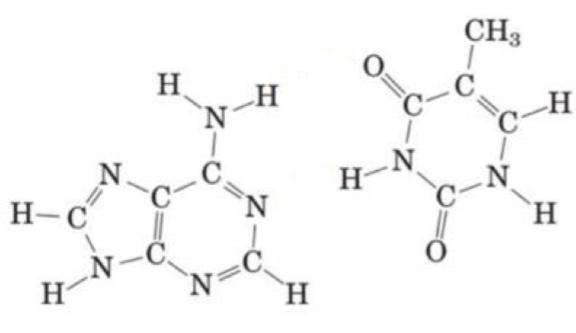
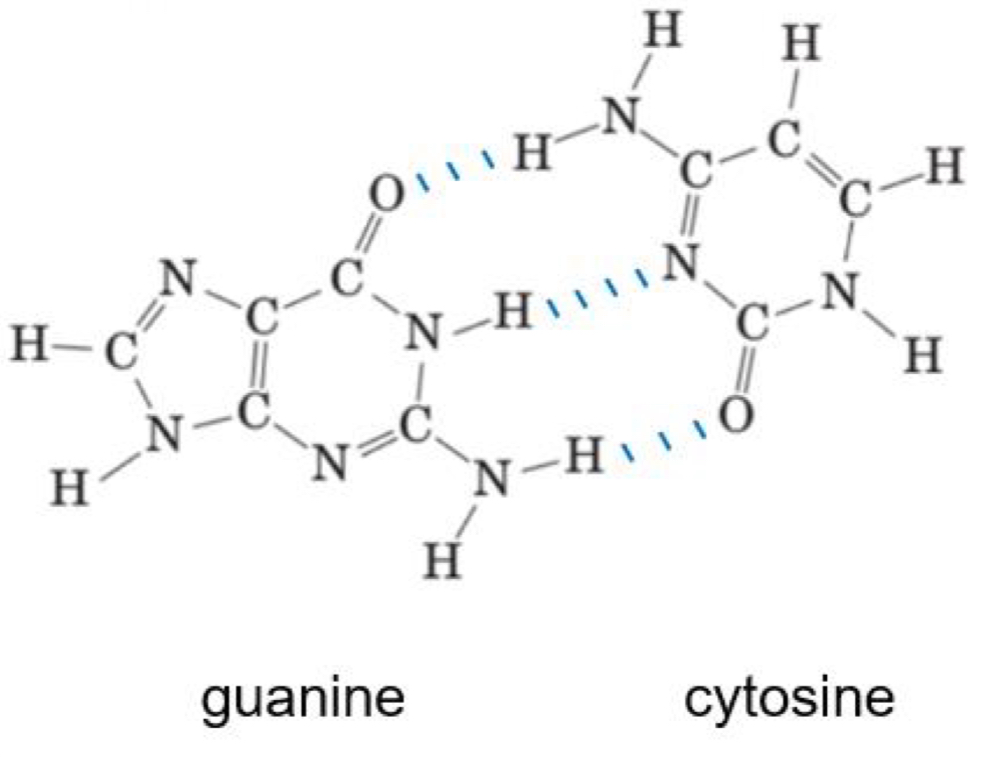
Name the following purine and pyrimidine bases and draw the hydrogen bonds that form between them
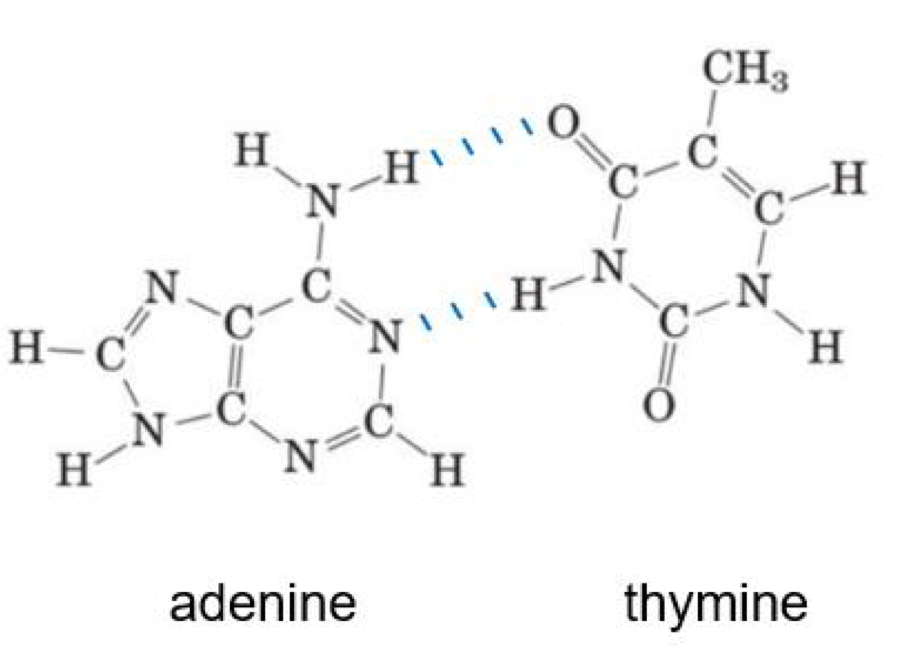
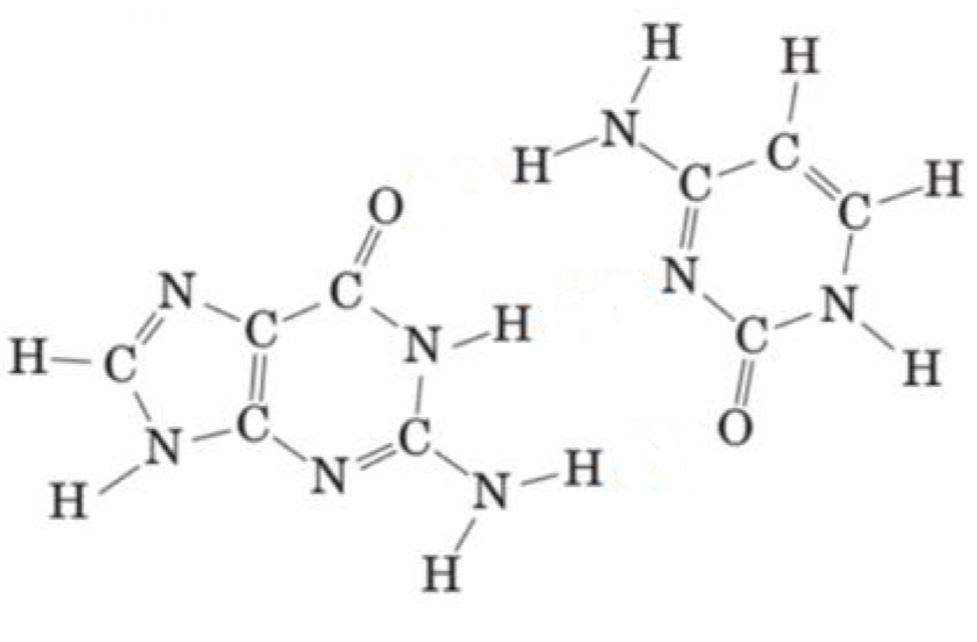
Name the following purine and pyrimidine bases and draw the hydrogen bonds that form between them
Explain briefly why we can say that bacterial DNA replication is semi conservative
When bacterial DNA replication occurs, each strand serves as a template strand; one strand of the replicated double strands is the original strand and the other is the newly synthesized strand
Explain briefly why we can say that bacterial DNA replication is semi discontinuous
The leading strand is synthesized continuously as a single strand, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously as Okazaki fragments
Name three enzymes of bacterial DNA replication that cleave phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribonucleotides
DNA polymerase I
DNA polymerase II
DNA polymerase III
Name that enzyme of bacterial DNA replication which a) creates phosphodiester bonds between ribonucleotides, b) cleaves phosphodiester bonds between ribonucleotides
a) primase
b) DNA polymerase I
Name those enzymes of bacterial DNA replication that cleave hydrogen bonds
Helicase enzyme
Name those four enzymes of bacterial DNA replication that create/seal phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribonucleotides
DNA polymerase I
DNA polymerase II
DNA polymerase III
DNA ligase
Which structural change of bacterial DNA will the formation and movement of the replication bubble lead to? Which enzyme of replication can correct this structural change?
Structural change : supercoil
Enzyme : topoisomerase II (and/or topoisomerase I)
Which newly synthesized DNA strand is formed by Okazaki fragments, and which enzymes are required for their synthesis?
Strand:
lagging strand
Enzymes:
Helicase
Primase
DNA polymerase III
DNA polymerase I
DNA ligase
Name and give the function of those enzymes that are required to join the Okazaki fragments
DNA polymerase I: removal of RNA primers while leaving the nick
DNA ligase: sealing of the nick by recreating the broken phosphodiester bond
Which enzyme of bacterial DNA replication removed the primers? Why is primer removal necessary?
enzyme: DNA polymerase I
why: the primer is RNA and must be replaced with DNA
Name and explain that characteristic based on which DNA polymerase III ( and not DNA polymerase I or II) is considered the main polymerase of bacterial DNA replication.
DNA polymerase III has the highest processivity, which is the average number of nucleotides added before the DNA polymerase dissociates
Name the three bacterial DNA polymerases and underline those which play a role in DNA replication
DNA polymerase I
DNA polymerase II
DNA polymerase III
explain briefly how bacterial DNA polymerase III will correct the incorporation of a non complementary nucleotide during bacterial replication?
DNA polymerase III removes a non- complementary nucleotide from the newly synthesized DNA strand by 3’ —> 5’ exonuclease activity and adds the correct complementary nucleotide by 5’—> 3’ polymerization activity
What is the role of the following enzymatic activities of DNA polymerase I during bacterial DNA replication? a) 3’-5’ exonuclease activity, b) 5’-3’ exonuclease activity
a) proofreading
b) removal of RNA primers
What is the difference between the mechanism of action of endonuclease and exonuclease?
endonuclease hydrolyze phosphodiester bonds at specific internal sites in a nuclei acid strand or molecule, reducing it to smaller and smaller fragments
exonuclease hydrolyze nucleic acids one by one from one end of the molecule by cleaving phosphodiester bonds either in 3’-5’ or 5’-3’ direction on one strand
What does a mismatch in the structure of the DNA mean and how does it affect the formation of secondary interactions between the deoxyribonucleotides?
meaning: occasional incorporation of incorrect nucleotides, leading to a non complementary base pairing
how: inappropriate hydrogen bonds between deoxyribonucleotides cause deformation in the structure of the DNA
What is the role of the DNA methylation in the process of bacterial mismatch repair?
Name the bacterial DNA methylase enzyme
role: promotion of the mismatch repair on the unmethylated strand by distinguishing between the newly synthesized DNA strand and the parent DNA strand
name: Dam methylase
Name those proteins that defect and localize the DNA alterations in the following bacterial repair processes, a) mismatch repair, b) base-excision repair, c) nucleotide-excision repair
a) Mut L and Mut S
b) DNA glycosylase
c) ABC exinuclease
Name the proteins that function as endonucleases in the following bacterial DNA repair processes. a) mismatch repair, b) base-excision repair, c) nucleotide-excision repair
a) Mut H
b) AP endonuclease
c) ABC exinuclease
Name the proteins that function as exonuclease in the following bacterial repair processes. a) base-excision repair, b) nucleotide-excision repair
a) DNA polymerase I
b) None because DNA Helicase removes a DNA fragment containing the damage, and there is no need for exonuclease action
Give the function of the following proteins of bacterial DNA repair processes. a) DNA photolyase, b) O6- methylguanine DNA methyltransferase, c) AlkB
a) correction of pyrimidine dimmer caused by exposure to UV light
b) correction of methylated nucleotides by removing the methyl group at O6 site of guanine
c) direct repair of alkylated bases