University of Toronto ANT100Y1 Midterm
1/313
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
314 Terms
What are the four main fields of Evolutionary Anthropology?
1. Primatology
2. Paleoanthropology
3. Forensic Anthropology
4. Medical Anthropology
Primatology
The study of our extant non-human primate relatives
Palaeoanthropology
The multidisciplinary study of the biological evolution of human & non-human primates.
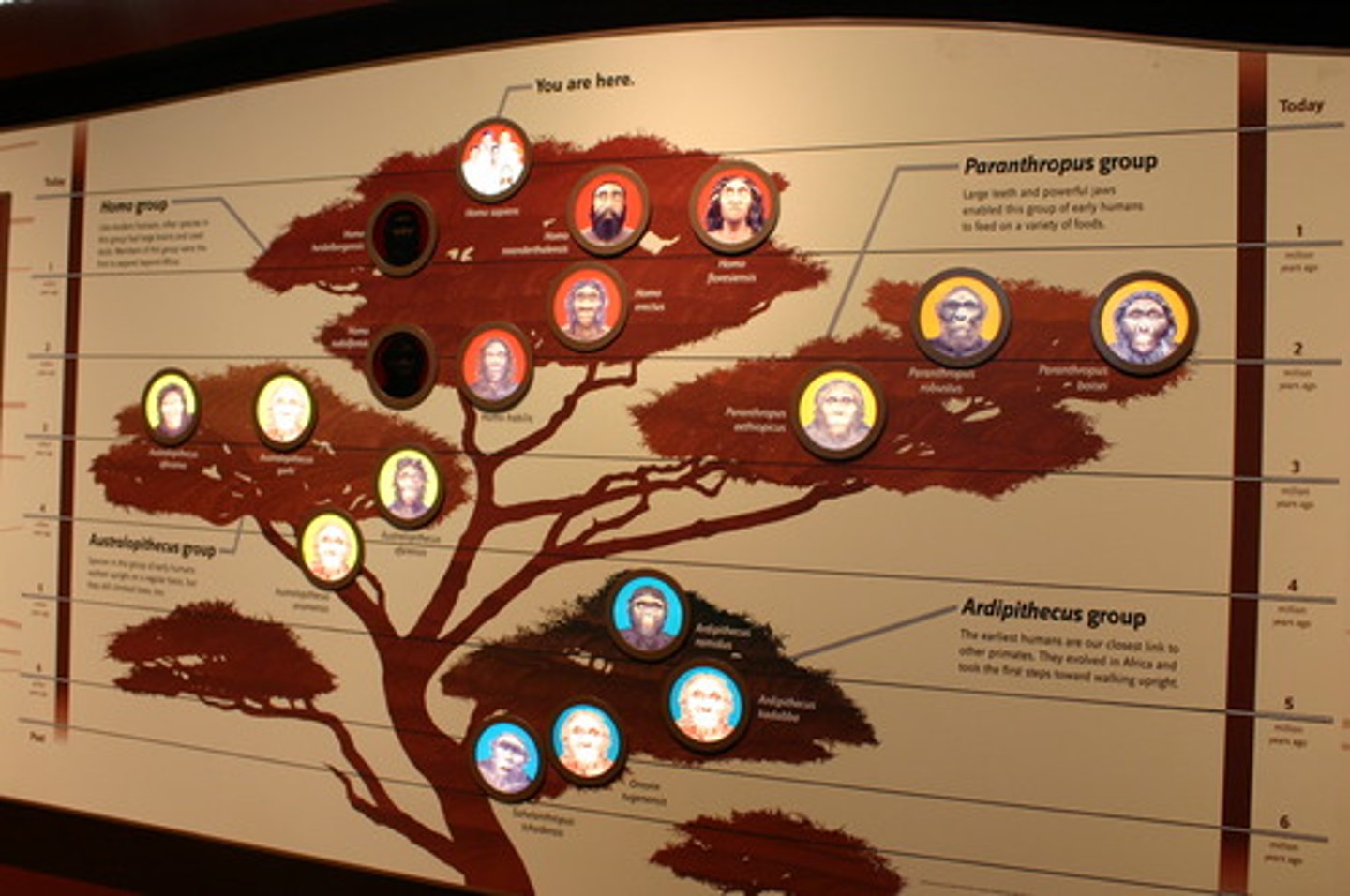
Human variation
Spatial & temporal variations in human features - size, shape, pigmentation, etc.

Medical anthropology
The study of how social, environmental, & biological factors influence health & illness of individuals in all size of a community
Forensic anthropology
Focuses only on the skeletal remains of humans
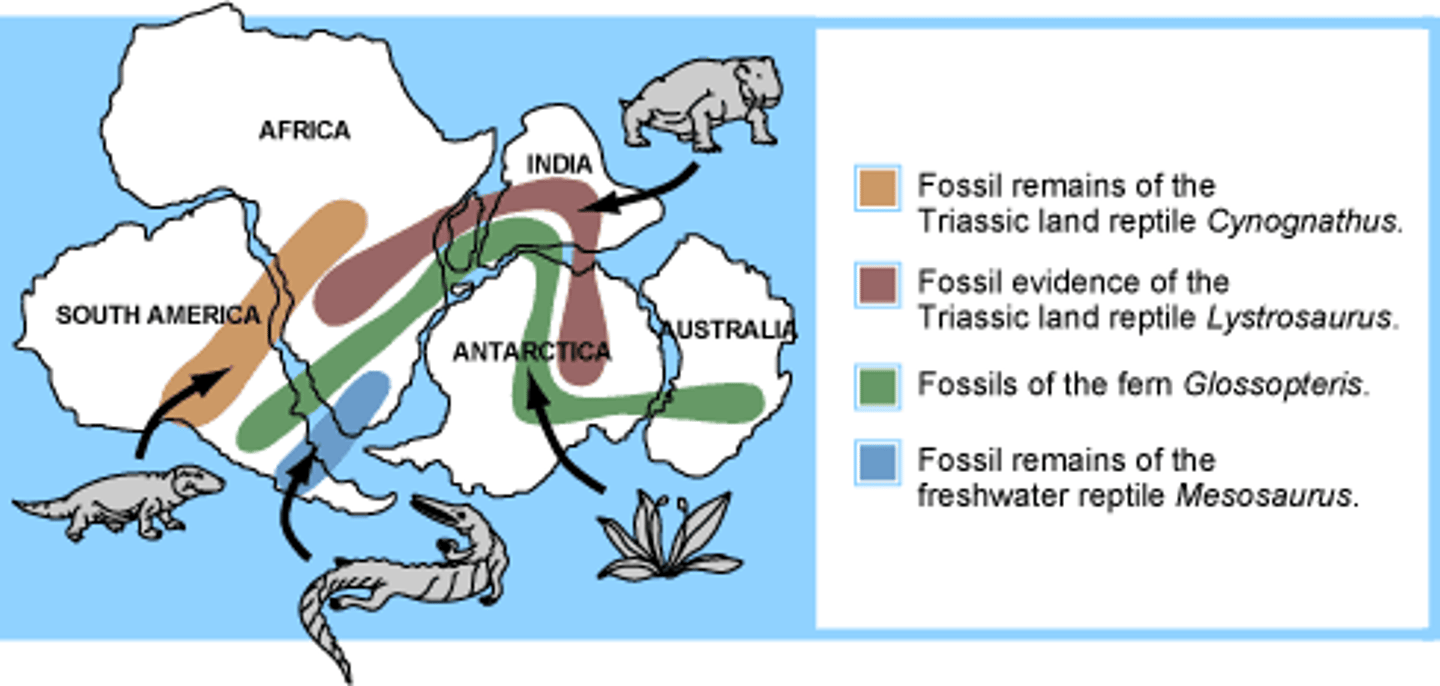
Biogeography
The study of where organisms live, at what abundance, and why they are or aren't there
Descriptive research
Collecting data about the study subjects or objects. Does not demonstrate causal relationships.
Causal research
Involves looking for one thing that happens that causes another to happen or change. (Cause + effect)
Applied research
The means by which a specific, recognized need can be met. "Basically, you actually do the thing, then see what happens."
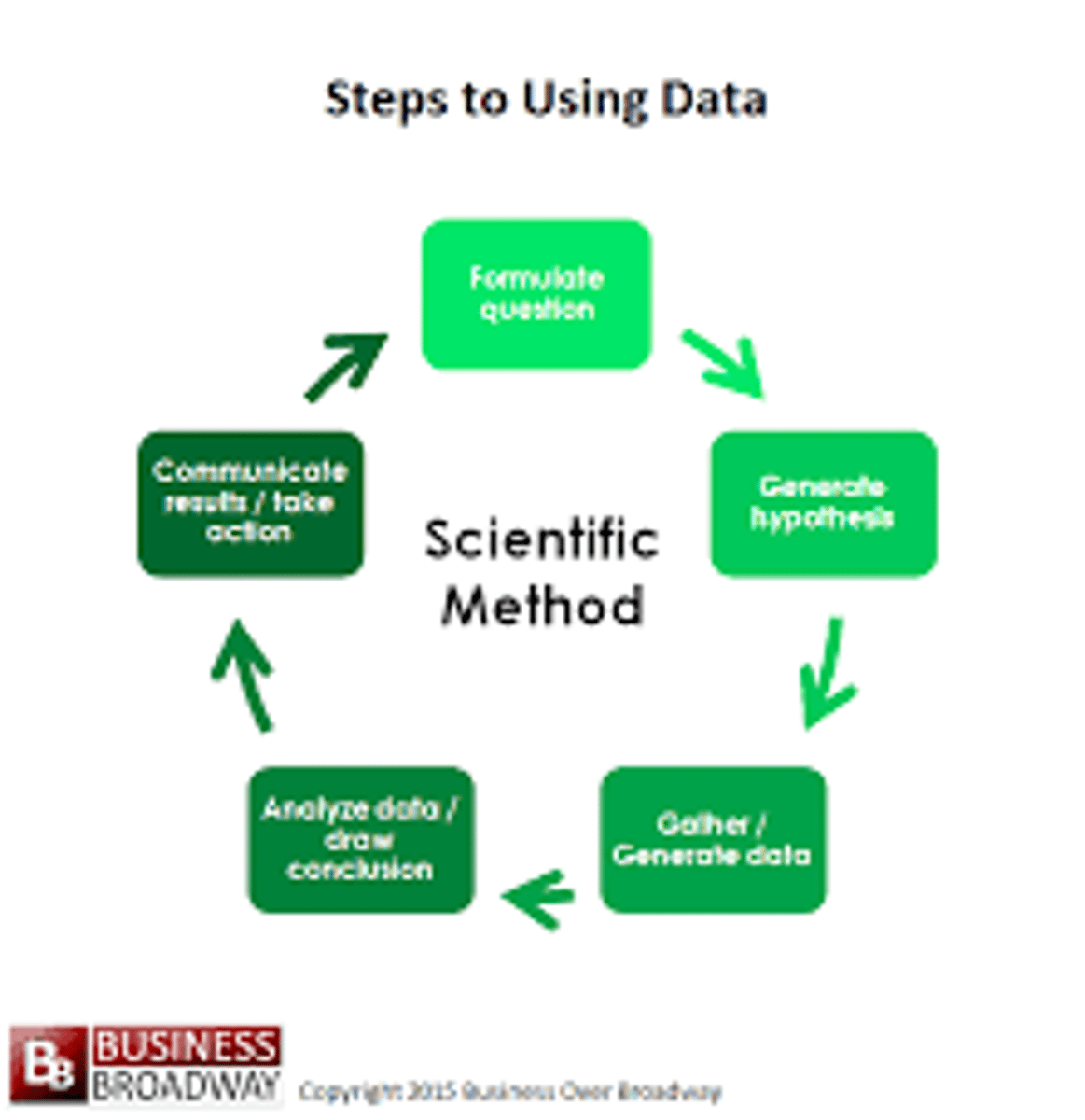
The scientific method
1. Observation of phenomena
2. Formulation of a hypothesis
3. Development of methods to test validity of hypothesis
4. Experimentation
5. Conclusion that supports or modifies the hypothesis
Carl Linnaeus
(1707-1778). Swedish physician and botanist. Father of taxonomy - responsible for the taxonomic system and binomial nomenclature.
Georges-Louis Leclerc
(1707-1788). French aristocrat, mathematician and naturalist. Wrote "Histoire Naturelle". First to observe adaptation

Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
(1744-1829). Developed the first cohesive theory of evolution, thought organisms could pass on characteristics through an "unknown nervous fluid".

Georges Cuvier
(1769-1832). Helped establish scientific disciplines of comparative anatomy and palaeontology. Invented catastrophism. Believed in the fixity of species.
Fixity of Species
The notion that species, once created, can never change; an idea diametrically opposed to theories of biological evolution.

The three ways in which population genetics can change
1. Natural selection
2. Genetic drift
3. Gene flow
Taxonomic system of classification
System in which species are grouped into broader categories called genera (genuses)
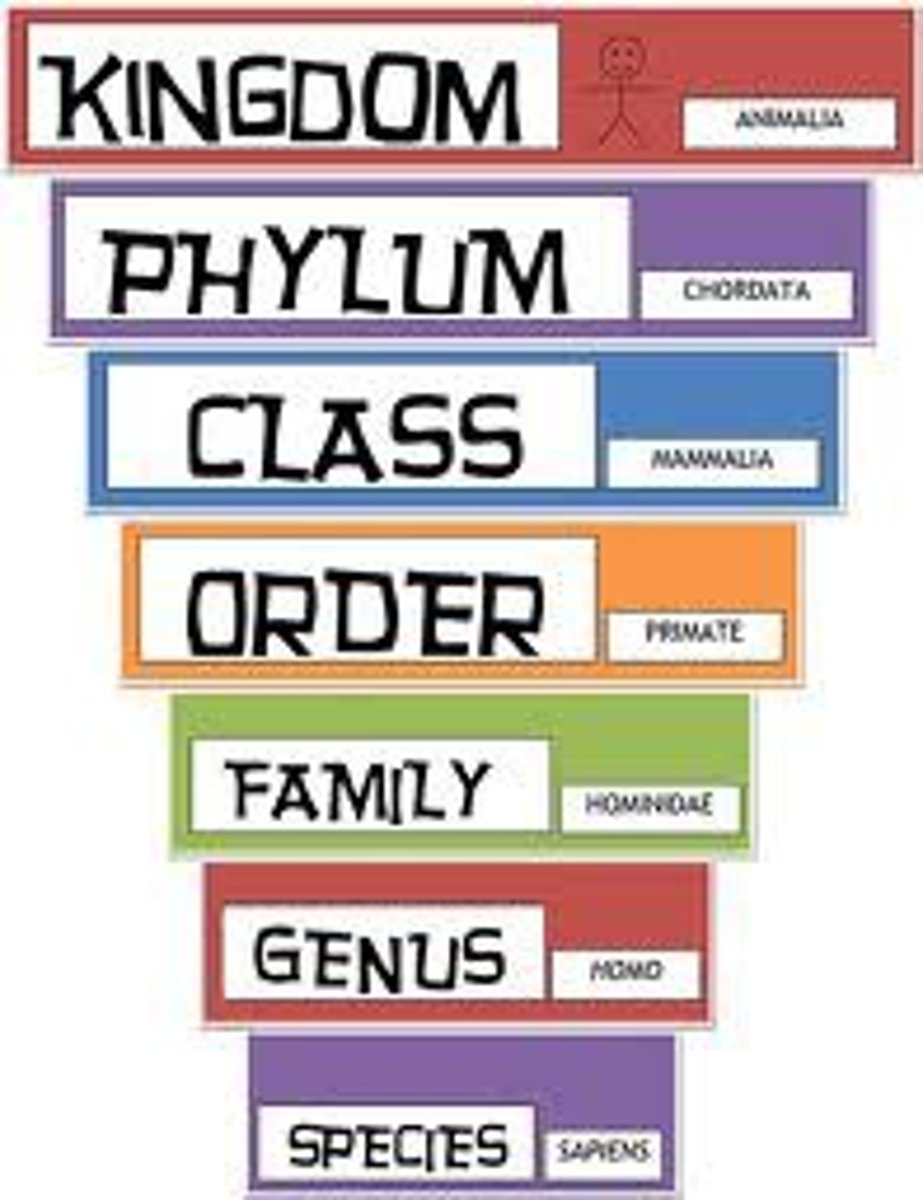
Binomial nomenclature
A system for giving each organism a two-word scientific name that consists of the genus name followed by the species name

Catastrophism
A theory that states that natural disasters such as floods and volcanic eruptions shaped Earth's landforms and caused extinction of some species. Allows for changes but doesn't refute Earth's biblical age.

James Hutton and Charles Lyell
Scientists who proposed the Earth was millions of years old due to their geological findings.

Uniformitarianism
Charles Lyell's idea that geologic processes have not changed throughout Earth's history.

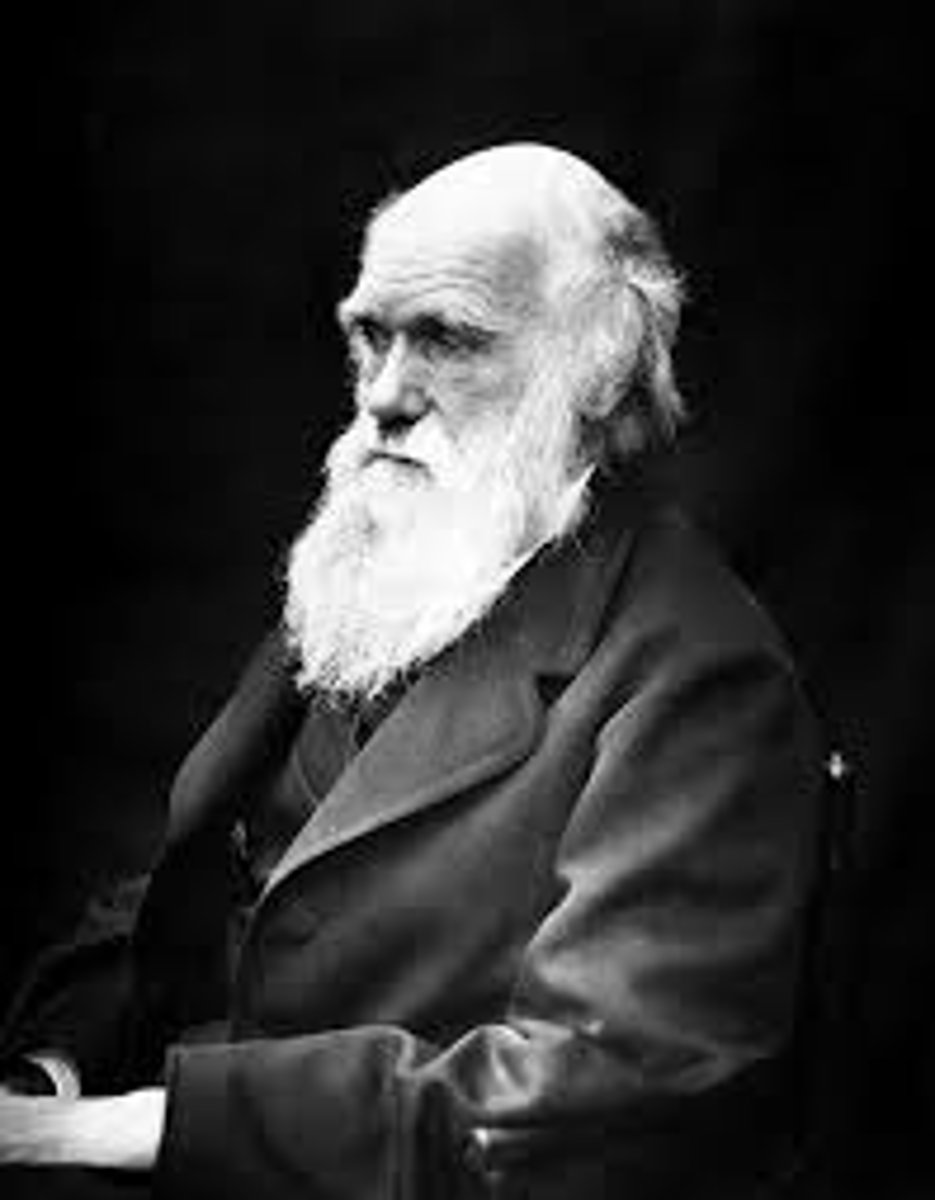
Charles Darwin
(1809-1882). English naturalist and scientist whose theory of evolution through natural selection was first published in 'On The Origin of the Species" in 1859.

Herbert Spencer
English philosopher and sociologist who applied the theory of natural selection to human societies (1820-1903); coined the term "Survival of the Fittest". Also a eugenicist lol

Gemmules
As proposed by Darwin, the units of inheritance, supposedly accumulated in the gametes so they could be passed on to offspring.
Gregor Mendel
(1822-1884). The "father of genetics". Gregorian monk who experimented with breeding pea plants.

Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.

Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism
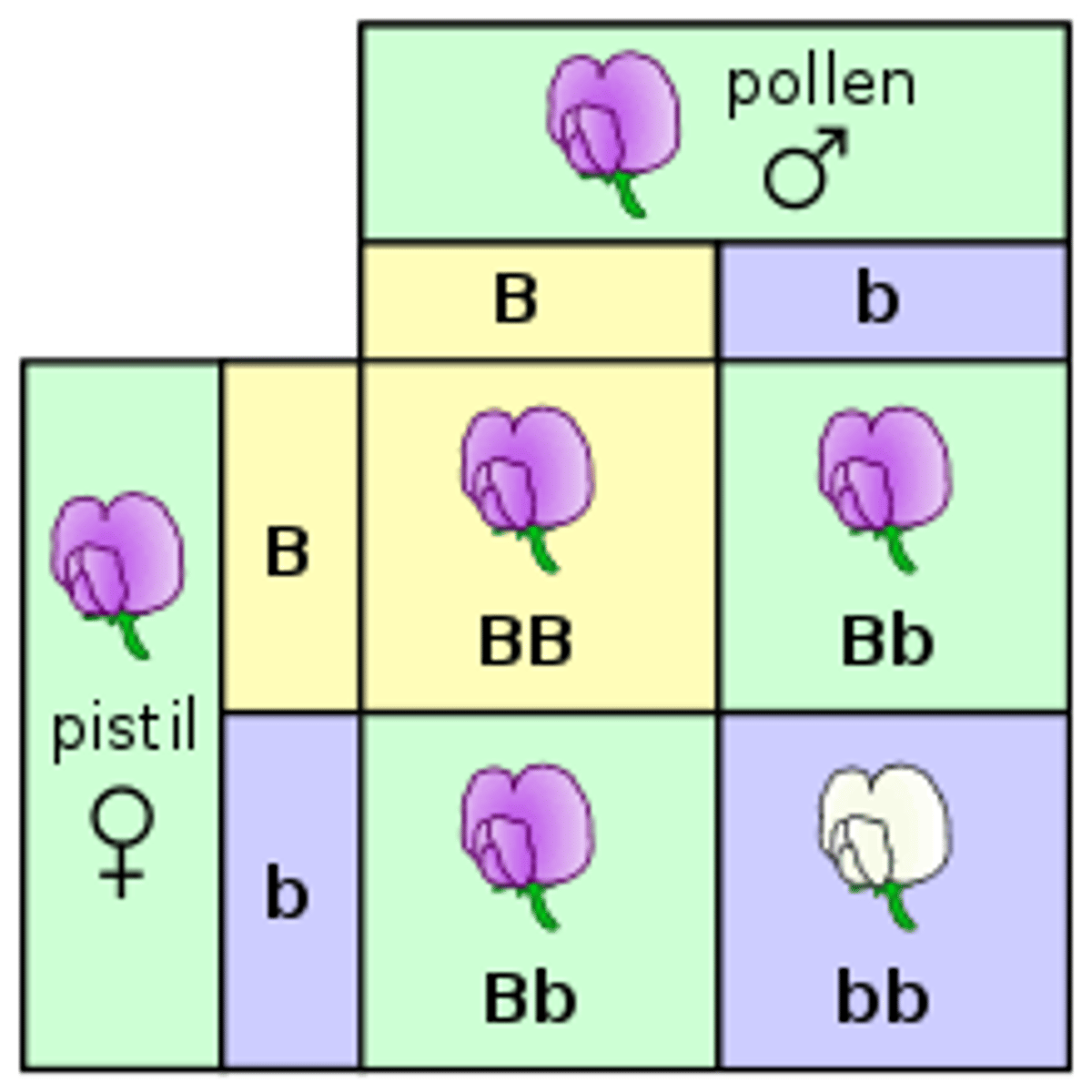
Microevolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations; small changes in biological evolution.
Stages of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PMAT)
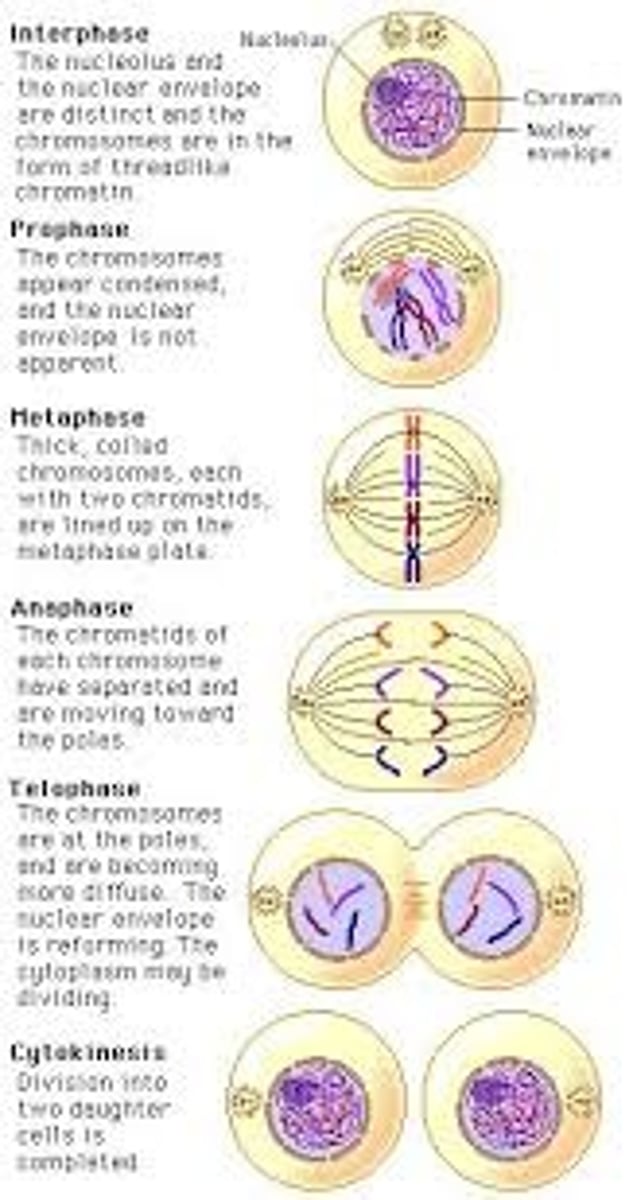
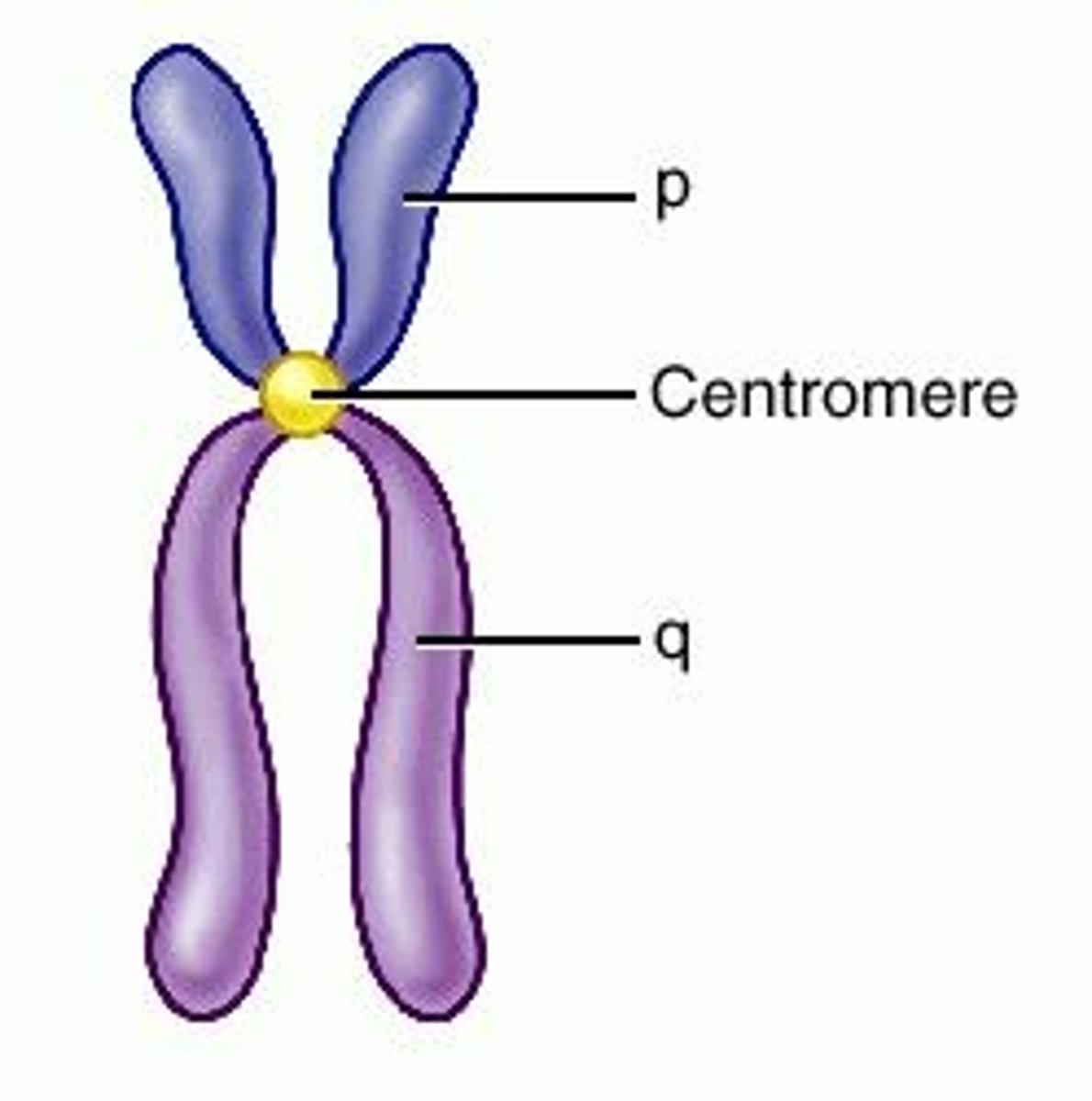
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
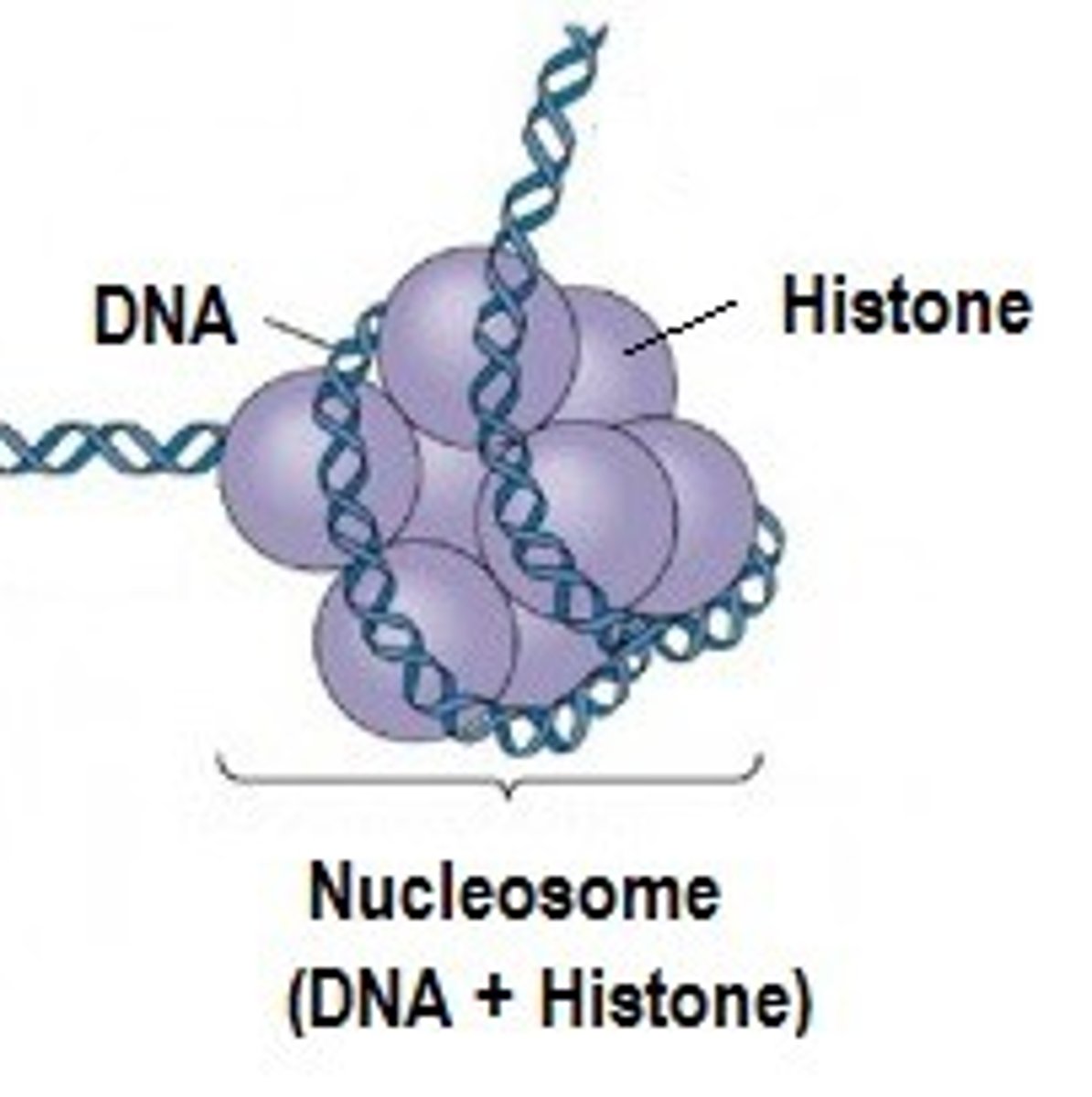
Histones
Spool-like proteins that each DNA strand is wrapped around
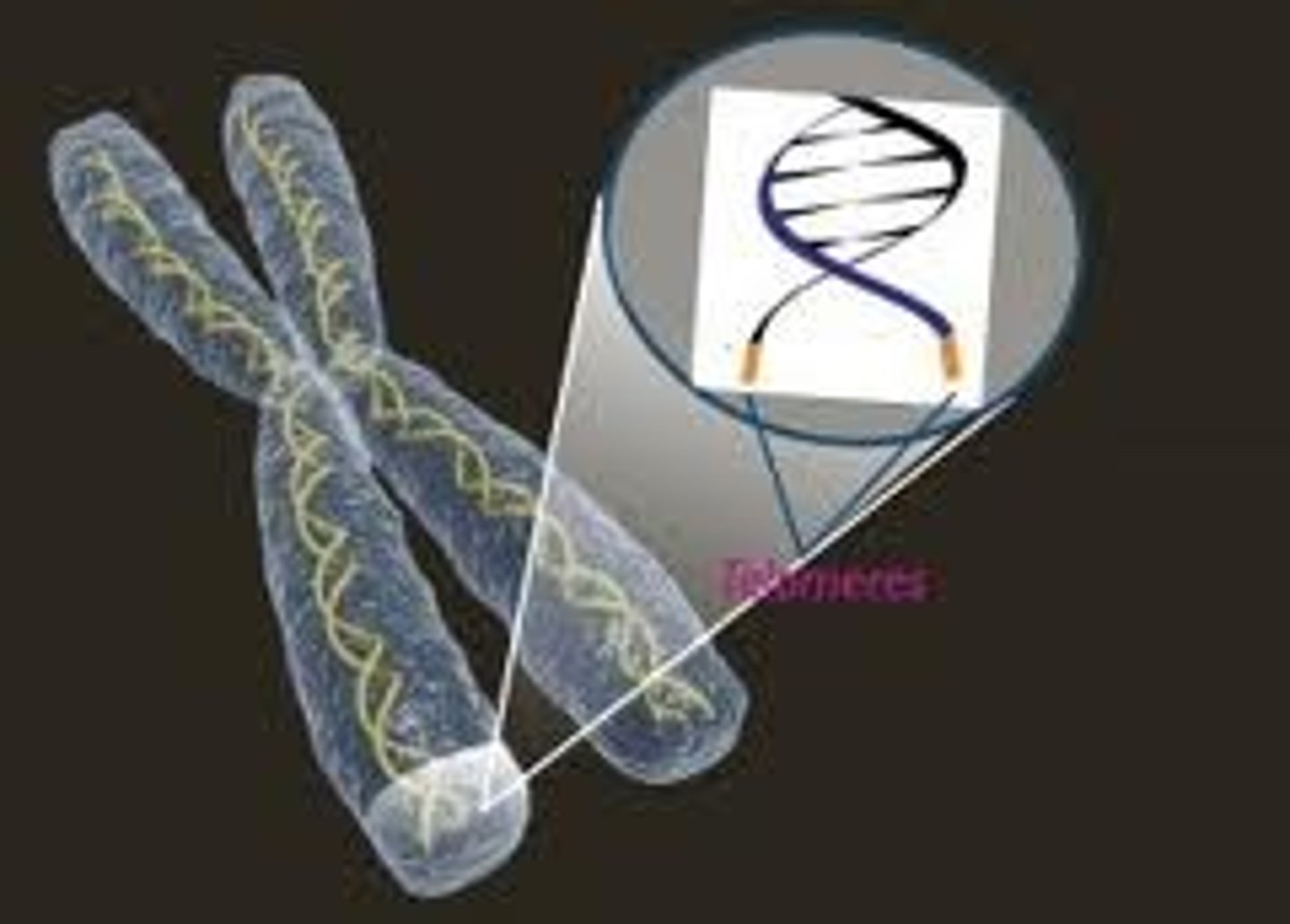
Telomeres
DNA at the tips of chromosomes
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins; 21 molecules that combine to form proteins
2 stages of protein synthesis
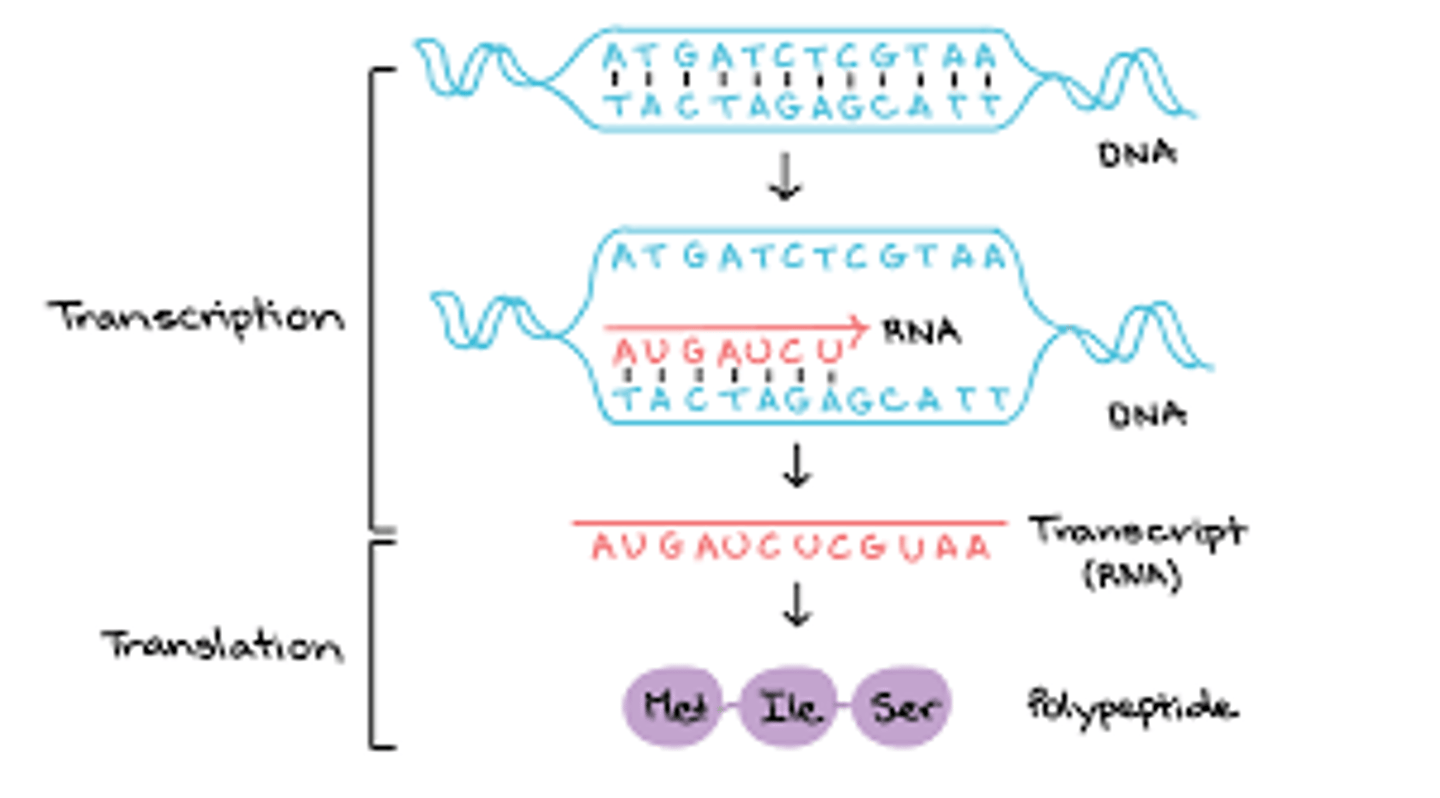
Transcription and translation
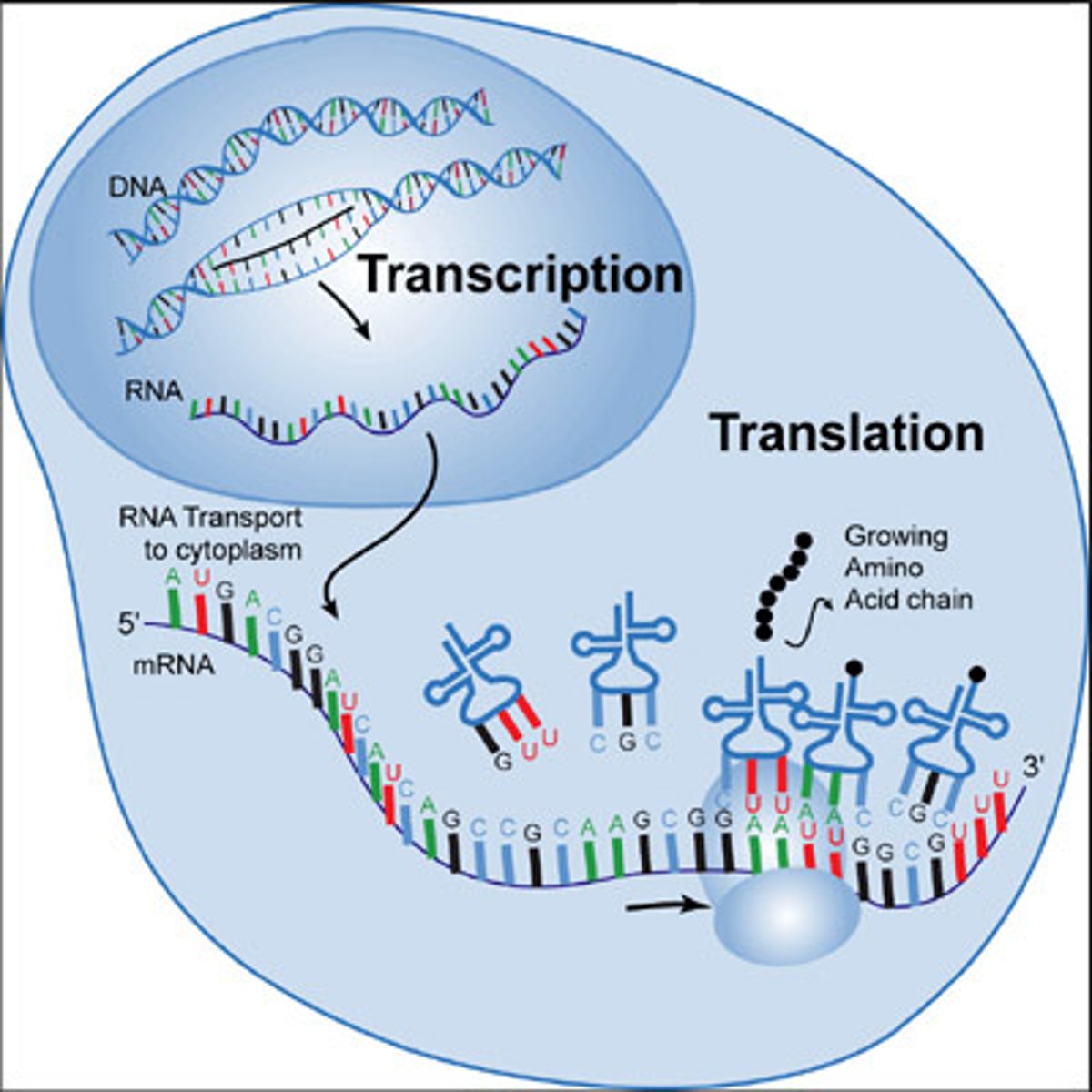
Transcription
The DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
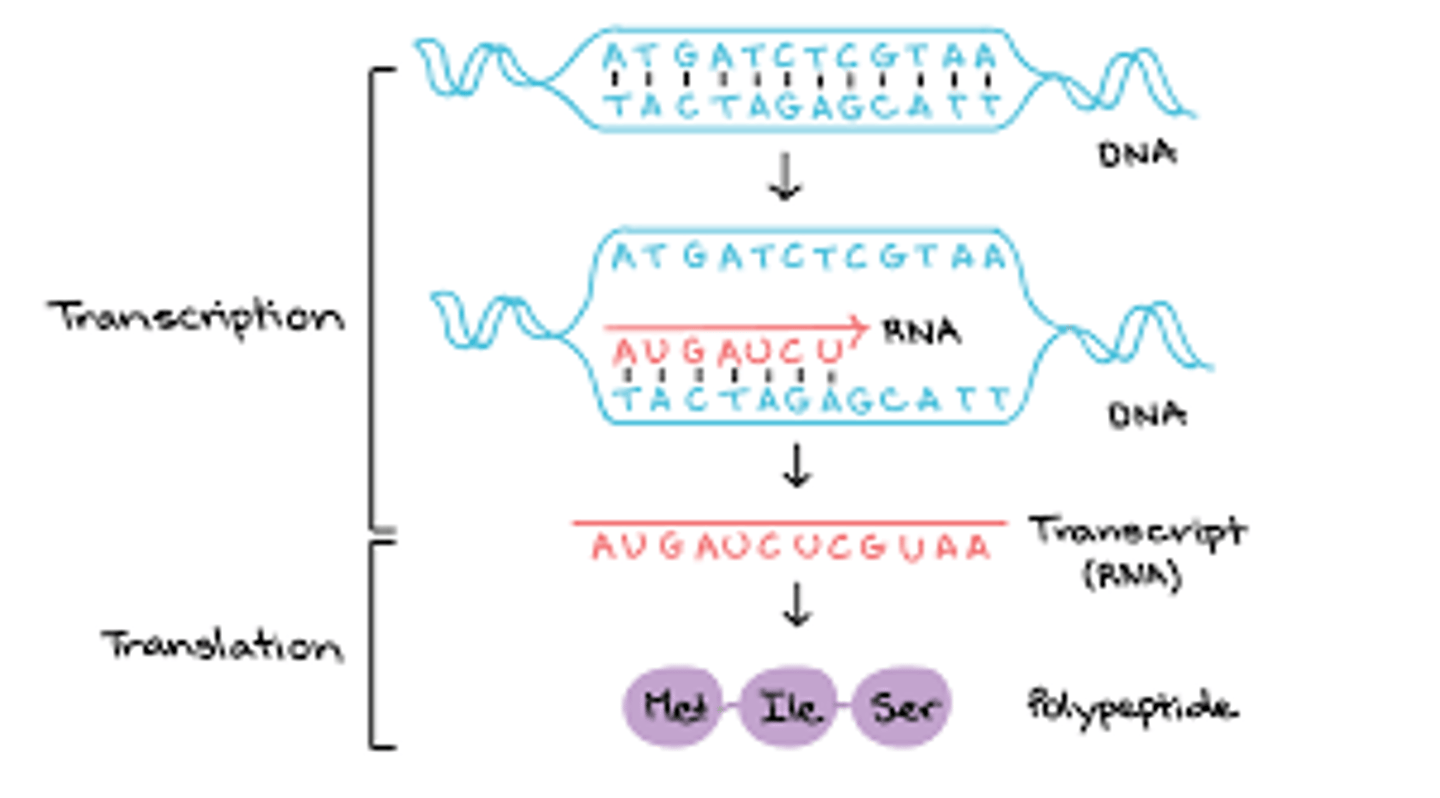
Translation
The mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
Helicase
Unwinds DNA
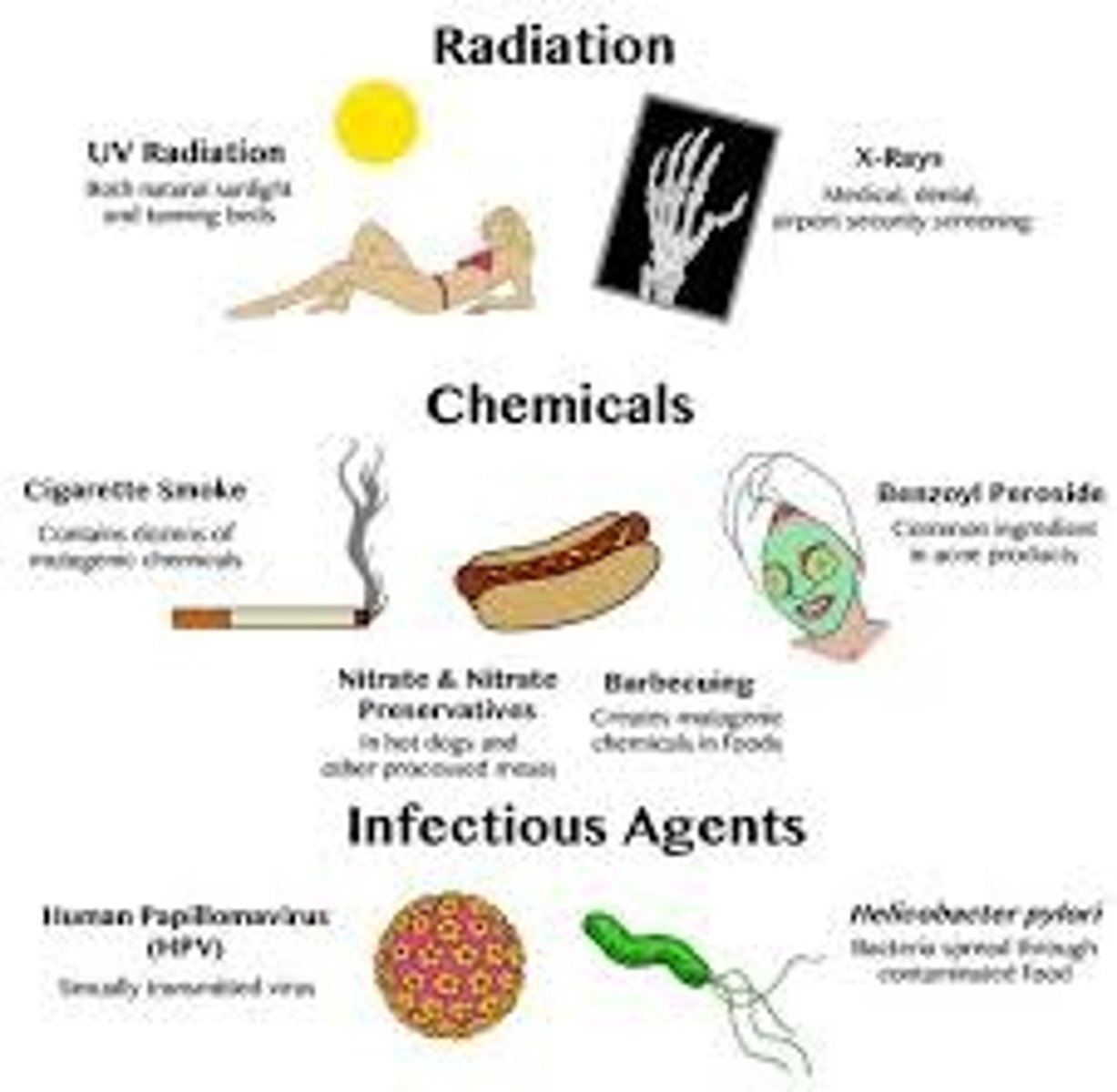
Mutation causes
1. Copying errors during cell division
2. Exposure to UV or ionizing radiation
3. Chemical mutagens
4. Viruses
Somatic cells
Body cells
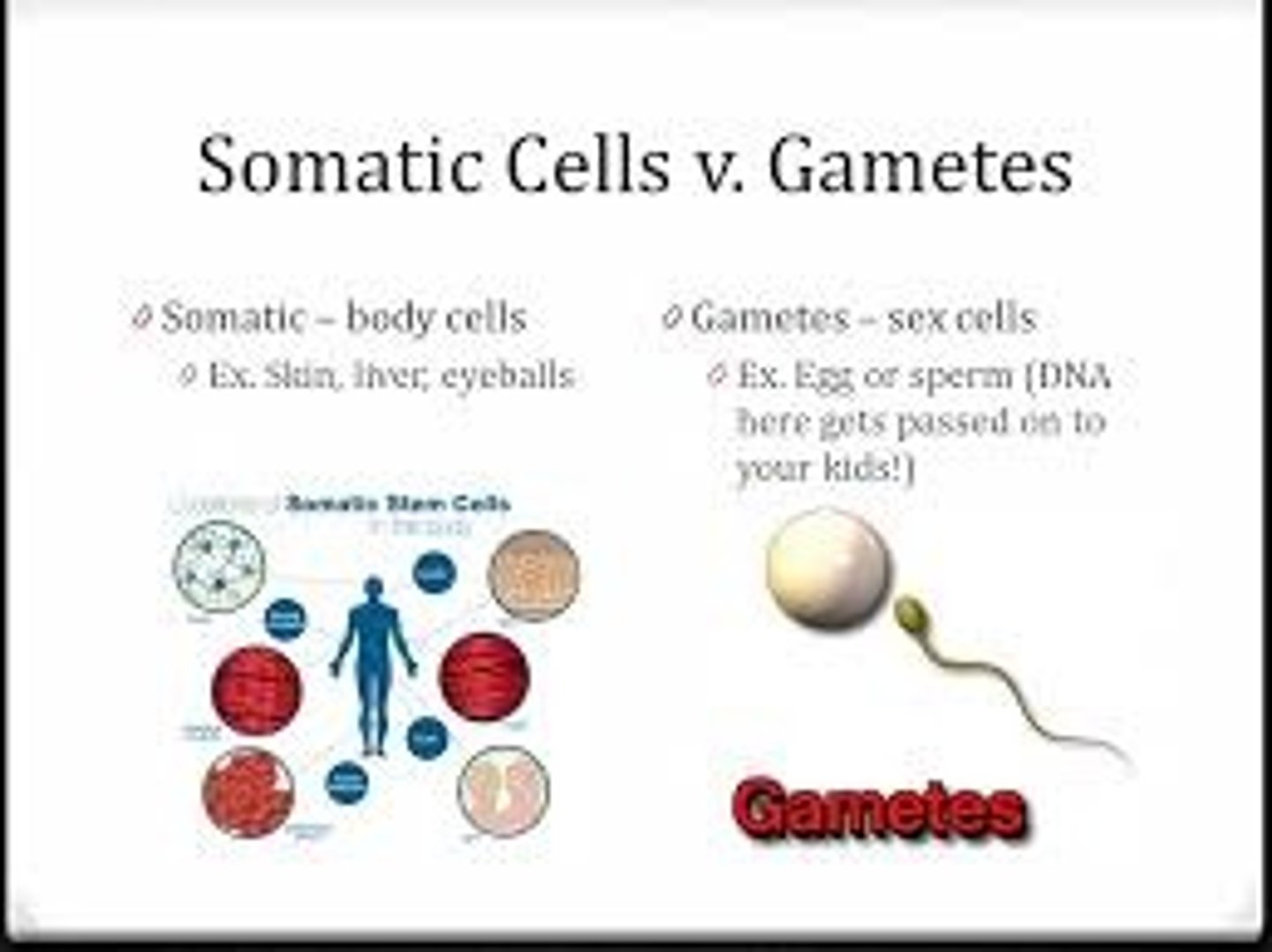
Germ cells
Sex cells
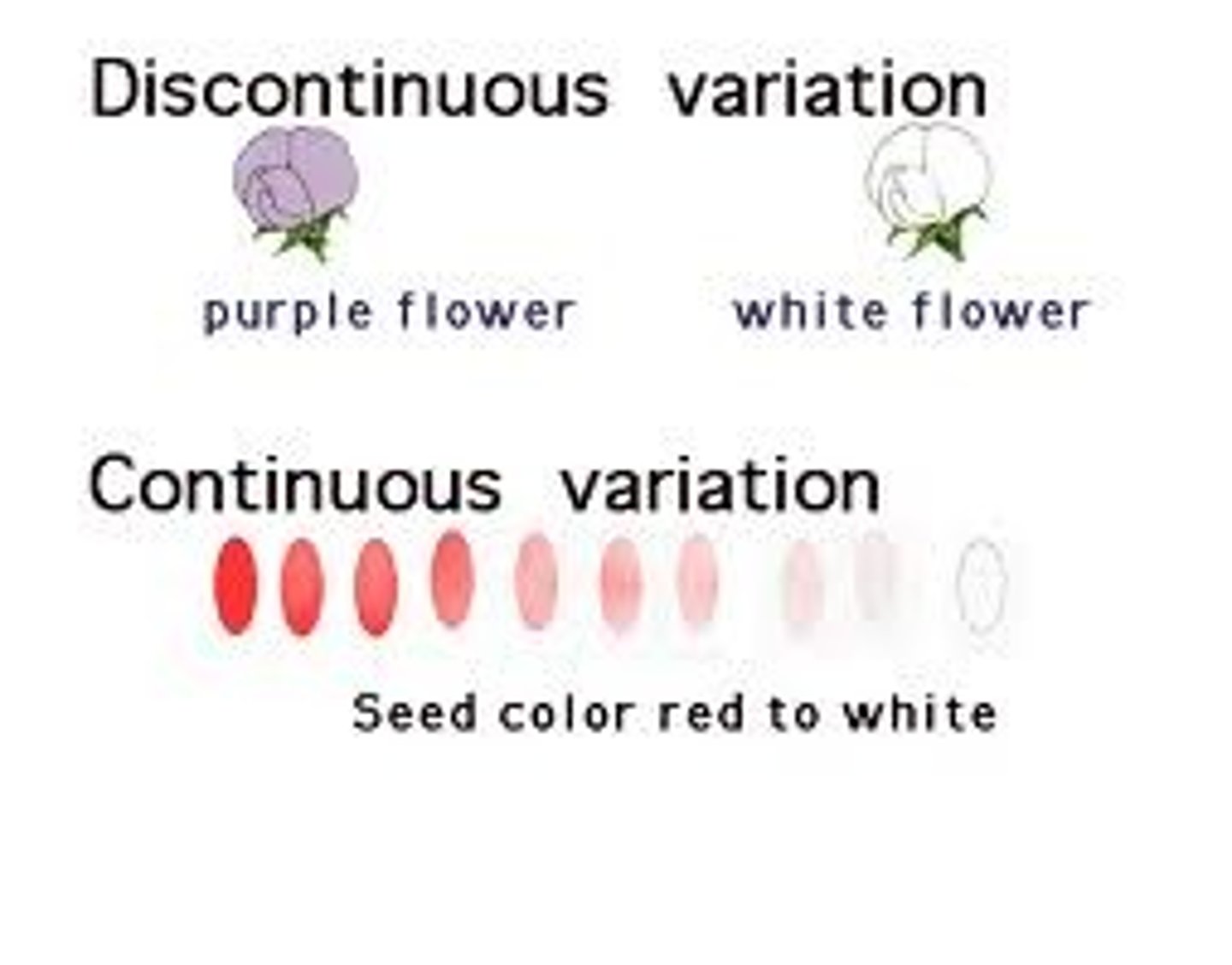
Discontinuous variation
Characteristics that have either one phenotype or another eg tongue rolling, eye colour etc.
Continuous variation
Variation on a spectrum (e.g. height in human beings).
Evolutionary synthesis
Emphasizes the combined action of the four mechanisms of change:
1. Natural selection
2. Genetic drift
3. Gene flow
4. Random mutations
Polygenic
A characteristic controlled by two or more genes
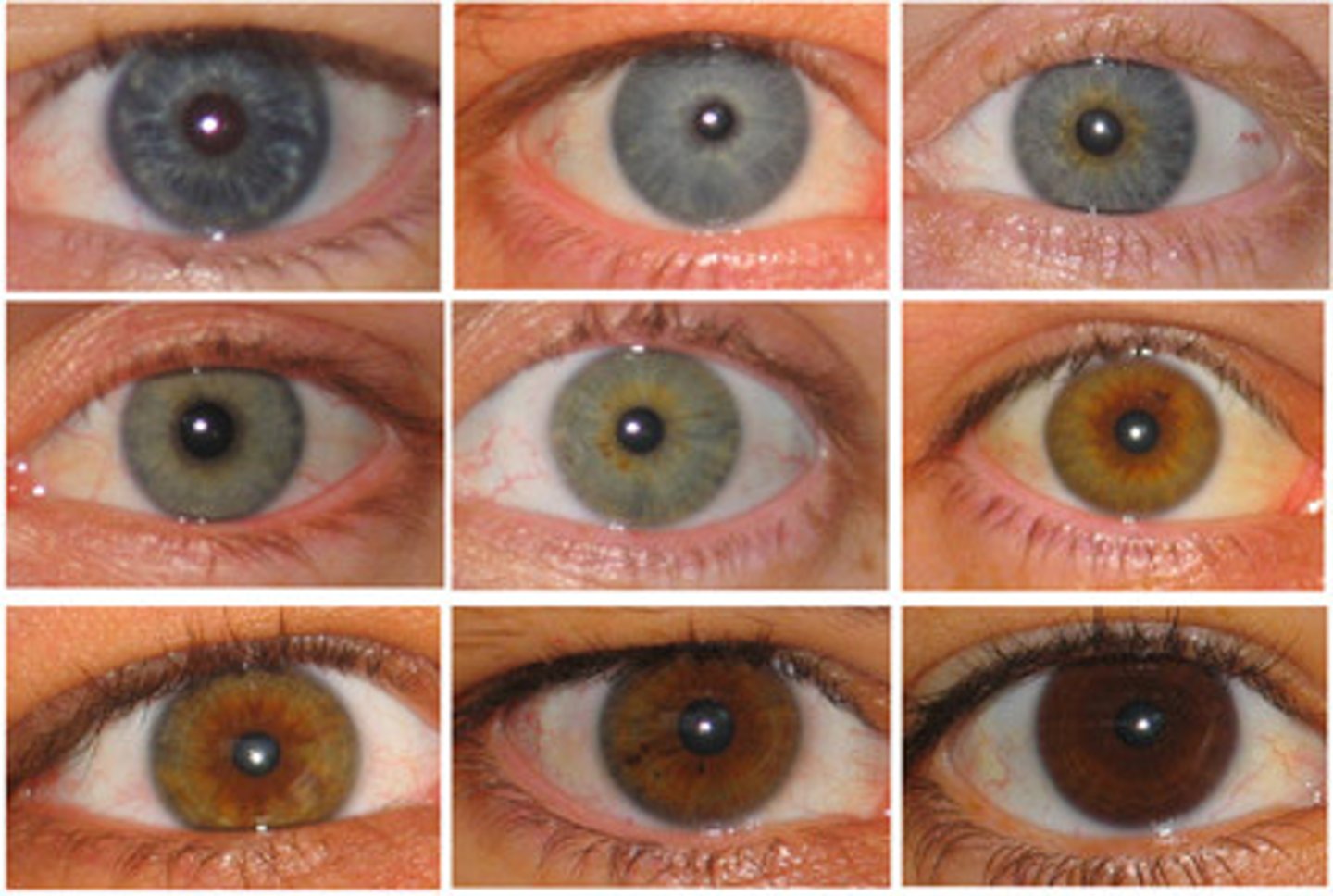
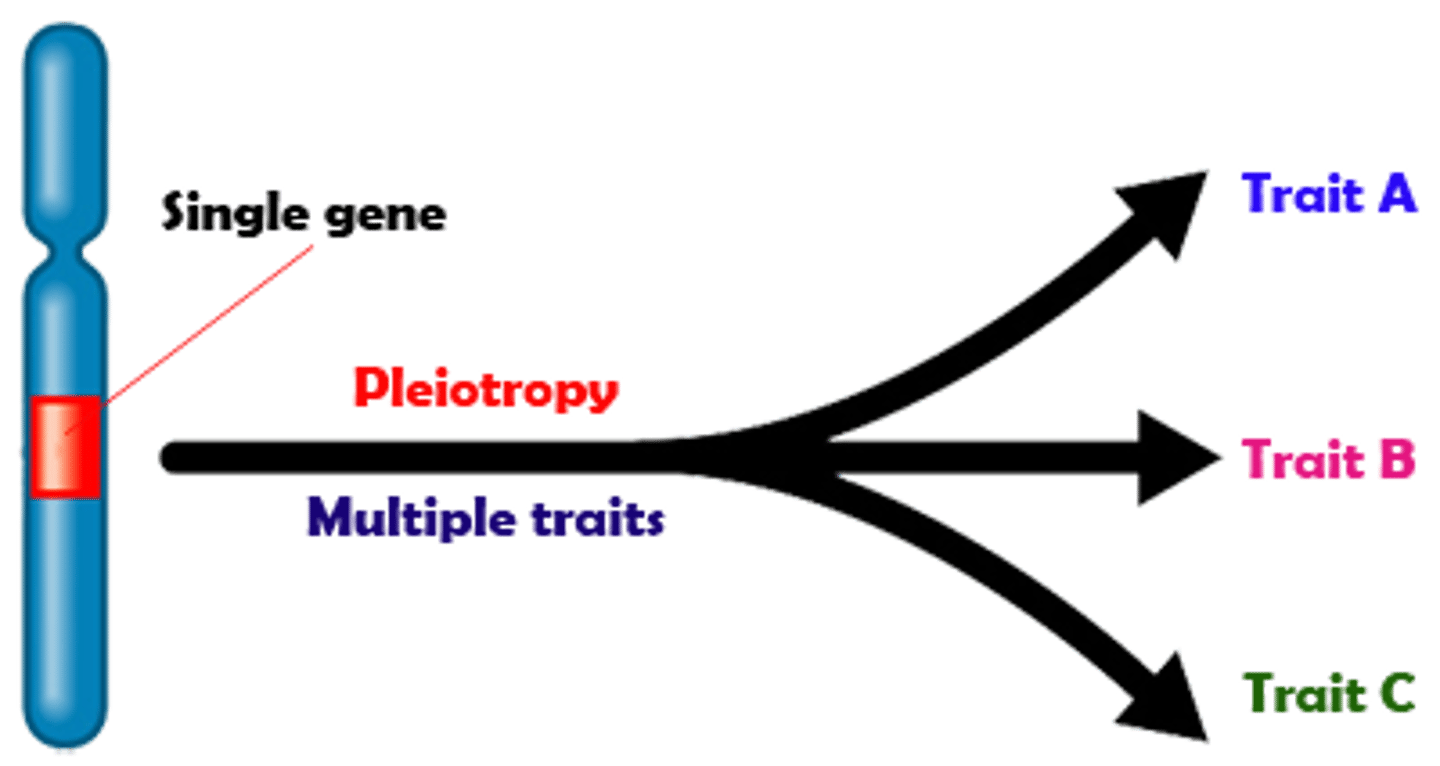
Pleiotropic
Many characteristics controlled by the same gene
Genetic drift
A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance
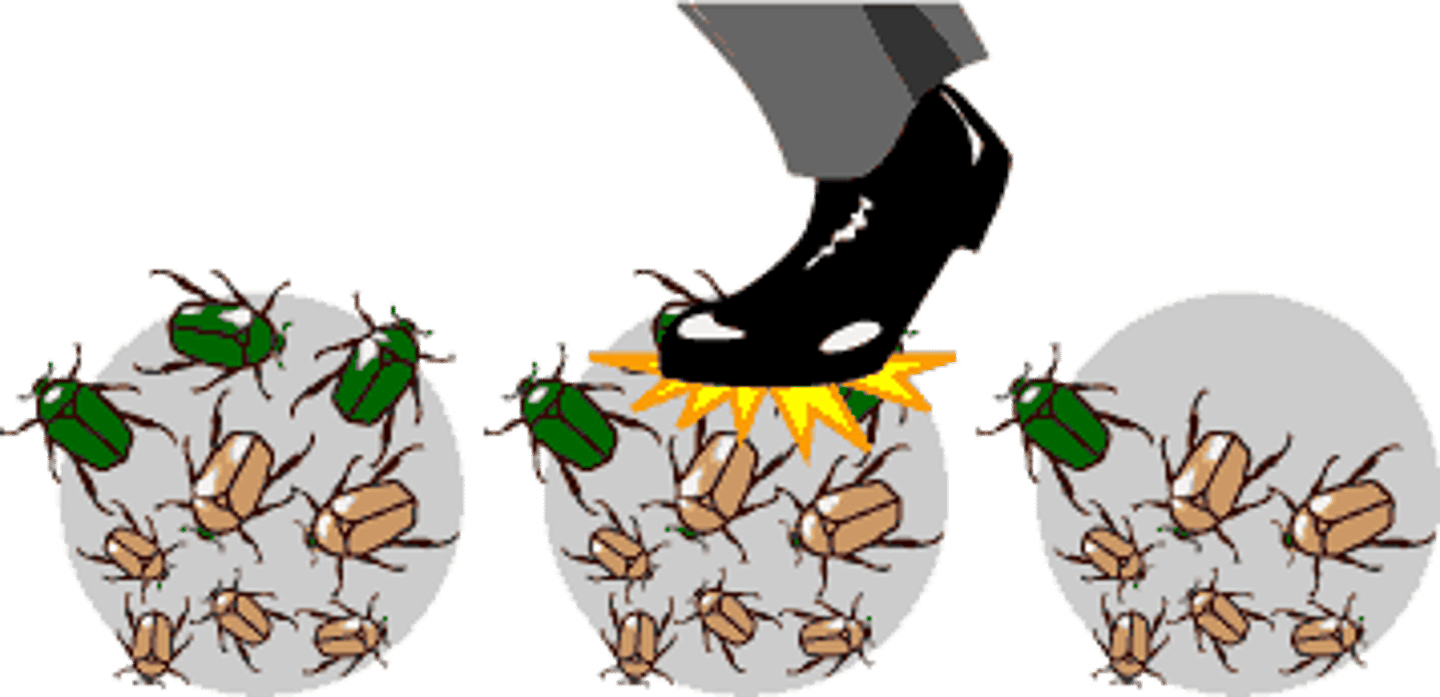

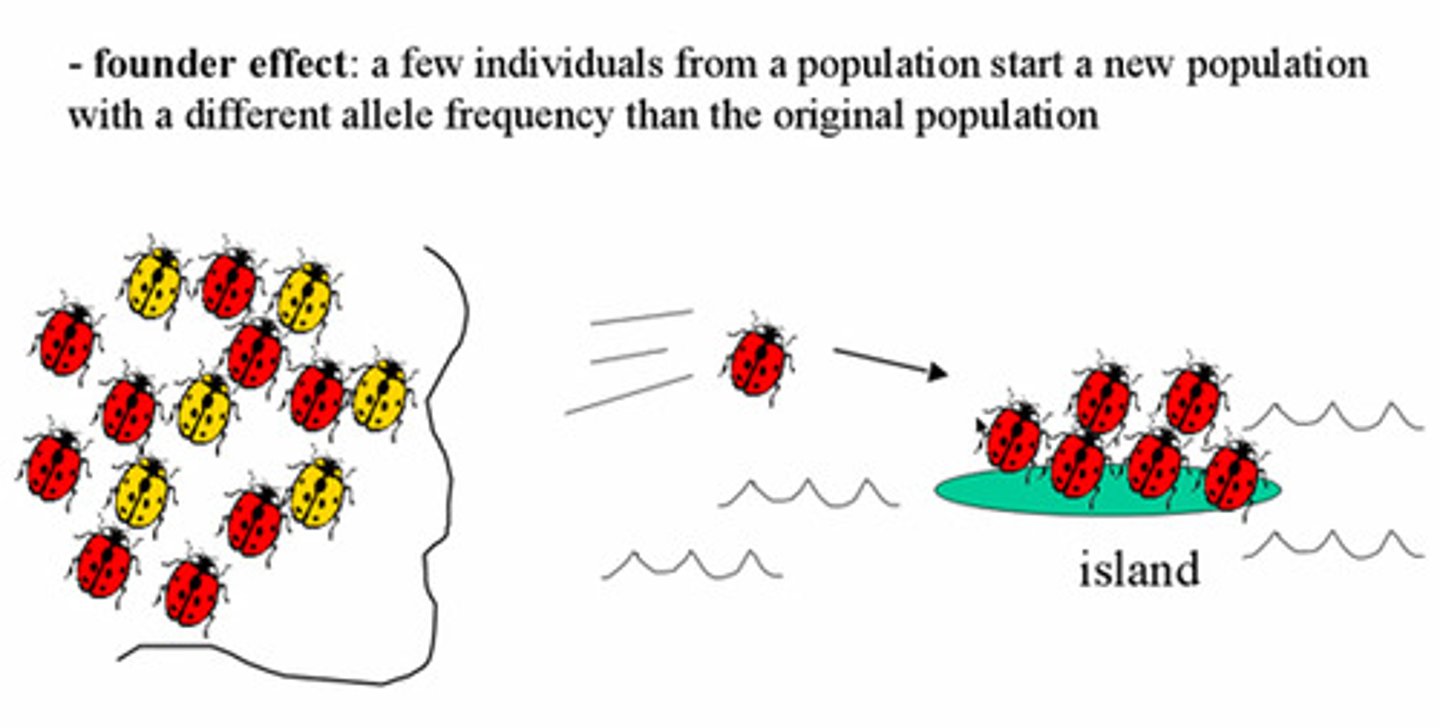
Genetic drift: founder effect
Occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population; causes reduced genetic variation from the original population.
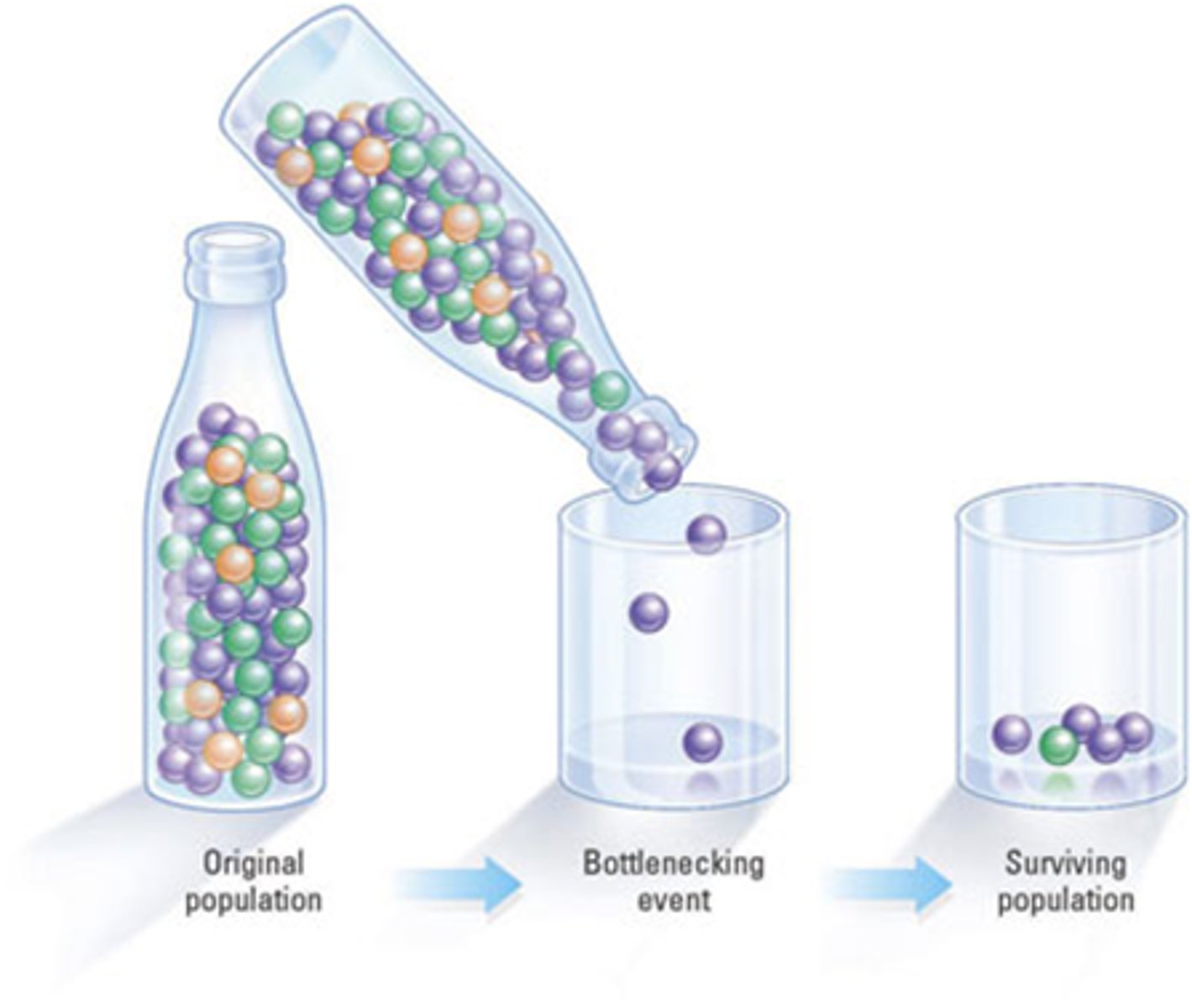
Genetic drift: bottleneck effect
The loss of variety (alleles) after an event that greatly reduces the size of the population. (can lead to extinction)
Antigenic drift
When small mutations in a virus accumulate and create an effect that can be beneficial or detrimental to the organism
Antigenetic shift
When rapid, large mutations create a change
Progressive co-evolution
Organisms become better adapted to their surroundings through evolutionary time
Escalatory co-evolution
The improvement in predatory adaptations may be matched by improvements in prey defences, and neither ends up any better off.
Co-speciation
A process in which two groups of organisms speciate in response to each other and at the same time.
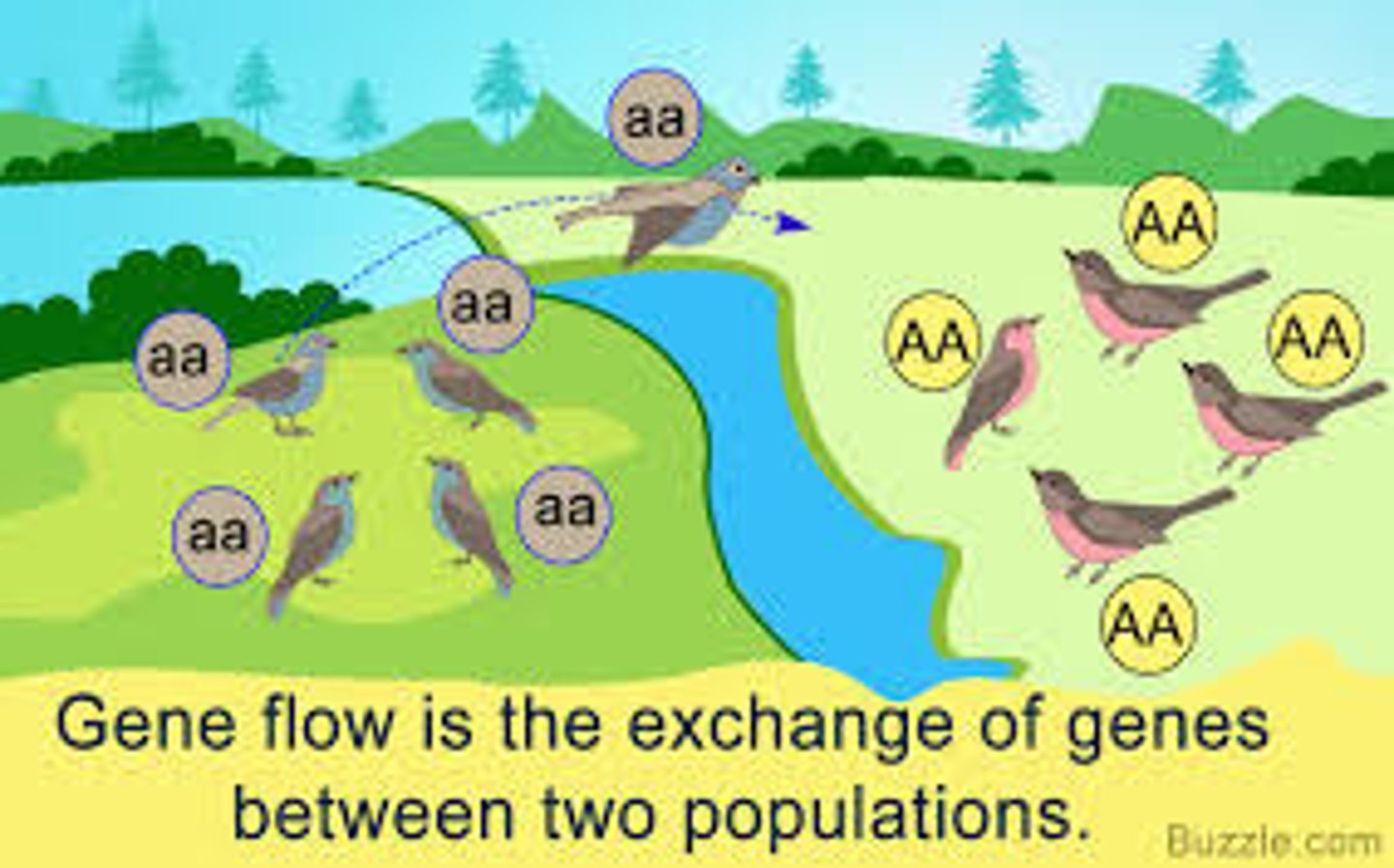
Gene flow
The movement of alleles from one population to another. Reduces genetic variation between populations.
Bioturbation
The disturbance of sedimentary deposits by living organisms
"Selection of" vs "selection for"
"Selection of": not on purpose;
"Selection for": on purpose
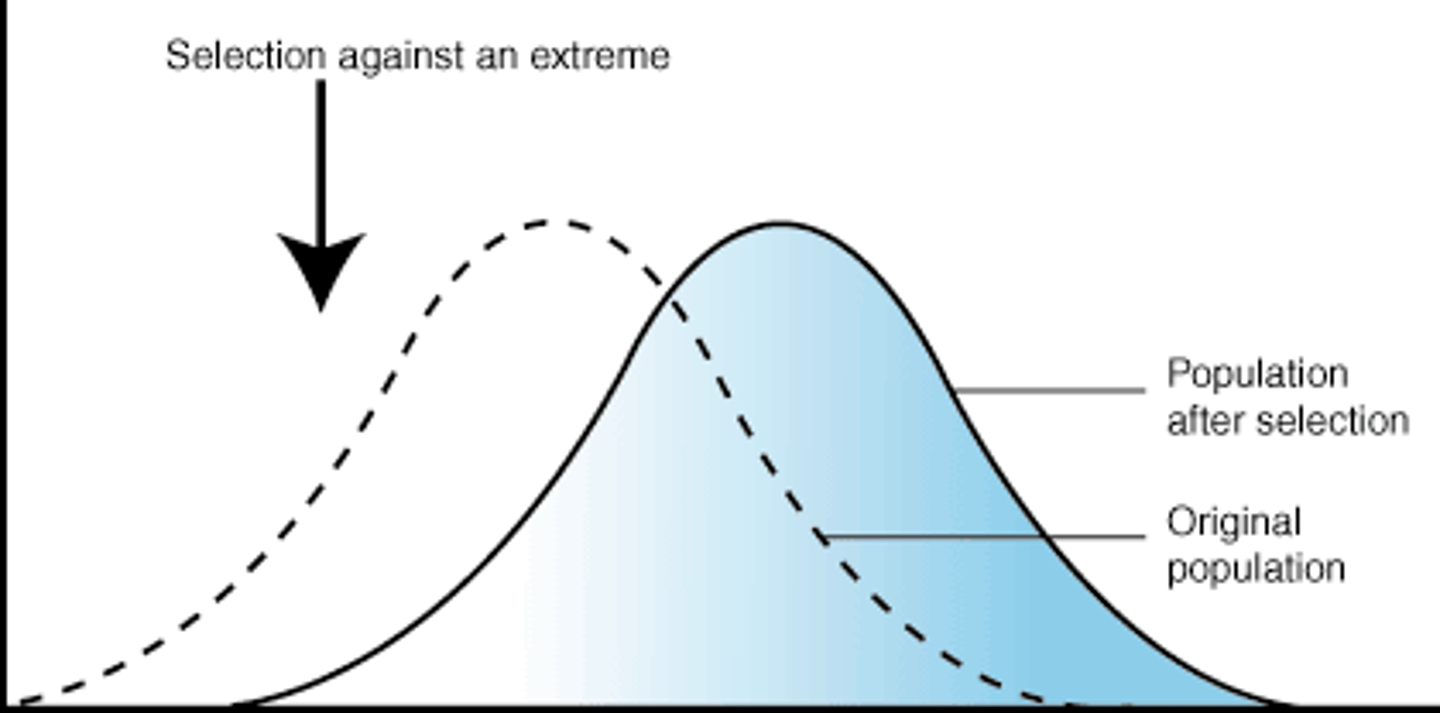
Directional selection
Occurs when natural selection favours one of the extreme variations of a trait.
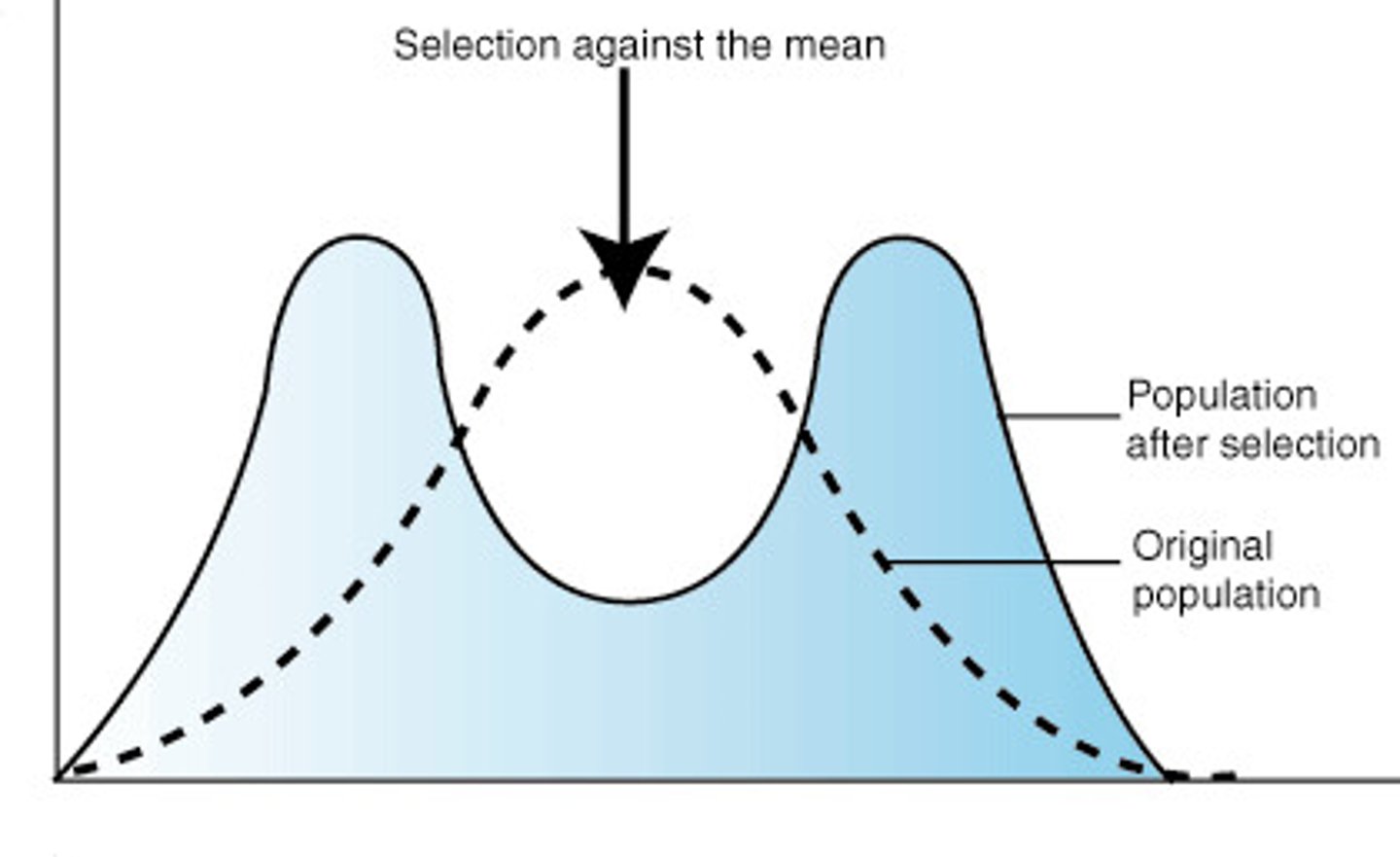
Stablizing selection
individuals with the average form of a trait have the highest fitness
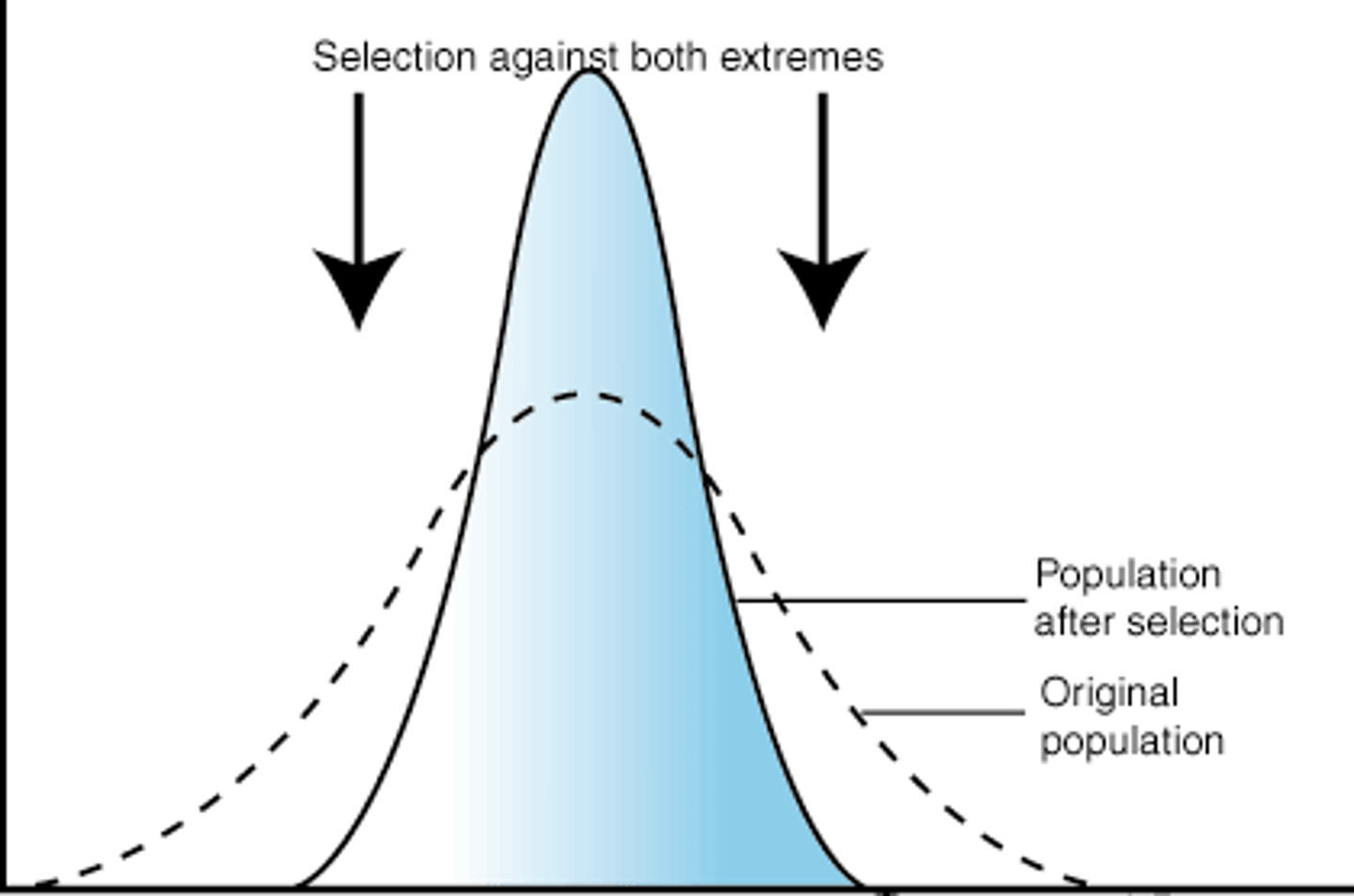
Disruptive selection
favours individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
Properties of fitness
A) The success of a biological entity in producing offspring , and B) represents the average contribution of an allele or genotype to succeeding generations
Sociobiology
the systematic study of how biology affects human social behaviour
Alfred Russel Wallace
(1823-1913). Co-discovered natural selection

The three postulates of Darwinian evolution
1. The struggle for existence
2. Variation in fitness
3. Inheritance of variations

Lamarckian blending
The idea that children should be a perfect blend of their parents
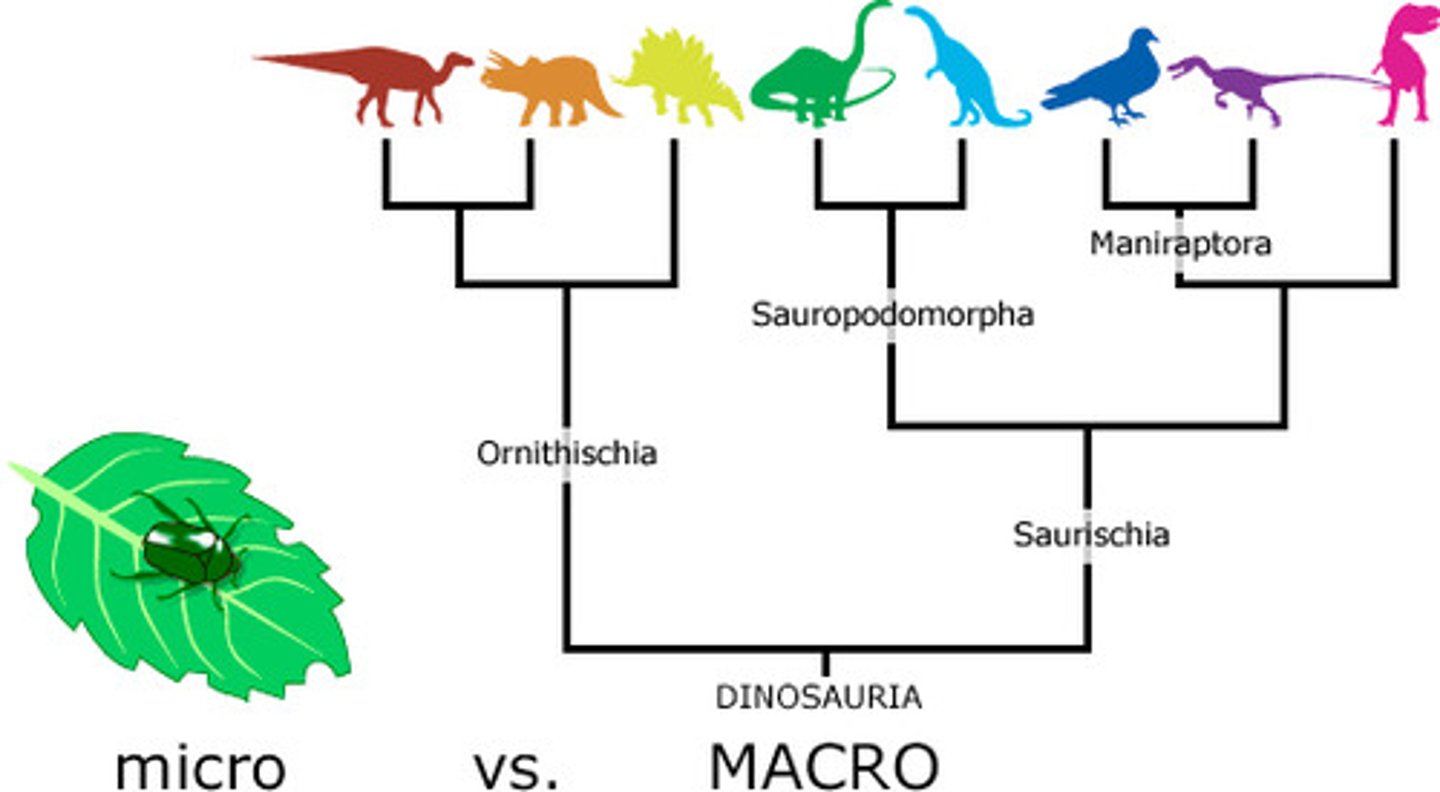
Macroevolution
large-scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time
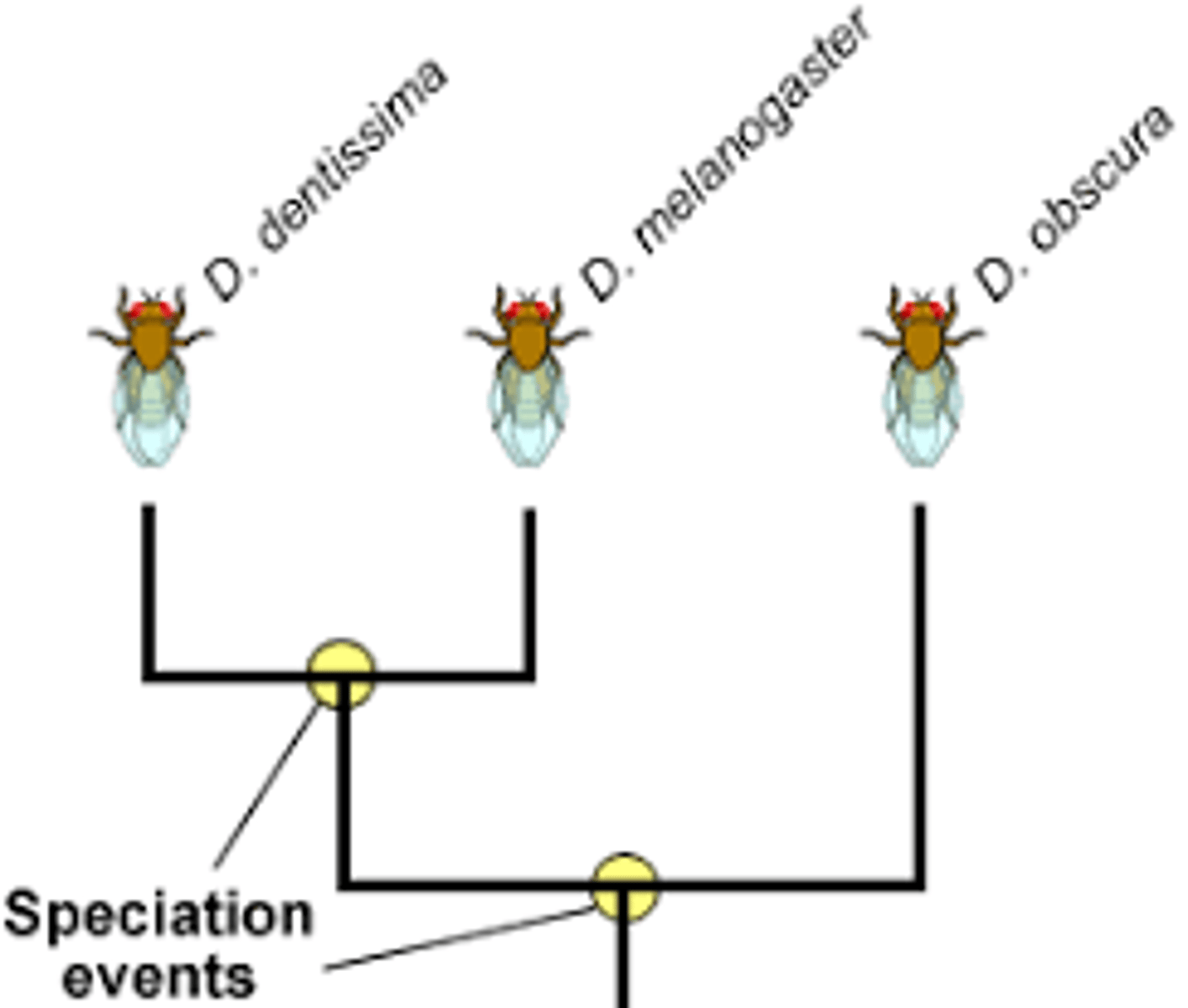
Speciation
Formation of new species
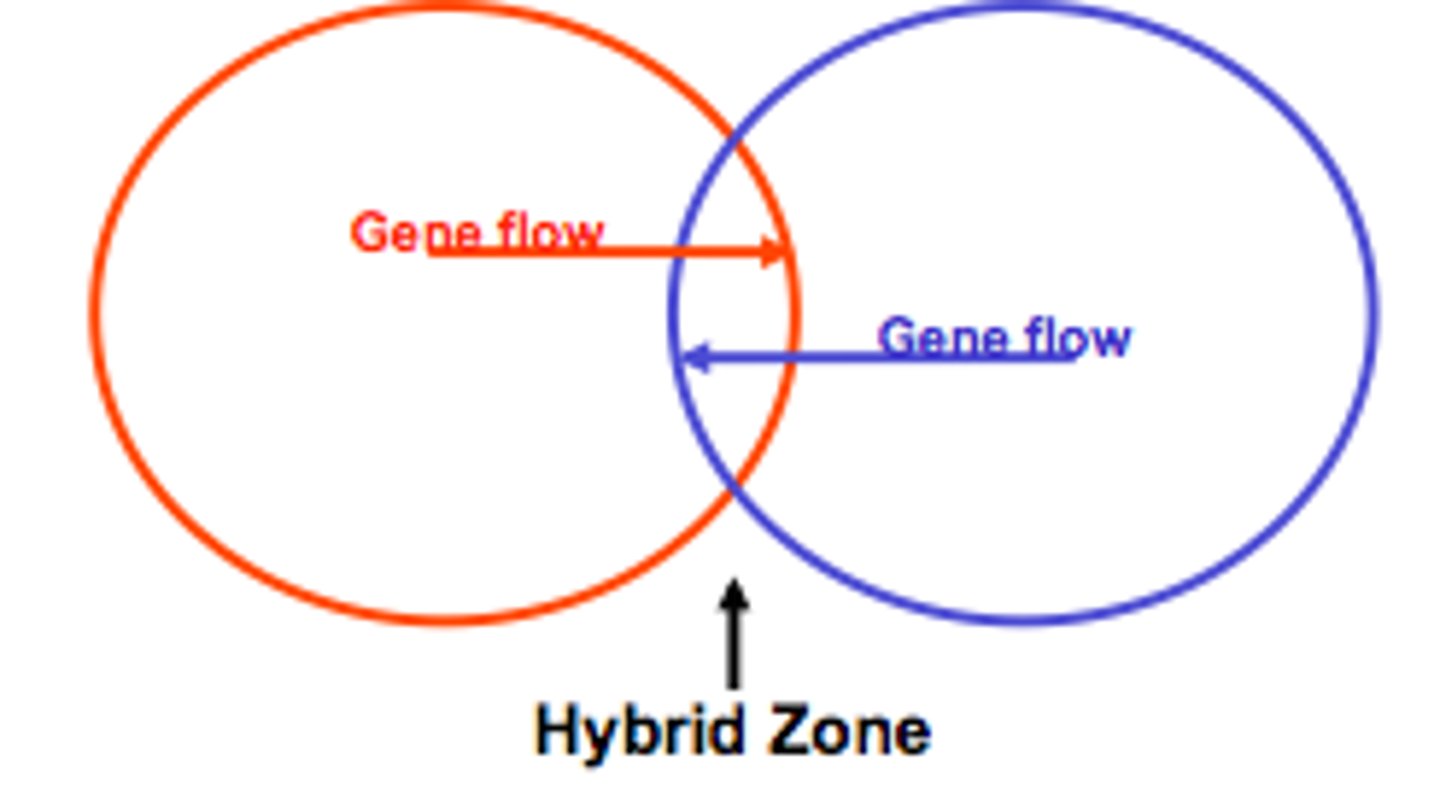
Hybrid zone
A region in which members of different species mate and produce hybrids
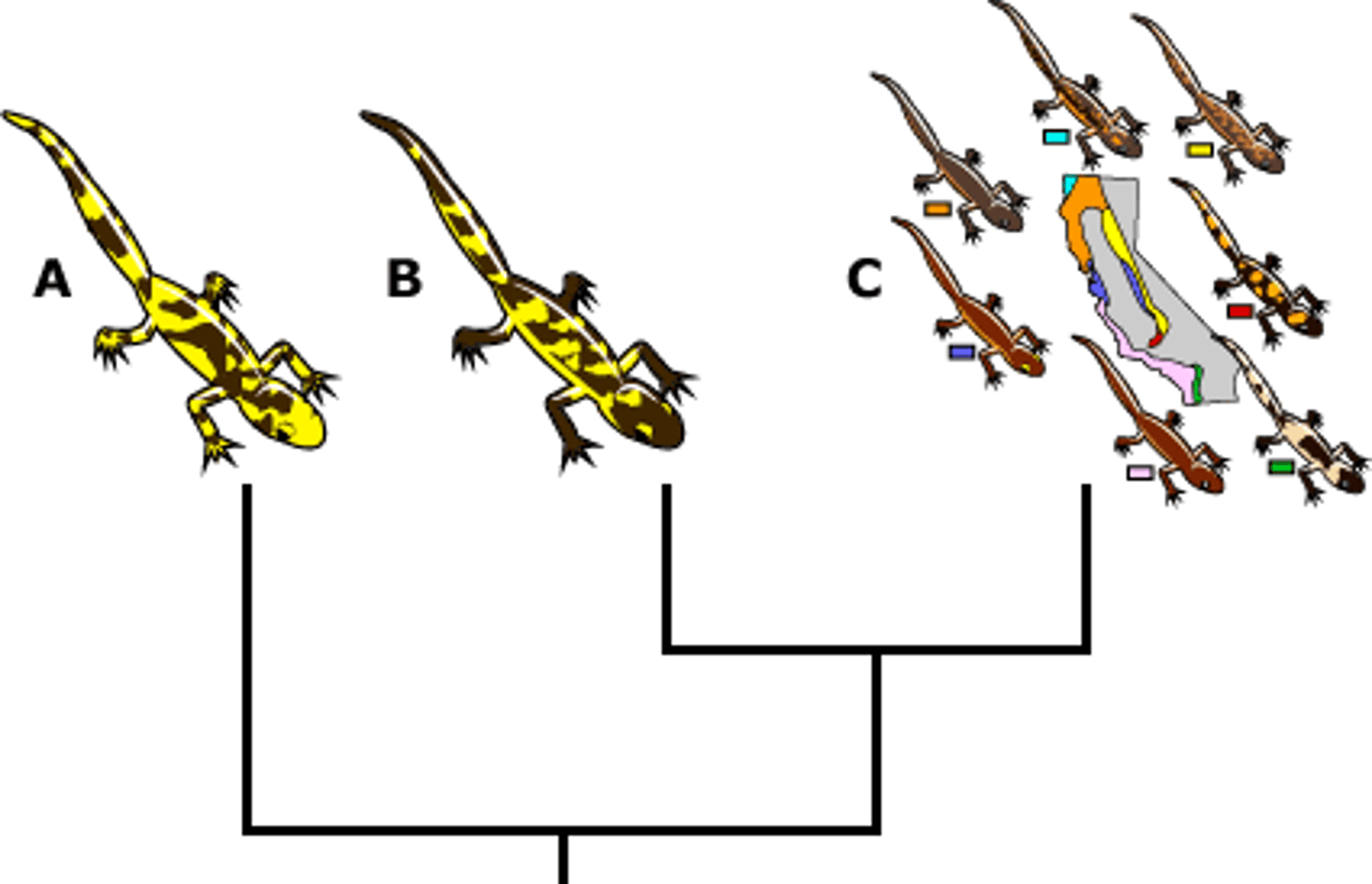
Biological species concept
A definition of species as a group of populations whose members have the potential to produce fertile offspring.

Phylogenetic species concept
A definition of species as the smallest group of individuals that share a common ancestor, forming one branch on the tree of life.
Character states
characters are usually described in terms of their states, for example: "hair present" vs. "hair absent," where "hair" is the character, and "present" and "absent" are its states.
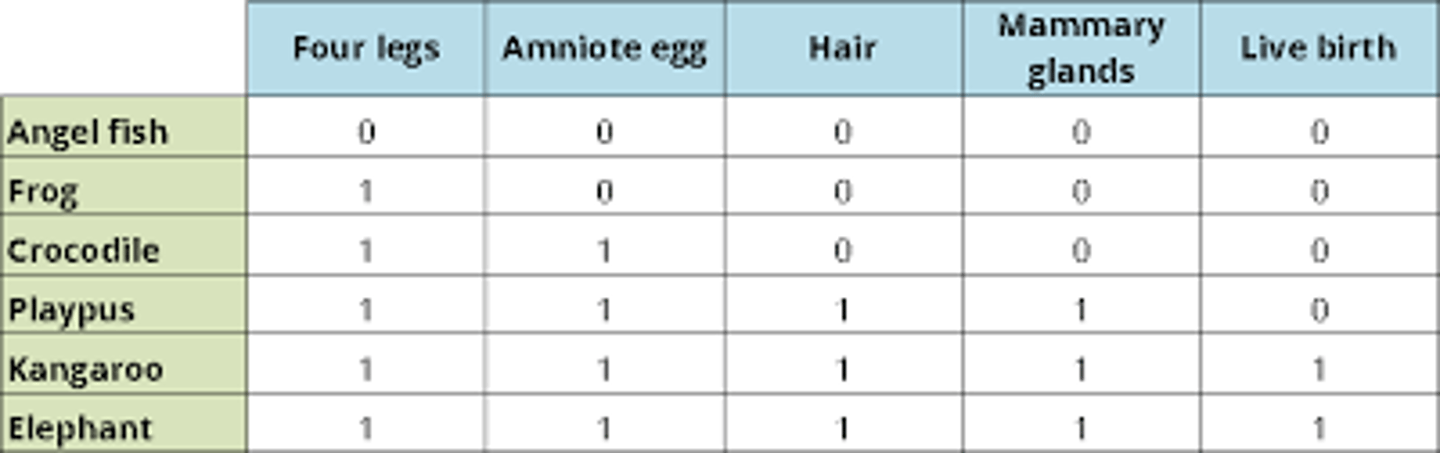
Character changes
Massive-scale macroevolutionary changes
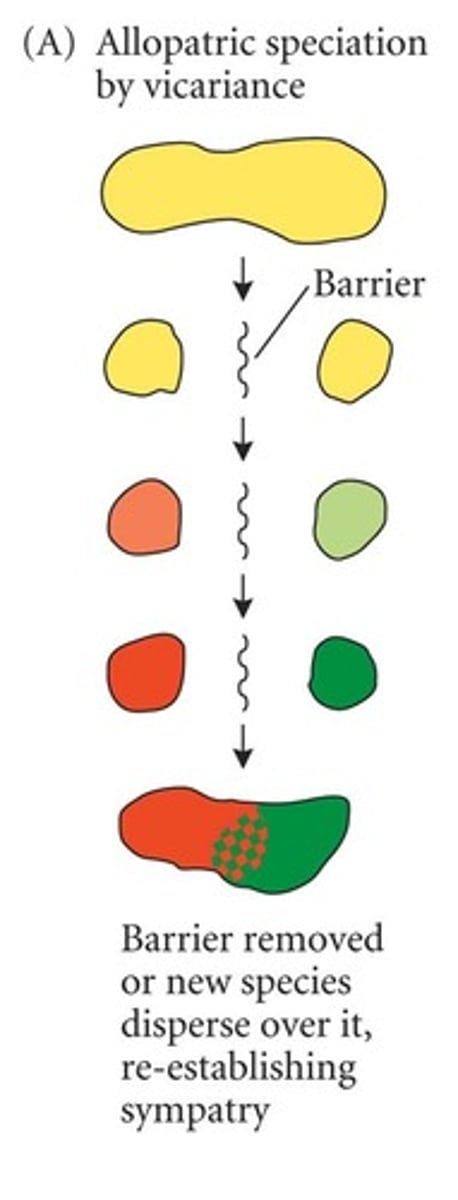
Allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
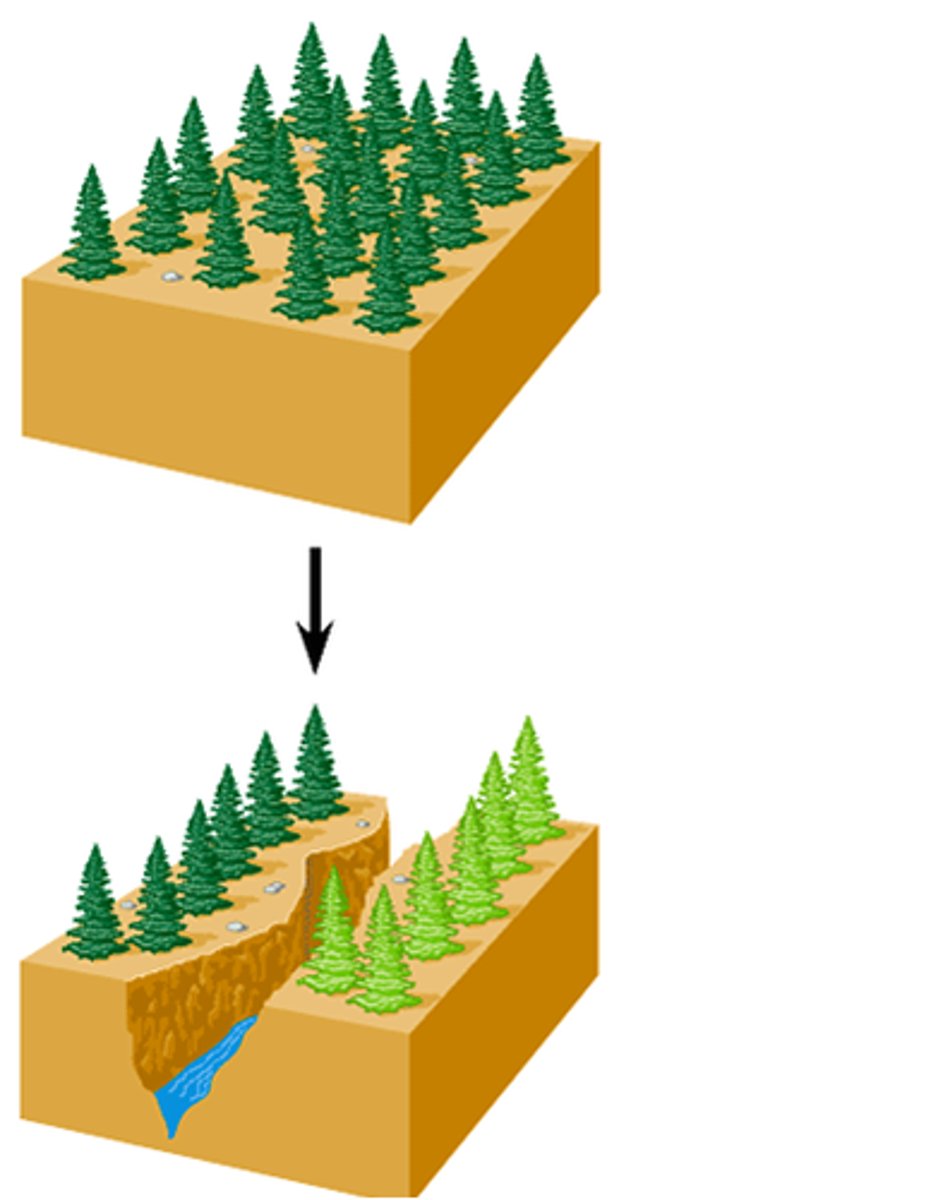
Vicariant speciation
Type of allopatric speciation - When a physical barrier creates large, geographically separated populations, which diverge and can no longer interbreed.
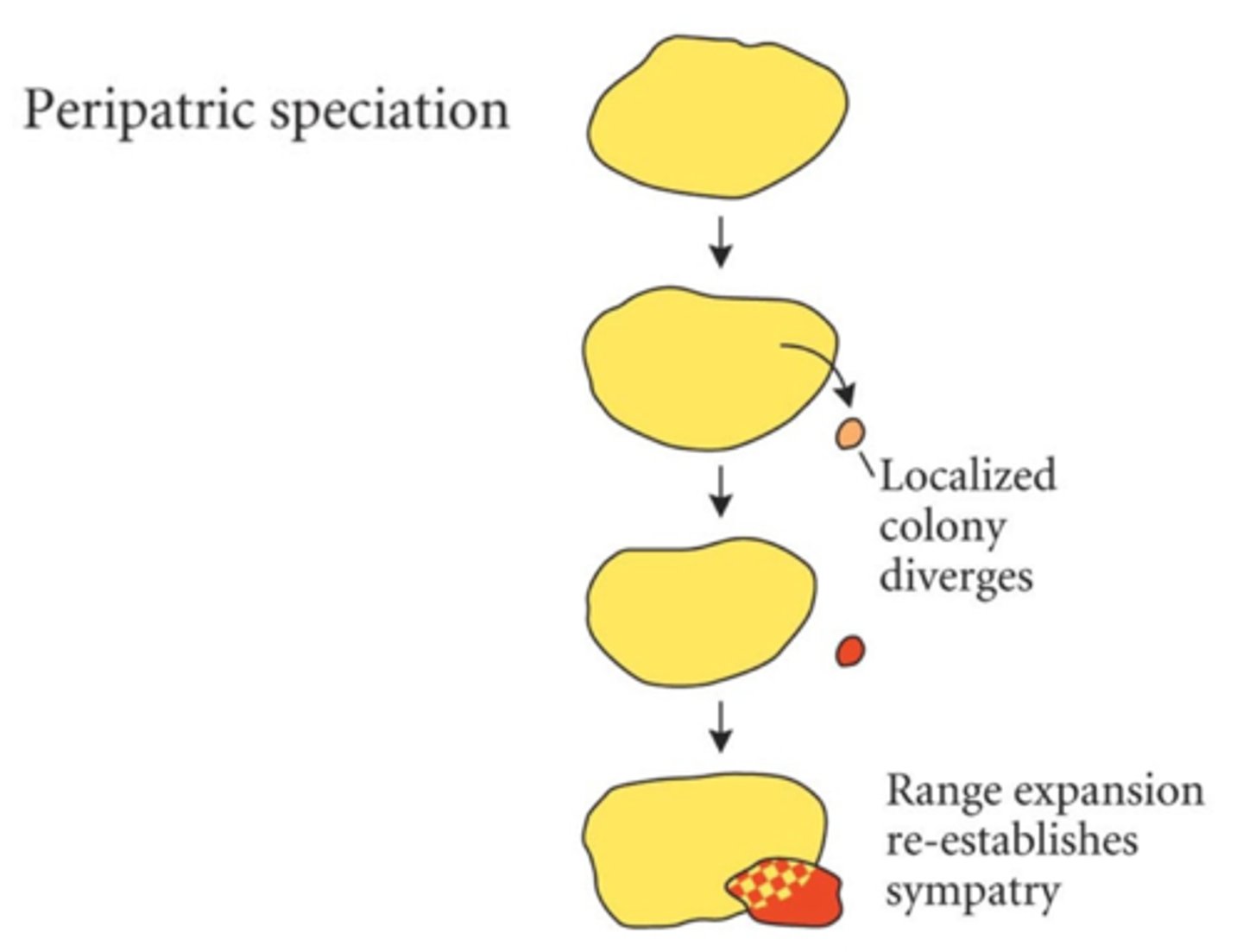
Peripatric speciation
A specific kind of allopatric speciation in which a few individuals from a mainland population disperse to a new location remote from the original population and evolve separately.
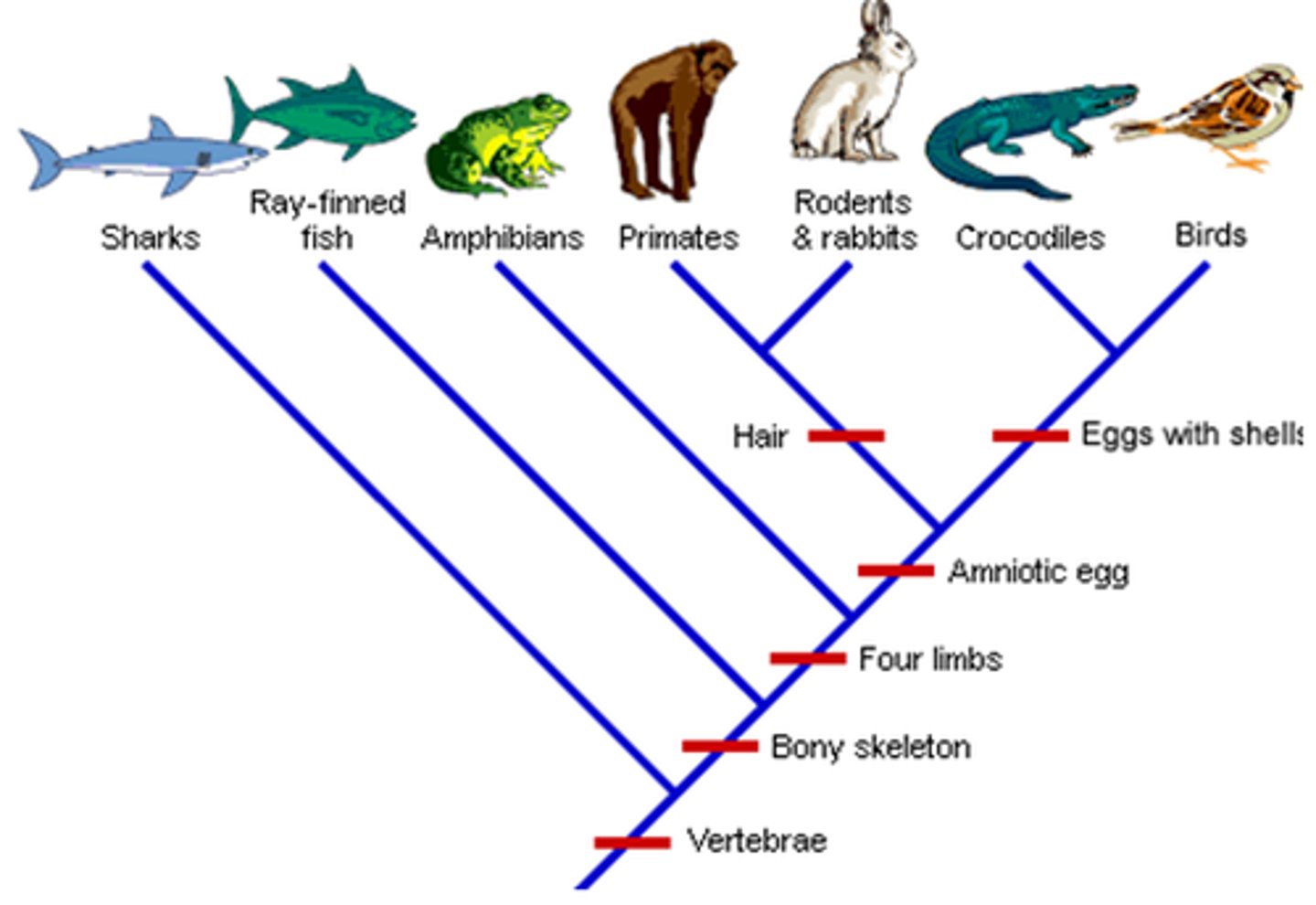
Cladistics
Classification based on common ancestry
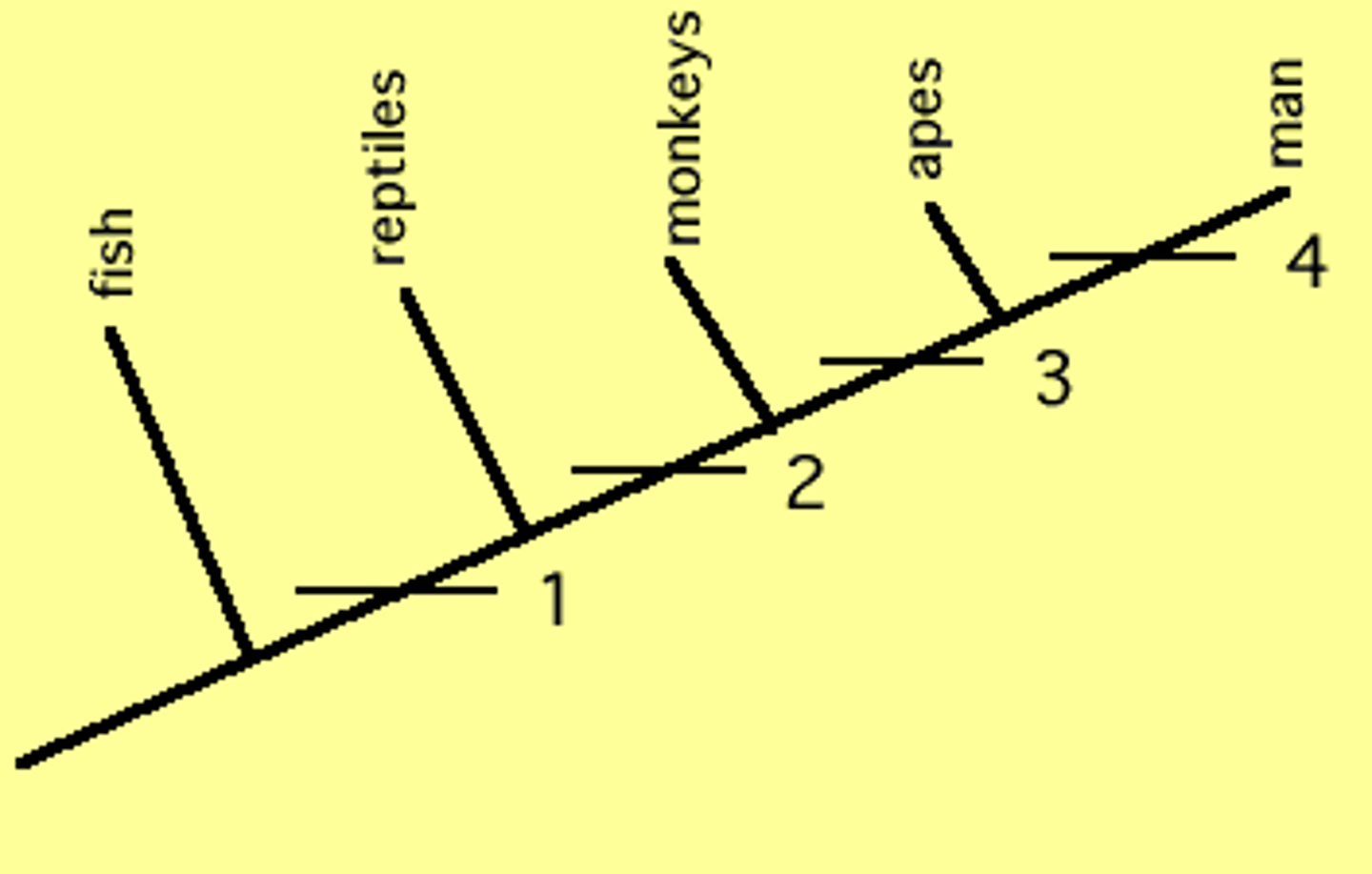
3 major assumptions of cladistics
1. changes in characteristics within lineages over time
2. all organisms descended from a common ancestor
3. when a lineage splits, it divides into exactly 2 groups
Cladogram/phylogenetic tree
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
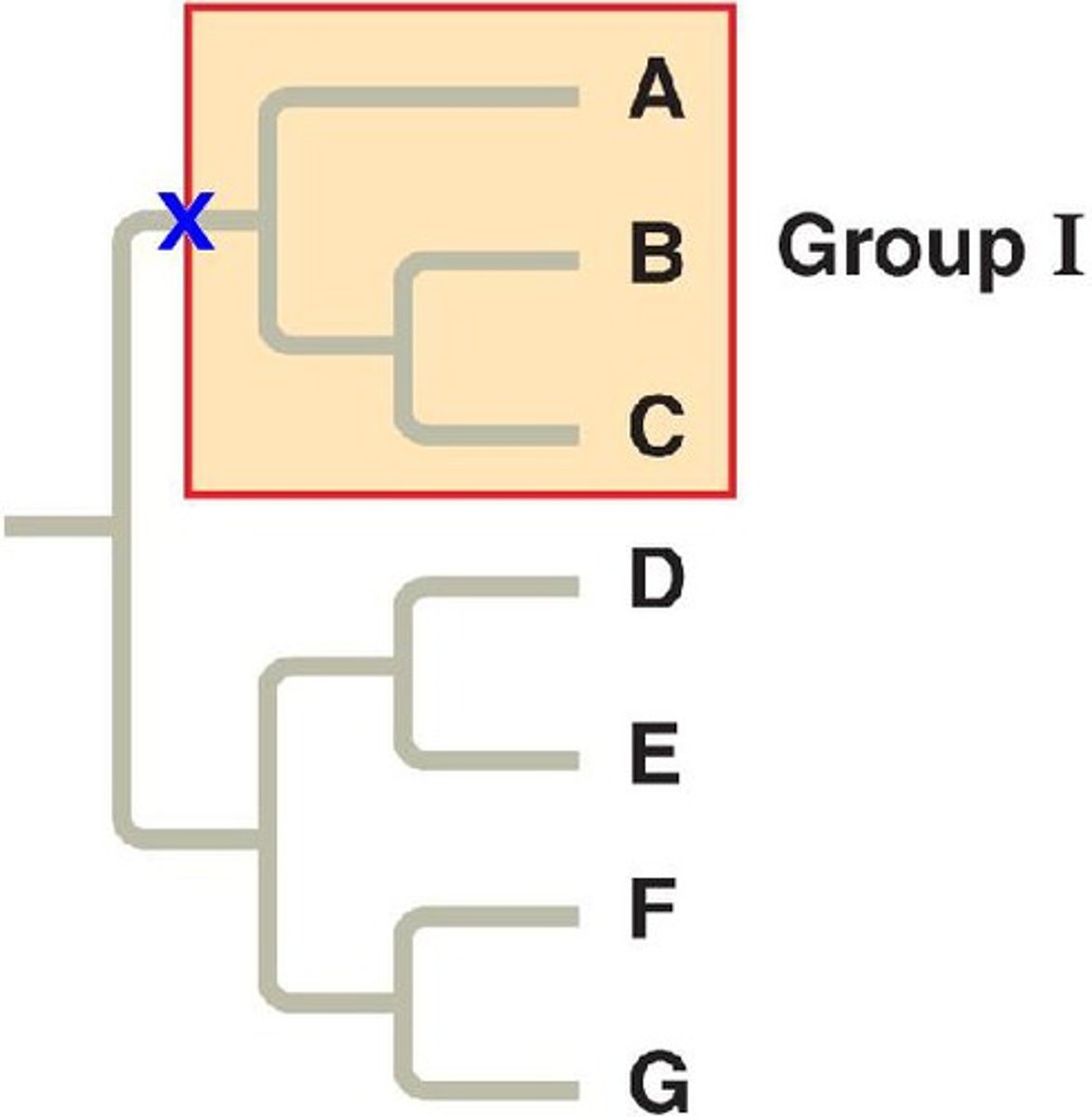
Clades
groups that include an ancestral species and all of its descendants
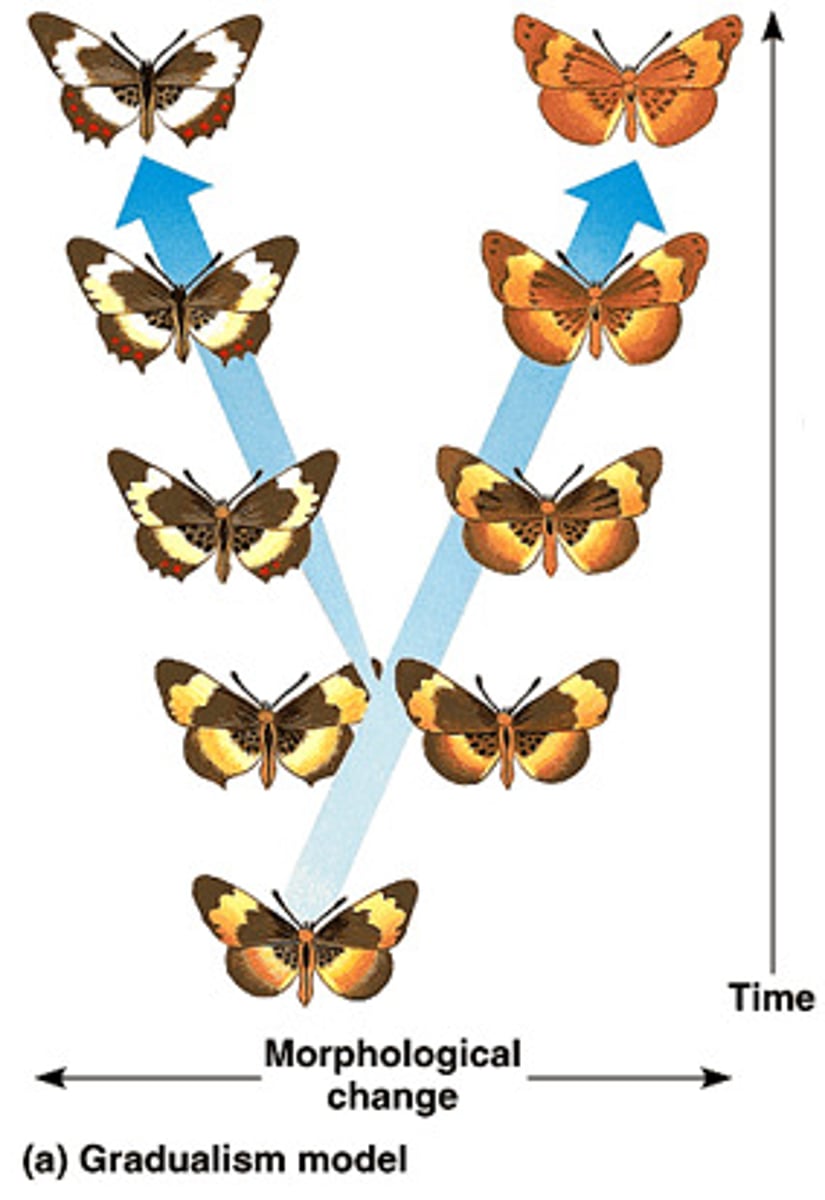
Phyletic gradualism
Species evolve by the accumulation of many small changes over a long time period
Punctuated equilibrium
Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change
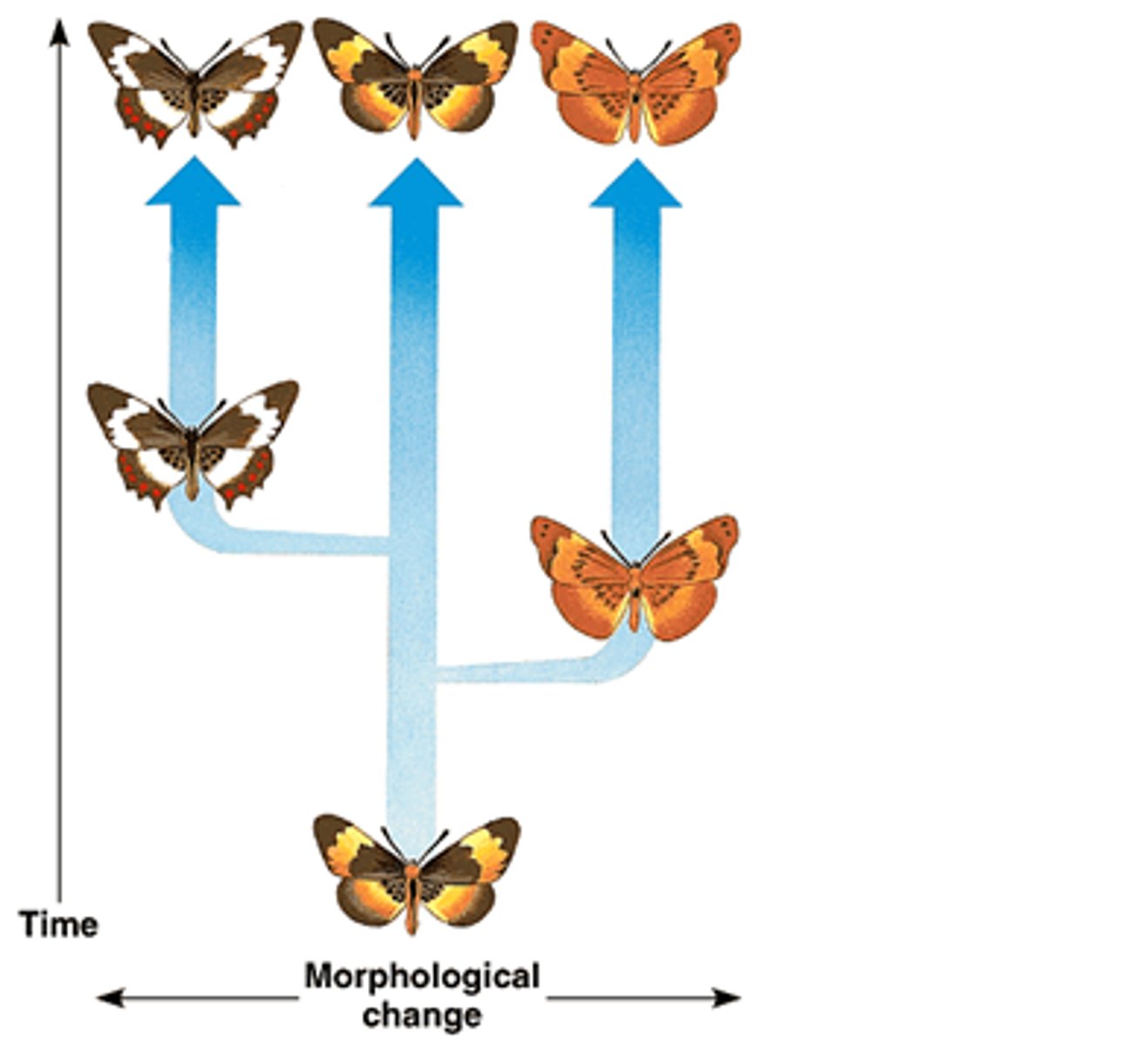
The "Red Queen" Hypothesis
Organisms that fail to change may go extinct
Foramum magnum on apes vs. humans
Apes: Back of the skull, for quadrupedal locomotion
Humans: Center of the the skull, for bipedal locomotion
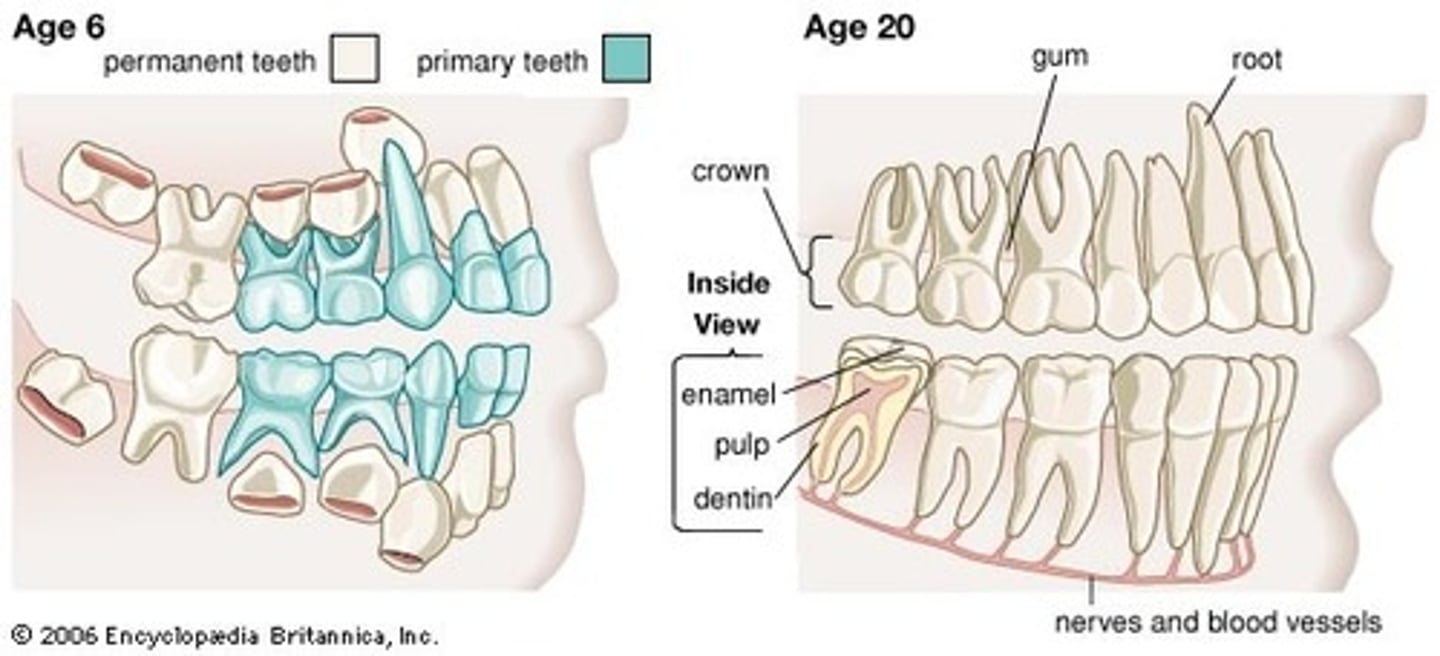
Diphyodonty
two sets of teeth, milk teeth and permanent teeth
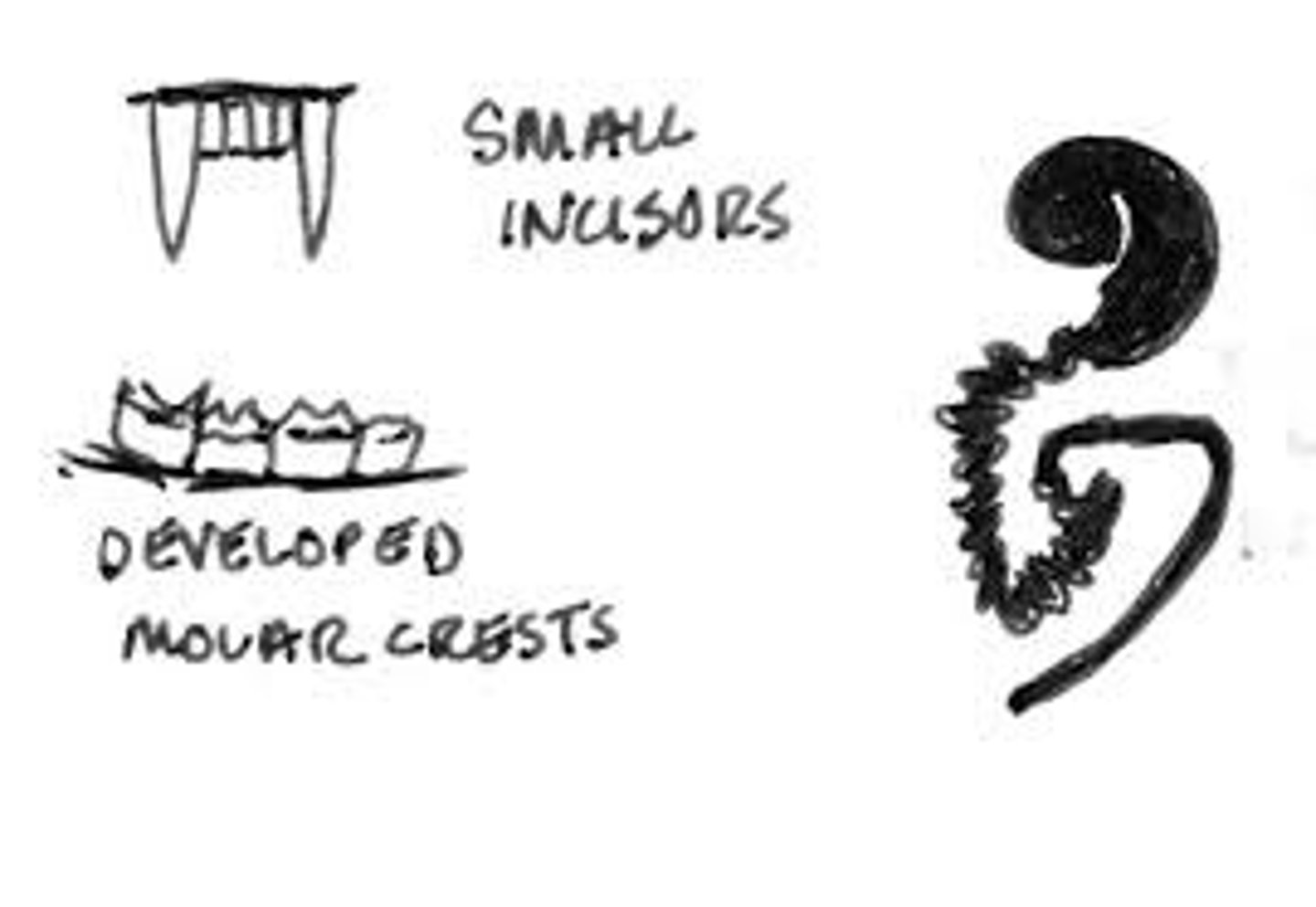
Folivore dental traits
Leaf eaters; thin enamel and long, sharp crests to slice leaves
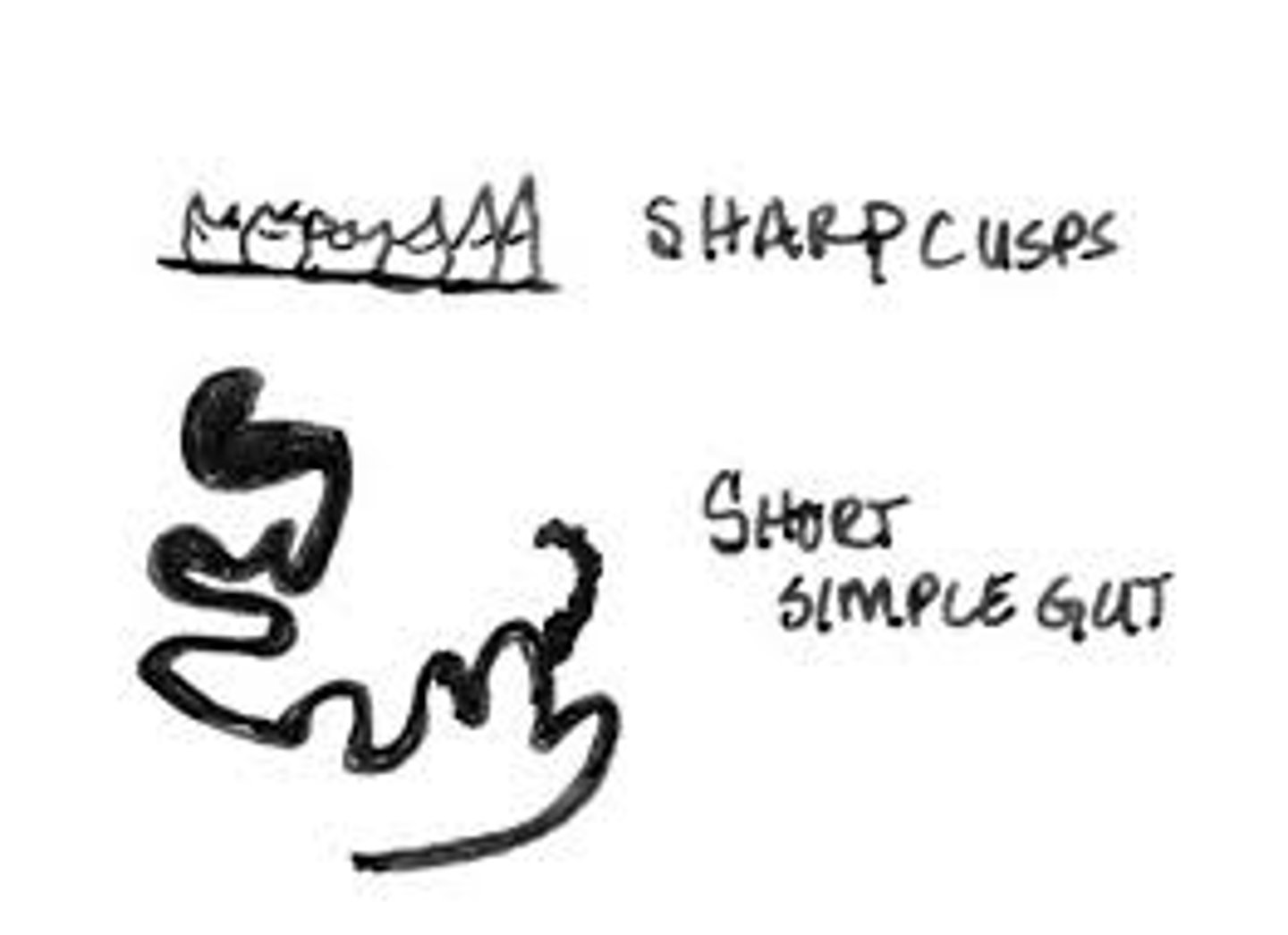
Frugivore dental traits
Fruit eaters; molars have low, rounded cusps for fruit pulp chewing

insectivore dental traits
Insect eaters; sharp cusps for cutting through exoskeletons
Bunodonty
Rounded or conical cusps on molars
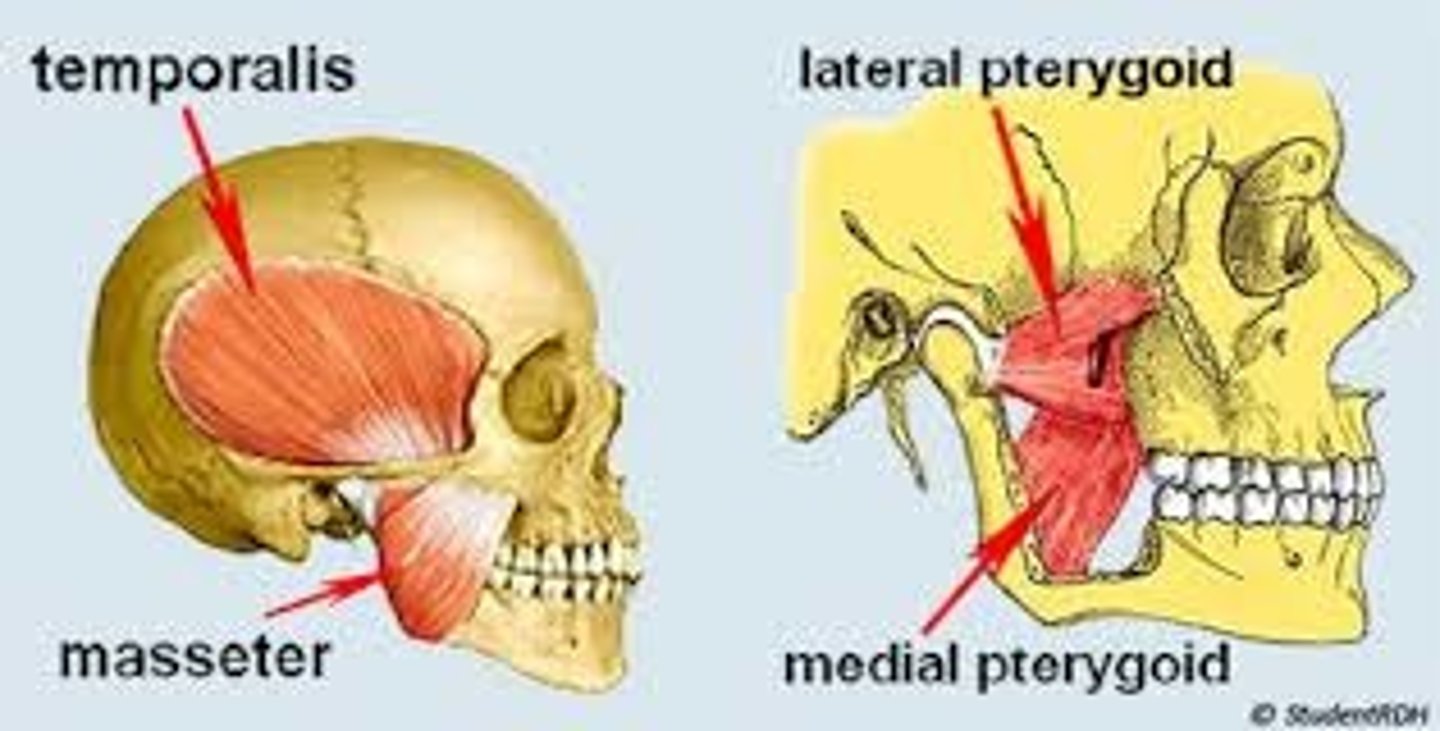
The four chewing muscles
1. Masseter
2. Temporalis
3. Medial pterygoid
4. Lateral pterygoid
Comparative method
Compares things (duh)
Molars and body size
Larger molars = larger body size
Supraorbital torus
Brow ridge - can be used to measure cranial capacity
Arboreal theory
Early primates were adapting to life in the trees. As the mouth was no longer needed for food procurement, the snout reduced in length and the eyes rotated front the side of the cranium to the front, allowing for the 3D vision of primates

Qualities of arboreal quadrupeds
- Narrow skeleton
- Long tail
- Long fingers
When did the first primates appear?
The Eocene
Qualities of terrestrial quadrupeds
- Short tails
- Short digits
Leaping quadrupeds qualities
- Longer legs than arms
- Long lumbar region
Suspensory quadruped qualities
- Longer arms than legs
- Long fingers
- Often no tail
- Rotary wrist joint
In which epoch did the first definitive primates show up?
The Eocene

Absolute differences
Refers to unique features that distinguish one species from another