CHA101L Quiz 6
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
Cribriform plate
* Horizontal plate of bone covered with small holes
2
New cards
Crista galli
* Vertical plate of bone in the median plane to which the falx cerebri is attached
3
New cards
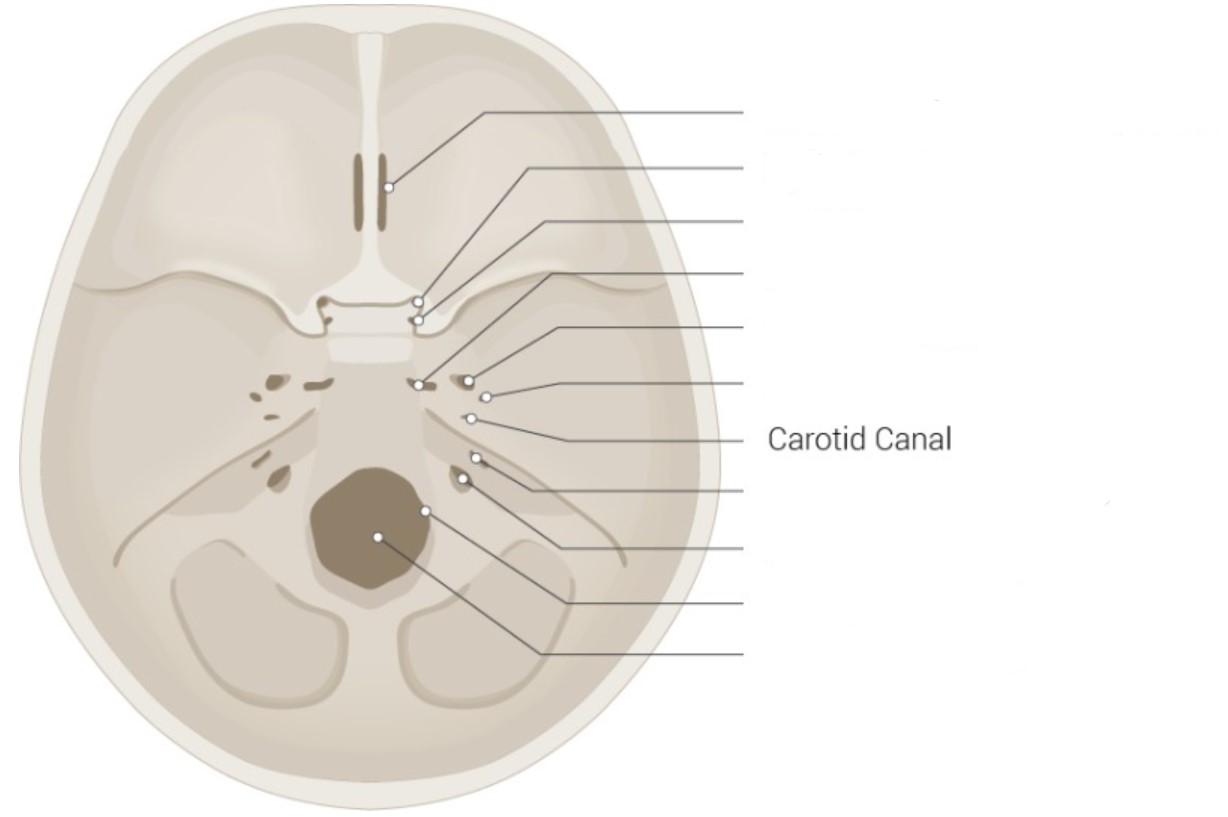
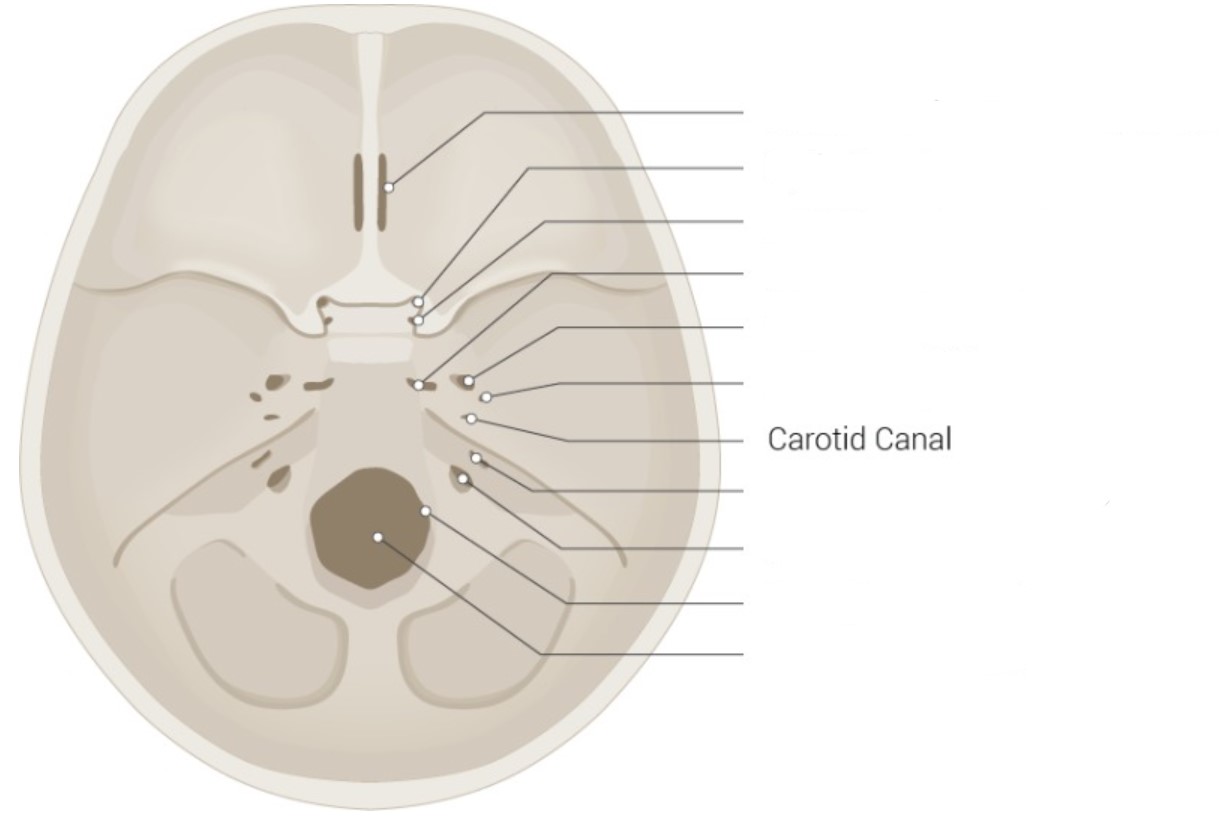
Identify
* Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
* Optic canal
* Foramen rotundum
* Foramen lacerum
* Foramen ovale
* Foramen spinosum
* Internal acoustic meatus
* Jugular foramen
* Hypoglossal canal
* Foramen magnum
* Optic canal
* Foramen rotundum
* Foramen lacerum
* Foramen ovale
* Foramen spinosum
* Internal acoustic meatus
* Jugular foramen
* Hypoglossal canal
* Foramen magnum
4
New cards
Longitudinal cerebral fissure
* Divides the cerebrum into right and left cerebral hemispheres
5
New cards
Lateral sulcus
* Largest valley visible from a lateral aspect
* Separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes
* Separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes
6
New cards
Central sulcus
* Lies on the lateral surface of the cerebrum
* Begins near the midpoint of the lateral sulcus, travels superiorly to reach the longitudinal cerebral fissure
* Serves as the boundary between the frontal and parietal lobes
* Begins near the midpoint of the lateral sulcus, travels superiorly to reach the longitudinal cerebral fissure
* Serves as the boundary between the frontal and parietal lobes
7
New cards
Precentral vs. postcentral gyrus
* Pre - immediately anterior to the central sulcus and contains the primary motor cortex
* Post - immediately posterior to the central sulcus and contains the primary sensory cortex
* Post - immediately posterior to the central sulcus and contains the primary sensory cortex
8
New cards
Upper motor neuron paralysis
* Stroke in the area of the pre/post central gyrus cause the upper motor neuron signals toward the spinal cord to be lost
* If upper motor neuron is lost, conscious control of movement, particularly skilled movement, is lost
* If upper motor neuron is lost, conscious control of movement, particularly skilled movement, is lost
9
New cards
Olfactory nerve (CN I)
* Exit: cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
* Function: sensory - smell
* Function: sensory - smell
10
New cards
Sign/symptom of olfactory nerve dysfunction
* Anosmia (lack of smell)
11
New cards
Optic nerve (CN II)
* Exit: optic canal
* Function: sensory - vision
* Function: sensory - vision
12
New cards
Sign/symptom of optic nerve dysfunction
* Various types of blindness
13
New cards
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
* Exit: superior orbital fissure
* Function:
* motor - to levator palpebrae superioris muscle and all extraocular muscles (except superior oblique and lateral rectus)
* parasympathetic - to sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles
* Function:
* motor - to levator palpebrae superioris muscle and all extraocular muscles (except superior oblique and lateral rectus)
* parasympathetic - to sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles
14
New cards
Sign/symptom of oculomotor nerve dysfunction
* Strabismus (abnormal alignment of the eye)
* Mydriasis (abnormal dilated pupil)
* Ptosis (drooping eyelid)
* Diplopia (double vision)
* Mydriasis (abnormal dilated pupil)
* Ptosis (drooping eyelid)
* Diplopia (double vision)
15
New cards
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
* Exit: superior orbital fissure
* Function: motor - to superior oblique muscle
* Function: motor - to superior oblique muscle
16
New cards
Sign/symptom of trochlear nerve dysfunction
* Diplopia (double vision)
17
New cards
Ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)
* Branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
* Exit: superior orbital fissure
* Function: sensory - from skin above the eye and cornea
* Exit: superior orbital fissure
* Function: sensory - from skin above the eye and cornea
18
New cards
Sign/symptom of ophthalmic nerve dysfunction
* Neuralgia (intense pain due to nerve damage) or anesthesia of appropriate skin region
* Loss of corneal blink reflex
* Loss of corneal blink reflex
19
New cards
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
* Branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
* Exit: foramen rotundum
* Function: sensory - from skin between the eye and lips
* Exit: foramen rotundum
* Function: sensory - from skin between the eye and lips
20
New cards
Sign/symptom of maxillary nerve dysfunction
* Neuralgia (intense pain due to nerve damage) or anesthesia of appropriate skin region
21
New cards
Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
* Branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
* Exit: foramen ovale
* Function:
* sensory - from anterior 2/3 of tongue (via lingual nerve), and skin over the mandible
* motor - to muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of the digastric, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini muscles
* Exit: foramen ovale
* Function:
* sensory - from anterior 2/3 of tongue (via lingual nerve), and skin over the mandible
* motor - to muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of the digastric, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini muscles
22
New cards
Sign/symptom of mandibular nerve dysfunction
* Loss of general sensation to anterior 2/3 of tongue
* Neuralgia (intense pain due to nerve damage) or anesthesia of appropriate skin region
* Chewing difficulty
* Neuralgia (intense pain due to nerve damage) or anesthesia of appropriate skin region
* Chewing difficulty
23
New cards
Abducens nerve (CN VI)
* Exit: superior orbital fissure
* Function: motor - to lateral rectus muscle
* Function: motor - to lateral rectus muscle
24
New cards
Sign/symptom of abducens nerve dysfunction
* Medial (internal) strabismus (eye move towards midline)
* Diplopia (double vision)
* Diplopia (double vision)
25
New cards
Facial nerve (CN VII)
* Exit: internal acoustic meatus
* Function: motor - to muscles of facial expression
* Function: motor - to muscles of facial expression
26
New cards
Sign/symptom of facial nerve dysfunction
* Facial paralysis or palsy (Bell’s palsy)
27
New cards
Chorda tympani
* Branch of the facial nerve (CN VII)
* Function:
* sensory - taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
* parasympathetic - to sublingual and submandibular glands
* Function:
* sensory - taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
* parasympathetic - to sublingual and submandibular glands
28
New cards
Sign/symptom of chorda tympani dysfunction
* Loss of taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
* Reduced salivation
* Reduced salivation
29
New cards
Parasympathetic branches of the facial nerve (CN VII)
* Function: parasympathetic - to lacrimal gland
* Dysfunction: loss of lacrimation (crying)
* Dysfunction: loss of lacrimation (crying)
30
New cards
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
* Exit: internal acoustic meatus
* Function: sensory - hearing and balance (innervates semicircular ducts, utricle and saccule)
* Function: sensory - hearing and balance (innervates semicircular ducts, utricle and saccule)
31
New cards
Sign/symptom of vestibulocochlear nerve dysfunction
* Hearing loss
* Loss of equilibrium
* Loss of equilibrium
32
New cards
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
* Exit: jugular foramen
* Function:
* sensory - taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue and general sensation from oropharynx
* motor - to stylopharyngeus
* parasympathetic - to parotid gland
* Function:
* sensory - taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue and general sensation from oropharynx
* motor - to stylopharyngeus
* parasympathetic - to parotid gland
33
New cards
Sign/symptom of glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction
* Loss of taste and general sensation to posterior 1/3 of tongue
* Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
* Loss of gag reflex
* Loss of salivation from parotid duct
* Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
* Loss of gag reflex
* Loss of salivation from parotid duct
34
New cards
Vagus nerve (CN X)
* Exit: jugular foramen
* Function:
* sensory - sensation from viscera of neck, thorax, and abdomen, and taste from epiglottis and palate
* motor - muscles of larynx, pharynx, and palate
* parasympathetic - to viscera of neck, thorax, and abdomen
* Function:
* sensory - sensation from viscera of neck, thorax, and abdomen, and taste from epiglottis and palate
* motor - muscles of larynx, pharynx, and palate
* parasympathetic - to viscera of neck, thorax, and abdomen
35
New cards
Sign/symptom of vagus nerve dysfunction
* Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
* Dysphonia (difficulty speaking/hoarseness)
* Sagging soft palate
* Uvula deviates to normal side
* Aspiration pneumonia
* Loss of visceral reflexes
* Tachycardia
* Decrease GI motility
* Decreases HCl
* more…
* Dysphonia (difficulty speaking/hoarseness)
* Sagging soft palate
* Uvula deviates to normal side
* Aspiration pneumonia
* Loss of visceral reflexes
* Tachycardia
* Decrease GI motility
* Decreases HCl
* more…
36
New cards
Accessory nerve (CN XI)
* Exit: jugular foramen
* Function: motor - to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
* Function: motor - to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
37
New cards
Sign/symptom of accessory nerve dysfunction
* Weakness in turning head and shrugging shoulders
38
New cards
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
* Exit: hypoglossal canal
* Function: motor - to muscles of the tongue (except palatoglossus)
* Function: motor - to muscles of the tongue (except palatoglossus)
39
New cards
Sign/symptom of hypoglossal nerve dysfunction
* When protruded, tongue deviates to the side of the lesion
40
New cards
Confluence of sinuses
* The connecting point of the superior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and transverse sinus
41
New cards
Drain into the hiatus semilunaris
* Frontal, maxillary, and anterior ethmoid sinuses
42
New cards
Roots
* Stylo →
* Palato →
* Mylo →
* Genio →
* Glossus →
* Hyo →
* Stylo →
* Palato →
* Mylo →
* Genio →
* Glossus →
* Hyo →
Roots
* → Styloid process
* → Soft palate
* → Molar
* → Chin
* → Tongue
* → Hyoid bone
* → Styloid process
* → Soft palate
* → Molar
* → Chin
* → Tongue
* → Hyoid bone
43
New cards
Genioglossus muscle
* Innervation: CN XII
* Actions: Helps to protrude tongue
* Actions: Helps to protrude tongue
44
New cards
Styloglossus muscle
* Innervation: CN XII
* Actions:
* Helps to elevate and retract tongue
* Helps to create trough for swallowing
* Actions:
* Helps to elevate and retract tongue
* Helps to create trough for swallowing
45
New cards
Hyoglossus muscle
* Innervation: CN XII
* Actions: Helps to depress and retract tongue
* Actions: Helps to depress and retract tongue
46
New cards
Palatoglossus muscle
* Innervation: CN X
* Actions:
* Helps elevate posterior aspect of tongue
* Helps form anterior arch
* Actions:
* Helps elevate posterior aspect of tongue
* Helps form anterior arch
47
New cards
\
Mylohyoid muscle
Mylohyoid muscle
* Innervation: CN V3
* Actions: raises hyoid during swallowing
* Actions: raises hyoid during swallowing
48
New cards
Geniohyoid muscle
* Innervation: CI (spinal nerve) via CN XII
* Actions:
* Draws hyoid up and forward during chewing
* Helps open mandible
* Actions:
* Draws hyoid up and forward during chewing
* Helps open mandible
49
New cards
Anterior belly of digastric muscle
* Innervation: CN V3
* Actions:
* Stabilizes hyoid during swallowing
* Swallowing, chewing, speech, breathing
* Lower mandible and elevate hyoid during swallowing
* Actions:
* Stabilizes hyoid during swallowing
* Swallowing, chewing, speech, breathing
* Lower mandible and elevate hyoid during swallowing
50
New cards
Posterior belly of digastric muscle
* Innervation: CN VII
* Actions:
* Swallowing, chewing, speech, breathing
* Lower mandible and elevate hyoid during swallowing
* Actions:
* Swallowing, chewing, speech, breathing
* Lower mandible and elevate hyoid during swallowing
51
New cards
Stylohyoid muscle
* Innervation: CN VII
* Actions: raises hyoid during swallowing
* Actions: raises hyoid during swallowing