Complications
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What do we need to do to prepare?
Look at
species, breed
pre-existing conditions
type of surgery
drugs used
positioning
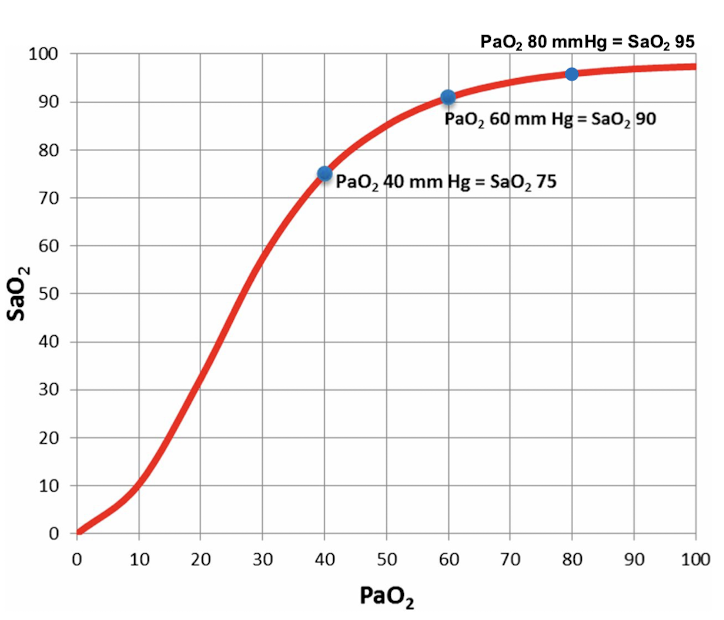
Hypoxemia
Mild → PaO2 < 80 mmHg or SpO2 <95%
Moderate → PaO2 < 60 mmHg or SpO2 < 90%
Severe → PaO2 < 40-45 mmHg or SpO2 < 80%
Cyanosis
5 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin or more
SpO2 of < 85% if Hb is normal
Lower if patient is anemic
Causes of hypoxemia
V/Q Mismatch: Atelectasis, pulmonary edema, pulmonary contusions,
thromboembolism, asthma…
R-L shunt: intra-cardiac or intra-pulmonary
Diffusion impairment: pneumonia, interstitial lung disease…
Hypoventilation (severe)
Decreased FiO2
Treat hypoxemia
Treat underlying problem → pay special attention during induction and recovery
inc FiO2 and check O2 source
lung re-expansion
bronchodilators
support and optimize ventilation
diuretic
surgical correction
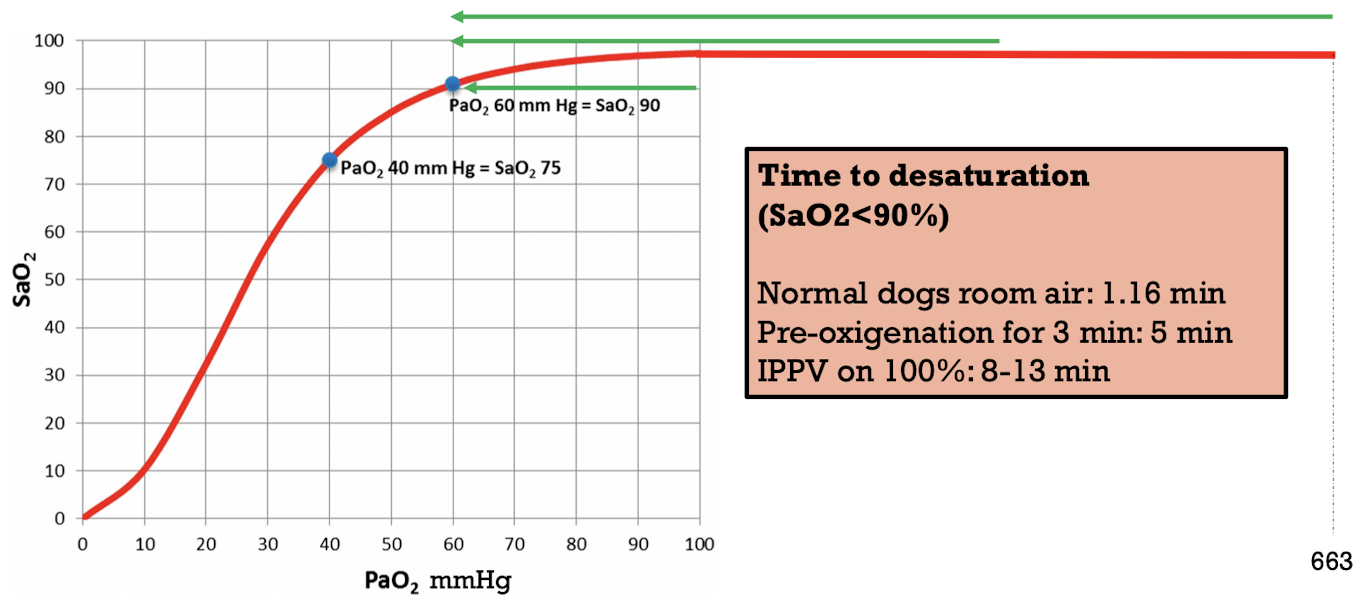
Apnea
> 1min without spontaneous breathing → common after induction → prevent by pre-oxygenating animal
excessive depth
additional drugs
hypocarbia → ventilating too much
excessive work to ventilate
inability to ventilate
cardiopulmonary arrest
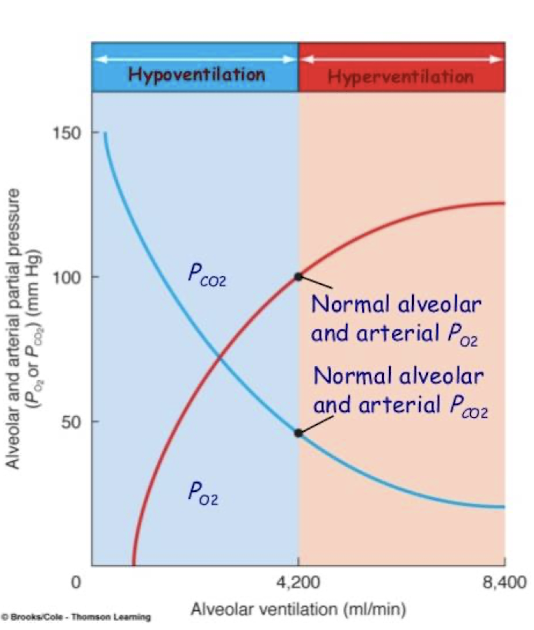
Hypoventilation
Happens the most because the drugs we give cause this
Alveolar hypoventilation as insufficient ventilation leading to hypercapnia
ETCO2 3-5 mmHg <PaCO2
caused by decrease in tidal volume (not taking enough breaths, or not fast enough), RR, inc dead space, or combo
Physiological effects of hypercapnea
stimulation of respiratory drive
respiratory acidosis
inc cerebral blood flow
CNS depression
sympathetic stimulation → inc HR & BP
hypoxemia
Causes of hypercapnea
anesthetic drug
obesity
inc abdominal pressure
neuro disorders
pathologies of thoracic wall or lungs, pneumothorax, pleural disorders, mass, trauma
age
hypothermia
positioning
equipment → dead space
inc CO2 production → hyperthermia, systemic absorption during lap spay
Treat hypercapnea
find underlying cause
know pre-existing conditions
measure ETCO2 and/or PaCO2
check drugs, anesthetic depth
correct body temp
equipment
support with ventilation
Hyperventilation
From inc respiratory rate → lead to hypocapnea and respiratory alkalosis
light plane
nociception
hypercapnia
hypoxemia
metabolic acidosis
Airway obstruction
Partial or total obstruction → Brachycephalic breeds predisposed
underlying issues
airway swelling
surgery
trauma
aspiration of foreign material
external pressure
equipment problems
Diagnose airway obstruction
Paradoxic breathing → thoracic wall sucks in, abdominal wall expands, open mouth breaking, nostril flare, neck flexed, stridor
prolonged inspiratory time
hypoxemia and/or cyanosis
rebreathing bag not working
capnograph wave abnormal or disappears
high pressure when trying to ventilate
Brachycephalic syndrome
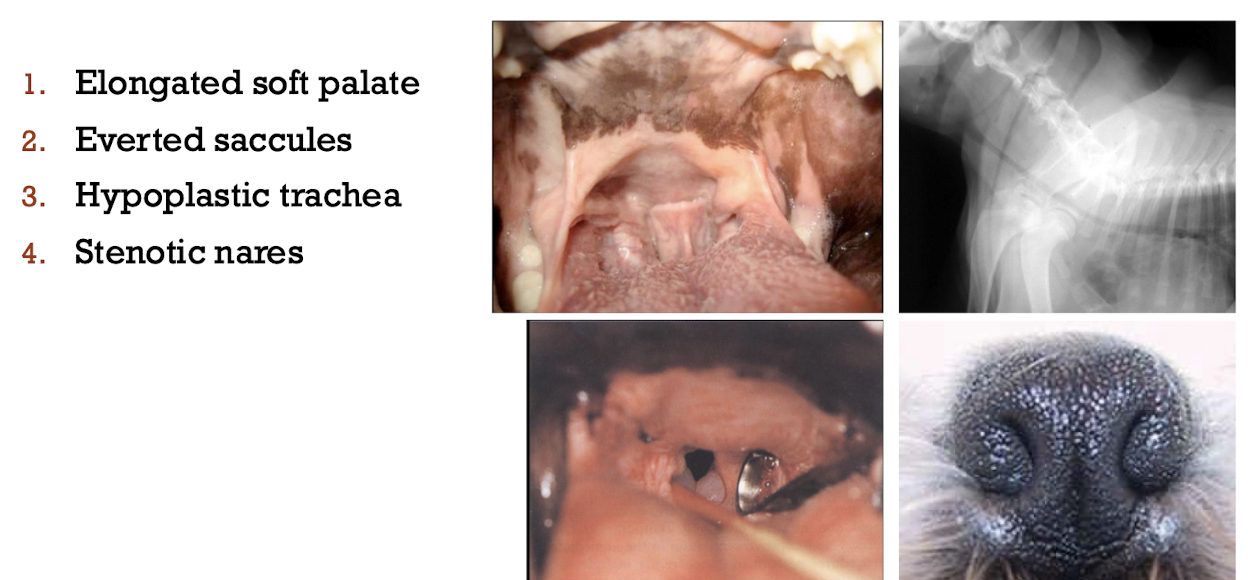
Upper airway disease
Problems at intubation or recovery → pre-oxygenate, small tube, local anesthetic application
laryngeal paralysis
laryngeal hemiplegia
laryngospasm
Lower airway disease
Problems during anesthetic maintenance if endo tube does not pass lesion
tracheal mass
tracheal stenosis
tracheal collapse
bronchospasm → asthma, reactive airway, anaphylaxis, bronchitis → when animal is intubated
Airway inflammation cause and treatment
Cause → respiratory distress/effort, surgery, trauma
treat → corticosteroids, local vasoconstrictors, dextrose 50%
Equipment problems
kinked, twisted ET tube
kinked breathing circuit
mucus/blood ET tube obstruction
pop-off closed → tension pneumothorax
Airway obstruction
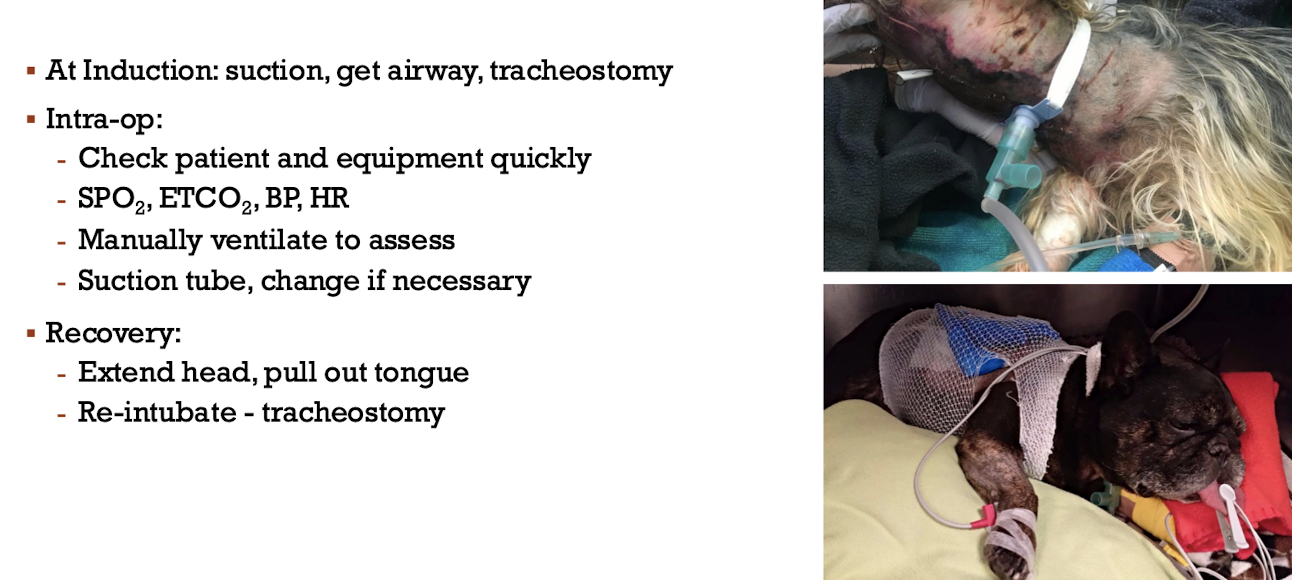
Tension pneumothorax
If can’t hear lung sounds, tap the chest!!

What do we consider for HR?
age
Size/breed
Resting HR

Why is HR so important?
Determines CO
O2 content
Blood pressure
What happens with slow HR?
Diastolic filling volume (preload), time (HR)
Too low will directly Dec CO and BP
What causes inc parasympathetic activity - Bradycardia?
Vagal tone → eye reflex, inc GI pressure, expiration
Drug induced → Alpha 2, opioids
Reflex mechanism due to hypertension → baroreflex response
Cardiac disease
Inc intracranial pressure → Cushing response
Electrolyte abnormalities
Hypothermia
When do we treat bradycardia?
Only if marked and affecting CO
look at blood pressure
Treat if rhythm is markedly irregular
How can we treat bradycardia?
vagal tone → Anticholinergics
Drug induced → reversal, lidocaine(for alpha 2), anticholinergics(not during hypertensive phase)
Reflex mechanism due to hypertension → control hypertension → baroreflex response Cardiac disease
Cardiac disease → anticholinergics, isoproterenol, pace maker
Intracranial pressure → control ICP
Electrolytes → Dec K, calcium gluconate
Hypothermia → warm up
Tachycardia
fast HR → SV Dec because it is not effectively filling, Dec CO, Dec BP
Inc O2 consumption → myocardial ischemia and arrhythmia
Tachycardia causes
Inc sympathetic activity
superficial anesthetic plane
Hypotension/hypovolemia
Hypercapnia/hyperthermia
Drug induced → ketamine, sympothomimetics, anticholinergics
Hyperthyroidism
Hypoxia/shock
Heart disease
Treat tachycardia
superficial plane/pain → check depth/analgesia
Hypotension/hypovolemia → correct fluids
Hypercapnia/hyperthermia Drug→ cool down, adjust ventilation
Drug induced → stop giving
Hypoxia/shock → improve oxygen delivery
How to recognize sinus rhythm?
ECG
regular rhythm?
All waves present and normal?
P & QRS are associated
Common dysrhythmias
Atrioventricular (AV) block*
▪ Atrial premature contractions (APC)
▪ Atrial fibrillation (AF)
▪ Ventricular premature contractions (VPC)*
▪ Ventricular tachycardia (VT)*
▪ Ventricular fibrillation (VF)
AV blocks
Conduction from atria to ventricles is not working
slow conduction → 1st degree AV black
P waves not followed by QRS complex (2nd & 3rd degree)
Bradycardia is common
Due to inc vagal tone
Drug induced → alpha 2, anticholinergics
Intrinsic cardiac disease
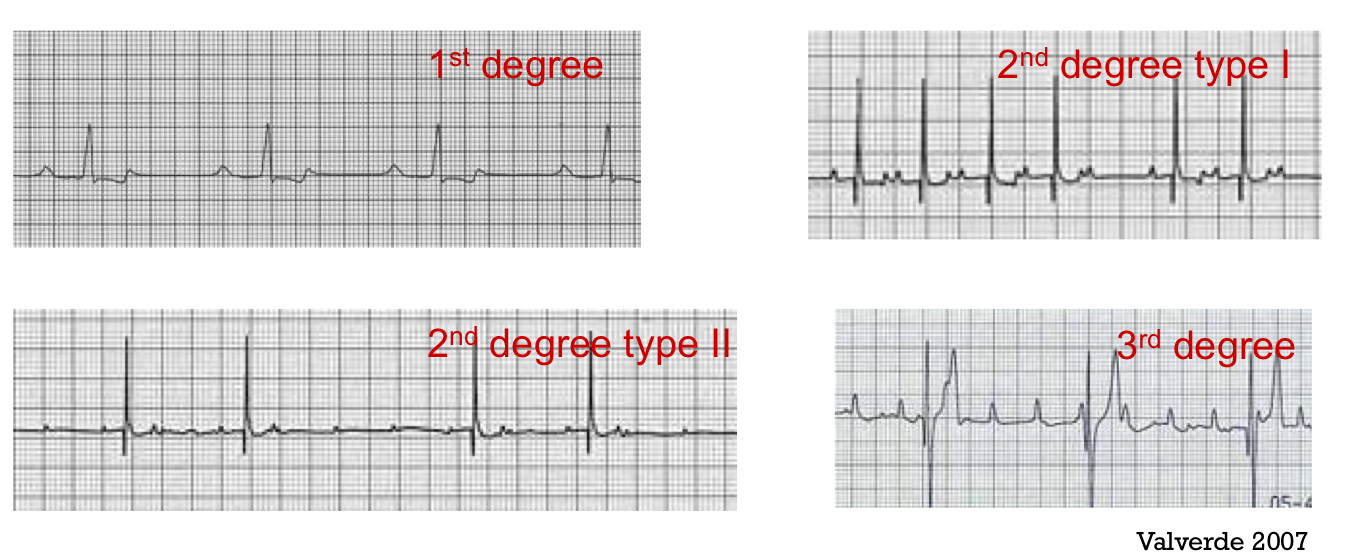
Treat AV blocks
reverse alpha 2
Anticholinergics
Isoproterenol
3rd degree needs a pacemaker
Ventricular premature contraction VPC
Ventricle is contracting during the wrong time - not following normal path, taking longer
No P waves
Premature
Bizarre QRS
Premature nature prevents adequate diastolic filling
pulse deficit
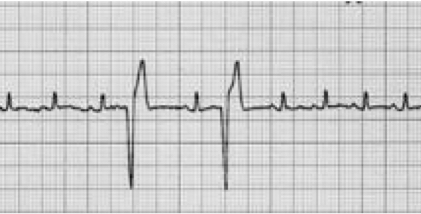
What causes VPC?
Heart disease, cardiomyopathies
Catecholamine release: pain, stress, inappropriate anesthetic plane
Myocardial hypoxia
Electrolytic abnormalities (Hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia)
Myocardial depressant factors (GDV, splenic tumors)
Arrhythmogenic drugs (thiopental, B1-agonists-sympathomimetics)
Irritation of ventricle, mechanical stimulation
Treat VPC
If blood pressure and CO affected
oxygenate
Improve cantractility
Control underlying cause → electrolytes, surgery
Lidocaine
Procainamide
Magnesium sulfate
Beta blockers
Amiodarone
Ventricular tachycardia
Lots of VPCs in sequence → high HR
can become ventricular fibrillation → always treat
Tachycardia is part of dysrhythmia
Some ethnology and treatment as for VPCs
Hypotension
Most common during general anesthesia → can cause Dec perfusion to tissues, damage to kidneys, muscles
measure with Doppler and oscillometric
Normal BP values
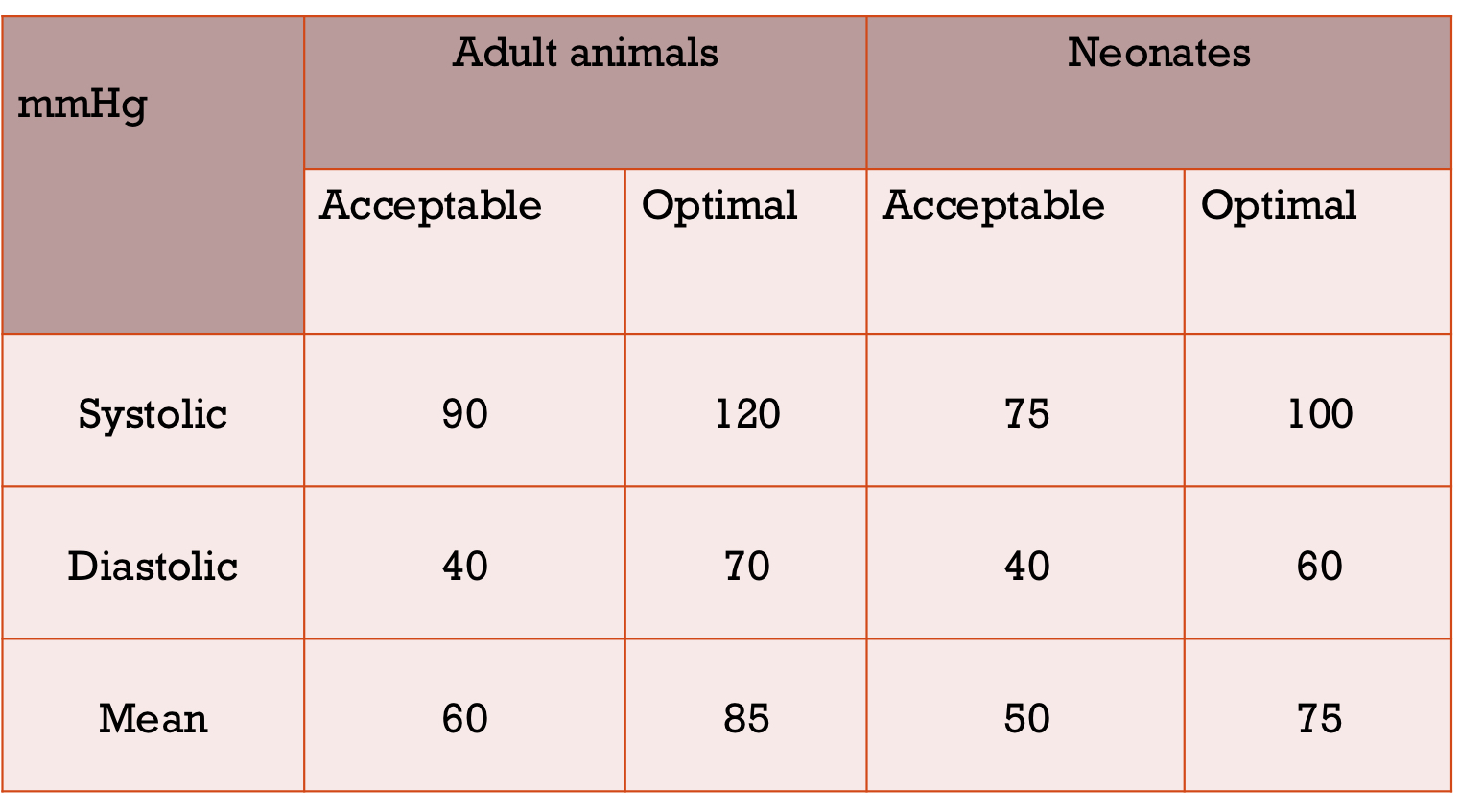
If your animal is healthy and is hypotensive, what is the most common reason for this?
too much gas
Hypotension causes
excessive depth
Hypovolemia
Peripheral vasodilation
Cardiac dysrhythmia
Dec cardiac contractility
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
Treat hypotension
too deep → check plane
Dehydrated → correct fluid
Bradycardia → anticholinergics
Tachycardia → hypovolemia, analgesia, anesthetic plane, beta blockers
Inc contractility → dopamine, NE
Vasodilation → inc vascular resistance → dopamine, NE, phenylephrine, epinephrine
Hypertension
usually associated with tachycardia initial phase
less common than hypotension
More common in cats
Inadequate depth
Drug induced
Hypercapnia
Hypoxia
Underlying disease
Hypovolemia
Hypovolemia leads to hypotension
hypotensive patient is not always hypovolemic
Results in Dec blood flow
Hypotension does not always result in Dec blood flow
Estimate blood loss
amount in suction bottle, lap sponges, gauze, hemodynamic state
HR inc
BP Dec
CO Dec
Hemodilution PCV & TS dec
Treat hypovolemia
Volume → isotonic crystalloids, colloids, hypertonic saline, blood products
Contractility → inotropes, balanced anesthesia → Dec cardiac depression
Vasoconstriction without fluid replacement will not inc CO
Dosing errors
wrong concentration
Math errors
Drawing up wrong drugs
Giving wrong drug
Do not wait until peak effect of the drug
Precautions to avoide dosing errors
Check label syringe
Check concentration
Double check volume math
Have reversal available
IV catheter complications
Non patent
Phlebitis from long term catheter
Leaky vein
Propofol and cats
Intubation problems
lack of visualization → use guide tube, look for condensation, CO2 monitor, scope to visualize
Esophageal intubation
Lack of movement of bag
Very low or no CO2 wave
Inability to seal cuff
Animal waking up
Hypoxemia
Hypothermia
< 36 C
temp drop with GA in 1st hr
Loss of temp regulation ability under GA
Vasodilation → acepromazine, inhalants
Large surface area:body mass ratio
Cold fluids
Cool operating room
Alcohol prep
Lavage during surgery
Why is hypothermia bad?
▪ Decrease metabolism leads to less anesthetic requirements: risk of anesthetic
overdose
▪ Prolonged recovery
▪ Postoperative wound infection
▪ Impairment of coagulation
▪ Increased shivering and discomfort during recovery,
▪ Increased blood viscosity
▪ Bradycardia, non responsive to anticholinergics
▪ Cardiac arrhythmias and arrest < 23 C
Prevent hypothermia
prevent heat loss → keep patient covered, avoid cold surfaces
Active warming → forced air blankets, water circulating heating pads, oat bags, hot dog, warm lavage, warm Iv fluids
Causes of hyperthermia
Iatrogenic
Warming devices
Large heavy coated animal undergoing diagnostics procedures associated with little heat loss
Metabolic derangement or disease
Malignant hyperthermia
Serotonin syndrome
Hyperthyroidism & Cushing
HYPP
Seizures
Opioids → cats
Hyperthermia consequences
hyper metabolism
Inc HR & RR
Metabolic acidosis
Seizures
Organ dysfunction
Treat by stopping warming devices
Regurgitation
Small ruminants will regurgitate the whole time
anesthetic drugs will relax LES
Can lead to aspiration pneumonia
Ulcerative esophagitis and stricture
Nasal and pharyngeal irritation
Prevent with cisapride and metoclopramide
Treat with anti acids, head down to drain, suction, lavage
Hypoglycemia
<4 mmol/L
in pediatric patients or small patients fasted for too long
Diabetes
Insulinoma
Hepatic disease
Prolonged recovery
Seizures
Treat with dextrose
Seizures
idiopathic epilepsy
Intracranial disease/trauma
Metabolic disease
Cerebral ischemia
Severe hyperthermia
Post myelogram contrast inj
Treat with → benzodiazepine, propofol, barbiturates, inhalants anesthetic, provide oxygen, check temp, glucose, electrolytes
Awake/moving
Inadequate depth monitoring
Apnea
Hypoventilation
Accidental extubation/loss of IV
Forget to turn vaporizer
Safety hazard
Always have induction top up available
Continuous monitoring
Poor recovery problems
Pain
Emergence delirium → waking up too fast, anxious animals, no sedative, noises and stimulation
Dysphoria → excitement, vocalization, lack of response to interaction after opioid administration
Horses
How do we treat delirium?
Give more sedation
How do we treat Dysphoria?
Titrate to effect with opiate reversal → naloxone