Medical Pathophysiology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is Pathology?
The study of changes in cells and tissues as a result of injury/disease
Focus on physical changes present in diseased organs and tissues
What is Pathophysiology?
Study of the functional changes that occur in the body as a result of injury/disease
focusses on abnormal functioning of diseased organ with application5 Aspects of Dise to medical procedures
6 Aspects of Disease Process
Pathogenesis
Etiology
Morphologic changes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnosis
Clinical Course
What is Pathogenesis?
Origination and development of illness or disease
3 Types of Etiology
Study of disease causation (why?)
Genetic → genes are responsible
Congenital → result of environmental influences that alter gene function
Acquired → encountered later in life produce the disease
What is a Nosocomial disease?
Acquired in healthcare
result of exposure to infection in health care environment
What is iatrogenic disease?
Acquired in healthcare
result of medical treatment (e.g. catheterization)
Epidemiology is what and needs to include what?
The study of disease in populations
Incidence, Prevalence, Morbidity, Mortality
What is Endemic?
Incidence and prevalence of a disease are predictable and stable
What is an Epidemic?
Dramatic increase in disease incidence in a population
What is a Pandemic?
Epidemic spreads across continents
What is Cell Atrophy?
Decrease in the size of the cell
Due to: decrease in functional demand, decrease oxygen supply, removal of signals, nutritional deprivation, ageing
What is Cell Hypertrophy?
Increase in cell size
Due to: increase in trophic (growth) signals, increase in demand (strength-building exercise)
What is Cell Hyperplasia?
increase in the number of cells
Due to: increase in growth cells, increase in demand
What is Cell Metaplasia?
Changing of one cell type to another
Cells adapt to chronic or persistent stressor
If the stimulus is removed, cells revert back to their original type
What is Cell Dysplasia?
change is cell size, shape, uniformity, arrangement and structure
Response to chronic and persistent stressors
Cellular Death - Apoptosis
involves a reduction is cell numbers by a process of self-destruction
programmed cellular death prompted by genetic signal
Reasons: cell age, attempt to decrease cell numbers, damaged genetic material
Cellular Death - Necrosis
Associated with inflammation
poor ATP production, excessive sodium, toxic chemicals accumulate
Types of Necrosis
Coagulative - protein denaturation, caused by hypoxia
Liquefactive necrosis - lysosomal digestive enzymes are released, leading to autolysis
Caseous - combination of above ^
Fat - adipose tissue, action of lipases
Gangrenous - death of tissue from severe hypoxia, bacterial invasion
Cerebral Atrophy
Pathophysiology
Reduction is the size of cells in the cerebrum of the brain - reduction in neuron size
Loss of neural function = neurologic disease
Clinical Manifestations
As atrophy progresses, the associated function becomes altered
Diagnosis
Etiology, MHx, signs and symptoms, imaging, neuro exam
Treatment
Prevention, interruption of injury process, slowing course of disease
Cardiac Hypertrophy (Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy)
Pathophysiology
Monocytes don’t continue to divide and replace themselves = increased cardiac muscle mass, increasing cardiac workload
Clinical Manifestations
variable clinical expression, left ventricle is main pump, impaired cardiac function, SOB, fainting, irregular heart rate
Diagnosis
family MHx, screening techniques, physical exam, stress testing
Treatment
Pharmacologic, surgery, alcohol ablation, activity restriction
Acromegaly
Increase in cell numbers (cellular hyperplasia) (abnormal growth)
Pathophysiology
results from excessive hormonal stimulation leading to excessive growth. If negative feedback loop fails, growth-hormone secretion continues by pituitary gland
Clinical Manifestations
Organ enlargement, excessive sweating/body odor, deep voice, snoring, skin changes, pituitary adenoma
Diagnosis
slow and insidious, delayed diagnosis, laboratory analysis, imaging studies
Treatment
pharmacologic, surgical, radiation therapy
Cervical Metaplasia and Dysplasia
Cells of the cervix respond to hormonal changes throughout reproductive life
Pathophysiology
Metaplasia: changing of cells types
Dysplasia: abnormal growth and differentiation
High estrogen level, precancerous condition,
Clinical Manifestations
asymptomatic, routine screening, early sexual activity
Diagnosis
Hx, physical exam, pap spear, diagnostic test, HPV testing
Treatment
cold therapy/surgery, hysterectomy, cone biopsy
Environmental Toxins and Cardiovascular Disease
Pathophysiology
exposure to environmental chemicals, air pollution, cigarettes, poisonous gases
Clinical Manifestations
aortic aneurysm, cataract, pneumonia, stroke, CHD, cancer
Diagnosis
physical exam (reduced exercise tolerance, difficulty brething, increased heart rate), lab studies
Treatment
stop smoking, pharmacologic treatment
What are the 3 lines of inflammatory Defense
1st: Skin and mucous membranes (physical barrier)
2nd: Inflammatory response (fever, proteins)
3rd: Immune response (antibodies, lymphocytes)
What are the 3 goals of inflammation?
Increase blood flow to site (vascular response)
Increase cells for healing at site (cellular response)
Remove injured tissue and prepare for tissue repair
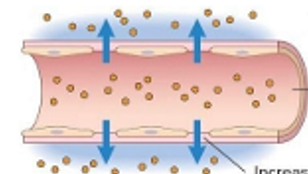
Fluid Movement: Exudate
high protein content and white and red blood cells
fluid and protein leakage
vasodilation and stasis
increased interendothelial spaces
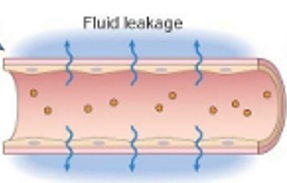
Fluid Movement: Transudate
low protein content, few cells
increased hydrostatic pressure
decreased colloid osmotic pressure
decreases protein synthesis
Inflammatory mediators can be derived from 2 places?
Cell derived: generated in cell plasma membrane/proteins
Plasma derived: continuously circulating
Cellular response 3 essential steps:
chemotaxis → moving cells to site of injury
cellular adherence → binding to migration site
cellular migration → between endothelial cells
What is Phagocytosis?
Inflammatory cells release more inflammatory mediators to attract more neutrophils
Neutrophils also release inflammatory mediators
Aggressive process to destroy/phagocytize causative agents
Healthy tissue is also damaged
What are the 5 cardinal signs of inflammation?
Redness
Heat
Swelling
Pain
Loss of function
What is the treatment of inflammation?
Reduce blood flow
decrease swelling
block chemical mediators
decrease pain
Acute Gastritis
Pathophysiology
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa and/or poor gastric perfusion
Cause
ingestion of irritating substances, too much stomach acid
Clinical Manifestations
abdominal pain, heartburn, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, hematemesis, anemia
Diagnosis
History, physical exam, endoscopic exam, stool analysis, blood count
Treatment
discontinue irritation substance, decrease gastric acid production
Pancreatitis
Pathophysiology
pancreas inflammation, injury of protective digestive feedback mechanism
Cause
excessive alcohol consumption, gallstones, idiopathic/unknown
Clinical Manifestations
upper abdominal pain, inflammatory response, digestive signs, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea
Diagnosis
physical exam, labs, imaging, blood count
Treatment
IV hydration, can result in ICU care, nothing-by-mouth
Burn injuries
Cause
direct contact with heat, radiation, chemicals, electricity
Classification
First-degree (superficial → skin damage only)
Second-degree (deep-partial → epidermal and upper dermal damage)
Third-degree (full thickness → entire thickness of skin)
Clinical Manifestations
1st: warmth, pain, swelling, LOF
2nd: blistering, edema, serous exudate
3rd: exudate, destroyed nerve ending
Diagnosis
Wound depths are classified according to the affected tissue layers, critical is more than 25%
Treatment
changing dressings, fluids/nutrition, antibiotics, cleansing, skin grafts, remove source of injury
Arthritis
Pathophysiology
inflammation of synovial membranes, onset 36-50 years, lack of trigger, causes deformity and erosion
Clinical Manifestations
insidious, severity, fever, 5 signs of inflammation, malalignment
Diagnosis
no definitive test, history, physical exam, bloods
Treatment
Pharmacologic (anti-inflammatory) and non-pharmacologic (rest, physical therapy, hot/cold therapy)
Chronic Gastritis
Pathophysiology
Spread by H. Pylori, t-cells infiltrate gastric mucosa, intense inflammation triggered
Clinical Manifestations
nausea, heartburn, vomiting, loss of appetite, dyspepsia (epigastric discomfort)
Diagnosis
endoscopic exam, breath test, biopsy, low B12 in blood
Treatment
antibiotics, raising pH, immunosuppressive drugs, intramuscular injections of B12
Chronic Pancreatitis
Pathophysiology
ongoing inflammation to pancreas, impacts endocrine functions
Cause
alcohol abuse, autoimmune, hereditary, idiopathic
Clinical Manifestations
long-term abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatty stools, weight loss
Diagnostic Criteria
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (gold std), amylase/lipase levels
Treatment
pain management, lifestyle changes, surgery
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Pathophysiology
chronic inflammatory bowel disorders of unknown origin, Crohn’s/Ulcerative Colitis, affect digestive tract, ulcerations,
Clinical Manifestations
quick stool transition time, fibrosis, loss of absorbative function, fever, weight loss, fatigue, abdominal pain, blood in stool
Diagnostic Criteria
History, Physical exam, endoscopy, radiography, stool cultures to rule out infection
Treatment
pharmacologic, dietary changes, surgery
Ulcerative Colitis
Pathophysiology
inflammation of the colon, only in large intestine, rectum-descending colon, ulceration occurs
Clinical Manifestations
diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdonimcal pain, fever, weight loss, fatigue, anemia
Diagnosis
history, physical exam, endoscopy, radiograph, blood count
Treatment
pharmacologic, dietary changes, surgery
3 Phases of Inflammation
Inflammatory Phase (0-3 days)
Proliferative/Repair Phase (4-21 days)
Remodeling Phase (3wks - 6mths)
What is Hemostasis?
vasocontraction and clot formation
protective scab formation (thrombus)
neutrophils move to injured site → followed by macrophages
How is wound structural integrity restored?
ECM is formed to decrease blood/fluid loss
attract fibroblasts, endothelial/epithelial cells
provisional matric is converted by macrophages
provisional matrix and granulation tissue is reabsorbed once wound is healed
Cutaneous wound healing by intention: Primary
small wounds with approximated edges heal by primary intention (e.g. paper cut)
heal quicker and easier
all areas heal at same time
scarring is minimal
Cutaneous wound healing by intention: Secondary
large pen wounds heal by secondary intention
heal from bottom-up
risk for infection and scarring
Complications of Healing: Infection
invasion by microorganisms
impairs all dimensions of wound healing
prolongs inflammatory response
Complications of Healing: Ulceration
Lack of adequate perfusion
crater-like lesion of skin or mucous membrane
Complications of Healing: Dehiscence
problem with scar formation
wound splits open (opens area to infection)
early after surgery → later in recovery period
Complications of Healing: Keloids
Hypertrophic scars: excessive collagen formation
cosmetic problem
removal = result in another keloid
Complications of Healing: Adhesion
impaired collagen deposition
main risk is due to abdominal surgery
pain, loss of organ function, restrict free movement
What is Granuloma Formation?
Granuloma: nodular inflammatory lesion that encases harmful substance
they form when the injury causing agents are difficult to control/poorly digested, foreign bodies are present