Macro final revision - Multiplier effect
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:33 PM on 12/31/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
1
New cards
What do changes in injections lead to?
A bigger change in national income
2
New cards
What does the increase in injections have a effect on?
Has a multiplier effect on national income (the multiplier)
3
New cards
How is the multiplier (K) calculated?
Multiplier (K) = Change in income / change in injections
4
New cards
What does MPW and MPC stand for?
MPW = Marginal Propensity to Withdraw
MPC = Marginal Propensity to Consume
MPC = Marginal Propensity to Consume
5
New cards
What is the multiplier sensitive to?
the Propensities - MPW and MPC
6
New cards
What does MPW + MPC equal?
1
7
New cards
What does a larger MPC mean?
The larger the MPC = the larger the multiplier is
8
New cards
What are two other equations for the multiplier?
Multiplier = 1/MPW
Multiplier = 1/(1-MPC)
Multiplier = 1/(1-MPC)
9
New cards
How is MPW calculated?
MPW = Change in withdrawals / Change in income
10
New cards
How the larger the MPW is, affect the multiplier effect?
The smaller the multiplier effect (the steeper the withdrawal function)
11
New cards
What does the multiplier look like on a graph, with a shift in injections?
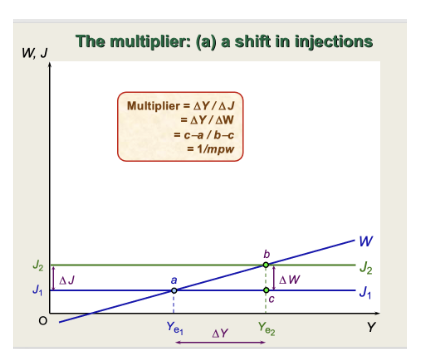
12
New cards
What does the multiplier look like on a graph, with a shift in withdrawals?
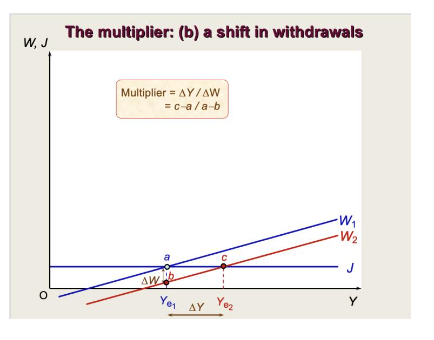
13
New cards
What is the income and expenditure approach? (three facts)
The MPC determines the slope of E function
The steeper the slope of the E function, the larger the size of the multiplier
The larger the MPC, the larger the size of the multiplier
The steeper the slope of the E function, the larger the size of the multiplier
The larger the MPC, the larger the size of the multiplier