PHA615 LAB: Classification Test for HC, Organic Halides, and Amines
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Solublity in H2SO4
tests for alkenes
positive: reacts with alkenes thru Ae rxn
negative: all HC
Ignition Test
more soot = aromatic
less soot = aliphatic
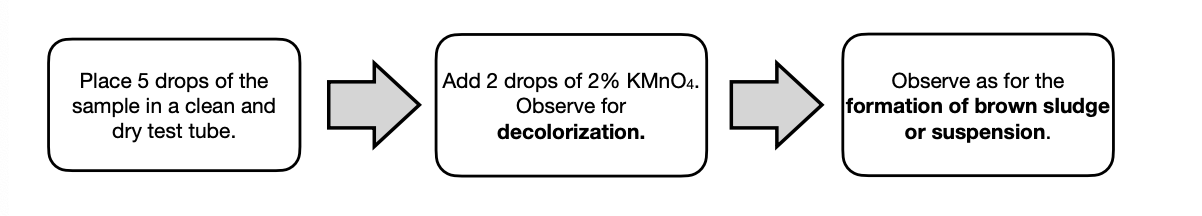
Baeyer’s Test
does not colorized/brown ppt = active saturation
no rxn = alkanes, aromatic
Baeyer’s Test
uses 2% KMnO4
Bromine Test
orange-brown = alkene/alkyne (due to Ae)
no rxn = alkane/aromatic
Bromine Test
Br2 in CCl4
Iodine Test
I2 solution
Iodine Test
tan-colored solid; to confirm presence of alkene/alkyne
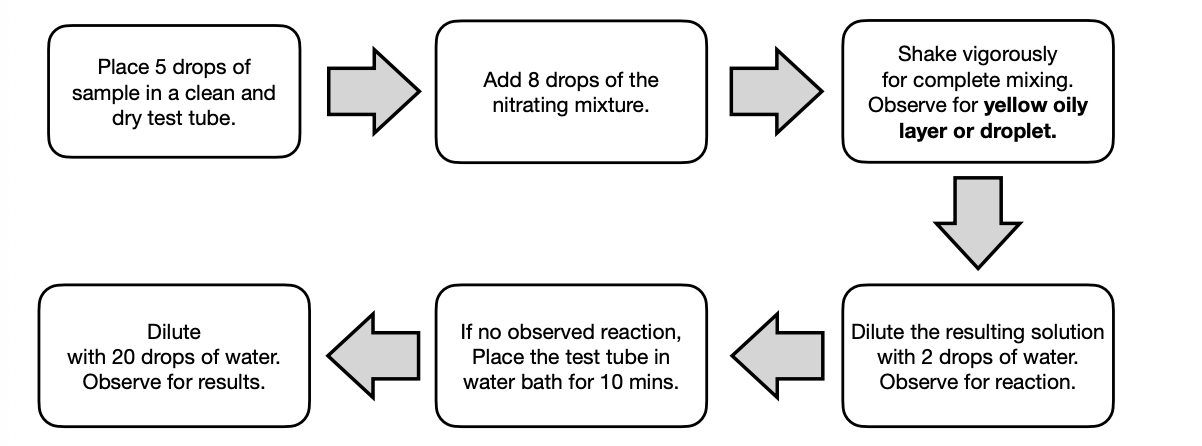
Nitration Test
yellow oily layer = aromatic
Nitration Test
H2SO4 and HNO3
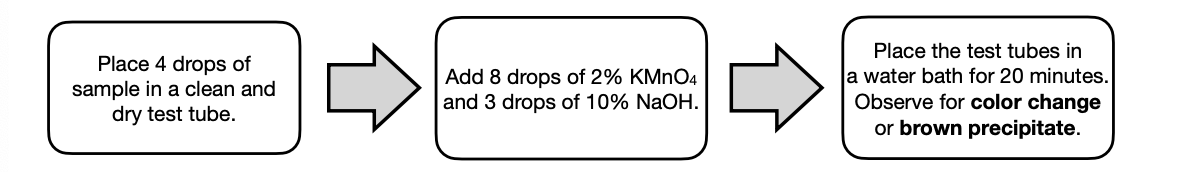
Basic oxidation
decolorized = alkenes and alkyl side chain
Basic oxidation
2% KMnO4
10% NaOH
Beilstein/Copper Halide Test
green flame test = presence of halide
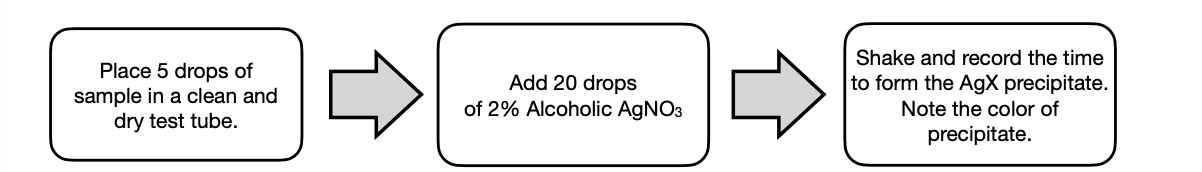
Rxn with Ethanolic AgNO3
classifies type of RX
faster in tertiary RX
Rxn with NaI in Acetone
classifies type of RX
faster in primary RX
Rxn with Ethanolic AgNO3
2% alcoholic AgNO3
Rxn with NaI in Acetone
15% NaI in anhydrous acetone
Hinsberg Test
tests for type of amine
1 - soluble
2- insoluble
3- no rxn
Hinsberg Test
10% NaOH and benzene sulfonyl Cl
Solubility w/ HCl and NaOH
HCl + Amine = Soluble
Solubility w/ HCl and NaOH
NaOH + Amine = insoluble
Hydrocarbons
is a one of the two general classifications of organic compounds. These compounds are composed entirely of C and H atoms that are arranged and bonded in specific ways.
Hydroxy
ROH and ArOH
Mercapto
thiol and sulfides
Amino
for amines
Amido
amindes
Halo
organic halides
Carbonyl
aldehydes and ketones
Carboxyl
carboxylic acid and derivatives
Branching
decreases HC length making the HC more compact and dense.
The # of carbon atoms
increases hydrophobicity = less polar.
H-bonding
-C=O, -COOH, -OH, -NH2
Dipole-Dipole
OH, -NH2, -X, -SH, -C=O, -COOH
London Dispersion / Hydrophobic
HC
Aromaticity
is based on distinct characteristics present in a hydrocarbon as well as its conformance to the Huckel’s rule.
Aromatic
is a hydrocarbon that contains one or more benzenelike rings and can be described as: • Cyclic • Planar • Possess conjugated double bonds (ex. C=C—C=C) • Possess 4n+2 π electrons (Huckel’s rule).
HC
are generally soluble in organic solvent / insoluble in water.
Solubility
is inversely related to melting point (↑ MP = ↓ solubility)
Combustibility
is a measure of how easily a substance bursts into flame through fire or combustion
Flammability
is the ease with which a combustible substance can be ignited causing fire, combustion, or even explosion.
Test of Unsaturation
It can be used to determine the presence of a double/triple bond (unsaturation) in a compound.
Test of Unsaturation
It can differentiate active unsaturation from aromatic compounds.
Test of Unsaturation
Baeyer’s test, Bromine test, and Iodine test
Baeyer’s test
uses KMnO4 and is a form of oxidation reaction which forms a brown suspension/sludge. It detects the presence of active unsaturation like in alkenes and alkynes
Bromine test
uses Br2 in CCl4 to confirm the presence of double/triple bonds. It is an addition reaction in which the Br2 solution is decolorized when mixed with unsaturated compounds.
Iodine test
uses I2 solution and is also an addition reaction used to confirm the presence of alkene/alkynes. The positive result for this test is the formation of a tan-colored solid while retaining the color of the I2 solution.
Nitration Test
is a common substitution reaction for aromatic molecules. It is used to detect the presence of benzene rings in a compound.
Nitration Test
The formation of a yellow oily layer confirms the presence of a benzene ring.
Basic Oxidation
This test uses KMnO4 in NaOH solution and is often referred to as mild oxidation.
Basic Oxidation
It can be used to detect the presence of alkene and benzylic carbon (must have benzylic hydrogen) that are both susceptible to oxidation.
Basic Oxidation
A brown precipitation or suspension confirm the presence of the target organic compounds.
Organic halides
or haloalkanes (RX) are organic compounds that contains a halogen moiety (-X = F, Cl, Br, and I).
RX
is soluble in organic solvent but are insoluble in water despite being polar.
RX
can exhibit dipole-dipole interactions because of the C-X bond where the polarity is shifted -X causing it to be polar.
RX
reacts via substitution and elimination reactions.
decreases
The bond strength of C-X _ as the size of the halogen increases. Iodine is a better leaving group during reactions compared to fluorine.
Beilstein Test
This is a flame test that detects the presence of halogens from samples.
Beilstein Test
It uses CuO that reacts with the halogen forming copper-halide compounds which is visible via the formation of blue-green flame.
SN1
unimolecular; reaction is dependent only on the RX
Tertiary RX with “stable” carbocation formed from their alpha carbons uses this mechanism.
SN2
bimolecular; reaction is dependent on the RX and the Nü. • This mechanism is common for primary and secondary RX.
SN1
Reaction with Alcoholic AgNO3. • The Ag in AgNO3 acts as a Lewis acid and promotes the formation of the carbocation. AgX is formed as a by-product together with the R+ .
SN2
Reaction with NaI in Acetone • The I- in NaI in acetone displaces the X in not sterically hindered RX (primary or secondary RX) resulting in R-I (alkyl iodide) and a NaX (Br or Cl) salt. • NaI is soluble in acetone but NaBr/NaCl are not and will form a precipitate indicating the occurrence of an SN2 reaction.
Amines
are nitrogen-containing organic compounds which can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of alkyl (R-) groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
RNH2
are basic and have a characteristic fishy odor and can exist as liquids (low carbon) or solids (higher carbon) depending on the number of carbons.
hydrogen bonding
The presence of H atoms results into _ which cause higher boiling for primary amines (BP primary > secondary > tertiary).
Amines
_ are soluble in water due to its ability to undergo H-bonding. However, as the size of the alkyl group increases, water solubility decreases.
Aromatic
_ amines (ex. Aniline) readily undergoes atmospheric oxidation can gets colored as a result
Hinsberg Test
This uses benzene sulfonyl chloride to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines
soluble
Primary amines forms alkali _ sulfonamide product.
insoluble
Secondary amines forms alkali _ sulfonamide product.
do not
Tertiary amines _ react.
blue-green
A _colored flame indicates the presence of Br, Cl, & I
Solubility with HCl and NaOH
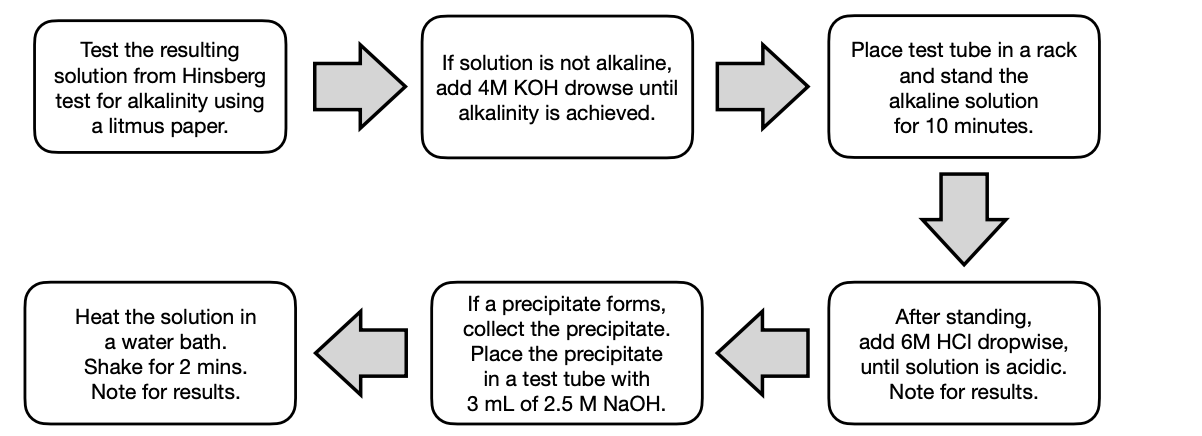
Hinsberg Test
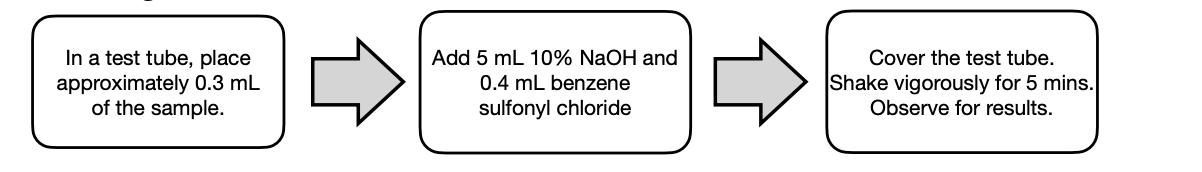
Reaction with NaI in Acetone

Reaction with Ethanolic AgNO3
Beilstein Test or Copper Halide Test

Basic Oxidation Test
Nitration Test
Baeyer’s test
Ignition Test

Solubility in H2SO4

Ignition Test
It can be used to classify aliphatic from aromatic hydrocarbons.
Aliphatic
HC burns with yellow flame that are less sooty
Aromatic
HC burns with yellow flame that are more soot
active unsaturation
A (+) decolorized result and (+) brown suspension/sludge in Baeyer’s test, confirms the presence of _ in cyclohexene.
Baeyer’s Test
KMnO4 with alkenes produces a vicinal diol or glycol. This is mild oxidation reaction.
Baeyer’s Test
KMnO4 does not affect alkanes (unreactive) and aromatic compounds (too stable, inactive unsaturation).
Bromine Test
will start as orange-brownish solution and will decolorize if the test is positive for the presence of alkenes or alkynes. • Br2 can undergo AE reaction mechanism to add itself to the double or triple bond. • Br2 can mix with aromatic compound in the presence of the appropriate catalysts, but will not react with alkanes upon mixing.
Nitration Test
The reaction occurs via SE mechanism which is specific for aromatic compounds. The nitrating mixture composed of H2SO4 and HNO3 creates the electrophile -NO2+ .
Basic Oxidation
Alkenes are able to undergo mild oxidation with KMnO4 resulting to a decolorized solution (similar to Baeyer’s test).
Alkyl side-chain on a benzene ring (benzylic position) is fairly resistant to oxidation but in an alkaline solution with KMnO4, the benyzlic hydrogen is easily oxidized into a -COOH moiety.
Chlorobenzene
_ did not react to either SN1 or SN2 because it is an aromatic halides.
SN1
Alkyl halide (RX) - faster reaction is observed with more stable carbocation. • Solvent - any polar solvent that increases the stability of the carbocation will also speed up the reaction rate. • Leaving group - best leaving groups are those that can stabilize the anion (eg., weakest bases).
SN2
Steric congestion - the more steric present, the slower the reaction. • Solvent - exposing the Nü to a more polar solvate = more reactive iodide. • Nucleophile - atoms from same family in periodic table, the larger members of the family are better Nü. • Leaving group - best leaving groups are those that can stabilize the anion (eg., weakest bases).
Hinsberg test
will differentiate primary, secondary, and tertiary amines based on the products they form.
HCl
In _ solutions, amine are soluble due to the ability to form H-bonding with the -Cl moiety. Amines + _ is a form of a neutralization reaction.
NaOH
In _ solutions, amines are insoluble due to lack of intermolecular attraction (amine only have weak H-bonding and dipole-dipole) to break the ionic bond within NaOH and the presence of hydrophobic moieties.