SKULL BONES & FEATURES
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
FRONTAL
front at neurocranium, articulates with PARIETALS, NASALS, MAXILLAE, SPHENOID, ETHMOID, LACRIMALS, ZYGOMATICS
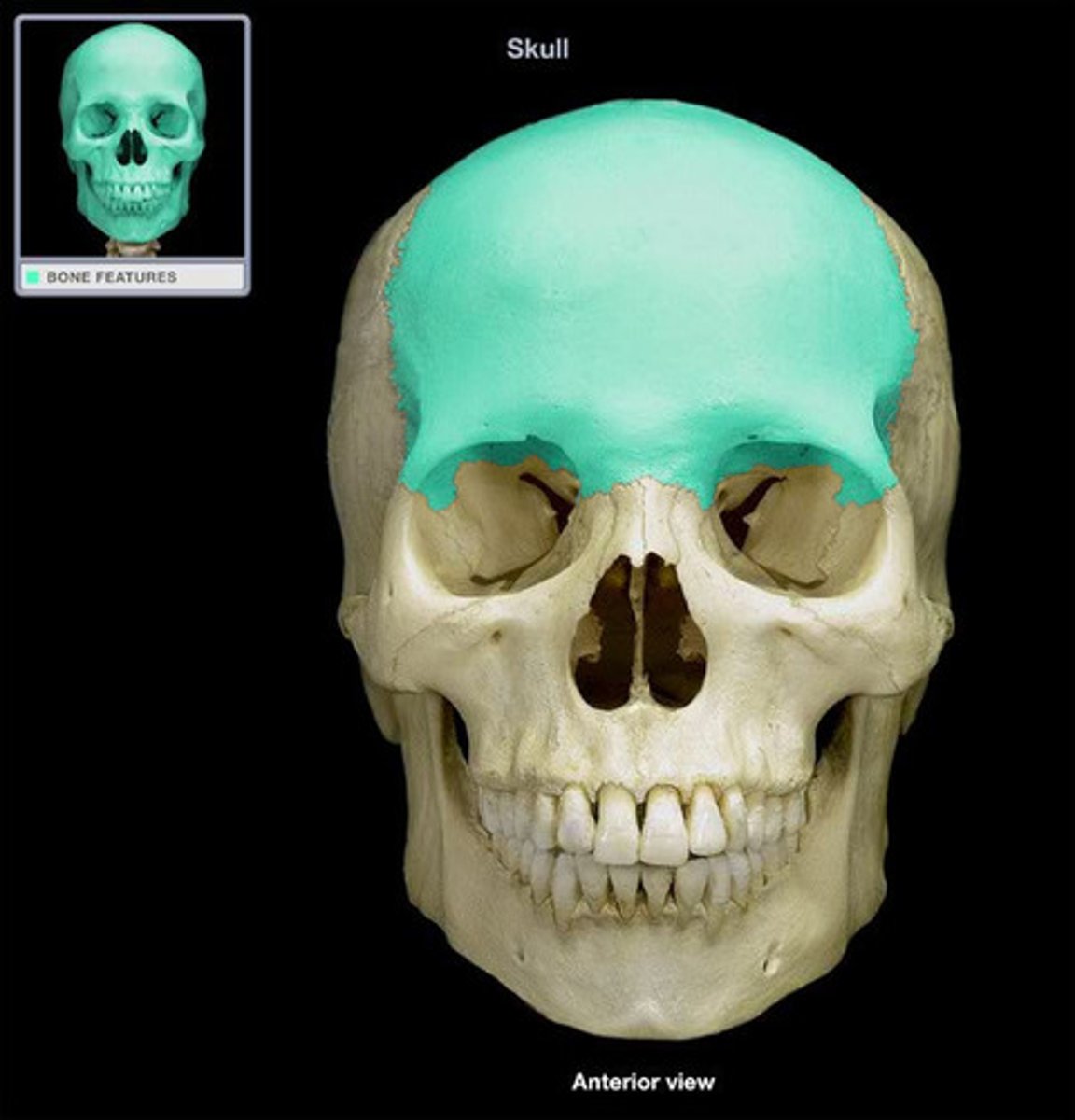
frontal squama (of FRONTAL)
forms the forehead
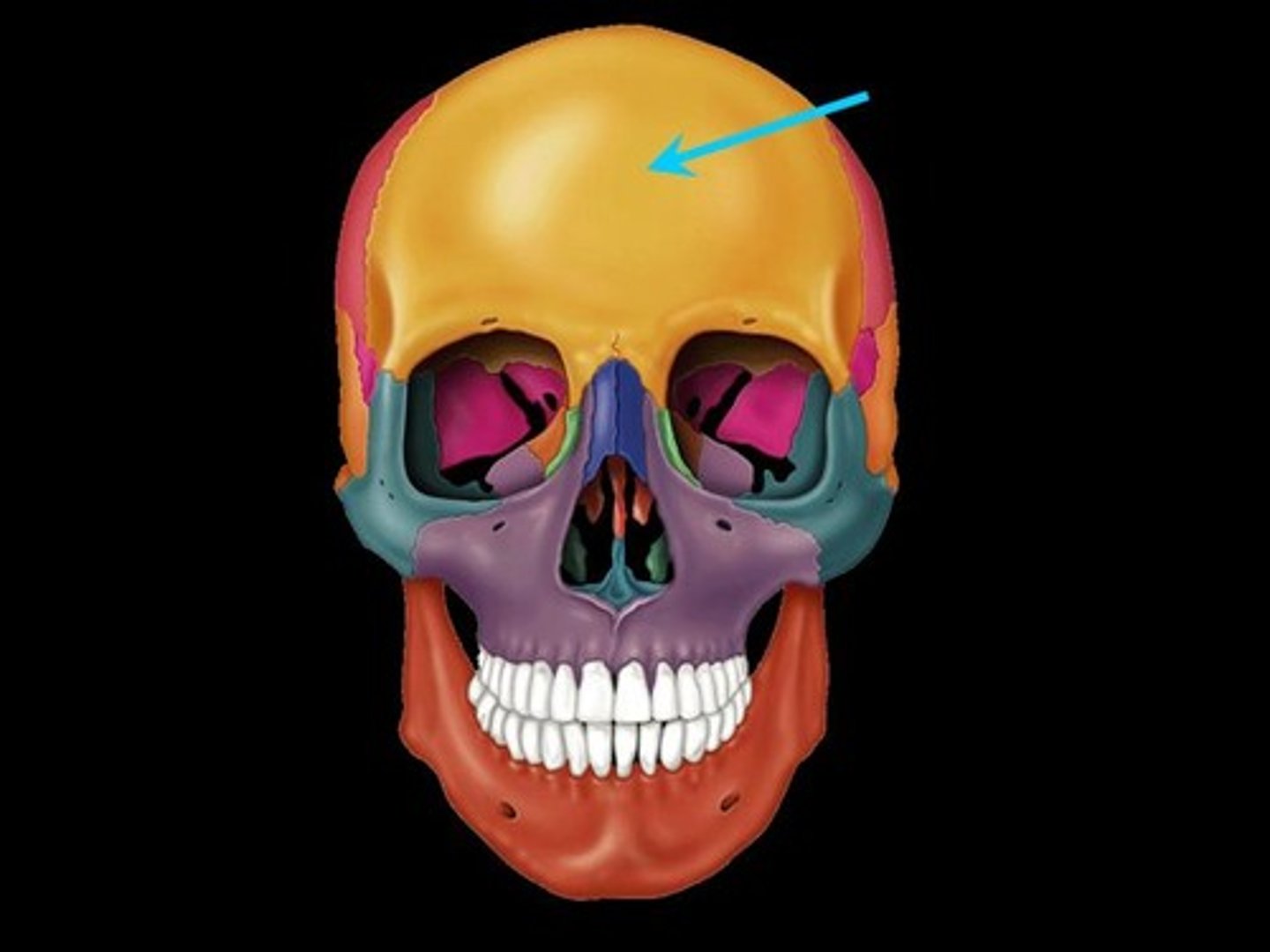
horizontal portion (of FRONTAL)
acts as roof for orbits and as a floor to the frontal lobes of the brain (essentially the same as pars orbitalis/orbital plate)
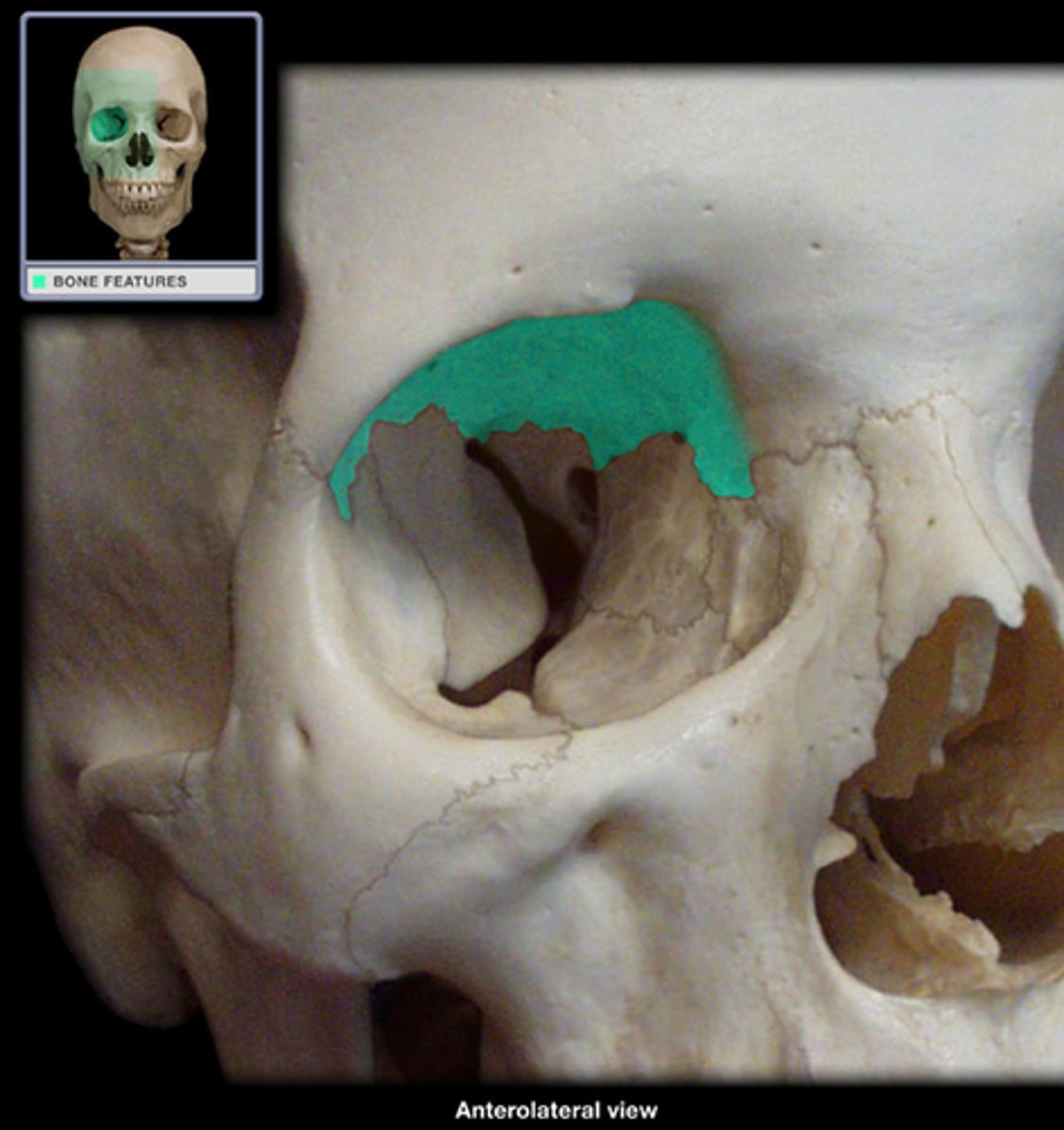
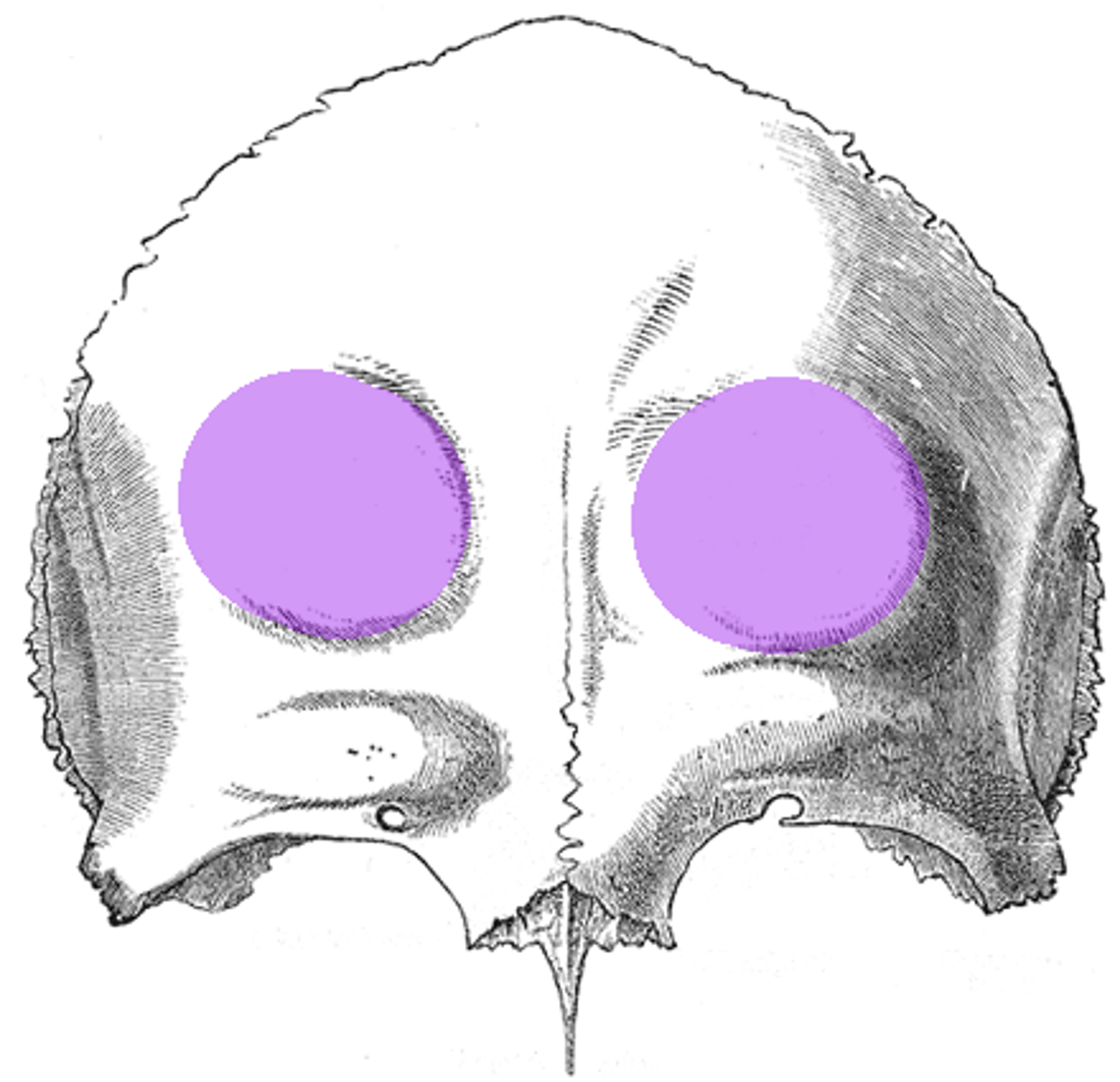
frontal eminences (of FRONTAL)
two rounded elevations on the frontal bone of the skul
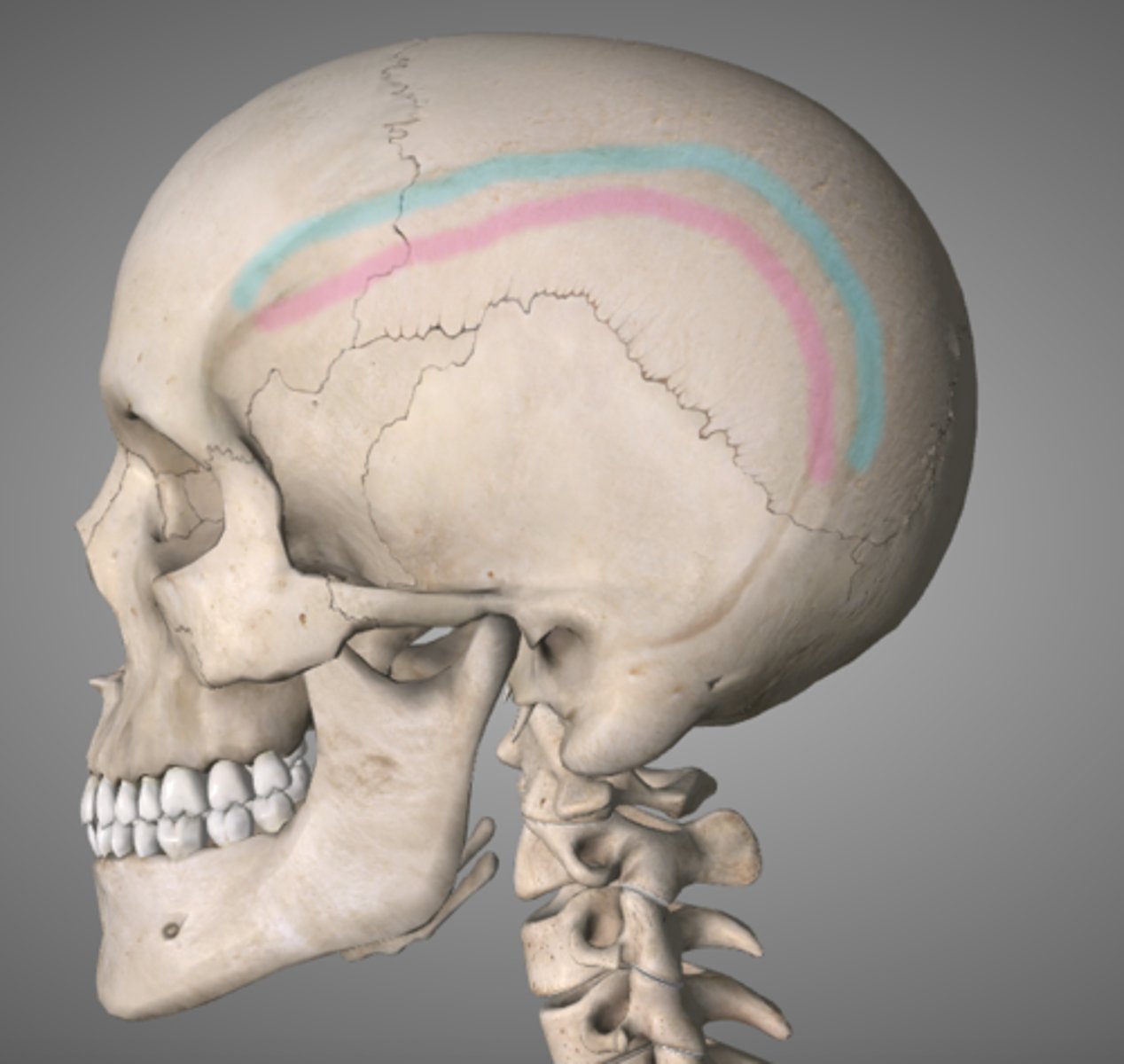
temporal lines (of FRONTAL)
lateral lines that mark the attachment of the temporalis muscles to the frontal bone (large jaw muscle)
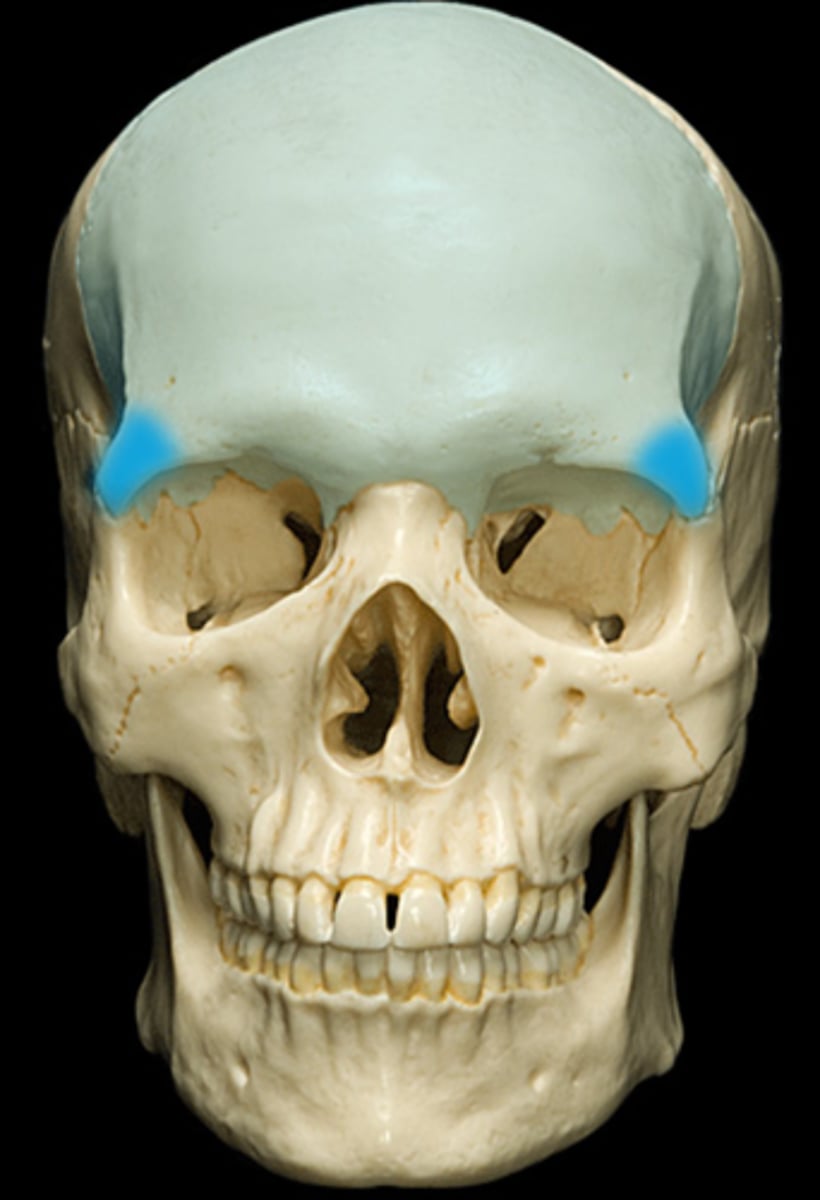
zygomatic processes (of FRONTAL)
form the most lateral and anterior corners of the frontal
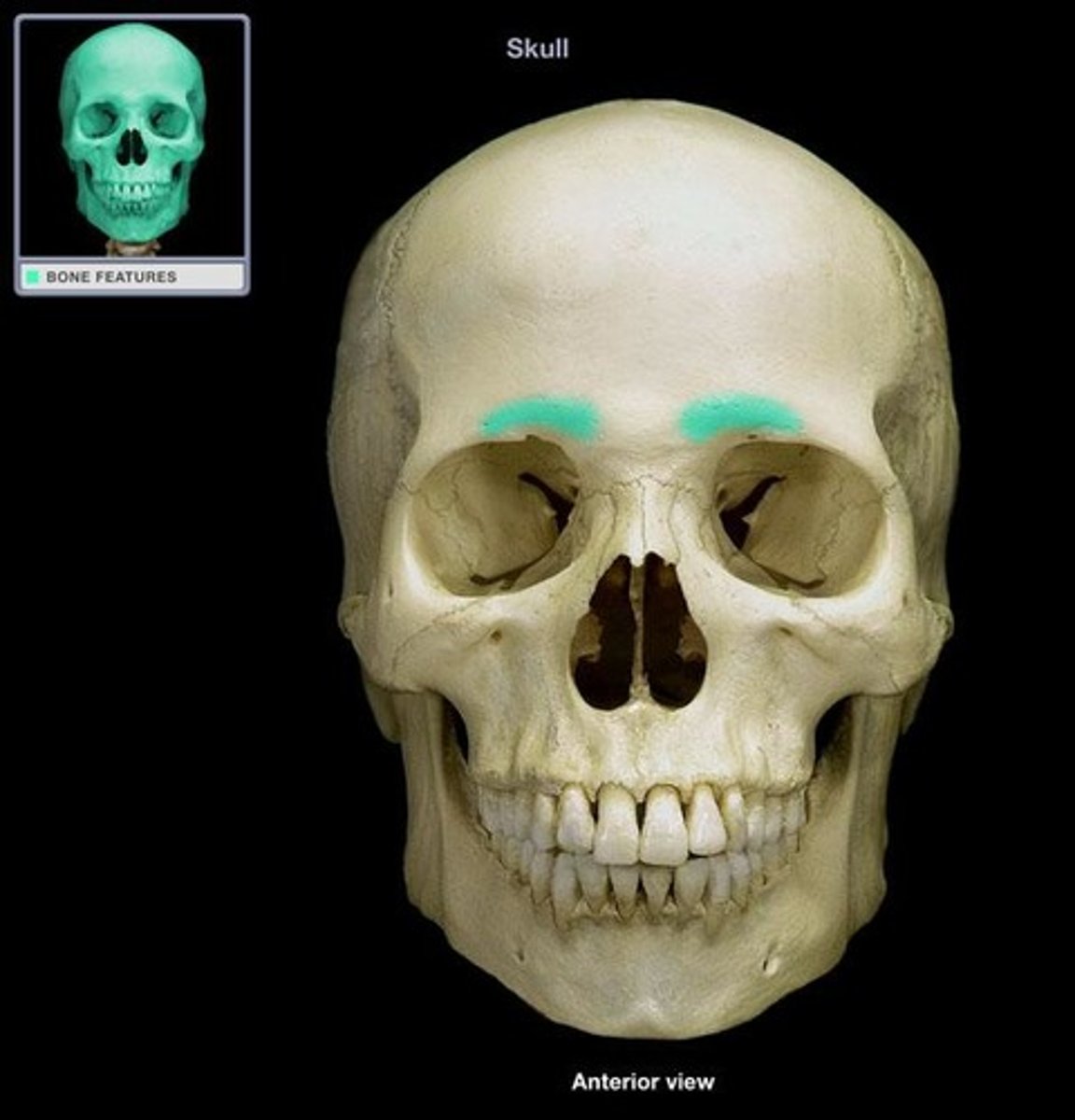
superciliary arches (of FRONTAL)
brow ridges
supraorbital margins (of FRONTAL)
upper orbital edges, notched/pierced by supraorbital foramen
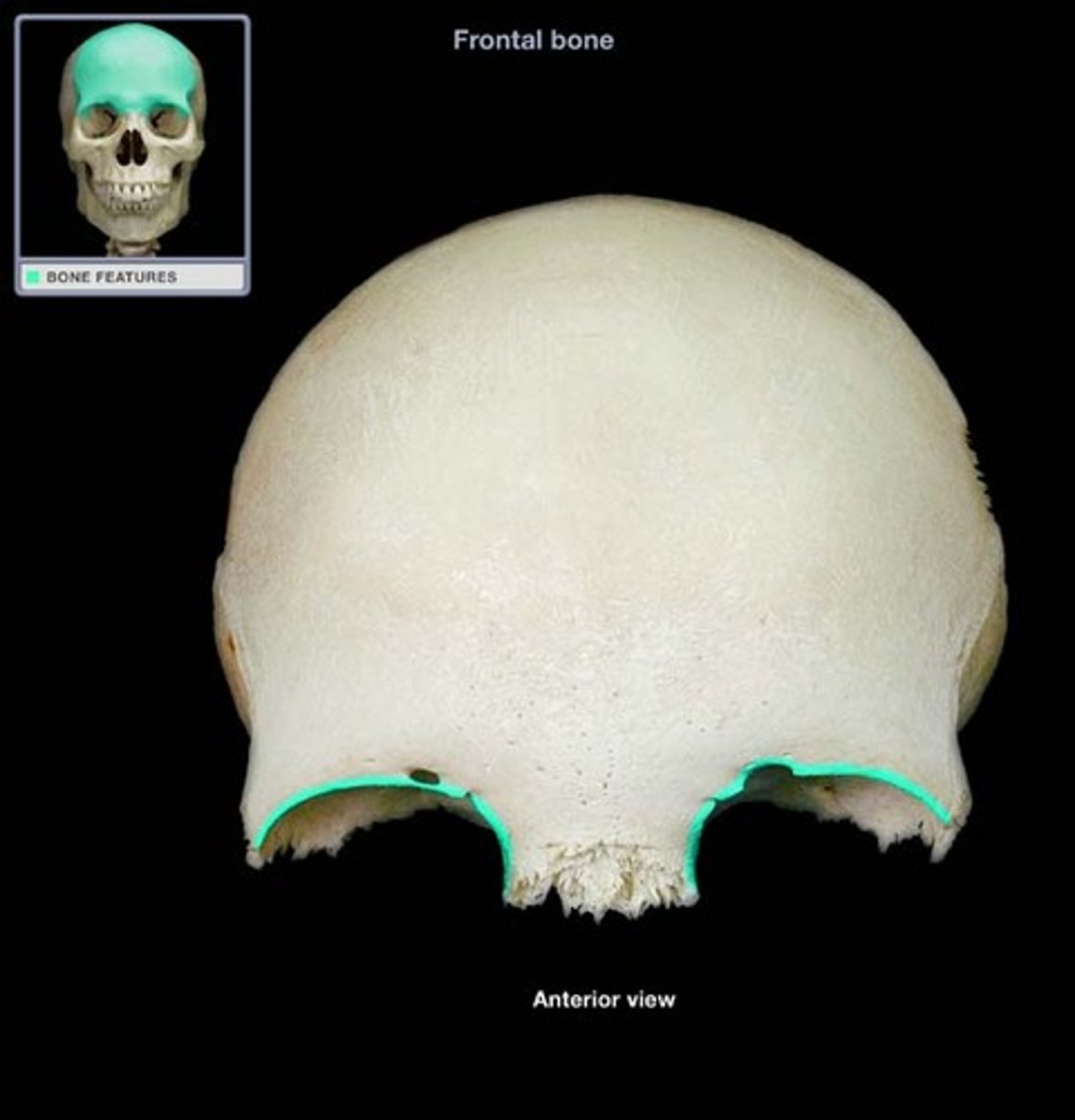
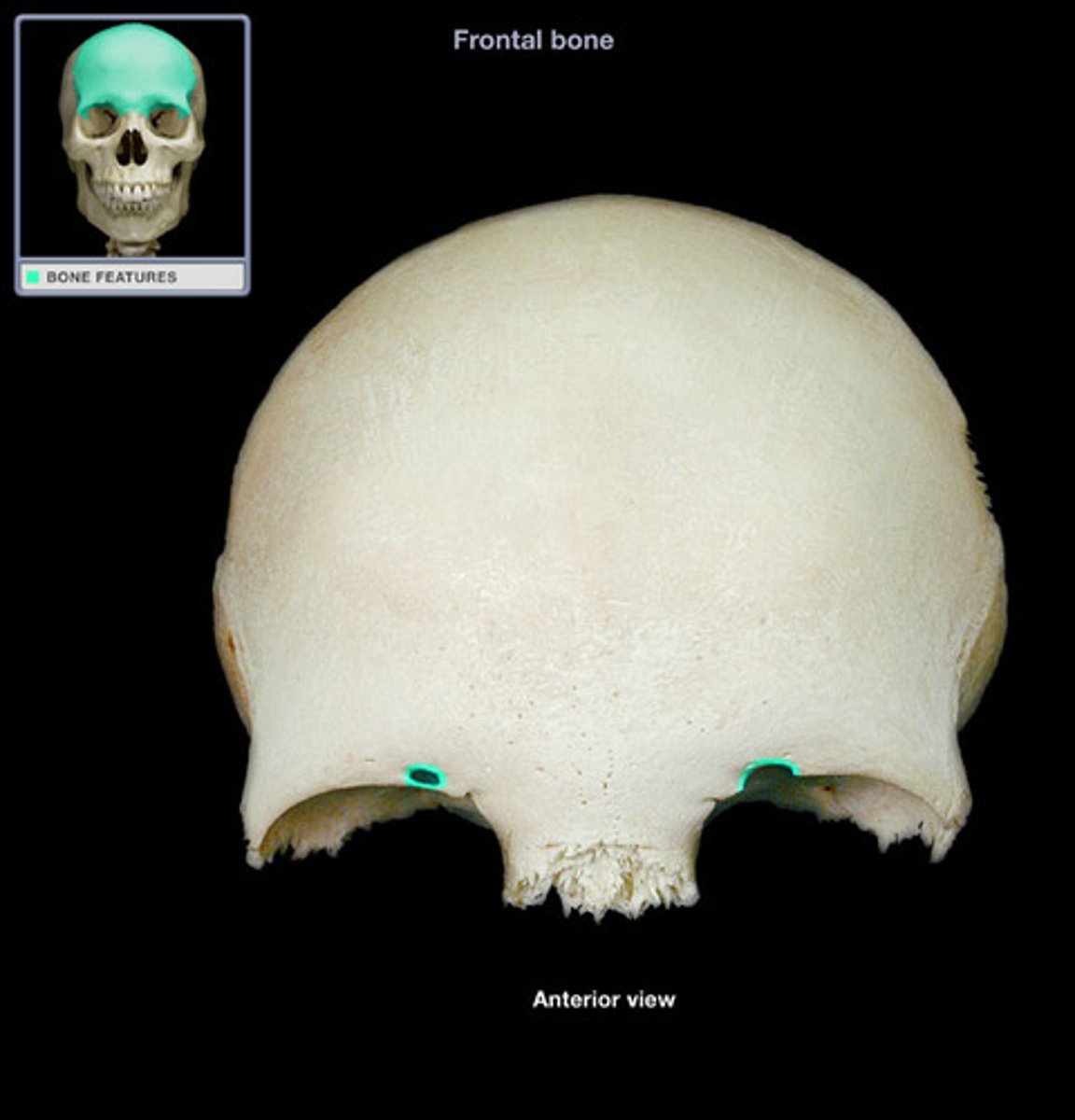
supraorbital notches/foramina (of FRONTAL)
set along medial half of superior orbital rim, transmit supraorbital vessels and nerves
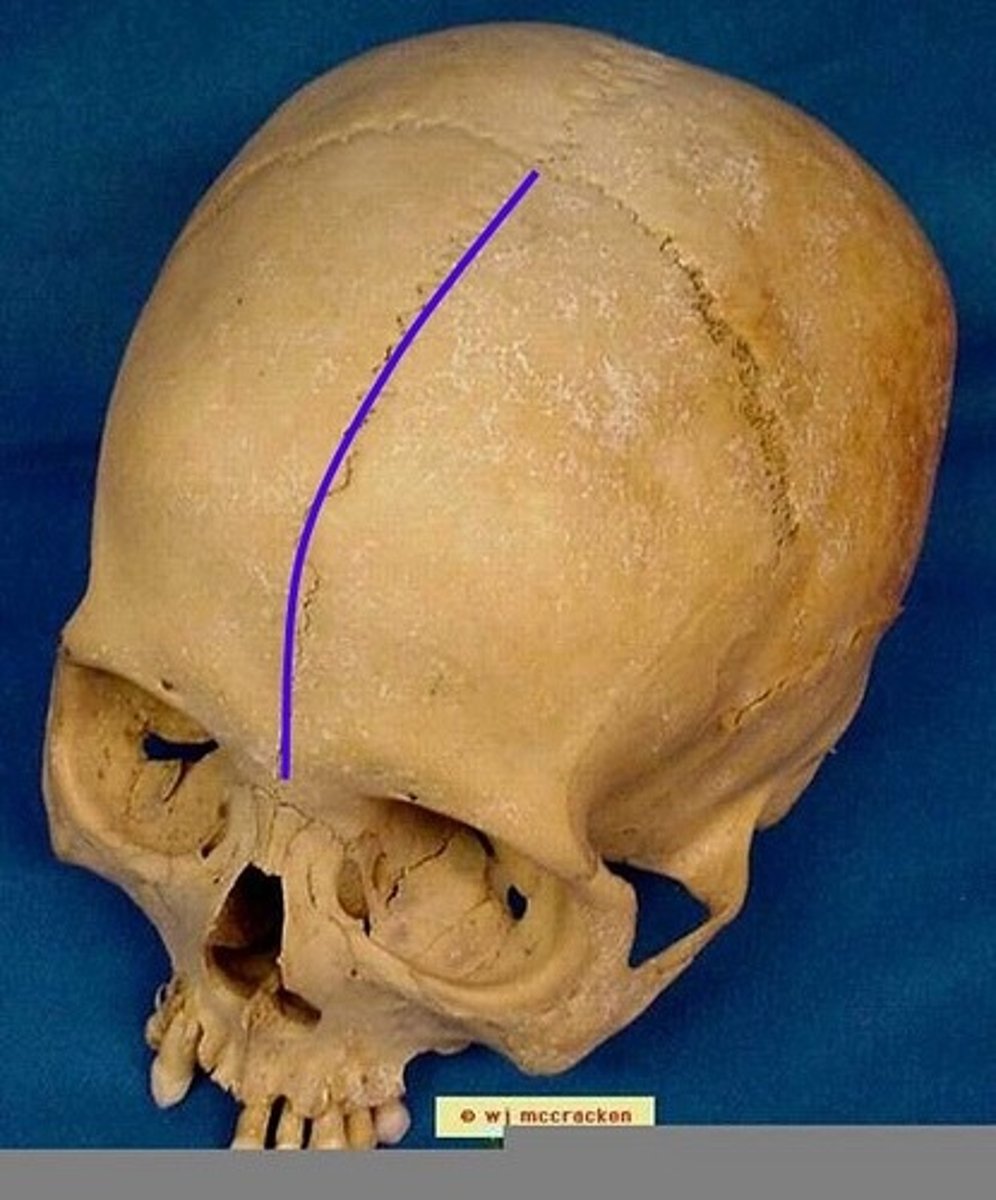
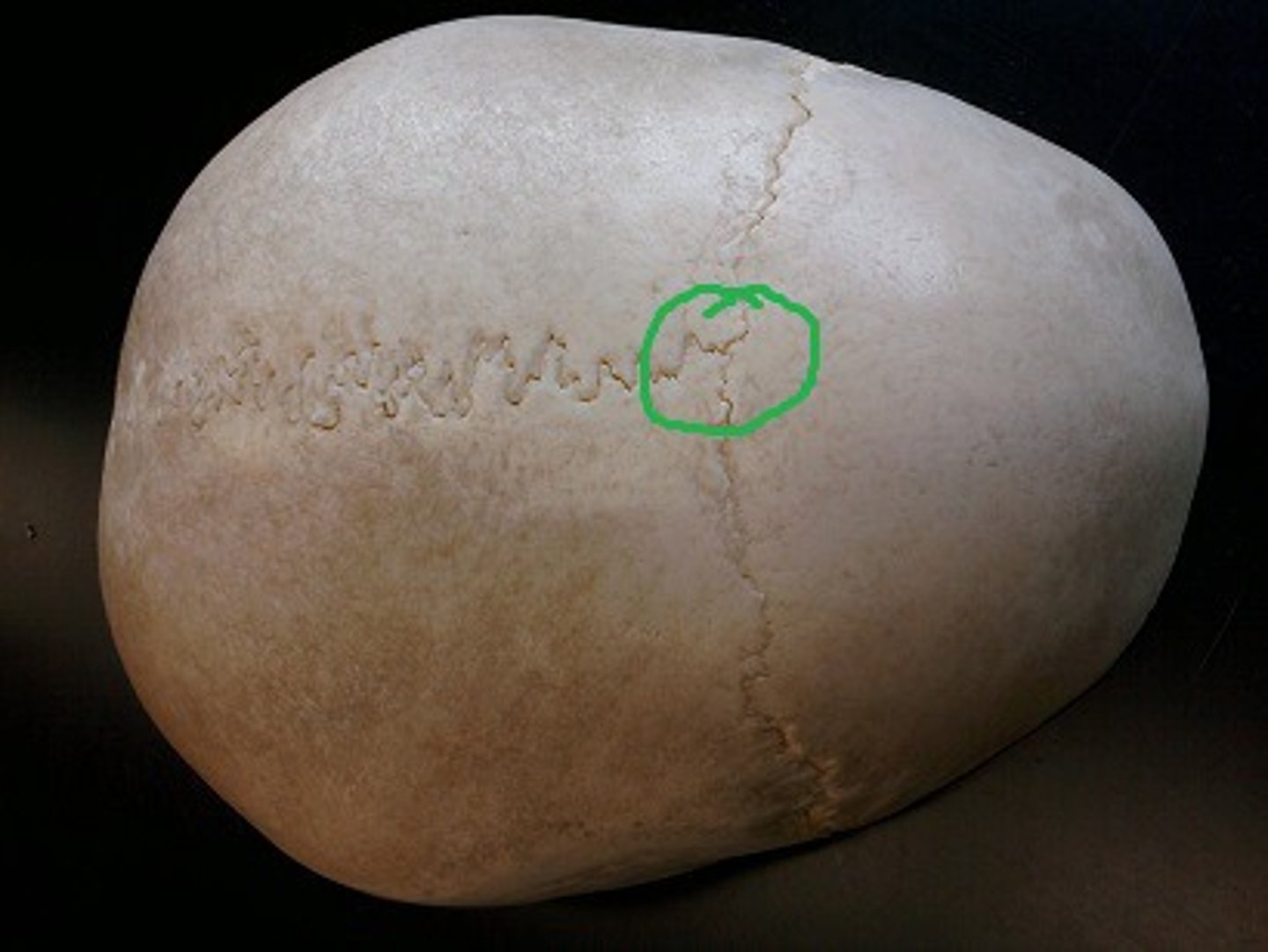
metopic suture (of FRONTAL)
suture located between the right & left frontal, normally fuses together before birth
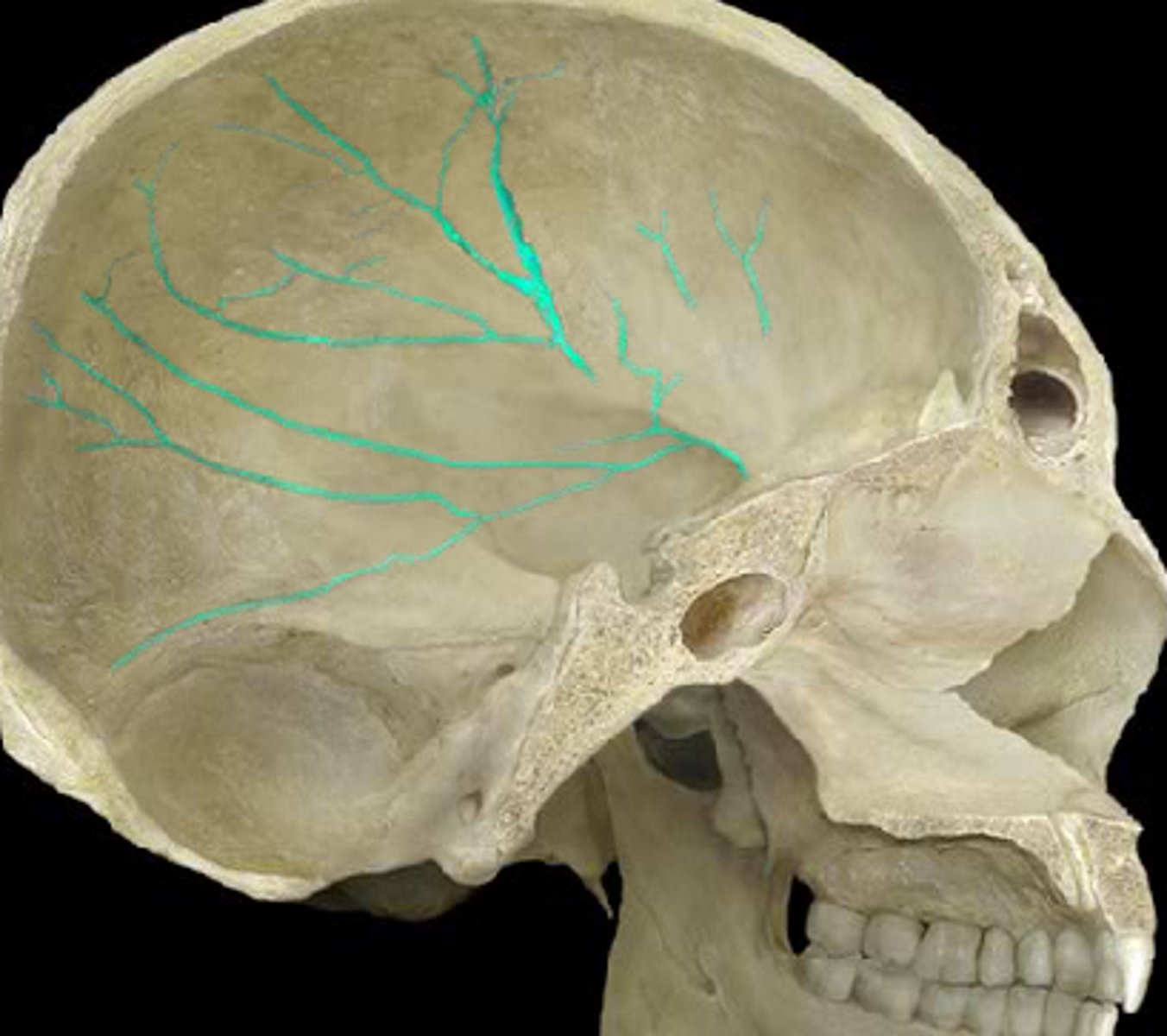
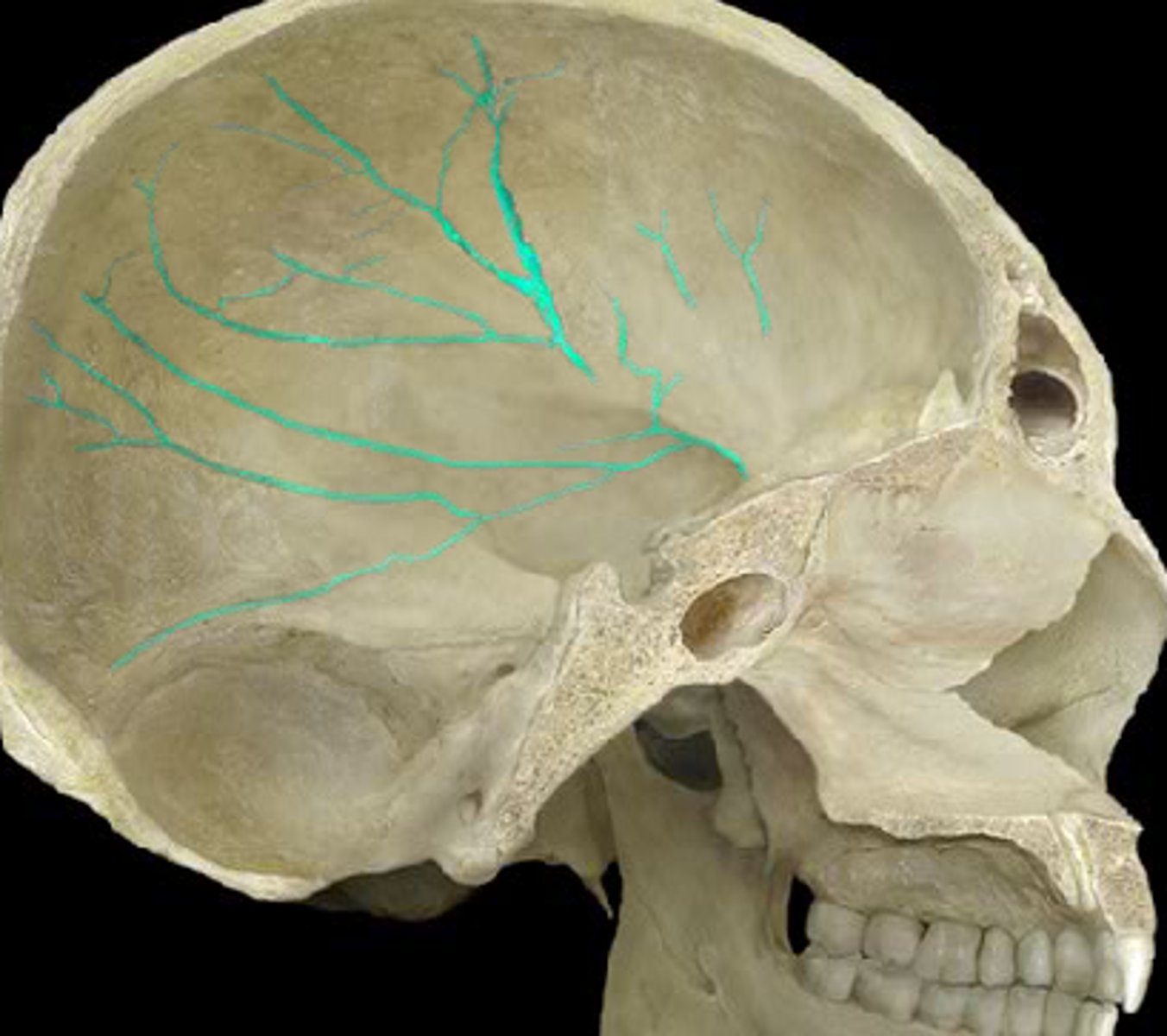
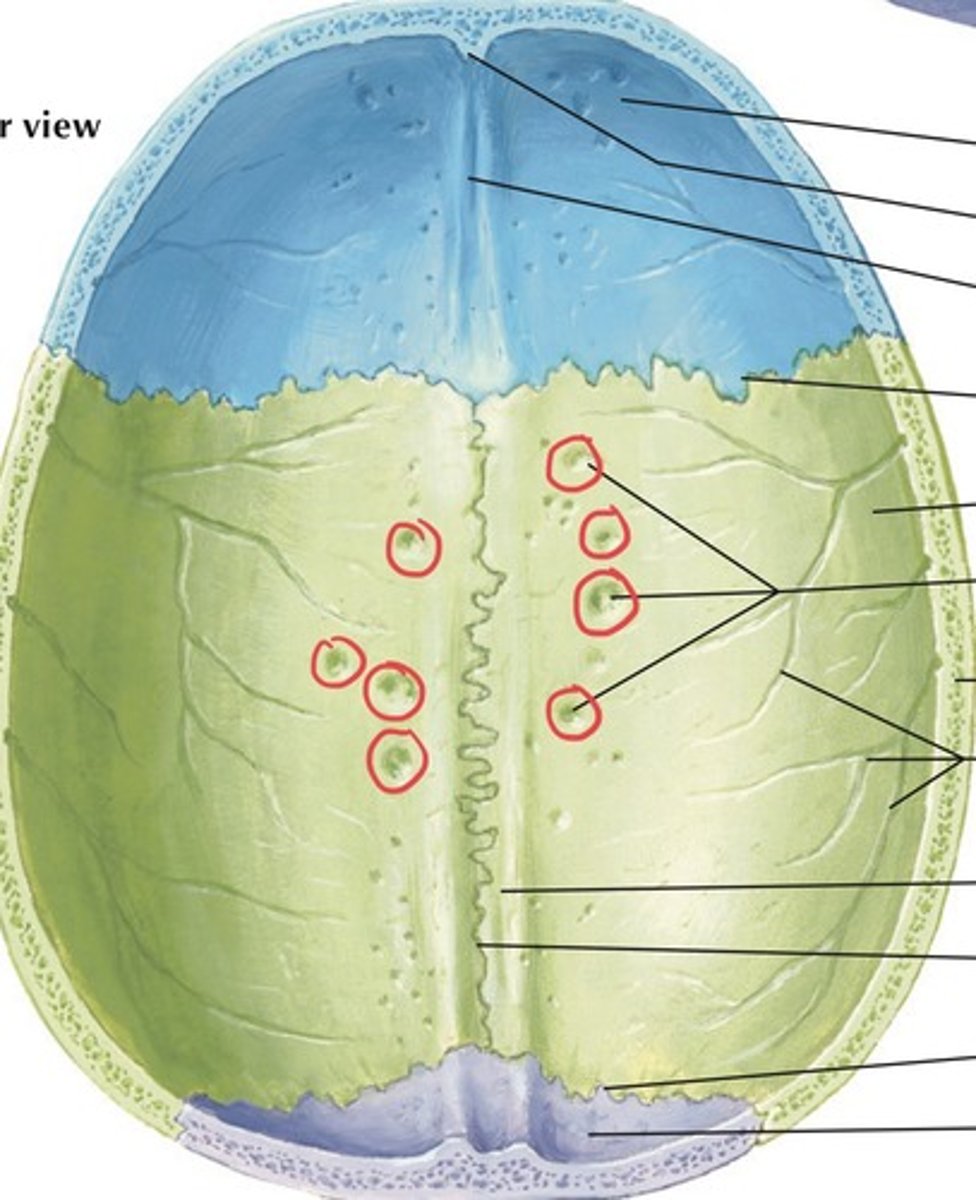
meningeal grooves (of FRONTAL)
indentations on frontal bone from middle meningeal arteries (blood pathways in brain/skull's soft tissues)
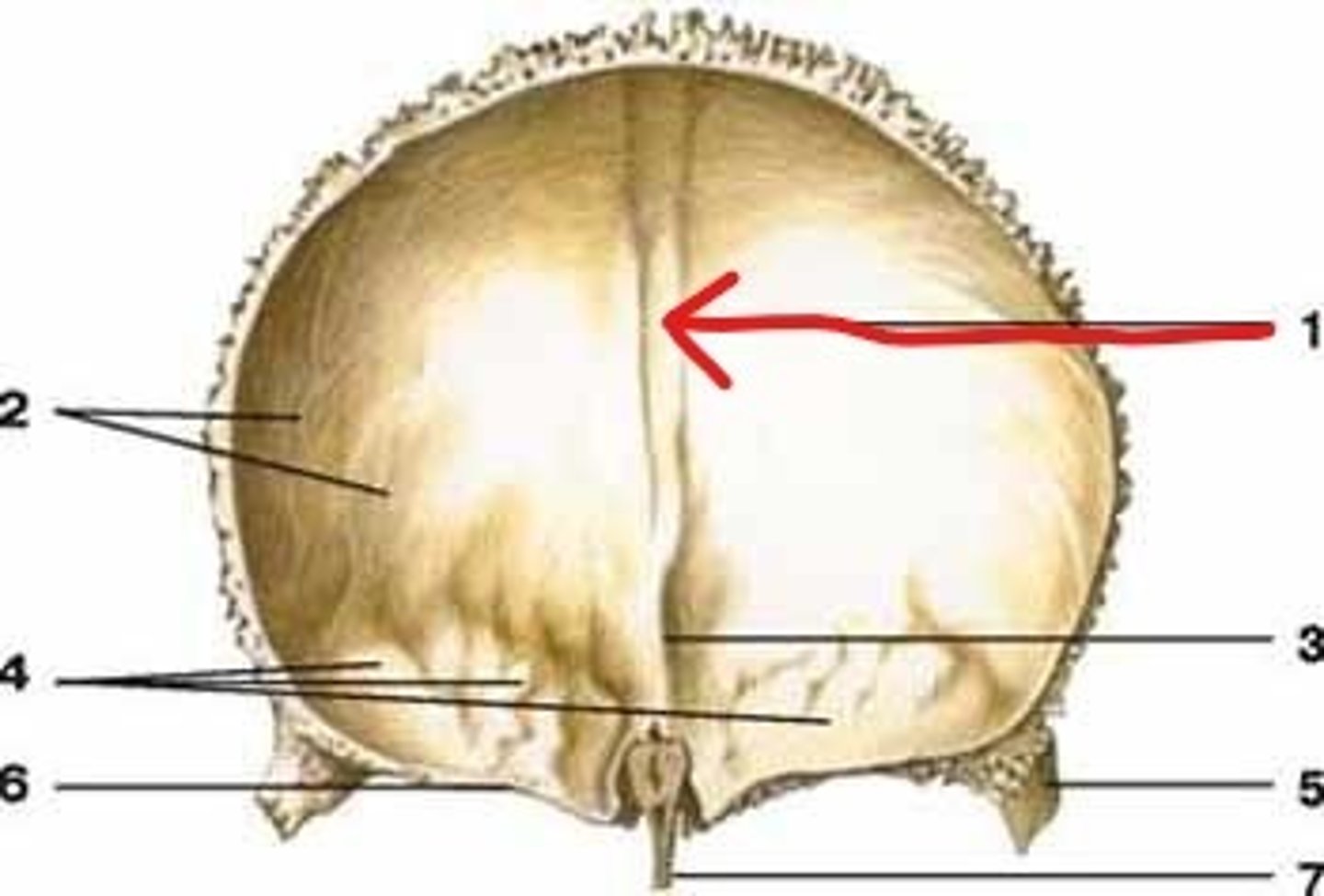
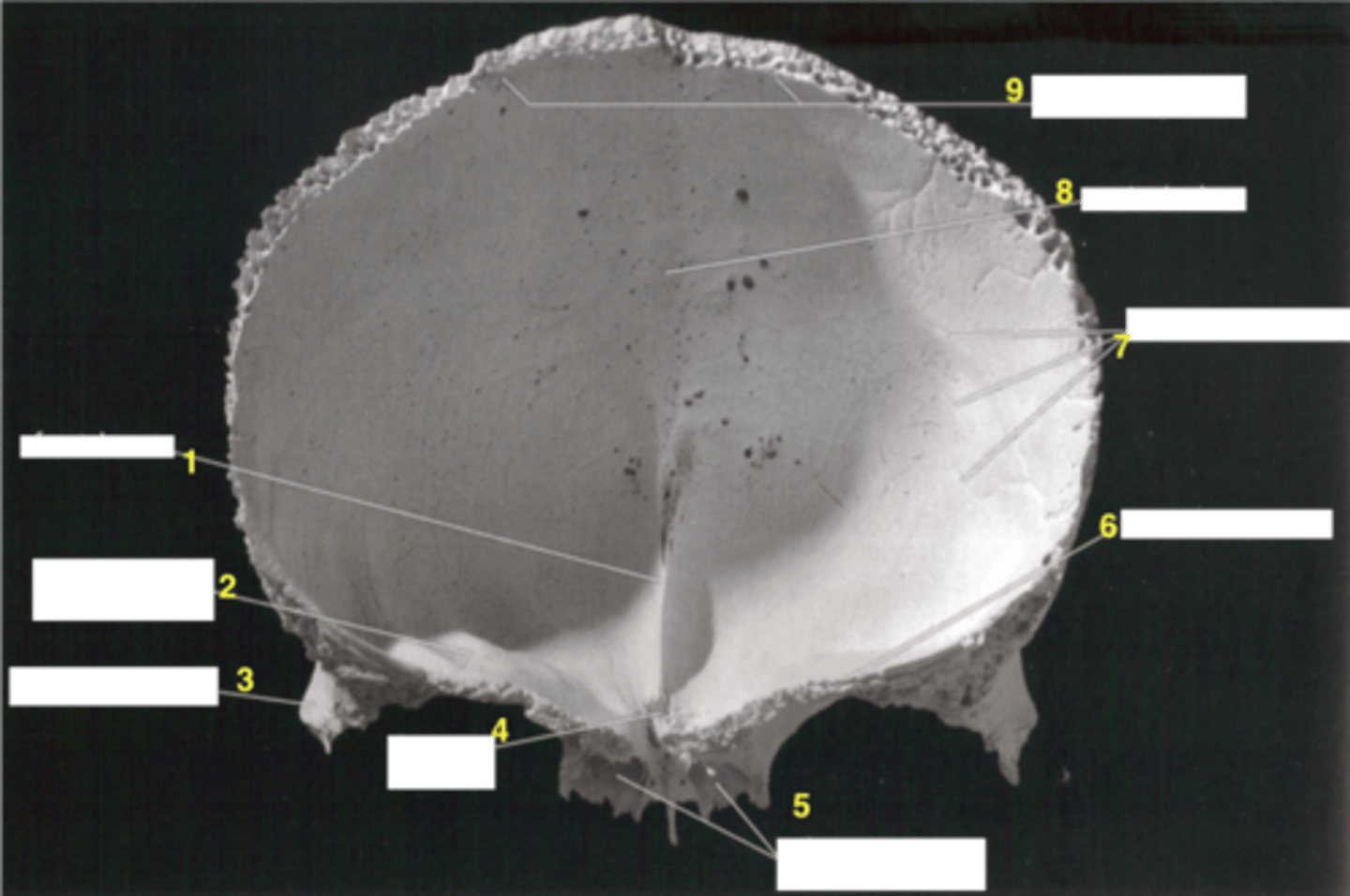
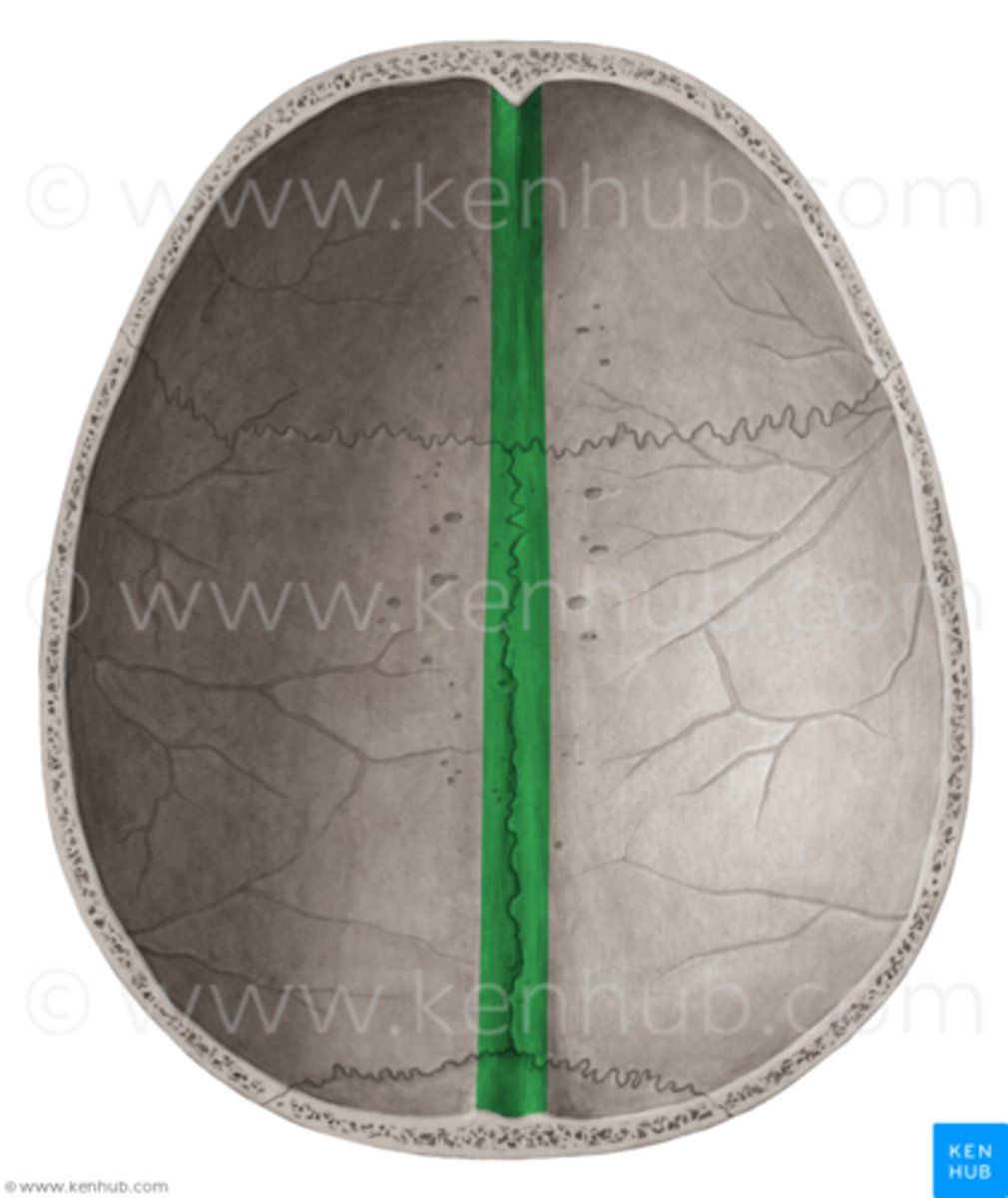
sagittal sulcus (of FRONTAL)
vertical groove that runs down the midline of the endocranial surface, lodges superior sagittal sinus
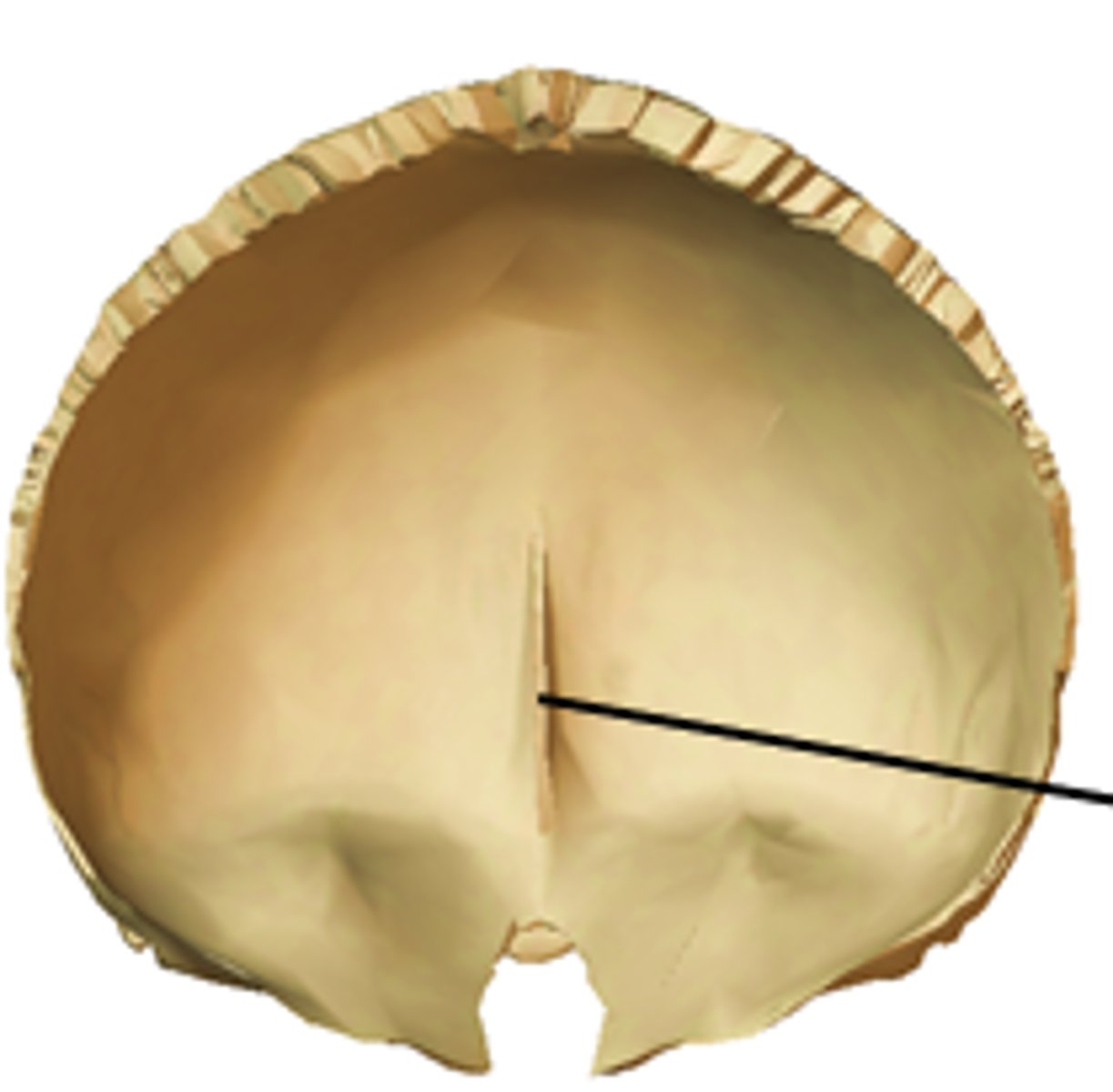
frontal crest (of FRONTAL)
midline crest merging with the anterior end of the sagittal sulcus
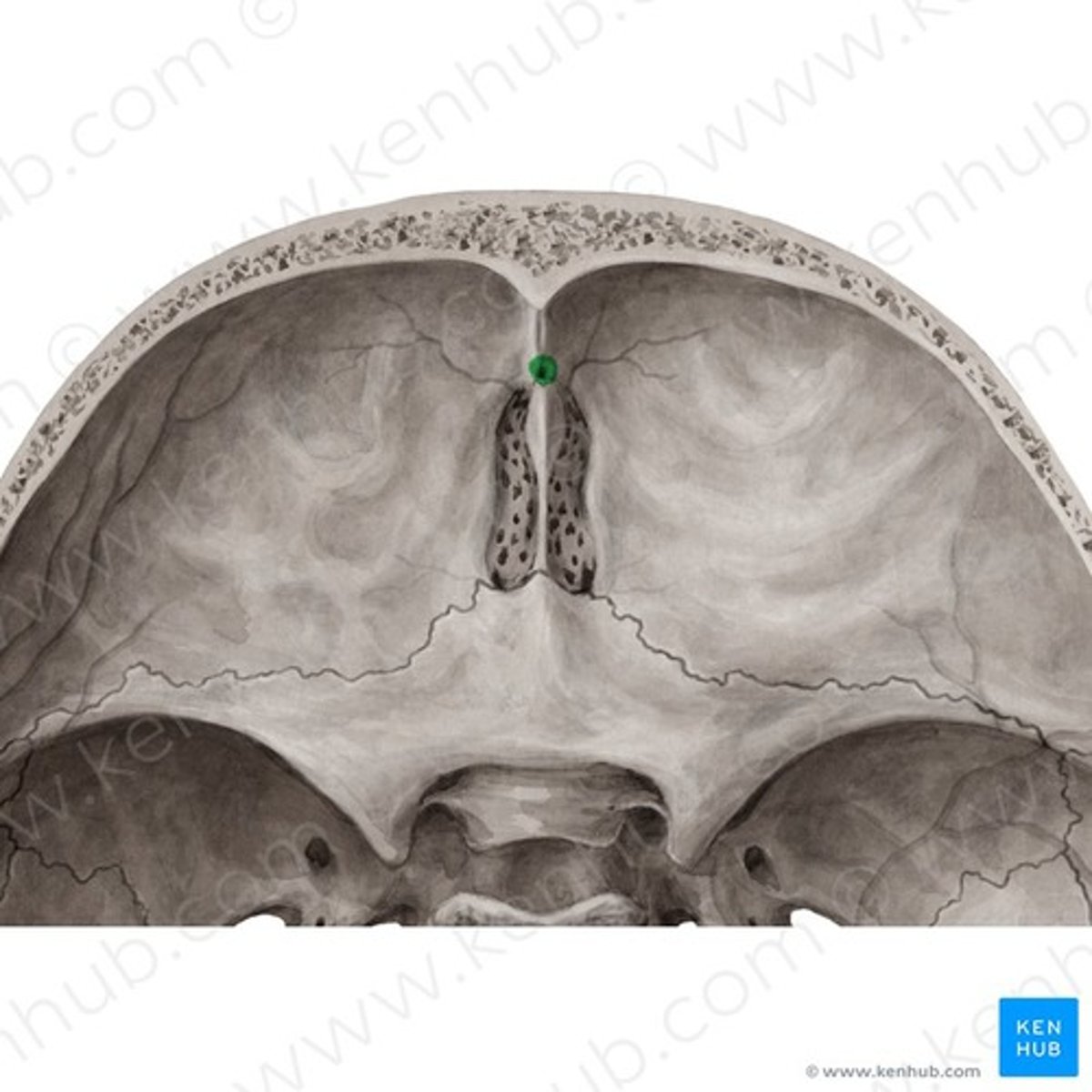
foramen cecum (of FRONTAL)
foramen (of varying size), found at root/base of frontal crest, (above cribriform plate/crista galli of sphenoid)
arachnoid fovea (of FRONTAL)
indentations on frontal bone from arachnoid mater layer of skull/brain's soft tissue
pars orbitalis/orbital plate (of FRONTAL)
horizontal portions of the frontal (essentially the same as horizontal portion)
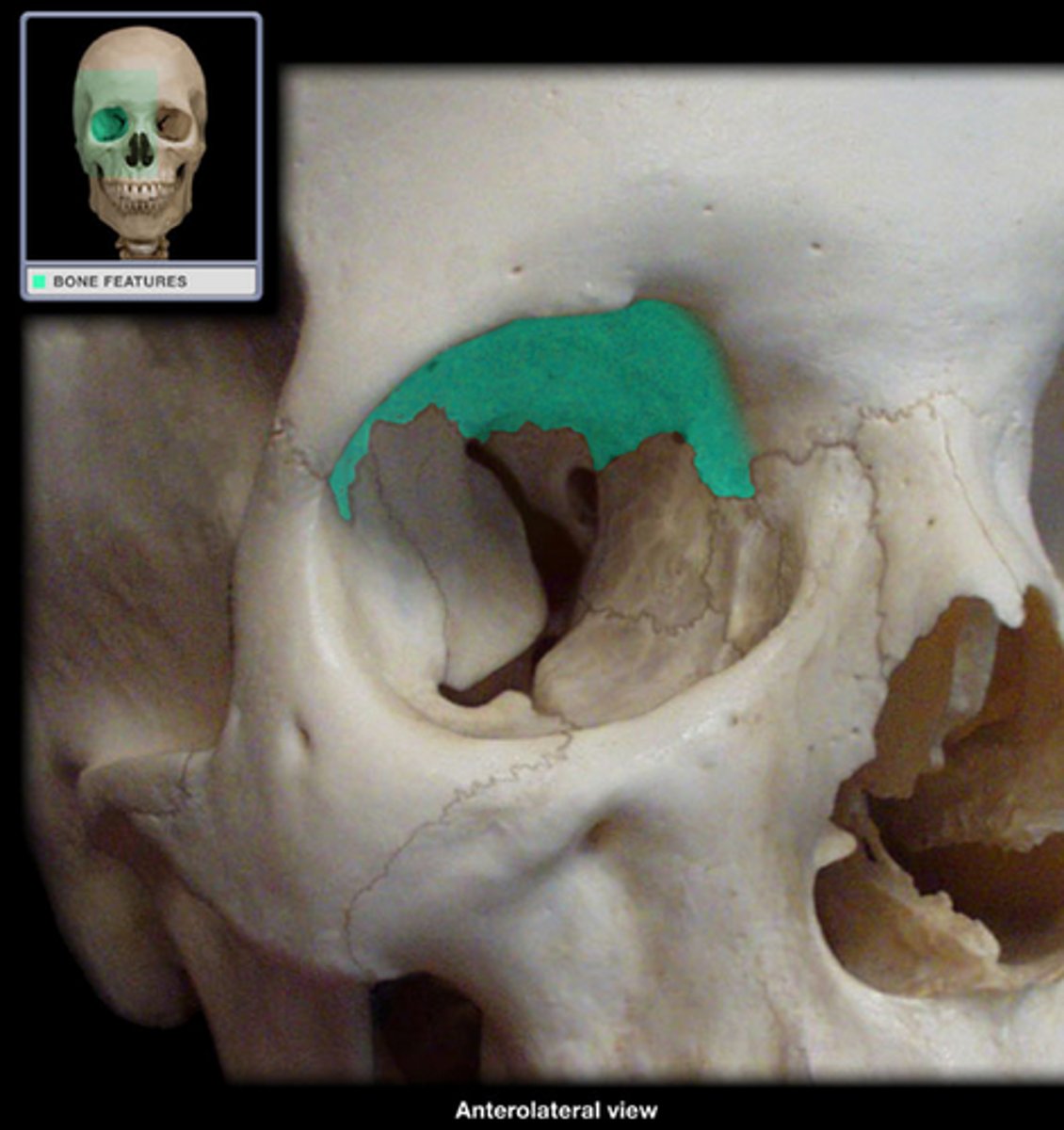
lacrimal fossae (of FRONTAL)
for the lacrimal glands, found at lateral inferior parts of orbital surface of frontal
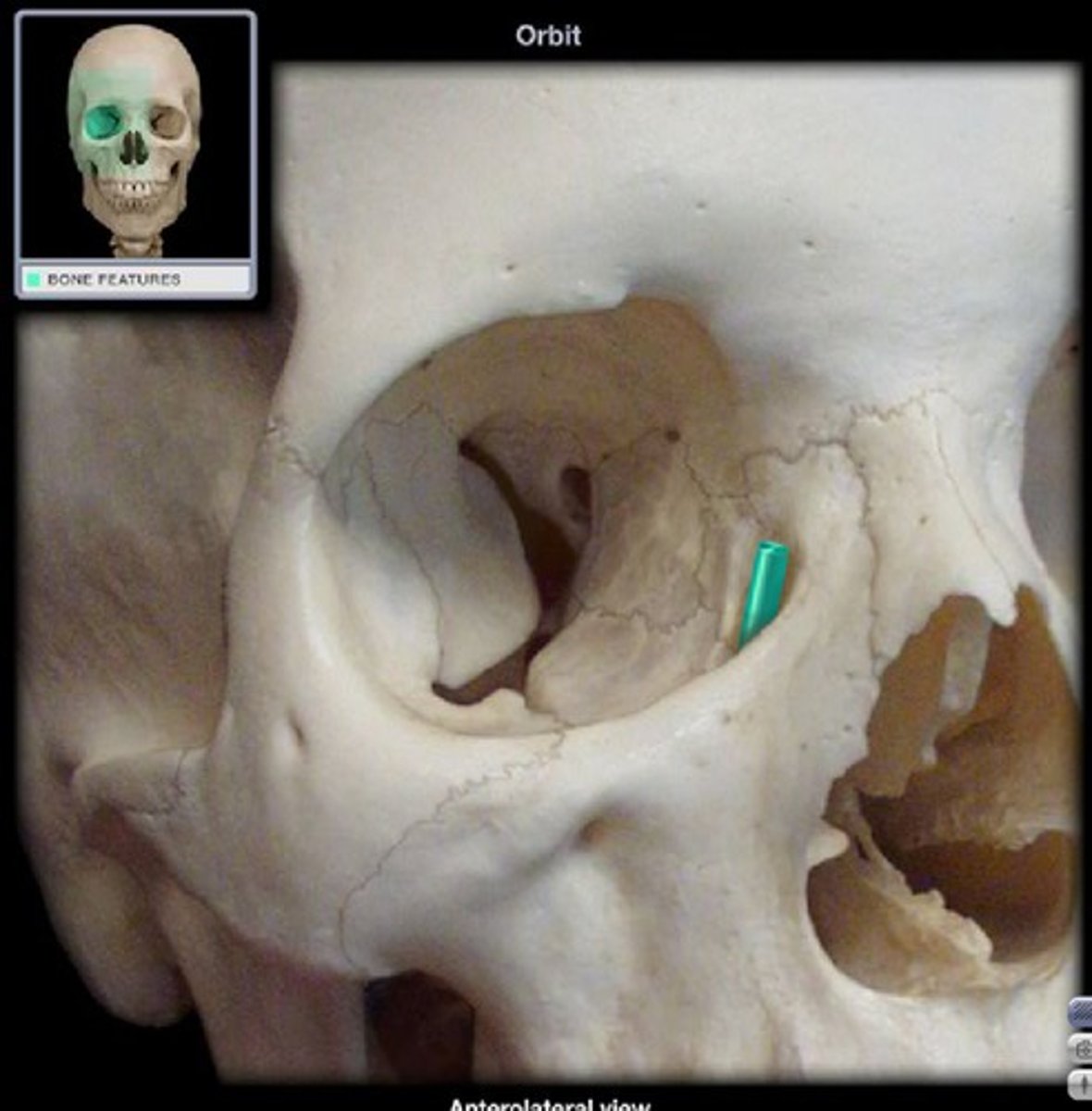
ethmoidal notch (of FRONTAL)
the gap separating the two orbital plates of the frontal
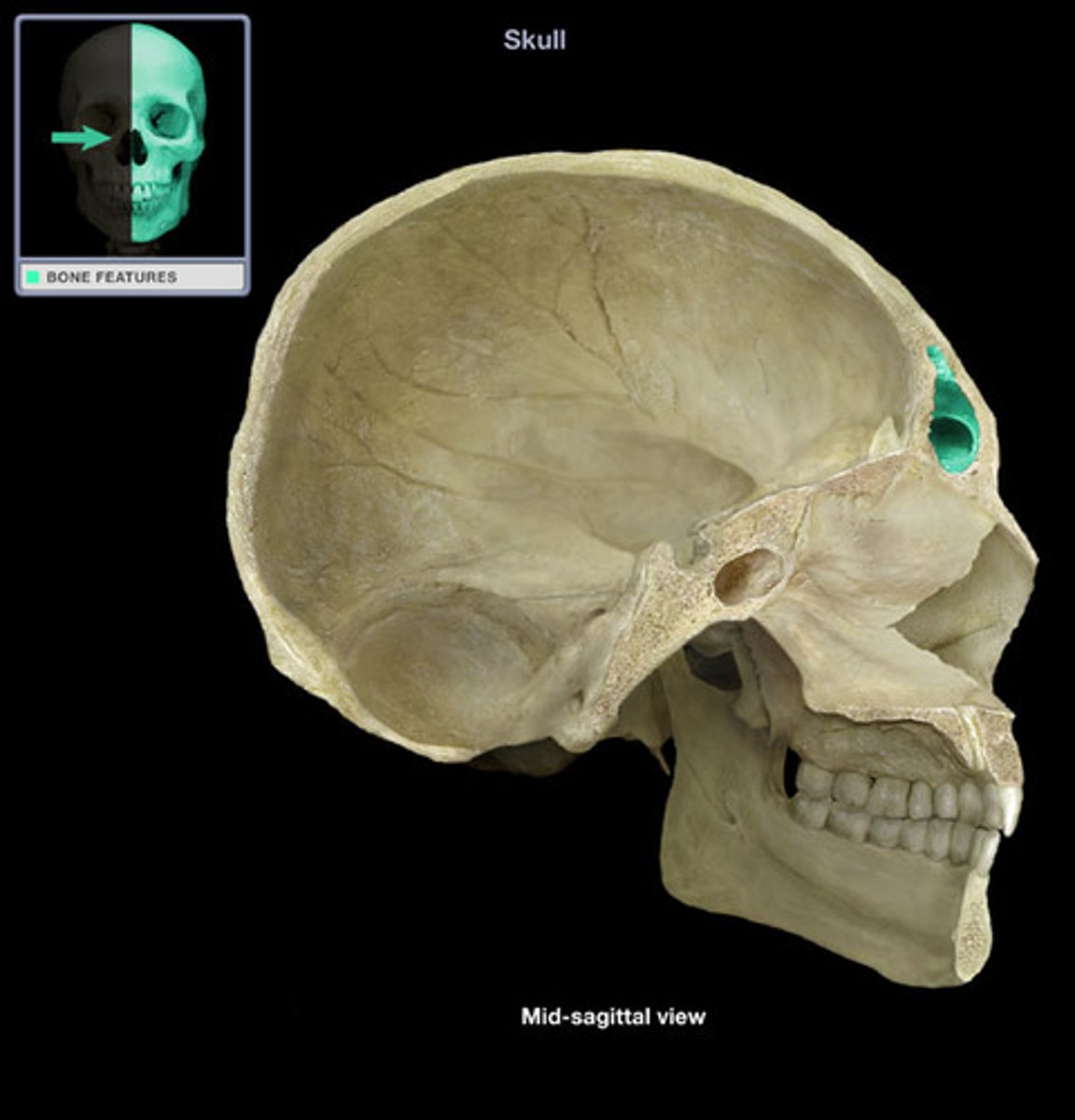
frontal sinuses (of FRONTAL)
negative space for air-filled cavity, located in the frontal bone just above the eyebrows
PARIETALS
form the sides and roof of cranial vault, each articulates with opposite PARIETAL and with FRONTAL, TEMPORAL, OCCIPITAL, SPHENOID
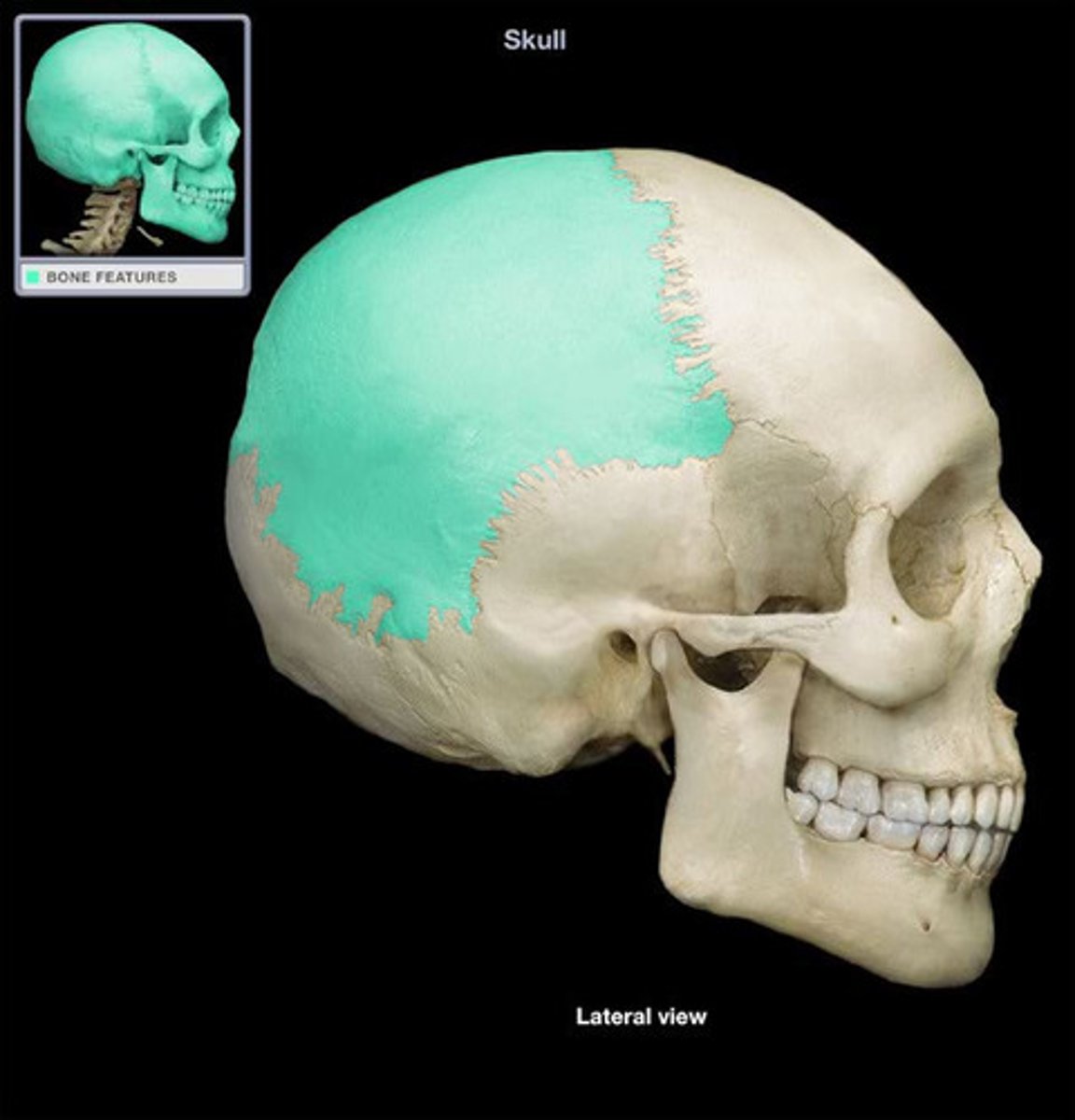
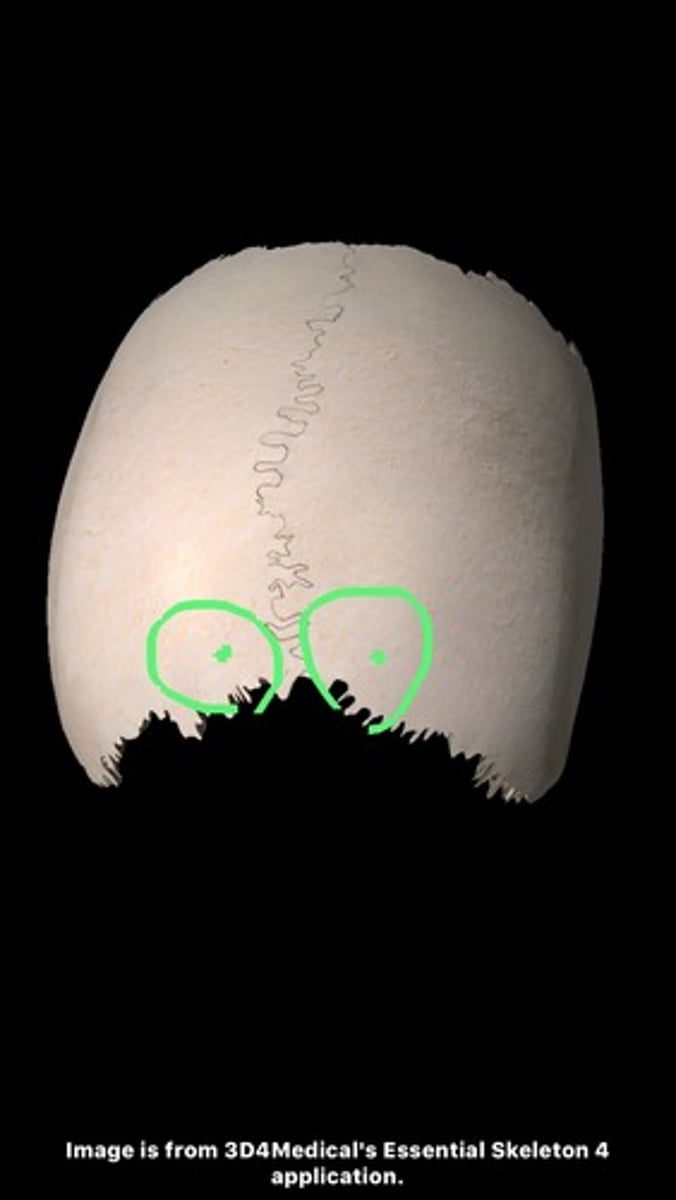
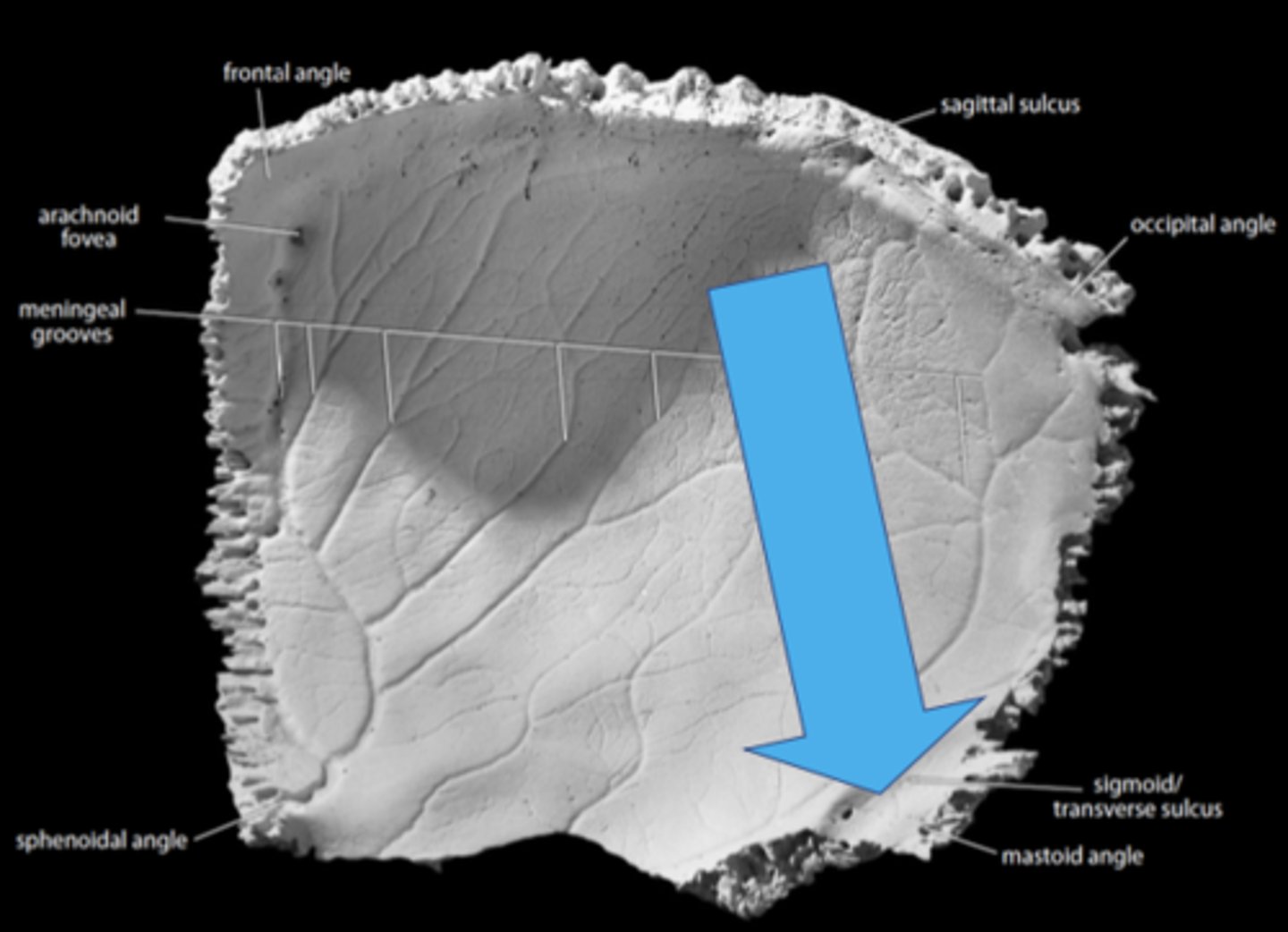
frontal angle (of PARIETALS)
located at bregma

sphenoidal angle (of PARIETALS)
located at pterion (where sphenoid, parietal, temporal, and frontal bones converge)
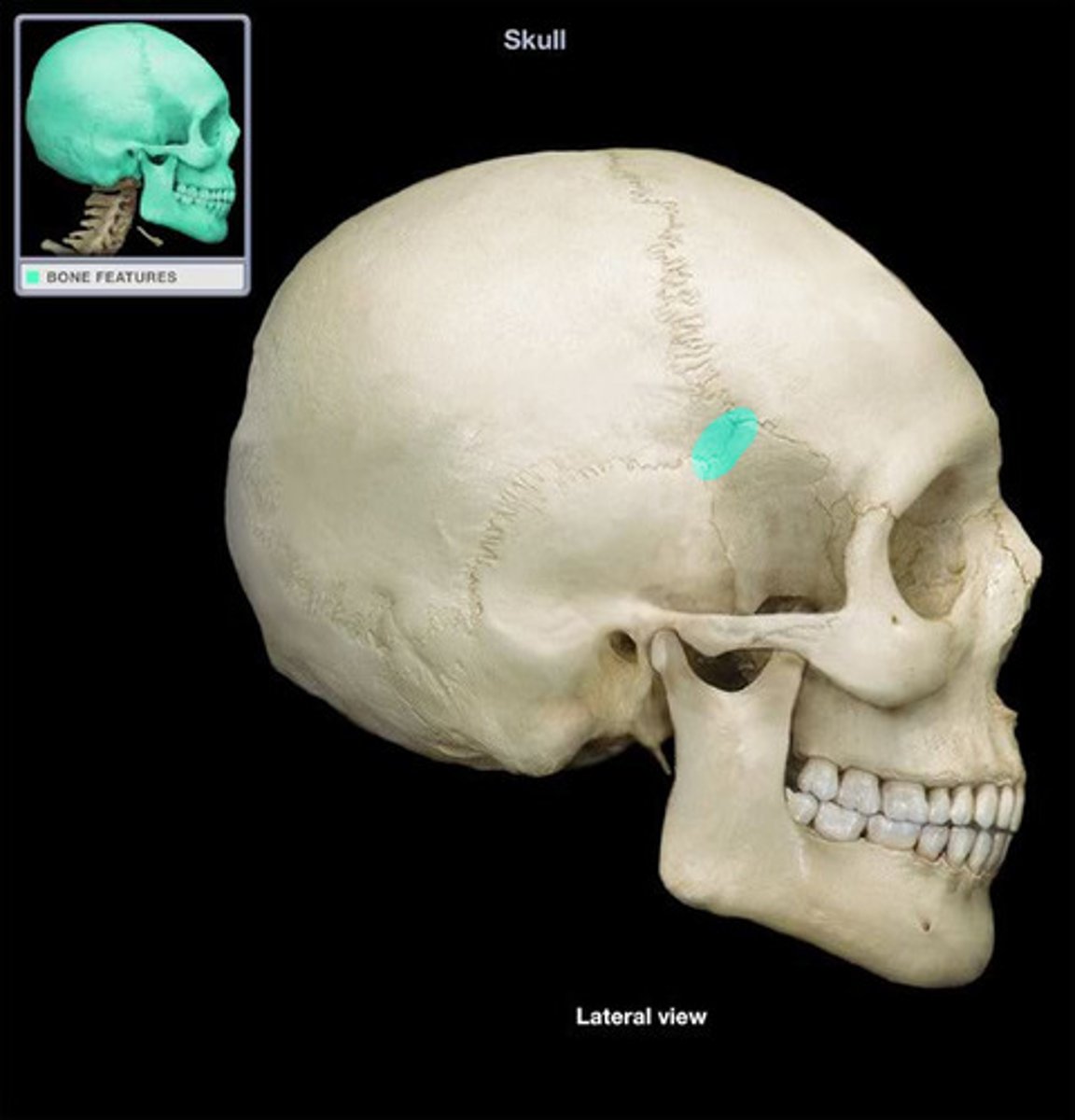
occipital angle (of PARIETALS)
located at lambda (intersection of sagittal and lamb-doidal sutures)
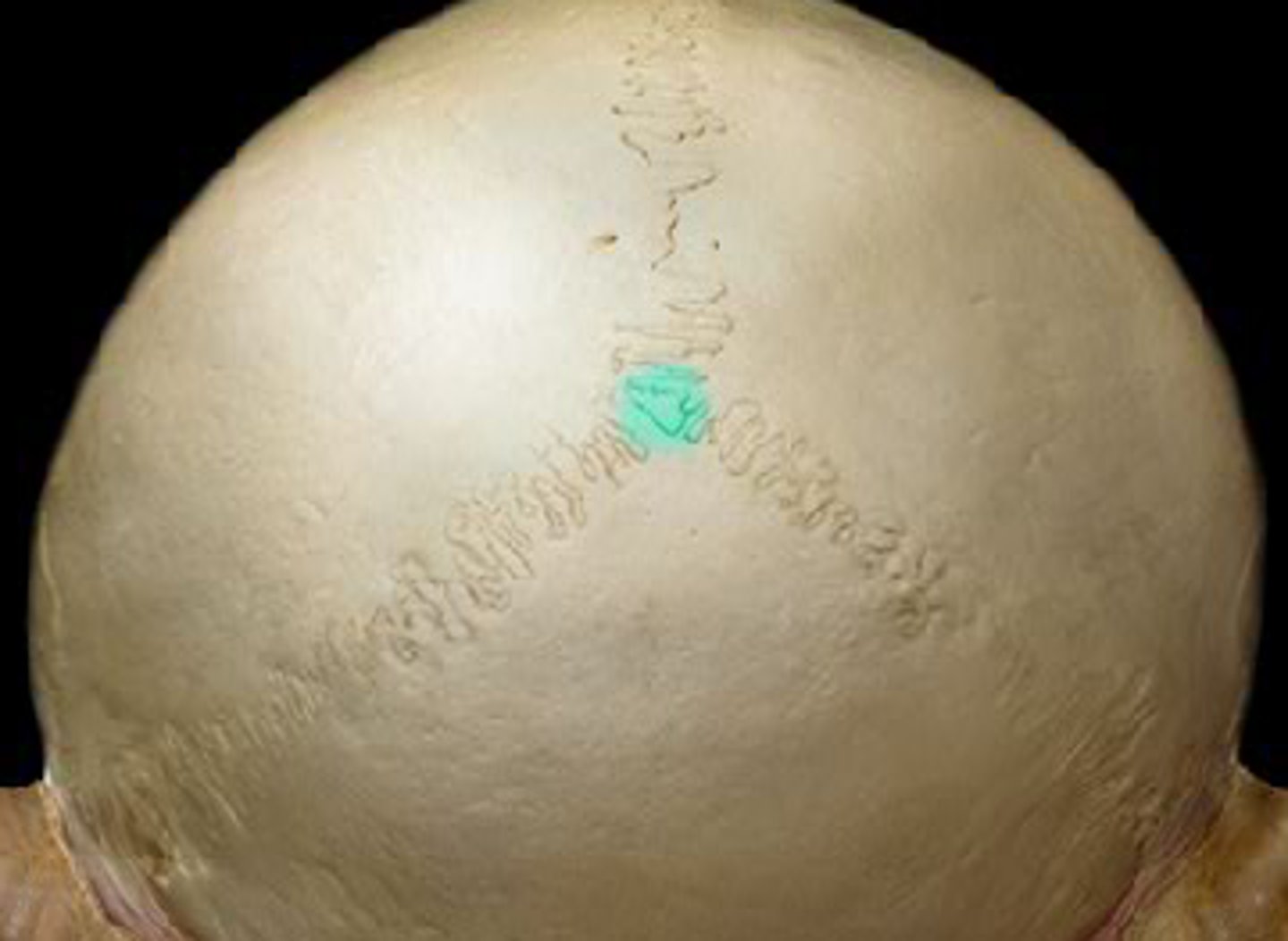
mastoid angle (of PARIETALS)
located at asterion (where lamb-doidal suture contacts the temporal; parietomastoid suture)
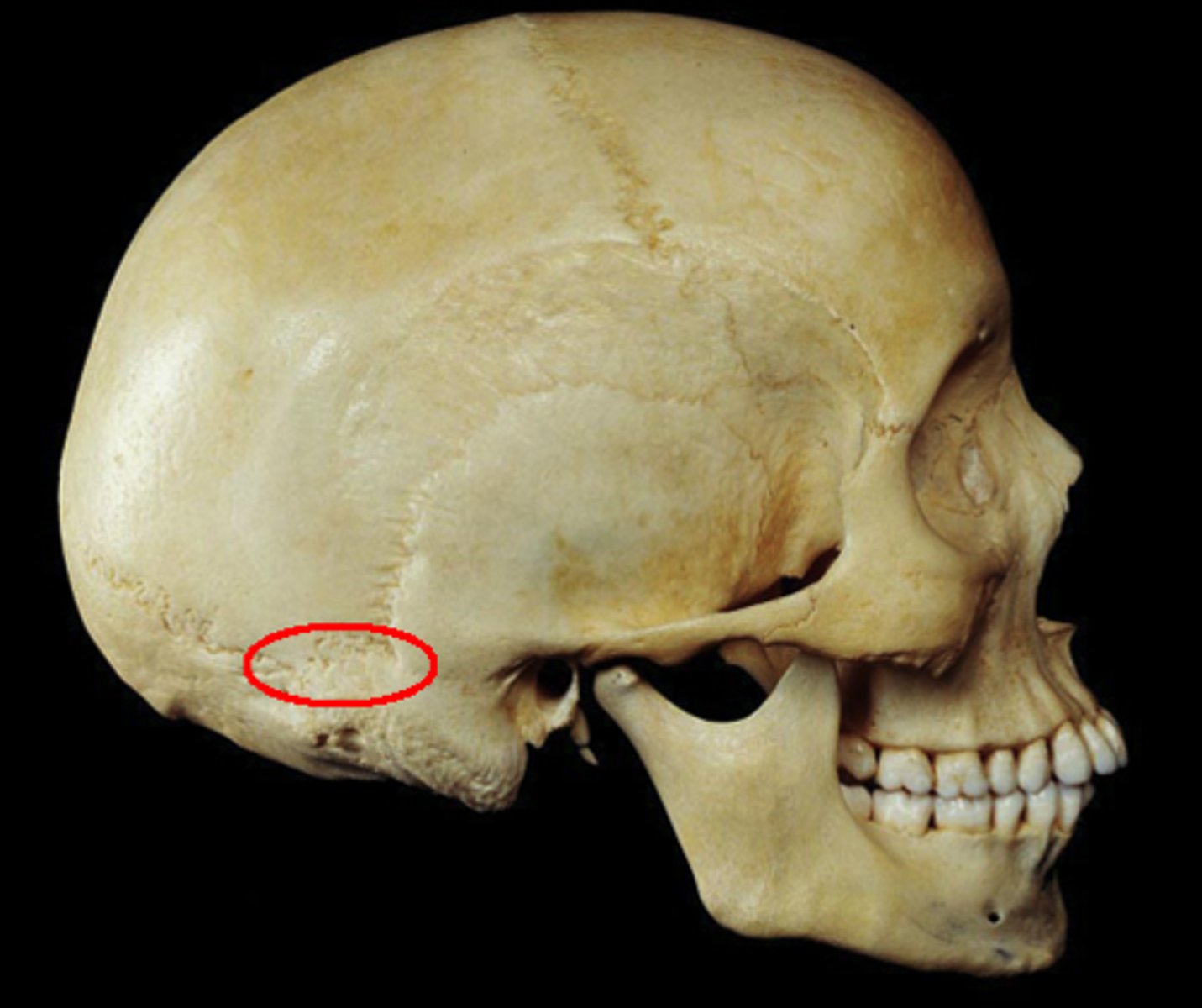
parietal eminence (of PARIETALS)
large, rounded eminence centered on the ectocranial surface of the parietal
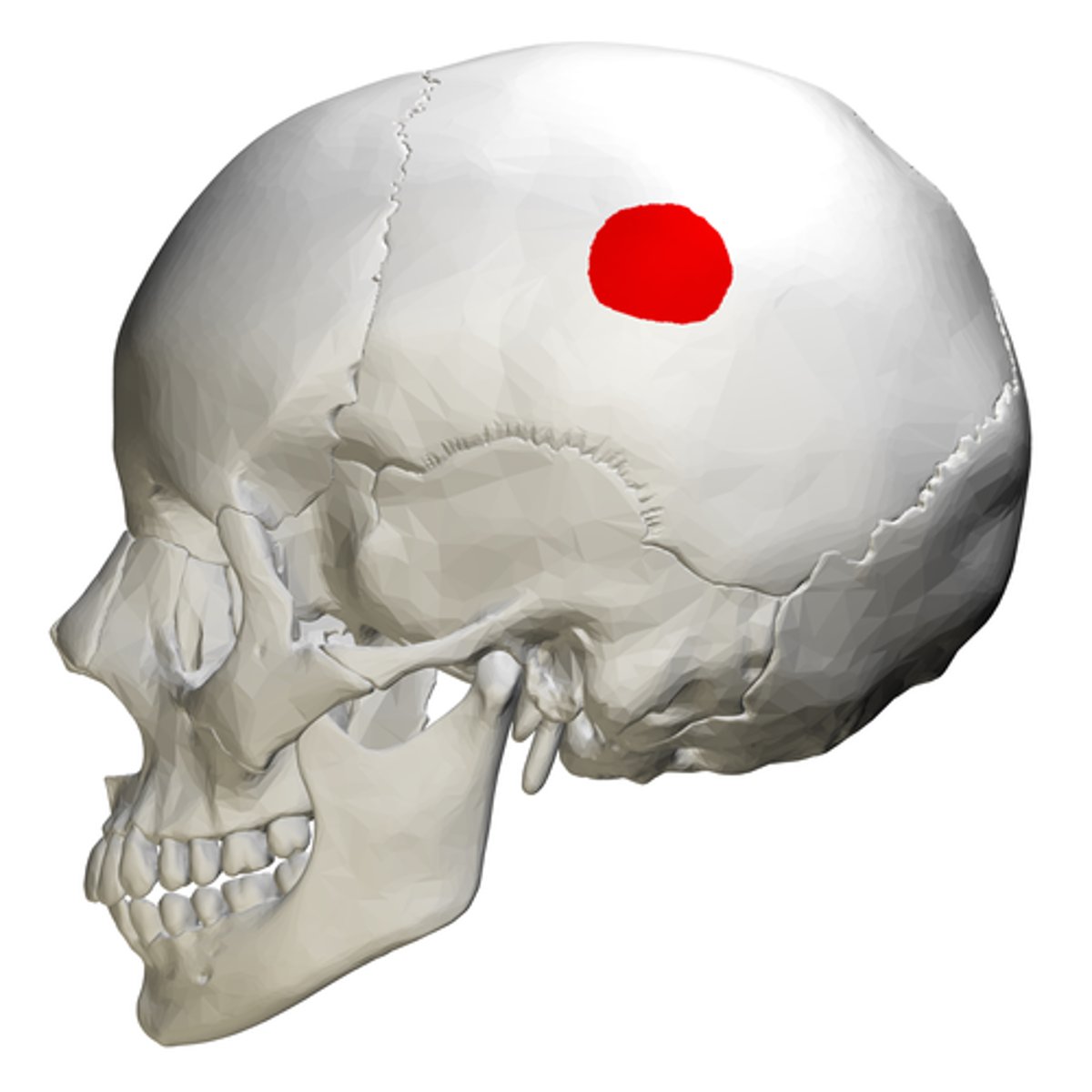
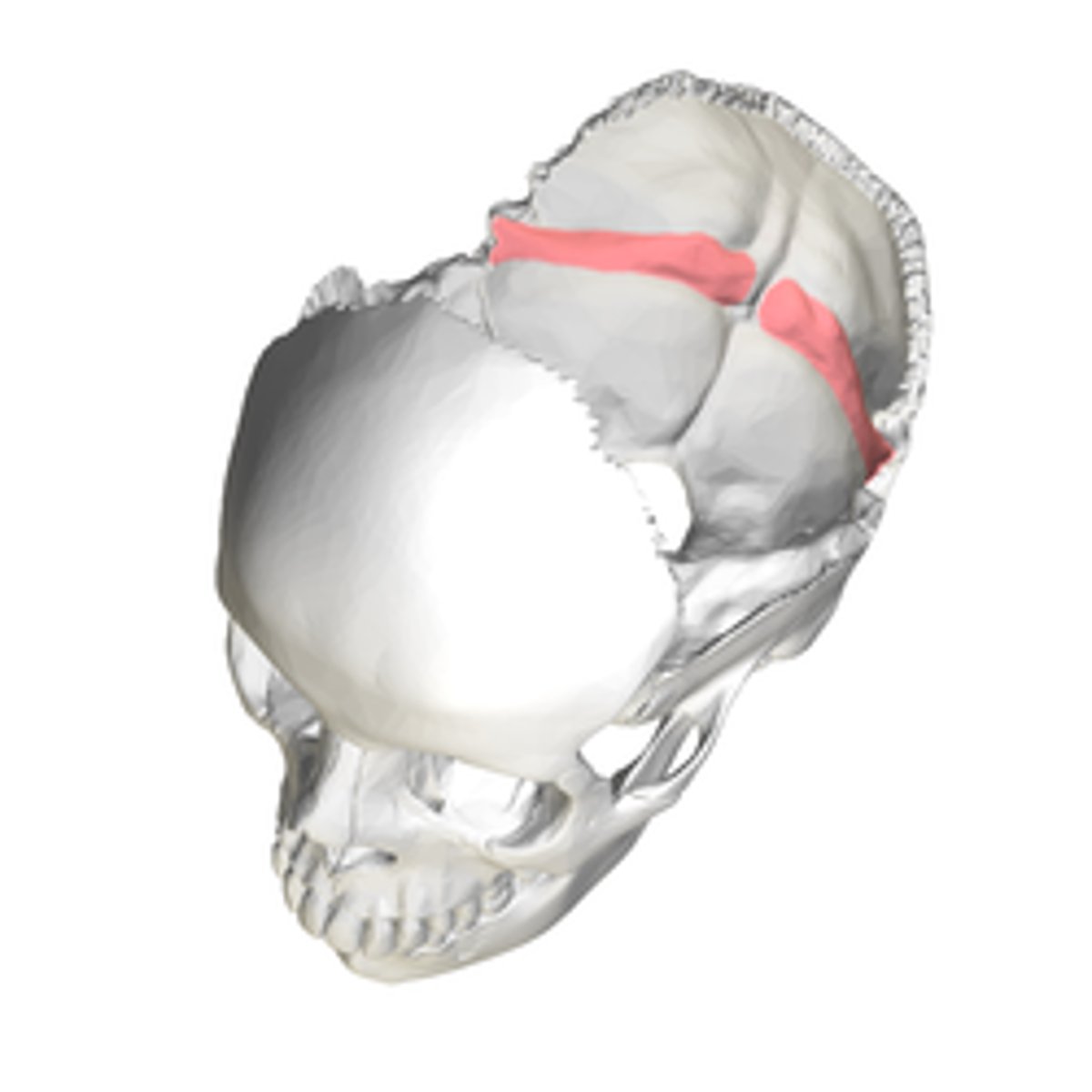
temporal lines (of PARIETALS): superior temporal line, inferior temporal line
arching anteroposteriorly, attachment site for temporalis muscles
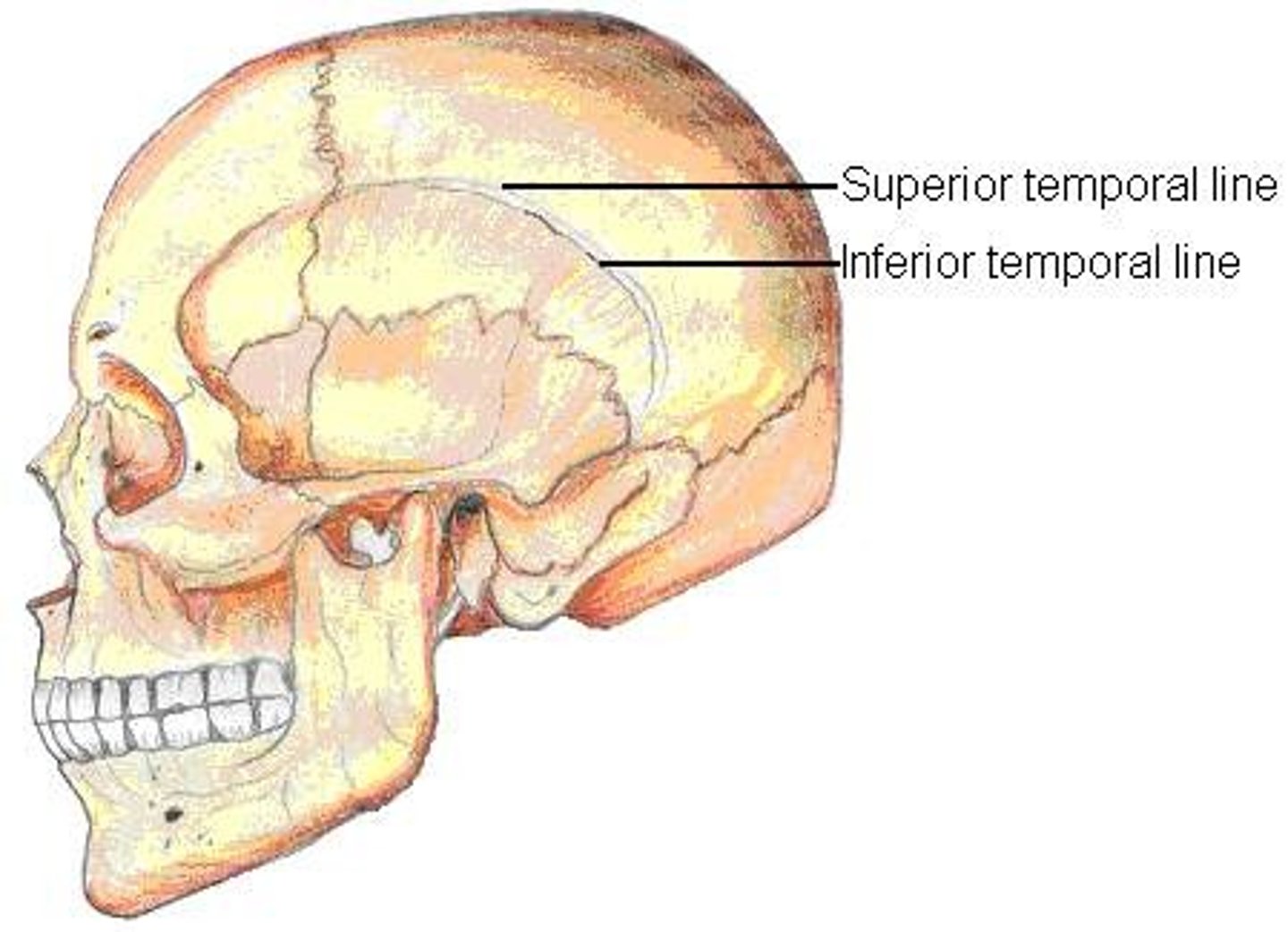
parietal foramen (of PARIETALS)
located close to the sagittal suture near lambda

parietal striae (of PARIETALS)
striations that pass posterosuperiorly on the ectocranial surface of the parietal
meningeal grooves (of PARIETALS)
indentations on parietal bones from meningeal arteries (blood pathways in brain/skull's soft tissues)
sagittal sulcus (of PARIETALS)
where parietals are articulated, posterior continuation of sagittal sulcus of FRONTAL
arachnoid fovea (of PARIETALS)
indentations on parietal bones from arachnoid mater layer of skull/brain's soft tissue
sigmoid sulcus (of PARIETALS)
crosses the mastoid angle of PARIETALS, cutting a groove on the endocranial surface, marks course of sigmoid sinus (drains blood from brain)
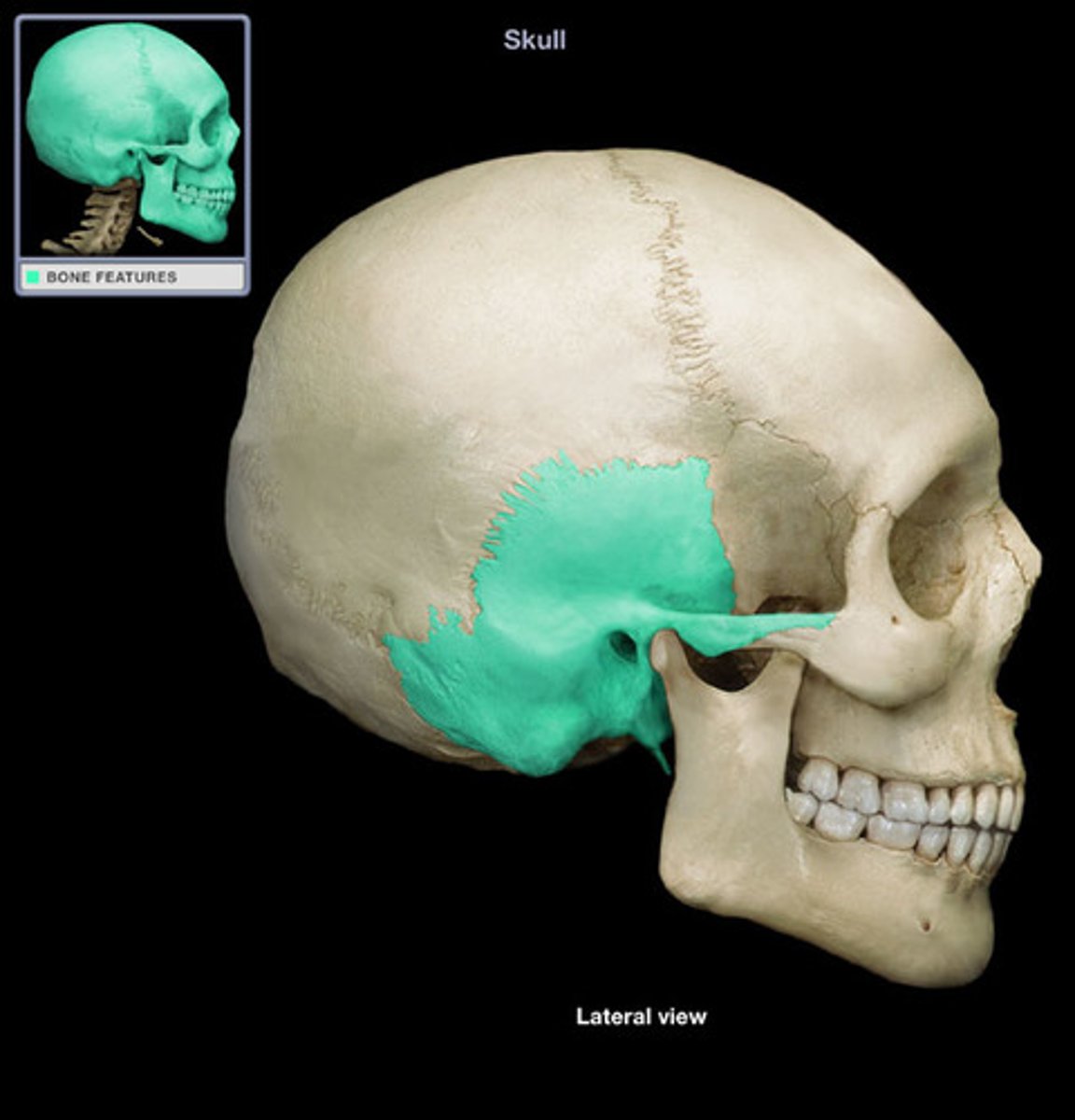
TEMPORALS
form transition between cranial wall and base, house ear ossicles, form upper surface of jaw joints
squama (of TEMPORALS)
thin, scale-like bone fragment that rises vertically from cranial walls and articulates with PARIETALS along squamosal sutures
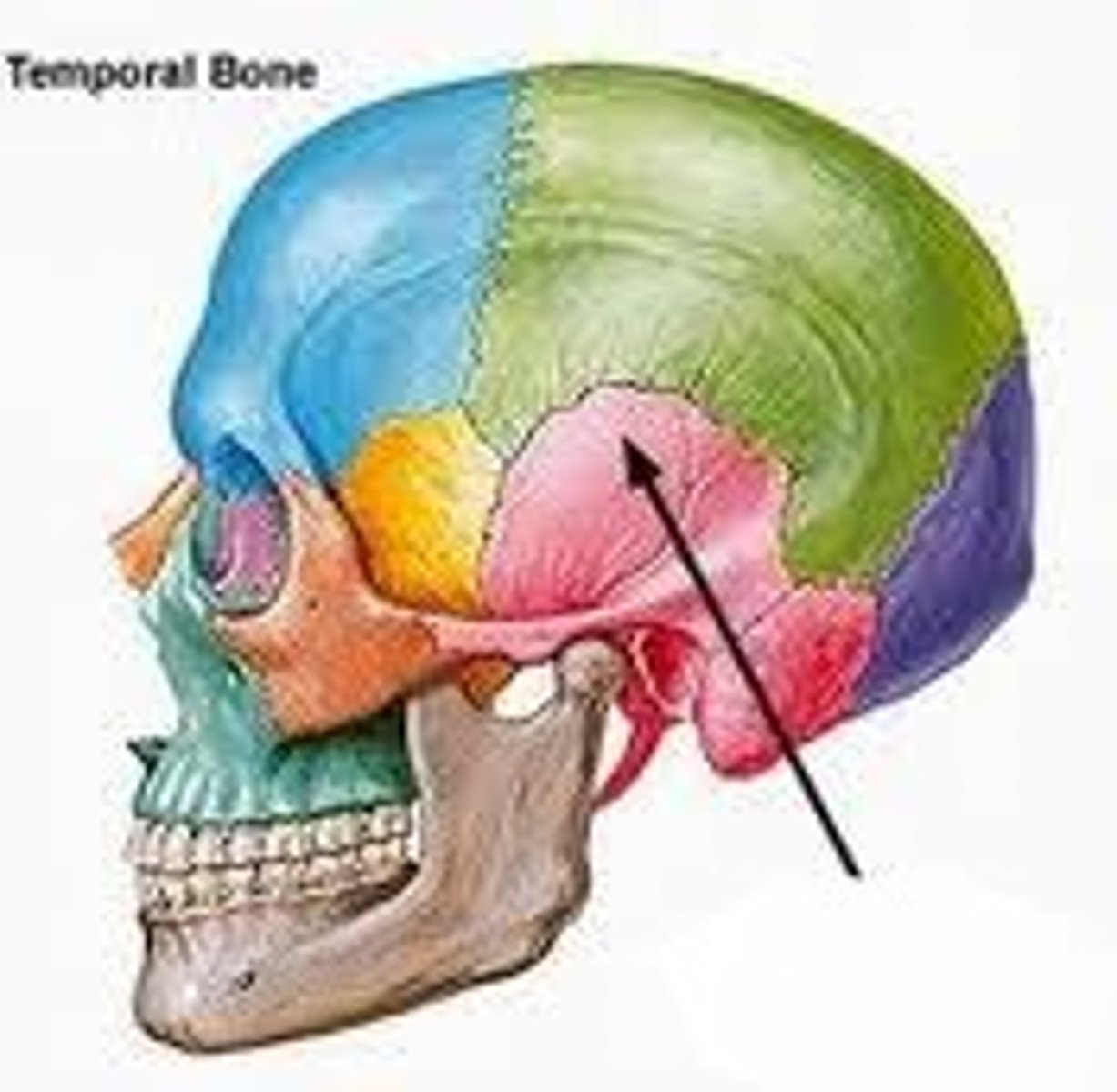
petrous portion (of TEMPORALS)
massive, dense bony part of TEMPORALS that houses ear ossicles, wedged between OCCIPITAL and SPHENOID
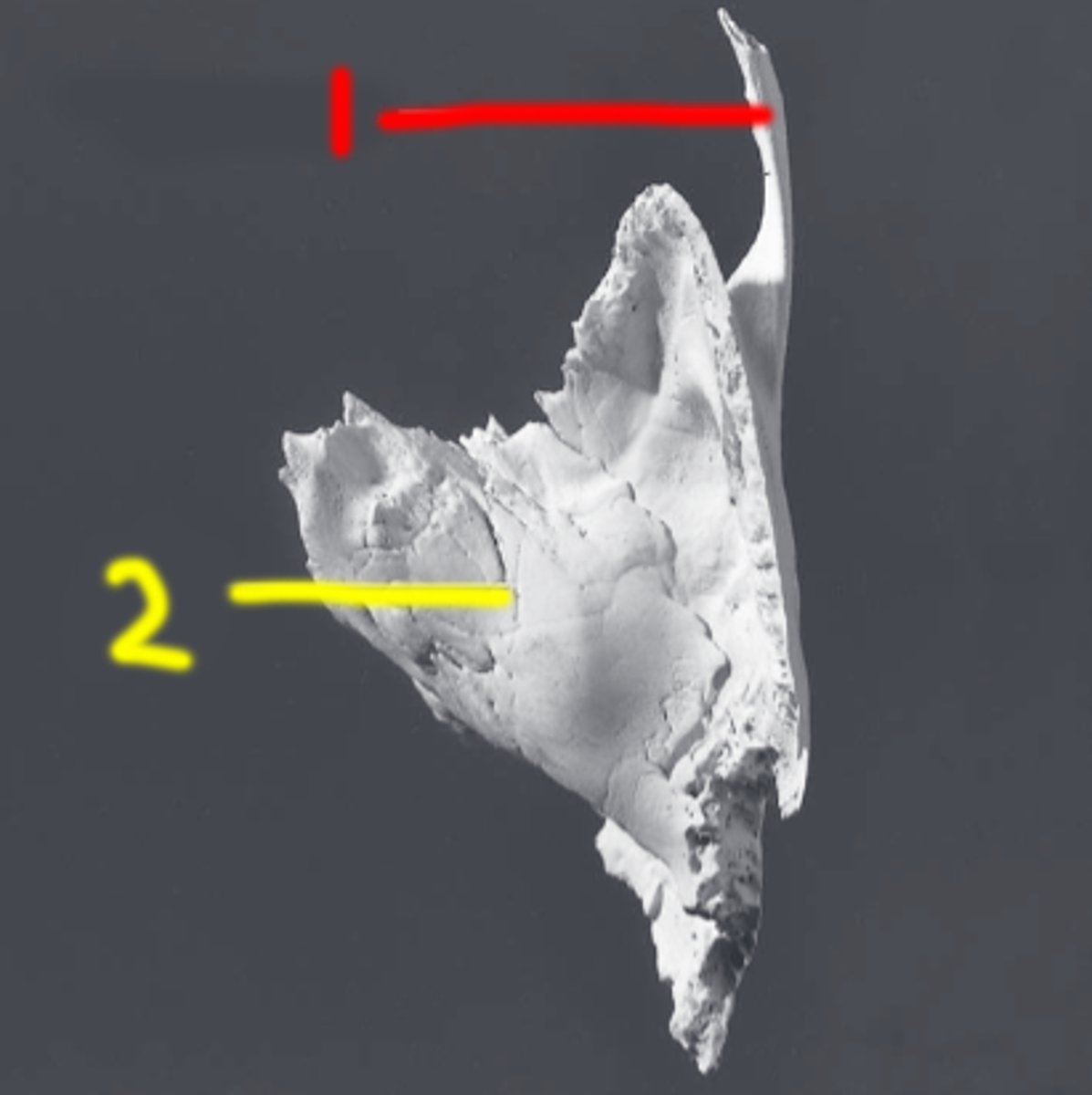

external/internal acoustic meatus (EAM/IAM) (of TEMPORALS)
external/internal opening of ear canal, passes anteromedially, inner end is closed by tympanic membrane
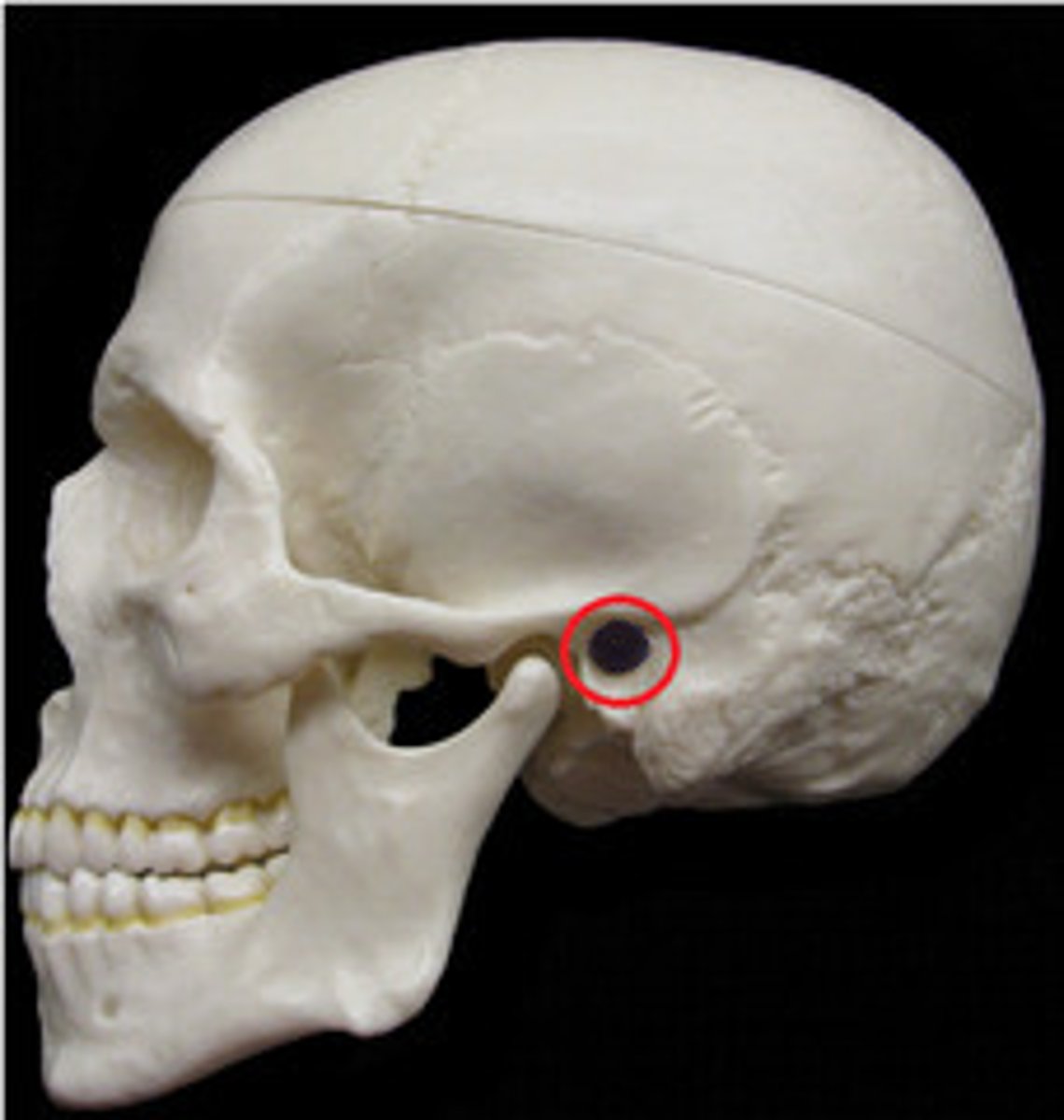
zygomatic process (of TEMPORALS)
slender process extending forward from squamous portion to contribute to the zygomatic arch
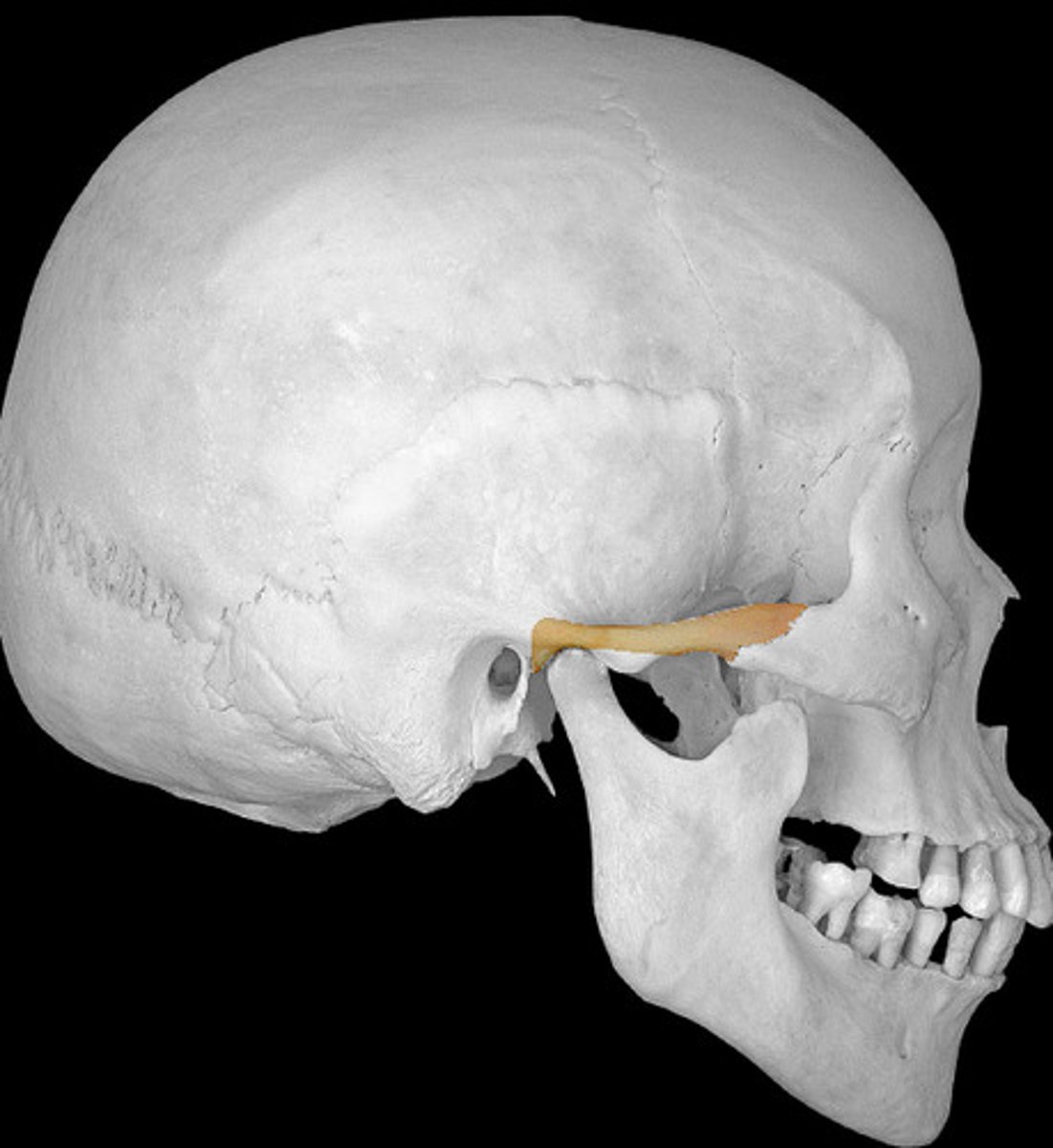
suprameatal crest (of TEMPORALS)
superior root of the zygomatic process, runs horizontally above EAM, farther forward than supramastoid crest
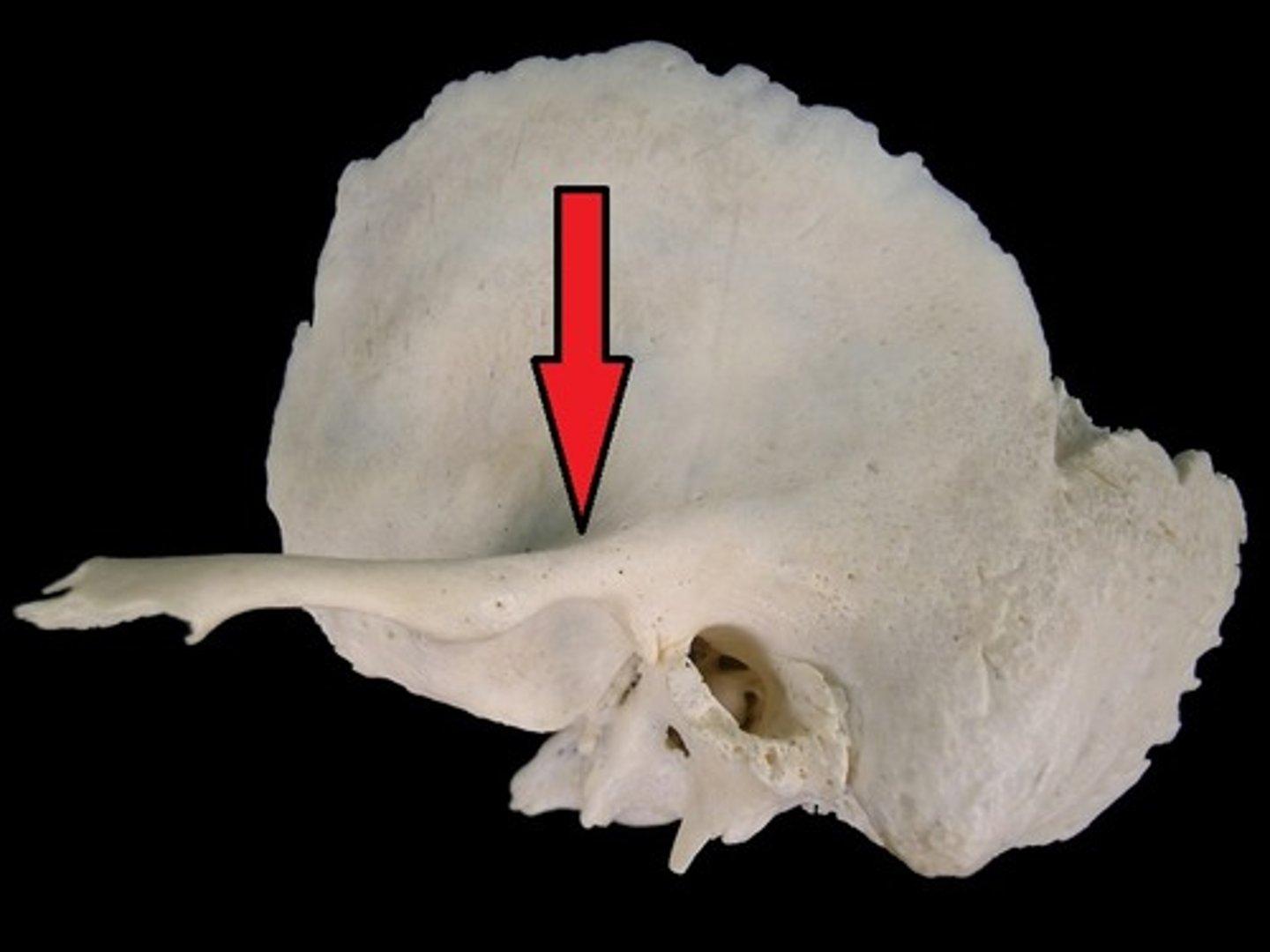
supramastoid crest (of TEMPORALS)
posterior extension of the suprameatal crest, above mastoid, farther back than suprameatal crest
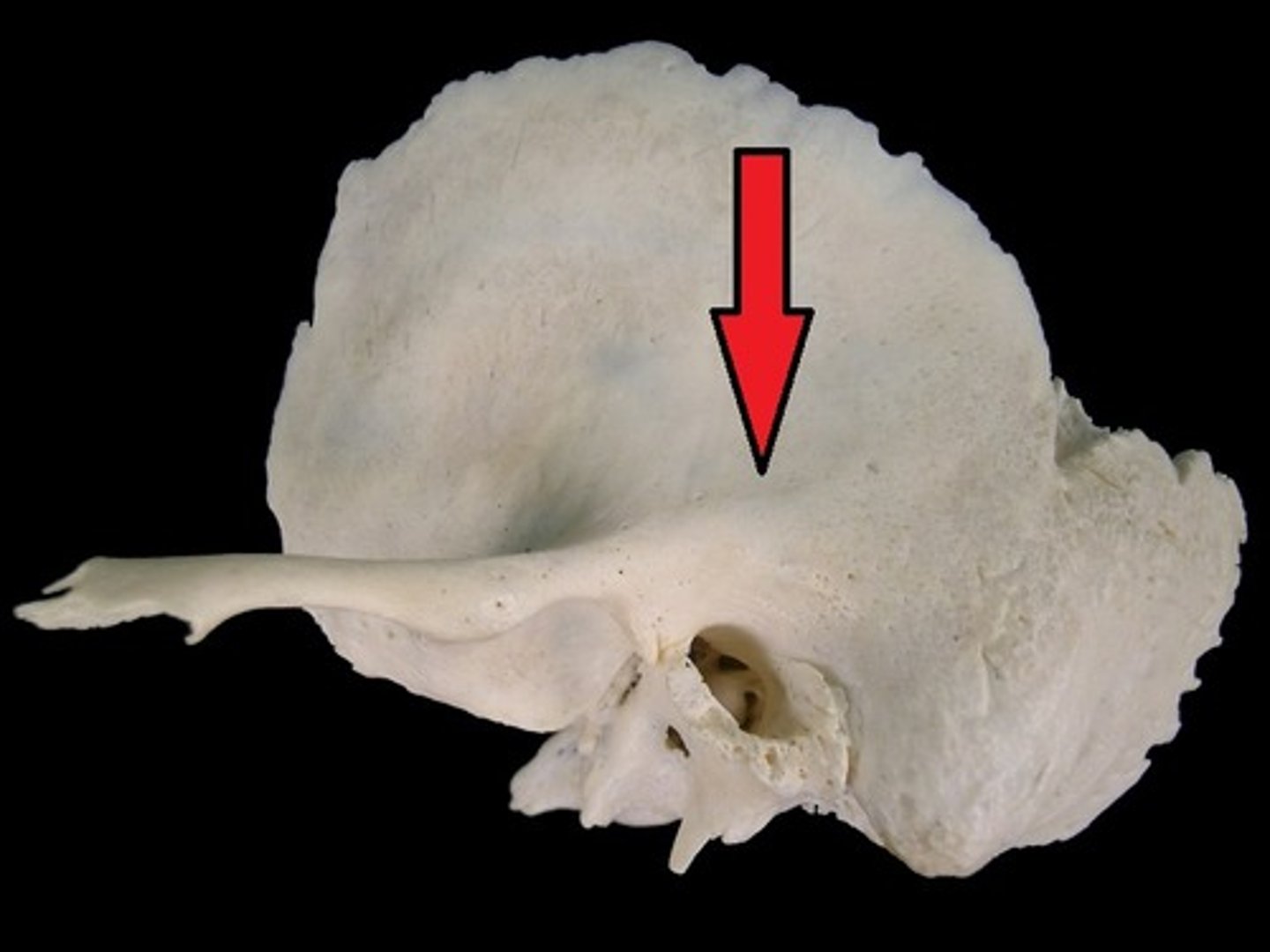
parietal notch (of TEMPORALS)
formed by the posterosuperior border of the TEMPORAL, where the squamosal and parietomastoid sutures meet
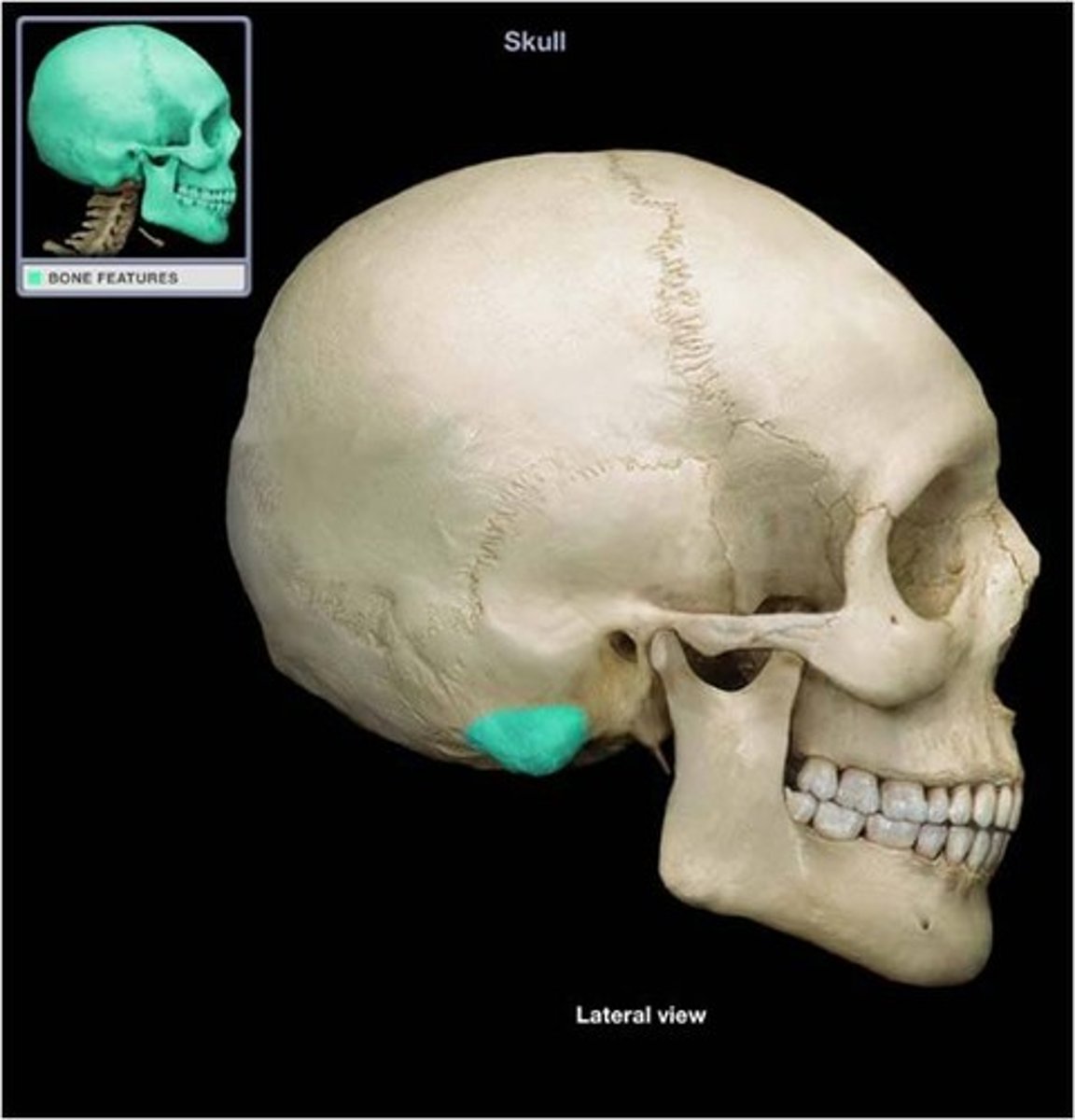
mastoid process (of TEMPORALS)
process of the temporal bone behind the EAM/IAM, at the base of the skull, for jaw muscle attachments (e.g. digastric muscle)
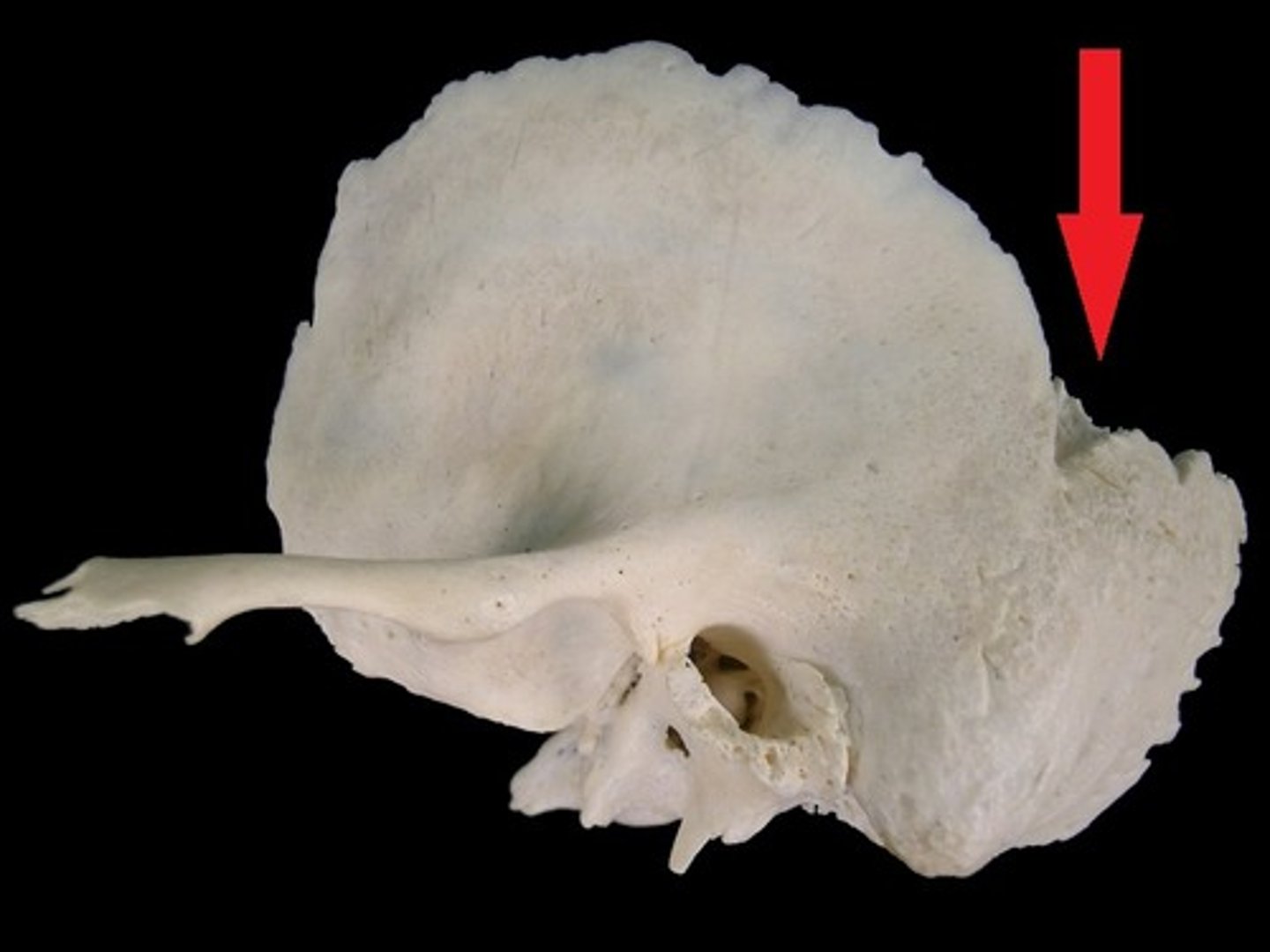
mastoid foramen (of TEMPORALS)
located near the posterior edge of the mastoid process along the occipitomastoid suture
mastoid notch/digastric groove (of TEMPORALS)
attachment of the digastric muscle, furrow medial to mastoid process
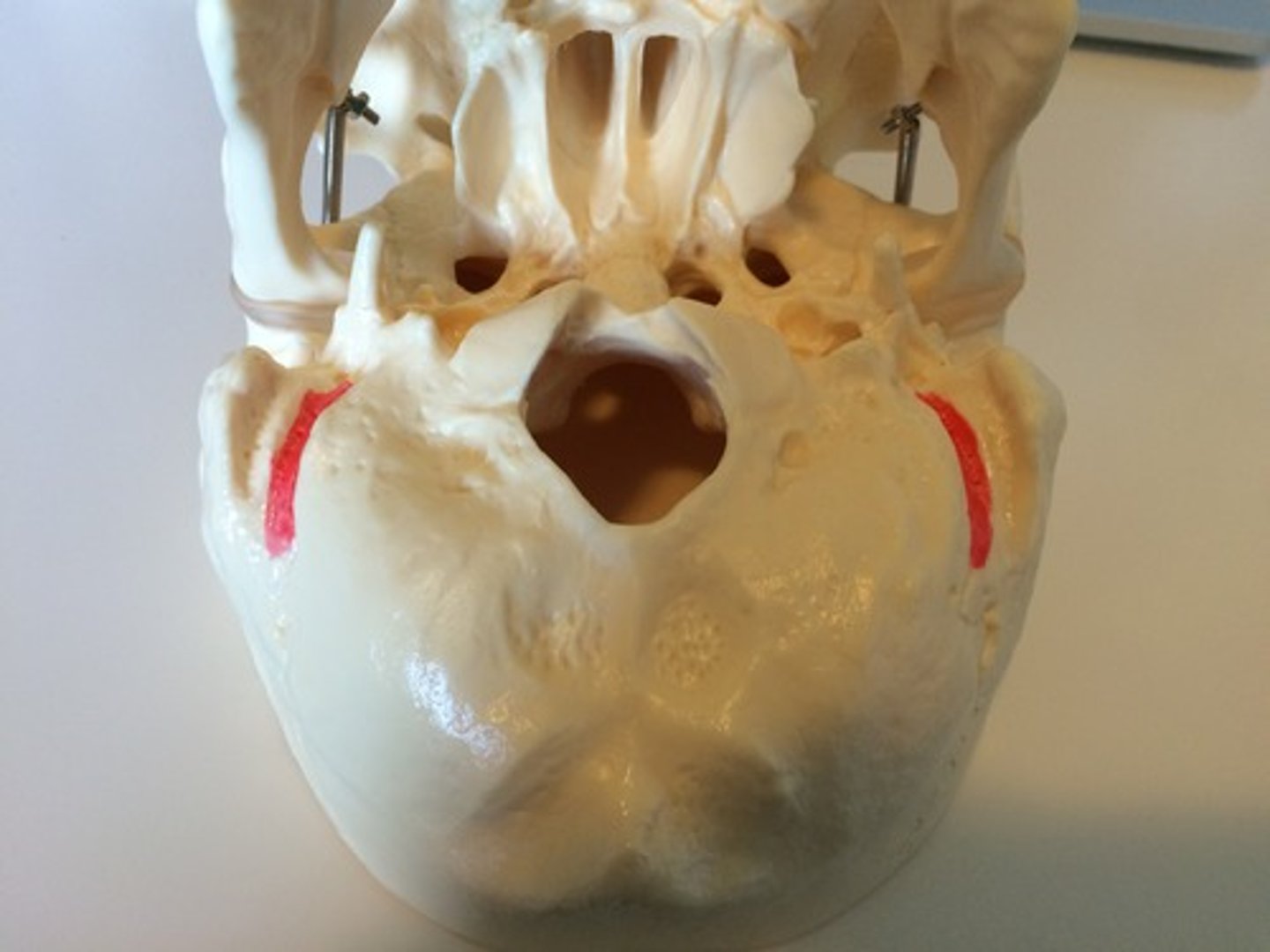
occipital groove/sulcus (of TEMPORALS)
lies just medial to the mastoid notch, shallow furrow that lodges the occipital artery
temporomandibular articular surface (of TEMPORALS)
smooth, articular surface inferior to the root of the zygomatic process
articular eminence (of TEMPORALS)
forms anterior portion of the temporomandibular articular surface
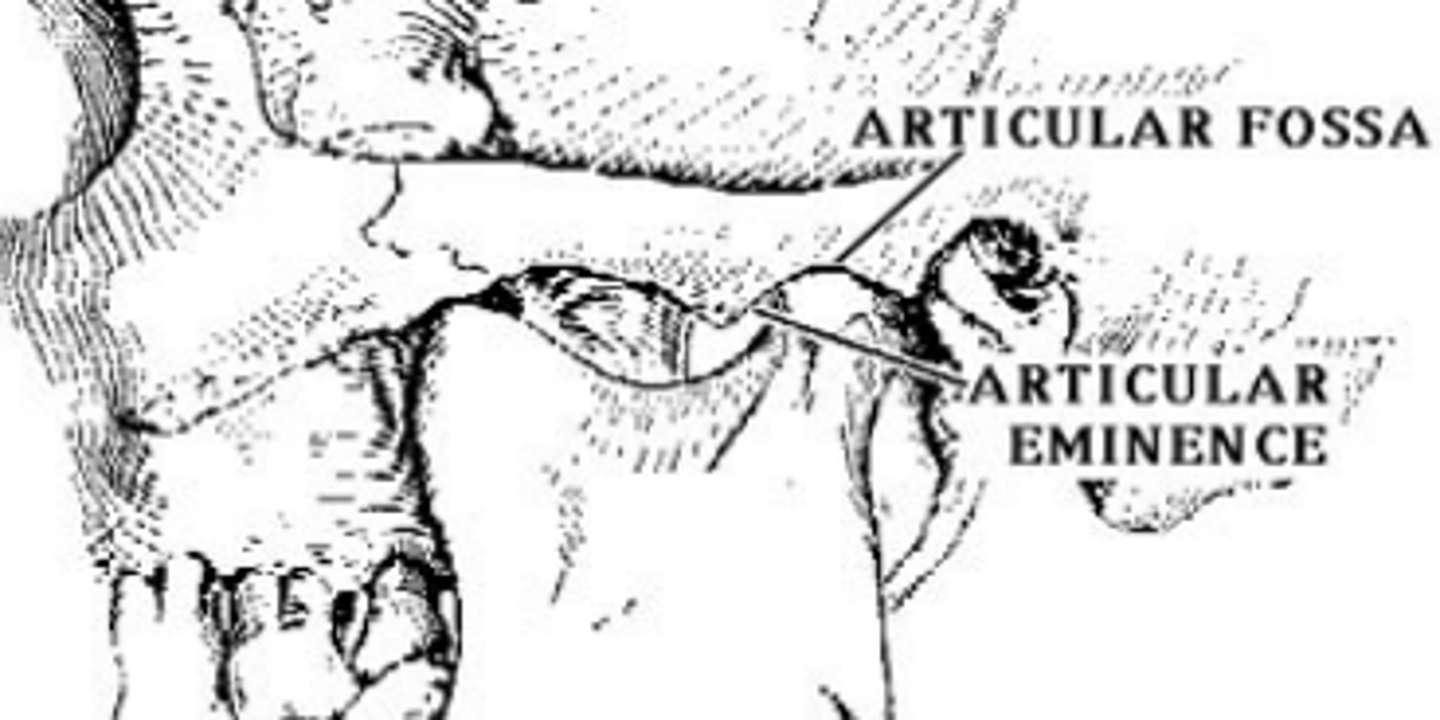
mandibular/glenoid fossa (of TEMPORALS)
lies posterosuperior to the articular eminence, bounded medially by sphenosquamosal suture
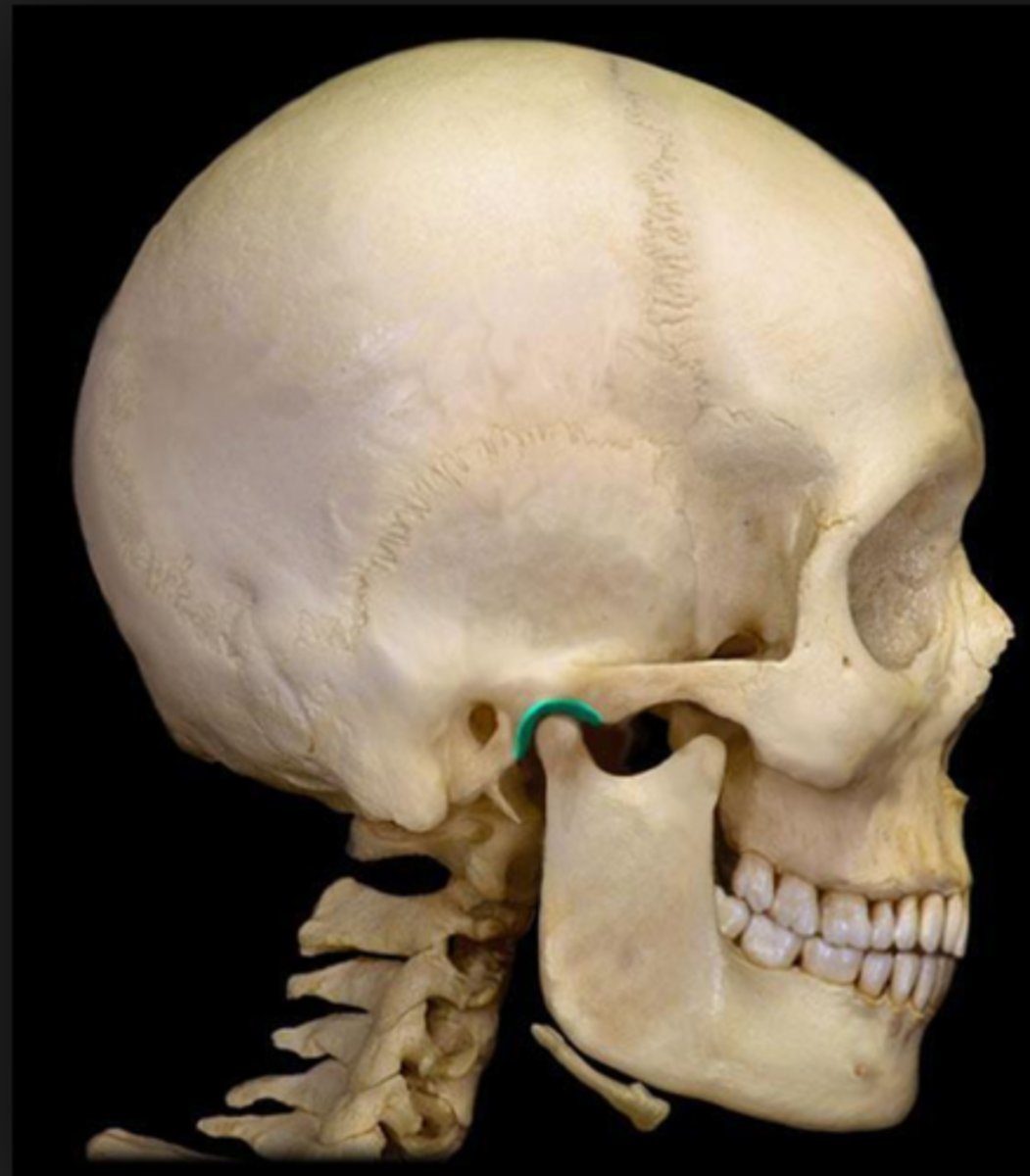
postglenoid process (of TEMPORALS)
projection that lies just anterosuperior to the EAM, interposed between the tympanic part (EAM and styloid process portion) of the bone
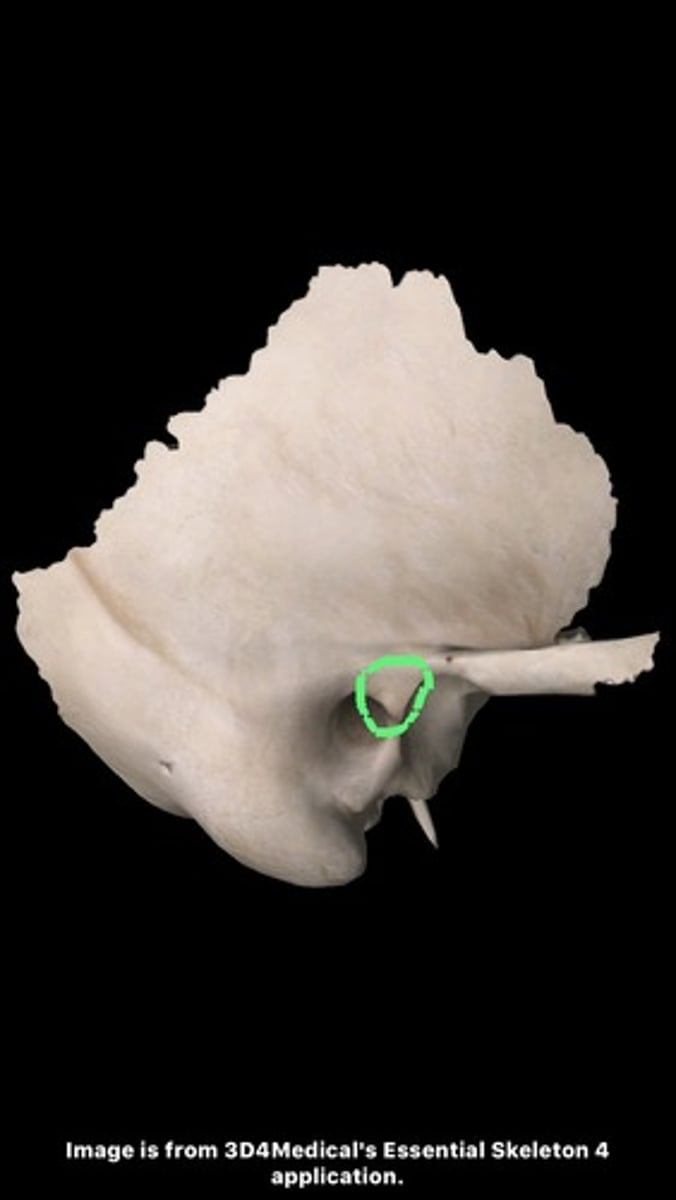
entoglenoid process (of TEMPORALS)
inferior projection of the articular surface at the medial edge of the articular eminence
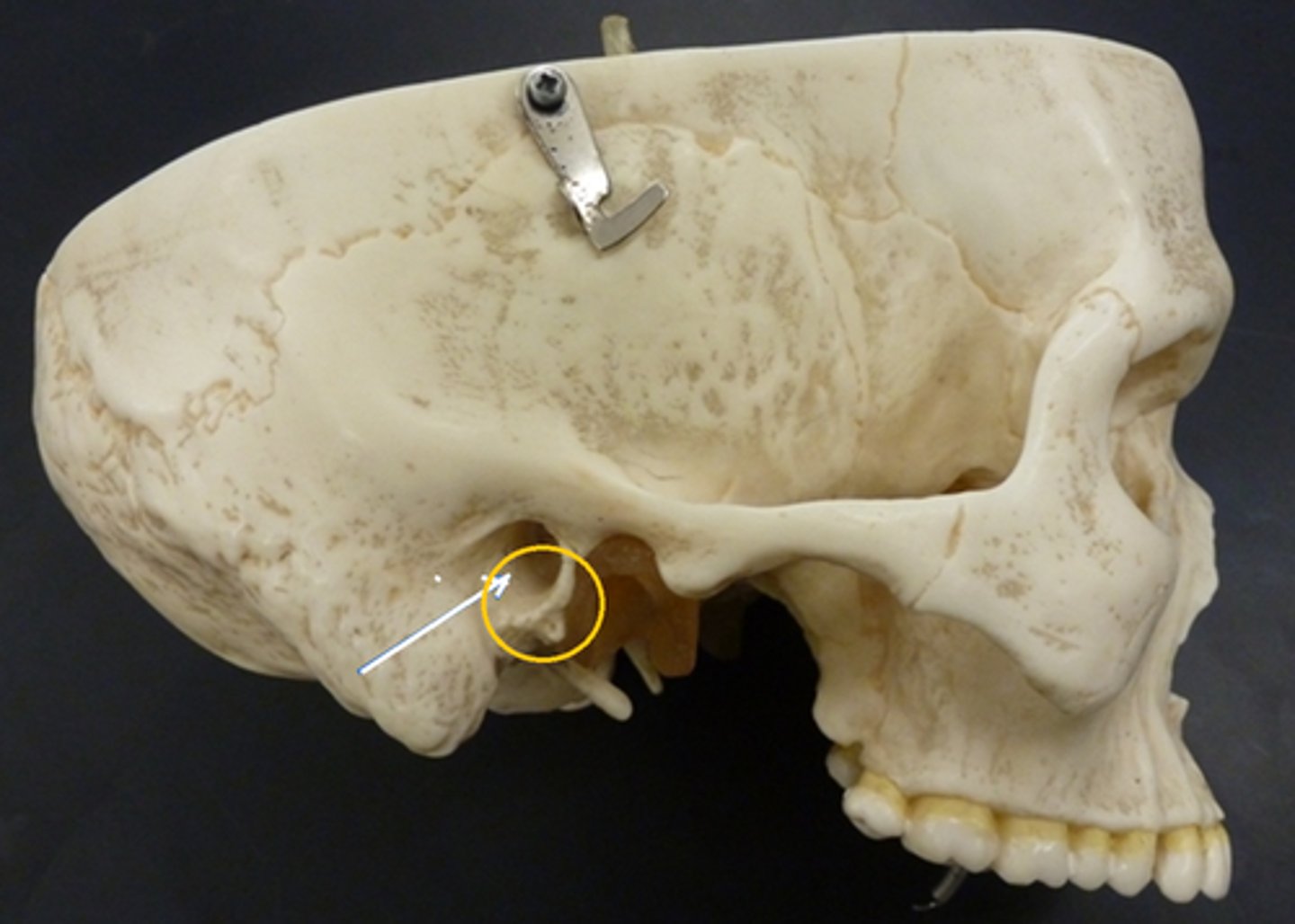
tympanic part (of TEMPORALS)
lies posterior to the TMI, its anterior surface forms the rear wall of the mandibular fossa
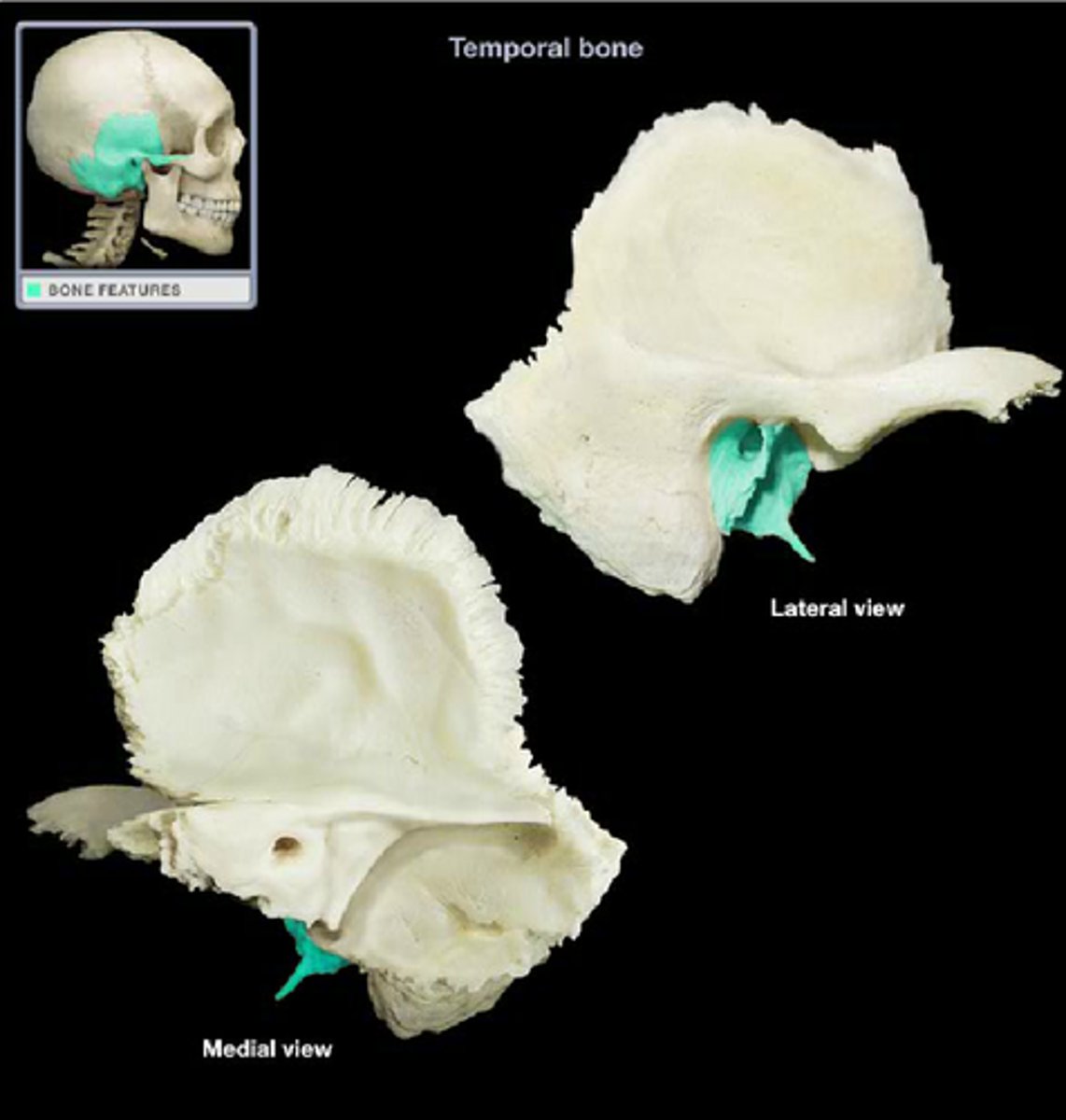
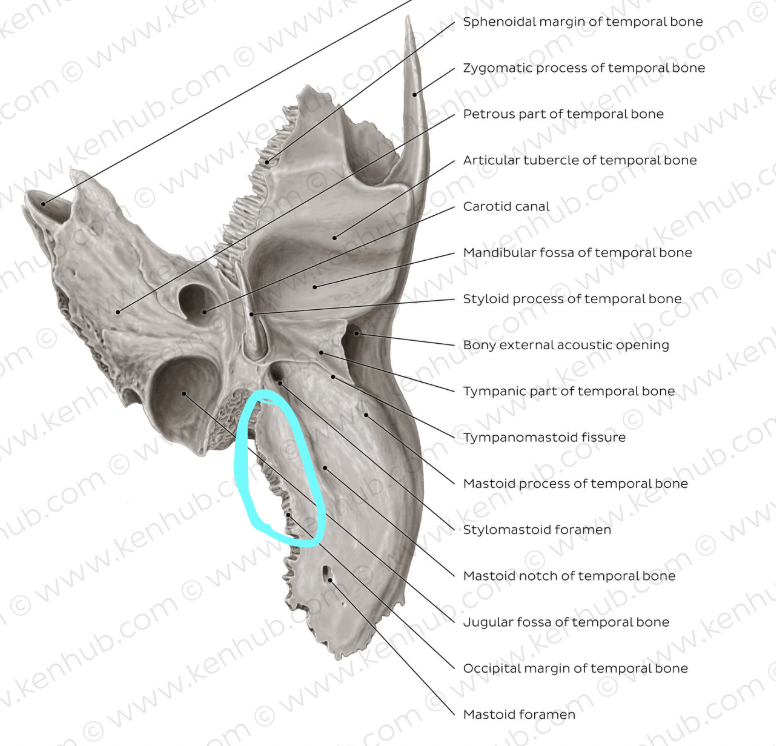
styloid process (of TEMPORALS)
thin, pointed bony rod that points anteroinferiorly from the base of the TEMPORAL
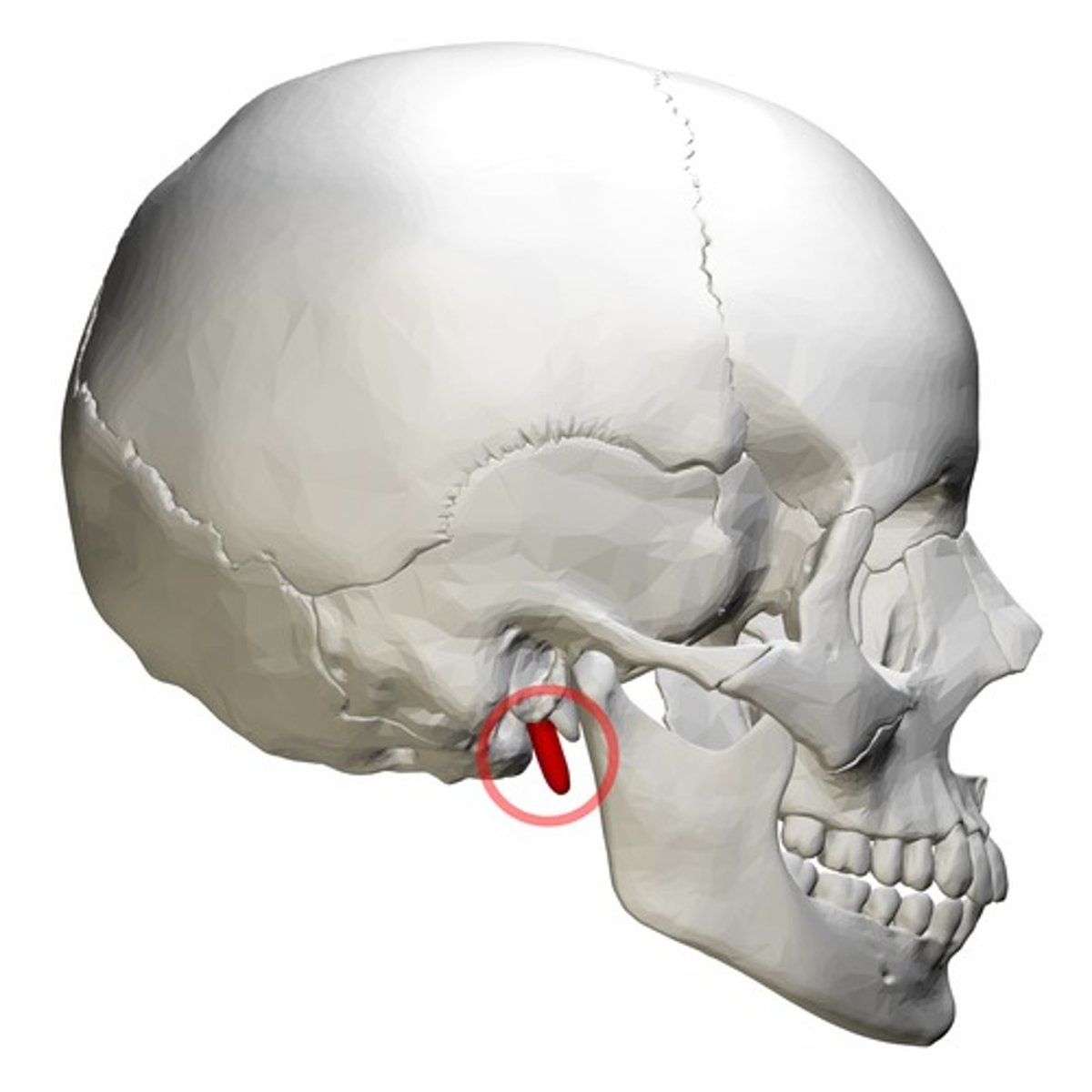
stylomastoid foramen (of TEMPORALS)
located immediately posterior to the base of the styloid process, for exit of facial nerve
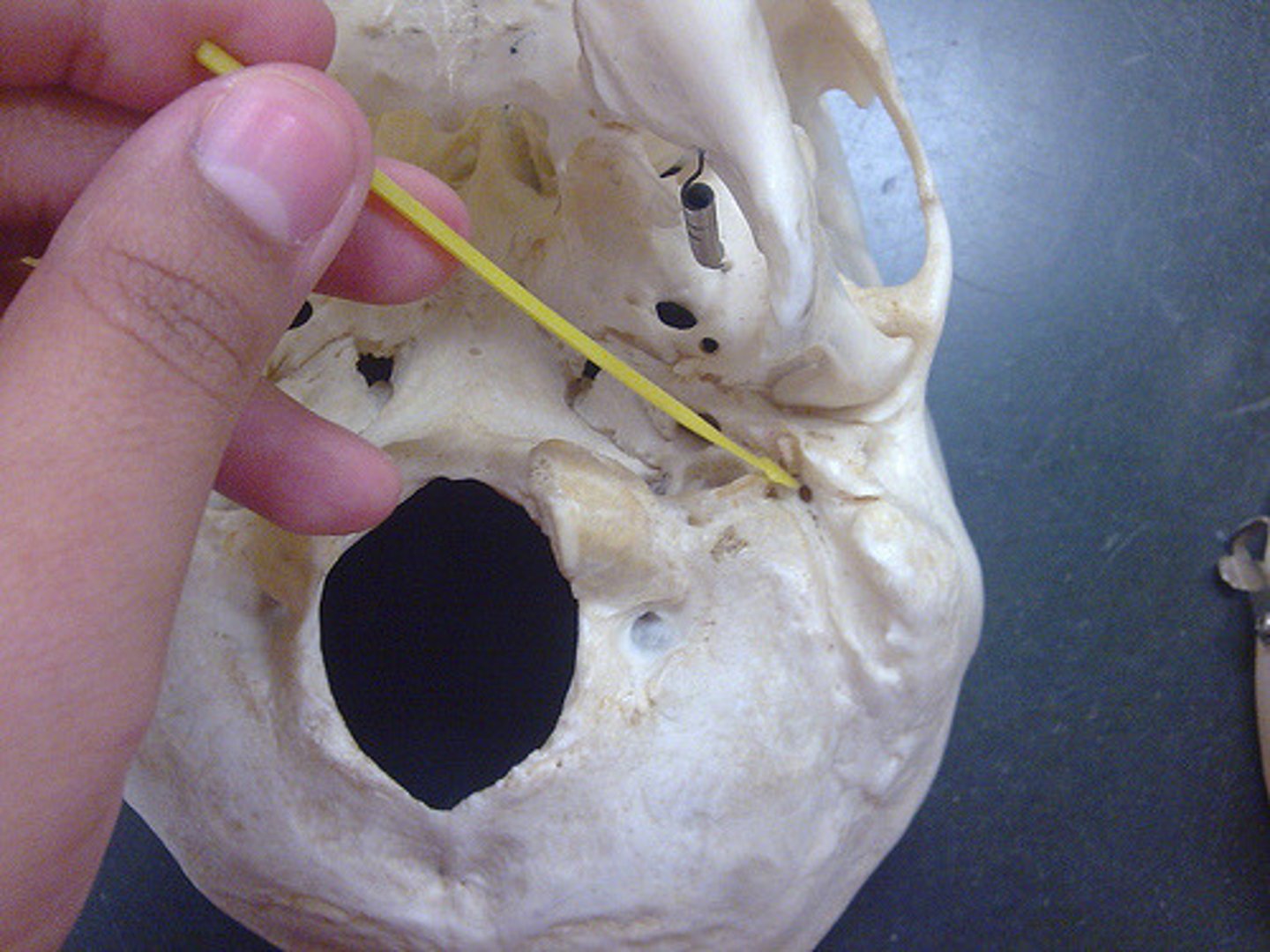
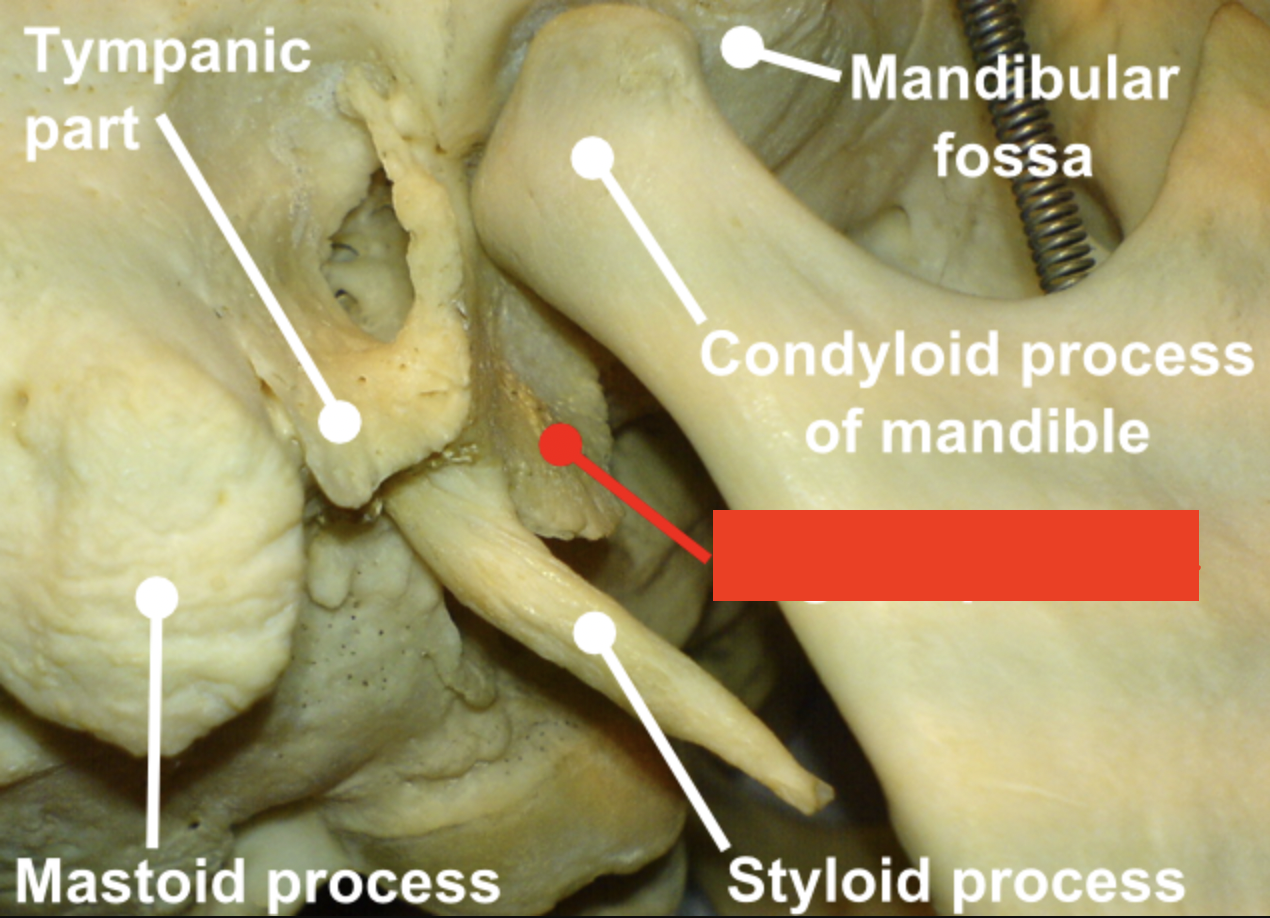
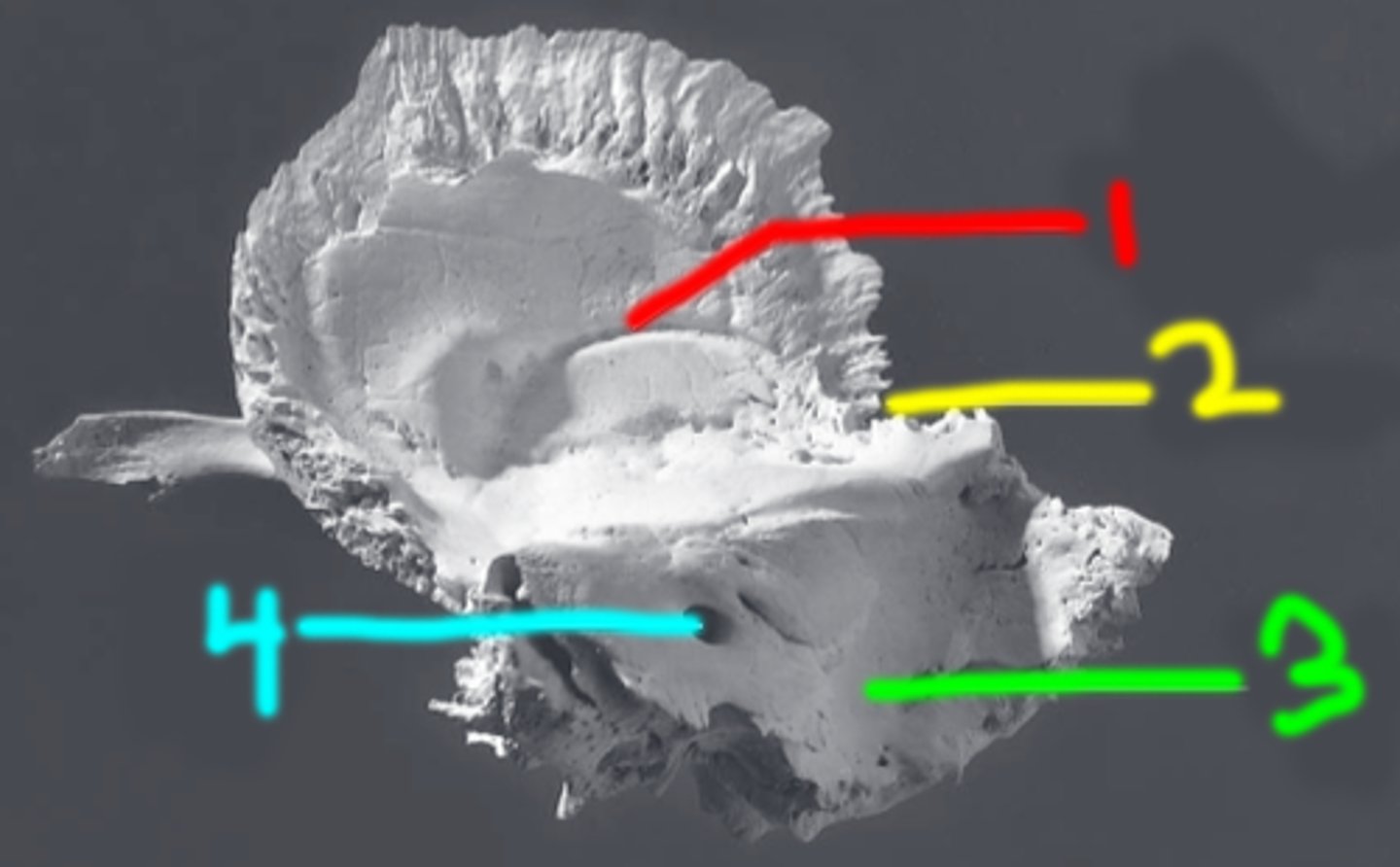
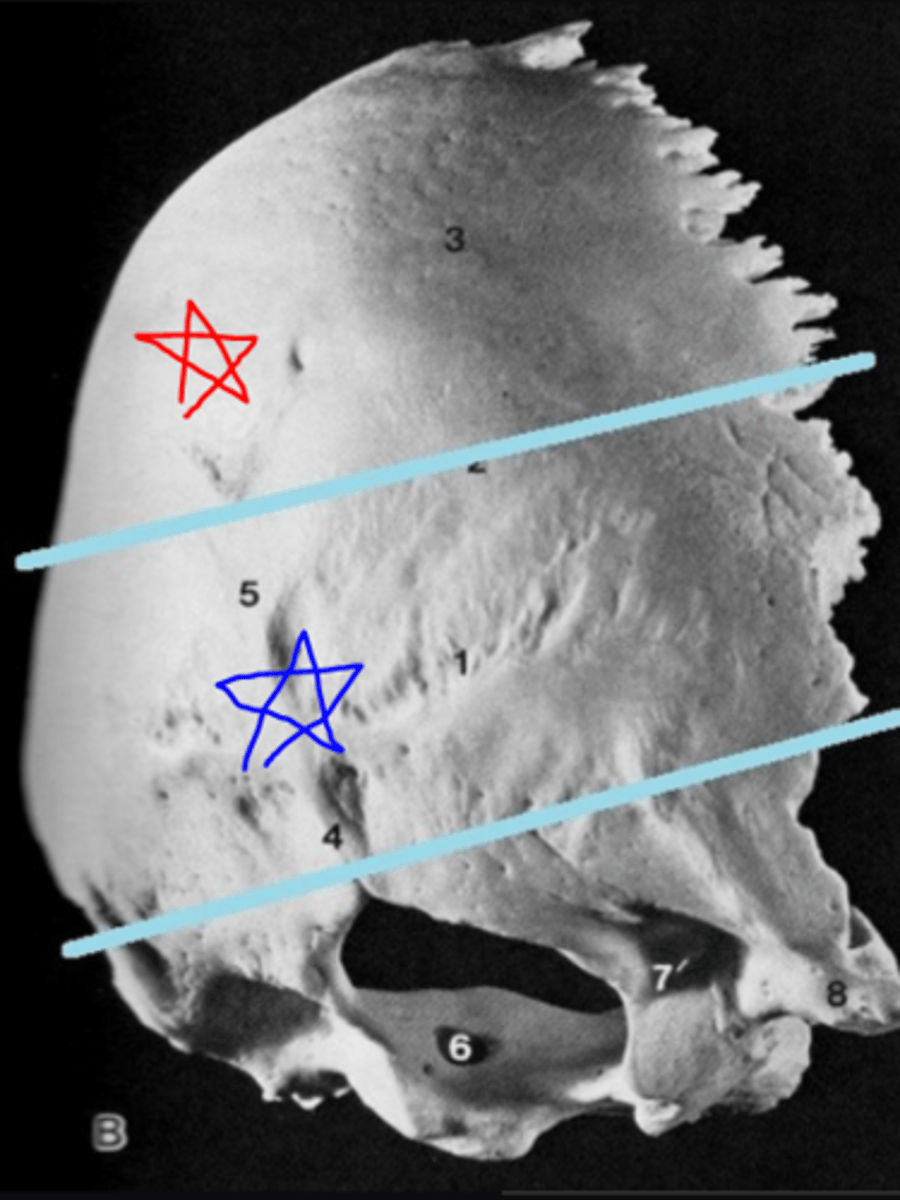
vaginal process (of TEMPORALS)
ensheaths the base of the styloid process (red box in image)
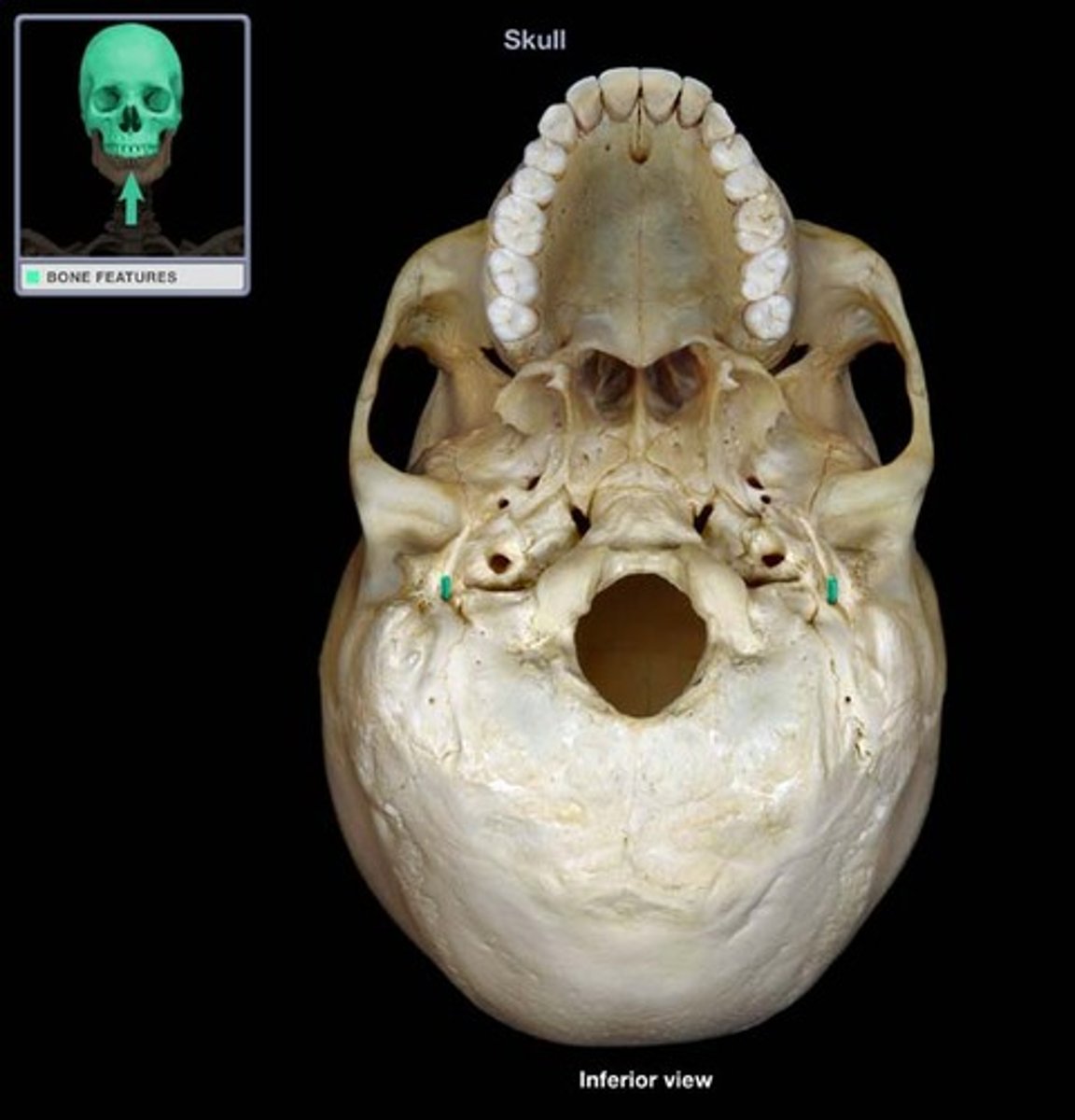
jugular fossa (of TEMPORALS)
located just medial to the base of the styloid fossa, deep fossa (blue box in image)
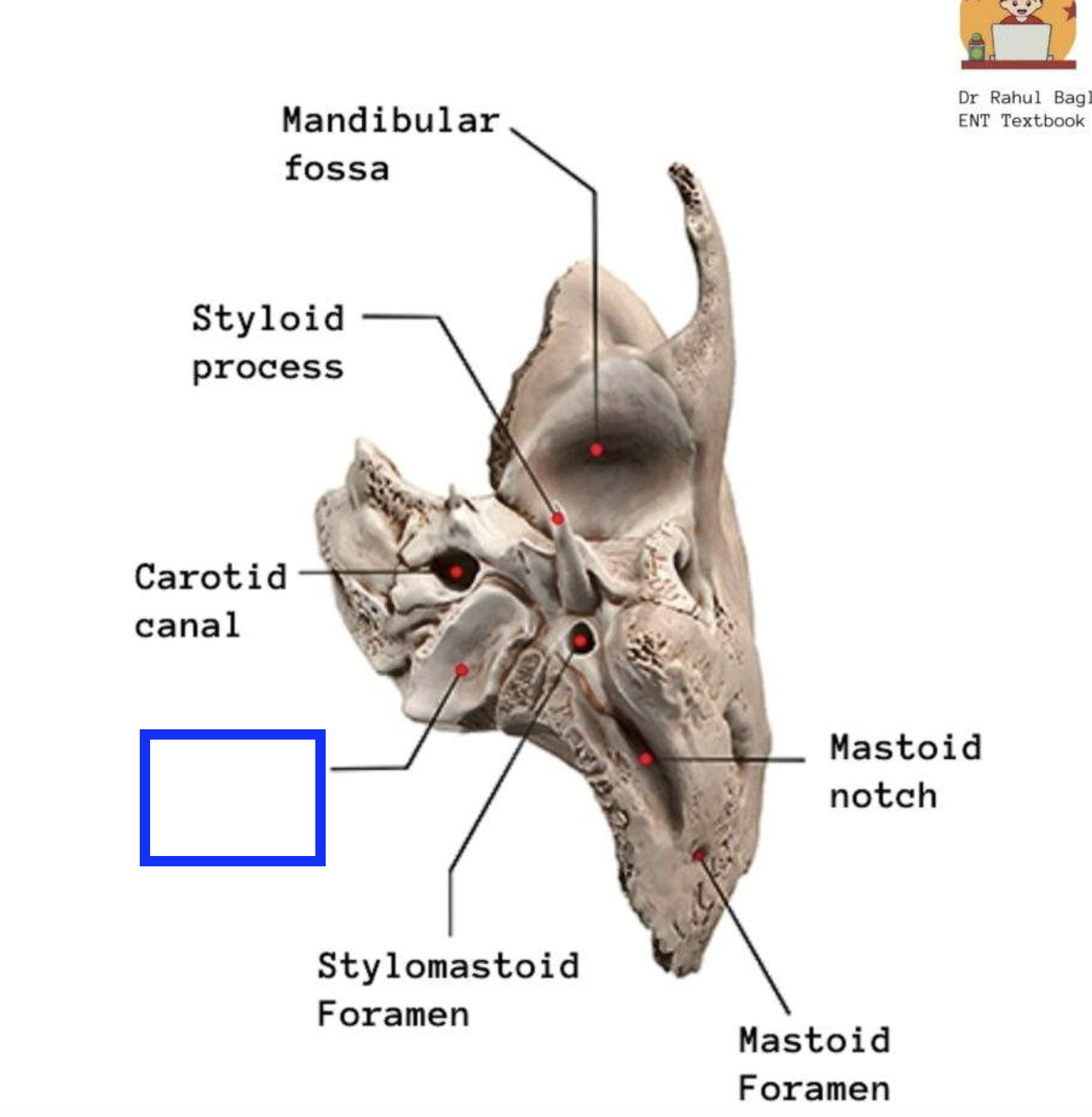
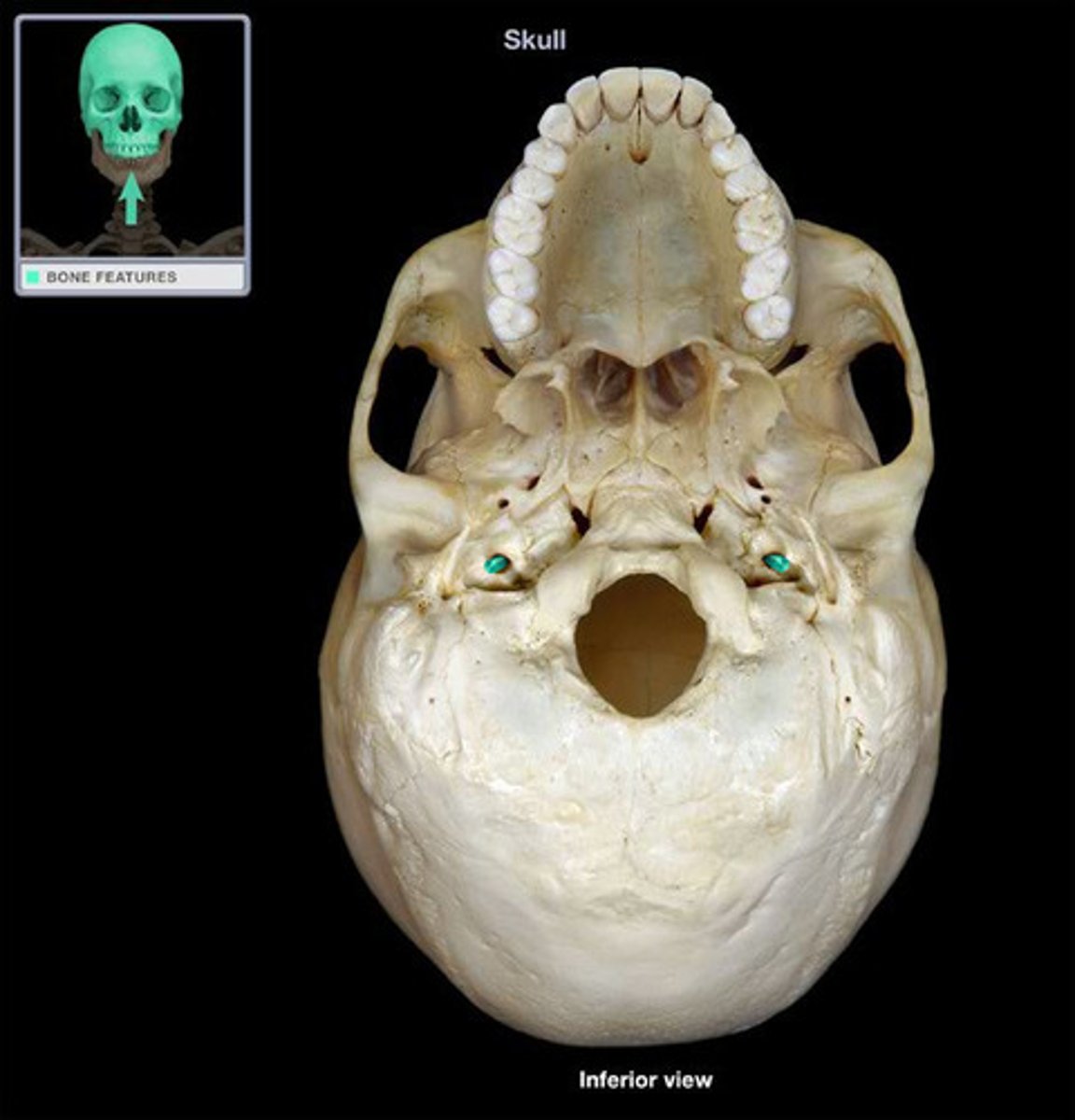
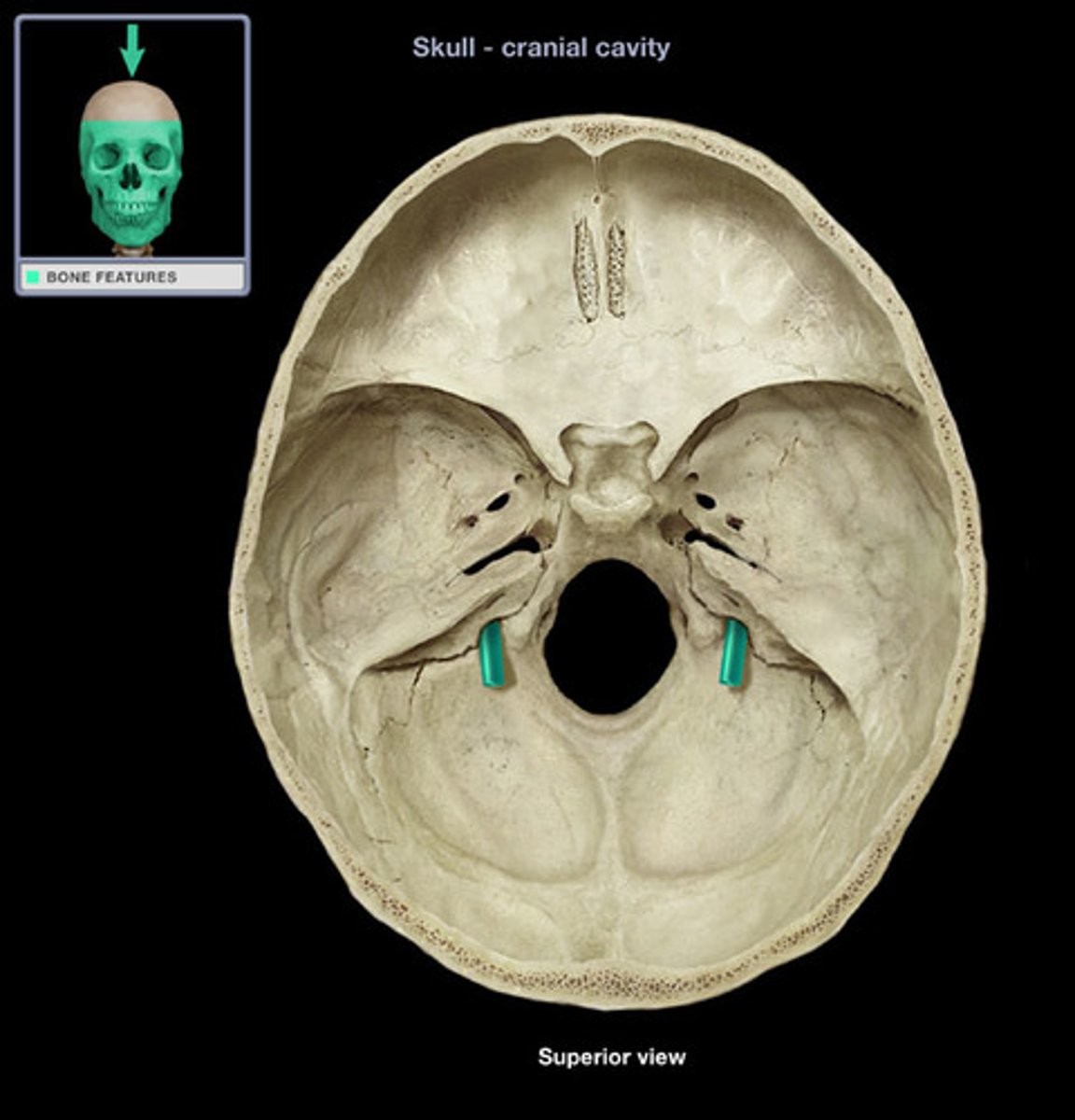
carotid canal (of TEMPORALS)
large circular canal that transmits the internal carotid artery, situated medial to the styloid process at the level of the sphenosquamosal suture, just anterior to jugular fossa
meningeal grooves (of TEMPORALS)
indentations on temporal bones from meningeal arteries (blood pathways in brain/skull's soft tissues)
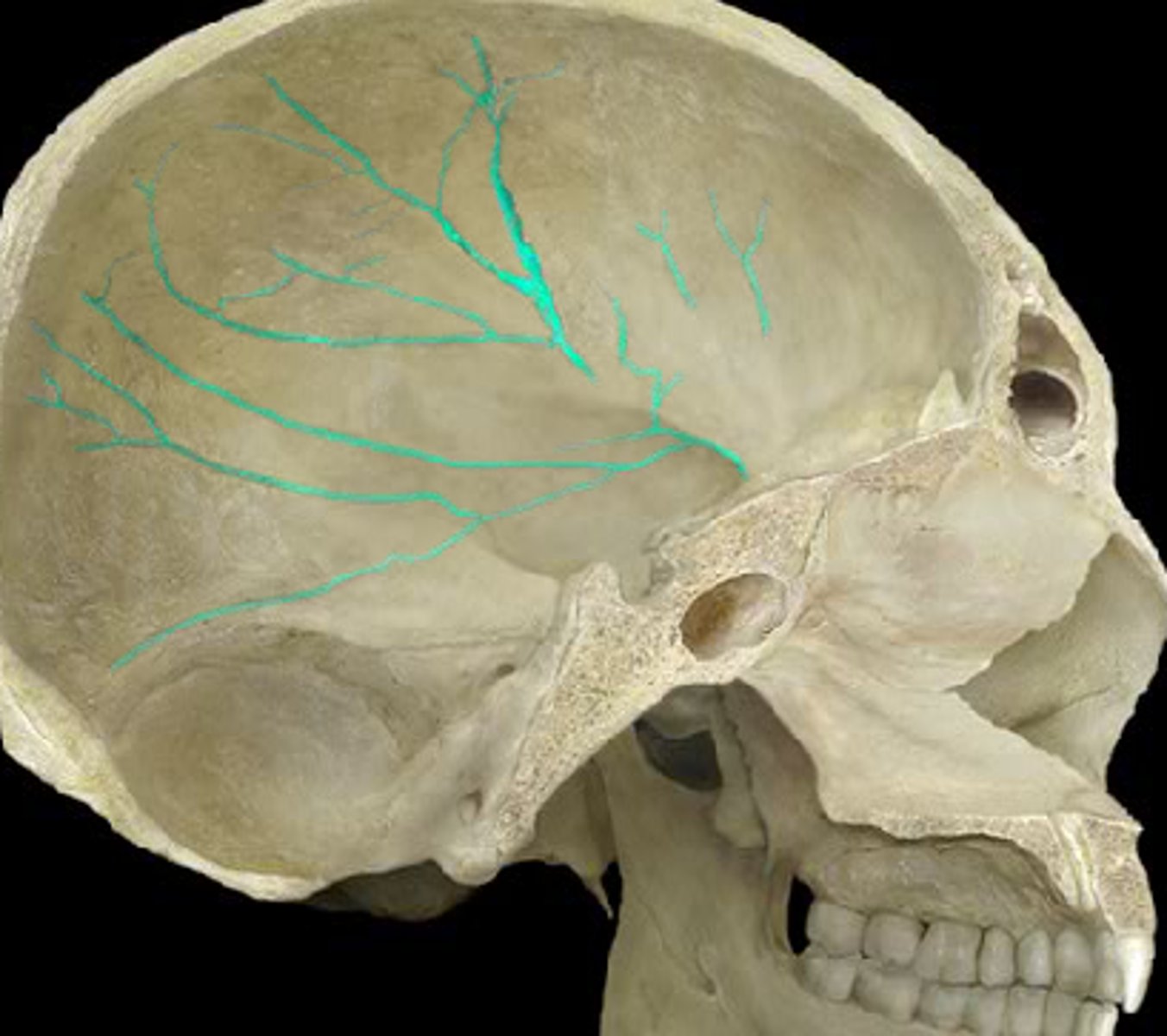
sigmoid sulcus (of TEMPORALS)
large, curving groove set at the posterior base of the petrous pyramid on the endocranial surface of mastoid part of TEMPORAL (3 in image)
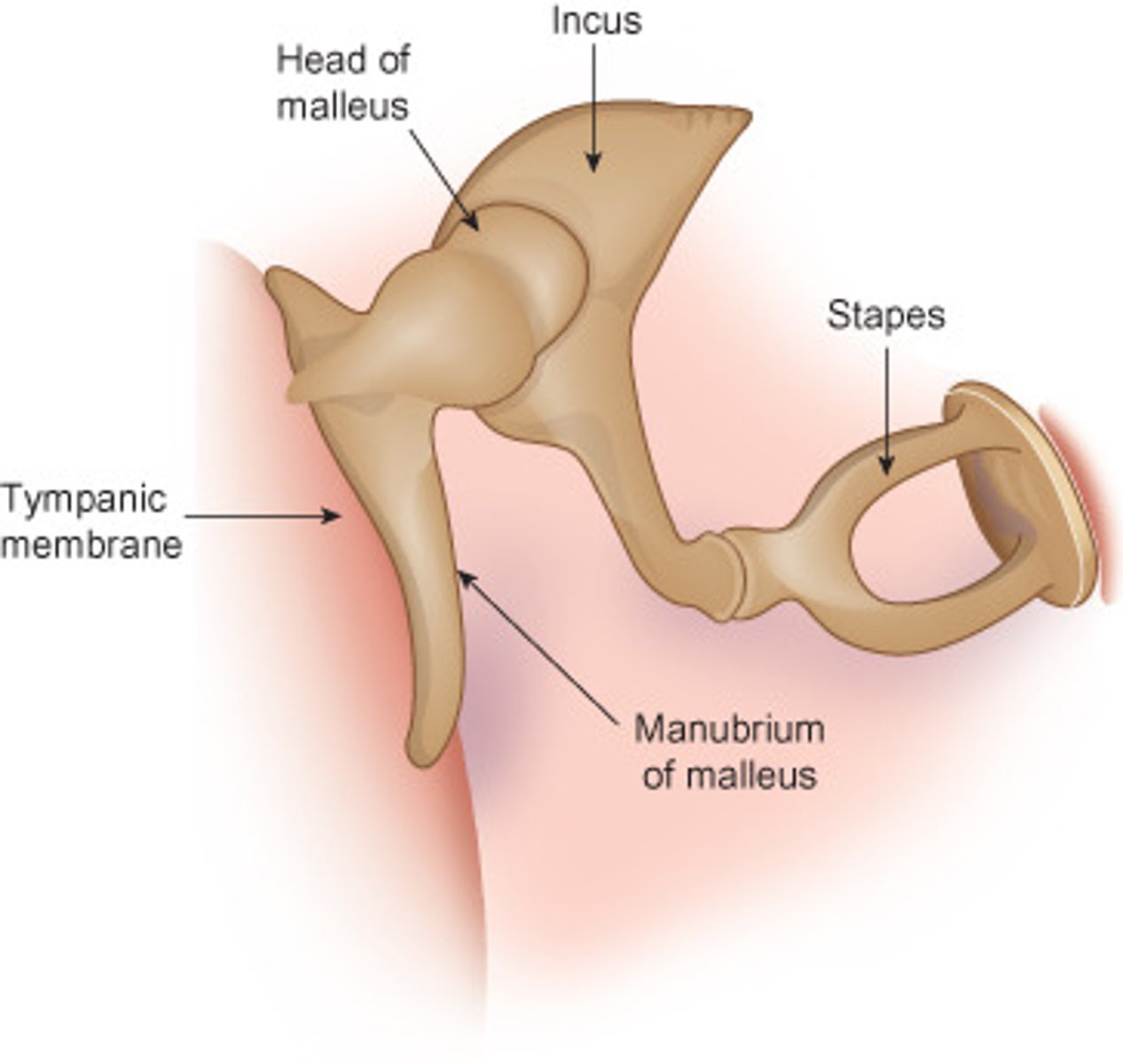
MALLEUS
hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
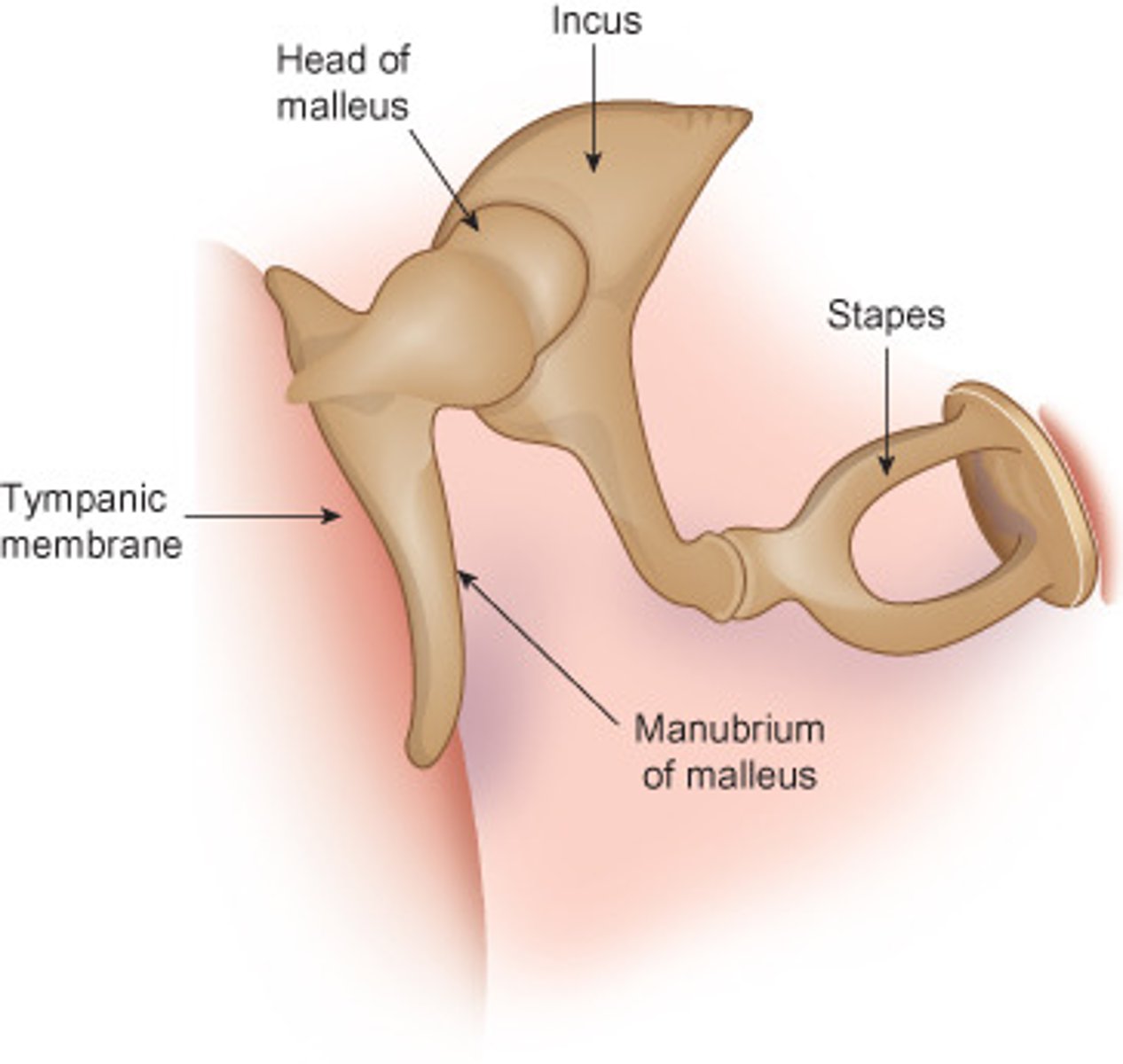
INCUS
anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
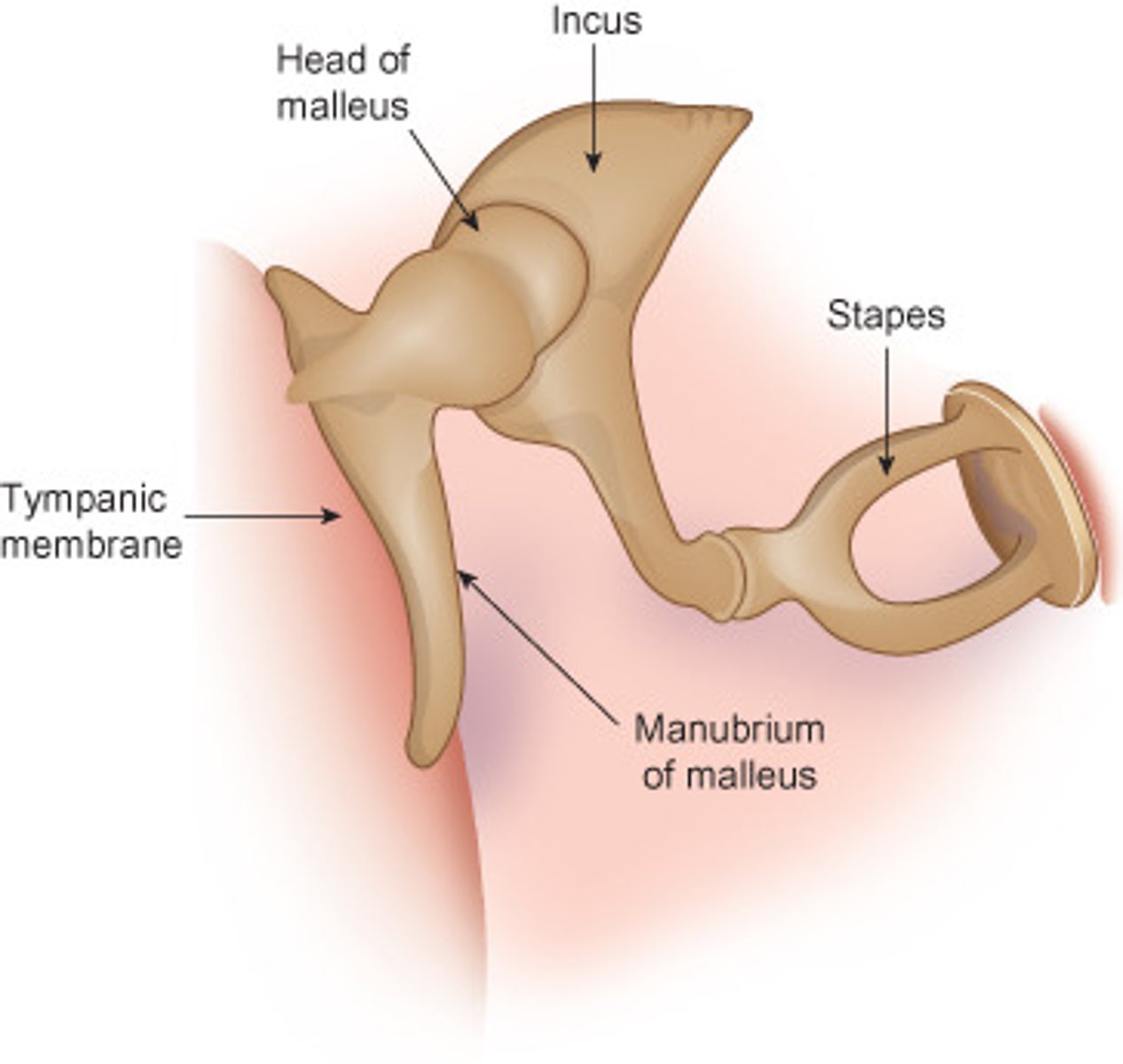
STAPES
stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
OCCIPITAL
rear of the cranium, articulates with TEMPORALS, SPHENOID, PARIETALS, C1
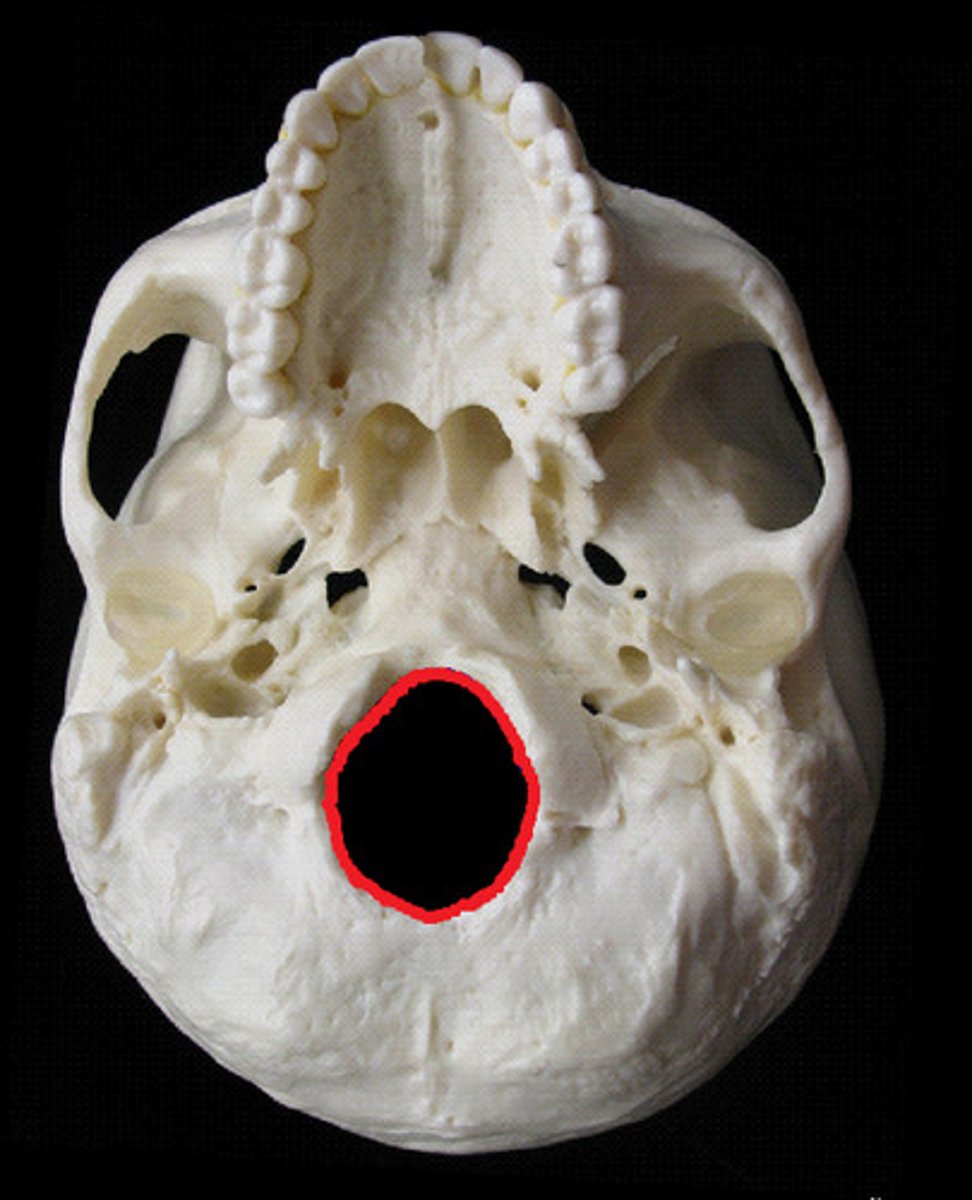
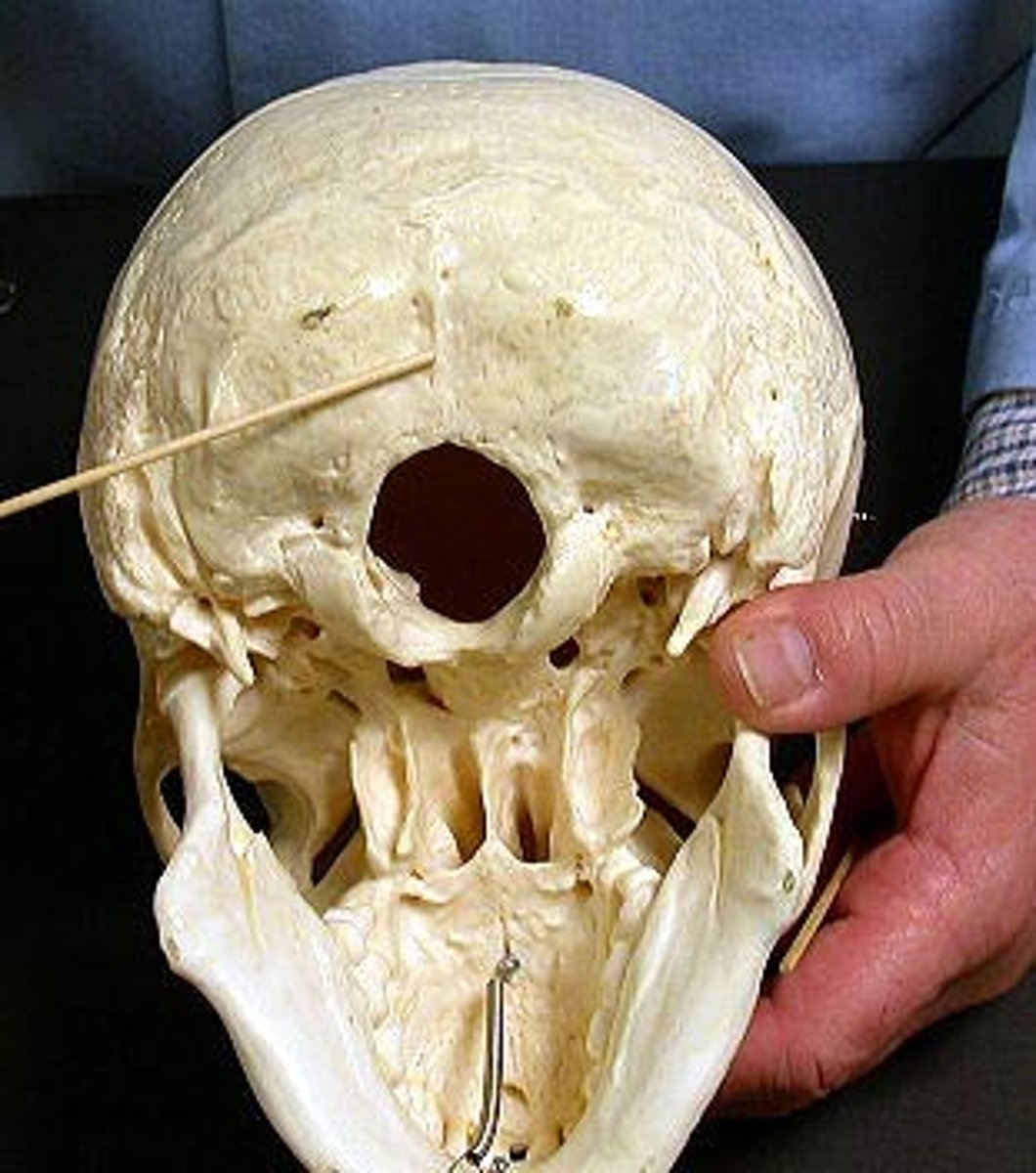
foramen magnum (of OCCIPITAL)
large hole in the OCCIPITAL through which the brain stem passes inferiorly into the vertebral canal
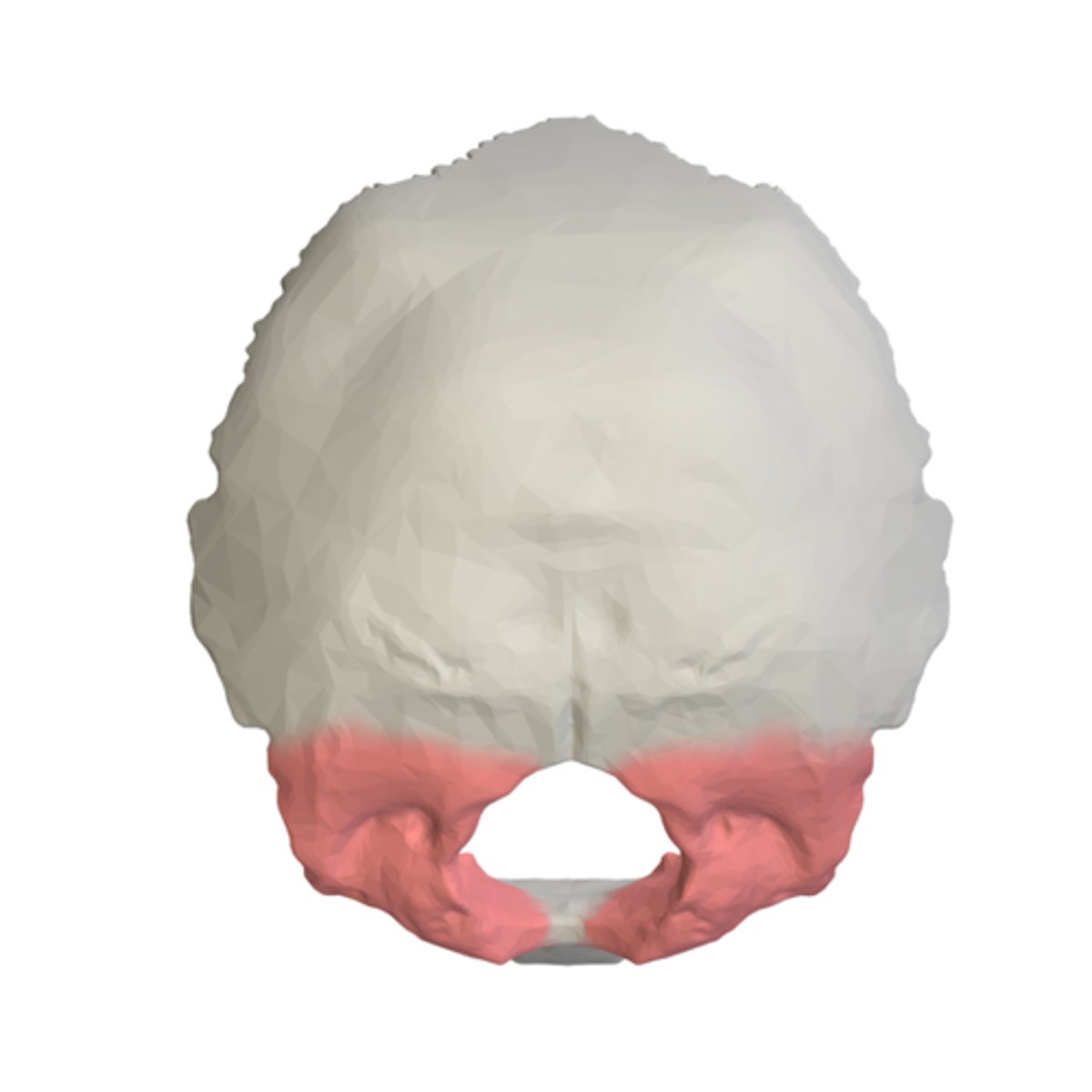
squamous portion (of OCCIPITAL)
largest portion, large plate of bone posterior and superior to the foramen magnum
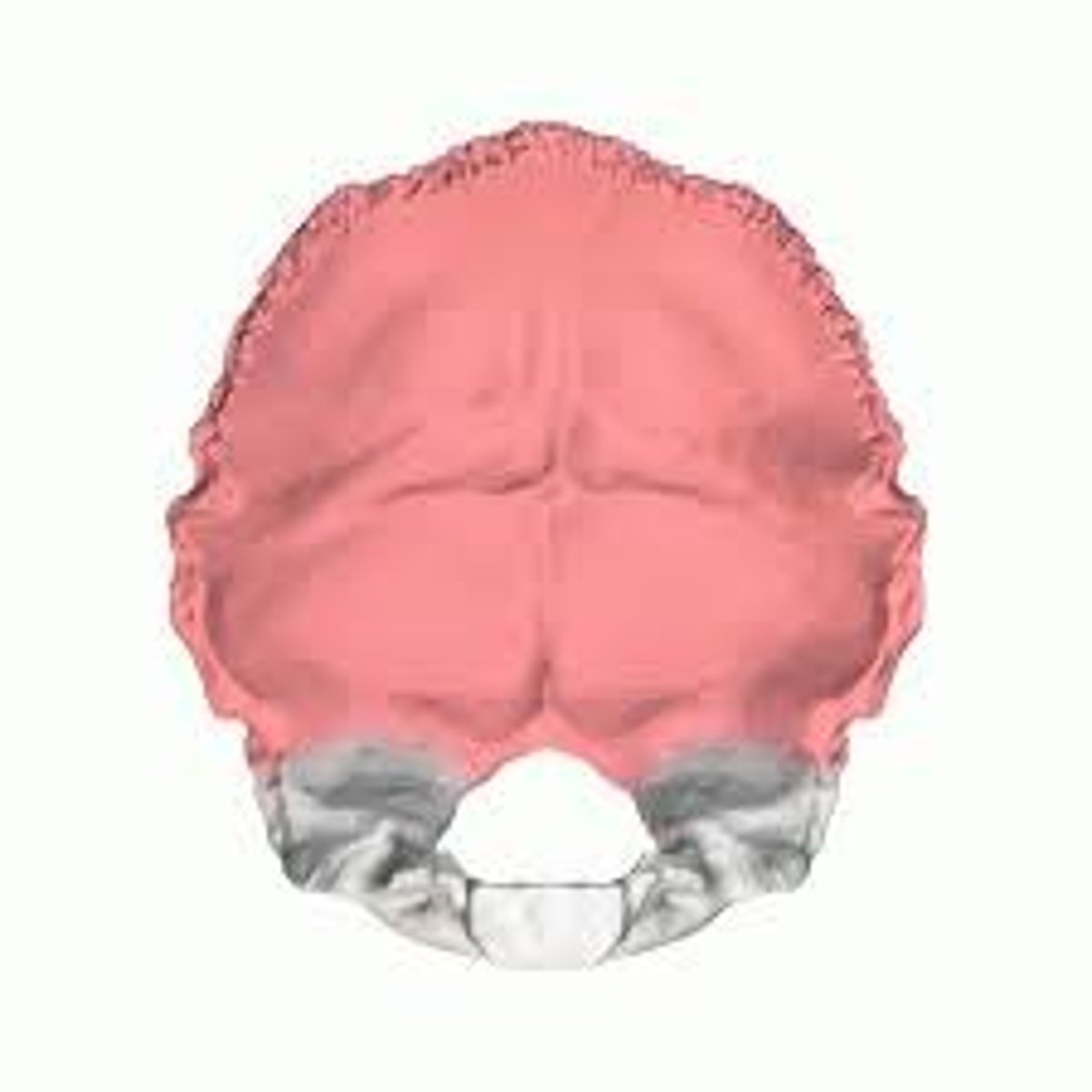
occipital planum, nuchal planum (of OCCIPITAL)
part of OCCIPITAL squamous portion that lies above the superior nuchal lines (red star)/ section of squamous portion inferior to the lines (blue star)
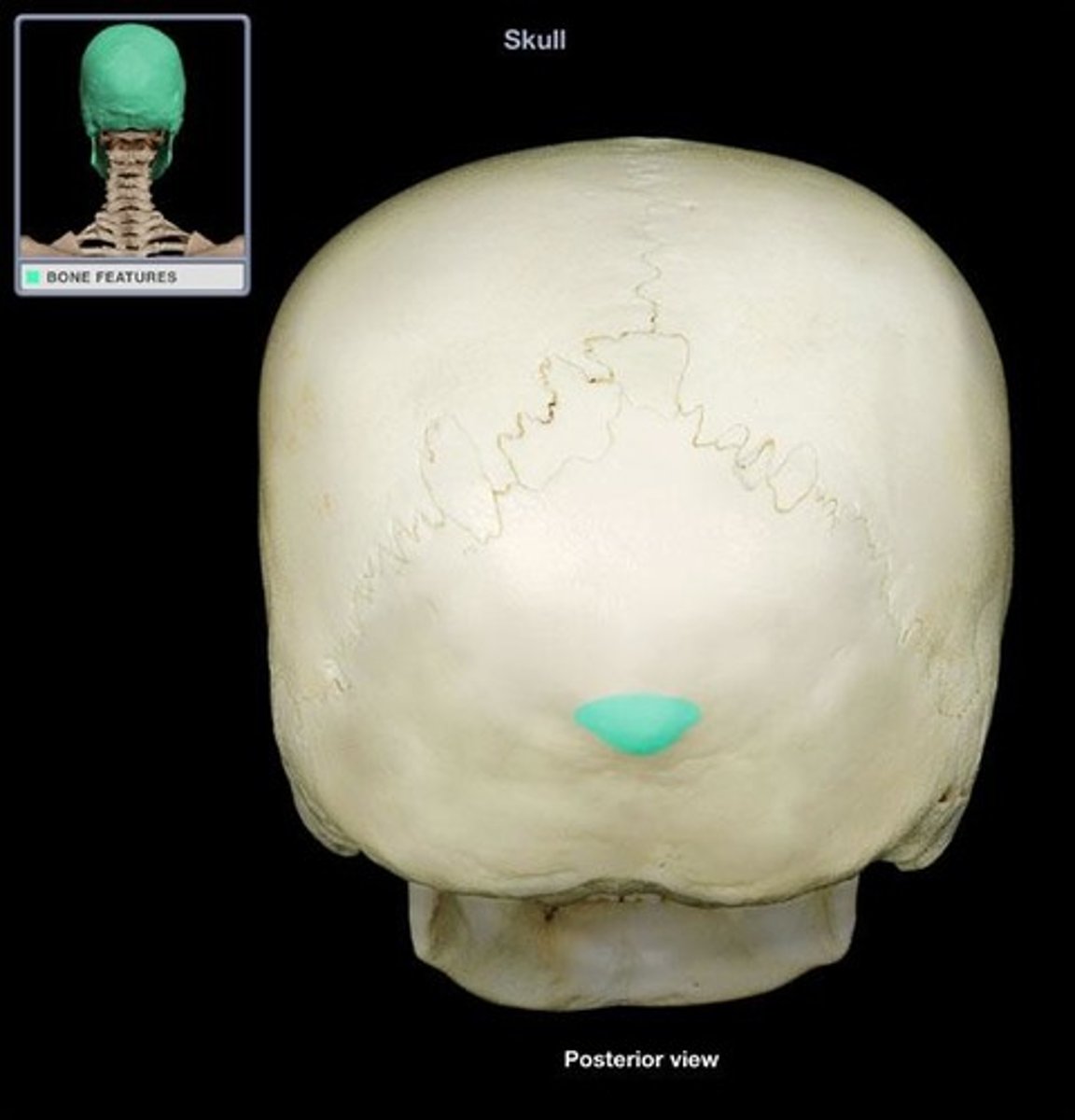
external occipital protuberance (of OCCIPITAL)
lies on ectocranial midline where the occipital and nuchal planes meet, *nuchal crest extends from this feature
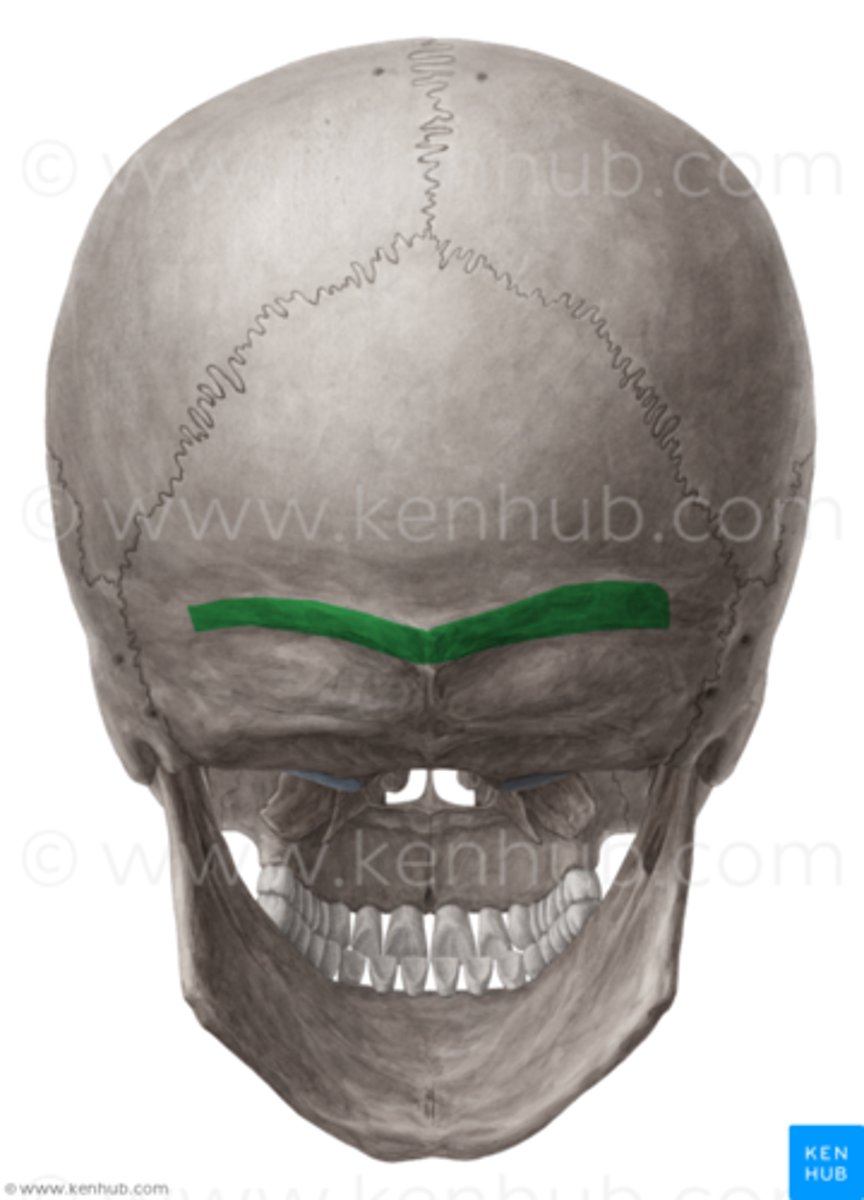
superior nuchal lines (of OCCIPITAL)
lies to either side of the midline on the ectocranial surface of the squamous portion, nuchal plane and occipital planes merge at these superiorly convex lines
inferior nuchal lines (of OCCIPITAL)
parallel to the superior lines, located about midway on the ectocranial nuchal plane
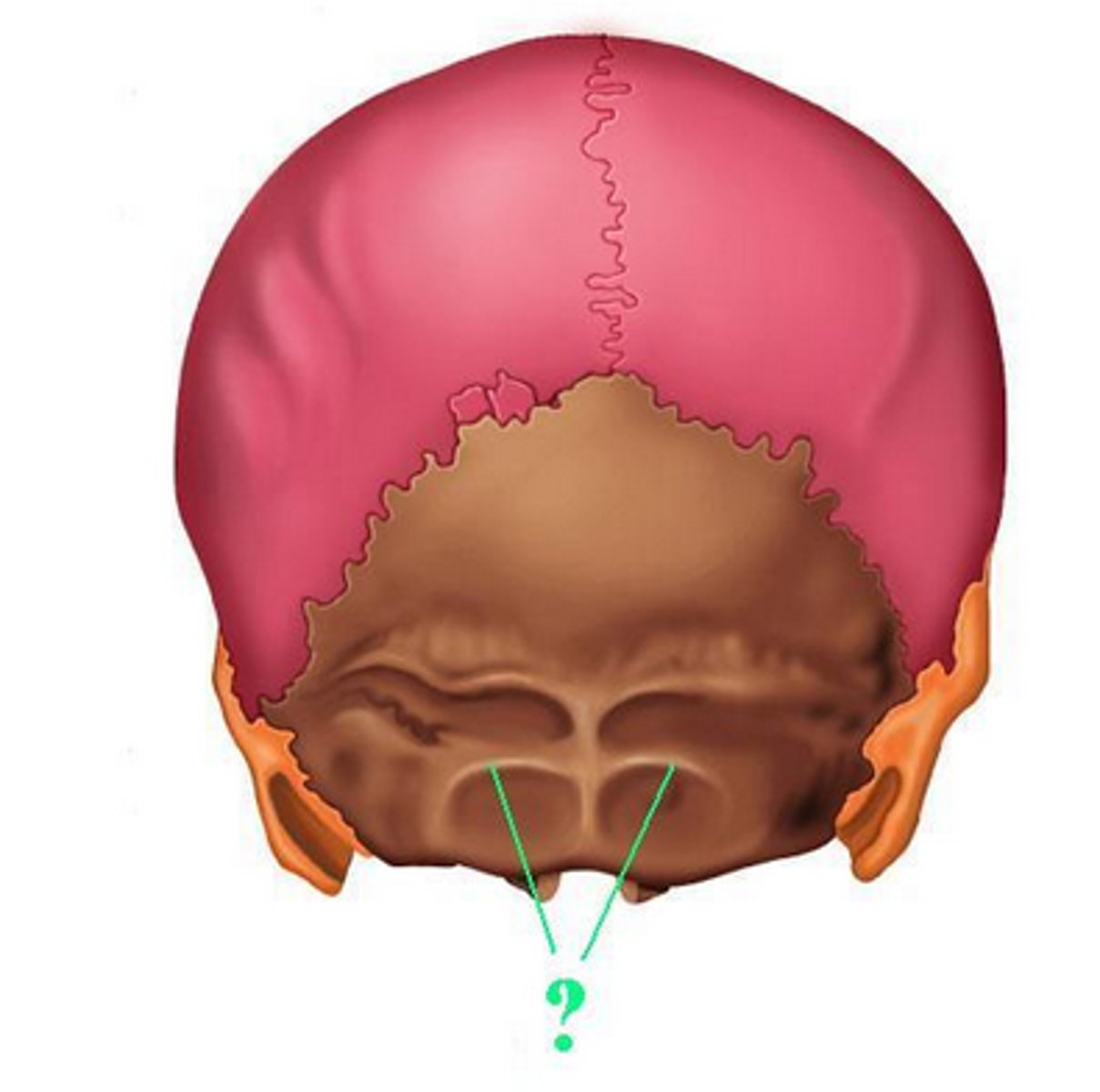
external occipital crest/median nuchal line (of OCCIPITAL)
median line/crest that passes between the right and left nuchal musculature, stretches from external occipital protuberance to the rear of the foramen magnum
basilar part (of OCCIPITAL)
thick, square projection anterior to the foramen magnum, articulates with petrous portion of both TEMPORALS and with SPHENOID via sphenooccipital suture
lateral/condylar parts (of OCCIPITAL)
lie to either side of the foramen magnum, articulating with the temporals
occipital condyles (of OCCIPITAL)
raised oval structures on either side of the foramen magnum, inferior surfaces are convex, articulate with C1
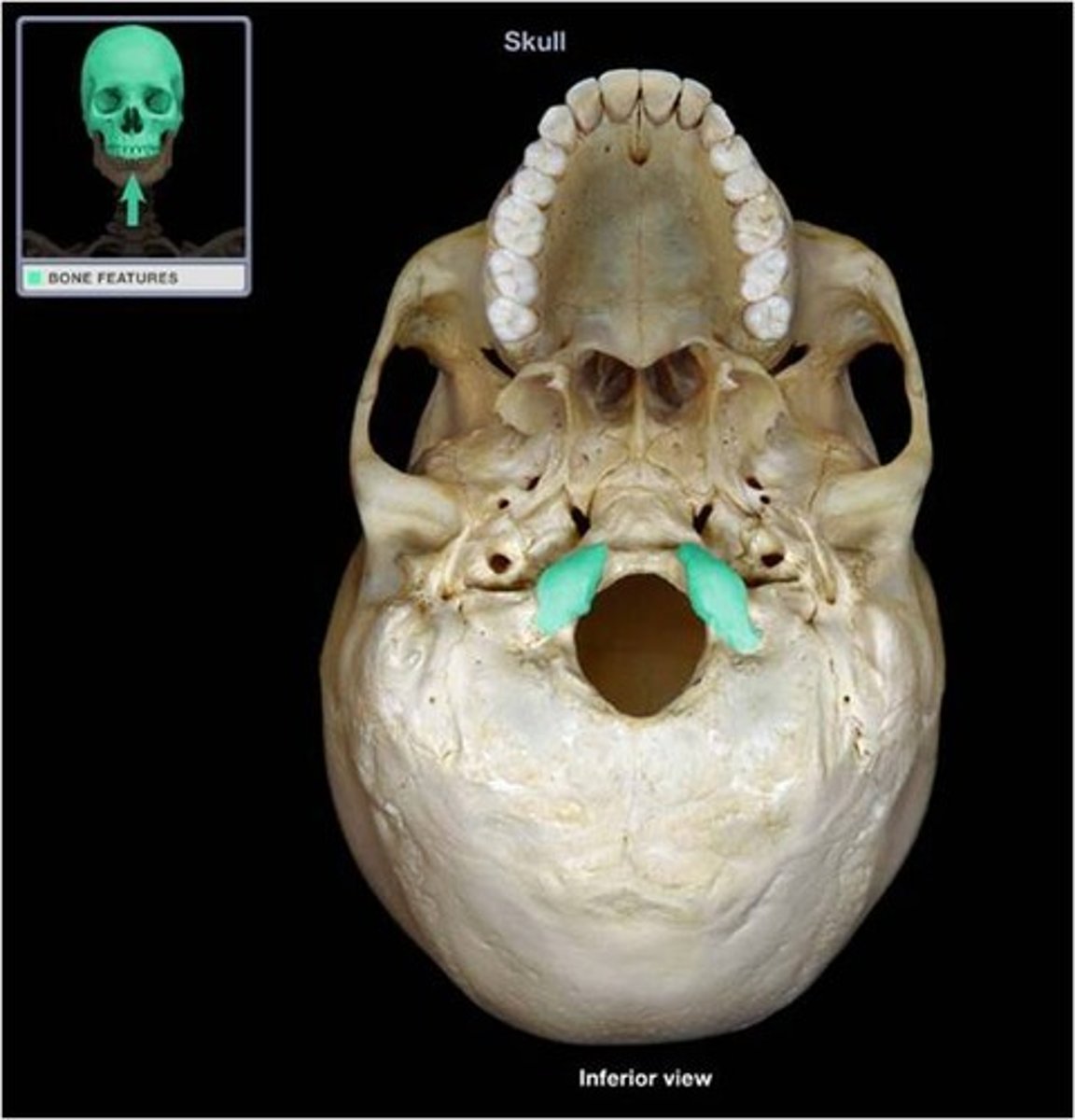
condylar fossae (of OCCIPITAL)
ectocranial depressions immediately posterior to the condyles, receive posterior margin of superior facet of C1
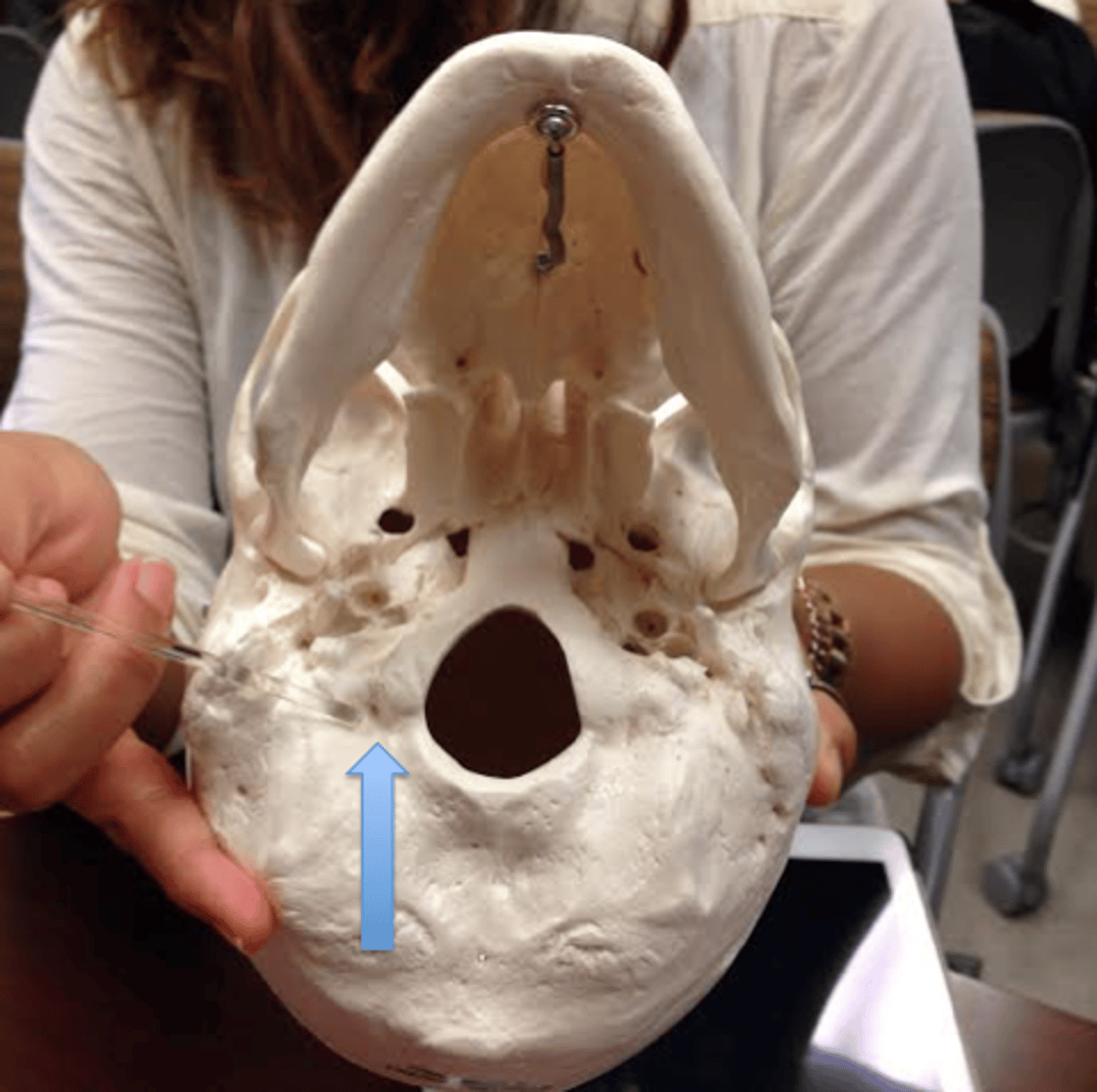
condylar foramina/canals (of OCCIPITAL)
perforate the occipital at the depth of the condylar fossae
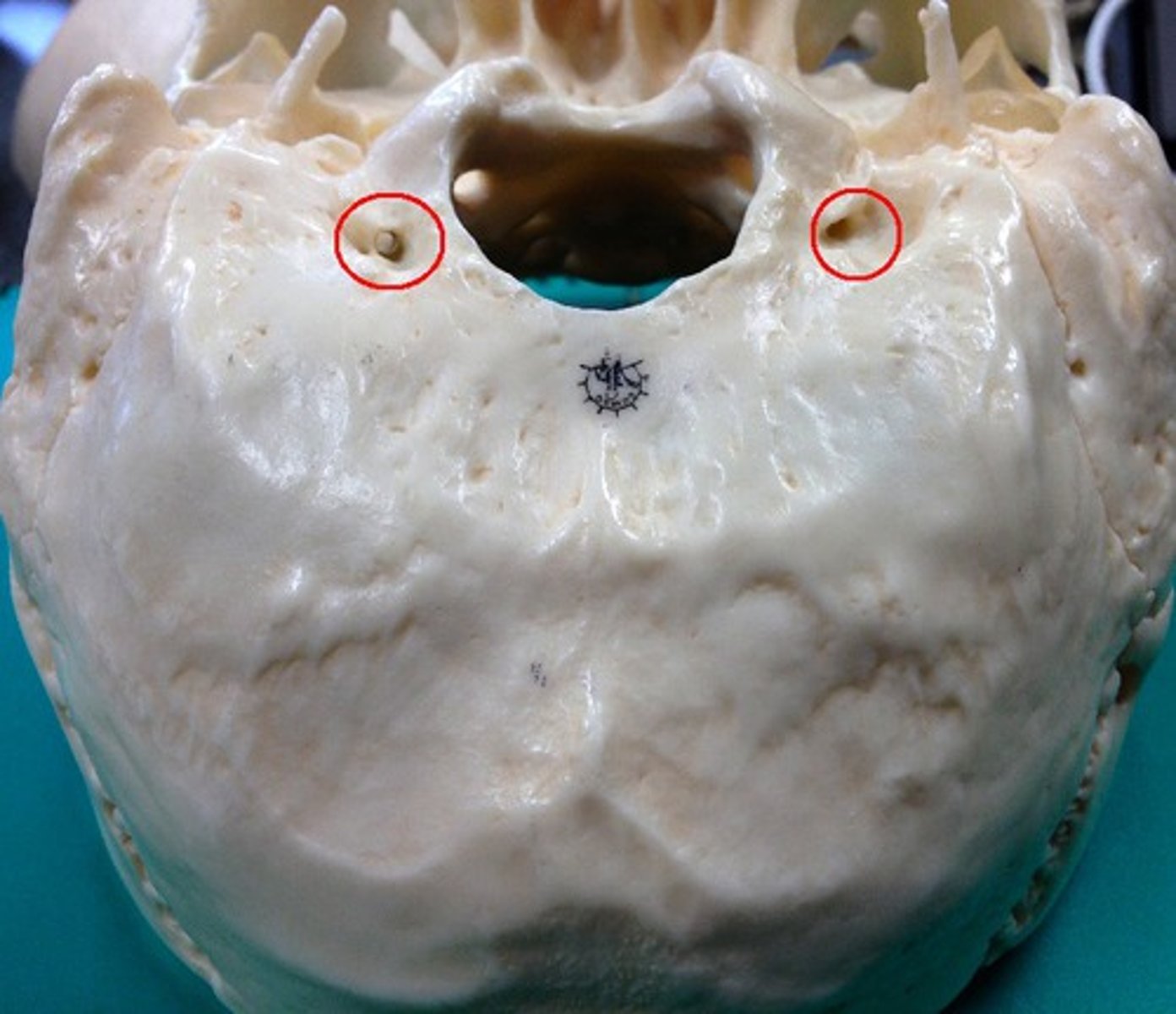
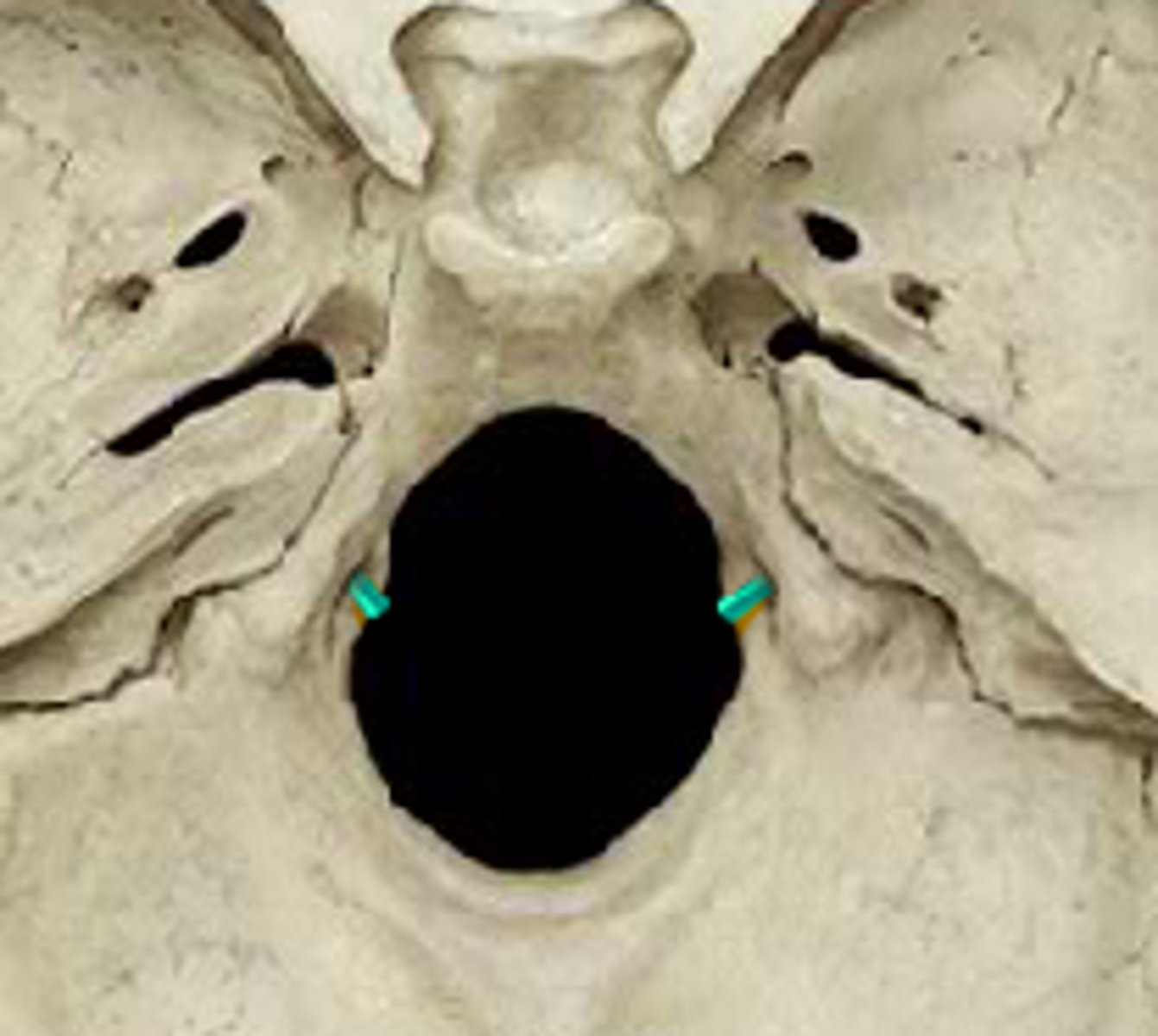
hypoglossal canals (of OCCIPITAL)
tunnels through the anterior part of the base of each condyle, exit for hypoglossal nerve
jugular processes (of OCCIPITAL)
laterally directed corners of the bone placed lateral to the condyles, the tips of these processes lie at the anteriormost point along the occipitomastoid suture
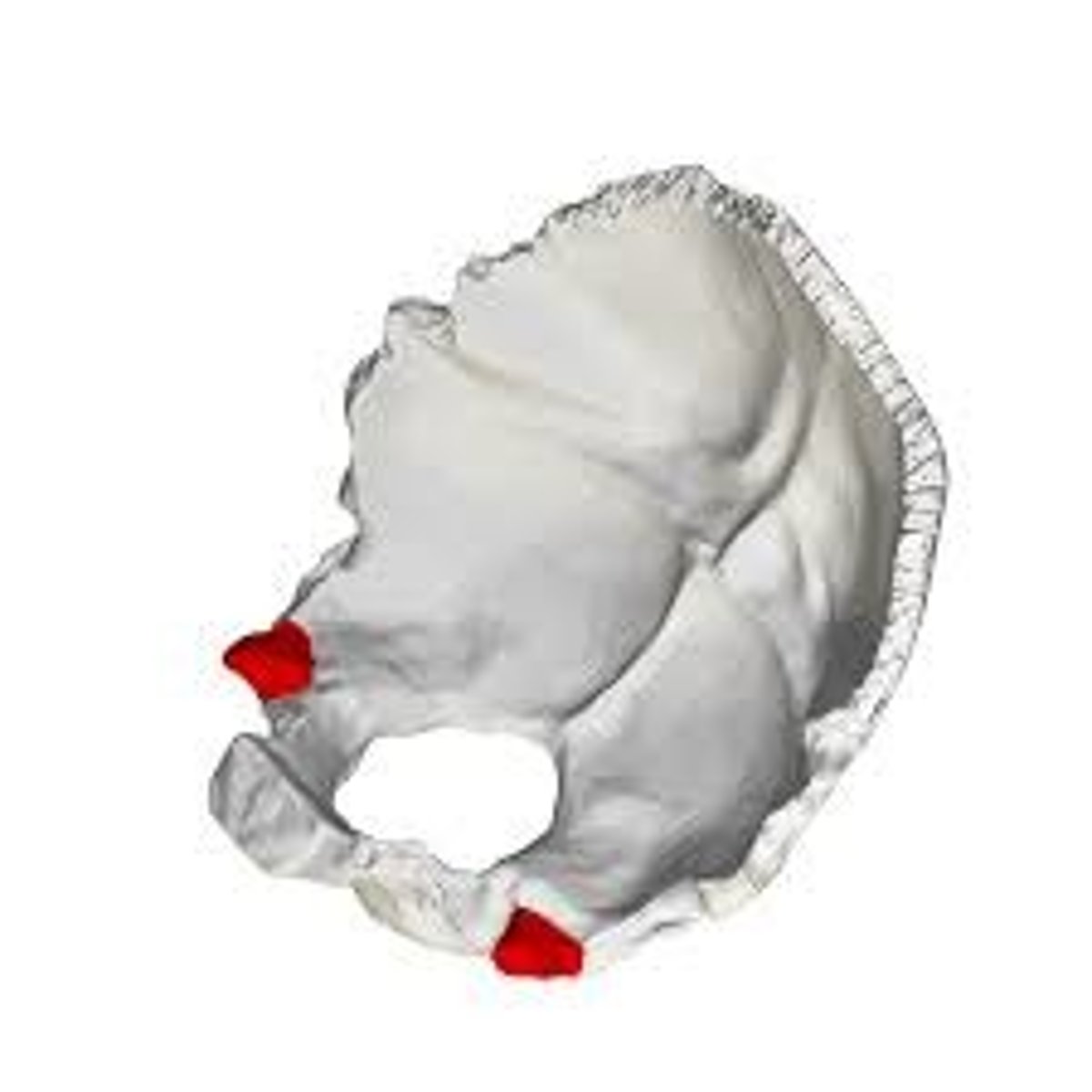
jugular notch/foramen (of OCCIPITAL)
excavated into the anterior surface of the jugular process, this notch forms the posterior half of the jugular foramen
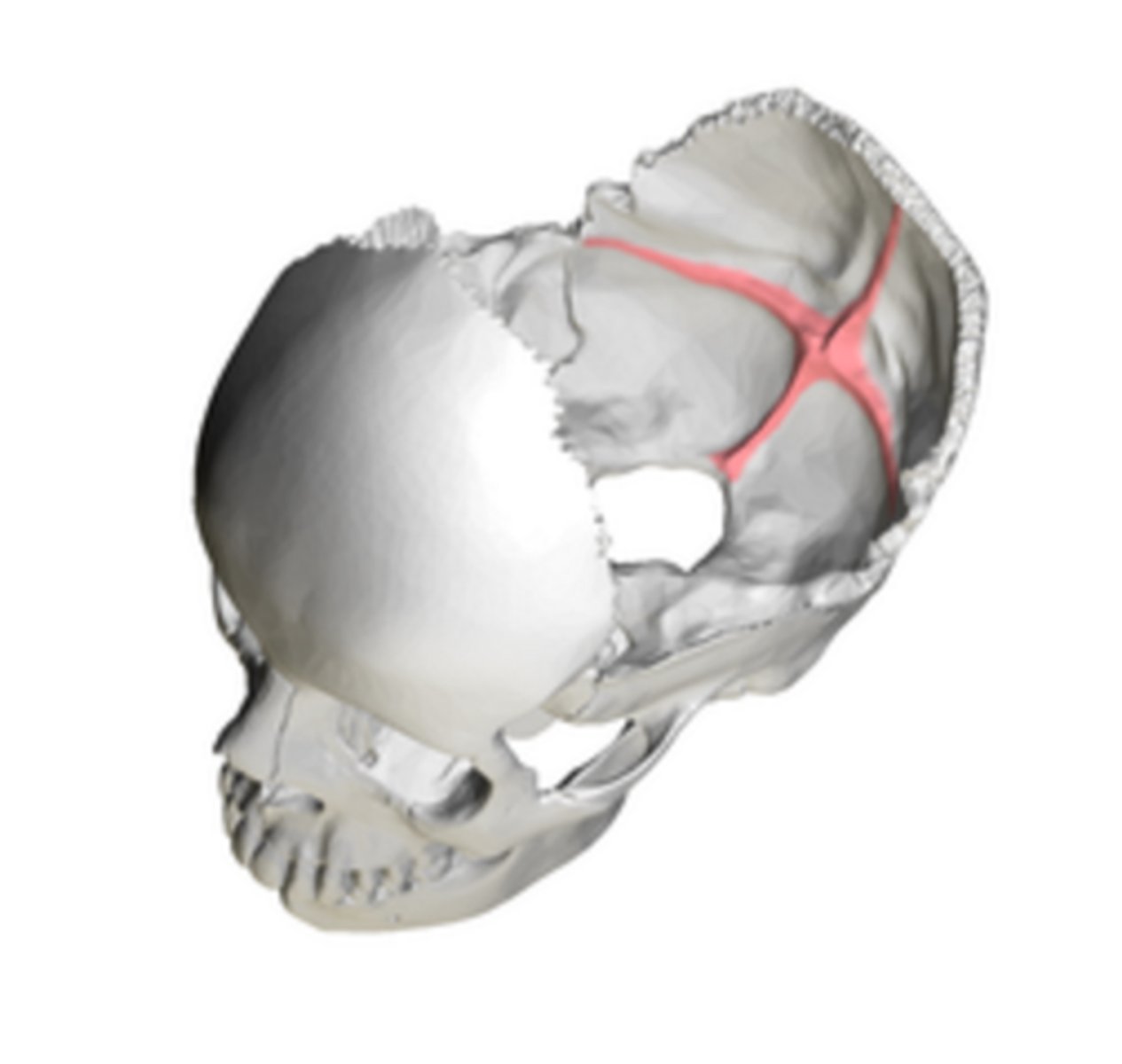
cruciform eminence (of OCCIPITAL)
divides the endocranial surface of the occipital squama into four fossae, cross-shaped (think crucifix) -- internal occipital protuberance is center point
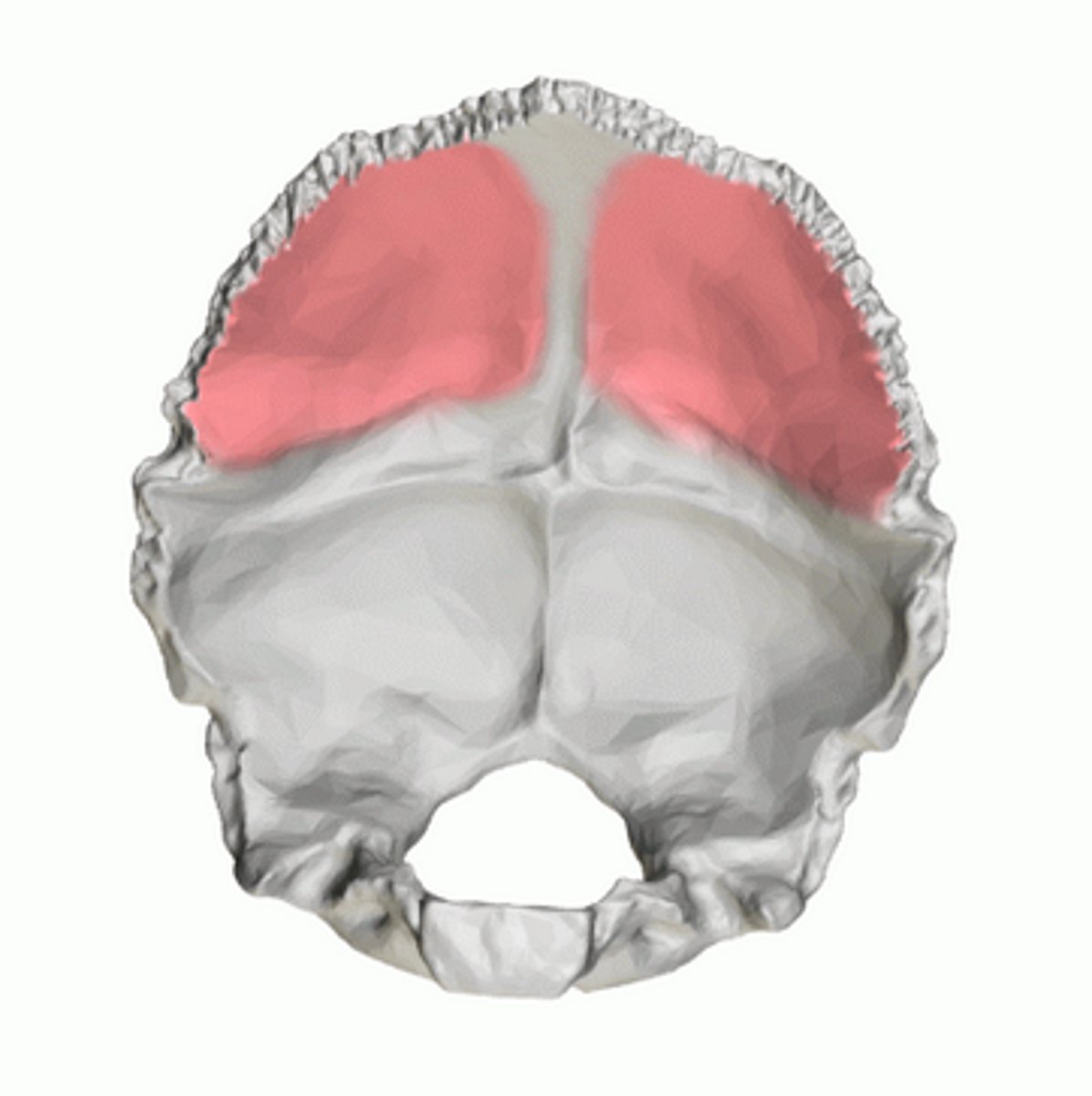
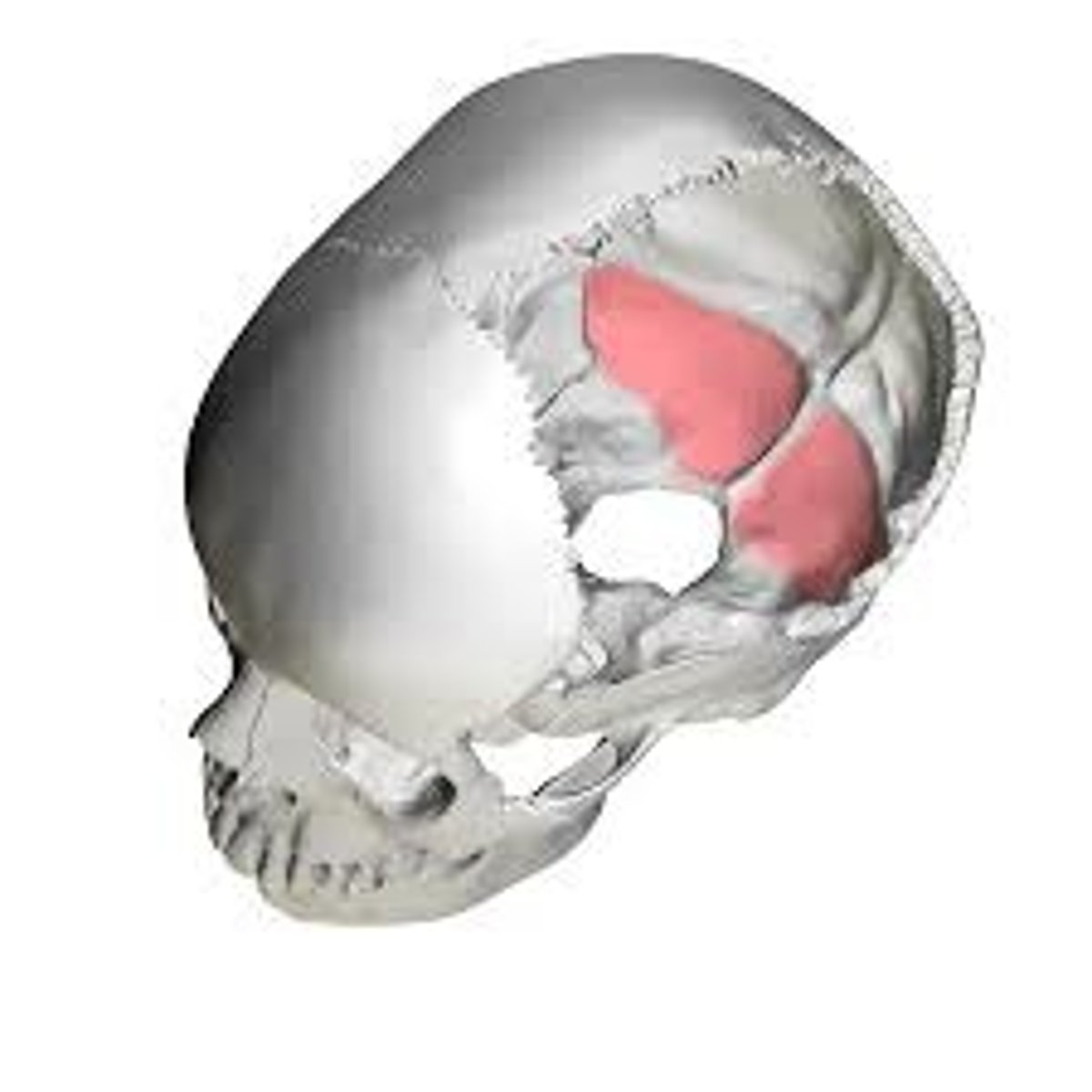
cerebral fossae (of OCCIPITAL)
triangular depressions below the lambdoidal suture on the endocranial surface of the OCCIPITAL, houses occipital lobes of cerebrum
cerebellar fossae (of OCCIPITAL)
occupy inferior part of endocranial surface of the occipital squama, houses cerebellar lobes
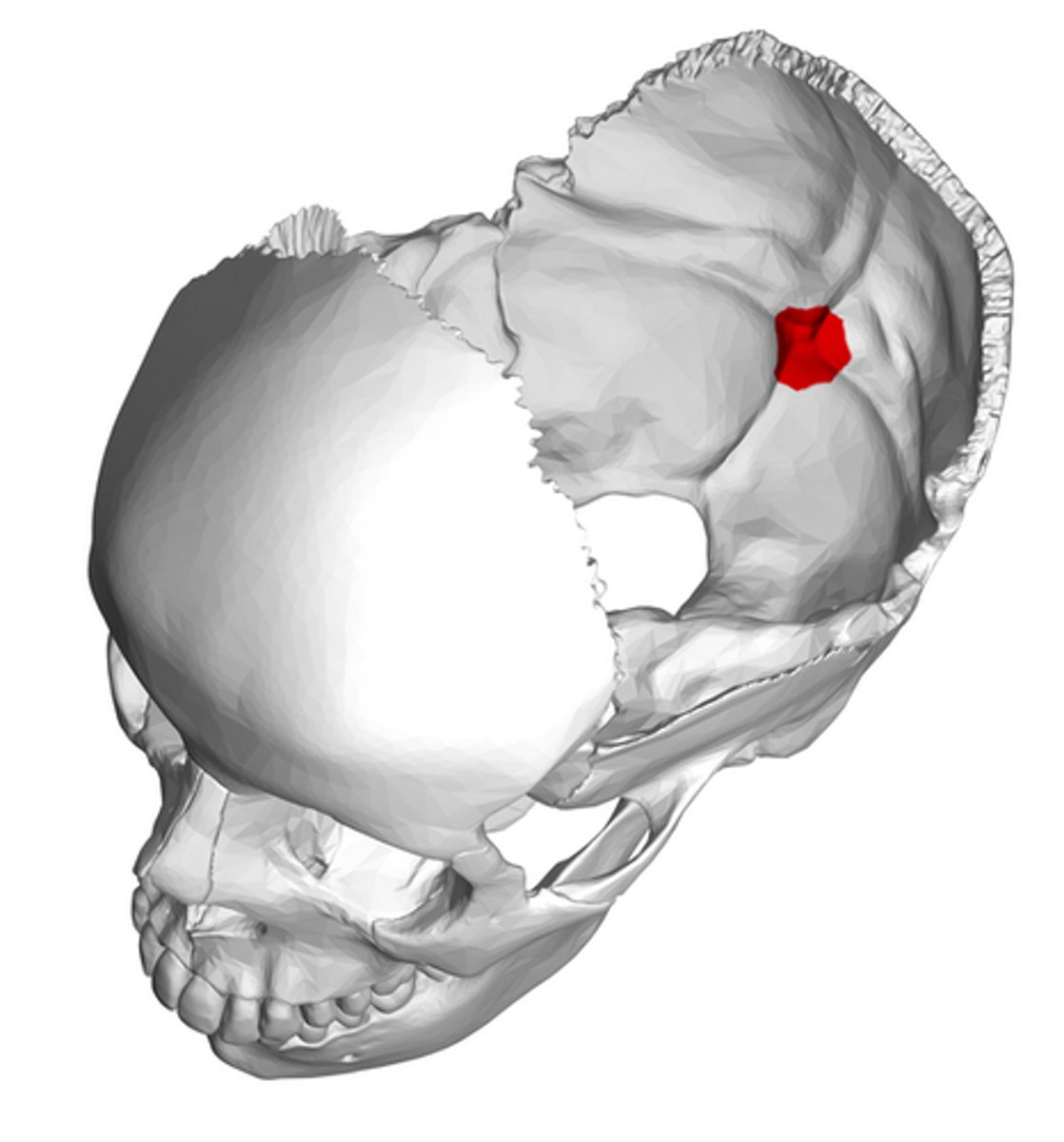
internal occipital protuberance (of OCCIPITAL)
lies at the center of the cruciform eminence
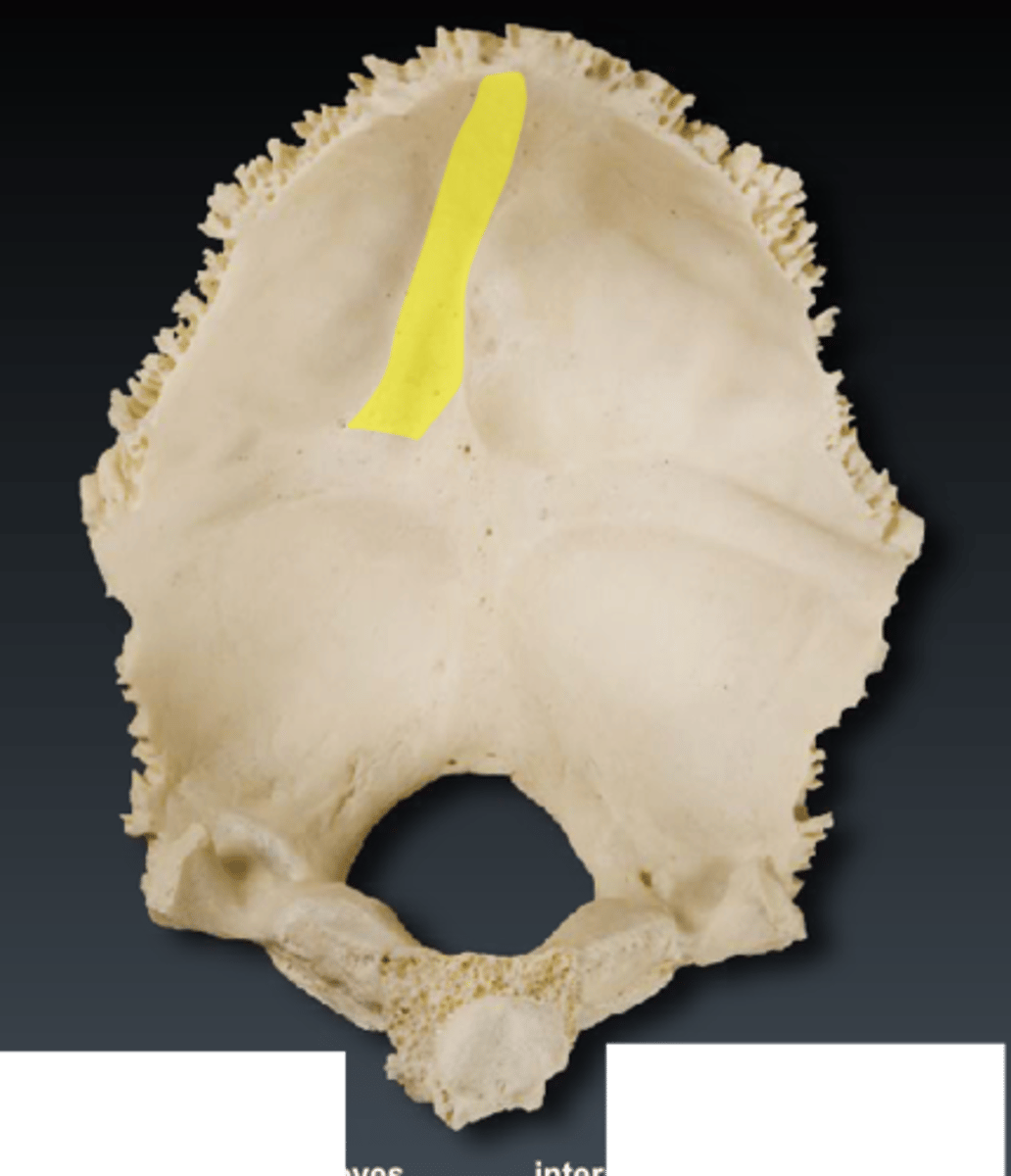
occipital (sagittal) sulcus (of OCCIPITAL)
passes superiorly from the internal occipital protuberance, deep endocranial groove marking the posterior extension of the sagittal sulcus
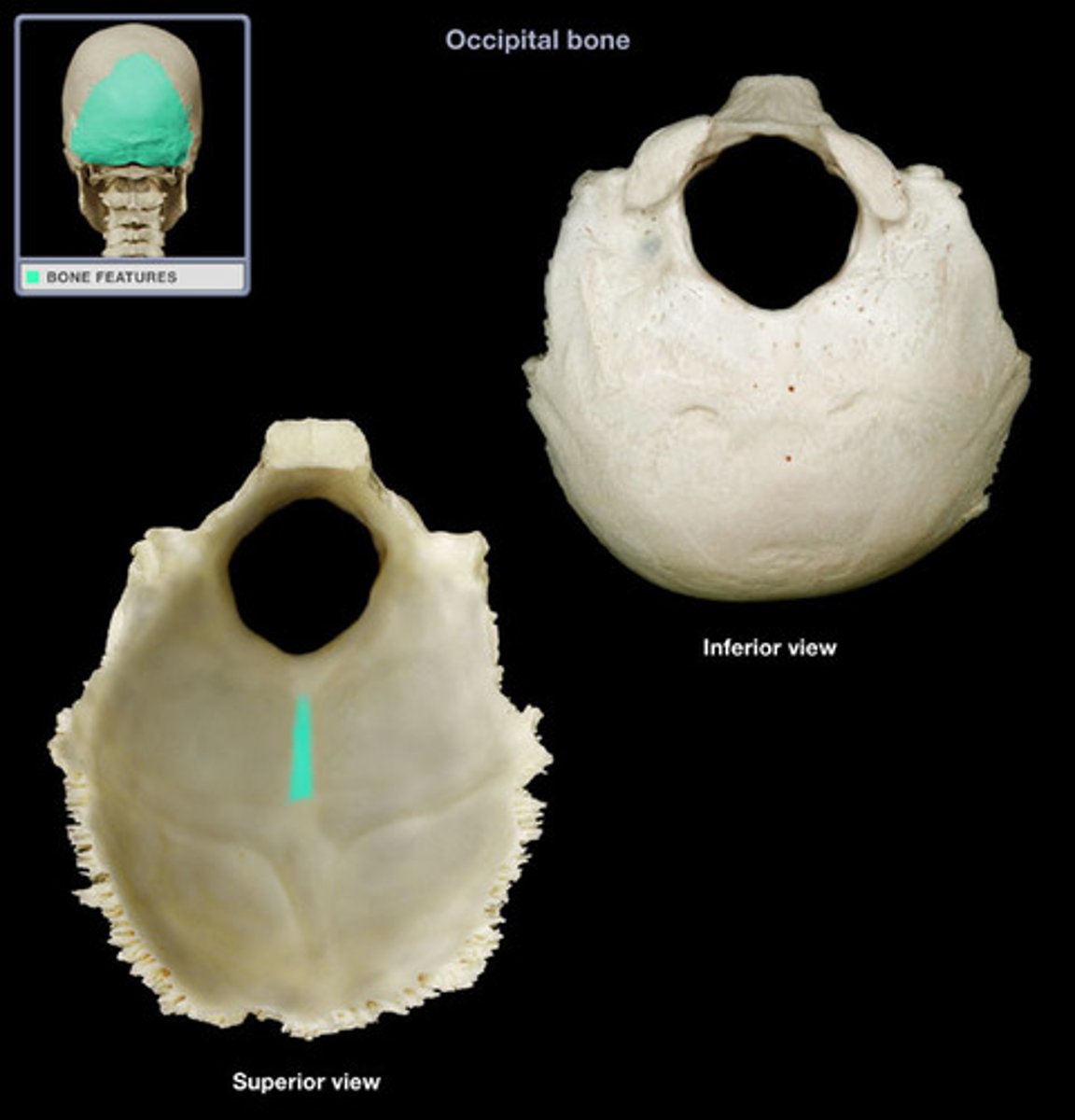
internal occipital crest (of OCCIPITAL)
inferior arm of the cruciform eminence
transverse sulci (sulcuses) (of OCCIPITAL)
form the transverse arms of the cruciform eminence, house the transverse sinuses
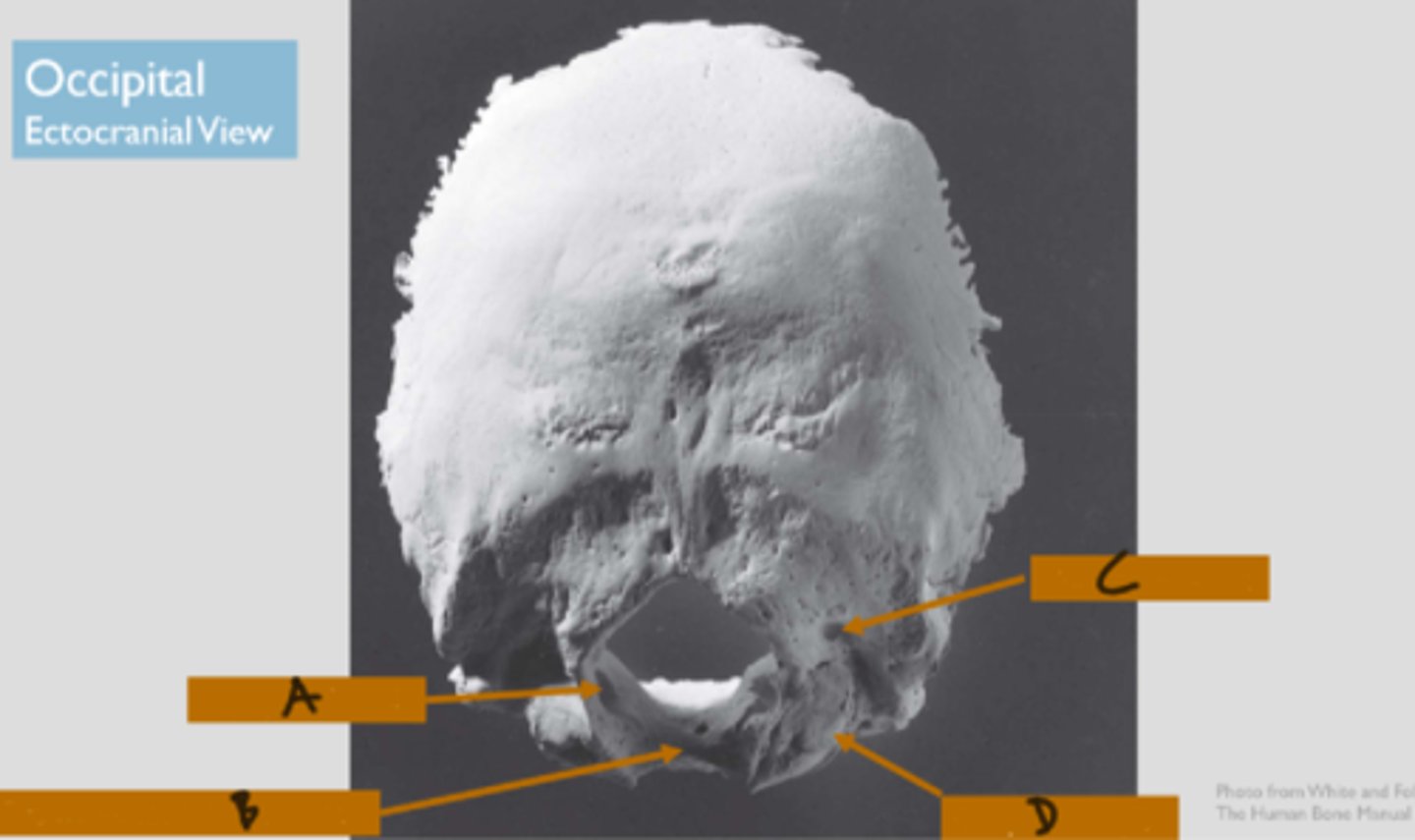
groove for the medulla oblongata (of OCCIPITAL)
hollowing on the endocranial surface of the basilar part of the occipital, the clivis (B in image)
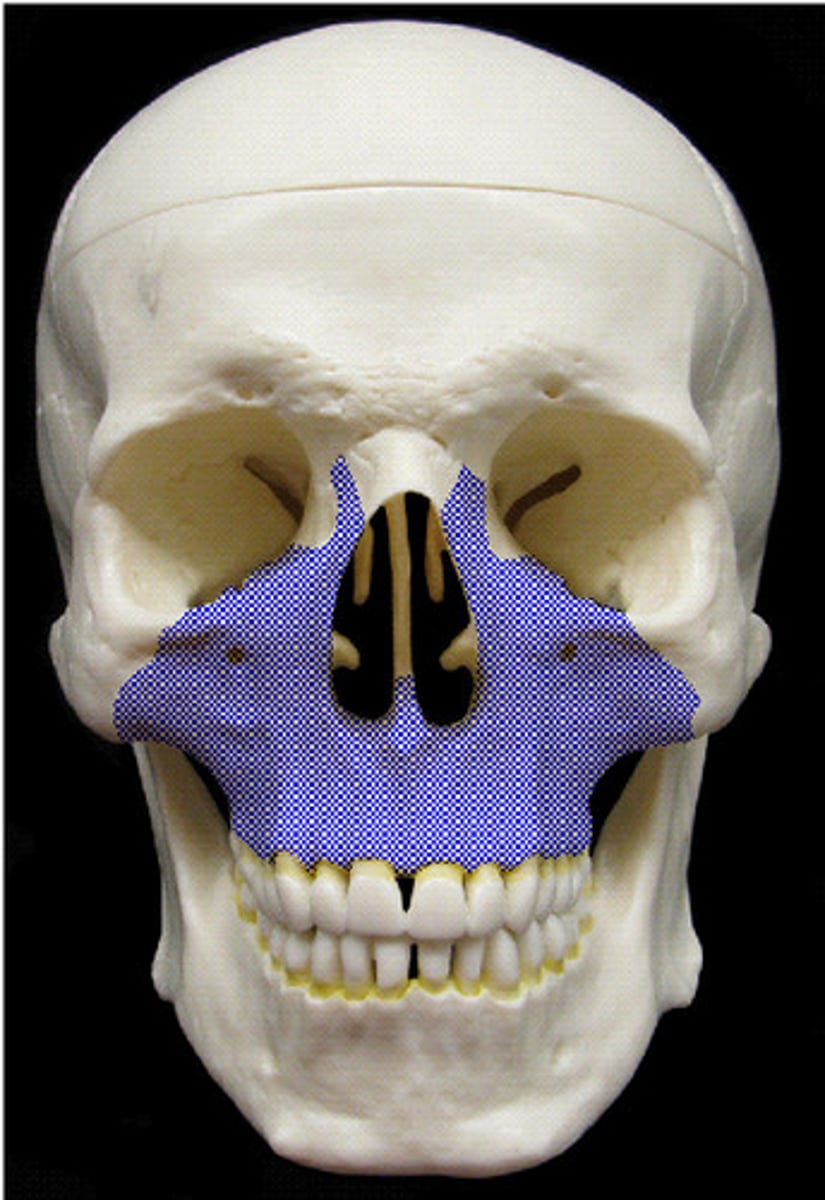
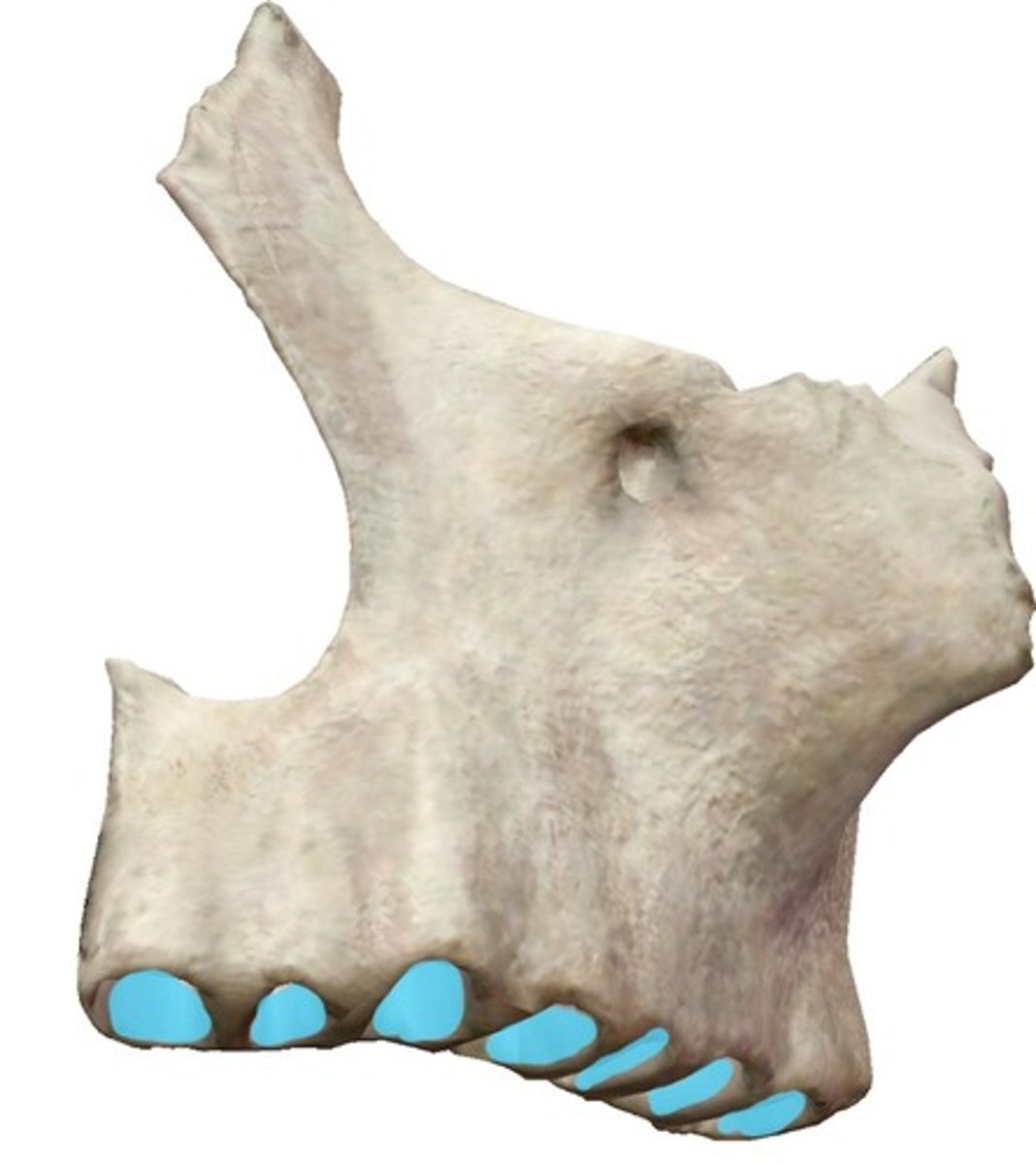
MAXILLAE
the two fused bones forming the upper jaw (upper teeth/alveoli)
alveolar process (of MAXILLAE)
horizontal portion of the maxilla that holds the tooth roots
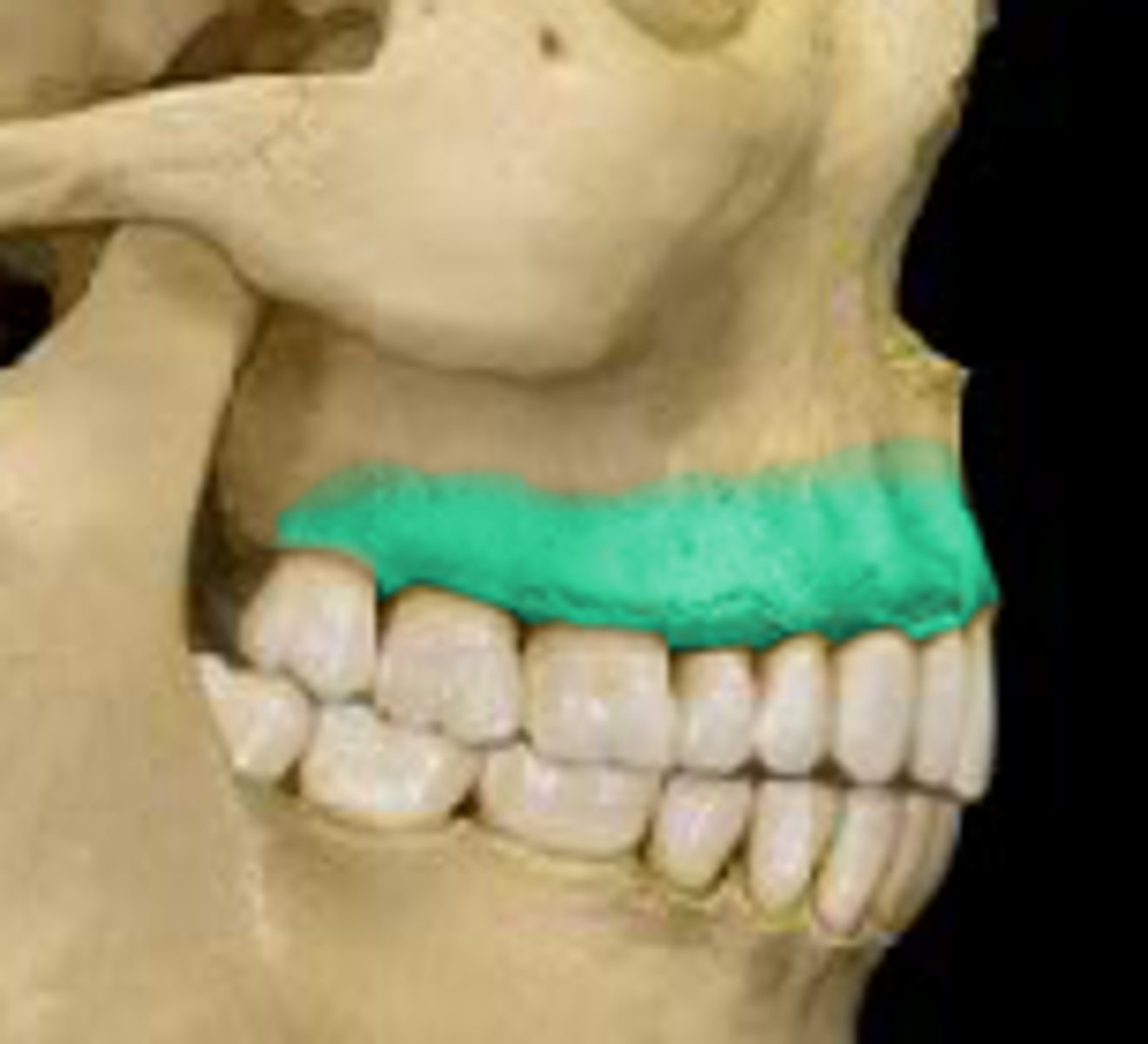
alveoli (of MAXILLAE)
for the tooth roots, cavities along the alveolar process
canine jugum (of MAXILLAE)
bony eminence over the maxillary canine root on the facial surface of the maxilla
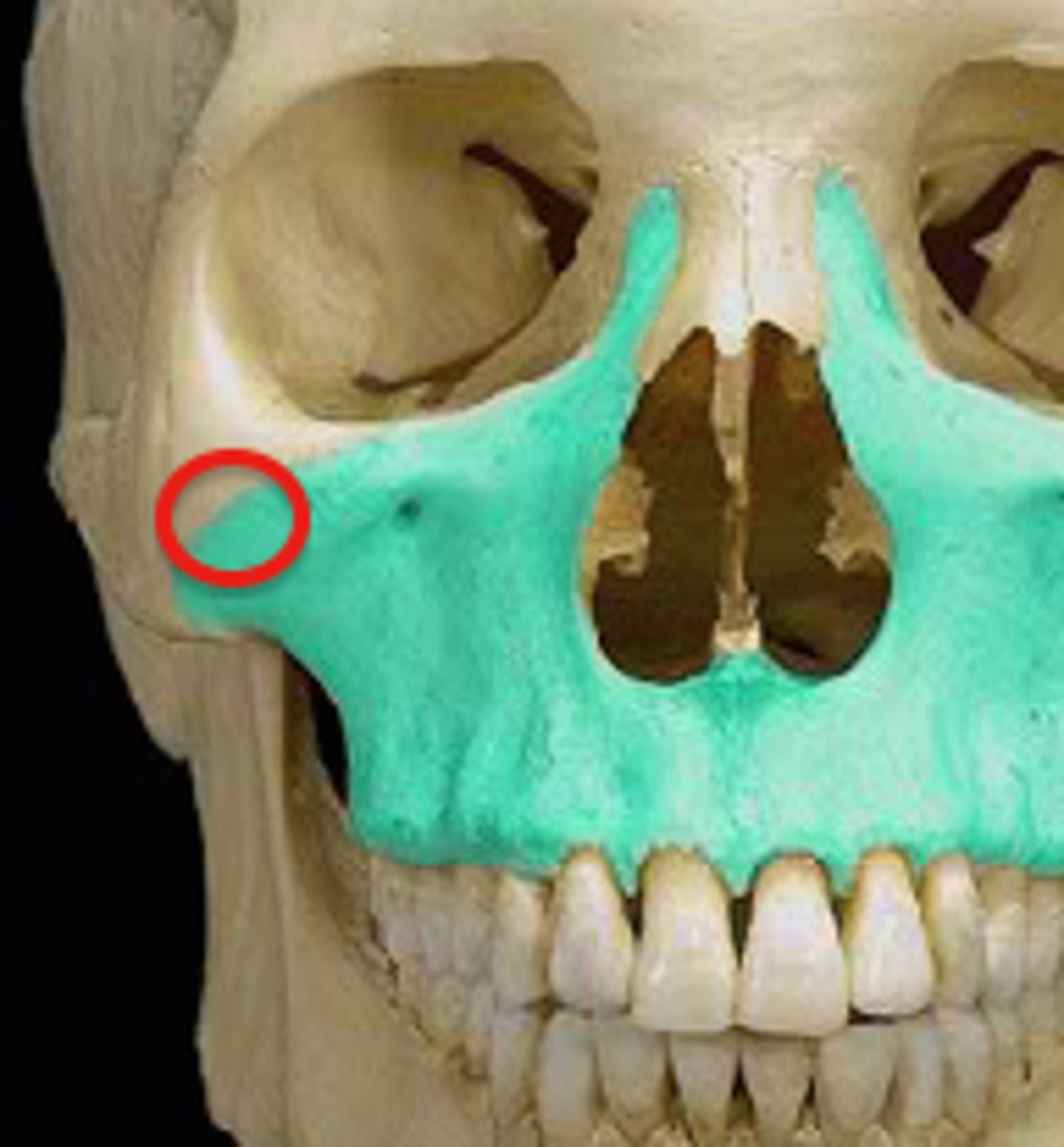
zygomatic process (of MAXILLAE)
forms much of the cheek, articulates with zygotmatic
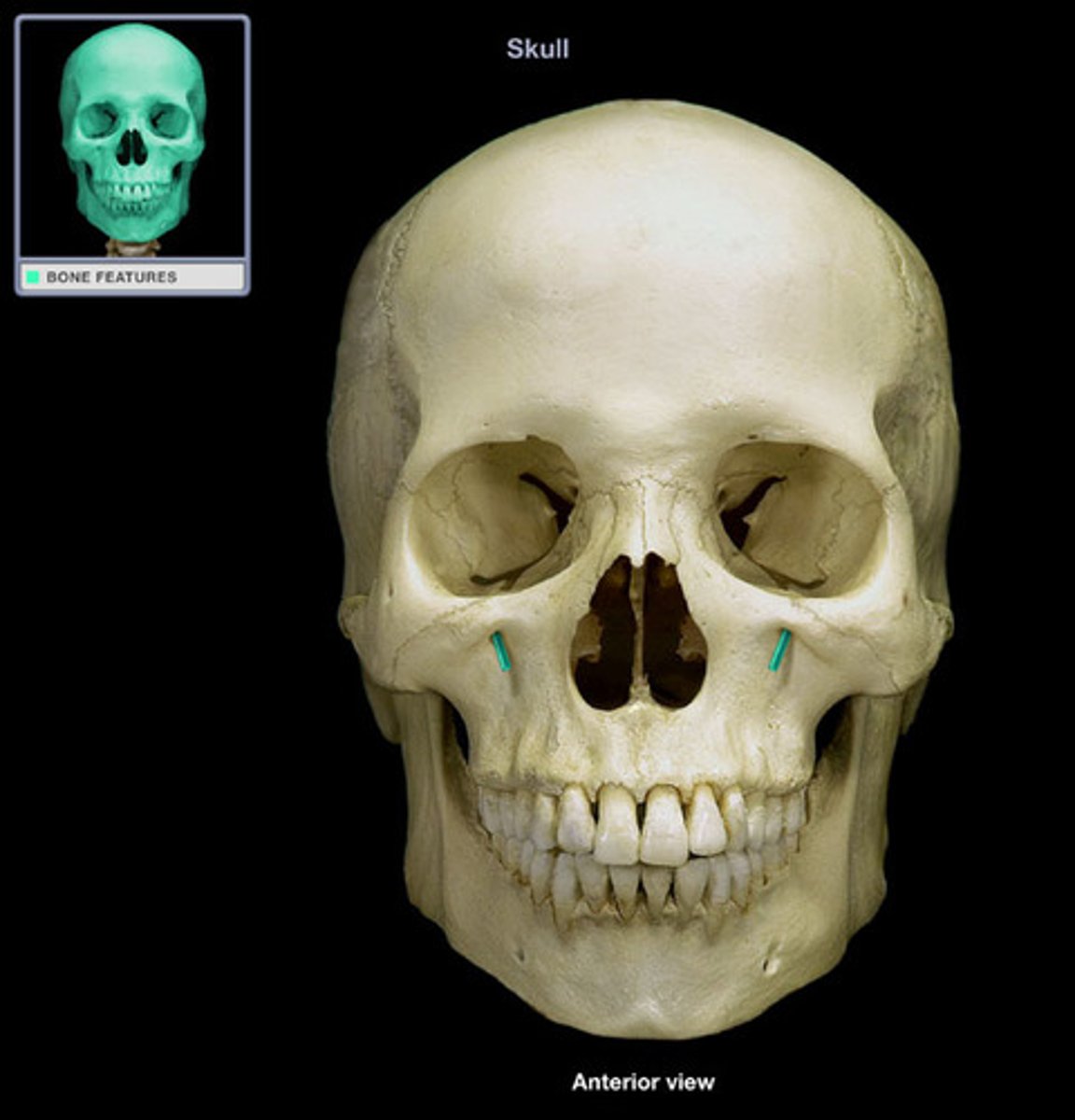
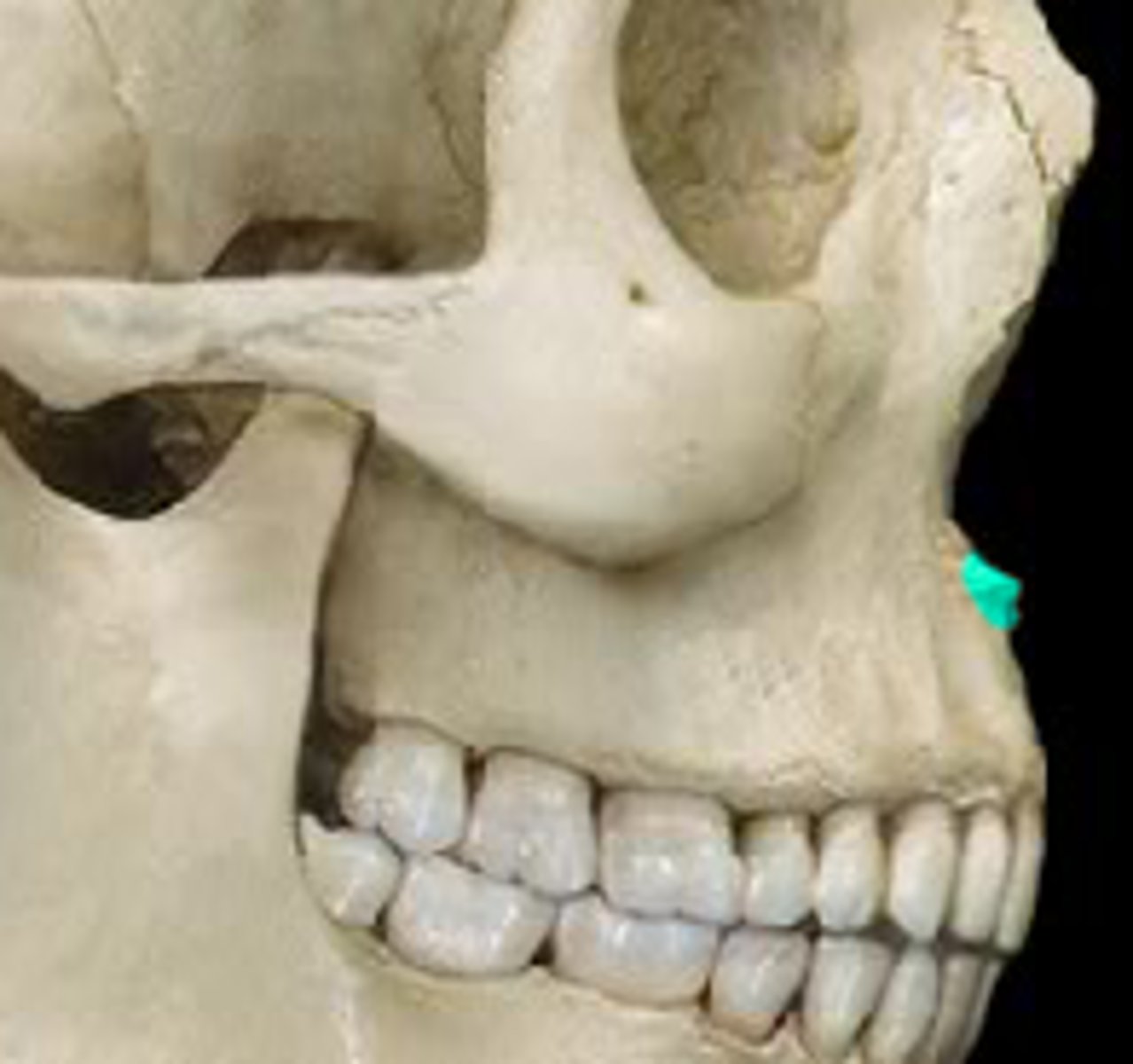
infraorbital foramen (of MAXILLAE)
located below the inferior orbital rim. on the facial surface, transmits infraorbital (trigeminal) nerve
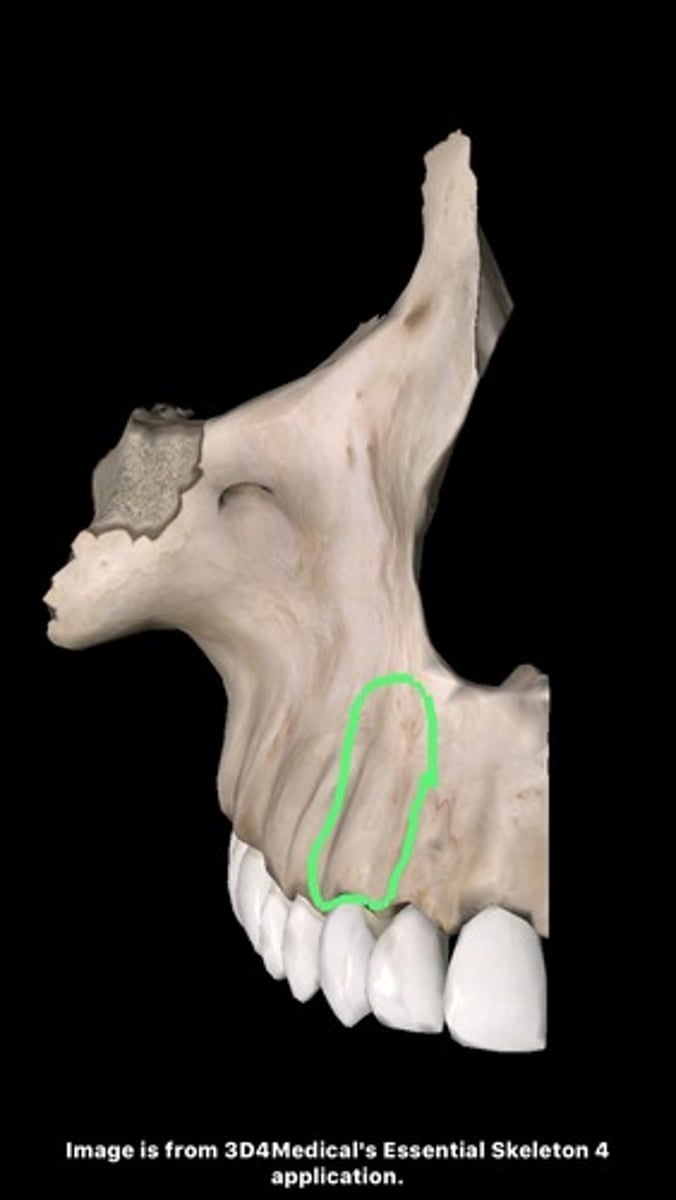
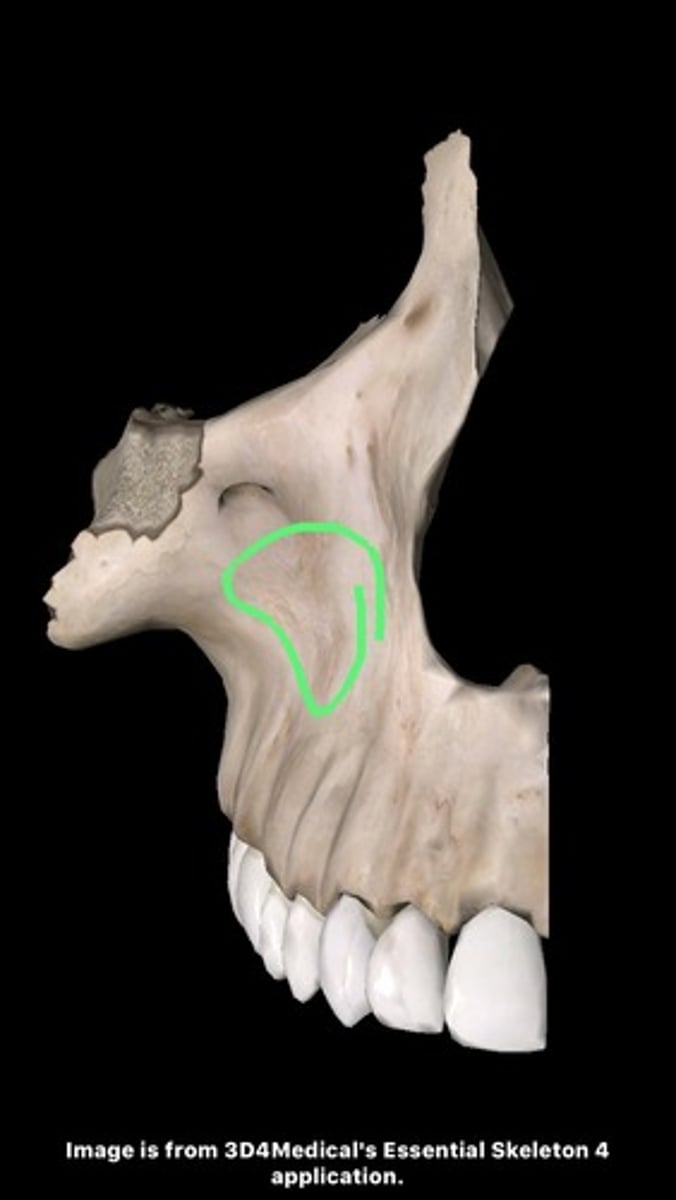
canine fossa (of MAXILLAE)
hollow located on facial surface just below infraorbital foramen, where zygomatic, frontal, and alveolar processes of maxilla come together
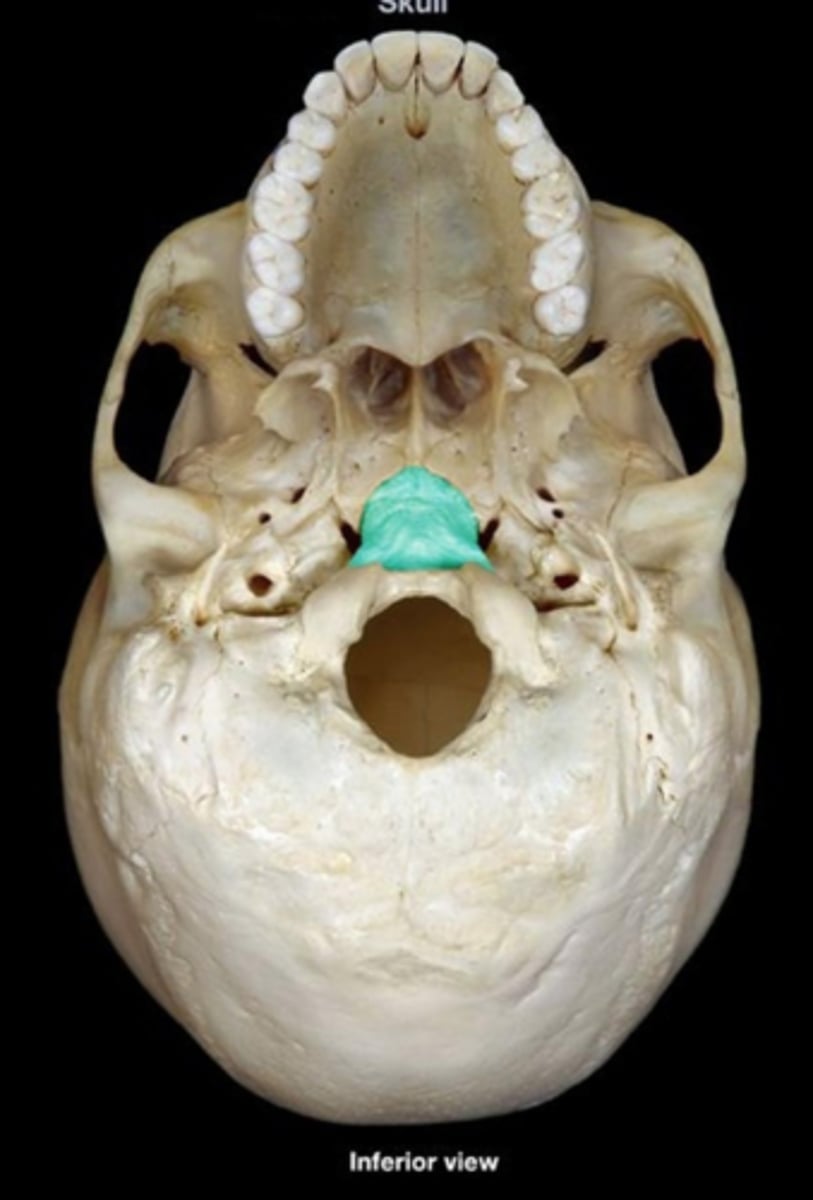
anterior nasal spine (of MAXILLAE)
thin projection of bone on the midline at the inferior margin of the nasal aperture
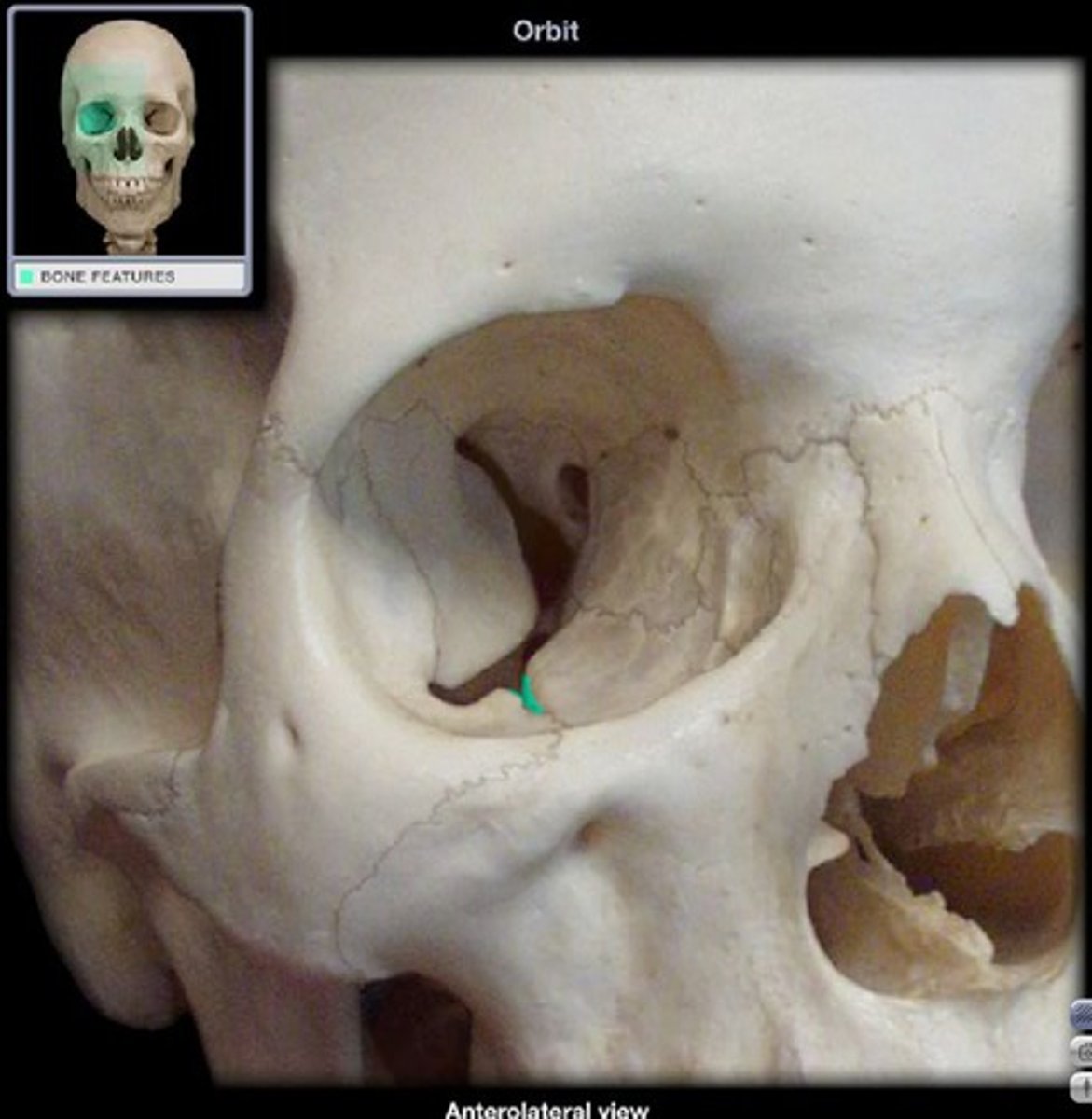
infraorbital sulcus/groove (of MAXILLAE)
centered on the posterior half of the orbital floor and opens posterosuperiorly, connects anteroinferiorly with the infraorbital foramen via infraorbital canal
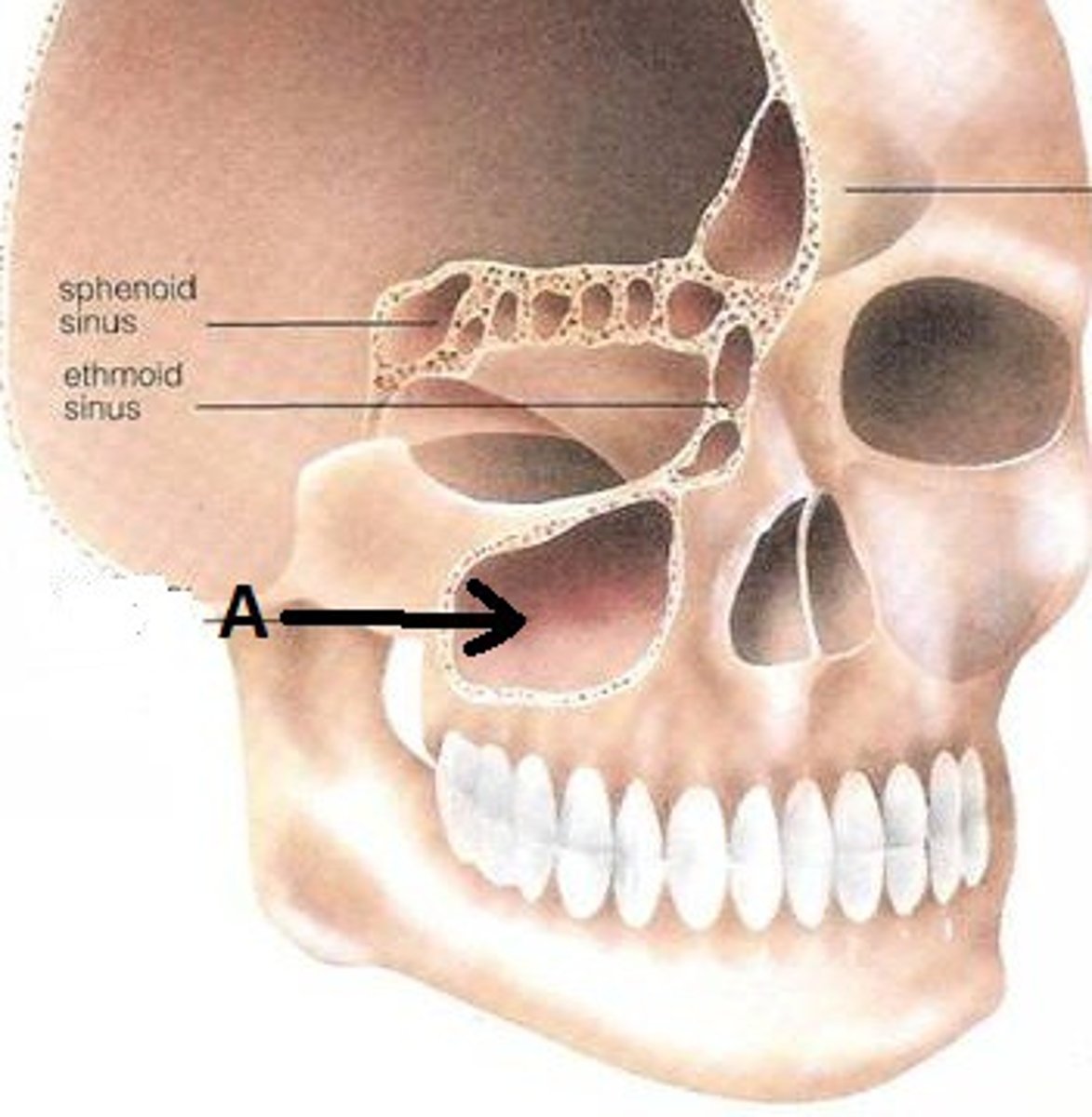
maxillary sinus (of MAXILLAE)
large negative space in the body of maxilla superior to the alveolar process and inferior to the orbital floor
frontal process (of MAXILLAE)
rises to articulate with the frontal, nasals, lacrimal, and ethmoid
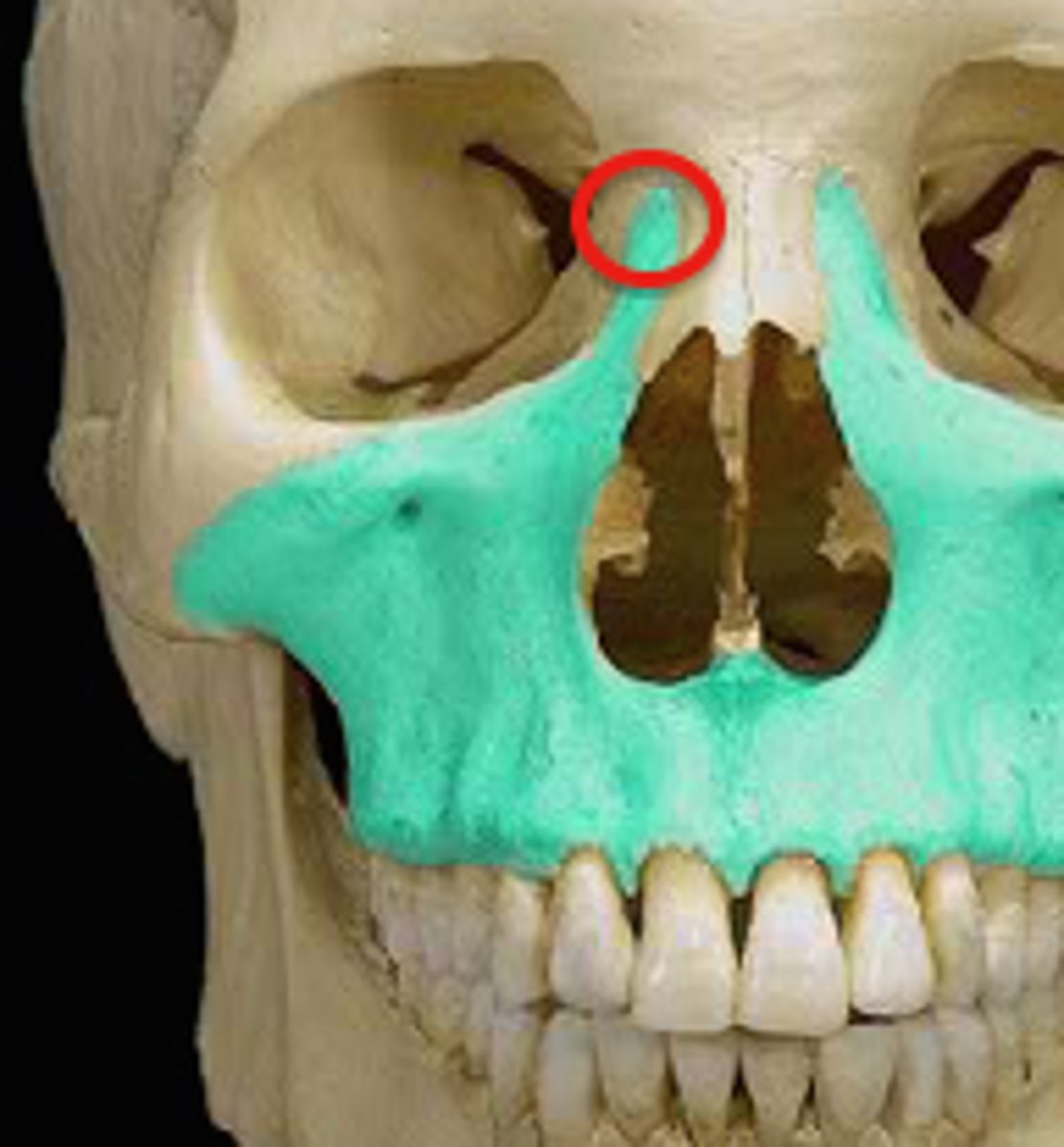
anterior lacrimal crest; lacrimal groove/canal (of MAXILLAE)
vertical crest located on the lateral aspect of the frontal process of the maxilla; maxilla combines with the lacrimal bone to form lacrimal groove and canal
palatine process (of MAXILLAE)
forms anterior two-thirds of the hard palate and floor of nasal cavity (end of plate of maxilla) (blue circle in image)
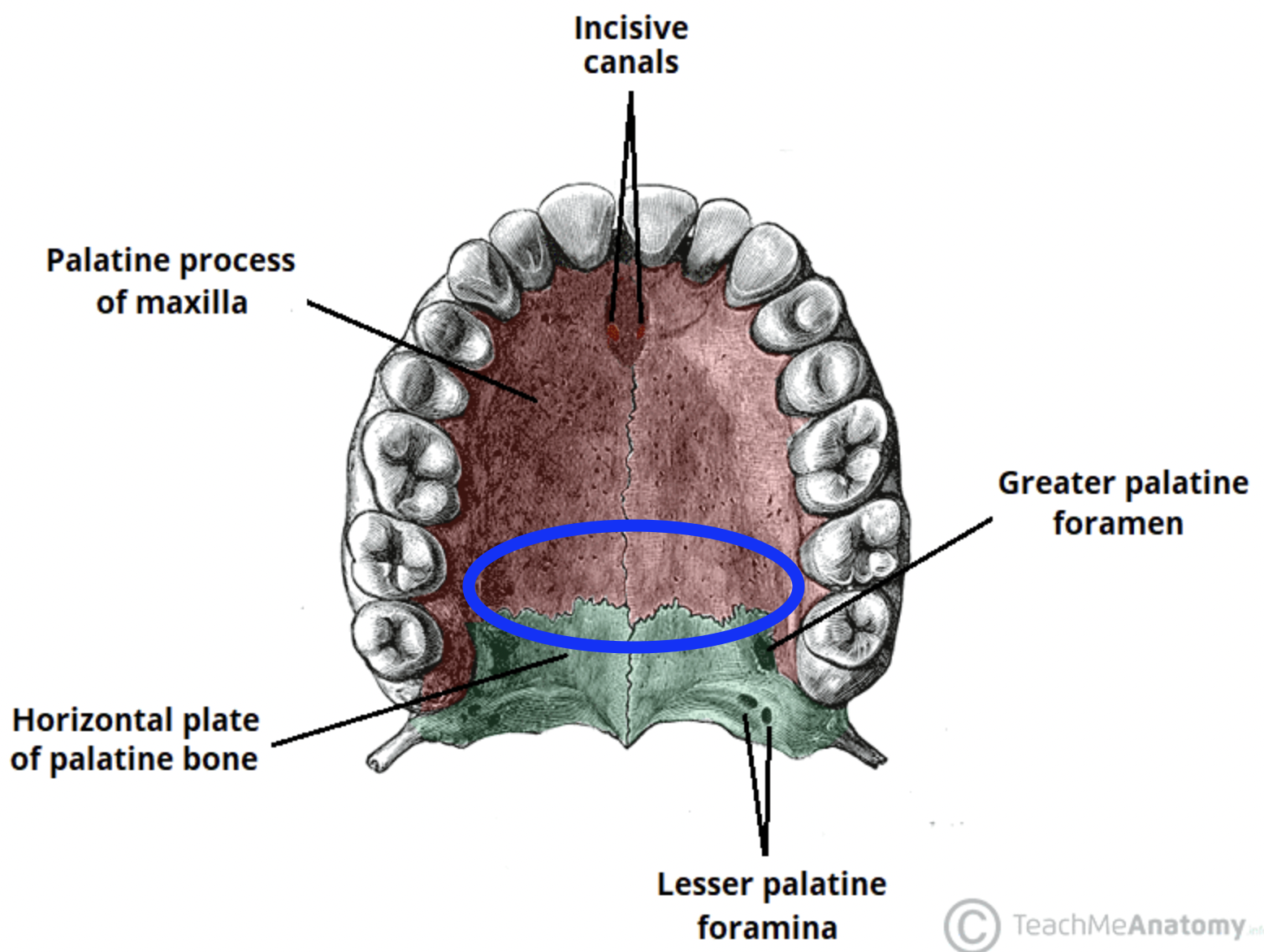
incisive foramen (of MAXILLAE)
perforated the anterior hard palate at the midline
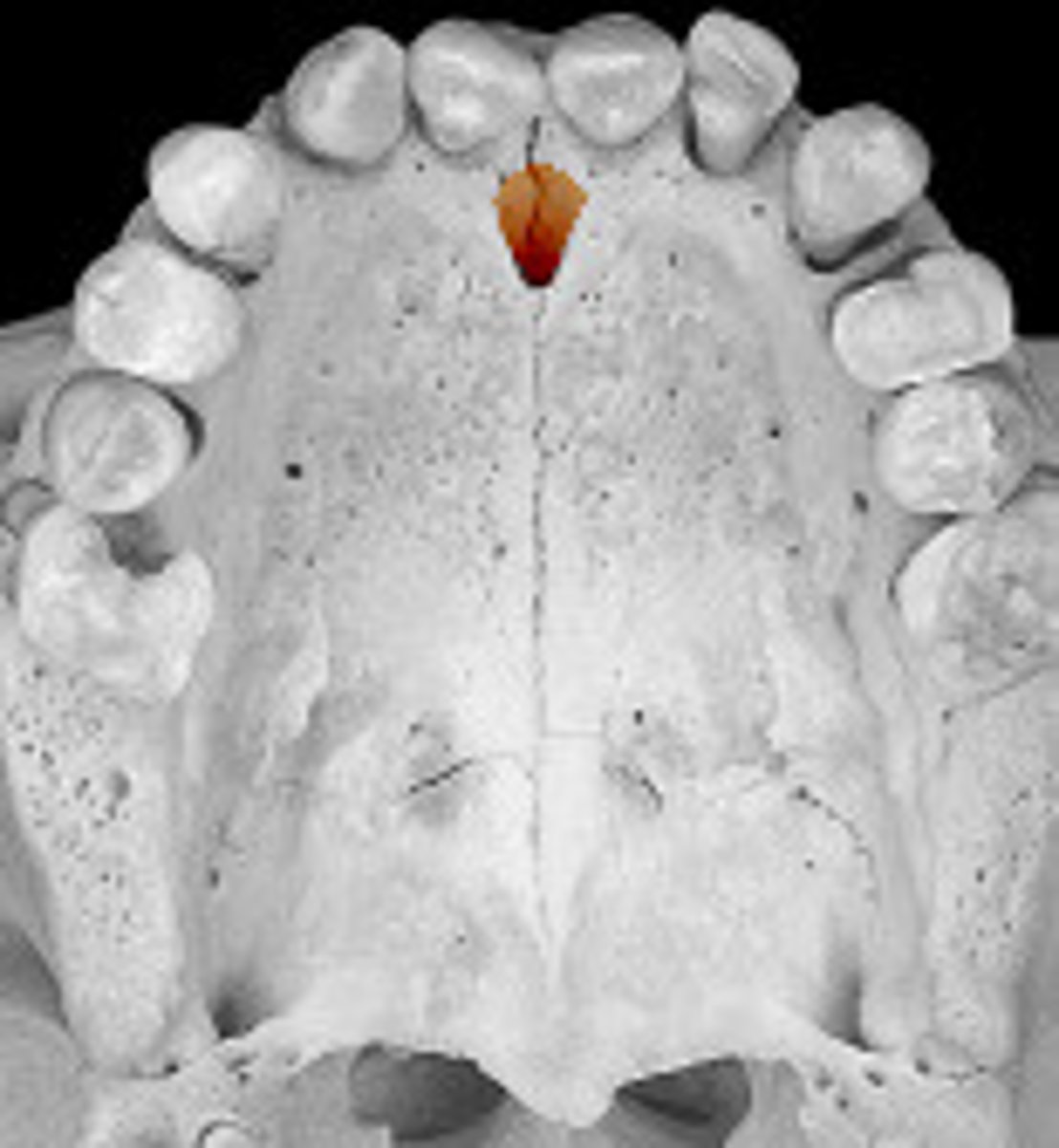
incisive canal (of MAXILLAE)
bilobate (has two lobes/parts), opening via the incisive foramen, with each lobe enclosed by one of the maxillae
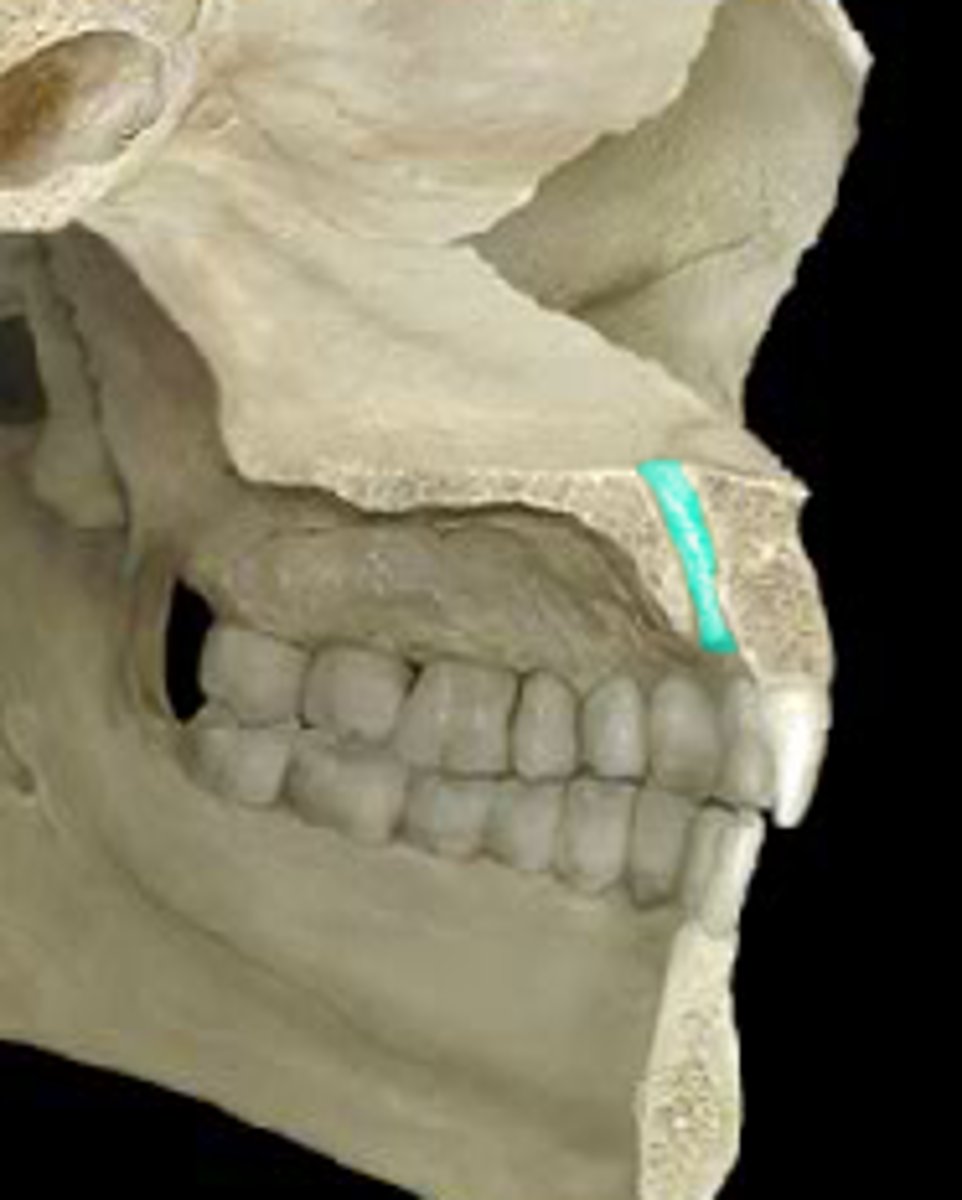
premaxillary suture (of MAXILLAE)
between palatine processes and premaxilla, seen in younger individuals