Stars Galaxies Midterm
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
AU (astronomical unit)
Earth’s avg distance to the Sun (approximately 93 million miles/150 million km)
doesnt depend n where earth is in elliptical orbit
Nuclear force binds ______
neutrons and protons together
Protons
positively charged particles in an atom's nucleus that help determine an element's identity.
Neutron
A subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom, with no electric charge and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton.
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle that orbits the nucleus of an atom, playing a key role in chemical bonding and reactions.
mega, kilo, centi, milli, etc

How long does it take light to travel to earth from the moon?
1 second
If something is 2000 light years away, how old do we see it when it reaches earth?
2000 years old
Order the beginning of the universe

Hypothesis
attempt @ explanation
Law
all samples meet same outcome (i.e. gravity); generalization
Fact
Statement significant to 1 thing
ex. the sky is blue
Theory
explains why & how; deeper than law
ex. Theory of relativity explains deeper gravity
Where would you see the most stars, north pole, south pole, equator?
Equator
Eclliptic
apparent path of constellations in the sky
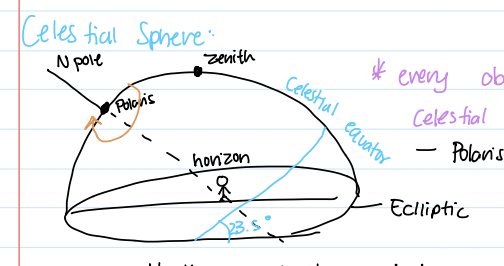
How do we know Earth is round?
Photos from space
Ships pass over the horizon
Round shadow on moon
N star moves to zenith as you move north
Ptolemaic vs Copernican model
Ptolemaic: geo-centric> stars orbit Earth
used complex epicycles to justify orbits
Copernican: helio-centric> earth orbits sun
still used complex epicycles to justify retrograde motion
circular orbits (not elliptical)
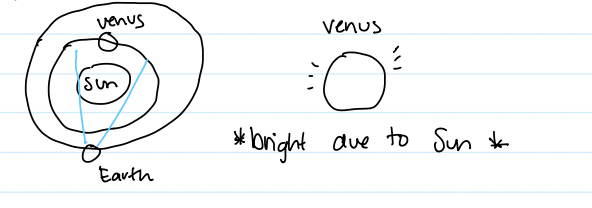
Phases of venus
observed by Galileo; justified helio-centric models because you cant see a full venus in a geo-centric (has to be opposite Earth in orbit)
went through all phases (could only happen in helio-centric)
What did Galileo prove when he observed jupiter’s moons?
Observed moons orbitting jupiter; proved things could orbit obj other than Earth
Why are lunar eclipses more pop than solar eclipses?
shadow of earth is bigger than shadow of moon (wider path)
Tycho Brahe & Kepler
Brahe: measured sky & planets; observation only; hired Kepler & kept work from him to keep the fame
Kepler: mathmatically predicted motion of planets using brahe’s observations
proved helio-centric modelKe
Kepler’s Laws
planets orbit the sun in elliptical orbits; Sun is also 1 of the foci
line joining planets to sun sweeps out in equal space, equal time
P²=a³ (linear relationship)
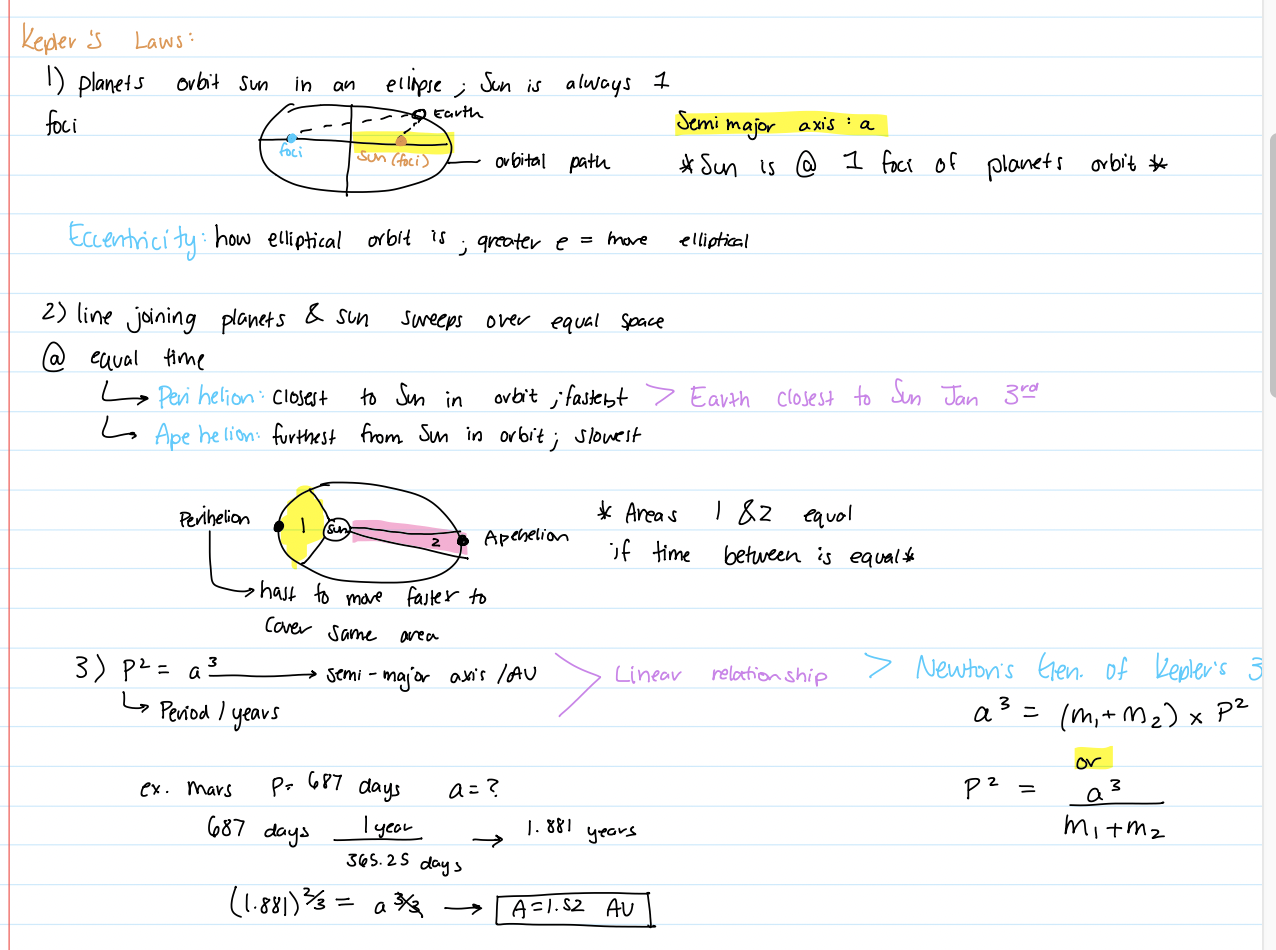
Eccentricity
how elliptical orbit is; higher eccentricity, more elliptical
Perihelion & Apehelion
Perihelion: closest to sun in orbit (fastest)
Apehelion: furthest from sun in orbit (slowest)

Orbital period vs rotational period (earth)
Orbital period: 365.25 days (1 revolution)
Rotational period: ~24 hr
Newton’s laws
every obj will stay in motion unless acted upon by equal and opp force
change in motion is prop to and in direction of force acting on it (i.e. heavier rocket needs more force to produce same acceleration)
For every action there is an equal and opp reaction (i.e. gun recoils when bullet is shot)
Asteriods & comets
Asteriods: reminents of Big bang, lie between mars and jupiter (asteriod belt is very empty)
Comets: high eccentricity
What happens if you shoot a bullet at orbital speed around earth (8 km/s)?
It orbits in a circle, 11 km/s escape velocity
Discovery of Neptune
william herschel thought uranus’ orbit had a discrepancy, turned out to be grav pull from neptune
confirmed newton’s theory of grav A
ascension vs declination
Asension: longitude (right to left)
Declination: latitude (up and down)
starts from vernal equinox (where celestial equator meets eclliptic)W
Where does the prime meridian go through?
Greenwich england (0,0)
Why are summer days hotter
days are longer, sun gets higher in sky (NOT because earth is closer to sun)
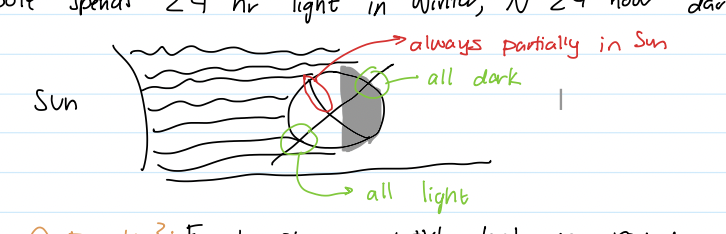
What happens @N and S pole because of the tilt of earth’s axis?
Spend ½ year in daylgith, ½ in night
ex. S pole spends 24 hours light in winter, N 24 dark
Solar vs Sidereal day
Solar: day as measured by position of sun on earth (24 hr)
Sidereal: day as measured by rotation of stars across meridian (23 hr and 56 min)
Does the moon rotate
Yes; the moon is tidally locked to earth (see relativly the same side); helps keep axis in check
Phases of the moon
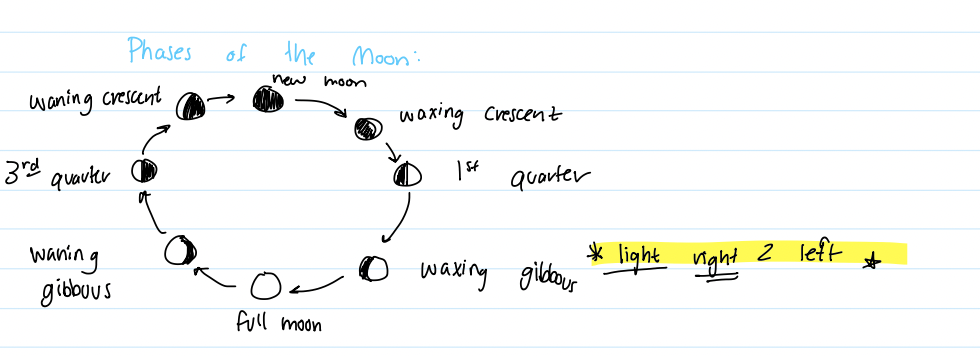
Why did Copernicus formulate a new model of the universe?
Ptolemaic model needed adjustments to predict the position of the planets
Motions described by geocentric model were too complex with use of epicycles & deferents
How does the path of the season change with the seasons?
Earth’s axis is tilted with respect to the solar ecliptic> sun gets lower in winter in N hemi