Embalming Glossary
1/317
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Science NBE Manual
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
318 Terms
Abdominal anatomical regions
2 systems of nomenclature employed for designating portions of the abdomen, which include a 9-region plane and a 4-quadrant plane
Abrasion
Antemortem injury resulting from friction of the skin against a firm object resulting in the removal of the epidermis
Abut
To bluntly adjoin another structure (ex. the line of eye closure)
Accessory chemical
A group of chemicals used in addition to vascular (arterial) and cavity embalming fluids; most applied to the body surface
Action level/AL (exposure limits)
A concentration of 0.5 ppm of formaldehyde calculated as an 8-hour TWA concentration as defined by OSHA
Active dye
An agent that will impart permanent color to tissues
Actual pressure
Pressure indicated by the injector gauge needle with the arterial tube open and arterial solution flowing into body
*Potential - Actual = Differential
Adipocere (grave wax)
Wax-like material produced by saponification of body fat in a body buried in alkaline soil
Aerobic
Characterized by the presence of free oxygen
Aerosolization
Dispersed minute particles of blood and water that become atomized and suspended in the air
Agglutination
Increased viscosity of blood brought about by the clumping of particulate-formed elements in the blood vessels
Agonal algor
Decrease in body temp immediately before death
Agonal coagulation
A change from a fluid into a thickened mass of blood immediately before death
Agonal dehydration
Loss of moisture immediately before death
Agonal edema
Escape of blood serum from an intravascular to an extravascular location immediately before death
Agonal fever
Increase in body temp immediately before death
Agonal
A period of time immediately before death
Agonal translocation
Redistribution of endemic microflora on a host-wide basis immediately before death
Algor mortis
Postmortem cooling of the body to the ambient temp
Alternate drainage
Injection/drainage method; embalming solution is injected, then stopped while drainage is opened
Amino acid
Building block of protein
Anaerobic
Characterized by the absence of free oxygen
Anasarca
Generalized edema in subcutaneous tissue
Anatomical guide
Descriptive reference for locating arteries and veins by means of identifiable anatomical structures
Anatomical limits
Points of origin and termination in relation to adjacent structures used to designate the boundaries of arteries
Anatomical position
Used as a reference in describing body parts to one another in which the body is erect, feet together, palms forward, and thumbs pointed away
Aneurysm
Localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel resulting in a weakness of the vessel
Aneurysm hook
Embalming instrument used for blunt dissection and raising vessels
Aneurysm needle
Embalming instrument used for blunt dissection with an eye in the hook portion for placing ligatures around raised vessels
Angular spring forceps
Drainage instrument designed for the removal of venous blood clots
Anomaly
Deviation from normal
Antecubital fossa
Triangular depression in front of the bend of the elbow
Antemortem
Before death
Anterior
Anatomical term of position and direction denoting the front or forward part; AKA ventral
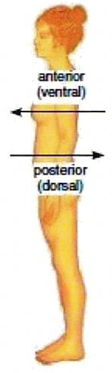
Anterior superior iliac spine
A palpable bony protuberance located on the ilium
Anticoagulant
Ingredient in embalming fluids that slows the natural postmortem tendency of blood to become viscous and prevents adverse reactions between blood and other embalming chemicals
Apparent death
Condition in which the manifestations of life are feebly maintained
Arterial fluid
Concentrated preservative embalming chemical for injection into the arterial system during vascular embalming
Arterial solution
Mixture of arterial fluid and water used for arterial injection and may include supplemental fluids
Arterial tube
Instrument used to inject embalming fluid into the vascular system
Arteriosclerosis
Disease of the arteries resulting in thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the arterial walls
Articulation
Juncture between 2+ bones or cartilage
Ascites
Accumulation of serous fluids in the peritoneal (abdominal) cavity
Asepsis
Freedom from infection and from any form of life; sterility
Asphyxia
Death beginning in the lungs due to an insufficient intake of oxygen
Aspiration
Removal of gas, fluids, and semi-solids from body cavities and hollow viscera by means of suction with an aspirator and trocar
Atheroma
Fatty degeneration or thickening of the walls of the larger arteries occurring in atherosclerosis
Autoclave
Apparatus used for sterilization by steam pressure
Autolysis
Self-destruction of cells; decomp of all tissues by enzymes of their own formation without microbial assistance
Autopsy
Postmortem examination of the organs and tissues of a body to determine the cause of death or pathological condition
Bactericide
Substance used to destroy bacteria
Biohazard
Biological agent or situation that constitutes a hazard to humans
Biohazardous waste
Any potentially infective, contaminated waste that constitutes a hazard to humans in the workplace
Biological death
Irreversible somatic death
Bischloromethyl ether/BCME
A carcinogen potentially produced when formaldehyde and sodium hypochlorite come into contact with each other
Bleach (sodium hypochlorite)
Chlorine-containing compound used for disinfection of inorganic/inanimate surfaces
Bleaching agent
Chemical used to lighten skin discolorations
Blood
Tissue that circulates through the vascular system and is composed of approximately 22% solids and 78% water
Bloodborne pathogens
Microorganisms present in human blood that can cause disease in humans
Bloodborne Pathogen Standard
OSHA mandate regulating the employee’s exposure to blood and other body fluids
Blood discoloration
Condition resulting from changes in blood composition, content, or location; either intravascular or extravascular
Blood vascular system
Circulatory network composed of the heart, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins
Blunt dissection
Utilizing manual techniques or round-ended instruments that separate rather than cut the superficial fascia surrounding blood vessels
Boil (furuncle)
Deep-seated inflammation in the skin, which usually begins as a subcutaneous swelling in a hair follicle
Bridge suture (interrupted suture)
Temporary suture consisting of individual stitches employed to sustain the proper position of tissues
Buffer
Substance capable of neutralizing acids and bases to maintain a constant pH
Bulb syringe
Self-contained manual pump made from soft rubber designed to create pressure to deliver arterial fluid as it passes through one-way valves located within the bulb
Cadaver
Dead human body used for medical purposes
Cadaveric lividity (livor mortis)
Intravascular red-blue discoloration resulting from postmortem hypostasis of blood
Cadaveric spasm (instantaneous rigor)
Immediate stiffening of the muscles of a dead human body
Calvarium
Superior portion of the cranium removed during cranial autopsy
Calvarium clamp
Device used to reattach the calvarium to the cranium after a cranial autopsy
Canalization
Formation of new channels in tissue
Capillary
Semi-permeable minute blood vessels allowing for the diffusion of arterial embalming fluid
Capillary permeability
Ability of substances to diffuse through capillary walls into the tissue spaces
Carbohydrate
Compound of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen that is an aldehyde or ketone derivative of polyhydroxy alcohol
Carbuncle
Circumscribed inflammation of the skin and deeper tissues that ends in suppuration and accompanied by systemic symptoms
Carcinogen
A cancer-causing chemical or material
Case analysis (embalming analysis)
Evaluation of the dead body prior to, during, and after the embalming procedure is completed
Cavitation
The formation of cavities in an organ or tissue; frequently seen in some forms of tuberculosis
Cavity embalming
Direct treatment of the contents of the body cavities and the lumina of the hollow viscera, usually accompanied by aspiration and injection of chemicals using a trocar
Cavity fluid
Concentrated embalming chemical injected into the cavities of the body following aspiration; can also be used in hypodermic and surface embalming
Cellular death
Death of the individual cells of the body
Center of arterial solution distribution
Ascending aorta and/or arch of the aorta
Center of venous drainage
Right atrium of heart
Centrifugal force machine
Embalming machine that uses an electrical pump to create pulsating and non-pulsating pressure
Chelate
Substance used as an anticoagulant in embalming solutions that binds metallic ions
Chemotherapy
Application of chemical agents in the treatment of disease in humans, primarily cancer, causing an elevated preservative demand
Clinical death
Phase of somatic death lasting from 5-6 mins during which life may be restored
Coagulating agent
Chemical or physical agents that bring about coagulation
Co-injection fluid
Primarily used to supplement and enhance the action of vascular solutions
Coma
Death beginning in the brain due to irreversible cessation of brain activity and loss of consciousness
Communicable disease
Disease that may be transmitted either directly or indirectly between individuals by an infection agent
Concurrent disinfection
Disinfection carried out during the embalming process
Concurrent drainage
Occurs continuously during the vascular injection
Condyle
Rounded articular process on a bone
Contaminated laundry
Laundry that has been soiled with blood or other potentially infectious materials
Contaminated sharps
Any contaminated object that can penetrate the skin including needles, scalpels, broken glass, and exposed wire ends
Cornea
Transparent part of the tunic of the eyeball that covers the iris and pupil and admits light into the interior
Corneal sclera button
Portion of the cornea recovered for transplantation