Topic 2-Genes and Health
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
Why do mammals have a small surface area to volume ratio?
Because they’re large
Because mammals are active, that means they also have a high … and this also means…
-metabolic rate
-lots of oxygen is needed for respiration and carbon dioxide needs to be removed
Where does gas exchange occur in humans?
Alveoli
What two boundaries do the exchange gases need to go through?
-capillary wall
-alveoli wall
How are the capillary and alveoli wall adapted for efficient gas exchange?
-large surface area to volume ratio
-this walls
-large difference in concentration
What are the alveoli made of?
-thin layer of squamous epithelial cells
-some collagen
-elastic fibres=causes recoil which helps move air out of the alveoli
How are the alveoli adapted?
-large surface area
-alveoli and capillary walls are one cell thick= short diffusion distance
-rich blood supply due to capillaries
-ventilation from breathing which helps maintain the concentration gradient
What is Ficks Law?
-Rate of diffusion is directly proportional to surface area and difference in concentration
-inversely proportional to thickness of gas exchange surface
-(surface area x difference in concentration gradient) / thickness of surface
Write an exam answer for Ficks Law in terms of Surface Area
-rate of diffusion is proportional to surface area
-mammalian lungs are adapted to this because there are many alveoli giving the lungs a very large surface area to volume ratio
Write an exam answer to Ficks Law in terms of difference in concentration
-rate of diffusion is proportional to difference in concentration
-mammalian lungs are adapted to this because they have an efficient ventilation system when breathing and a rich blood supply with many capillaries and steady heart rate
Write an exam answer to Ficks Law in terms of thickness of gas exchange surface
-diffusion is inversely proportional to thickness of gas exchange surface
-mammalian lungs are adapted to this because the exchange surface is very short only being two cells thick
-the epithelial cells in mammal lungs are squamous making them thinner
What are the intercostal muscles?
Contract and relax to move ribs during breathing
What two types of cells are in the trachea?
-goblet cells
-ciliated epithelial cells
What is a goblet cell?
Release mucus to trap dust and pathogens
What is a cilliated epithelial cell?
Cilia waft mucus up to mouth to swallow, preventing lung infections
What are squamous epithelial cells?
Flat epithelial cells
How are fish gills adapted for gas exchange?
-many lamella-large surface area
-thin diffusion pathway= rapid diffusion
-counter current system(water and blood flow in opposite directions)-maintains a constant concentration gradient
Describe and explain how the lungs of a mammal are adapted for rapid gas exchange
-large surface area
-short diffusion distance
-concentration gradient maintained by ventilation
-describe Ficks law
-concentration gradient maintained by blood flow
Use Ficks law of diffusion to explain the adaptations of mammalian gas exchange surfaces
-rate of diffusion is directly proportional to surface area =alveoli has a large surface area
-rate of diffusion is directly proportional to difference in concentration=breathing maintains a difference in gas concentration
-rate of diffusion is directly proportional to difference in concentration= blood flow maintains a difference in gas concentrations
-rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to thickness of gas exchange surface =walls of alveoli and capillary are one cell thick
-diffusion distance is reduced due to flattened cells forming alveoli and capillary walls
Determine why animal A doesn’t need a circulation system but animal B does
-both have the same volume
-animal A has a larger surface area
-animal A has a larger surface area to volume ratio
-so sufficient surface area in animal A for diffusion
-distance to cells in centre in the centre of A is shorter than for B allowing shorter diffusion distance
What kind of structure do cell membranes have?
Fluid mosaic structure
What are cell membranes composed of?
Lipids(mainly phospholipids), proteins and carbohydrates
When was the fluid mosaic model suggested and what does it describe?
1972-describes the arrangement of molecules in the membrane
What do phospholipids form and why are they fluid?
-A continuous bilayer
-fluid because the phospholipids are constantly moving
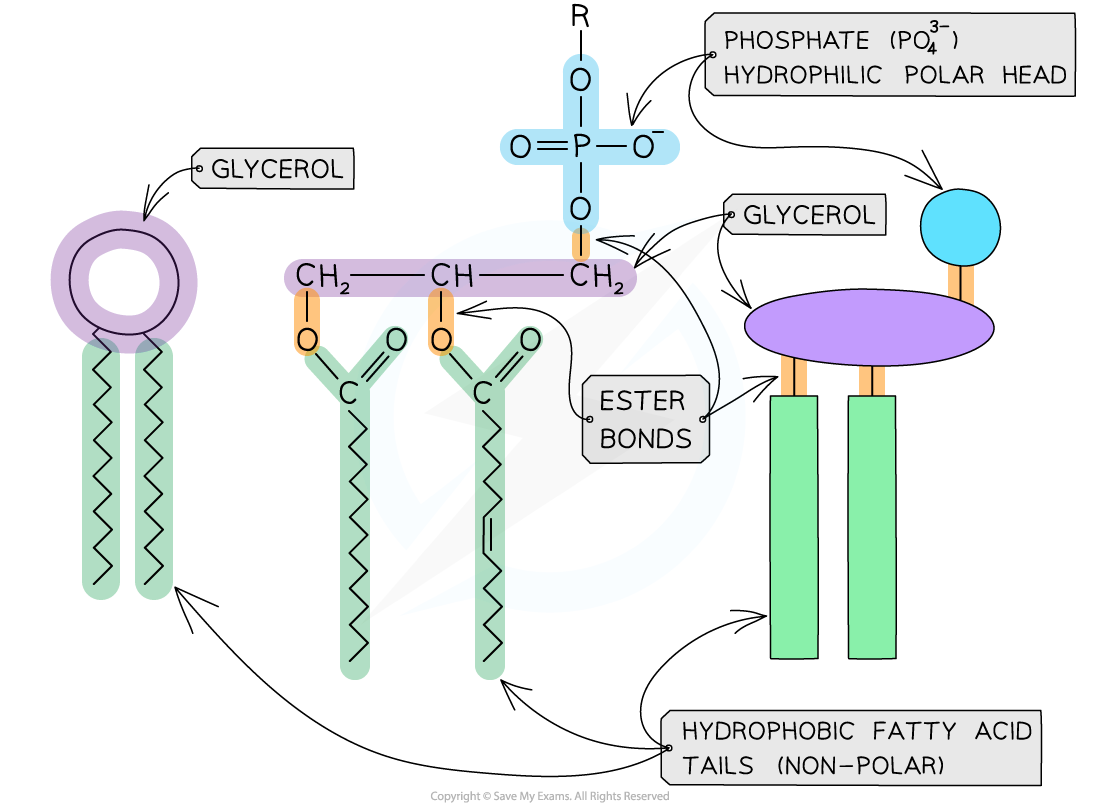
Draw and annotate a phospholipid molecule
-hydrophilic head attracts water
-hydrophobic tail repels water
-due to this they automatically arrange themselves into a bilayer where the hydrophilic head faces out towards the wate
-hydrophobic fatty acid tail is on the inside meaning the membrane doesn’t allow water soluble substances like ions through it
What are the properties of protein molecules?
-randomly scattered through the bilayer
-can move within the bilayer
-some have carbohydrate chains attached called glycoproteins
What are the properties of lipids?
-some have carbohydrate chains attached called glycolipids
Describe the properties of cholesterol
-type of lipid
-at low temperatures it makes the membrane more fluid
-fits in between phospholipids forming bonds between them
How was the fluid mosaic model made?
-electron microscope-showed 3 layers in cell membrane
-improved electron microscope techniques showed bilayer of phospholipids and analysis showed random distribution of proteins not a continuous layer
-fused mouse and human cell-membrane proteins completely intermixed showing the membrane was fluid
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of free water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration of water molecules to an area of low water molecules
Where will the net movement of water molecules be through osmosis?
To the area of lower concentration of water molecules
What are the properties of cell membranes?
-fluid=the components can move relative to one another
-flexible=due to the cholesterol
-selectively permeable=only allows certain molecules to pass through
What is passive transport?
-no metabolic energy (no need for ATP)
-through the phospholipids of proteins
What processes are included in passive transport?
-diffusion
-osmosis
-facilitated diffusion
Describe the properties of diffusion
-small, non charged, non polar molecules
-high to low concentration
-passive
Describe the properties of osmosis
-small, non charged, non polar molecules
-high to low water concentration
-low to high solute concentration
-passive
Eg.water is polar but small enough to pass through
Describe facilitated diffusion
-through proteins
-channel proteins(like a tunnel)
-carrier proteins( change shape)
-both passive
-both high to low concentration
-hydrophilic(polar) and ions that are larger than carbon dioxide cannot simply diffuse through
-unable to cross the hydrophilic tail
What do carrier proteins do?
-Move large molecules into or out of the cell
-down the concentration gradient
-different carrier proteins facilitate the diffusion of different molecules
How do carrier proteins work?
1)a large molecule attaches to a carrier protein in the membrane
2)the protein changes shape
3)this releases the molecules on the opposite side of the molecule
How do channel proteins work?
-form pores in the membrane for charge particles to diffuse through
-down the concentration gradient
-different channel proteins facilitate the diffusion of different charged particles
Describe active transport
-uses metabolic energy from hydrolysis of ATP
-through carrier proteins
-low to high concentration
-against the concentration gradient
What is the process of active transport similar to?
Facilitated transport
Describe ATP and how it’s produced
-produced by respiration
-acts as an immediate source of energy in the cell
-when ATP is hydrolysed (broken down) in the cell, energy is released.
-this energy is used to move the molecule against its concentration gradient
Describe endocytosis/exocytosis
-for very large molecules eg. Proteins ,lipids
-a cell can surround a substance with a section of its cell membrane
-the membrane pinches off to form a vesicle inside/outside the cell
-requires us of ATP for energy
Describe exocytosis
-substances produced by cell needs to be released
-vesicles containing these substances pinch of from the sacs of the Golgi apparatus and move towards the cell membrane
-vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents outside the cell
-some substances aren’t released outside the cell and are instead inserted straight into the cell membrane
Describe the structure of a cell membrane
-phospholipid bilayer
-orientation due to hydrophobic/hydrophilic regions
-proteins
-describe channel/carrier protein structure of position(extrinsic,intrinsic,transmembrane)
-cholesterol, glycoprotein, glycolipid
Why can large molecules enter the cell?
-can’t enter the cell
-membrane is impermeable to large molecules
What is the name of the bond that joins the fatty acid molecule to a glycerol molecule in the phospholipid?
Ester bond
Which molecule is involved in cell recognition?
Glycoproteins
Which molecules allow ions to diffuse into the cell?
-channel proteins
What does isotonic mean?
-solution that has the same solute concentration as another solution
-no net movement of water molecules
-overall concentration on both sides of the cell membrane remains constant
What does hypertonic mean?
-solution has a high solute concentration than another solution
-water molecules will move out of the cell causing crenation
What does hypotonic mean?
-solution that has a lower solute concentration than another solution
-water particles will move into the cell causing the cell to expand and eventually lyse
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribose nucleic acid
What does DNA do?
-stores genetic information
-all instructions needed to grow and develop
What does RNA stand for?
Ribonuceic acid
What does RNA do?
Transfers genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes
What do ribosomes do?
Read RNA to form polypeptides in a process called translation
What are ribosomes made of?
RNA and proteins
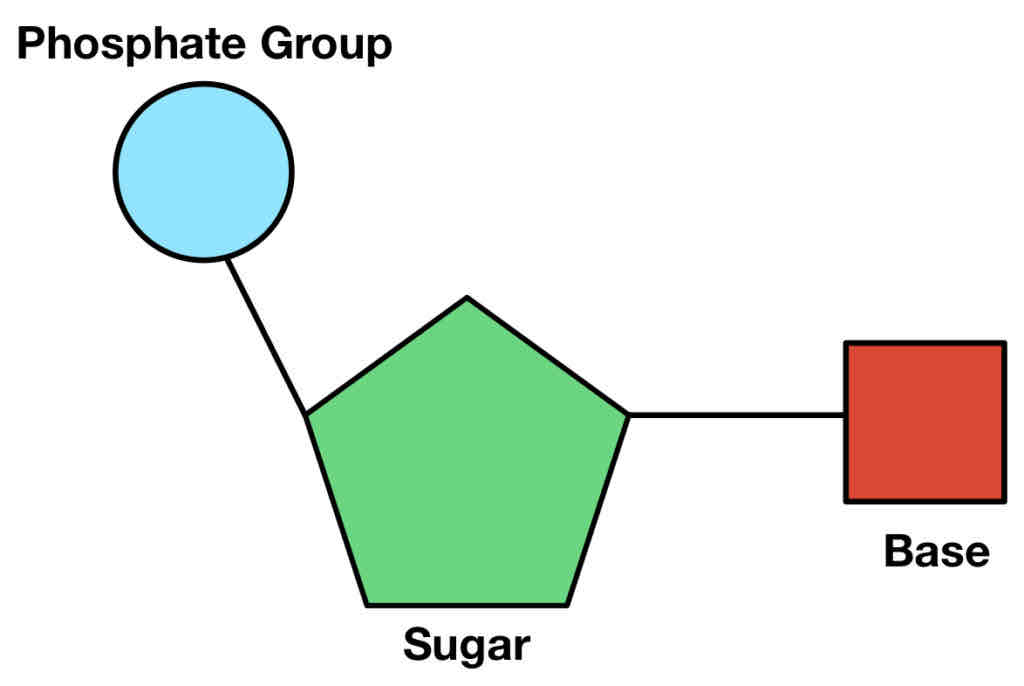
What is a mono nucleotide?
A single nucleotide
What is a mono nucleotide made of?
-pentose sugar(sugar with 5 carbon atoms)
-organic nitrogenous base
-phosphate group
What do mono nucleotides make up?
They’re monomers that make up RNA and DNA
What does organic mean?
Contains carbon
What is the pentose sugar in a DNA mono nucleotide called?
Deoxyribose
What are the 4 possible bases for DNA?
-Adnenine(A)
-Thymine(T)
-Cytosine(C)
-Guanine(G)
What kind of pentose sugar is in RNA mono nucleotides?
Ribose
What are the 4 possible bases for RNA?
-Uracil(U)
-Cytosine(C)
-Adenine(A)
-Guanine(G)
What does a mono nucleotide look like?
What is a dinucleotide?
Two mono nucleotides
How are mono nucleotides joined?
-condensation reaction=between the phosphate of one mono nucleotide and the sugar group of another
-water is the by product
What kind of bond is formed between the sugar and phosphate?
Phosphodiester bond
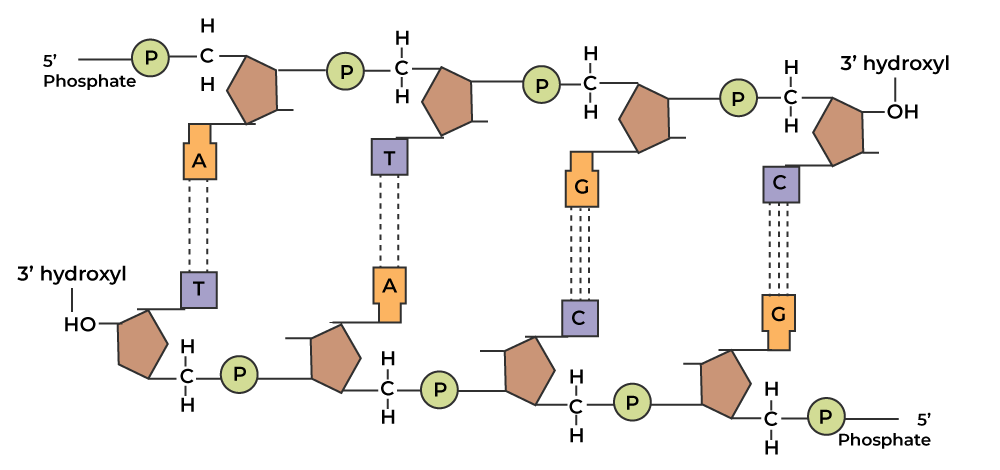
How many strands of polynucleotides are DNA and RNA made of?
-DNA=2 and coils into a double helix
-RNA=1
How are 2 DNA polynucleotides joined together?
Hydrogen bonds
What are the complementary base pairs?
-A and T:2 hydrogen bonds (tea for two)-T is replaced with U for RNA
-C and G:3 hydrogen bonds ( C and G for three)
How is the DNA double helix formed?
Two antiparallel (running in opposite directions) polynucleotide strands twist
Draw two joined polynucleotide strands
When was the double helix structure and the fact that DNA carries genetic code found?
1953
Why does a phospholipid bilayer have the same permeability to oxygen as a cell surface membrane?
-oxygen is a small, non polar molecules
-oxygen is able to diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer
-cell surface membrane has a phospholipid bilayer
Why is permeability different for chloride ions(Cl-) in the phospholipid bilayer and the cell surface membrane?
-chloride ions are charged
-chloride ions can’t diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer
-chloride ions need a carrier protein to move across a membrane
Why is the rate of osmosis different in the cell surface membrane and phospholipid bilayer?
-cell membrane is more permeable to water
-water can move across the phospholipid bilayer
-water can also move channel proteins
What is a gene?
A series of mono nucleotide bases on a DNA molecule that codes for the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide
What determines the order of amino acids in a particular protein?
The order of mono nucleotide bases in a gene
What is each amino acid coded by?
3 bases (called a triplet) in a gene
What are the sequence of bases in a section of DNA used as to make proteins called?
A template
What is the sense strand?
The strand that is not being transcribed
Where are DNA molecules found?
Nucleas
Where are ribosomes found?
The cytoplasm
Why can DNA move out of the nucleus?
It’s too large
What is the section of DNA copied by?
mRNA
What is the process of mRNA copying a section of DNA called?
Transcription
What is mRNA used for when it leaves the nucleas?
It is used to synthesise a protein in translation
Describe messenger RNA
-made in the nucleus during transcription
-three adjacent bases are called a codon
-carries the genetic code from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where it is used to make a protein during translation
Explain how mRNA control the process of translation(3 marks)
-contains start codon that acts as a signal to start translation
-ensures ribosomes start translation at the correct place
-mRNA has a stop codon to signal the end of translation
-to produce a complete polypeptide
Describe transfer RNA
-found in the cytoplasm
-it has an amino acid binding site at one end and a sequence of 3 bases at the other end called an anticodon
-carries the amino acids that are used to make proteins to the ribosomes during translation
Describe the importance of tRNA in protein synthesis(3 marks)
-have a triplet anticodon at one end and a region where a specific amino acid can attach
-bind with their specific amino acid and bring them to mRNA
-for a peptide bond to form
Contrast the structure of mRNA and tRNA?(3 marks)
-tRNA is longer
-mRNA is a straight molecule whereas tRNA is a folded molecule
-mRNA contains no hydrogen bonds while tRNA has some hydrogen bonds
What are codons and anticodons also called?
Triplets
What is the genetic code?
The sequence of base triplets in DNA or mRNA, which codes for specific amino acids
What does it mean if the code is non overlapping?
Base triplets don’t share their bases
What does it mean if the genetic code is degenerate?
There are more possible combinations of triplets than there are amino acids
(20 amino acids but 64 possible triplets)