Virology Module 1 Quiz and iClicker Questions
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
A cabbage looper is infected with what kind of viruses?
An insect virus and a baculovirus
Which of the following viruses infect bacteria?
bacteriophage
Which of the following was the first virus discovered?
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Which of the following animal viruses is proven to be a beneficial virus in the mouse?
Murine Noro Virus (MNV)
Virus classification usually does not use species level instead a viral genus is described with which of the following alternatives?
All of the others are used as alternatives to species in describing a viral genus (nucleotide sequences, isolates, host range, serotypes)
Which of the following statement is true about the Curvularia Thermal Tolerance Virus (CThTV)?
CThTV infects Curvularia protruberata fungus, and when the infected fungus colonizes in the Dicanthelium lanugiosum grass species; it offers thermal tolerance of the grass in a three-way symbiosis.
Which of the following is the BEST definition of a virus?
Viruses are often ultra-microscopic obligate intracellular molecular parasites, which absolutely need a living cell or, in exceptional cases, cell extract with ribosomes of a host to replicate.
Which of the following statements is FALSE in the context of our current knowledge of viruses?
All viruses are ultra-microscopic and can be visualized only by electron microscopes.
Which of the following can never be found in any virus as per current knowledge?
ribosomes
Mimivirus and Pandoravirus completely changed our previous perception of viruses. Which of the following is true about this change in perception?
They are giant viruses and the only type of viruses that can be visualized by light microscopes.
Which is a key concept first discovered about viruses that distinguished them from other microorganisms?
They were small enough to pass through a 0.2 micron filter
What type of stains are used in an electron microscope to visualize viruses?
negative stain
Which statement is true?
Our genome contain many retroviral sequences
all viruses make us sick and can be lethal
our immune system cannot handle most viral infections
humans are usually infected with one virus at a time
we are all infected with infectious retroviruses
Our genome contain many retroviral sequences
Human feces have an abundance of what kind of viruses?
Plant viruses
Rahul is a graduate student who isolated what he believes is a novel serotype of the Nipah virus from a bat population in India. He wants to perform transmission electron microscopy on the isolated and purified Nipah virus virion particles. Which of the following stains do you think is appropriate and why?
Uranyl acetate as it is heavy metal salt and a negative stain
Which of the following defines a “virion”?
An infectious virus particle
Which of the following reservoirs do not harbor viruses?
Soil, oceans, rivers and lakes
healthy living organisms
polar ice caps and snowy mountains
atmosphere
All of the above
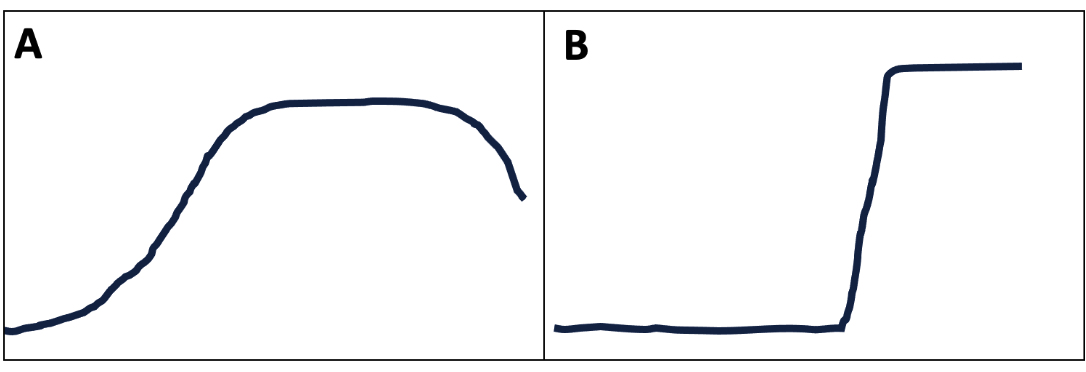
From the following hypothetical growth rate graphs can you predict to whom A and B graphs belong to?
(1) A: Streptococcus pyogenes B: HIV
(2) A: Coronavirus B: Vibrio Cholera
(3) A. E. coli B. Influenza virus
1 and 3 can be correct
Which of the following attributes in virus classification?
Presence or absence of a lipid membrane outside the capsid (envelope)
Dimension of virion and the capsid
Symmetry of the protein shell (capsid)
Nature and sequence of the nucleic acid
All of the other attribute in virus classification
Which of the following is true concerning bacterial vs. viral replication?
Viruses must assemble using pre-formed components?
Which of the following is FALSE about viruses?
A. They are obligate parasites
B. Every animal carries a large number of defective viral genome remnant
C. They must infect eukaryotic or prokaryotic living or dead cells to replicate
D. None of the above is False; all are true
They must infect eukaryotic or prokaryotic living or dead cells to replicate
You want to visualize some T1 bacteriophage infecting E.coli. Which of the following methods would you consider “the best” to visualize the bacteriophage?
A. Infect the E.coli, once lysed, filter media with a cheesecloth, negative stain the filtrate sample, and do transmission electron microscopy.
B. Infect the E.coli, once lysed filter media with a 0.2μM filter, negative stain the filtrate sample, and do light microscopy
C. Infect the E.coli, once lysed filter media with a 0.2μM filter, negative stain the filtrate sample, and do transmission electron microscopy
D. Infect the E.coli, once lysed filter media with a 0.2μM filter, positive stain the filtrate sample, and do light microscopy
Infect the E.coli, once lysed filter media with a 0.2μM filter, negative stain the filtrate sample, and do transmission electron microscopy
Tissue Culture Infectious Dose 50% (TCID50) is used to express viral titer/concentration from which of the following viral assay
End point dilution assay
What does “viral titer” mean in a sample?
It is the measurement of concentration of a virus in a sample
Which Multiplicity of Infection (MOI) is best suited for a multi-step growth cycle?
0.1
What is the principle of a hemagglutination assay?
Some viruses can clump (agglutinate) the red blood cells to form a lattice that doesn’t sink to the bottom of an assay plate well and gives a distinct difference in appearance from the non-infected red blood cells which without hemagglutination sink at the bottom of the well and looks like a “red button”
Which statistical method is used to determine the Multiplicity of Infection (MOI)?
Poisson distribution
Viral cytopathic effect can be best described as…
Cells showing pathological signs due to viral infection
Which of the following assays involved the principle of immobilizing viral antigens or anti-viral antibodies on a solid support and assaying their interactions (binding or not), which can be detected by a secondary antibody with an indicator?
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Which of the following statement best describes an “eclipse period” of a virus growth cycle?
It is the period upon infection, when the virus is actively replicating its genome and forming structural components of the virus inside the infected cells
When viruses are grown in embryonated chicken eggs for vaccine production, which part(s) of the egg is/are used?
Chorioallantoic membrane, amniotic cavity, yolk sac, allantoic cavity
Which Multiplicity of Infection (MOI) is best suited for a single-step growth cycle?
10
Which of the following were used to grow animal viruses before the development of growing animal viruses in cell culture?
Live animals and embryonated chicken eggs
Which of the following statements best describes the ‘principle of the plaque assay’?
An infectious viral particle, when allowed to infect a monolayer of cells and the viral dispersion is restricted by an overlaying gel like agar, kills cells around the cell that it initially infected; which causes a clear zone due to death of the cells called a plaque.
If cells are infected at a MOI=10 in a one-step growth cycle experiment, in the growth curve, you will likely see …
a single burst of virus release
Human gastrointestinal cells are resistant to cabbage looper baculovirus. Which of the following best describes the statement?
human gastrointestinal cells do not have receptors for the cabbage looper baculovirus
A _____ and _______ cell is the only cell that can take up a virion and replicate it
susceptible and permissive
Animal cell cultures infected with certain viruses show the formation of syncytia. What best describes syncytia?
fusion of multiple cells to form giant cells
In the ‘particle to pfu ratio’, particle can best be described as:
a virus which may or may not be infectious
Which of the following term is used for a virus particle that can establish a plaque?
Plaque Forming Unit (PFU)
When doing a plaque assay, what is the purpose of adding a semi-solid agar overlay on the monolayer of infected cells?
to restrict viral diffusion after lysis of infected cells to distant cells on the plate beyond the neighboring cells
Why doesn’t every virus particle form a plaque when added to a cell monolayer?
Some virus particles may be defective and unable to infect the cells; some of the virus particles may have mutations to make them replication incompetent; some virus particles may have a defective genome packaged into them, which can’t form all the required components of new virions; some viruses naturally can’t form plaques because they do not lyse the cells but come out of the cells gradually by budding and don’t kill the cells immediately
Despite easy maintenance, immortality and ability to grow in high density the transformed cell lines are not used to cultivate viruses for vaccine production; why?
The transformed cell lines are often aneuploid with defective chromosomes and may have oncogenic genes which can contaminate the vaccine preparation and may cause cancer in the vaccine recipients
Upper and lower respiratory tract epithelial cells are susceptible to influenza virus. Which of the following best describes the statement?
The upper and lower respiratory tract epithelial cells have the receptors for the influenza virus.
Which of the following in certain cell types will you consider as viral cytopathic effects?
syncytium formation, rounding up and detachment of cultured cells, dark inclusion bodies in the nucleus or cytoplasm different from a normal cell, nuclear shrinking and/or proliferation of membranes
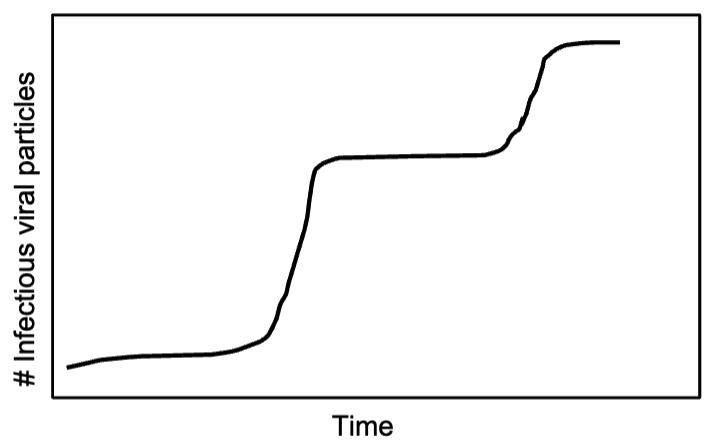
You are performing a growth
characteristic experiments of a
poliovirus strain with BHK cells. You
have multi-well plates with 106 cells in
each well. To obtain a growth curve like the one
on the right figure, which of the
following moi will you use to infect the
cells?
A. 0.01
B. 10
C. 100
D. 1000
0.01
Which of the following statement/s is/are FALSE?
A. Viral titer can be expressed as Plaque Forming Unit (PFU) for all viruses
B. Each plaque is formed by one infectious viral particle or virion
C. To perform a plaque assay, hot molten agar is layered over the cells to
fix and kill them for visualization by crystal violet
D. All of the other statements are false
To perform a plaque assay, hot molten agar is layered over the cells to fix and kill them for visualization by crystal violet
Which of the following can’t be coded by any viral genome?
ribosomes
Why is mRNA placed at the center of the Baltimore scheme?
because mRNA must be made from all viral genomes
A hypothetical viral genome sequence below:
3'-UUA UGC CCG CAG CCU AGU CUC UGC ACG UAC-5'
Where will you place this virus following the Baltimore classification scheme?
(Please assume the above sequence is a complete genome sequence of the virus in the correct orientation).
(-) ssRNA virus
All free-living organisms have a much larger genome size than all known viruses.
false
What was the principle/method that Hershey & Chase used to discover that viral nucleic acid (DNA) is the genetic or hereditary molecule and not protein?
They labeled T4 bacteriophage proteins with radioactive sulfur and DNA with radioactive phosphorus and analyzed the progeny virions for the radioactivity in their proteins or DNA
To make mRNA; a (-) strand RNA virus must synthesize which of the following intermediate strand?
Nothing. The (-) strand RNA can be used as template to make mRNA
Which statement about viral RNA genomes is correct?
some (+) ssRNA genomes may be translated to make viral protein
Which of the following virus genome type can be replicated by the host DNA polymerase?
some dsDNA genomes
Which of the following properties can be observed in the diverse RNA genome types of the viruses?
Sometimes proteins can be attached to the viral genomes; most RNA genomes are transcribed and replicated by viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase with retrovirus and hepatitis delta satellite as exceptions; some genomes can form extensive stem-loop structures to form secondary and tertiary structures; some double-stranded RNA genomes can be segmented
Viroids are thought to be the relics of the RNA world and made up RNA and only one protein.
False
Production of the infectious virus after transformation of cells by viral DNA is called ______
Transfection
How did Hershey & Chase, in 1952, determine that nucleic acid is the genetic material of the bacteriophages?
By labeling the viral proteins with radioactive sulfur and the viral nucleic acid with radioactive phosphorous and following the presence of these radioactive molecules in the proteins and nucleic acid of the progeny bacteriophages
A dsDNA virus will use which of the following enzyme to replicate its genome?
viral DNA polymerase or Host DNA polymerase
Which of the following phenomena are observed in viruses with segmented genomes that viruses with unimolecular genomes can’t exhibit?
reassortment
How many viral genome types exist and which viral genome type was not included in the original “Baltimore Scheme’ to make mRNA from different viral genomes?
7 and gapped DNA virus
What information may be encoded in a viral genome?
enzymes to replicate the viral genome
Which enzyme is responsible for the transcription of most viral RNA genomes?
RNA dependent RNA polymerase
Which of the following is true for a retrovirus?
Retroviruses contain reverse transcriptase and can catalyze DNA intermediates from RNA immediately upon infection that can be integrated into host chromosomes as provirus
A part of a viral genome sequence is below:
3’ … UGC CCU ACG … 5’
What sequence will be the mRNA made from that portion of the viral genome?
5’ … ACG GGA UGC … 3’
Which DNA genome, on entry into the cell, can be immediately copied into mRNA?
dsDNA
Unit 3: In order to determine the genetic material, Hersey & Chase labeled the phage _______________ with radioactive sulfur 35S in one set of
experiments and the ________________ with the radioactive phosphorus 32P in another set of experiments.
A. Nucleic Acid, Protein
B. Protein, DNA
C. RNA, Protein,
D. Protein, RNA
protein, DNA
Unit 3: In an RNA virus, which of the following statements is true?
A. They may have a single copy of a double-stranded RNA genome or
may have segmented double-stranded RNA genome
B. They may have a single copy of a negative-stranded RNA genome or
may have segmented negative-strand RNA genome
C. They may have a single copy of a positive-stranded RNA genome or
may have segmented positive-strand RNA genome
D. All of the above statements are true
All of the above statements are true
Unit 3: Which of the following statements is true?
A. All viruses must make tRNAs (transfer RNAs ) in an infectious cycle
B. All viruses must make rRNA (ribosomal RNAs) in an infectious cycle
C. All viruses must make mRNAs (messenger RNAs) in an infectious cycle
D. All of the above statements are true
All viruses must make mRNAs (messenger RNAs) in an infectious cycle
Which of the following property is exhibited by ALL animal viruses with helical symmetry
they are always enveloped with a membrane of cellular origin
What is the definition of the term “genetic economy”, observed in viruses as proposed by Crick and Watson?
As the viral genomes are small; the viral particles would be built with many copies of a few viral proteins
Discovery of which of the following biophysical technique is considered as the beginning of the structural virology era.
electron microscopy
Which of the following is the definition of a ‘subunit’ in a virus structure?
it is a single folded polypeptide chain present in the viral structure
Which of the following describes the “T” number of an icosahedron?
the number of facets per triangular face of an icosahedron
The Poliovirus with triangulation number (T) = 3 is made up of 3 capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 (VP4 is buried inside the capsid). What kind of interactions among these proteins are expected and observed at the 6-fold axis vs. 5-fold axis as per Casper and Klug’s theory of quasiequivalence?
The bonding interactions between the protein subunits on the six-fold axis and five-fold axis are similar; The bonding interactions between the protein subunits on the six-fold axis and five-fold axis vary slightly due to the conformational flexibility of the protein subunits; The bonding interactions between the protein subunits on the six-fold axis and five-fold axis are not identical
If you have a large icosahedral virus; to reach the closest 5-fold axis of one another, you need to travel 5 hexagons in the H vector direction and 2 hexagons in the K vector direction. Which of the following will be the triangulation number (T) of the virus and how many subunits will it require to build the capsid>
T=39 and 2340 subunits
Viruses may have double or triple icosahedral shells as observed in Reoviruses and Rotaviruses and all the shells must have the same triangulation number (T)
false
The unit 1Å (Angstrom), used frequently to describe dimensions of viruses and viral structures is equal to:
0.1 nm, 10^-10 meters, 0.0001 micron
Pepino mosaic virus (a tomato plant virus) has a left-handed helical symmetry. There are 8.7 capsid protein subunit copies per turn of the helix and the pitch (P) of the helix is 34.6Å. Which of the following numbers corresponds to the axial rise per subunit of the capsid protein subunit in the above virus?
~3.97A
Viral capsids are metastable because:
they must protect the viral genome outside the cell; they must come apart and release the genome into a cell; they have not obtained a minimum free energy conformation; they are spring loaded
Which of the following axis of symmetry is NOT found in an icosahedral virus structure with T=1 or the presence of the 60 subunits?
6
The Poliovirus: T=3 is made up of 180 subunits and SV40 with T=7 is made up of 420 subunits
False
What is the structural role of the Matrix (M) protein observed in the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)?
the matrix protein helps as a scaffolding protein to tightly organize the genome RNA enwrapped with nucleocapsid (N) protein
Which of the following number of subunits, when present in a virus, will NOT form “quasiequivalent” structures among the subunits?
60
A “promoter” of a virus structure can be defined as….
it is the structural or asymmetric unit from which capsids or nucleocapsids are built
Which of the following common protein topology/motif are found in viruses with icosahedral symmetry?
beta barrel jelly role
Which of the following characteristics are associated with viral membrane (envelope) associated proteins?
they are integral membrane proteins; they are often glycoproteins; their ectodomains can play roles in attachment and fusion with the host cell; their internal domains can play roles in assembly of the virus
Which of the following virus/es has/have a unique portal for nucleic acid delivery and packaging (in the capsid) at only one of 12 vertices of the icosahedron?
herpesvirus
A nucleocapsid inside an enveloped virus may have __________ symmetry.
icosahedral or helical
When a capsid contains more than 60 subunits, each occupies a ____________ position.
quasiequivalent
Which of the following is NOT the function of the viral structural proteins?
form structure that can prevent binding to host cell receptors
Which of the following is the function of the structural proteins of a virus?
protecting the viral genome; making a metastable capsid to protect the viral genome and also come apart when a proper signal is present; delivery of the viral genome; forms structures that can interact with the host cell membrane in enveloped viruses
Unit 4: A viral helical capsid has the following symmetry values: the pitch of the helix is 100Å, and the axial rise per subunit is 10Å. Calculate the number of subunits per turn of the helix.
A. 0.1
B. 1
C. 10
D. 1000
10
Unit 4: Find the triangulation number T and the number of subunits in the following icosahedral viral capsid, where the h vector equals 10, and the
k vector equals 10.
A. 100, 180
B. 300, 180
C. 100, 1800
D. 300, 1800
300, 1800
How is the Herpesvirus delivered into the nucleus?
alignment of the Herpesvirus portal on the nuclear pore followed by injection of the DNA genome which is packed with high pressure inside the capsid
Which of the following mode of entry is NOT used by the enveloped viruses?
non-specific endocytosis triggered by the viral nucleocapsid protein
To gain entry into the cell Adenoviruses use ______________________ receptor that binds to the ___________________ portion of the viral fiber protein and the co-receptor ________________________ that binds to the _______________________ portion of the fiber protein.
CAR, knob, integrin, penton base
Which of the following statement is NOT true about Ebolavirus entry into the cell?
the Ebolavirus GP protein is cleaved by an endosomal protease in neutral pH
Which of the following viruses need a receptor to gain entry into the cell?
insect viruses