cardiac muscle and smooth muscle
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what’s the functional component of a myofibril?
sarcomere
what do intercalated disk contain? what’s their function?
desmosomes
gap junctions
acts as z lines - anchor site for actin in the last sarcomere of the cell

desmosomes function
found in intercalated disks
permit two adjacent cells to attach and creating long strings of cardiac muscles
gap junctions function
found in intercalated disks
allows cells to communicate
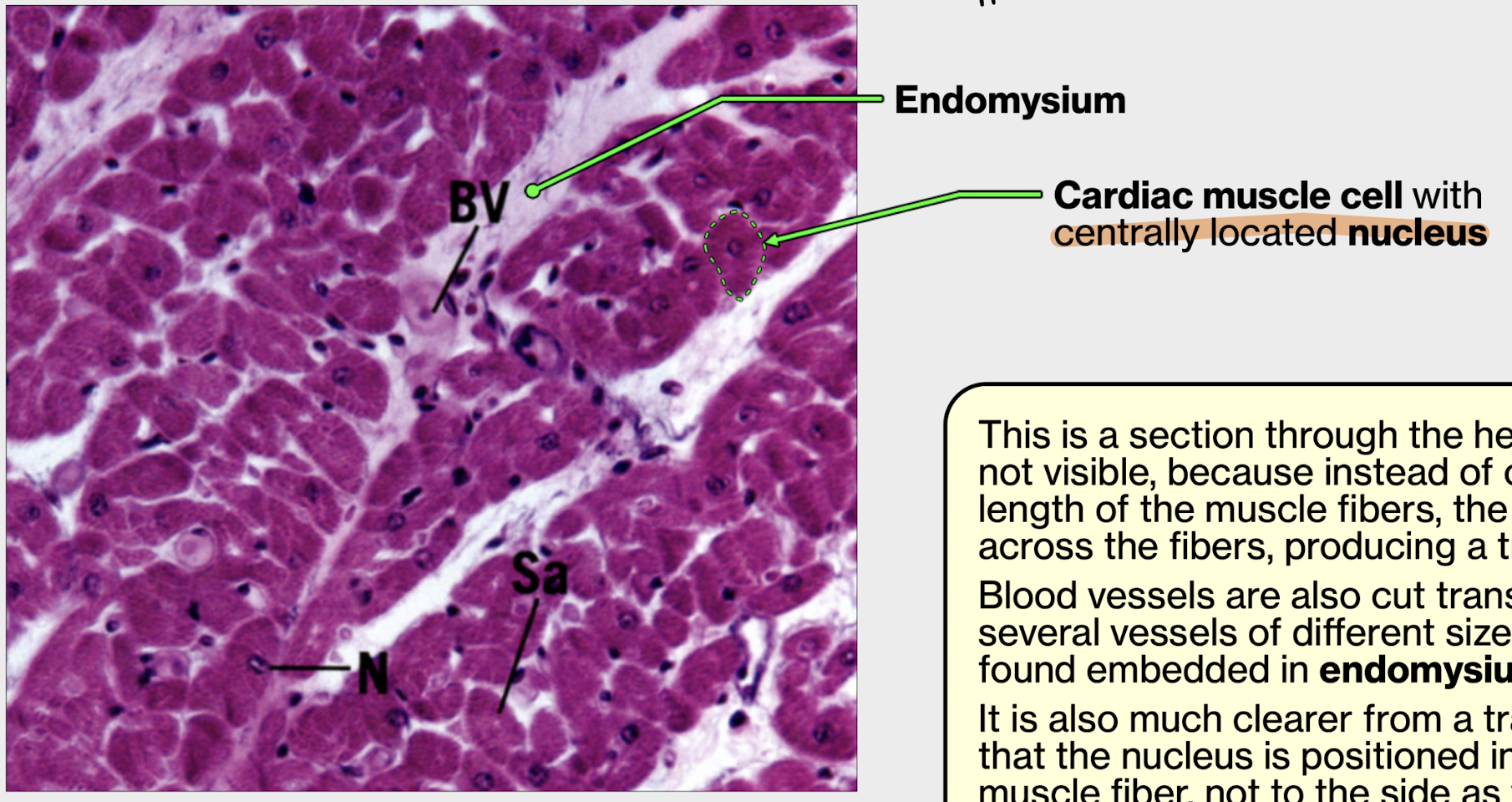
endomysium has two functions in cardiac muscle
CT covers individual cell
supports capillaries between cardiac cells
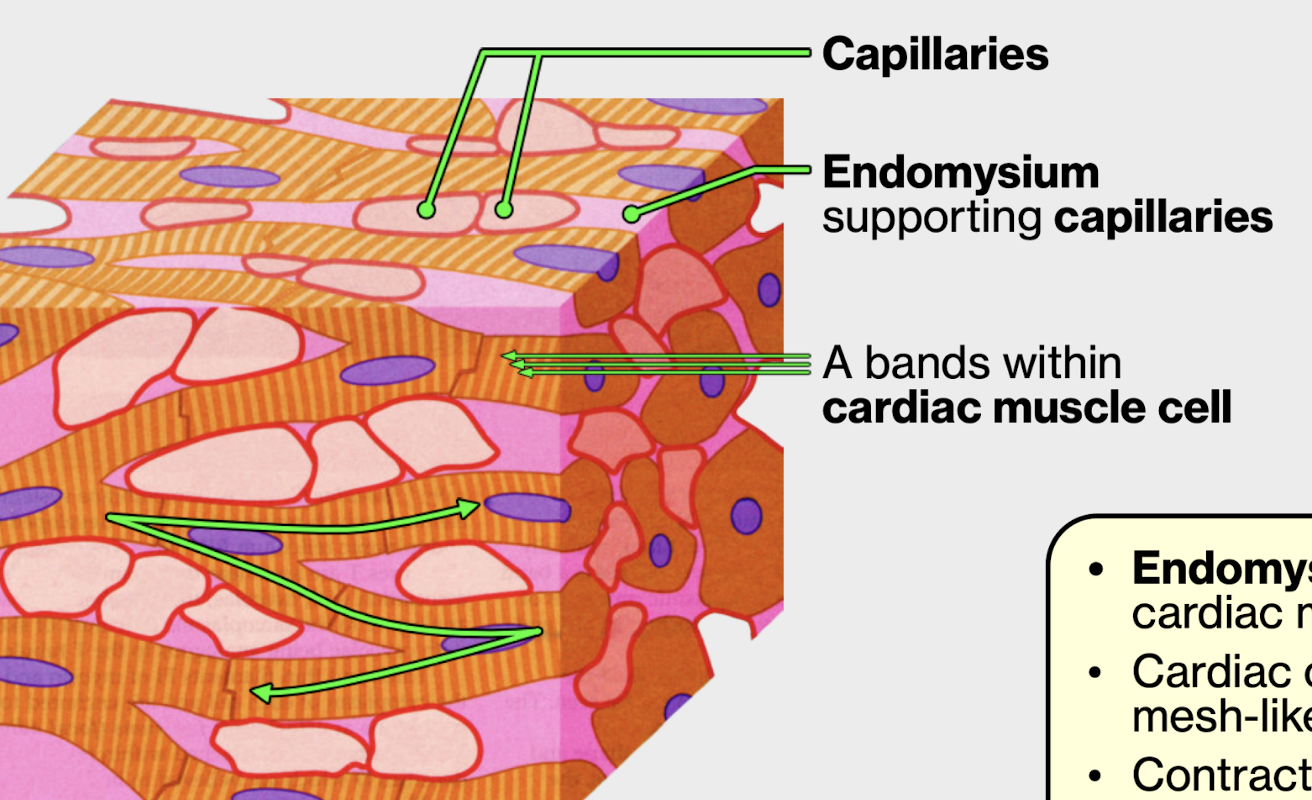
what does it mean by the sarcoplasmic reticular being “leaky” ?
Ca 2+ ions constantly leaking out, initiating contractions over and over
how is the internal rhythm of the heart modulated?
by autonomic (sympathetic & parasympathetic) external input to the cardiac conduction system (SA, AV nodes, Purkinje fibers)
what is part of the cardiac conduction system?
SA, AV nodes and Purkinje fibers
why is the contraction of the heart rhythmic?
DUE TO LEAKY SACOPLASMIC RETICULUM
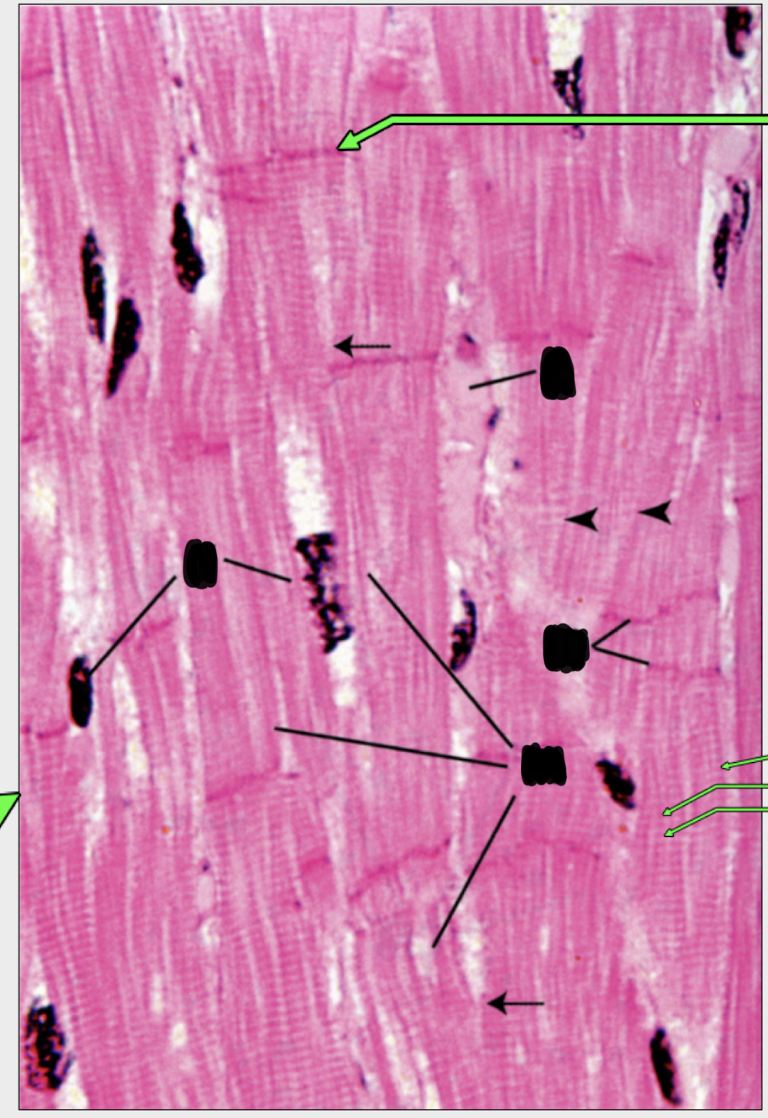
can you identify;
cardiac muscle cells
nucleus
intercalated disks
striations showing evidence of myofibrils and sarcomeres
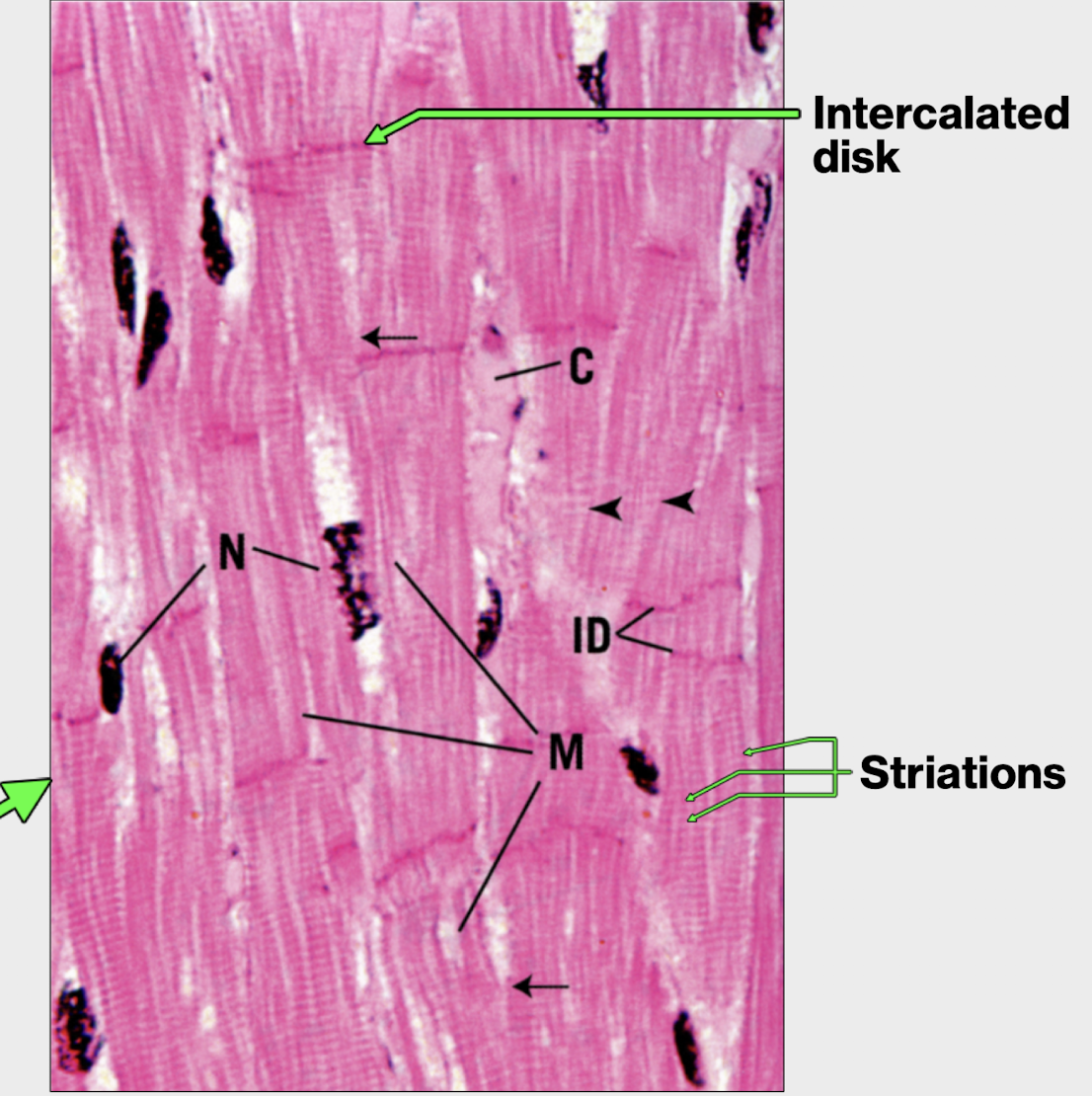
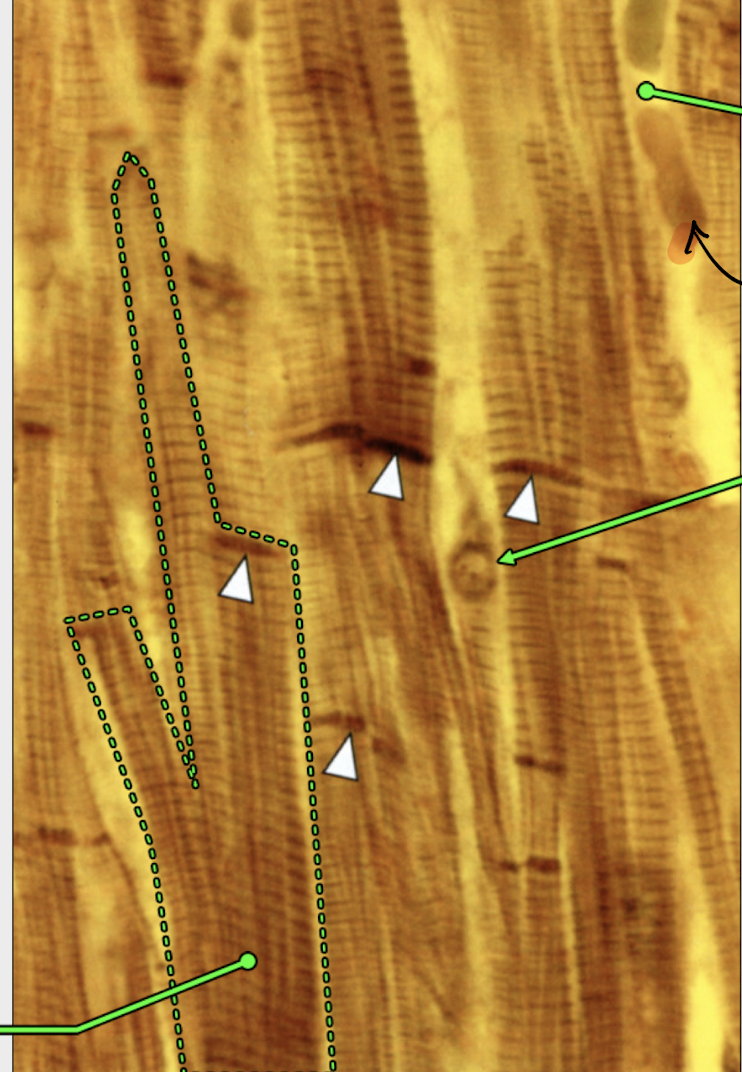
can you identify the structures
white arrows - pointing at intercalated disks
capillaries found on the upper right side - red blood cells flowing by
nucleus - circle in the middle
dotted lined - cardiac muscle cell
notice it forming two branches - skeletal muscle WOULD NOT do this

identify structure green arrows are pointing
lipofuscin
what are lipofuscin?
turnover of cellular material in lysosomes
accumulates with aging as cardiac muscle cells and most skeletal muscle cells do not undergo mitosis
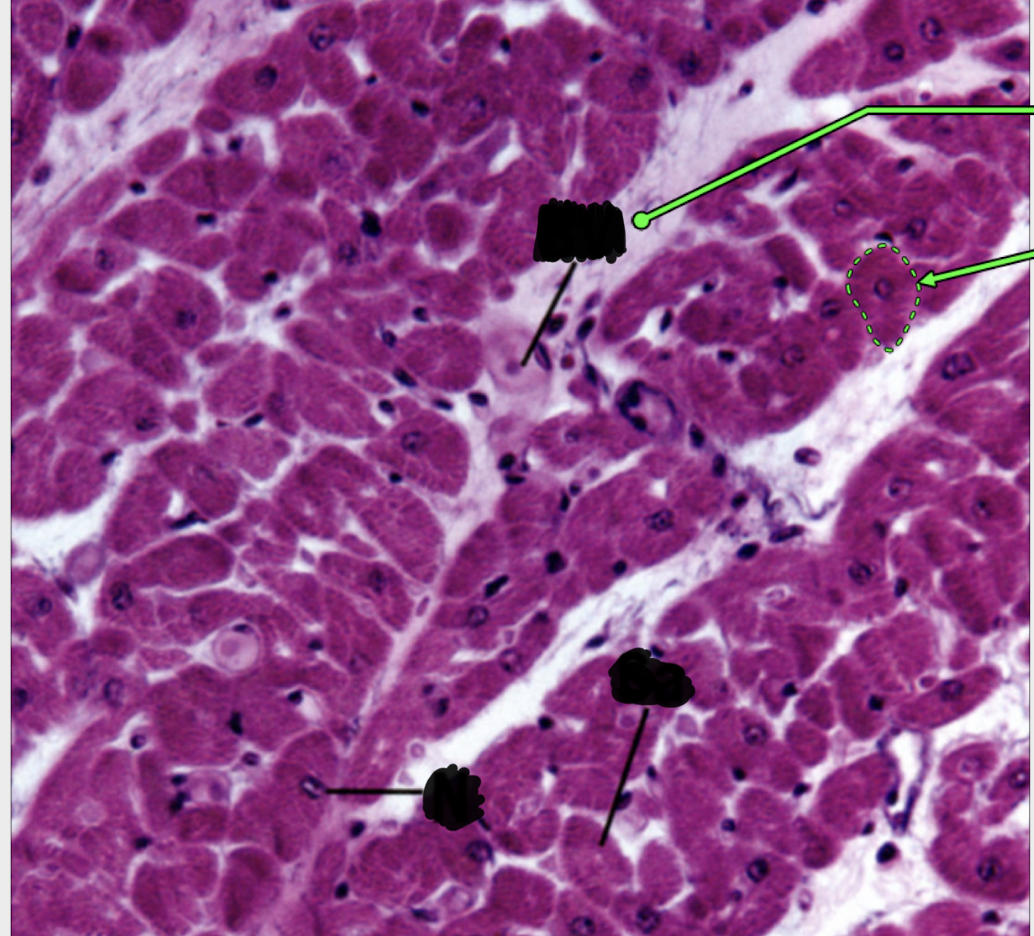
what are you looking at?
cardiac muscle cell transverse section
notice the blood vessel found embedded in endomysium
nucleus of cell found in the middle — opposite of skeletal muscle
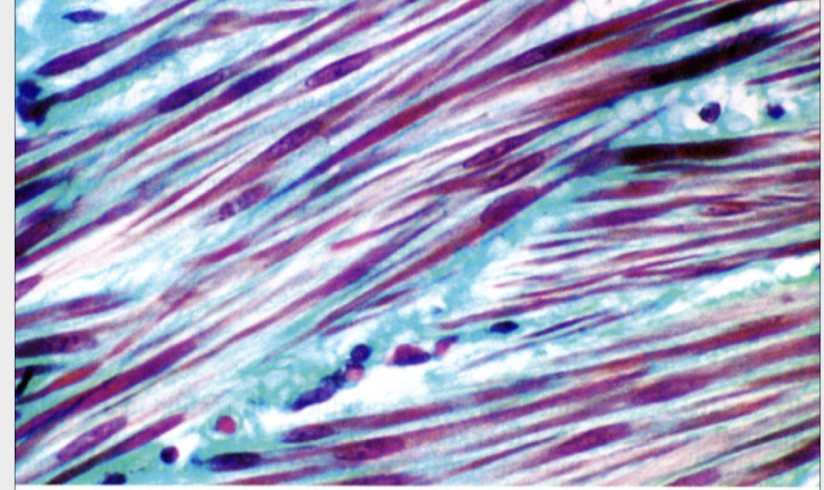
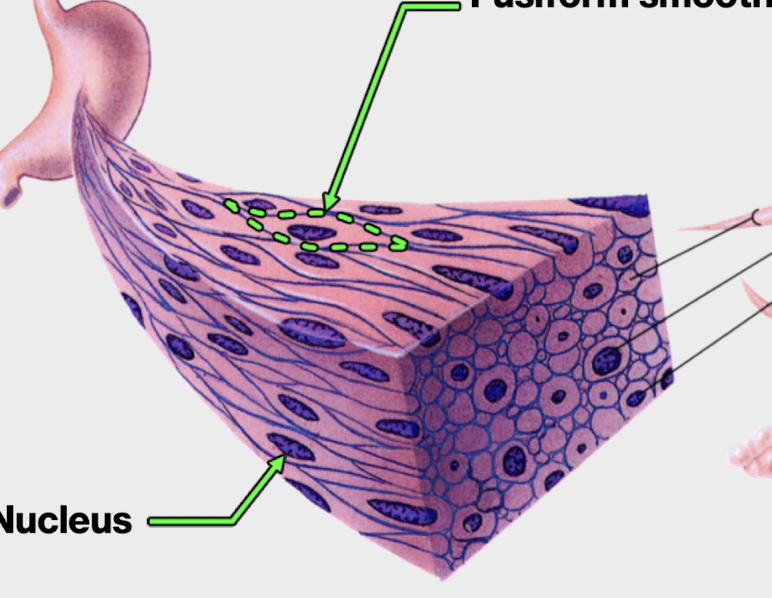
what type of shape does smooth muscle cell have?
fusiform shape
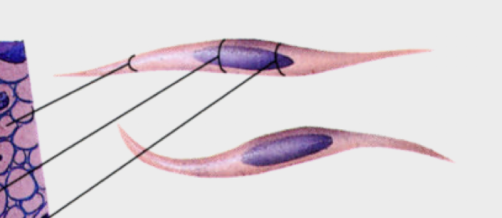
how does the nucleus of the smooth muscle cell look?
elongated in the center of the cell
how are adjacent cells in smooth muscle connected to each other?
gap junctions
multiunit
each smooth muscle cell is innervated directly by a nerve
unitary
only a few smooth muscle cells are innervated, transmit depolarizing signal to adjacent cells via gap junctions
do smooth muscle cells have sarcomeres?
no, but rather as a lattice that crosses through the cell
still contain actin and myosin*, DO NOT CONTAIN MYOFIBRIL
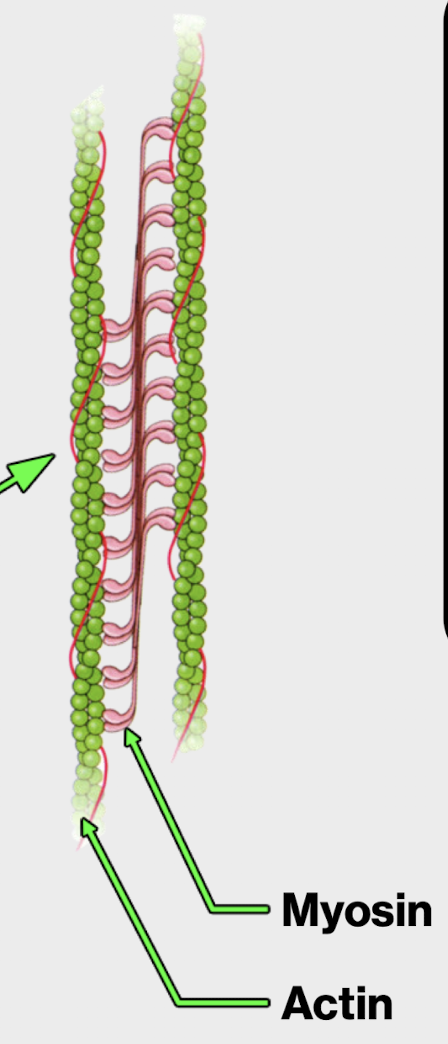
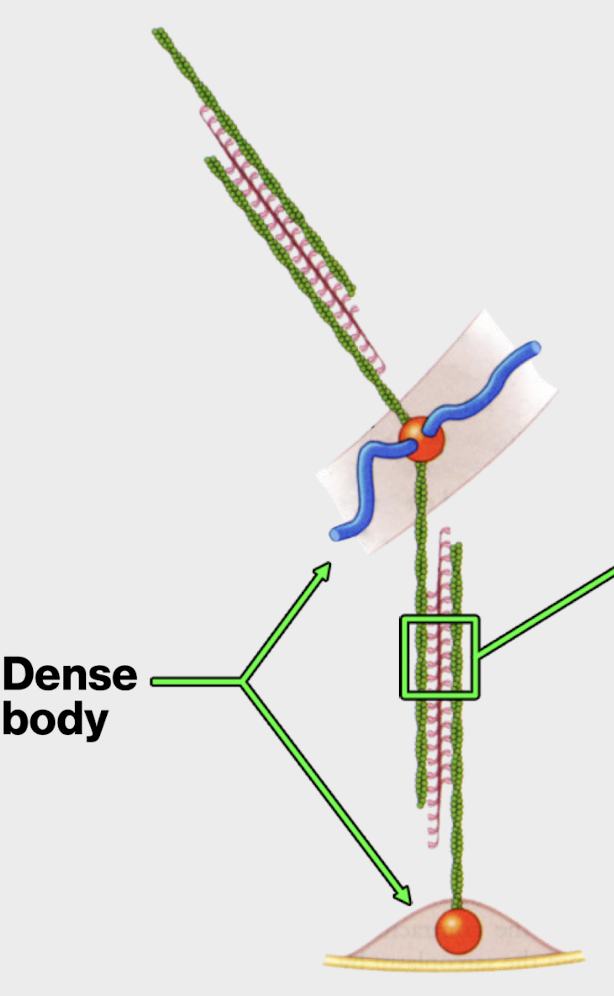
dense bodies
of a smooth muscle cell
protein complexes where contractile units are anchored at the cell wall and where they meet inside the cell
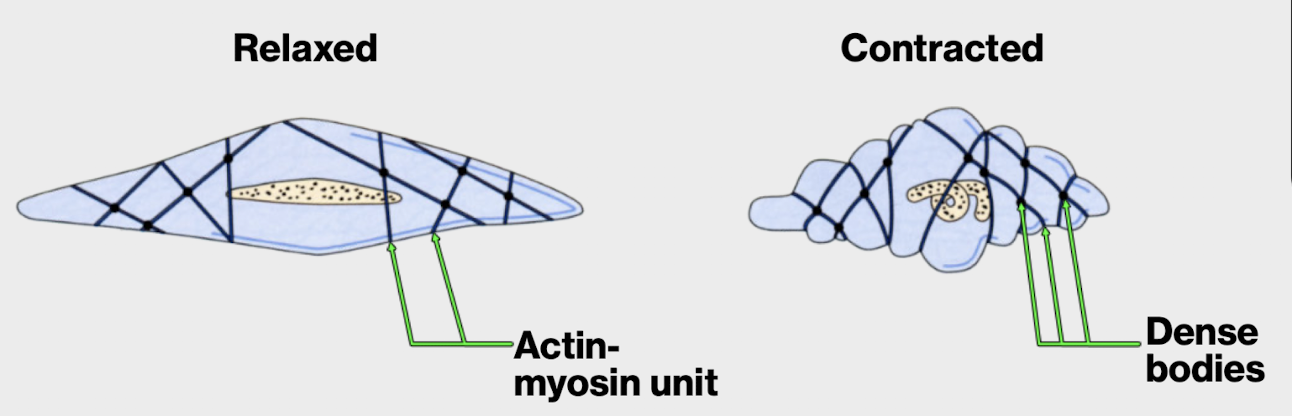
what type of contraction does a smooth cell have?
slow prolonged contraction
contraction shortens the cells in more than one direction
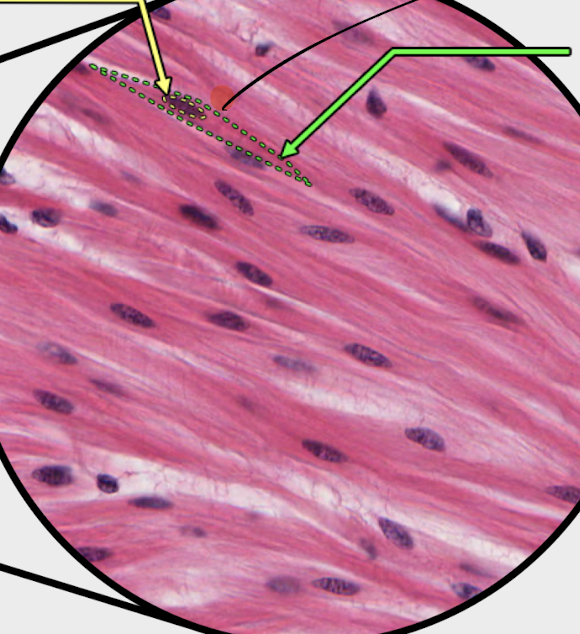
name the indicated structure
smooth muscle cell
notice its fusiform shape and elongated nuclei
what type of connective tissue are smooth muscle cells surrounded by?
reticular fibers
very THIN CT
what’s required to visualized the CT that surrounds smooth muscle cells?
extra stain; Masson trichrome stain
-reticular fibers (CT) is so thin that is not able to be visualized by regular H&E stain