Laboratory Parameters
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
True about blood urea nitrogen:
a. Normal level is 8-18 mg/dL
b. Produced in the liver
c. Excreted by the kidneys
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Blood urea nitrogen is increased in:
a. Renal disease
b. High protein intake
c. Upper GI bleeding
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Component of the muscles that is excreted by the kidneys.
a. Urea
b. Creatinine Kinase
c. Lactate Dehydrogenase
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
b. Creatinine
Normal GFR.
a. >90 mL/min
b. 60-89 mL/min
c. 45-59 mL/min
d. 30-44 mL/min
e. 15-29 mL/min
f. <15 mL/min
a. >90 mL/min
GFR in end stage CKD.
a. >90 mL/min
b. 60-89 mL/min
c. 45-59 mL/min
d. 30-44 mL/min
e. 15-29 mL/min
f. <15 mL/min
f. <15 mL/min
Found in tissues that use high ATP.
a. Urea
b. Creatinine Kinase
c. Lactate Dehydrogenase
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
b. Creatinine Kinase
Isozymes of Creatinine Kinase:
a. CK-MM
b. CK-BB
c. CK-MB
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Isozymes of Creatinine Kinase in the heart.
a. CK-MM
b. CK-BB
c. CK-MB
d. a and b
e. All
c. CK-MB
In myocardial infarction, the following are increased except:
a. CK-MB
b. AST
c. Troponin 1
d. LDH
e. None
e. None
The first to increase during myocardial infarction thus the gold standard for its diagnosis.
a. CK-MB
b. AST
c. Troponin 1
d. LDH
c. Troponin 1
Lactate Dehydrogenase isozymes high in the heart.
a. LDH 1,2
b. LDH 2
c. LDH 3
d. LDH 4
e. LDH 5
a. LDH 1,2
Lactate Dehydrogenase isozymes high in the heart and RBC.
a. LDH 1,2
b. LDH 2
c. LDH 3
d. LDH 4
e. LDH 5
b. LDH 2
Lactate Dehydrogenase isozymes high in the lungs
a. LDH 1,2
b. LDH 2
c. LDH 3
d. LDH 4
e. LDH 5
c. LDH 3
Lactate Dehydrogenase isozymes high in the kidney and placenta.
a. LDH 1,2
b. LDH 1
c. LDH 3
d. LDH 4
e. LDH 5
d. LDH 4
Lactate Dehydrogenase isozymes high in the liver and skeletal muscles.
a. LDH 1,2
b. LDH 2
c. LDH 3
d. LDH 4
e. LDH 5
e. LDH 5
Also known as SGPT.
a. Urea
b. Creatinine Kinase
c. Lactate Dehydrogenase
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
Liver specific and monitored when taking statins.
a. Urea
b. Creatinine Kinase
c. Lactate Dehydrogenase
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
Also known as SGOT.
a. Urea
b. Creatinine Kinase
c. Lactate Dehydrogenase
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
Present in the liver and heart.
a. Urea
b. Creatinine Kinase
c. Lactate Dehydrogenase
d. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
e. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
Low in liver damage.
a. AST
b. ALT
c. Both
d. None of these
d. None of these - both are HIGH in liver damage.
High in heart damage.
a. AST
b. ALT
c. Both
d. None of these
a. AST
Degradation product of hemoglobin.
a. Bilirubin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
c. Acid Phosphatase
d. Amylase, Lipase
e. Albumin
a. Bilirubin
True about bilirubin except:
a. Conjugated form is with glucuronic acid while unconjugated form is bound to albumin
b. Increased conjugated form may indicate hepatobilliary obstruction
c. Increased unconjugated form may indicate liver disease, hemolysis, and kernicterus
d. Measured through Schilling's test
e. None
d. Measured through Schilling's test
Bilirubin levels is measured through Van den Bergh reaction.
Schilling's test is for vitamin B12.
True about kernicterus:
a. Sulfonamide displace bilirubin in albumin
b. Free bilirubin causes encepalopathy especially in infants as they lack glucuronidation
c. Treated with blue light or phenobatbital
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Found in high levels in bile ducts, placenta, and bone.
a. Bilirubin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
c. Acid Phosphatase
d. Amylase, Lipase
e. Albumin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is increased in the following conditions except:
a. Biliary obstruction
b. Osteomalacia
c. Hyperparathyroidism
d. Paget's disease
e. BPH
f. None
e. BPH - it is the ACID phosphatase which is increased in BPH
Prostate specific antigen which is increased in BPH and prostate cancer.
a. Bilirubin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
c. Acid Phosphatase
d. Amylase, Lipase
e. Albumin
c. Acid Phosphatase
Increased in acute pancreatitis.
a. Bilirubin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
c. Acid Phosphatase
d. Amylase, Lipase
e. Albumin
d. Amylase, Lipase
Provides intravascular osmotic pressure.
a. Bilirubin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
c. Acid Phosphatase
d. Amylase, Lipase
e. Albumin
e. Albumin
Albumin is decreased in:
a. Liver disease
b. Malnutrition
c. Nephropathy
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
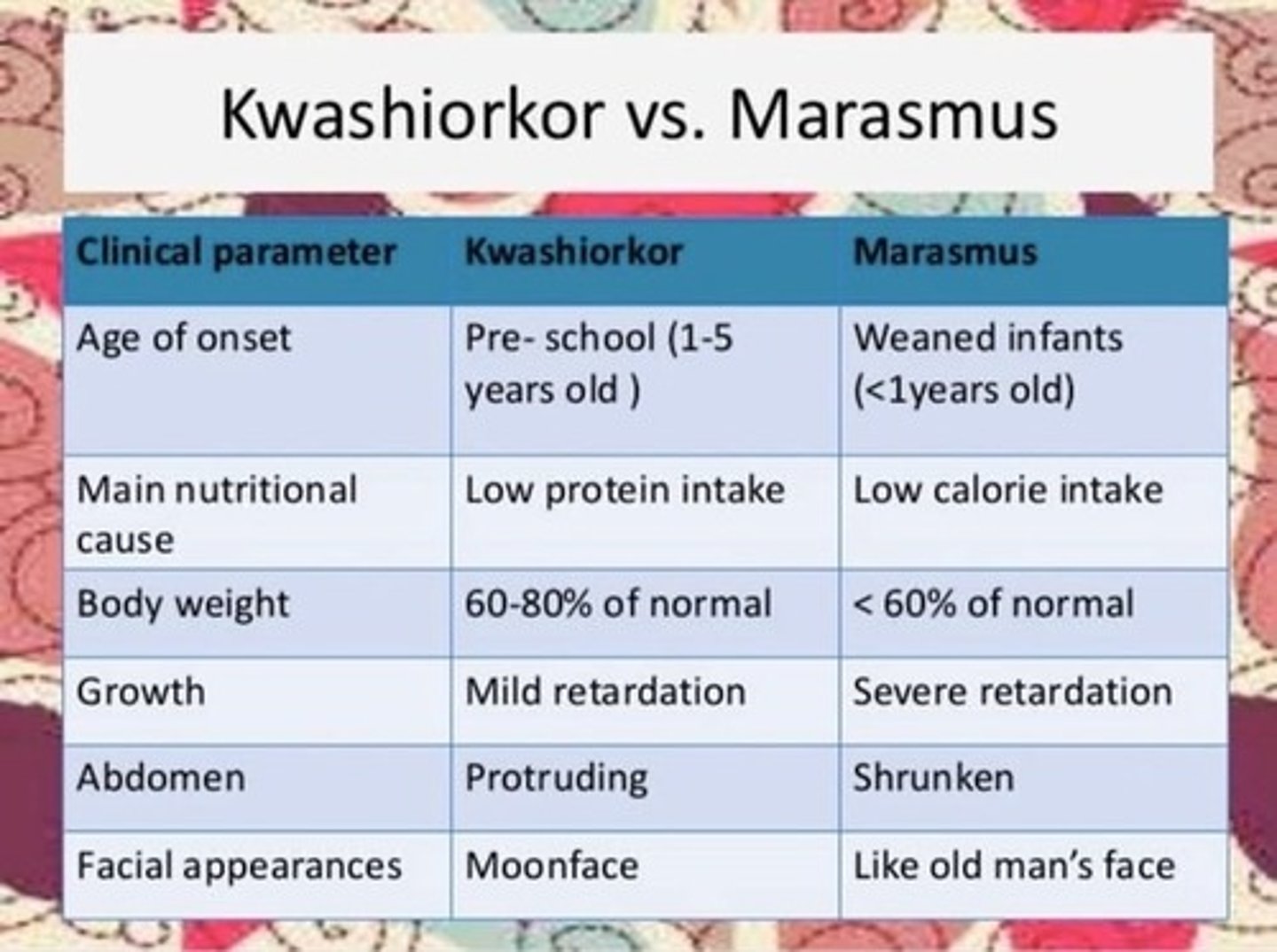
Deficiency in protein.
a. Kwashiorkor
b. Marasmus
a. Kwashiorkor
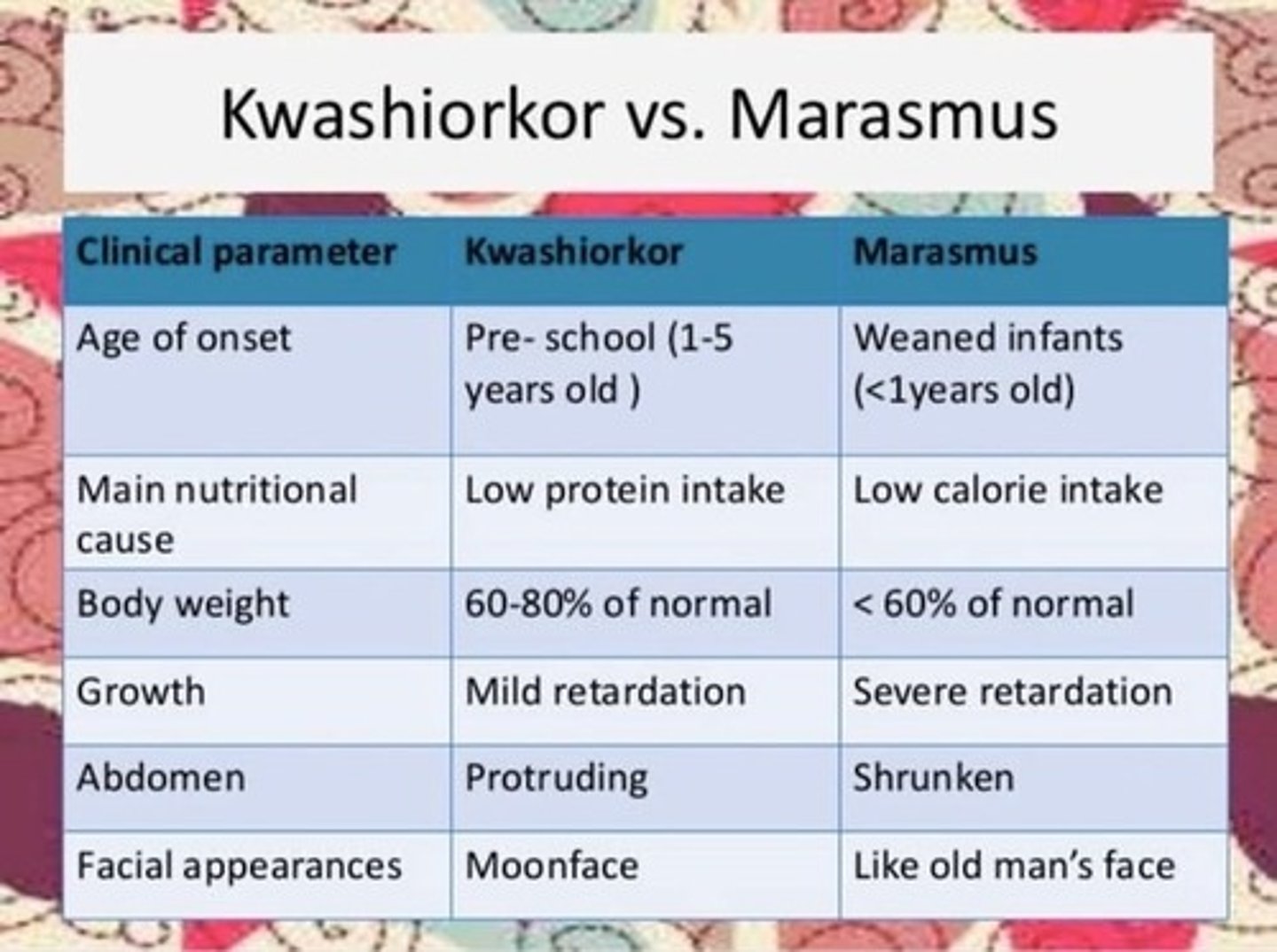
Deficiency in calories or energy.
a. Kwashiorkor
b. Marasmus
b. Marasmus
To which nonpolar drugs bind:
a. Alpha1 acid glycoprotein
b. Albumin
c. Lipoprotein
d. a and b
e. All
c. Lipoprotein
To which acidic and neutral drugs bind:
a. Alpha1 acid glycoprotein
b. Albumin
c. Lipoprotein
d. a and b
e. All
b. Albumin
Low level of this is manifested as edema and ascites (bloating abdomen).
a. Bilirubin
b. Alkaline Phosphatase
c. Acid Phosphatase
d. Amylase, Lipase
e. Albumin
e. Albumin
Uric acid is from metabolism of purine and is increased in the following except:
a. Gout
b. Cancer
c. Using thiazides
d. Using loop diuretics
e. Using niacin and aspirin
f. None
f. None
Normal blood glucose:
a. <100mg/dL
b. 110mg/dL
b. 110mg/dL
Normal fasted blood glucose:
a. <100mg/dL
b. 110mg/dL
a. <100mg/dL
Blood test that shows average blood sugar level over the past two to three months (120 days).
a. Uric acid
b. Blood sugar
c. HbA1c
d. C-reactive protein
e. Lipids
c. HbA1c
Non-specific indicator if acute inflammation.
a. Uric acid
b. Blood sugar
c. HbA1c
d. C-reactive protein
e. Lipids
d. C-reactive protein
Normal HbA1c.
a. 6%
b. 6.5%
c. 7%
d. 7.5%
b. 6.5%
Normal total lipids:
a. <200 mg/dL
b. <180 mg/dL
c. <130 mg/dL
d. >40 mg/dL
e. >50 mg/dL
a. <200 mg/dL
Normal TAG:
a. <200 mg/dL
b. <180 mg/dL
c. <130 mg/dL
d. >40 mg/dL
e. >50 mg/dL
b. <180 mg/dL
Normal LDL:
a. <200 mg/dL
b. <180 mg/dL
c. <130 mg/dL
d. >40 mg/dL
e. >50 mg/dL
c. <130 mg/dL
Normal HDL in male:
a. <200 mg/dL
b. <180 mg/dL
c. <130 mg/dL
d. >40 mg/dL
e. >50 mg/dL
d. >40 mg/dL
Normal HDL in female:
a. <200 mg/dL
b. <180 mg/dL
c. <130 mg/dL
d. >40 mg/dL
e. >50 mg/dL
e. >50 mg/dL
Major extra cellular cation.
a. Sodium
b. Potassium
c. Chloride
d. Magnesium
e. Calcium
f. Phosphate
a. Sodium
Indication of fluid status.
a. Sodium
b. Potassium
c. Chloride
d. Magnesium
e. Calcium
f. Phosphate
a. Sodium
Normal level: 135-145 mEq/dL
Normal amount of sodium but increased amount of water.
a. Dilutional hyponatremia
b. Depletional hyponatremia
a. Dilutional hyponatremia
Low sodium and low water content.
a. Dilutional hyponatremia
b. Depletional hyponatremia
b. Depletional hyponatremia
Consequence of edematous states such as HF or Liver cirrhosis.
a. Dilutional hyponatremia
b. Depletional hyponatremia
a. Dilutional hyponatremia
Consequence of vomiting, diarrhea, hypoaldosteronism, and renal disease.
a. Dilutional hyponatremia
b. Depletional hyponatremia
b. Depletional hyponatremia
Happen in dehydration, diureis, and diabetes.
a. Hyponatremia
b. Hypernatremia
b. Hypernatremia
Responsible for excitability of muscles, nerves, and acid-base balance.
a. Sodium
b. Potassium
c. Chloride
d. Magnesium
e. Calcium
f. Phosphate
b. Potassium
Caused by vomiting, diarrhea, diuretics (except K-sparing), alkalosis.
a. Hypokalemia
b. Hyperkalemia
a. Hypokalemia
Due to excessive cellular breakdown, hypoaldosteronism, acidosis.
a. Hypokalemia
b. Hyperkalemia
b. Hyperkalemia
Chloride in wide anion gap.
a. Increased
b. Decreased
b. Decreased
Magesium in renal disease:
a. Increased
b. Decreased
a. Increased
40% albumin bound.
a. Sodium
b. Potassium
c. Chloride
d. Magnesium
e. Calcium
f. Phosphate
e. Calcium
Calcium is decreased in:
I. Vitamin D deficiency
II. HypoPTH
III. HyperPTH
IV. High Vitamin D
V. Paget's Disease
VI. Usage of Thiazides
a. I, II, III, IV, V, VI
b. I, II, IV
c. I, II
d. III, IV, V, VI
c. I, II
Calcium is increased in:
I. Vitamin D deficiency
II. HypoPTH
III. HyperPTH
IV. High Vitamin D
V. Paget's Disease
VI. Usage of Thiazides
a. I, II, III, IV, V, VI
b. I, II, IV
c. I, II
d. III, IV, V, VI
d. III, IV, V, VI
Phosphate is decreased in the following except:
a. High Al level
b. HyperPTH
c. Renal disease
d. HypoPTH
e. a and b
f. None
d. HypoPTH
Phosphate is increased in:
a. High Al level
b. HyperPTH
c. Renal disease
d. HypoPTH
e. a and b
f. None
d. HypoPTH
Form of bone mineral.
a. Ca hydroxyapatite
b. Ca methoxyapatite
c. Ca phoshatide
d. Ca sulfaphosphatide
a. Ca hydroxyapatite
Primary hormone for bone mineral homeostasis.
I. Calcitonin
II. Parathyroid Hormone
III. Calcitriol
IV. Glucucorticoids
V. Estrogen
a. I, II, III, IV, V
b. I, II, III
c. I, II
d. IV, V
e. III, IV, V
b. I, II, III
Calcitonin is produced in the?
a. Liver
b. Spleen
c. Bone marrow
d. Thyroid
d. Thyroid
Promote osteoblast activity increasing deposition of Ca and PO4 to the bones.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
a. Calcitonin
Lower blood levels of Ca and PO4.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
a. Calcitonin
Promote osteoclast activity increasing resorption of Ca and PO4 from the bones.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
b. Parathyroid Hormone
Biphosphonates as drug for osteoporosis inhibit the action of which?
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
b. Parathyroid Hormone
Increase blood level of Ca but not PO4.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
b. Parathyroid Hormone
Formed from metabolism of 7-dehydrocholesterol into cholecalciferol.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
c. Calcitriol
Vitamin D3.
a. Cholecalciferol
b. Calcitriol
a. Cholecalciferol
Precursor of Vitamin D synthesis.
a. Cholecalciferol
b. Calcitriol
a. Cholecalciferol
Active Vitamin D.
a. Cholecalciferol
b. Calcitriol
b. Calcitriol
Increase blood Ca and PO4 level.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
c. Calcitriol
Antagonize vitamin D decreasing Ca absorption and increasing Ca excretion.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
d. Glucucorticoids
Antagonize PTH bone resorption decreasing blood Ca.
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid Hormone
c. Calcitriol
d. Glucucorticoids
e. Estrogen
e. Estrogen
Normal blood pH.
a. 7.35-7-45
b. 38-42 mmHg
c. 22-28 mEq/L
a. 7.35-7-45
Normal blood CO2.
a. 7.35-7-45
b. 38-42 mmHg
c. 22-28 mEq/L
b. 38-42 mmHg
Normal blood HCO3.
a. 7.35-7-45
b. 38-42 mmHg
c. 22-28 mEq/L
c. 22-28 mEq/L
Respiratory acidosis.
a. High CO2
b. Low CO2
c. High HCO3
d. Low HCO3
a. High CO2
CO2 is acidic
Respiratory alkalosis.
a. High CO2
b. Low CO2
c. High HCO3
d. Low HCO3
b. Low CO2
CO2 is acidic.
Metabolic alkalosis.
a. High CO2
b. Low CO2
c. High HCO3
d. Low HCO3
c. High HCO3
Metabolic acidosis.
a. High CO2
b. Low CO2
c. High HCO3
d. Low HCO3
d. Low HCO3
In normal anion gap, there is decreased in:
a. Cl
b. HCO3
c. K
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
b. HCO3
In wide anion gap, there is decreased in:
a. Cl
b. HCO3
c. K
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
"Anion"
During this condition, compensatory acidosis occur wherein the goal of the body is to increase blood CO2 level.
a. Respiratory acidosis
b. Respiratory alkalosis
c. Metabolic acidosis
d. Metabolic alkalosis
d. Metabolic alkalosis
Increase CO2 (acidic) counteract metabolic alkalosis (basic).
To which paper bag breathing is a remedy?
a. Respiratory acidosis
b. Respiratory alkalosis
c. Metabolic acidosis
d. Metabolic alkalosis
d. Metabolic alkalosis
Hyperventilation can be a result of:
a. Respiratory acidosis
b. Respiratory alkalosis
c. Metabolic acidosis
d. Metabolic alkalosis
c. Metabolic acidosis
During hyperventilation, goal of the body is to decrease blood CO2 decreasing blood acidity thus counteracting metabolic acidosis.