international economics exam 3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
less, increase, increase
If e goes form $2/E to $1/E, EU goods are ___ expensive
Imports will ___
Demand for E will ___
more
If e goes from $1/E to $2/E, Europeans will supply ___ Euros
flexible
The US has a ___ exchange rate regime
more, increase, demand, right, depreciate, appreciate
Suppose the demand for EU goods goes up
Americans need ___ Euros, which would ___ demand for Euros
The ___ curve will shift to the ___
$ will ___ and Euros will ____
fixed, low, export
China has a ____ exchange rate regime
China intervenes to keep the value of Yuan ____. This will help with the country’s ____
depreciate, appreciate, decrease, 5, lower, less, demand, left, 0
If the US demands more Chinese goods, $ will ____ and Yuan will ____
To address this issue, China can ____ its interest rate
For instance, you deposited $100 in a Chinese bank when the interest rate was 5%
Your interest income would be $___
The new interest rate would be ___ than 5%
Hence, investing in China is ___ attractive
This will cause the ____ curve to shift to the ____
So we are back to a fixed rate level
However, the main limitation of this policy choice is that the interest rate cannot go below ___
depreciate, appreciate, increase, supply, right
If the US demands more Chinese goods, $ will ___ and Yuan will ____
To address this issue, China can ____ dollar reserves
To do so, China will offer a lot of Yuan in the market in exchange for $
This will cause the ____ curve to shift to the ___
2, 4, EU, EU, increase, demand, right, depreciate, appreciate
Suppose i = 2% and if = 4%. You are investing $100 in either country
In the US, your interest income would be $___
In the EU, your interest income would be $___
Which market will give you a higher interest income? ___ market
As we put our money in the ___ market, the demand for Euros will ____
This will cause the ___ curve to shift to the ___
Hence, $ will ___ and Euros will ___
10, 6, US, US, decrease, demand, left, appreciate, depreciate
Suppose i = 5% and if = 3%. You are investing $200 in either country
In the US, your interest income would be $___
In the EU, your interest income would be $___
Which market will give you a higher interest income? ___ market
As we put our money in the ___ market, the demand for Euros will ____
This will cause the ___ curve to shift to the ___
Hence, $ will ___ and Euros will ___
depreciate, appreciate, 5, 6, 10, in 90 days, EU, increase, increase, depreciate, appreciate
Suppose today’s e = $1.2/E and e^ex = $2/E in 90 days
This means that investors expect $ to ____ and E to ____
You invested $100 in the European bond market when the interest rate is 5%
Your interest rate payment is E___
You can either convert it back to the dollar today or in 90 days
If you do it today, your realized gain will be $___
If you do it in 90 days, your realized gain will be $___
So, which exchange rate yields a higher income? The exchange rate _____
Hence , your expectations will lead you to put money in the ___ market. So demand for E will ____
This will cause the actual exchange rate to ___, meaning that $ will ____ and E will ___
appreciate, depreciate, 3, 4.5, 3, today, US, decrease, decrease, appreciate, depreciate
Suppose today’s e = $1.5/E and e^ex = $1/E in 90 days
This means that investors expect $ to ____ and E to ____
You invested $100 in the European bond market when the interest rate is 3%
Your interest rate payment is E___
You can either convert it back to the dollar today or in 90 days
If you do it today, your realized gain will be $___
If you do it in 90 days, your realized gain will be $___
So, which exchange rate yields a higher income? The exchange rate _____
Hence , your expectations will lead you to put money in the ___ market. So demand for E will ____
This will cause the actual exchange rate to ___, meaning that $ will ____ and E will ___
purchasing power parity, determines, long run, E, law of one price, absolute PPP, relative PPP
PPP stands for __________. It ____ the exchange rate in the ____
For instance, if $1 can get you 2 pencils and €1 can get you 3 pencils, PPP tells us that which currency is more valuable? ___
There are three assumptions of PPP
____
____
____
law of one price
The Big-Mac index is based on the _____
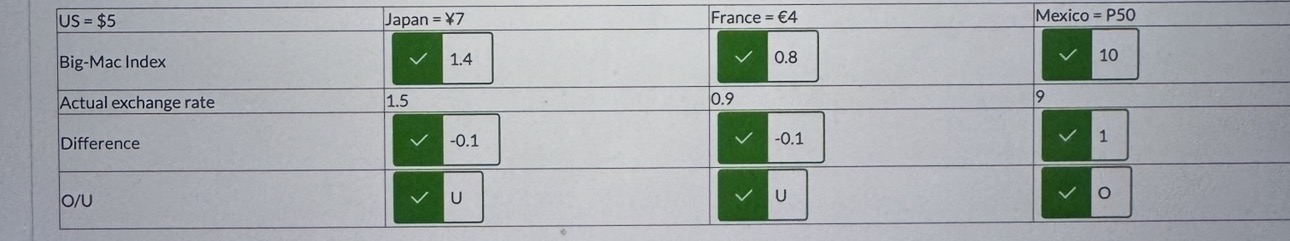
150, 300, 0.5, absolute PPP
US CPI = 150
EU HICP = 300
Then, the exchange rate between the dollars and the euros should be (____/____) = ____
This is based on the _____
2, positive, increase, depreciate, appreciate, -1.1, negative, decrease, appreciate, depreciate, relative PPP
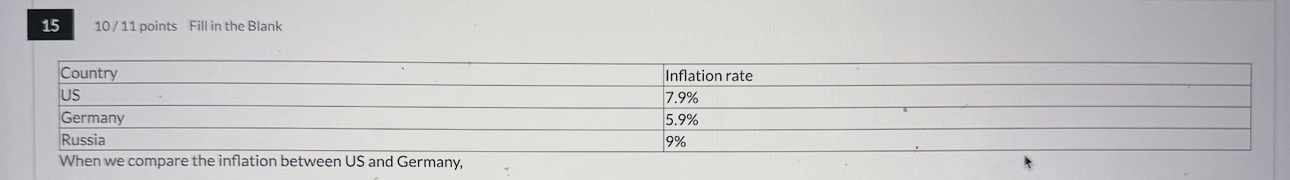
US - Germany = ___%
This value is ____, which implies that the exchange rate will ___
So $ will ___ and E will ____
When we compare the inflation between US and Russia,
US - Russia = ___%
This value is ____, which implies that the exchange rate will ____
So $ will ____ and Rubles will ___
This is based on the _____