Mechanical Properties of Solids
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are different types of loads and how do materials respond to them?
static loads: loads that remain constant over time
dynamic loads: loads that change over time, such as impact
environmental loads: loads caused by environmental factors like temperature, humidity, or corrosion
How do materials respond to Static Loads?
materials experience Elastic Deformation or Plastic Deformation if the load exceeds the yield strength
Very high static Loads can cause fracture
ex. a building column supporting a roof
How do materials respond to Dynamic Loads?
can cause fatigue, leading to fracture at lower stress levels than static loads
ex. car wheels hitting bumps
How do materials respond to Environmental Loads?
thermal expansion can cause internal stresses, and corrosion can weaken materials
ex. rust weakening a bridge
What is Tensile Testing?
mechanical test that measures how a material responds to pulling or stretching forces
sample is pulled until it breaks, while force and elongation are recorded
What is tensile testing used for?
to determine:
yield strength (when permanent deformation starts)
ultimate tensile strength (UTS) (maximum stress before breaking)
Elongation/strain (how much it stretches/ductility)
Modulus of Elasticity (stiffness of the material)
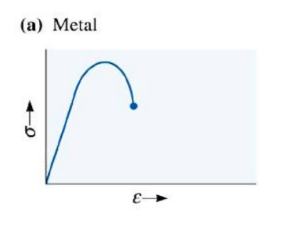
What does a tensile stress strain curve look like for metals?
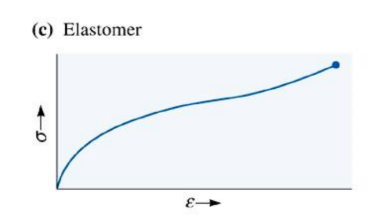
what does a tensile stress-strain curve look like for elastomer?
what does a tensile stress-strain curve look like for ceramics, glasses and concrete?

What is engineering stress?
the applied force divided by the original cross-sectional area of a matieral
σ = F/Ao
What is engineering strain?
the change in length of a material divided by its original length
ε = ΔL/Lo
What is yield strength?
the stress at which a material begins to deform permanentl
What are elastic properties obtained from the tensile test?
Young’s Modulus (E) E = S/e
Poisson’s ratio (v) v = -elateral/elongitudinal
Modulus of Resilience (Er) Er = (1/2)(yield strength)(strain at yielding)
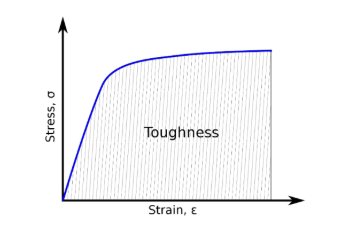
what is tensile toughness?
the energy absorbed by a material prior to fracture
the are under the stress-strain curve
what is ductility?
the ability of a material to be permanently deformed without breaking when a force is applied
How does temperature affect the mechanical behaviour of materials?
High Temperatures:
decreases yield strength and UTS → material is softer and more ductile
increases plastic deformation
Lower Temperatures:
increases strength but decreases ductility → materials become more brittle
can lead to fracture at a lower stress under impact or dynamic loads
Dislocations:
higher temp → dislocations move more easily → easier plastic deformation
lower temp → dislocations move less → materials resist deformation
What is the Bend Test for Brittle Materials?
a mechanical test used to measure the flexural strength of brittle materials
what is flexural strength or modulus or rupture?
the stress requires to fracture a specimen during a bend test
what is the flexural modulus?
the modulus of elasticity calculated from the bend test results
What is Hardness?
resistance to penetration by sharp objects
macro-hardness: hardness measured using loads >2 N
micro-hardness: hardness measured using loads <2 N
nano-hardness: hardness of materials measured at 1-10m, length using very small forces (~100μN)
What is an Impact Test?
measures the how much a material can absorb a sudden load without breaking
What is Impact Toughness?
the energy absorbed by a material during fracture during the impact test
what are the properties obtained from the impact test?
ductile to brittle transition temperature (DBTT): the temperature below which a material behaves in a brittle manner in an impact test