Cardiac Contractility/Pre/Afterload
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Alpha motor, end-plate depolarization
Skeletal Muscle Contraction
Each fiber is innervated by an __ __ neuron
Motor neuron initiates an __-__ __ to trigger muscle action potential
Intercalated, gap junctions
Cardiac Muscle Contraction
Fibers (cells) connected by __ discs
Electrical current from adjacent cells travel through __ __ (electrical synapses) to trigger cardiomyocyte action potential
Pacemaker, contractile
Cardiac Depolarization is initiated by __ cells
Spreads through __ cells of heart via electrical synapses
SA, AV, atria, apex, upward
Cardiac Conduction/Electrical Cycle
(1) __ node depolarizes
(2) Electrical activity goes rapidly to __ node via internodal pathways
(3) Depolarization spreads more slowly across __ (part of heart) → Conduction slows thru AV node
(4) Depolarization moves rapidly thru ventricular conducting system to __ of heart
(5) Depolarization wave spreads __ from apex
Rapidly, sustained, DHPRs, RyR
Unlike neurons/skeletal muscle cells → Cardiac action potentials:
__ reach threshold (phase 0), and have a __ plateau (phase 2)
Use L-Type Ca2+ Channels = __s
Ca2+ influx → __ (channel) opening → Ca2+ release
Phase 0
Rapid Na+ influx thru open fast Na+ channels (Card AP)
Phase 1
Transient K+ channels open and K+ efflux returns TMP to 0 mV (Card AP)
Phase 2
Influx of Ca2+ thru L-type Ca2+ channels electrically balanced from K+ efflux thru delayed rectifier K+ channels (Card AP)
Phase 3
Ca2+ channels close but delayed rectifier K+ channels remain open and return TMP to -90 mV (Card AP)
Phase 4
Na2+, Ca2+ channels closed, open K+ rectifier channels keep TMP stable at -90 mV (Card AP)
Brief, summation
Skeletal muscle refractory period
__ action (brief/long); facilitates __ation/tetanus
Long, diastole
Cardiac muscle refractory period
__ action (brief/long); facilitates __ (filling chambers with blood)
SERCA, Na/Ca2+ enhancer
Both Cardiac and Skeletal muscle relaxation rely on
__ pumps Ca2+ back into sarcoplasmic reticulum
Only in Cardiac muscle relaxation is also
__/__ __ (NCX): Pumps Ca2+ out of cells
Ejection fraction, stroke volume
The __ __ (ratio of heart) is directly related to cardiac force production
More forceful contraction means a greater __ __ (measure of cardiac force)
Myocardial fiber length, contractility
Cardiac force is affected by (2) factors
B1, S, AC, cAMP, adenyl cyclase, A, contraction
Positive ionotropic effect
__ receptors on cardiomyocytes (ANS)
G_ protein
Activate __ + __ (2nd messengers)
Protein kinase _
Increase muscle __ (action)
Stretches, myofilament, stroke volume, cross-bridges
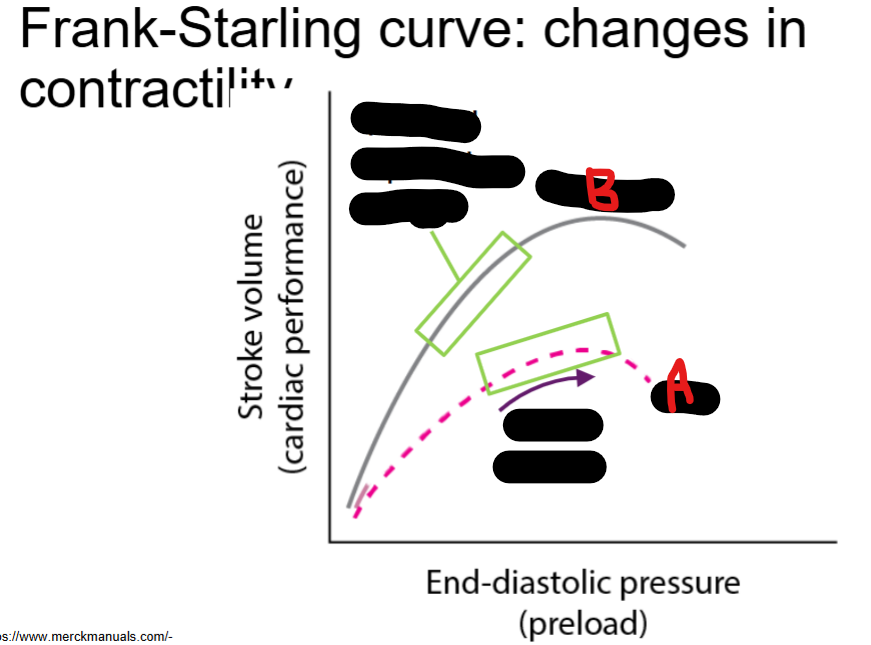
Frank-Starling Law
As ventricle fills in diastole, it __
Lengthening of myofiber optimizes__ overlap and increases contraction force (i.e. __ __)
Overstretch in myofiber → Dysfunction
overworking actin and myosin filaments barely form __-__ with low overlap from overstretch
Preload, diastolic, diastolic
__load is the degree of ventricular stretch (due to volume)
It is estimated by the end-__ volume and end-__ pressure (systolic vs diastolic)
Sarcomere, calcium
Increasing __ length also makes cardiac muscle more sensitive to __ (ion) → Increasing contractility
Catecholamines, ionotropic, lusitropic
__ (neurot class) alter ionotropy and lusitropy
More forceful contractions favor positive __tropic effect
Increase opening of DHPRs → Increase Ca2+ influx and release (via RyR)
Faster relaxation favor positive __tropic effect
Increase SERCA activity → Increase Ca2+ reuptake
Preload, contractility, afterload
__load and myocardial __ have a positive feedback effect to stroke volume
__load on the other hand has a negative feedback to stroke volume
Afterload
Force ventricle must overcome to circulate blood ; load against which heart ejects blood
Systolic, stenosis
Elevated__ BP → greater afterload
Resistance - Aortic __ (valve disease) → greater afterload
Afterload, O2, ATP
To overcome increased __ (pressure) and maintain cardiac output, heart must work harder: Increase __ and __ consumption for heart tissues
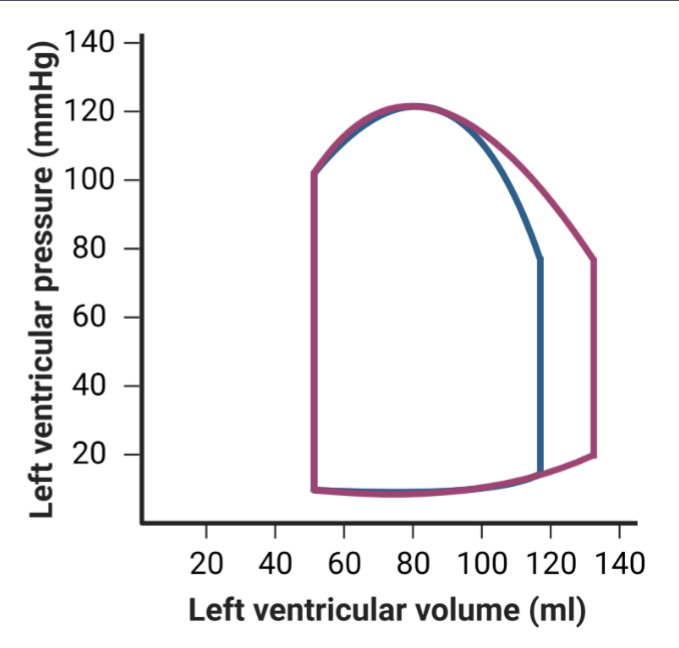
Increase in preload
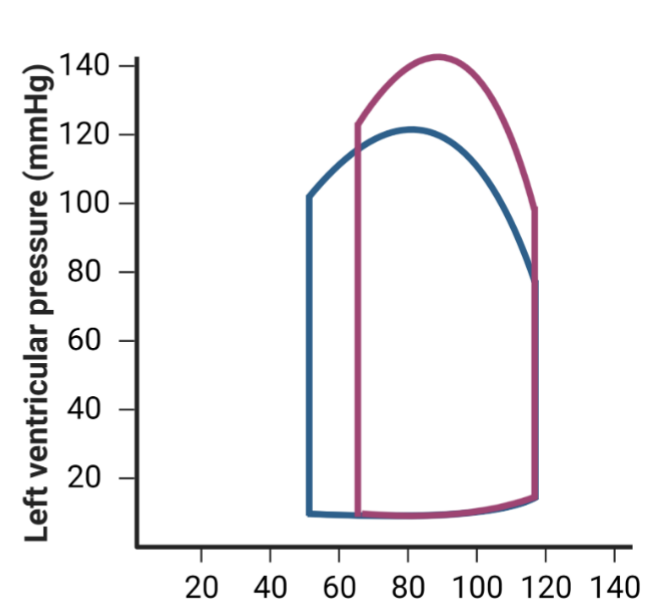
Increase in afterload
failure, preload, normal curve
A = heart __ due to poor __load
B = __