Chem 1 Lab Final (UF)
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
density is an _________ property of matter
intensive
% error formula
(actual - expected) / expected x 100%
measurements are said to be _______ if they yield very similar results when repeated in the same manner.
precise

a measurement is considered ________ when it yields a result very close to the true or accepted value.
accurate
NaCl solution is
non hazardous
magnesium sulfate is
non hazardous
manganese sulfate is
a health hazard, corrosive, and an environmental hazard
cupric sulfate is
an irritant and an environmental hazard
titrant
the substance being added to the analyte. The titrant is usually of known concentration.
analyte
the substance being analyzed. Often of unknown concentration.
the __ is the point at which the titrant and analyte are present in a stoichiometric equivalent ratio based on their reaction.
equivalence point
end point
where the titration ends in reality. If you are using a visual indicator, this would be where you observe the completion of the rxn.
titration curve
this can be a pH v.s. Volume curve, showing change in pH as titrant is added, for an acid/base rxn. Or it could be a graph of potential v.s. Volume of titrant added. There are other options as well...
sulfuric acid is
corrosive
ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate is
oxidizer, health hazard, irritant, and environmental hazard.
when the atmosphere exerts more pressure than the gas, use
Pgas = Patm - Pfluid
when the gas exerts more pressure than the atmosphere, use
Pgas = Patm + Pfluid
if the fluid is mercury, then
the pressure of the fluid is equal to the difference in height of the fluid level in units of millimeters
the pressure exerted by a fluid due to gravity can be calculated by the equation
P = hdg
- where P is the pressure of the fluid in units of pa
- h is the height of the fluid in meters
- d is the density of the fluid in kg/m^3
- and g is the acceleration due to gravity 9.81m/s^2
h1d1 =
h2d2
KE
3/2RT
Ptotal =
PA + PB
Ptotal
Pgas + Pvapor
units of pressure
- 1 atm = 760 mmHg
- 1 atm = 760 Torr
- 1 atm = 101325 Pa
- 1 atm = 1013 mbar
3M HCl solution
can cause severe burns and eye damage. Do not breathe, mist, or spray. May cause respiratory irritation. May be harmful if swallowed.
Mg:
flammable solid. Keep away from heat, sparks, open flames, and hot surfaces. No smoking.
both acids and bases can be corrosive (T/F)
T
halogens are unreactive (T/F)
F
mercury is readily absorbed through the skin (T/F)
F
oxidizing agents and reducing agents should be stored close to one another for safety (T/F)
F
peroxides can be stored indefinitely (T/F)
F
pyrophoric substances can burn spontaneously in air (T/F)
T
flammable liquids should be used with care near sources of ignition (T/F)
T
cryogenics are stored at high temperatures (T/F)
F
electricity can be hazardous (T/F)
T
Mg is considered flammable (T/F)
T
Mg reacts w/ water and acid solutions (T/F)
T
this concentration of HCl solution is considered flammable (T/F)
F
water can be safety added to this concentration of aqueous HCl solution.
T
this concentration of aqueous HCl is light blue in color.
F
it is safe to wash with water if one's skin is exposed to magnesium chloride solution.
T
magnesium chloride solution is considered flammable.
F
hydrogen gas is considered a carcinogen.
F
hydrogen gas is considered flammable.
T
hydrogen gas is considered an asphyxiant.
T
the last part of the lab involves...
adding a heated sample of metal to room temperature water. The temp. Change is used to determine the specific heat of the metal, and to identify the metal.
molar enthalpy of solution:
deltaH/moles
The transfer of heat resulting from an acid/base neutralization is called
enthalpy of neutralization, deltaHneutralization
qsolution=
-qrxn
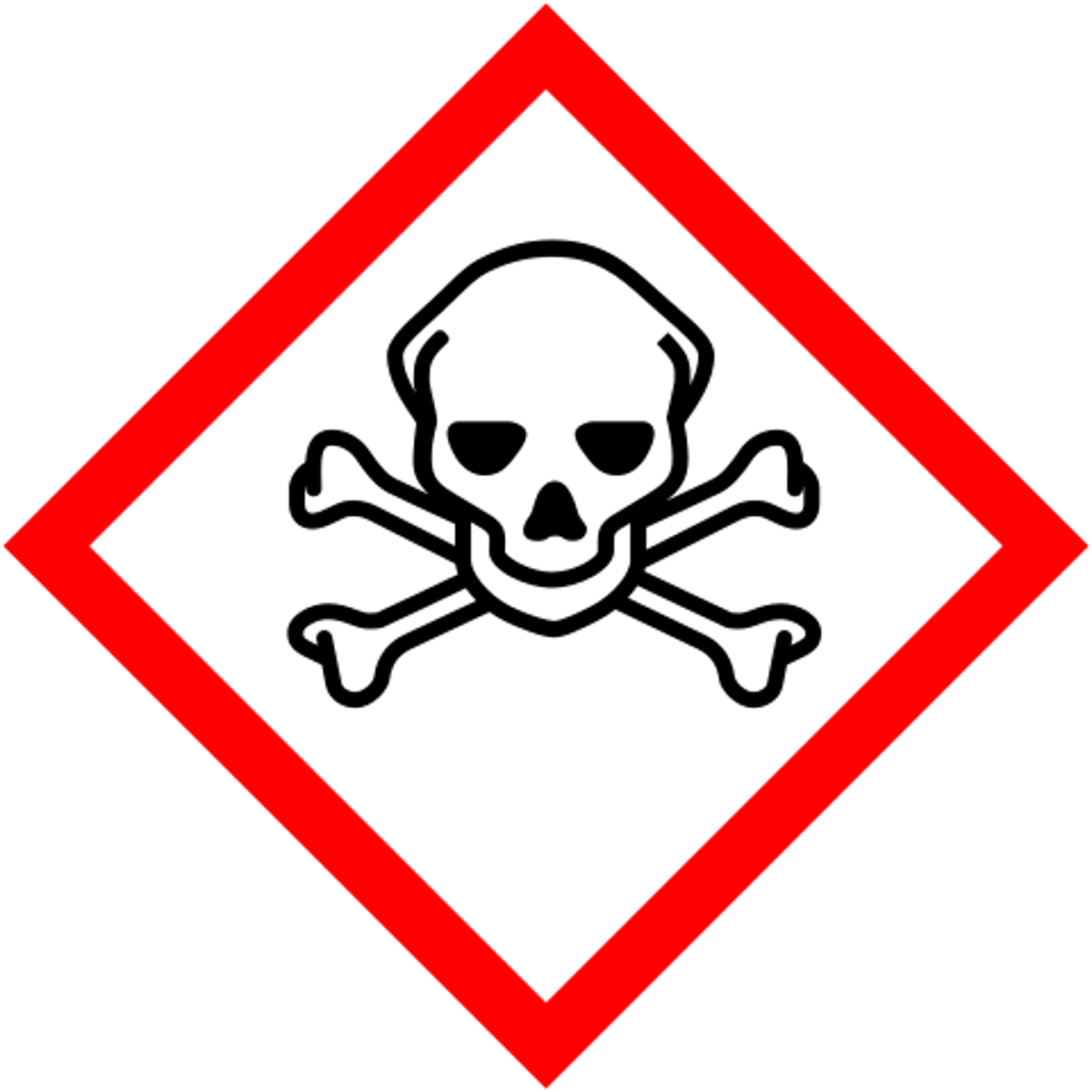
Skull and Cross Bones pictogram
acute toxicity (fatal or toxic)

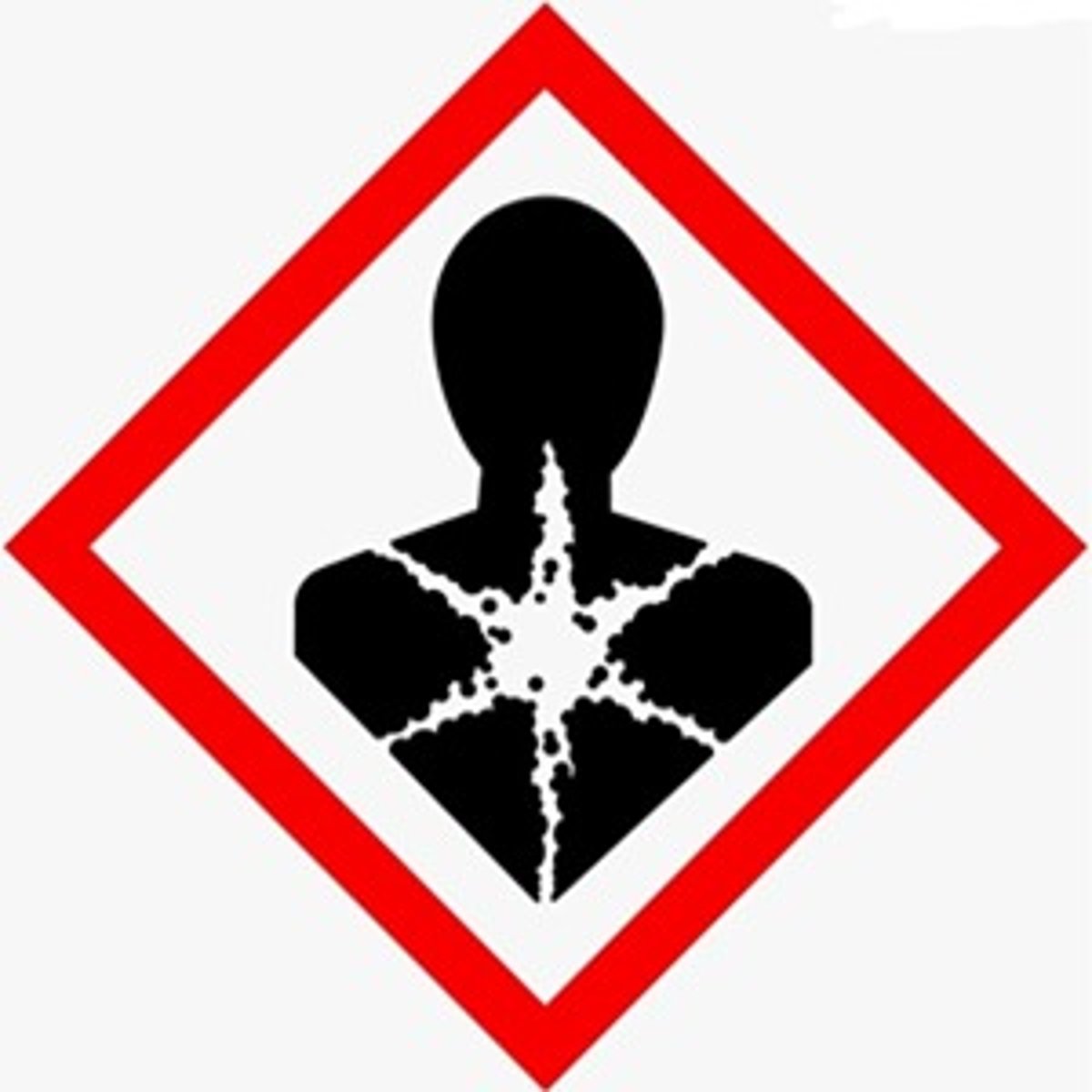
Person with white star on chest pictogram
Health Hazard

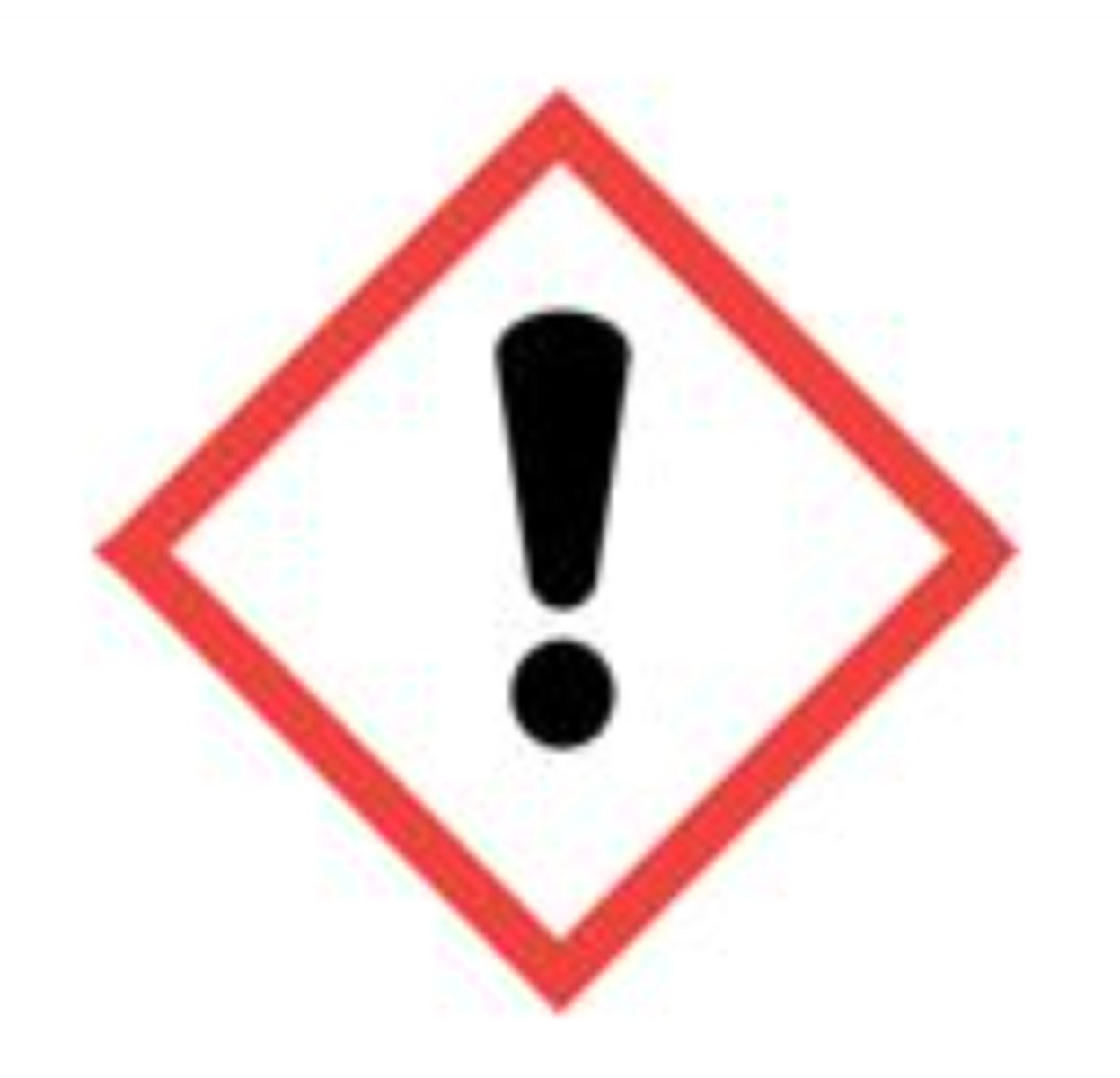
Exclamation mark pictogram
Irritant, Acute toxicity

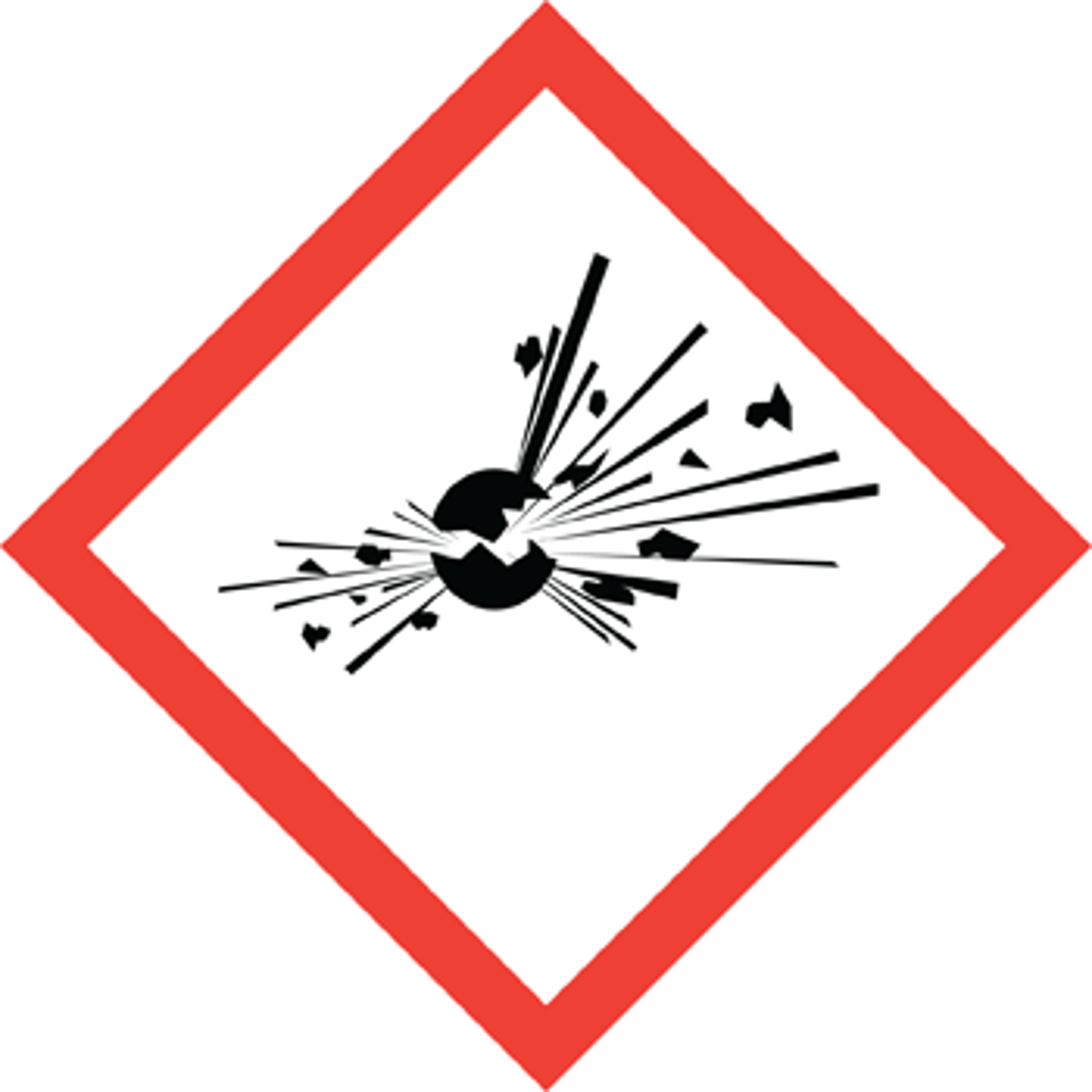
Exploding pictogram
Explosive

Flame over circle pictogram
Oxidizers

Environment pictogram
Aquatic toxicity

Glass cylinder pictogram
Gases under pressure

2 test tubes being poured pictogram
Skin Corrosion and burns, eye damage

which pictogram(s) appear on the SDS for silver nitrate? select all that apply.
- irritant
- skin corrosion/burns
- oxidizer
what is the "signal word" for silver nitrate?
danger
what happens when silver nitrate is heated to composition?
may emit toxic fumes
what should be used to extinguish a fire containing silver nitrate?
water
is silver nitrate light sensitive?
yes
what color is silver nitrate?
colorless
what effect (if any) does silver nitrate have on aquatic species?
toxic
what is the melting point of 1-naphthol, according to the SDS?
96 C
is 1-naphtol air and/or light sensitive?
both air and light sensitive
what do the pictograms for 1-naphthol indicate? select all that apply.
- skin corrosion/burns
- irritant
A = Edc
- where...
- c is measured in mol L^(-1)
- d is measured in cm
- E is measured in L mol^(-1) cm^(-1)
blue 1 is
non hazardous
lambda max
is the wavelengths at which the absorbance of a given compound is greatest (characteristic of the substance)
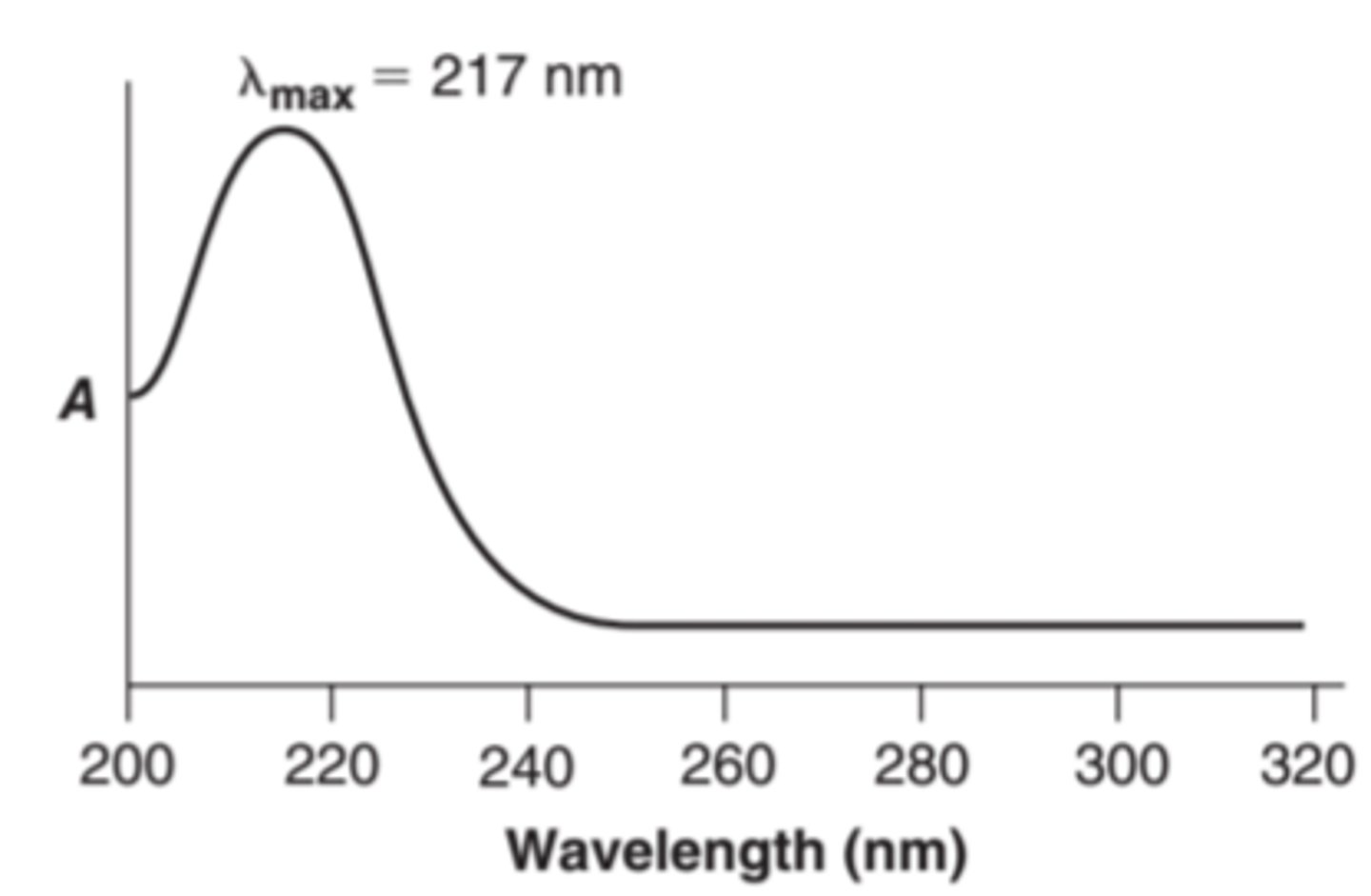
electromagnetic radiation is aka
visible light
Particular energies are aka
wavelengths
Transmittance (T) is the fraction of light at a given wavelength that passes through a light absorbing medium. Transmittance is defined as: T = I/I0
where...
- I0 is the intensity of the incident radiation entering the medium
- I is the intensity of the transmitted radiation leaving the medium
- T is often expressed as percent transmittance, %T = 100(I/I0)
Transmittance of light through a solution decreases exponentially w/ distance or concentration. It is thus more often useful to describe the process in terms of absorbance (A), the proportion of light absorbed by the medium. Absorbance is defined as: A = log10(I0/I) = -log10T
when no light is absorbed, I =I 0 and A = 0
why should the Y-intercept of the linear trendline be very close to 0?
a y-intercept of 0 indicates 0 absorbance at 0 M concentration of colored solute.
what is the CAS registery number for sodium hypochlorite? Enter the number including dashes, for example xxx-xx-x or xx-xxx-xx, depending on how many digits are in each of the three sections.
7681-52-9
which is the best definition of asphyxiant?
can result in suffocation
which is the best definition of lachrymator?
can irritate eyes and cause tearing
which is the best definition of teratogen?
can cause birth defects
which is the best definition of mutagen?
can cause genetic mutation
which is the best definition of corrosive?
can cause damage to living tissue
describe the method of spectrophotometry
"We'll be using a spectrophotometer to monitor the absorbance of the dye sample at its lambda max."
describe how absorbance relates to concentration
the more concentrated the solute is, the more light it will absorb (A = Edc)
for zero-order rxns: [A]t = -kt + [A]0,
- mol/L v.s. Time
- slope
for first-order rxns: ln[A]t = -kt + ln[A]0,
- ln[A] v.s. Time
- slope
for second-order rxns: 1/[A]t = kt + 1/[A]0,
- L/mol v.s. Time
- + slope
describe the bleaching process in general terms
"when the dye molecule interacts w/ an oxidizing agent such as common household bleach (which contains the active ingredient NaOCl), its conjugated system is broken and the molecule can no longer absorb energy in the visible spectrum. As a result, it is decolorized."
which is the best definition of the term 'cryogenic'?
being or related to a low temp.
ionic compounds are
usually strong electrolytes and can be expected to dissociate in aqueous solution.
molecular compounds are
usually non-electrolytes. They do not form ions. Resulting solutions do not conduct electricity.
molecular acids can
partially or wholly dissociate, depending on their strength
determine which molecules or ions are responsible for conductivity of solutions
The size of the conductivity value depends on the ability of the aqueous solution to conduct electricity.
discuss how the conductivity of solutions depends on the number of ions in the compound and on the type of compound
- strong electrolytes produce large #s of ions, which results in high conductivity values
- weak electrolytes result in low conductivity
- non-electrolytes result in no conductivity
calcium chloride (CaCl2) solution is
non hazardous
Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) solution is
non hazardous
Acetic acid (HC2H3O2) solution, dilute is
non hazardous
phosphoric acid (H3PO4) solution is
harmful if swallowed; do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. Causes severe burns and eye damage.
boric acid (H3BO3) solution is
non hazardous
HCl, dilute is
harmful if swallowed, inhaled or in contact with skin. causes skin and eye irritation.
methanol (CH3OH) solution:
may be harmful if swallowed