Cross sectional anatomy Module 6 Pathology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
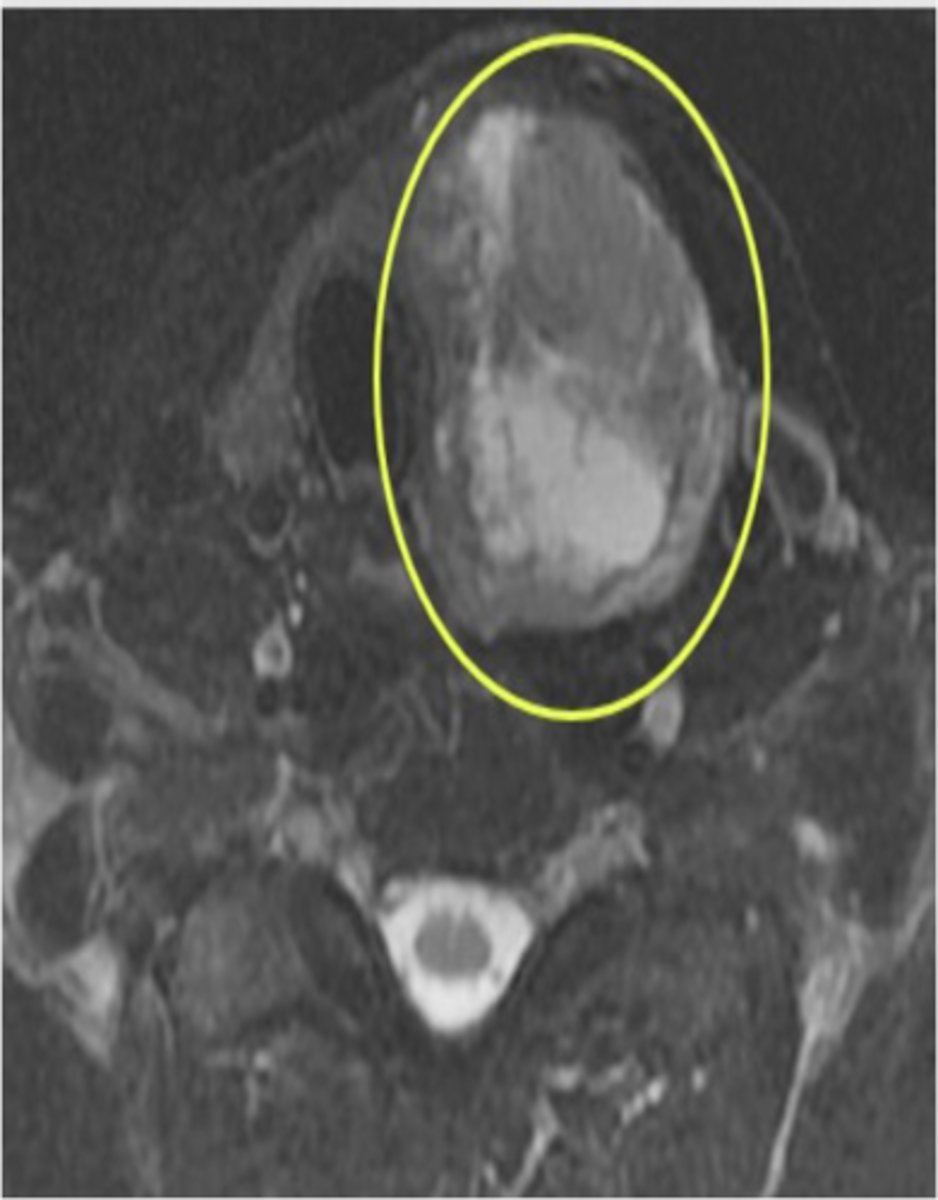
Thyroid Cancer
Abnormal cells multiply in the thyroid, forming a tumor.
Aortic Aneurysm
Balloon-like bulge in the aorta, can dissect or rupture.
Pulmonary Embolus
Blood clot in the pulmonary arteries, often caused by deep vein thrombosis.
Pericardial Effusion
Excess fluid collection in the pericardial space.
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Primary lung cancer associated with inhaled carcinogens.
Pneumothorax
Air enters the pleural space, causing lung collapse.
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
Controls metabolism and releases hormones for energy use.
(responsible for how you use energy, how you produce heat, and how you consume oxygen)
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Inside the lower anterior portion of the neck. around the level of cricoid cartilage
Is thyroid cancer treatable?
Yes, when caught early it is one of the most treatable forms of cancer
Why does a thyroid mass appear nonsymmetrical?
Because the thyroid gland is bilobed.
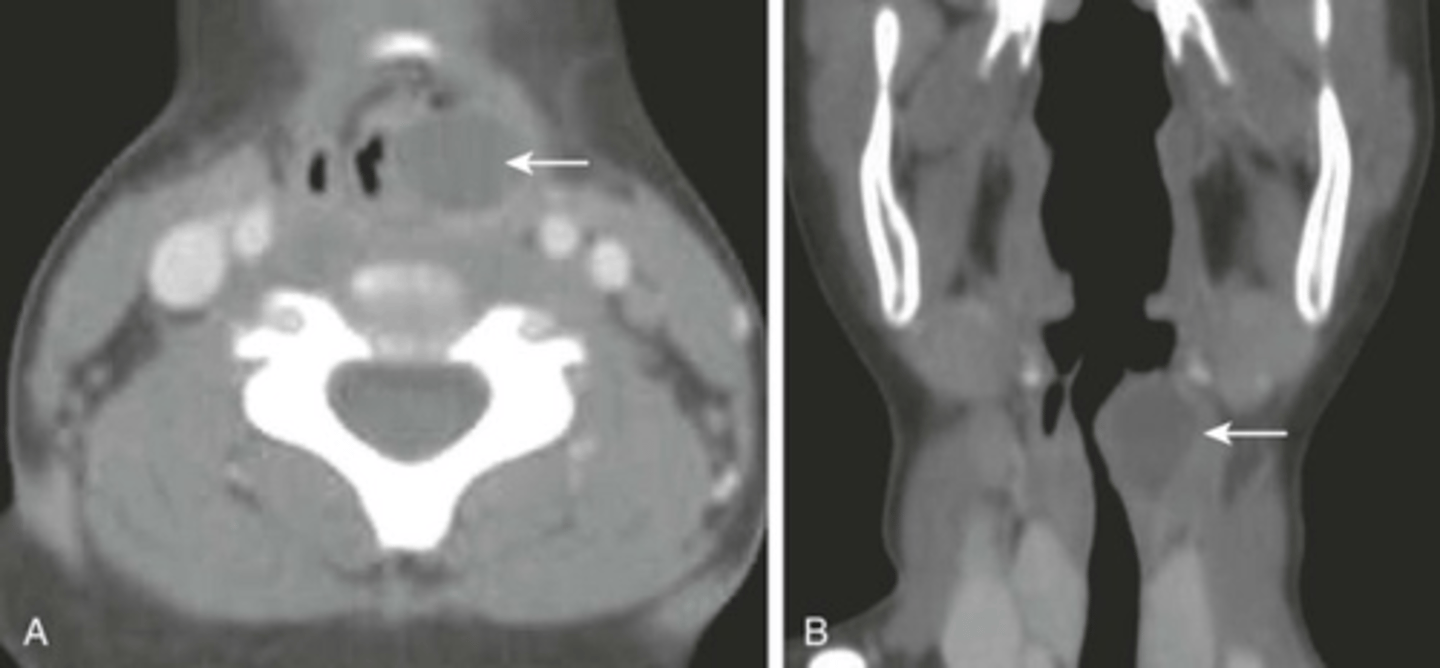
Esophageal Cancer
Cancer that begins in the cells lining the esophagus.
How common is esophageal cancer?
The 6th most common cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
Where is the esophagus located in relation to the trachea?
Posterior (behind) the trachea.
What can an enlarged or contrast-filled structure posterior to the trachea indicate?
An abnormality in the esophagus.
When is the esophagus typically enlarged?
During the process of swallowing.
When should the esophagus be filled with contrast?
When oral contrast is given.
What is stridor?
Medium to high pitched respiratory noise caused by partial obstruction of the large airways at the level of the pharynx, larynx, and/or trachea.
When is stridor typically heard?
On inspiration, but can be heard on expiration if the obstruction is more distal.
Why are children and neonates more susceptible to getting stridor?
Due to their immature airways and smaller diameter.
What are some adult causes of stridor?
Acute epiglottitis, anaphylaxis, vocal cord dysfunction, inhalation of foreign body, and cancer/tumor.
How can stridor be visualized on images?
As a black (air-filled) and completely open airway.
What happens when something obstructs the airway?
Stridor occurs.
What does an aortic aneurysm look like?
Balloon-like bulge in the aorta.
What does a dissected aortic aneurysm look like?
Grayish line through the contrast-filled vessel.
What happens during aortic aneurysm dissection?
Force of blood splits layers of artery wall, causing blood to leak.
What happens during aortic aneurysm rupture?
Aneurysm bursts completely, causing internal bleeding.
What can cause an aortic aneurysm?
High blood pressure or inherited connective tissue disorders.
What are some signs and symptoms of an aortic aneurysm?
-Sharp, sudden pain in chest or upper back
-shortness of breath
-trouble breathing or swallowing.
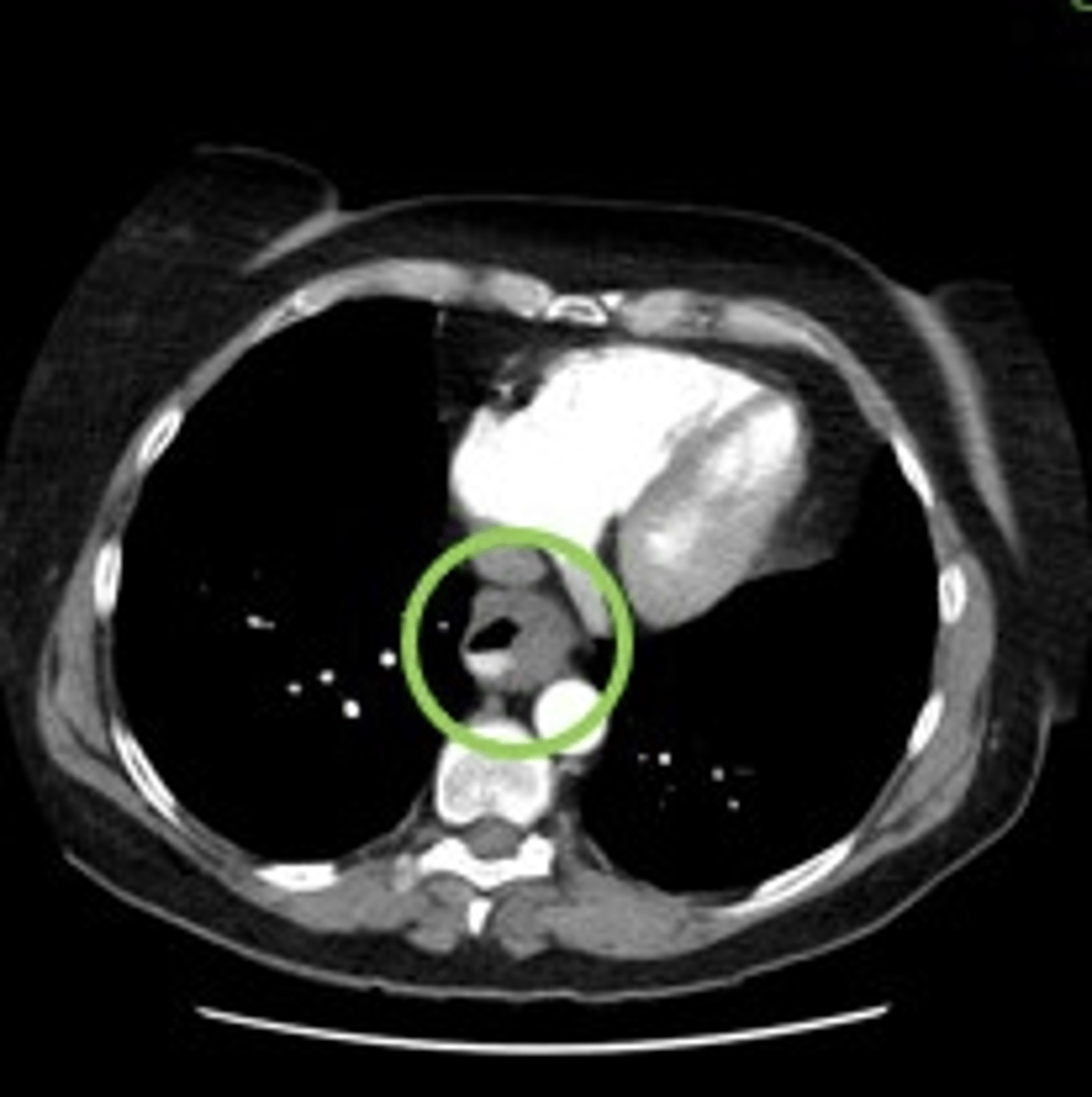
What is a pulmonary embolus (PE)?
A blood clot in the main pulmonary arteries.
What is the most common cause of a pulmonary embolus (PE)?
Blood clots that travel from deep veins in the legs.
What are some other causes of a pulmonary embolus (PE)?
Heart disease, cancer, surgery, clotting disorders, COVID-19.
What can happen if a pulmonary embolus (PE) is left untreated?
Heart strain and potential death.
How can a pulmonary embolus (PE) be identified on an image?
By looking for dark gray areas within a contrast-filled artery.
Where can a pulmonary embolus (PE) extend to?
Lobar and segmental pulmonary arteries.
What is pericardial effusion?
Excess fluid in the pericardial space.
What causes pericardial effusion?
Infectious and noninfectious processes.
How much fluid is normally present in the pericardial sac?
Approximately 30-50 mL.
What are the symptoms of pericardial effusion?
Dyspnea, reduced exercise tolerance, impaired cardiac output, and death in severe cases.
What is bronchogenic carcinoma?
Primary lung cancer associated with inhaled carcinogens.
How can bronchogenic carcinoma be divided?
Non-small cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma.
What are the clinical differences between non-small cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma?
Presentation, treatment, and prognosis.
What percentage of lung cancer cases are asymptomatic?
Up to 50%.
What are common symptoms of lung cancer?
Cough and dyspnea (SOB).
What specific symptoms may be associated with central tumors?
Coughing up blood (hemoptysis).
What specific symptoms may be associated with peripheral lesions?
Lateral chest pain.
How does bronchogenic carcinoma appear on imaging?
Abnormal mass with speculated/non-uniform borders in the lungs or mediastinum.
What is pneumothorax?
Air entering the pleural space causing lung collapse.
What are the common causes of pneumothorax?
Spontaneous, injury-related, iatrogenic.
What are the signs and symptoms of pneumothorax?
Chest pain, cough, shortness of breath, blue skin, fatigue.
How does pneumothorax appear on imaging?
Solid black with no lung markings.